Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning, Protein Expression, and Purification
2.2. Crystallization
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction Data Acquisition, Structure Solution, and Refinement
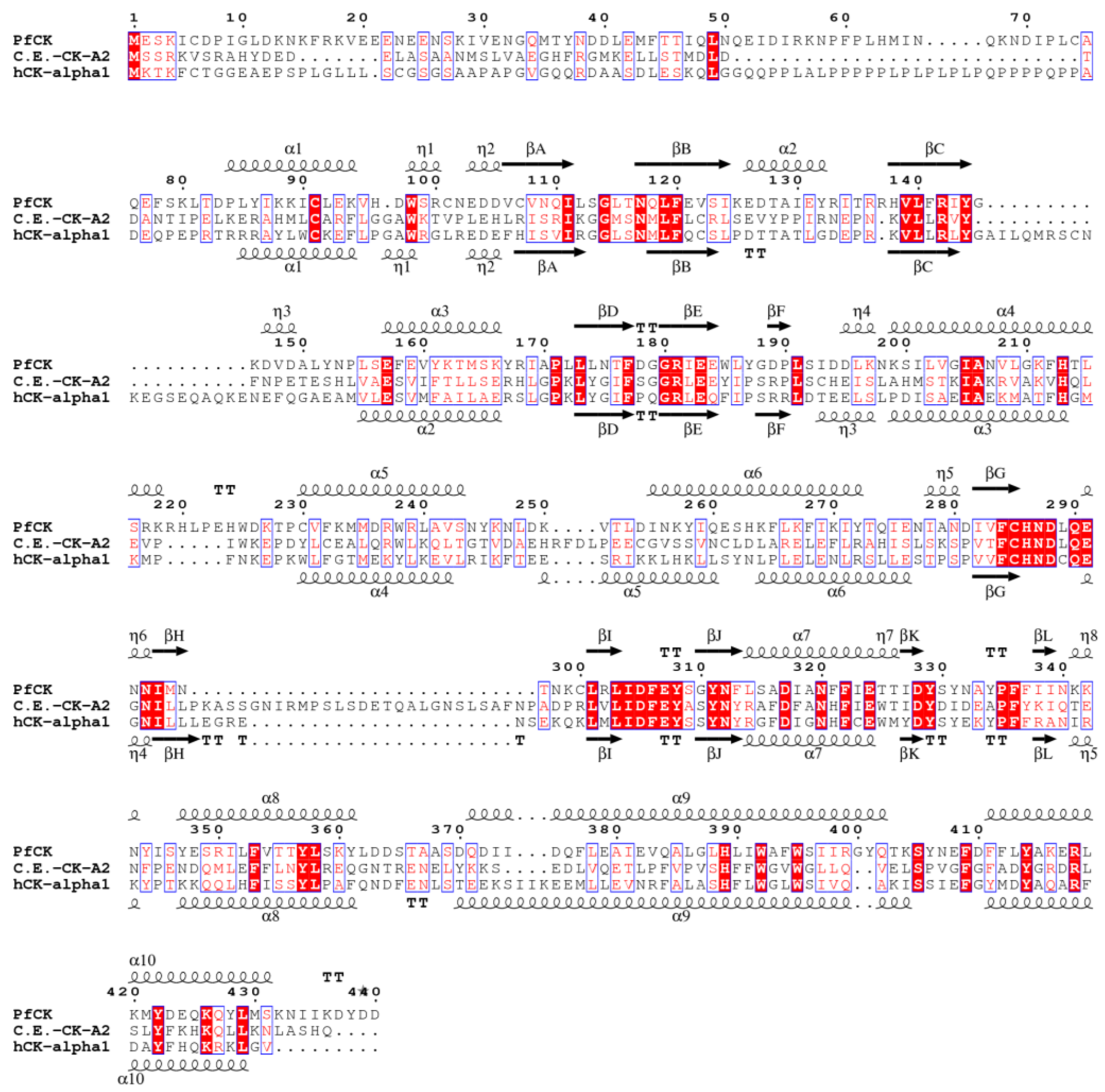
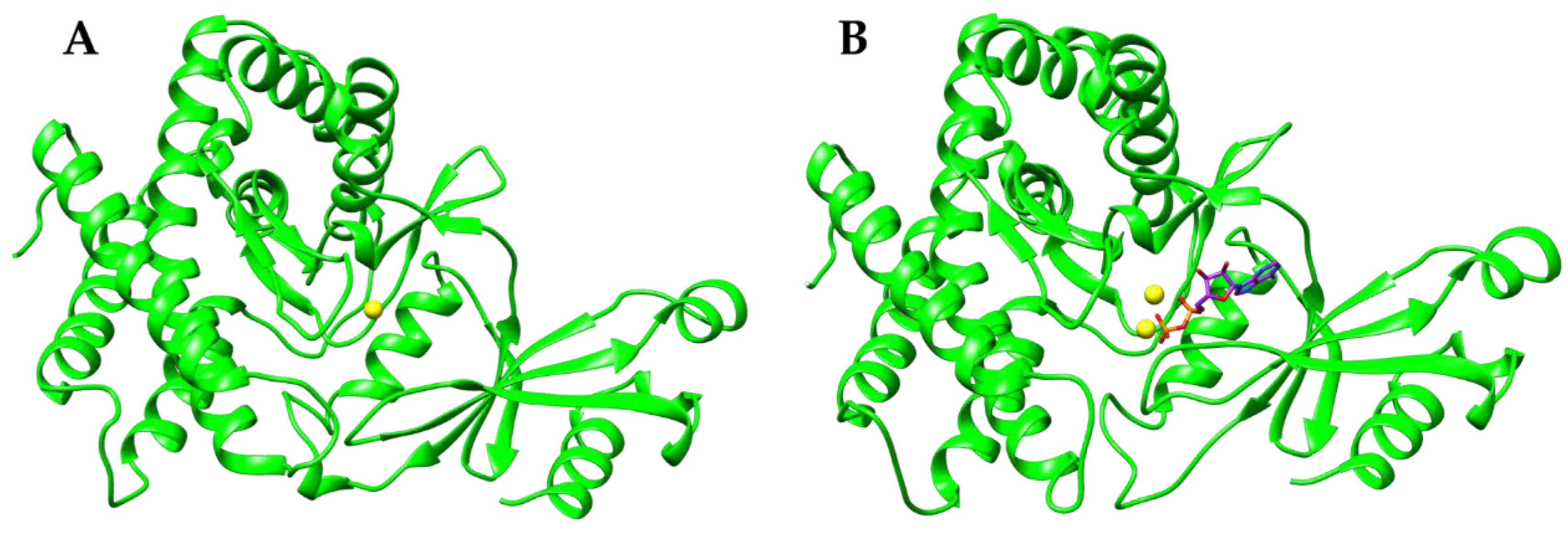
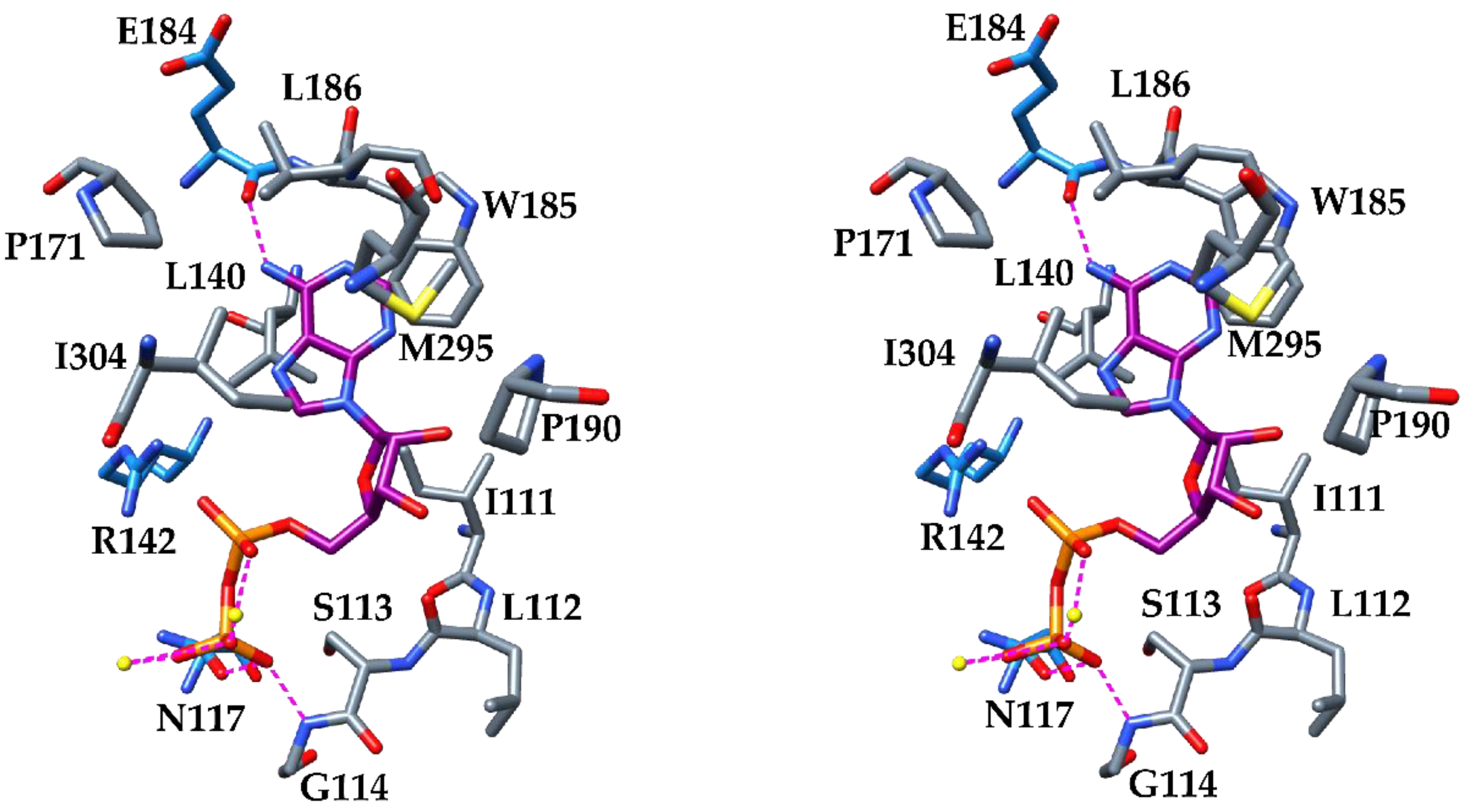
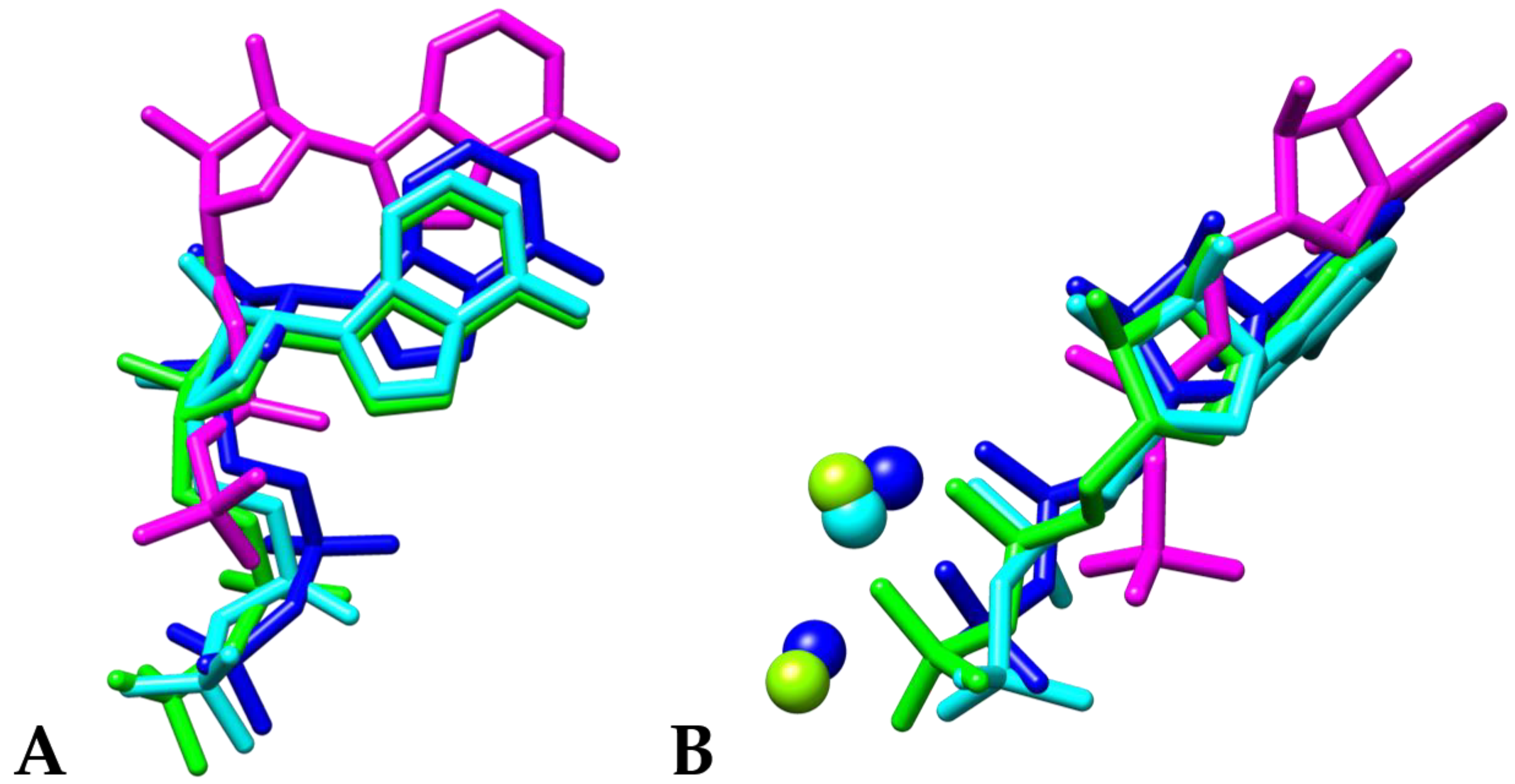
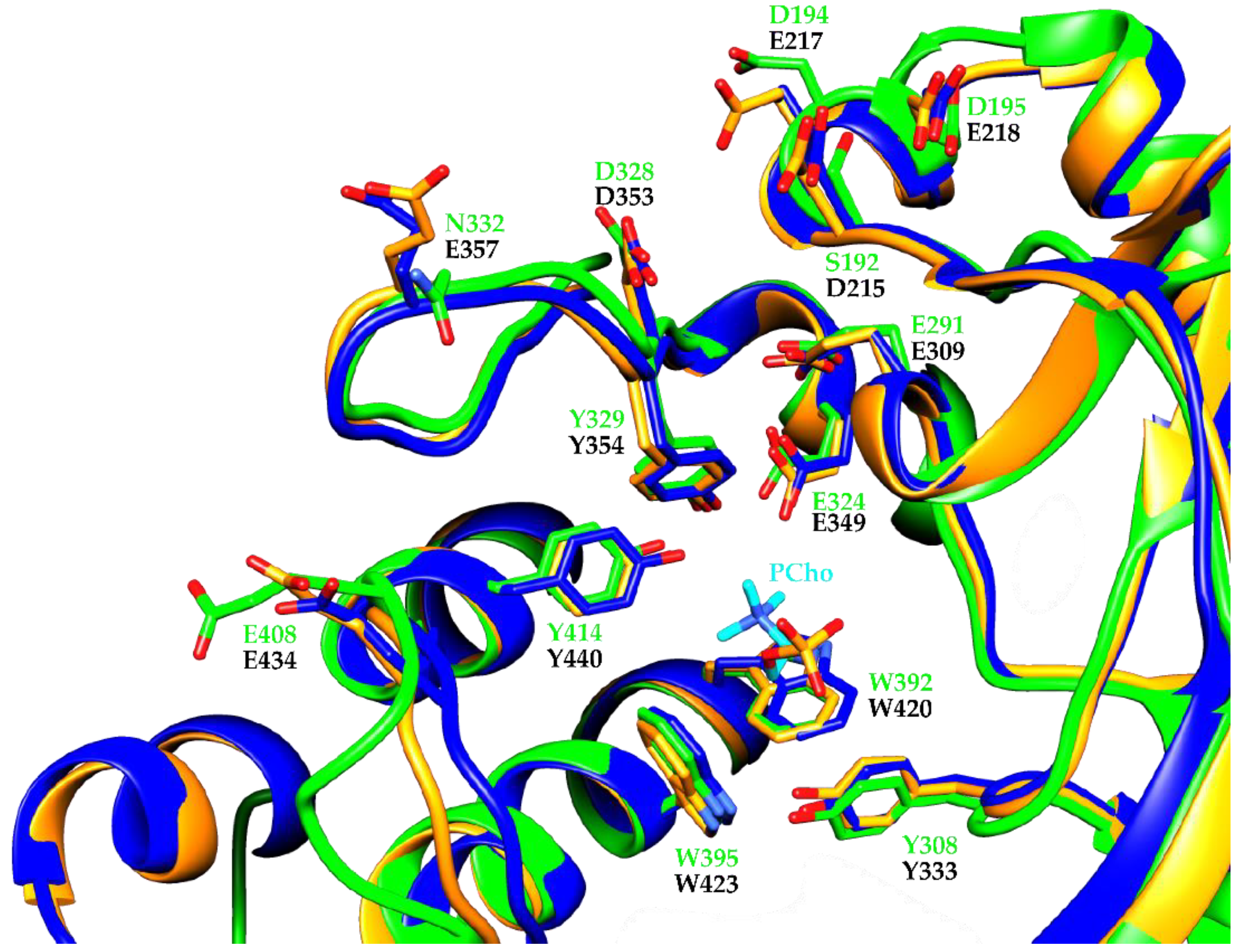
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9789241565721. [Google Scholar]
- Mitamura, T.; Marie, N.; Palacpac, Q. Lipid metabolism in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes: Possible new targets for malaria chemotherapy. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.Z.; Lane, K.D.; Xia, L.; Sá, J.M.; Wellems, T.E. Plasmodium genomics and genetics: New insights into malaria pathogenesis, drug resistance, epidemiology, and evolution. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, B.; Leroy, D.; Fidock, D.A. Antimalarial drug resistance: Linking Plasmodium falciparum parasite biology to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S. Science, medicine, and the future. Malar. BMJ 1997, 325, 730–732. [Google Scholar]
- Trampuz, A.; Jereb, M.; Muzlovic, I.; Prabhu, R.M. Clinical review: Severe malaria. Crit. Care 2003, 7, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraschi, T.F.; Parashar, A.; Hooks, M.; Rubin, H. Perturbation of red cell membrane structure during intracellular maturation of Plasmodium falciparum. Science 1986, 232, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, A.P.; Moll, G.N.; Slotboom, A.J.; Roelofsen, B.; Op den Kamp, J.A.F. Selective internalization of choline-phospholipids in Plasmodium falciparum parasitized human erythrocytes. BBA-Biomembranes 1991, 1063, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H.J.; Calas, M.; Giral, L.; Piquet, G.; Rubi, E.; Thomas, A.; Peters, W.; Slomianny, C.; Herrera, S. Present development concerning antimalarial activity of phospholipid metabolism inhibitors with special reference to in vivo activity. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1994, 89 (Suppl. 2), 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calas, M.; Cordina, G.; Bompart, J.; Bari, M.B.; Jei, T.; Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H. Antimalarial activity of molecules interfering with plasmodium falciparum phospholipid metabolism. Structure-activity relationship analysis. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 2623, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancelin, B.M.L.; Calas, M.; Bompart, J.; Cordina, G.; Martin, D.; Bari, M.B.; Jei, T.; Druilhe, P.; Vial, H.J. Antimalarial activity of 77 phospholipid polar head analogs: Close correlation between inhibition of phospholipid metabolism and in vitro plasmodium falciparum growth. Blood 1998, 91, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Calas, M.; Vidal-Sailhan, V.; Herbuté, S.; Ringwald, P.; Vial, H.J. Potent inhibitors of Plasmodium phospholipid metabolism with a broad spectrum of in vitro antimalarial activities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2590–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, N.; Choi, J.Y.; Voelker, D.R.; Mamoun, C. Ben Role of phospholipid synthesis in the development and differentiation of malaria parasites in the blood. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 17308–17316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vial, H.J.; Ancelin, M.L. Malarial lipids. In Malaria: Parasite Biology, Phatogenesis, and Protection; Sherman, I.W., Ed.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H.J. Choline kinase activity in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes: Characterization and utilization as a parasite-specific marker in malarial fractionation studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)/Lipids Lipid Metab. 1986, 875, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H.J. Quaternary ammonium compounds efficiently inhibit Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro by impairment of choline transport. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 29, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salom-Roig, X.; Hamze, A.; Calas, M.; Vial, H. Dual molecules as new antimalarials. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2005, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrottes, S.; Caldarelli, S.; Wein, S.; Périgaud, C.; Pellet, A.; Vial, H. Choline analogues in malaria chemotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3454–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pessi, G.; Choi, J.Y.; Reynolds, J.M.; Voelker, D.R.; Ben Mamoun, C. In vivo evidence for the specificity of Plasmodium falciparum phosphoethanolamine methyltransferase and its coupling to the Kennedy Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12461–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déchamps, S.; Shastri, S.; Wengelnik, K.; Vial, H.J. Glycerophospholipid acquisition in Plasmodium—A puzzling assembly of biosynthetic pathways. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, S.; Ghezal, S.; Buré, C.; Maynadier, M.; Périgaud, C.; Vial, H.J.; Lefebvre-Tournier, I.; Wengelnik, K.; Cerdan, R. Contribution of the precursors and interplay of the pathways in the phospholipid metabolism of the malaria parasite. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibellini, F.; Smith, T.K. The Kennedy pathway-de novo synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, V.; Maity, P.; Guha, M.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum choline kinase by hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide: A possible antimalarial mechanism. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, T.; Moneriz, C.; Diez, A.; Bautista, J.M.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Cebrián, A.; Lacal, J.C. Antiplasmodial activity and mechanism of action of RSM-932A, a promising synergistic inhibitor of Plasmodium falciparum choline kinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5878–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serran-Aguilera, L.; Nuti, R.; Lopez-Cara, L.C.; Rios-Marco, P.; Carrasco, M.P.; Marco, C.; Entrena, A.; Macchiarulo, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Choline kinase active site provides features for designing versatile inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrán-Aguilera, L.; Denton, H.; Rubio-Ruiz, B.; López-Gutiérrez, B.; Entrena, A.; Izquierdo, L.; Smith, T.K.; Conejo-García, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Plasmodium falciparum choline kinase inhibition leads to a major decrease in phosphatidylethanolamine causing parasite death. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiafino-Ortega, S.; Baglioni, E.; Pérez-Moreno, G.; Marco, P.R.; Marco, C.; González-Pacanowska, D.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P.; López-Cara, L.C. 1,2-Diphenoxiethane salts as potent antiplasmodial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancelin, M.L.; Vial, H.J. Several lines of evidence demonstrating that Plasmodium falciparum, a parasitic organism, has distinct enzymes for the phosphorylation of choline and ethanolamine. FEBS Lett. 1986, 202, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, V.; Guha, M.; Maity, P.; Kumar, S.; Raghunandan, R.; Maulik, P.R.; Mitra, K.; Halder, U.C.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Molecular characterization and localization of Plasmodium falciparum choline kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2006, 1760, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberge, B.; Gannoun-Zaki, L.; Bascunana, C.; Tran Van Ba, C.; Vial, H.; Cerdan, R. Comparison of the cellular and biochemical properties of Plasmodium falciparum choline and ethanolamine kinases. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, T.G.G.; Kontogiannis, L.; Johnson, O.; Powell, H.R.; Leslie, A.G.W. iMOSFLM: A new graphical interface for diffraction-image processing with MOSFLM. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2011, 67, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.W.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.-W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Peisach, D.; Gee, P.; Kent, C.; Xu, Z. The crystal structure of choline kinase reveals a eukaryotic protein kinase fold. Structure 2003, 11, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malito, E.; Sekulic, N.; Cun, W.; Too, S.; Konrad, M.; Lavie, A. Elucidation of human choline kinase crystal structures in complex with the products ADP or phosphocholine. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeff, E.D.; Bourne, P.E. Structural evolution of the protein kinase–like superfamily. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Tempel, W.; Finerty, P.J.; MacKenzie, F.; Dimov, S.; Vedadi, M.; Park, H.W. Crystal structures of human choline kinase isoforms in complex with hemicholinium-3: Single amino acid near the active site influences inhibitor sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16330–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Crystallographic Table | PfChoK Apo Form | PfChoK ADP-Bound Form |
| Protein Data Bank ID | 6YXS | 6YXT |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 | P 21 21 21 |
| Cell dimensions | ||
| a, b, c (Å) | 66.41, 68.82, 104.80 | 66.45, 67.99, 105.11 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Resolution (Å) | 57.53–2.00 (2.11–2.00) | 68.00–2.20 (2.32–2.20) |
| Total reflections | 263,600 (40,520) | 125,859 (17,449) |
| Unique reflections | 33,217 (4770) | 24,873 (3571) |
| Multiplicity | 7.9 (8.5) | 5.1 (4.9) |
| Completeness (%) | 100.0 (100.0) | 99.90 (100.0) |
| Rmerge | 0.203 (1.736) | 0.146 (1.593) |
| Mean I/sigma(I) | 8.00 (1.3) | 6.5 (1.00) |
| Wilson B-factor (Å2) | 24.5 | 37.1 |
| CC1/2 | 0.995 (0.429) | 0.994 (0.486) |
| Reflections used in refinement | 33,149 (3242) | 24,706 (2339) |
| Reflections used for Rfree | 1739 (159) | 1230 (114) |
| Rwork | 0.2063 (0.3247) | 0.2305 (0.4671) |
| Rfree | 0.2385 (0.3812) | 0.2553 (0.4983) |
| Total number of non-H atoms | 3277 | 3165 |
| protein | 3020 | 3028 |
| ligands | 53 | 41 |
| solvent | 204 | 96 |
| Protein residues | 359 | 359 |
| RMS bonds (Å) | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| RMS angles (°) | 0.53 | 0.66 |
| Ramachandran plot | ||
| Favored/allowed/outliers (%) | 96.36/2.80/0.00 | 92.16/5.60/2.24 |
| B-factor (average) (Å2) | 38.25 | 57.15 |
| protein | 37.84 | 57.32 |
| ligands | 49.42 | 50.23 |
| solvent | 41.36 | 54.66 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torretta, A.; Lopez-Cara, L.C.; Parisini, E. Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum. Crystals 2020, 10, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070613
Torretta A, Lopez-Cara LC, Parisini E. Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum. Crystals. 2020; 10(7):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070613
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorretta, Archimede, Luisa Carlota Lopez-Cara, and Emilio Parisini. 2020. "Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum" Crystals 10, no. 7: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070613
APA StyleTorretta, A., Lopez-Cara, L. C., & Parisini, E. (2020). Crystal Structure of the Apo and the ADP-Bound Form of Choline Kinase from Plasmodium falciparum. Crystals, 10(7), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10070613






