Abstract
In the present study, the catalytic activity of palladium oxide (PdOx) supported on ceria nanorods (CeO2-NR) for aerobic selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol (BnOH) to benzaldehyde (PhCHO) was evaluated. The CeO2-NR was synthesized hydrothermally and the Pd(NO3)2 was deposited by a wet impregnation method, followed by calcination to acquire PdOx/CeO2-NR. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), temperature programmed reduction (TPR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Brunauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) surface area analysis, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). In addition, the TPR-reduced PdOx/CeO2-NR (PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red) was studied by XRD, BET, and XPS. Characterizations showed the formation of CeO2-NR with (111) exposed plane and relatively high BET surface area. PdOx (x > 1) was detected to be the major oxide species on the PdOx/CeO2-NR. The activities of the catalysts in BnOH oxidation were evaluated using air, as an environmentally friendly oxidant, and various solvents. Effects of temperature, solvent nature and palladium oxidation state were investigated. The PdOx/CeO2-NR showed remarkable activity when protic solvents were utilized. The best result was achieved using PdOx/CeO2-NR and boiling ethanol as solvent, leading to 93% BnOH conversion and 96% selectivity toward PhCHO. A mechanistic hypothesis for BnOH oxidation with PdOx/CeO2-NR in ethanol is presented.
1. Introduction
The catalytic activity of supported noble metals not only showed dependence on the properties of metal particles [1,2,3] but may also depend on the type and characteristics of the chosen support [4]. Higher surface area of the nano-structure supports might help with better dispersion of the metal, and if a strong affinity between support and particles occurs, low metal leaching can be achieved. The nature of the support can also affect the electronic structure of the metal and/or, modify the catalytic reaction by itself [5,6,7].
Benzaldehyde (PhCHO) is considered a critical fine and intermediate chemical [8]. Oxidation of toluene and hydrolysis of benzal chloride are common ways of PhCHO production; but in the former the selectivity is low, and the latter leads to undesirable chlorine contamination [9]. PhCHO can be produced from catalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol (BnOH) using environmentally friendly oxidants such as air or O2, which are advantageous over the expensive and toxic stoichiometric oxidants such as chromium and manganese salts [10]. The oxidation can proceed through PhCHO to benzoic acid (PhCOOH) as the final product [11] (Scheme 1); therefore, it is crucial for a catalytic system to show high PhCHO selectivity.
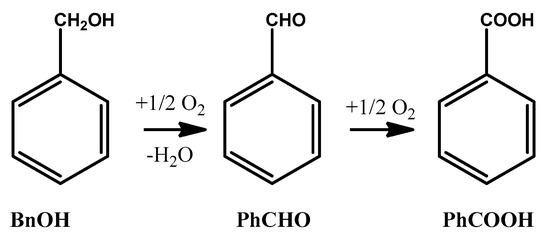
Scheme 1.
Oxidation of benzyl alcohol (BnOH) to benzaldehyde (PhCHO) and final benzoic acid (PhCOOH).
Utilizing noble metals to catalyze aerobic oxidation of BnOH to PhCHO is widely investigated. For instance, ruthenium [12,13,14] and gold [15,16,17,18,19] are proved to be efficient catalysts for selective BnOH oxidation. In 1977, palladium-catalyzed oxidation of alcohols by molecular oxygen was performed for the first time [20]. More recently, palladium nanoparticles in BnOH to PhCHO oxidation with air or O2 were studied on various supports [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Supported bimetallic Au/Pd nanoparticles have been investigated [27,28,29,30,31,32] as well.
CeO2 is a reductive oxide, efficient as support for metals such as Pd, Pt, and Au to catalyze reactions such as amination of alcohols [33] and oxidation of CO [34] and alcohols [35]. The reason is the enhanced surface area and high amount of surface-active sites (oxygen vacancies) on nano ceria in comparison with other common supports [35,36,37]. The CeO2 support with different morphologies such as nanorod, nanocube, or nano-octaedron may differently effect the catalytic performances, as observed for lean methane combustion over palladium ceria catalysts [38] and in BnOH oxidation over palladium supported on CeO2 truncated octahedra and cubes [39]. Cu or Ni supported on ceria nanorods (CeO2-NR) led to a higher activity compared with other support morphologies; in particular, the nanorod morphology showed better activity in the CO oxidation [40], in the dry reforming of methane [41], and in the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methane and methanol [42]. Zhang et al. reported that the bimetallic Au/Pd supported on CeO2-NR showed remarkable catalytic activity and selectivity in BnOH oxidation using molecular oxygen [37]. The catalytic activity of reduced palladium single atoms supported on different ceria morphologies, namely nanocube, nanorod, and truncated octahedron, in BnOH oxidation using molecular oxygen as oxidant was investigated by Xin et al. [43]. The best result was achieved using CeO2-NR as support, leading to 26.6% BnOH conversion and 100% PhCHO selectivity. This result was slightly higher than that achieved using truncated octahedral CeO2 as support (~24% BnOH conversion), even though both CeO2 morphologies exposed the (111) plane, which has a synergy with palladium for catalyzing selective BnOH oxidation [43]. The catalysts were reduced at the final stage of preparation, but as shown in the work of Tan et al., keeping palladium in metallic state on CeO2-NR is a problematic task [44].
The aim of the present research work was to investigate the activity of the oxidized palladium supported on CeO2-NR for the BnOH oxidation, considering that most research works on palladium/ceria catalysts in BnOH oxidation were focused on reduced palladium. For this purpose, we prepared an oxidized palladium supported on ceria nanorods (PdOx/CeO2-NR) catalyst (2 wt.% Pd) and studied its catalytic activity and its PhCHO selectivity in aerobic BnOH oxidation. Structural, morphological, and redox properties of the synthetized materials were studied, together with the effects of temperature and solvent on the catalytic activity. Finally, the activity of PdOx/CeO2-NR was compared with that of reduced PdOx/CeO2-NR (PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red), and mechanistic aspects are discussed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
The synthesized samples were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and their patterns are shown in Figure 1. The CeO2-NR showed the main reflections of pure cubic fluorite structure of CeO2 (Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) card 81-0792) [45], with the average crystallite size of 23.3 nm and cubic cell size of 0.5419 nm (Table 1). The XRD pattern of the PdOx/CeO2-NR sample showed peaks assigned to CeO2 having almost the same position, intensity, and full width at half maximum (FWHM) of CeO2-NR, indicating no effect of Pd-loading on the particle size and on the crystal structure of CeO2 (Table 1). No peaks of PdO phase were observed, suggesting that PdO is highly dispersed or that the PdO loading was below the detection limit of XRD. In addition, the most intense peak of PdO, expected to be very close to the (200) reflection of CeO2, may be hardly distinguishable. The XRD pattern of the PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red, reduced by H2 up to 500 °C, was very similar to that of CeO2, with no remarkable changes in crystal structure or particle size (Table 1), indicating that ceria was unaffected by the reduction process. No peaks of metallic palladium (Pd0) were observed, suggesting that it was well dispersed or not detectable [46,47].
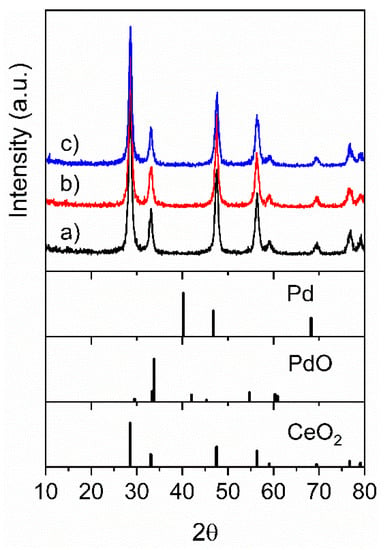
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples: (a) ceria nanorods (CeO2-NR), (b) PdOx/CeO2-NR, and (c) reduced PdOx/CeO2-NR (PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red).

Table 1.
Textural properties and CeO2 cell size of the samples.
A H2-TPR experiment was performed to analyze the reducibility and the oxygen storing capacity of PdOx/CeO2-NR. The reduction was conducted up to 500 °C and maintained at the final temperature for 1 h, to avoid any sintering of ceria and of Pd at higher temperatures. H2-TPR profiles of CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR are reported in Figure 2. The profile of the pure CeO2-NR shows a broad reduction feature with onset at about 300 °C, increasing up to 500 °C, assigned to Ce4+ → Ce3+ reduction on the surface of ceria [48,49].
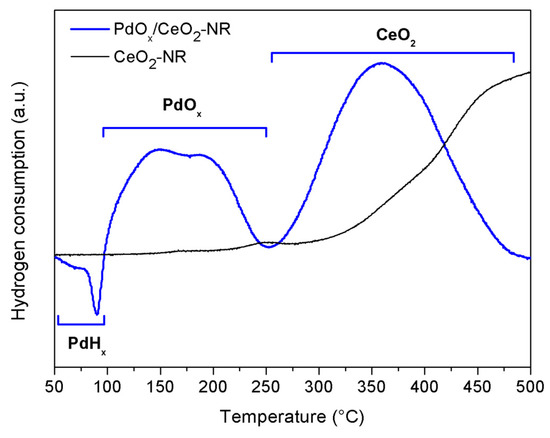
Figure 2.
Temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR) profiles of the samples: CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR.
TPR profile of PdOx/CeO2-NR showed several peaks: a negative peak at 90 °C, a broad peak in range 100–250 °C, with two maxima at 147 and 190 °C and a peak in temperature range 250–475 °C with a maximum at 360 °C. The negative peak at 90 °C is assigned to the hydrogen released by the decomposition of Pd hydride phase formed by the reduction of some palladium oxide at the early stage of the TPR measurement [33,50,51,52]; a similar negative peak was observed in previous works [50,53] and its position depended on preparation method and on the amount of Pd supported on ceria [54]. The broad peak in the range 100–250 °C is assigned to reduction of palladium oxide to Pd0 and is in agreement with the reduction temperature range (70–170 °C), observed on the TPR profile of a catalyst with similar Pd content [55]. The maximum at 190 °C might be due to reduction of less reducible PdOx species in solid solution with CeO2 lattice. The reduction peak at 360 °C is due to surface reduction of ceria that occurs at significantly lower temperature in comparison with the surface reduction observed at around 500 °C in TPR profile of pure CeO2-NR. This shift to lower temperatures (roughly 140 °C) can be explained by the promoting effect of Pd on the surface reduction of ceria through the hydrogen spill-over [48]. The hydrogen spill-over phenomenon did not permit a correct quantitative evaluation of the extent of Pd and CeO2 reduction from the TPR peak integration. The produced PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red from TPR was tested in BnOH oxidation reaction as well.
CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR were investigated by TEM and the images are shown in Figure 3. The CeO2-NR sample showed a uniform well-developed structural anisotropy characteristic of the rod-like morphology with the average length of 110 nm and the average width of 9 nm (Figure 3a). In addition, 0.31 nm fringe distances assessed in CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR (Figure 3b, d) were in good agreement with d value of the ceria (111) plane and were the only crystalline planes observed. In some published researches, (100) and (110) exposed planes are reported for CeO2-NR [38,46,56]. However, palladium supported on the (111) plane of CeO2 seems to have a particular synergy with the support, showing higher activity and selectivity in methane combustion, CO oxidation, and BnOH oxidation [38,39,43]. As shown in Figure 3c, after palladium deposition, the average length of nanorods decreased up to 55 nm. The lack of evidence of palladium particles in the HRTEM images of PdOx/CeO2-NR, might be attributable to the high dispersion of palladium oxide species on the surface of the support, in agreement with XRD analysis.
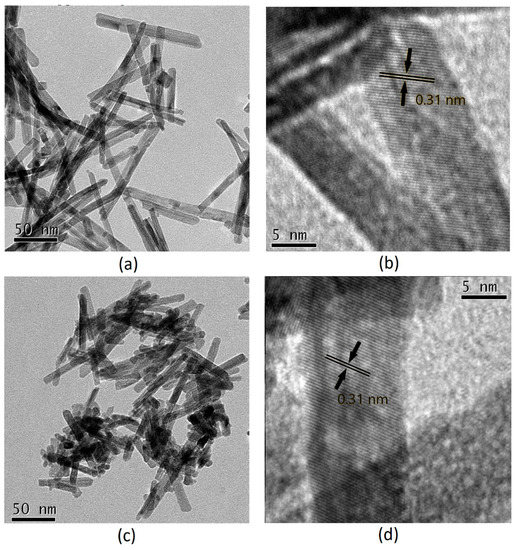
Figure 3.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images of: (a) and (b) CeO2-NR; (c) and (d) PdOx/CeO2-NR.
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis was utilized to estimate the surface areas of pure support CeO2-NR, PdOx/CeO2-NR, and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red catalysts (Figure 4 and Table 1). The BET surface area of pure ceria nanorods was 116 m2g−1, comparable to the 106 m2g−1 reported by Wang et al. [46] for ceria nanorods prepared by the same method. The surface area of PdOx/CeO2-NR was 88 m2g−1, in agreement with analogous Pd/CeO2 system [44]. As expected, the palladium deposition caused a decrease of support surface area. The BET surface area of PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red was 93 m2g−1, slightly higher than the surface area of PdOx/CeO2-NR. This might be attributable to the decrease of the amount of palladium on the surface or to the decrease of Pd particle size.
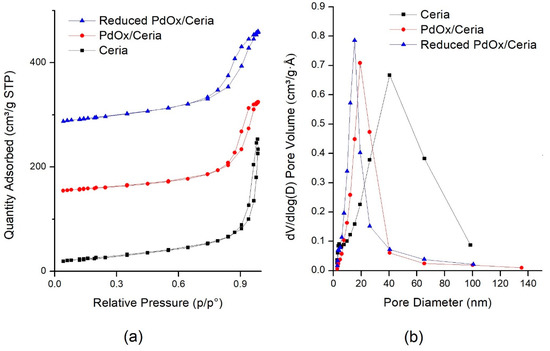
Figure 4.
Brunauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) analysis of the catalysts: (a) Nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherms as a function of p/p°; (b) pore-size distributions (PSD).
Pure CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR catalysts showed N2 adsorption–desorption curves V-Type, with H1-Type hysteresis loop for ceria-NR and H2-Type hysteresis loop for PdOx/CeO2-NR catalyst (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) classification). All these features are characteristic of well-developed and uniform mesoporous morphology (Figure 4a) but denote that the palladium oxide addition changed the sample porosimetry. Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) pore-size distribution profiles (PSD), reported on Figure 4b, showed a pore distribution in the range 0–100 nm, centered at 40 nm for pure ceria, and narrower PSD profiles centered at about 15–20 nm for PdOx/CeO2-NR, due to mesopores with very uniform dimension. The average pore dimension was 19 nm for pure CeO2-NR and 16 nm for the PdOx/CeO2-NR sample (Table 1), suggesting that the addition of palladium caused a decrease of both pore volume and pore size of the support. The hysteresis of the PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red sample is at a lower relative pressure P/P0. After the reduction of the catalyst, a further pore size decrease was observed.
To have a deeper insight of the electronic and chemical properties at the surface of the Pd/Ce-based catalysts, XPS studies have been performed. Ce 3d spectra of CeO2-NR, PdOx/CeO2-NR, and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red are reported in Figure 5. By following a peak-fitting procedure, five spin orbit pairs related to Ce 3d were individuated, and the resulting components were associated with Ce3+ and Ce4+ ions by comparison with literature data [57,58]. The amount of oxygen vacancy of ceria is correlated to the amount of Ce3+ [38]. From the peak areas, Ce3+/Ce4+ ratios were calculated, and the results are reported in Table 2. The Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio for PdOx/CeO2-NR is 0.24, equal to that of CeO2-NR, and in good agreement with the literature data about calcined CeO2-NR [40], indicating no effect of Pd loading on the surface Ce3+ concentration. Unexpectedly, the Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio of the reduced catalyst was 0.22, slightly lower than those of pure ceria and PdOx/CeO2-NR, but in agreement with literature related to reduced CeO2-NR catalysts [3].
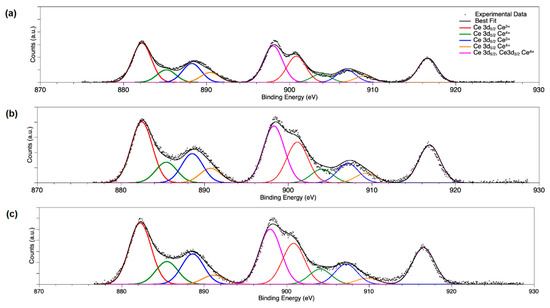
Figure 5.
X-ray photo electron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of Ce 3d region for the samples: (a) CeO2-NR, (b) PdOx/CeO2-NR, and (c) PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red. All Ce 3d5/2 spin-orbit components, as well as the Ce 3d3/2 peaks at higher BE (binding energy) values (diagnostic for the presence of Ce4+ ions), appear as bold lines in the spectra.

Table 2.
Atomic percent values of palladium species in PdOx/CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red, collected from XPS study.
Photoelectron profiles of PdOx/CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red are shown in Figure 6, and the detailed atomic percent values of observed Pd species are reported in Table 2. The most intense signal in Pd 3d spectrum of PdOx/CeO2-NR has the Pd 3d5/2 component at 337.76 eV BE, a binding energy value indicative for oxidized palladium (PdOx, x > 1); the less intense component at lower BE values (Pd 3d5/2 BE = 335.58 eV) is associated with 10% of PdO [58].
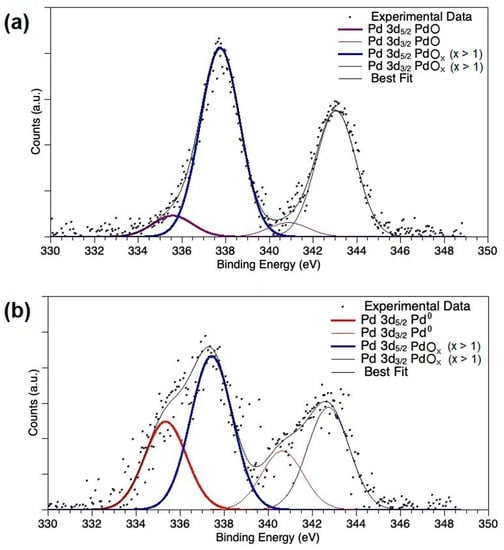
Figure 6.
XPS spectra of Pd 3d region for (a) PdOx/CeO2-NR and (b) PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red.
In PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red XPS spectra, a Pd 3d component at low BE (Pd 3d5/2 BE = 334.67 eV) is indicative of metallic palladium (Pd0) [58], whereas the signal around 337.76 eV BE is still observed. According to Table 2, 63.5% of Pd in the reduced catalyst contributes to this component. This large amount of oxidized palladium can be interpreted as the result of re-oxidation of surface Pd when exposed to air after H2-TPR. An alternative interpretation of the high-BE Pd 3d signal is the formation of a Pd−O−Ce structure, similar to the PdxCe1−xO2−δ solid-solution phase [59,60]; in this structure, Pd would act as an electron-donor toward CeO2.
Furthermore, it is observed in Table 2 that the atomic percentage of Pd decreased from 0.13% to 0.06% after reduction. This might be due to Pd diffusion into the bulk of the ceria support or to Pd sintering during the reduction process. This result is also in agreement with the higher BET surface area of PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red in comparison with the PdOx/CeO2-NR.
2.2. Catalytic Activity
The catalytic activity in BnOH oxidation was investigated using either PdOx/CeO2-NR or PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red catalyst. Oxidation of BnOH was performed in a constant-stirring-tank-reactor system (CSTR) including a round-bottom three-neck flask equipped with reflux condenser, gas inlet, and thermometer. Table 3 shows the reaction conditions of BnOH oxidation as well as the BnOH conversions and PhCHO selectivities measured by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) using cyclooctanone as internal standard. Air or oxygen was used as oxidant. In preliminary catalytic tests using oxygen as oxidant, the BnOH conversions were similar to those obtained using air. Therefore, all the subsequent reactions were performed in air. The effects of temperature, solvent nature, and Pd oxidation state were studied. CeO2-NR showed no catalytic activity for BnOH oxidation when either toluene or ethanol were utilized as solvent (Table 3, experiments 1 and 2, respectively), proving that the ceria support was not active, similar to the observation by Xin et al., for the aerobic BnOH oxidation catalyzed by pure ceria [43]. In all experiments, PhCHO was the only major product and the selectivity of PhCHO was 96% or more.

Table 3.
Aerobic oxidation of BnOH to PhCHO: reaction parameters and results.
2.2.1. Effect of Temperature and Solvent
The BnOH oxidation was first performed using PdOx/CeO2-NR in toluene at 50 °C and air at a flow of 20 mL/min. The conversion was very low, reaching 9.4% after five hours of reaction, even with a reaction selectivity of 100%. To obtain better conversions, the reaction was tested at higher temperatures (65 and 100 °C) and up to the boiling point of toluene (111 °C). As expected, the conversion increased up to 35% (Table 3, experiment 6), maintaining 100% selectivity.
Due to the low BnOH conversion in toluene (9–35%), other solvents were utilized, namely acetonitrile (AcCN), ethanol, methanol, and tetrahydrofuran (THF). The oxidation of BnOH, using different solvents at nearly 65 °C after 5 h, is presented in Table 3. The highest conversions were achieved using ethanol and methanol as solvents (50% and 41%, respectively). In the same conditions, the BnOH conversions using either toluene or AcCN were 14% and 6%, respectively.
The best result of BnOH oxidation by PdOx/CeO2-NR was achieved utilizing the protic ethanol at boiling point (78 °C). In this condition, 93% conversion and 96% selectivity were achieved (Table 3, experiment 10). This was significantly larger than the results achieved using toluene at 111 °C (35%) or AcCN at 82 °C (14%) (Table 3, experiments 6 and 8, respectively). In the experiments with ethanol, benzyl ester is detected as a secondary product, probably derived from benzoic acid due to the presence of alcoholic solvent.
The 93% BnOH conversion and 96% PhCHO selectivity, achieved by utilizing PdOx/CeO2-NR (with (111) exposed plane of CeO2-NR) in ethanol, are slightly higher than those acquired by Wang et al. (84.6% BnOH conversion, 92.8% PhCHO selectivity) [39], in the reaction catalyzed by palladium oxide supported on truncated octahedral ceria with (111) and (100) exposed plane, at almost the same temperature and higher catalyst/substrate ratio. Wang et al. also prepared and used cubic CeO2 with (100) exposed plane as support for palladium oxide, which led to significantly lower BnOH conversion (34.0%), suggesting the important role of the ceria morphology and the synergy between palladium and the CeO2 (111) plane in the catalytic activity. On the other hand, the result achieved by PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red (Table 3, experiment 13) is almost similar to that obtained by Xin et al. (26.60% BnOH conversion) using reduced palladium supported on CeO2-NR [43].
Looking at the proticity, polarity, and boiling point of the utilized solvents (Table 4), the collected data might suggest that the polarity of the solvent has a negative effect on the catalytic performance of PdOx/CeO2-NR for BnOH oxidation, given the different conversions obtained using toluene, a non-polar solvent, and AcCN, a polar one. This hypothesis can be strengthened by the observation that substrate conversion using ethanol is higher than the more polar methanol solvent, in the same conditions.

Table 4.
Properties of solvents used in BnOH oxidation reactions.
On the other hand, it seems that the proticity of the solvent plays an important role in increasing the BnOH conversion, since the best results at 65 °C were achieved by using the protic and polar ethanol and methanol solvents. Thus, it can be hypothesized that solvent properties may have an influence on the reaction mechanism and, if the solvent is both polar and protic, the effect of proticity is dominating. In similar experiments of BnOH oxidation, when Al-Saeedi et al. used Cu oxide nanoparticles as catalyst [61], the more polar DMSO solvent gave the better conversion. However, only aprotic solvents (acetone, AcCN, DMF, and DMSO) were utilized in that research work.
2.2.2. Effect of Pd Oxidation State
To study the effect of the oxidation state of Pd on the aerobic BnOH oxidation, the catalyst reduced by H2-TPR was utilized, with toluene or ethanol as solvent at their boiling points (Table 3, experiments 13 and 14, respectively). To compare the catalytic activity of PdOx/CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red, in toluene and ethanol, the conversions of BnOH are reported in Figure 7. When toluene solvent was used, the catalytic activity of PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red was lower than that of PdOx/CeO2-NR (25% versus 35%). This result might be attributable to a decrease of Pd amount on the surface after reduction process, in agreement with XPS results. On the other hand, when ethanol solvent was used, the PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red showed a BnOH conversion of 13%, considerably less than that of the PdOx/CeO2-NR (93%). Consequently, using reduced palladium, the polarity and/or proticity of the solvent look detrimental to the catalytic activity. This is in line with literature data, in which these kinds of reactions are generally performed with aprotic apolar solvents such as toluene or xylene [62].
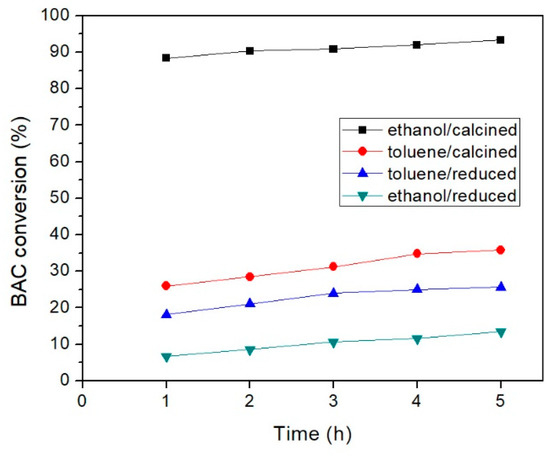
Figure 7.
BnOH conversion using PdOx/CeO2-NR or PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red catalysts, as a function of time. Reaction conditions: BnOH 0.16 mmol, catalyst mass 32 mg, reaction temperature 78 °C for ethanol and 111 °C for toluene.
2.2.3. Mechanistic Aspects of BnOH Aerobic Oxidation, Catalyzed with PdOx/CeO2-NR
The mechanism of the alcohol’s oxidation over Pd0 has been extensively studied [61,62,63,64]. It foresees oxygen chemisorption on palladium surface, assisted homolytic cleavage of the O–H bond of BnOH mediated by oxygenated Pd, and formation of an alkoxide–palladium bond and a PdOH. The subsequent hydrogen abstraction by a near Pd0, permits the release of the PhCHO and of a molecule of water.
The different behavior of PdOx/CeO2-NR, when used in toluene or ethanol, strengthens the hypothesis that the mechanism of BnOH oxidation with this catalyst, might be different from that described by Chan-Thaw et al. [64]. In PdOx/CeO2-NR, XPS data stated that no Pd0 is present on the surface; thus, it cannot catalyze the displacement of the hydrogen from the alkoxide intermediate. Furthermore, after the oxidation reaction, XPS analysis of used PdOx/CeO2-NR showed a change in the PdO/PdOx ratio in favor of the less oxidized species (see Table S1 and Figure S1, Supporting Information). All these evidences, together with the high BnOH conversion obtained with the polar protic ethanol as solvent (Table 3, experiment 10), may be explained with an heterolytic mechanism in which PdOx/CeO2-NR participates in a redox cycle [65]. Since the reaction in the highly polar AcCN gave low conversion (Table 3, experiment 8), the protonation of PdOx by a protic solvent seems kinetically crucial (Scheme 2). The more electrophilic protonated metal oxide (II in Scheme 2) may react with BnOH, producing the addition product III which, after proton release, should give the alkoxide–palladium IV. The reaction may then proceed by a proton abstraction assisted either by another PdOx, or by the ceria surface oxygen [43], and finally, the elimination of water and PhCHO by redox participation of the metal catalyst. The reduced catalyst V is then re-oxidized by molecular oxygen. Further study should be done to confirm this hypothesis.
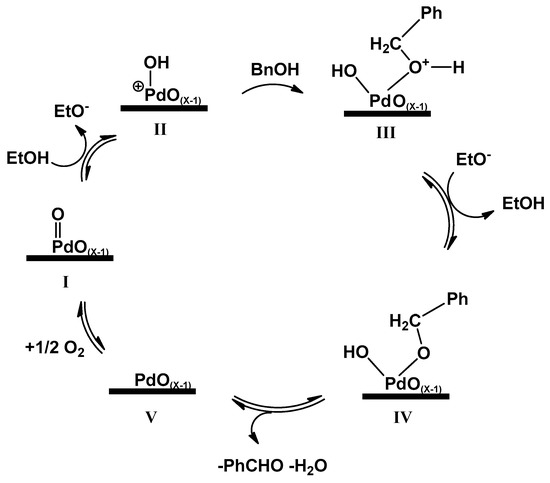
Scheme 2.
Suggested mechanism of BnOH oxidation catalyzed by PdOx supported on CeO2-NR in ethanol solvent. The thick lines represent the CeO2-NR support.
2.2.4. Leaching and Reusability Tests
The recyclability of PdOx/CeO2-NR was studied by recovering and reusing the catalyst used in experiment 10 of Table 3, for two more rounds of reaction, without any pre-treatment. BnOH conversion decreased in the second and third round to 73% and 54%, respectively, but the selectivity of PhCHO remained almost constant (Table 3 experiments 10(II) and 10(III) respectively). Calcining the catalyst after each catalytic round in ethanol might fully recover the catalytic performances.
To assess any possible leaching of palladium from the CeO2-NR support during the BnOH oxidation, a leaching test was conducted (Table 3, experiment 15). The catalyst was removed after 45 min by centrifugation and the reaction was carried on with the remaining ethanolic solution. After the catalyst was removed, no progress was observed in oxidation reaction because the BnOH conversion and PhCHO selectivity values remained constant afterward. Thus, no considerable palladium leaching occurred during the reaction.
3. Materials and Methods
Toluene (anhydrous, 99.8%), ethanol (for HPLC, ≥99.8%), AcCN (for HPLC, ≥99.9%), methanol (≥99.8% GC), THF (anhydrous, ≥99.9%), diethyl ether (≥99.8%), benzyl alcohol (ACS reagent, ≥99.0%), benzaldehyde (≥99.5%), NaOH and cerium (III) nitrate hexahydrate (99% trace metal basis) were bought from Sigma Aldrich, Germany. Cyclooctanone (~99% GC) and Celite (filter cel) were purchased from Fluka, Germany. Palladium (II) nitrate dehydrate (40% Pd) was provided from Alfa Aesar, Germany.
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
CeO2-NR was prepared according to a previously published method [46]. That is, 1.30 g of Ce(NO3)3·6H2O was dissolved in 20 mL of water and then added to an alkali solution formed by dissolving 14.40 g NaOH in 40 mL of water in a Teflon bottle under intense stirring for 30 min. Afterward, to perform a hydrothermal treatment on the mixture, the Teflon bottle was placed in a stainless-steel autoclave vessel. Then, the vessel was tightly sealed and put in oven at 100 °C for 24 h. Next, the obtained purple precipitate was separated by vacuum filtering over a paper filter, washed several times with distilled water and ethanol, and dried at 120 °C for 24 h. The dried solid was milled in an agate mortar and calcined at 400 °C for 5 h.
PdOx/CeO2-NR was prepared by depositing palladium nitrate on CeO2-NR via the wet impregnation process aiming at achieving a CeO2/Pd molar ratio of 95/5 (2 wt.% Pd) and a final calcination. A volume of 10.0 mL of 0.0200 M aqueous solution of Pd(NO3)2·2H2O was gradually added to 1.00 g of CeO2-NR in a flask while stirring and heating at 60 °C for 2 h. Afterward, the water was evaporated and the solid was dried at 120 °C for 24 h in oven, followed by milling and calcination at 500 °C for 5 h to achieve PdOx/CeO2-NR. This catalyst was applied in BnOH oxidation reaction. In addition, 250.0 mg of prepared PdOx/CeO2-NR was subjected to reduction by H2-TPR (described in Section 2.1), and the produced PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red was utilized in BnOH oxidation to study the effect of Pd oxidation state on the catalytic behavior of the palladium/ceria system.
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
XRD patterns were recorded using a Scintag X1 diffractometer equipped with a Cu Kα (λ = 1.5418 Å) source and the Brag–Brentano θ–θ configuration in the 2θ = 10°–80° range, with 0.05° step size and 3 s acquisition time. CeO2 crystallite size was calculated by Scherrer’s equation from the main diffraction peak.
TEM images were acquired using a FEI-Thermo Fisher Scientific Tecnai (MA, United States) 12 G2 Twin instrument, operating at primary electron beam energy of 120 keV, equipped with a “post-column” Gatan Biofilter (CA, United States) electron energy filter, a Gatan 794 IF Peltier cooled charge-coupled device-based slow scan camera, equipped with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) system. The used catalysts were dispersed in isopropyl alcohol and ultra-sonicated for 15 min. Then a drop of the suspension (~20 μL) was placed on a copper TEM grid (400 mesh), covered by an amorphous carbon film.
A H2-TPR experiment was performed by a Thermo Scientific TPDRO1100 flow apparatus. The PdOx/CeO2-NR (0.250 g) was pre-treated in a flow of 10% O2/He mixture (20 cm3 min−1) at 300 °C for 30 min. The H2-TPR was conducted flowing 30 cm3 min−1 of 5% H2/Ar mixture from 50 up to 500 °C with a rate of 10 °C min−1, maintaining the final temperature for 60 min. Then the sample was cooled down to 50 °C in the same mixture, followed by heating in pure Ar up to 350 °C (10 °C min−1) to remove chemisorbed hydrogen, and then cooling down to room temperature. The H2 consumption and release were measured by a thermal conductivity detector (TCD). A trap was utilized before flowing into the TCD detector to remove the generated H2O in the reduction process.
The surface areas of the synthesized materials were measures by N2 adsorption isotherms at 77 K using a Micrometrics Gemini V apparatus. Before the measurement, the sample was heated at 200 °C in He for 2 h. The surface area was calculated by the BET method in equilibrium pressure range 0.05 < P/P° < 0.3. From the desorption branch of the hysteresis loop using the BJH method, the pore size distribution was obtained, and the total pore volume was calculated from the maximum adsorption point at P/P° = 0.99.
XPS measurements were carried out at the materials science beamline (MSB) at the Elettra synchrotron radiation source (Trieste, Italy). MSB, placed at the left end of the bending magnet 6.1, is equipped with a plane grating monochromator that provides light in the energy range of 21−1000 eV. The ultra high vacuum (UHV) endstation, with a base pressure of 2 × 10−10 mbar, is equipped with a SPECS PHOIBOS 150 hemispherical electron analyzer, low-energy electron diffraction optics, a dual-anode Mg/Al X-ray source, an ion gun, and a sample manipulator with a K-type thermocouple attached to the rear side of the sample. Photoelectrons emitted by C 1s, O 1s, Pd 3d, and Ce 3d core levels were detected at normal emission geometry using photon energy of 630 eV impinging at 60°. Energy resolution of binding energies are reported after correction for charging using the aliphatic C 1s as a reference (BE 285.0 eV) [66]. Core level spectra were fitted with a Shirley background and Gaussian peak functions [67].
3.3. Catalytic Tests
Catalytic oxidation of BnOH was conducted in a 25 mL three-neck flask equipped with reflux condenser, thermometer, and gas inlet. Either 16 or 32 mg of catalyst and 10 mL of 0.016 M solution of BnOH were added to the flask following by heating in a silicon oil bath, stirring (700 rpm), and bubbling air or oxygen with the flow of 20 mL/min. Cyclooctanone was used as internal standard for calculating the BnOH conversion and PhCHO selectivity by Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
Samples from the reactions were passed over a celite path by eluting with diethyl ether and analyzed by GC-MS. The analyses were carried out on a Shimadzu VG 70/250S apparatus equipped with a Supelco SLB™ column (30 m, 0.25 mm, and 0.25 m film thickness). The analyses were performed using a temperature profile at 50 °C for 4 min followed by a 10 °C/min temperature gradient until 250 °C for 10 min. The injector temperature was 250 °C.
Recyclability test was conducted by performing the aerobic BnOH oxidation in ethanol at 78 °C for three rounds. In each round, after 5 h the catalyst was separated by centrifuge (10,000 rpm, 20 min), washed three times with ethanol, and dried at room temperature to be used in the next round. Leaching test was conducted using 16 mg PdOx/CeO2-NR catalyst in the aerobic BnOH oxidation in ethanol at 78 °C. After 45 min, the catalyst was removed by centrifuge (10,000 rpm, 20 min) and the remaining solution was subjected to reaction conditions again.
4. Conclusions
In this study, environmentally friendly aerobic and selective oxidation of BnOH to PhCHO catalyzed by PdOx/CeO2-NR heterogeneous catalyst was investigated. Palladium nitrate was deposited by wet impregnation method on the hydrothermally synthesized CeO2-NR, and a final calcination at 500 °C led to preparation of palladium oxide supported on CeO2-NR. XPS data showed that after final calcination, there was 90% PdOx, (x > 1) and 10% PdO on the surface of the support. The activity of PdOx/CeO2-NR catalyst was higher in protic solvents: the best result was achieved using boiling ethanol as a green solvent, leading to 93% BnOH conversion and 96% selectivity. On the contrary, the reduced sample, PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red, worked better in aprotic toluene (25% conversion) than in protic ethanol (13% conversion), in line with literature data. The different behavior of PdOx/CeO2-NR and PdOx/CeO2-NR-Red catalysts, suggests the possibility of dissimilar reaction mechanisms. With PdOx/CeO2-NR catalyst, a heterolytic and/or solvent proton donation mechanism might explain the higher conversion in protic solvent. The deepening of these hypotheses requires further experiments and analysis planned in future research work.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/9/10/847/s1, Table S1: Binding Energy, Full Width Half Maximum and atomic percent values of Pd3d5/2 components for the fresh and used PdOx/CeO2-NR samples. Figure S1: XPS spectra of Pd 3d region for (a) fresh PdOx/CeO2-NR, and (b) used PdOx/CeO2-NR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, and validation, S.S.M., I.L., and D.T.; formal analysis, S.S.M., I.L., S.T., C.B., and S.C.; investigation, S.S.M., P.L., and I.L.; resources, D.T., I.L., S.T., C.B., and S.C.; data curation and visualization, S.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.M., I.L., and C.B.; writing—review and editing, D.T., S.T., I.L., and P.L.; supervision, D.T. and I.L.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Ministero dell’Istruzione dell’Università e della Ricerca (MIUR)—Departments of Excellence, 2017—legge 232/2016—art.1, commi 314–337 awarded to Dept. of Science, University Roma Tre, Rome, Italy for 2018–2022.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Isaifan, R.J.; Ntais, S.; Baranova, E.A. Particle size effect on catalytic activity of carbon-supported Pt nanoparticles for complete ethylene oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 464–465, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, J.K.; Luisetto, I.; Tuti, S.; Meneghini, C.; Battocchio, C.; Iucci, G. Ni supported on YSZ: XAS and XPS characterization and catalytic activity for CO2 methanation. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 10331–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, E.; Tuti, S.; Luisetto, I. Structure-Sensitivity of CO2 Methanation over Nanostructured Ni Supported on CeO2 Nanorods. Catalysts 2019, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somorjai, G.A.; Tao, F.; Park, J.Y. The Nanoscience Revolution: Merging of Colloid Science, Catalysis and Nanoelectronics. Top. Catal. 2008, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwalski, F.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Lamonier, J.-F. Synergistic Coupling of the Redox Properties of Supports and Cobalt Oxide Co3O4 for the Complete Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds. Catal. Lett. 2010, 137, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojluechaia, S.; Chavadeja, S.; Schwankb, J.W.; Meeyoo, V. Catalytic activity of ethylene oxidation over Au, Ag and Au–Ag catalysts: Support effect. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comotti, M.; Li, W.C.; Spliethoff, B.; Schüth, F. Support Effect in High Activity Gold Catalysts for CO Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Lou, L.-L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde with hydrogen peroxide over alkali-treated ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 306, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.R.; Chaudhari, P.A.; Narkhede, V.S. Solvent-free liquid phase oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde by molecular oxygen using non-noble transition metal containing hydrotalcite-like solid catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2003, 4, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingaiah, N.; Reddy, K.M.; Babu, N.S.; Rao, K.N.; Suryanarayana, I.; Prasad, P.S.S. Aerobic selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol over vanadium substituted ammonium salt of 12-molybdophosphoric acid. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.E.; Ide, M.S.; Davis, R.J. Selective oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes over supported metal nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, I.E.; Giles, P.R.; Tsukazaki, M.; Chellé-Regnaut, I.; Urch, C.J.; Brown, S.M. Efficient, Aerobic, Ruthenium-Catalyzed Oxidation of Alcohols into Aldehydes and Ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 12661–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksman, A.; Marino-Gonza′lez, A.; Mairata i Payeras, A.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Sheldon, R.A. Efficient and Selective Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols into Aldehydes and Ketones Using Ruthenium/TEMPO as the Catalytic System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6826–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Mizuno, N. Supported Ruthenium Catalyst for the Heterogeneous Oxidation of Alcohols with Molecular Oxygen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4538–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Xu, T.; Su, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, Y. Gas-Phase Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol to Benzaldehyde with Molecular Oxygen over Unsupported Nanoporous Gold. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Huang, J.; Du, M.; Sun, D.; Abdul-Rauf, I.; Lin, W.; Hong, Y.; Li, Q. Liquid phase oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde with novel uncalcined bioreduction Au catalysts: High activity and durability. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, H. Metal-Organic Framework Supported Gold Nanoparticles as a Highly Active Heterogeneous Catalyst for Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 13362–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.L.; Hu, Q.; Tian, H.; He, C.; Hao, Z.P. Characteristics of Au/HMS catalysts for selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qin, F.; Yang, Z.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. New Reaction Pathway Induced by Plasmon for Selective Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation on BiOCl Possessing Oxygen Vacancies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.F.; Schwartz, J. Homogeneous catalytic oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones by molecular oxygen under mild conditions. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Abedi, S.; Clark, J.H.; Budarin, V. Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Alcohols Using a Recoverable Catalyst: The Role of Mesoporous Channels of SBA-15 in Stabilizing Palladium Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 4894–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, S.F.J.; Brydson, R.M.; Gass, M.H.; Harvey, I.; Newman, A.D.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. High-Activity, Single-Site Mesoporous Pd/Al2O3 Catalysts for Selective Aerobic Oxidation of Allylic Alcohols. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 8747–8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Cao, D.; Liu, C. Preparation and Characterization of Covalent Organic Polymer Supported Palladium Catalysts for Oxidation of CO and Benzyl Alcohol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shang, J.-K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.-X. Palladium nanoparticles supported on mesoporous carbon nitride for efficiently selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol with molecular oxygen. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 542, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Das, B.; Deka, B.K.; Park, Y.B.; Bhargava, S.K.; Bania, K.K. Pd/Cu-Oxide Nanoconjugate at Zeolite-Y Crystallite Crafting the Mesoporous Channels for Selective Oxidation of Benzyl-Alcohols. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35453–35462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, S.; Mokhtari, J.; Mirjafari, Z. Solvent-free and melt aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohols using Pd/Cu2(BDC)2DABCO–MOF prepared by one-step and through reduction by dimethylformamide. R. Soc. Chem. 2017, 7, 40881–40886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, D.I.; Barker, D.; Edwards, J.K.; Taylor, S.H.; Knight, D.W.; Carley, A.F.; Hutchings, G.J. Solvent-free oxidation of benzyl alcohol using titania-supported gold–palladium catalysts: Effect of Au–Pd ratio on catalytic performance. Catal. Today 2007, 122, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedziak, P.J.; He, Q.; Edwards, J.K.; Taylor, S.H.; Knight, D.W.; Tarbit, B.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Oxidation of benzyl alcohol using supported gold–palladium nanoparticles. Catal. Today 2011, 163, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.; Baiker, A. Beneficial Interaction of Gold and Palladium in Bimetallic Catalysts for the Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6191–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Dou, B.J.; Li, J.J.; Cheng, J.; Hu, Q.; Hao, Z.P.; Qiao, S.Z. Catalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol on Au or Au–Pd nanoparticles confined in mesoporous silica. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 92, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lim, H.; Tang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Sun, T.; Yan, Q.; Yang, Y. Solvent-free aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol over Pd monometallic and Au–Pd bimetallic catalysts supported on SBA-16 mesoporous molecular sieves. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 380, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaji, M.; Chadwick, D. Au-Pd Bimetallic Nanoparticles Immobilised on Titanate Nanotubes: A Highly Active Catalyst for Selective Oxidation. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 4353–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Tomer, A.; Perrussel, G.; Ousmane, M.; Katryniok, B.; Dumeignil, F.; Ponchel, A.; Liebens, A.; Pera-Titus, M. A Pd/CeO2 “H2Pump” for the Direct Amination of Alcohols. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3347–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jia, A.-P.; Lu, J.-Q.; Luo, L.-F.; Huang, W.-X.; Luo, M.-F. Synergetic Effects of PdO Species on CO Oxidation over PdO–CeO2 Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 19789–19796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Dewil, R. CeO2 Nanocrystalline-Supported Palladium Chloride: An Effective Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Alcohols by Oxygen. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaimess, M.; Lin, Z.; Weng, W.; Dimitratos, N.; Dummer, N.F.; Taylor, S.H.; Bartley, J.K.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Oxidation of benzyl alcohol by using gold nanoparticles supported on ceria foam. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z.; Tao, R.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z. In-situ loading ultrafine AuPd particles on ceria: Highly active catalyst for solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Q.; Guan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, F. Typical crystal face effects of different morphology ceria on the activity of Pd/CeO2 catalysts for lean methane combustion. Fuel 2018, 233, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Jianxin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Qin, R.; Wu, C.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, L. The synergy between atomically dispersed Pd and cerium oxide for enhanced catalytic properties. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6643–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykaki, M.; Pachatouridou, E.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Iliopoulou, E.; Andriopoulou, C.; Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Boghosian, S.; Konsolakis, M. Ceria nanoparticles shape effects on the structural defects and surface chemistry: Implications in CO oxidation by Cu/CeO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 230, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, D.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J. Morphology Dependence of Catalytic Properties of Ni/CeO2 Nanostructures for Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 10009–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, J. Morphology control of ceria nanocrystals for catalytic conversion of CO2 with methanol. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5582–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, X.; Dong, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Gu, L.; Luo, J.; Rong, H.; et al. Revealing the Active Species for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation by Using Uniform Supported Palladium Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 4642–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhou, K. Support Morphology-Dependent Catalytic Activity of Pd/CeO2 for Formaldehyde Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8675–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, R.; Li, Q.-J.; Yao, M.-G.; Zou, B.; Cui, T.; Liu, B.-B.; Liu, J. Study of high pressure structural stability of CeO2 nanoparticles. Chin. Phys. C 2013, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-W.; Yu, W.-Z.; Du, P.-P.; Xu, H.; Jin, Z.; Si, R.; Ma, C.; Shi, S.; Jia, C.-J.; Yan, C.-H. Crystal Plane Effect of Ceria on Supported Copper Oxide Cluster Catalyst for CO Oxidation: Importance of Metal–Support Interaction. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Tang, R.; Shang, N.; Feng, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, C. Pd nanoparticles supported on CeO2 as efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from formaldehyde solution at room temperature. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.-Y.; Meng, M.; Xian, H.; Tu, Y.-B.; Li, X.-G.; Ding, T. The Nanomorphology-Controlled Palladium-Support Interaction and the Catalytic Performance of Pd/CeO2 Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2009, 133, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisetto, I.; Tuti, S.; Romano, C.; Boaro, M.; Di Bartolomeo, E. Dry reforming of methane over Ni supported on doped CeO2: New insight on the role of dopants for CO2 activation. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 30, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnatowska, M.; Kepinski, L.; Mista, W. Structure evolution of nanocrystalline Ce1−xPdxO2−y mixed oxide in oxidizing and reducing atmosphere: Reduction-induced activity in low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 117–118, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hayes, R.E.; Wu, X.; Semagina, N. 100° Temperature Reduction of Wet Methane Combustion: Highly Active Pd–Ni/Al2O3 Catalyst versus Pd/NiAl2O4. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, G.; Groppo, E.; Piovano, A.; Pellegrini, R.; Leofanti, G.; Lamberti, C. Preparation of supported Pd catalysts: From the Pd precursor solution to the deposited Pd2+ phase. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11204–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, F.; Menegazzo, F.; Signoretto, M.; Canton, P.; Fagherazzi, G.; Pernicone, N. Consecutive Hydrogenation of Benzaldehyde Over Pd Catalysts Influence of Supports and Sulfur Poisoning. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 219, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.F.; Hou, Z.Y.; Yaun, X.X.; Zheng, X.M. Characterization study of CeO2 supported Pd catalyst for low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. Catal. Lett. 1998, 50, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, R.; Lingaiah, N.; Sreedhar, B.; Suryanarayana, I.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Obuchi, A. Highly stable Pd/CeO2 catalyst for hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z. Insights into the Surface-Defect Dependence of Photoreactivity over CeO2 Nanocrystals with Well-Defined Crystal Facets. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4851–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, J.Z.; Weber, W.H.; Gandhi, H.S. Surface Characterization of Alumina-Supported Ceria. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 4964–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database. Version 4.1. Available online: https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 15 October 2018).
- You, R.; Li, Z.; Cao, T.; Nan, B.; Si, R.; Huang, W. Synthesis in Glovebox: Utilizing Surface Oxygen Vacancies to Enhance Atomic Dispersion of Palladium on Ceria for CO Oxidation and Propane Combustion. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Wei, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Insight Investigation of Active Palladium Surface Sites in Palladium-Ceria Catalysts for NO + CO Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13614–13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeedi, S.; Abdel-Rahman, L.; Abu-Dief, A.; Abdel-Fatah, S.; Alotaibi, T.; Alsalme, A.; Nafady, A. Catalytic Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol Using Nanosized Cu/Ni Schiff-Base Complexes and Their Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Catalysts 2018, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savara, A.; Chan-Thaw, C.E.; Rossetti, I.; Villa, A.; Prati, L. Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation on Carbon-Supported Pd Nanoparticles: Elucidating the Reaction Mechanism. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 3464–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zope, B.N.; Hibbitts, D.D.; Neurock, M.; Davis, R.J. Reactivity of the Gold/Water Interface During Selective Oxidation Catalysis. Science 2010, 330, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Thaw, C.; Savara, A.; Villa, A. Selective Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation over Pd Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohs, J.M. Site requirements for the adsorption and reaction of oxygenates on metal oxide surfaces. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4136–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Physical Electronics Inc.: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shirley, D.A. High-Resolution X-ray Photoemission Spectrum of the Valence Bands of Gold. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 4709–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).