Thermoelectric Properties of CoCrFeNiNbx Eutectic High Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With a rise in Nb content in the CoCrFeNiNbx alloys, the amounts of eutectic structure and phase interface increased, which decreased the electrical conductivity.
- (2)
- The thermal conductivity of the CoCrFeNiNbx alloys increases with the increase in temperature. The CoCrFeNiNb0.45 full eutectic alloy exhibited the lowest thermal conductivity at a high temperature (T > 573 K).
- (3)
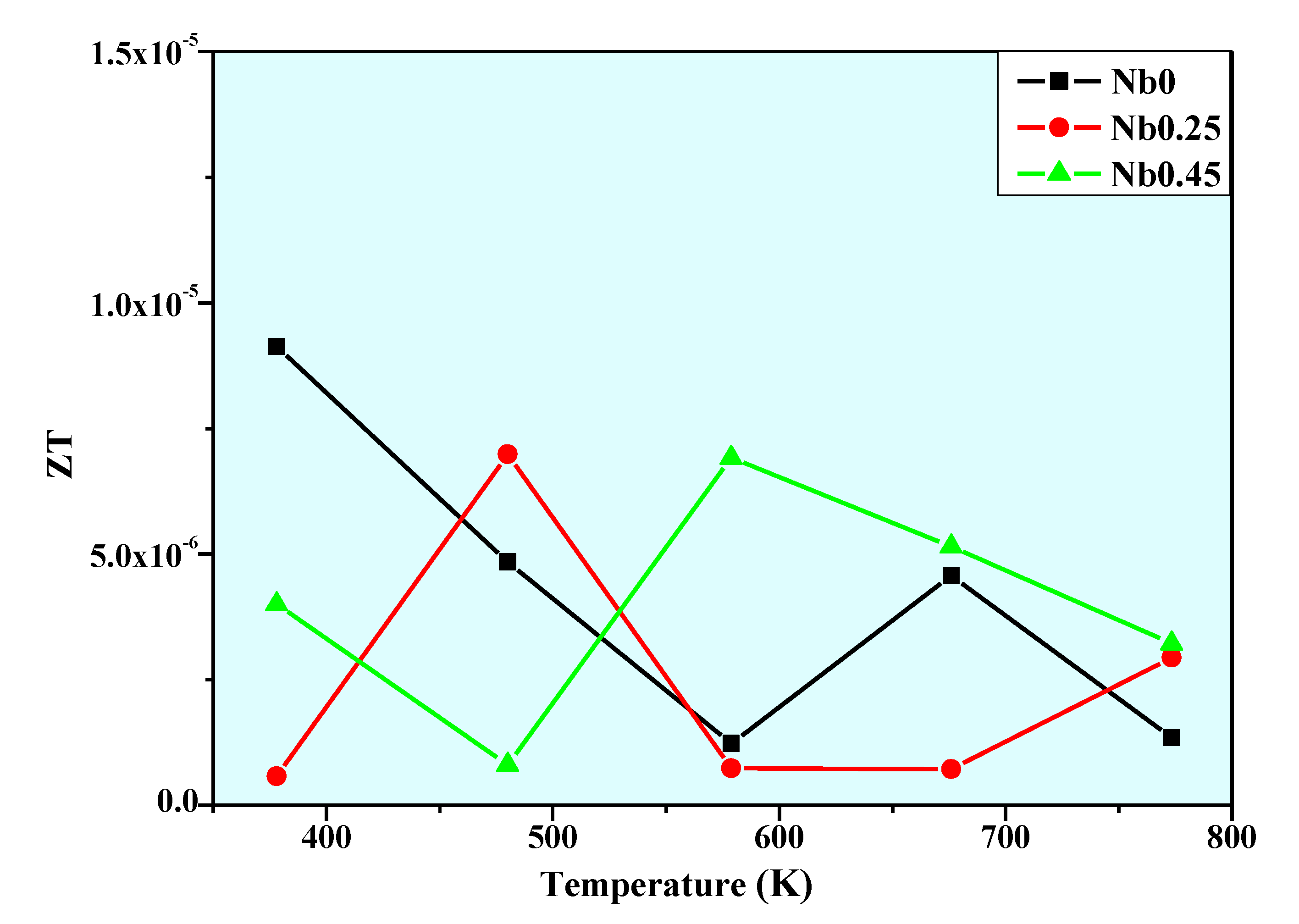
- The CoCrFeNiNb0.45 full eutectic high entropy alloy has the highest ZT at high temperature (T > 573 K), which resulted from the lower thermal conductivity of the CoCrFeNiNb0.45 alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Ge, B.; Li, W.; Lin, S.; Shen, J.; Chang, Y.; Hanus, R.; Snyder, G.J.; Pei, Y. Vacancy-induced dislocations within grains for high-performance PbSe thermoelectrics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, H.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on the enhancement of figure of merit from bulk to nano-thermoelectric materials. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Tritt, T.M. Advances in thermoelectric materials research: Looking back and moving forward. Science 2017, 357, eaak9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Hinterding, R.; Feldhoff, A. High power factor vs. high zT—A Review of thermoelectric materials for high-temperature application. Entropy 2019, 21, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoetzel, J.; Schneider, T.; Mueller, M.M.; Kleebe, H.-J.; Wiggers, H.; Schierning, G.; Schmechel, R. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Si-WSi2 nanocomposites. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Pedersen, S.H.; Yin, H.; Hung, L.T.; Iversen, B.B. Discovery of high-performance low-cost n-type Mg3Sb2-based thermoelectric materials with multi-valley conduction bands. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Shuai, J.; Cai, W.; Ren, Z.; Sui, J. Mechanical properties of nanostructured thermoelectric materials α-MgAgSb. Scr. Mater. 2017, 127, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Han, G.; Yang, L.; Cheng, L.; Zou, J. Nanostructured thermoelectric materials: Current research and future challenge. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. 2012, 22, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, G.; Guo, C.Y. Polypyrrole nanostructures and their thermoelectric performance. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High Entropy Alloys Fundamentals and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy Design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beke, D.L.; Erdélyi, G. On the diffusion in high-entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Wu, Y.; He, J.Y.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Grain growth and the Hall–Petch relationship in a high-entropy FeCrNiCoMn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liaw, P.K. Alloy design and properties optimization of high-entropy alloys. JOM 2012, 64, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.D.; Yurchenko, N.Y.; Sokolovsky, V.S.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. An AlNbTiVZr0.5 high-entropy alloy combining high specific strength and good ductility. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.T.; Gao, M.C.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Feng, R.; Chen, S.Y.; Liaw, P.K.; Hawk, J.A.; Zhang, Y. Tailoring magnetic behavior of CoFeMnNiX (X = Al, Cr, Ga, and Sn) high entropy alloys by metal doping. Acta Mater. 2017, 130, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, T.; Jin, K.; Gao, N.; Xiu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Bei, H.; Weber, W.J.; Sun, K.; et al. Radiation-induced segregation on defect clusters in single-phase concentrated solid-solution alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 127, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Xie, X.; Brechtl, J.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: Al-content and potential scan-rate dependent pitting behavior. Corros. Sci. 2017, 119, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.; Wang, T.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.; Jie, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jie, J.; Kang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Ruan, H.; et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Sheikh, S.; Lu, Y.P.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Guo, S.; Tsuji, N. Ultrafine-grained AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2016, 4, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Sheikh, S.; Clark, I.T.; Park, M.H.; Okawa, T.; Guo, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Tsuji, N. Cold-rolling and recrystallization textures of a nano-lamellar AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2017, 84, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Liaw, P.K. Promising properties and future trend of eutectic high entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Kai, J.J.; Wang, J. A casting eutectic high entropy alloy with superior strength-ductility combination. Mater. Lett. 2019, 253, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yao, Z.; Huang, X.; Du, F.; Li, C.; Chen, A.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoxCrFeNi3-x eutectic high-entropy-alloy system. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 823, 153886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Munroe, P.R.; Baker, I. Martensitic phase transformation in a f.c.c./B2 FeNiMnAl alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 7831–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Rahul, M.R.; Kottada, R.S.; Phanikumar, G. Hot deformation behaviour and processing map of Co-Cu-Fe-Ni-Ti eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 664, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, Ł.; Morgiel, J.; Świątek, Z.; Czerwiński, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the new Nb25Sc25Ti25Zr25 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.J.; Cheng, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.J.; Dang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, C.T. Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 656, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Liu, C.T. Anomalous solidification microstructures in Co-free AlxCrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 557, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.M.; Li, J.S.; Wang, J.; Kou, H.C. Seaweed eutectic-dendritic solidification pattern in a CoCrFeNiMnPd eutectic high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2017, 85, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.Y.; Li, B.S. A novel Fe20Co20Ni41Al19 eutectic high entropy alloy with excellent tensile properties. Mater. Lett. 2018, 216, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qiao, D.X.; Lu, Y.P.; Ren, Z.; Cao, Z.Q.; Wang, T.M.; Li, T.J. Direct solidification of bulk ultrafine-microstructure eutectic high-entropy alloys with outstanding thermal stability. Scr. Mater. 2019, 165, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, D.X.; Lu, Y.P.; Wang, T.M.; Cao, Z.Q.; Li, T.J. Effect of Niobium on Microstructure and Properties of the CoCrFeNbxNi High Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 33, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, J.L.; Brown, E.; Woltornist, S.J.; Adamson, D.H. Thermal and electrical properties of nanocomposites based on self-assembled pristine graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondheimer, E.H. Mean free path of electrons in metals. Adv. Phys. 1952, 1, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Böyük, U.; Çadırlı, E.; Maraşlı, N. Measurements of the microhardness, electrical and thermal properties of the Al–Ni eutectic alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, S.K.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure, thermophysical and electrical properties in AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009, 163, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, X.; Qi, J.; Yang, F.; Wei, F.; He, Y.; Meng, Q.K.; Sun, Z. Microstructures and electrothermal properties of AlxCrFeNi multi-component alloys. Vacuum 2017, 144, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, M.; Muller, S.; Voss, K.O.; Trautmann, C.; Volklein, F.; Gooth, J.; Nielsch, K.; Toimil-Molares, M.E. Influence of surface states and size effects on the Seebeck coefficient and electrical resistance of Bi1-xSbx nanowire arrays. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3169–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingo, N.; Hauser, D.; Kobayashi, N.P.; Plissonnier, M.; Shakouri, A. Nanoparticlein alloy approach to efficient thermoelectrics: Silicides in sige. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, J.F.; Alexander, W. (Eds.) CRC Materials Science and Engineering Handbook, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
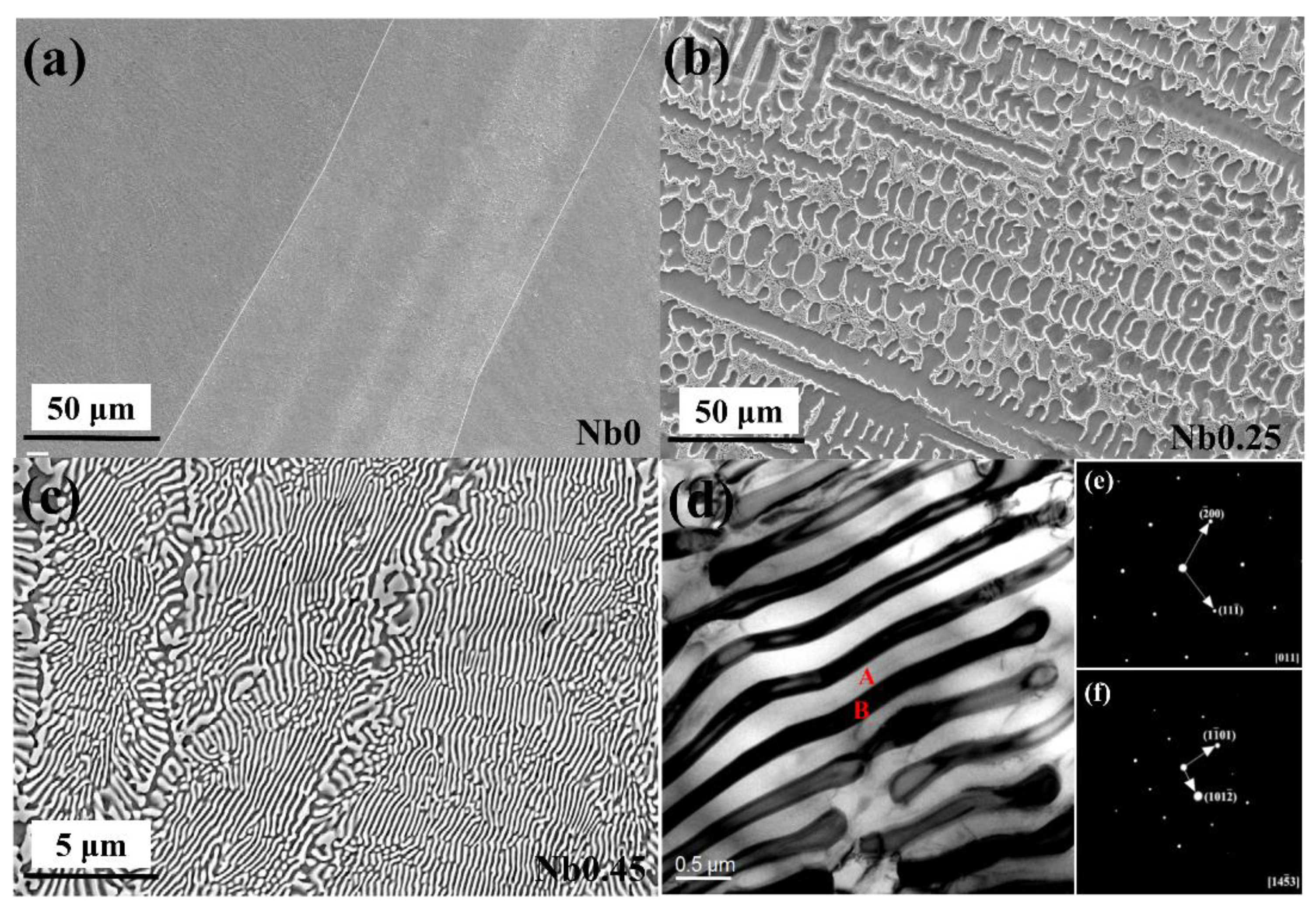
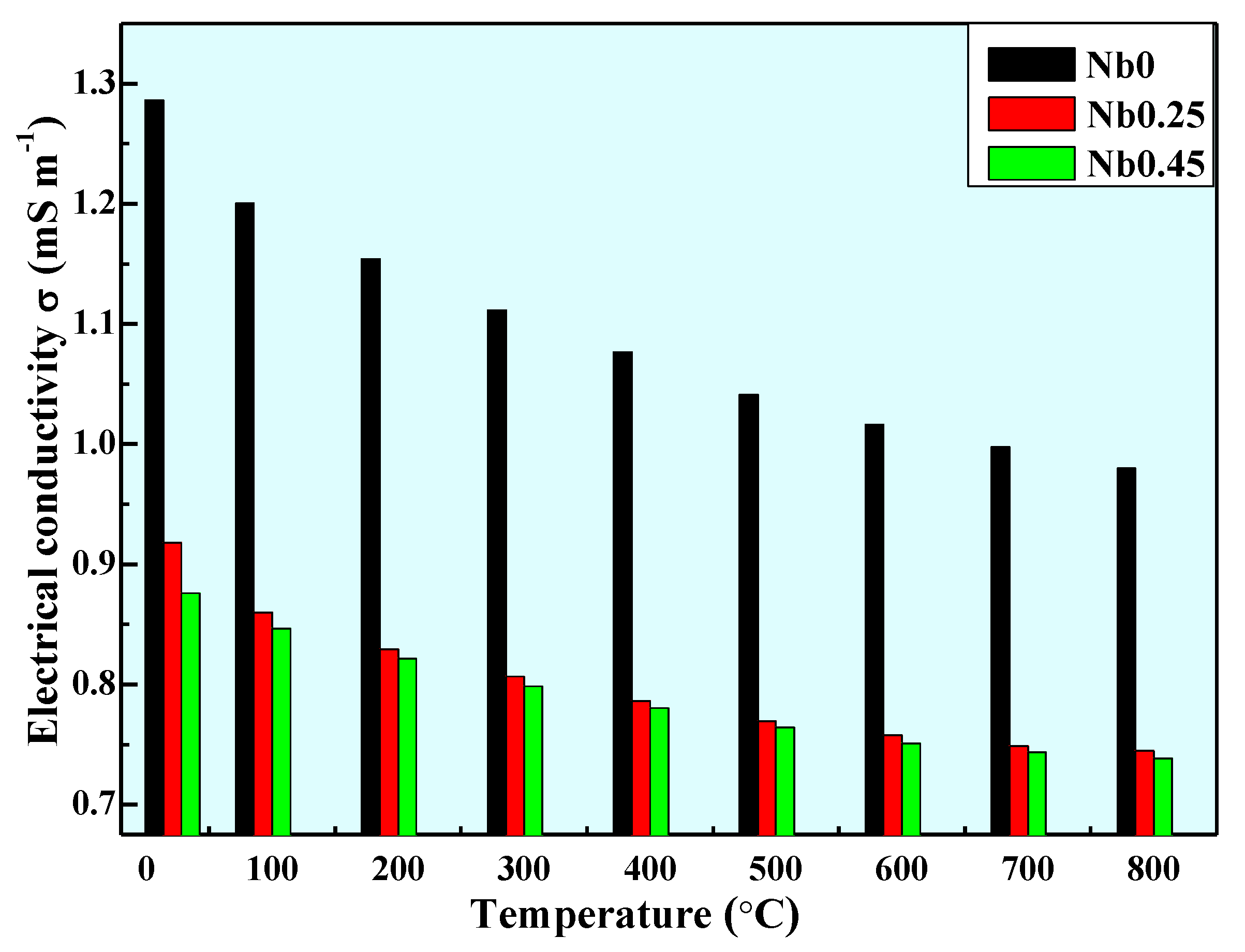
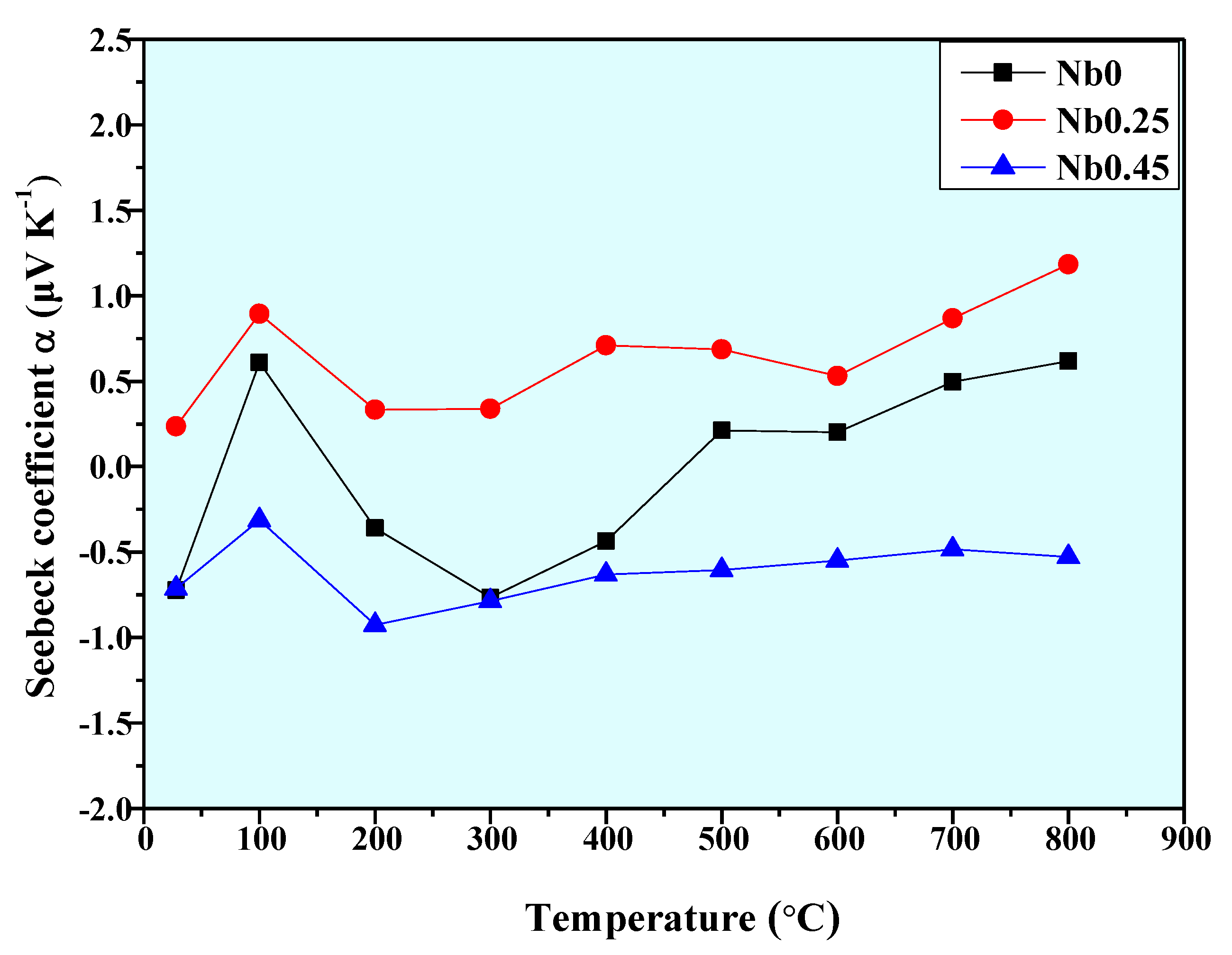
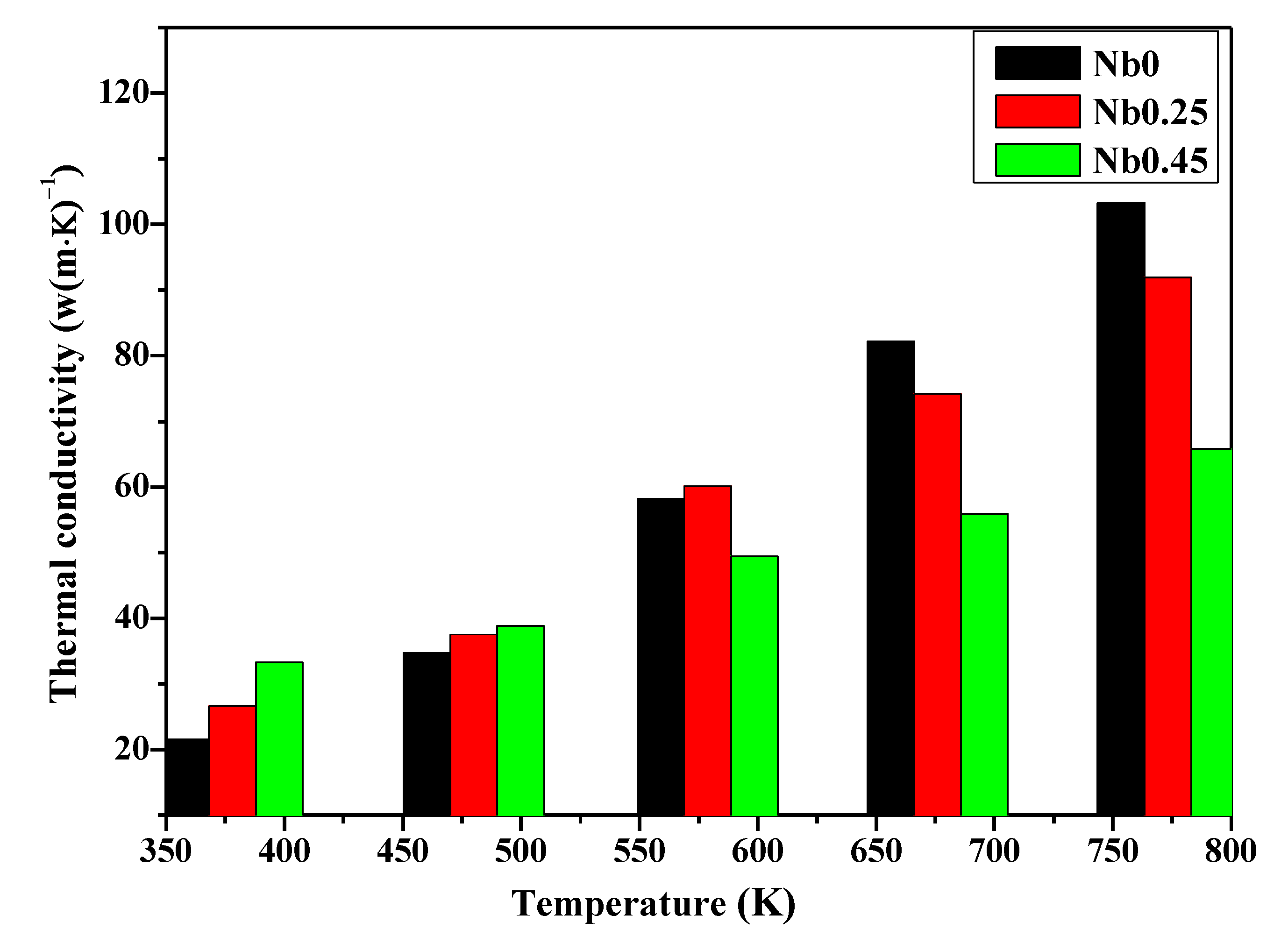
| Alloys | Temperature | 28 °C | 100 °C | 200 °C | 300 °C | 400 °C | 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | 800 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb0 | Electric resistance (μΩ·m) | 0.7776 | 0.8330 | 0.8665 | 0.8996 | 0.9289 | 0.9605 | 0.9840 | 1.0026 | 1.0205 |
| Electrical conductively (mS·m−1) | 1.286 | 1.2004 | 1.1541 | 1.1116 | 1.0766 | 1.0411 | 1.0162 | 0.9974 | 0.9799 | |
| Nb0.25 | Electric resistance (μΩ·m) | 1.0894 | 1.1629 | 1.2056 | 1.2399 | 1.2719 | 1.2996 | 1.3202 | 1.3354 | 1.3430 |
| Electrical conductively (mS·m−1) | 0.918 | 0.8599 | 0.8295 | 0.8065 | 0.7862 | 0.7695 | 0.7575 | 0.7488 | 0.7446 | |
| Nb0.45 | Electric resistance (μΩ·m) | 1.1417 | 1.1810 | 1.2173 | 1.2527 | 1.2811 | 1.3082 | 1.3313 | 1.3448 | 1.3540 |
| Electrical conductively (mS·m−1) | 0.8759 | 0.8467 | 0.8215 | 0.7982 | 0.7806 | 0.7644 | 0.75112 | 0.7436 | 0.7385 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, K.; Jiang, H.; Huang, T.; Wei, M. Thermoelectric Properties of CoCrFeNiNbx Eutectic High Entropy Alloys. Crystals 2020, 10, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090762
Han K, Jiang H, Huang T, Wei M. Thermoelectric Properties of CoCrFeNiNbx Eutectic High Entropy Alloys. Crystals. 2020; 10(9):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090762
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Kaiming, Hui Jiang, Tiandang Huang, and Mingyu Wei. 2020. "Thermoelectric Properties of CoCrFeNiNbx Eutectic High Entropy Alloys" Crystals 10, no. 9: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090762
APA StyleHan, K., Jiang, H., Huang, T., & Wei, M. (2020). Thermoelectric Properties of CoCrFeNiNbx Eutectic High Entropy Alloys. Crystals, 10(9), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090762






