Physical Characteristics of Cilostazol–Hydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals Prepared Using a Spray Drying Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of Samples by Physical Mixing
2.2.2. Preparation of Samples Using the Solvent Evaporation Method
2.2.3. Preparation of Samples Using the Slurry Method
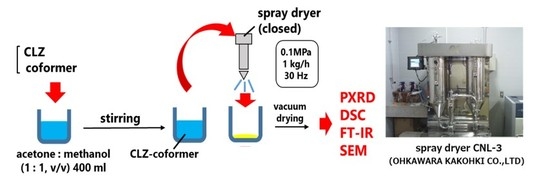
2.2.4. Preparation of Spray Dried Samples
2.3. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Dissolution Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cocrystals of CLZ and Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives
3.2. Characteristics of the CLZ-4HBA Cocrystals Prepared Using the Solvent Evaporation, Slurry, and Spray Drying Methods
3.3. Characteristics of CLZ-2,4DHBA Cocrystals Prepared Using the Solvent Evaporation, Slurry, and Spray Drying Methods
3.4. Characteristics of CLZ-2,5DHBA Cocrystals Prepared Using the Solvent Evaporation, Slurry, and Spray Drying Methods
3.5. Physical Characterization of Spray-Dried CLZ–Hydroxybenzoic Acids Cocrystals
3.6. Dissolution Behavior of Spray-Dried CLZ–Hydroxybenzoic Acids Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schultheiss, N.; Newman, A. Pharmaceutical cocrystals and their physicochemical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2950–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi-Jafari, M.; Padrela, L.; Walker, G.M.; Croker, D.M. Creating cocrystals: A review of pharmaceutical cocrystal preparation routes and applications. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 6370–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric amorphous solid dispersions: A review of amorphization, crystallization, stabilization, solid-State characterization, and aqueous solubilization of biopharmaceutical classification system class II drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrela, L.; de Azevedo, E.G.; Velaga, S.P. Powder X-ray diffraction method for the quantification of cocrystals in the crystallization mixture. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 38, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N.; Kawahata, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Tomono, K.; Fukami, T. Comparison of the relative stability of pharmaceutical cocrystals consisting of paracetamol and dicarboxylic acids. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddleston, M.D.; Patel, B.; Day, G.M.; Jones, W. Cocrystallization by freeze-drying: Preparation of novel multicomponent crystal forms. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trask, A.V.; Motherwell, W.D.S.; Jones, W. Pharmaceutical cocrystallization: Engineering a remedy for caffeine hydration. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Daurio, D.; Nagapudi, K.; Alvarez-Nunez, F. Manufacture of pharmaceutical co-crystals using twin screw extrusion: A solvent-less and scalable process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1693–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradiya, H.G.; Islam, M.T.; Halsey, S.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Snowden, M.J.; Douroumis, D. Continuous cocrystalization of carbamazepine and trans-cinnamic acid via melt extrusion processing. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 3573–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurohr, C.; Marchivie, M.; Lecomte, S.; Cartigny, Y.; Couvrat, N.; Sanselme, M.; Subra-Paternault, P. Naproxen–nicotinamide cocrystals: Racemic and conglomerate structures generated by CO2 antisolvent crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 4616–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K.; Koide, T.; Takata, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Ono, M.; Inoue, M.; Fukami, T.; Yonemochi, E. Characterization and quality control of pharmaceutical cocrystals. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2016, 64, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friščić, T.; Childs, S.L.; Rizvi, S.A.; Jones, W. The role of solvent in mechanochemical and sonochemical cocrystal formation: A solubility-based approach for predicting cocrystallisation outcome. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 11, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalaweh, A.; Velaga, S.P. Formation of cocrystals from stoichiometric solutions of incongruently saturating systems by spray drying. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 3302–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.; Serrano, D.R.; Worku, Z.A.; Norris, B.A.; Healy, A.M. Production of cocrystals in an excipient matrix by spray drying. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.; Serrano, D.R.; Worku, Z.A.; Madi, A.M.; O’Connell, P.; Twamley, B.; Healy, A.M. Engineering of pharmaceutical cocrystals in an excipient matrix: Spray drying versus hot melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, D.R.; Walsh, D.; O’Connell, P.; Mugheirbi, N.A.; Worku, Z.A.; Bolas-Fernandez, F.; Galiana, C.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Healy, A.M. Optimising the in vitro and in vivo performance of oral cocrystal formulations via spray coating. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 124, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossjohann, C.; Serrano, D.R.; Paluch, K.J.; O’Connell, P.; Vella-Zarb, L.; Manesiotis, P.; Mccabe, T.; Tajber, L.; Corrigan, O.I.; Healy, A.M. Polymorphism in sulfadimidine/4-aminosalicylic acid cocrystals: Solid-state characterization and physicochemical properties. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, M.U.; Uppoor, R.S.; Conner, D.P.; Seo, P.; Vaidyanathan, J.; Volpe, D.A.; Stier, E.; Chilukuri, D.; Dorantes, A.; Ghosh, T.; et al. Impact of the US FDA “Biopharmaceutics classification system” (BCS) guidance on global drug development. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4334–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinno, J.; Kamada, N.; Miyake, M.; Yamada, K.; Mukai, T.; Odomi, M.; Toguchi, H.; Liversidge, G.G.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Effect of particle size reduction on dissolution and oral absorption of a poorly water-soluble drug, cilostazol, in beagle dogs. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, M.; Miyake, M.; Kawato, M.; Bando, M.; Toda, Y.; Kato, T.; Fukami, T.; Ozeki, T. Impact of the dissolution profile of the cilostazol cocrystal with supersaturation on the oral bioavailability. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urano, M.; Kitahara, M.; Kishi, K.; Goto, E.; Tagami, T.; Fukami, T.; Ozeki, T. Physical Characteristics of Cilostazol–Hydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals Prepared Using a Spray Drying Method. Crystals 2020, 10, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040313
Urano M, Kitahara M, Kishi K, Goto E, Tagami T, Fukami T, Ozeki T. Physical Characteristics of Cilostazol–Hydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals Prepared Using a Spray Drying Method. Crystals. 2020; 10(4):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040313
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrano, Maho, Megumi Kitahara, Kae Kishi, Eiichi Goto, Tatsuaki Tagami, Toshiro Fukami, and Tetsuya Ozeki. 2020. "Physical Characteristics of Cilostazol–Hydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals Prepared Using a Spray Drying Method" Crystals 10, no. 4: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040313
APA StyleUrano, M., Kitahara, M., Kishi, K., Goto, E., Tagami, T., Fukami, T., & Ozeki, T. (2020). Physical Characteristics of Cilostazol–Hydroxybenzoic Acid Cocrystals Prepared Using a Spray Drying Method. Crystals, 10(4), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040313