Magnetic Chitosan-Supported Silver Nanoparticles: A Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
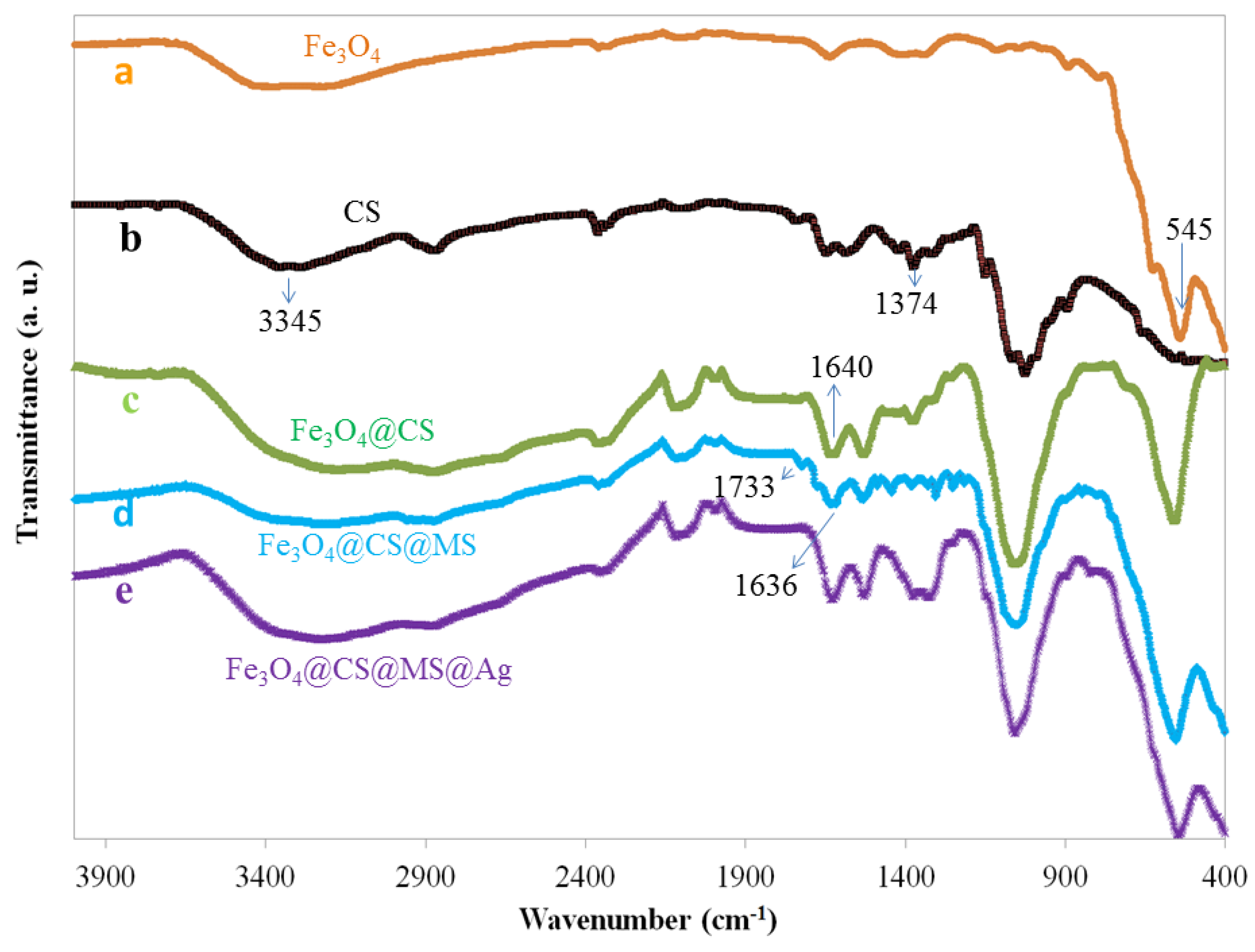
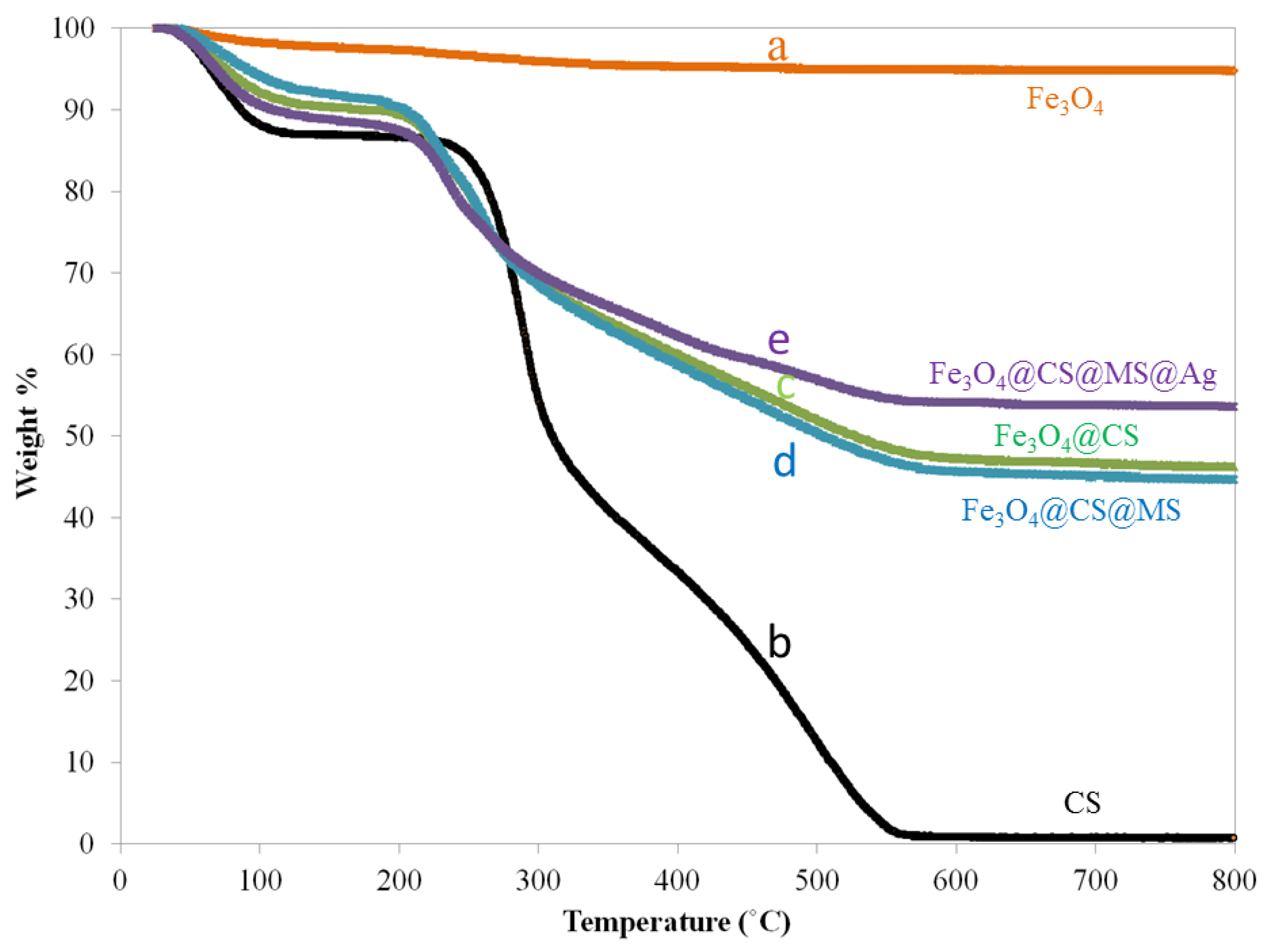
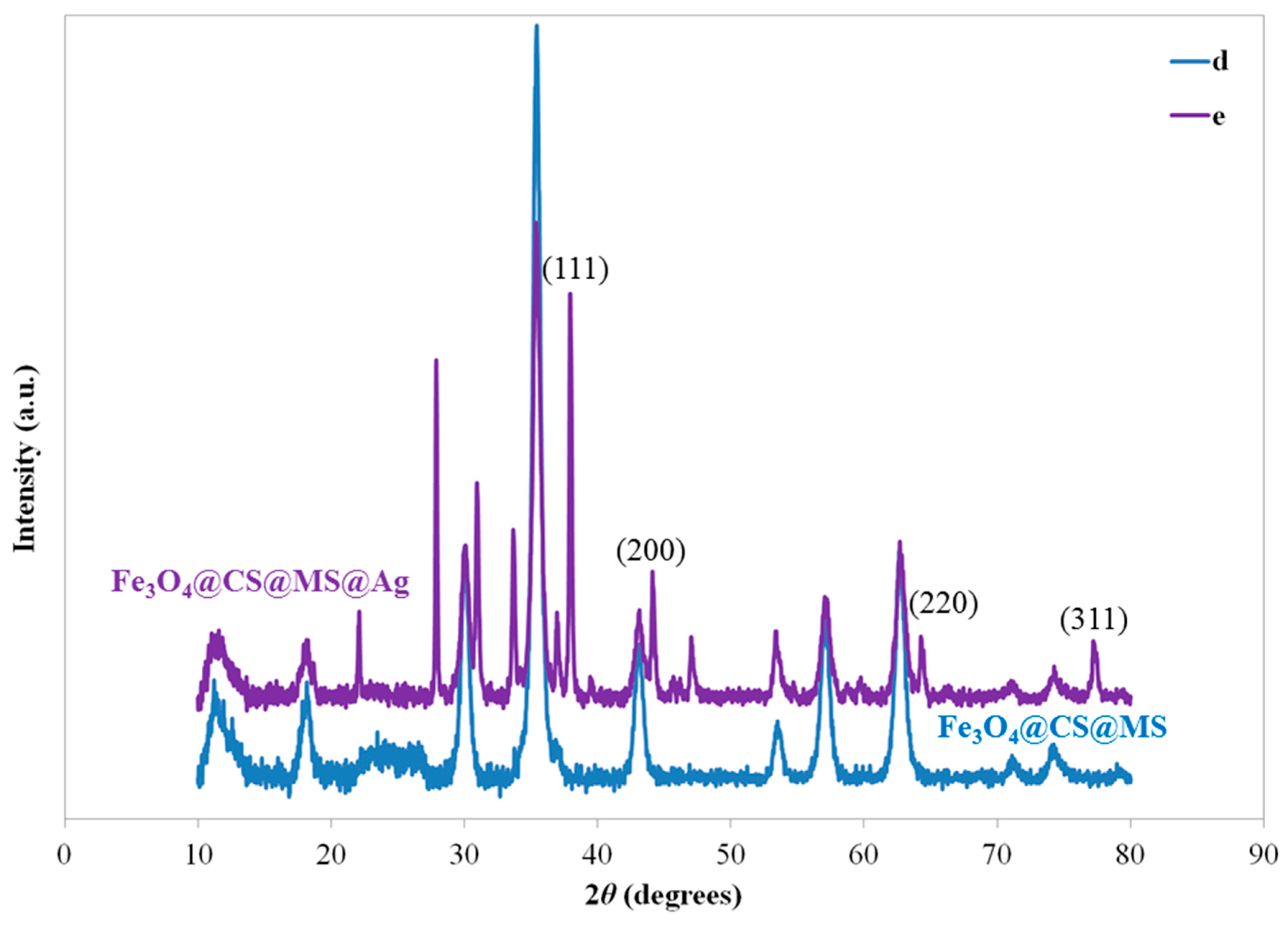
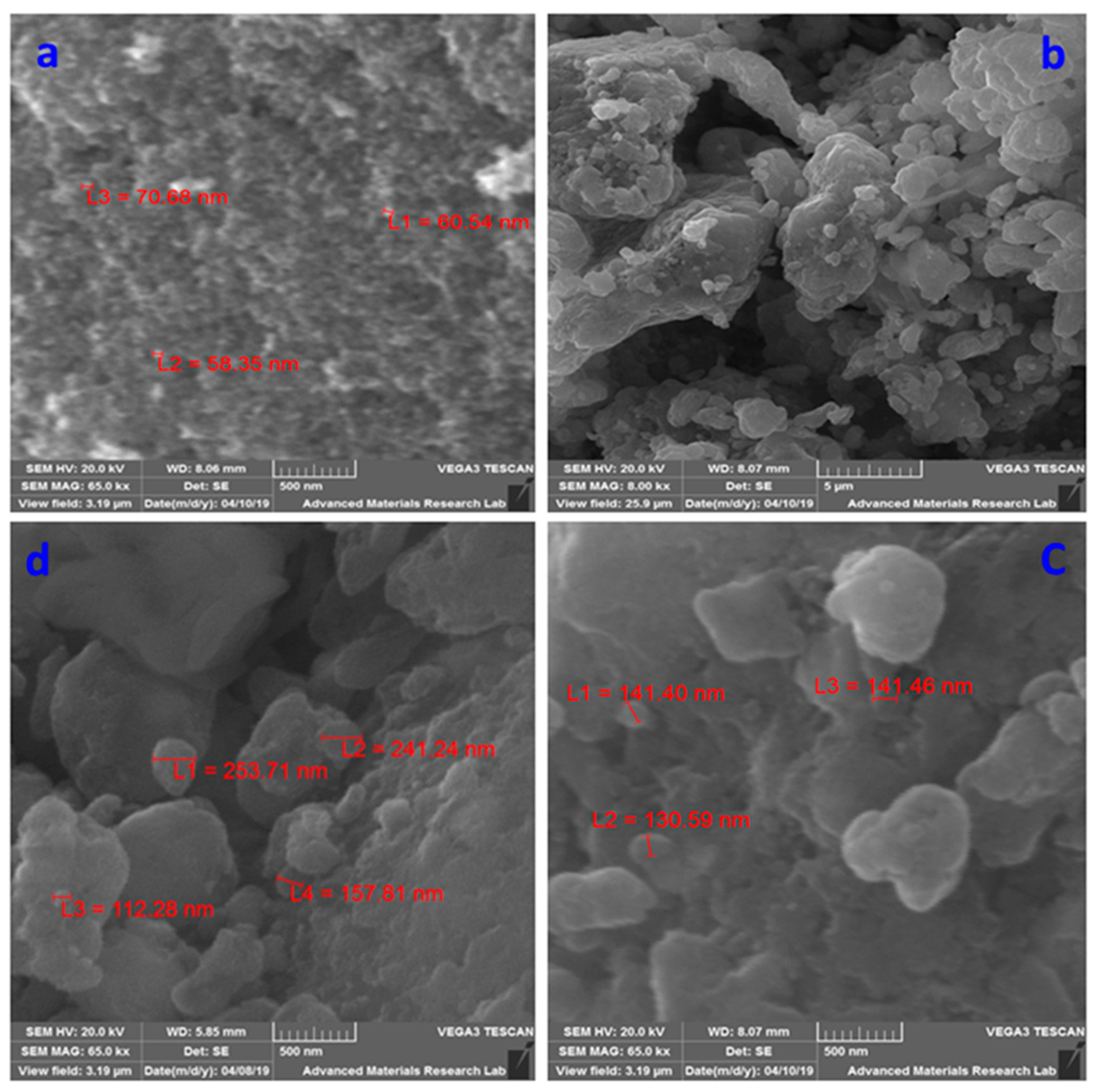
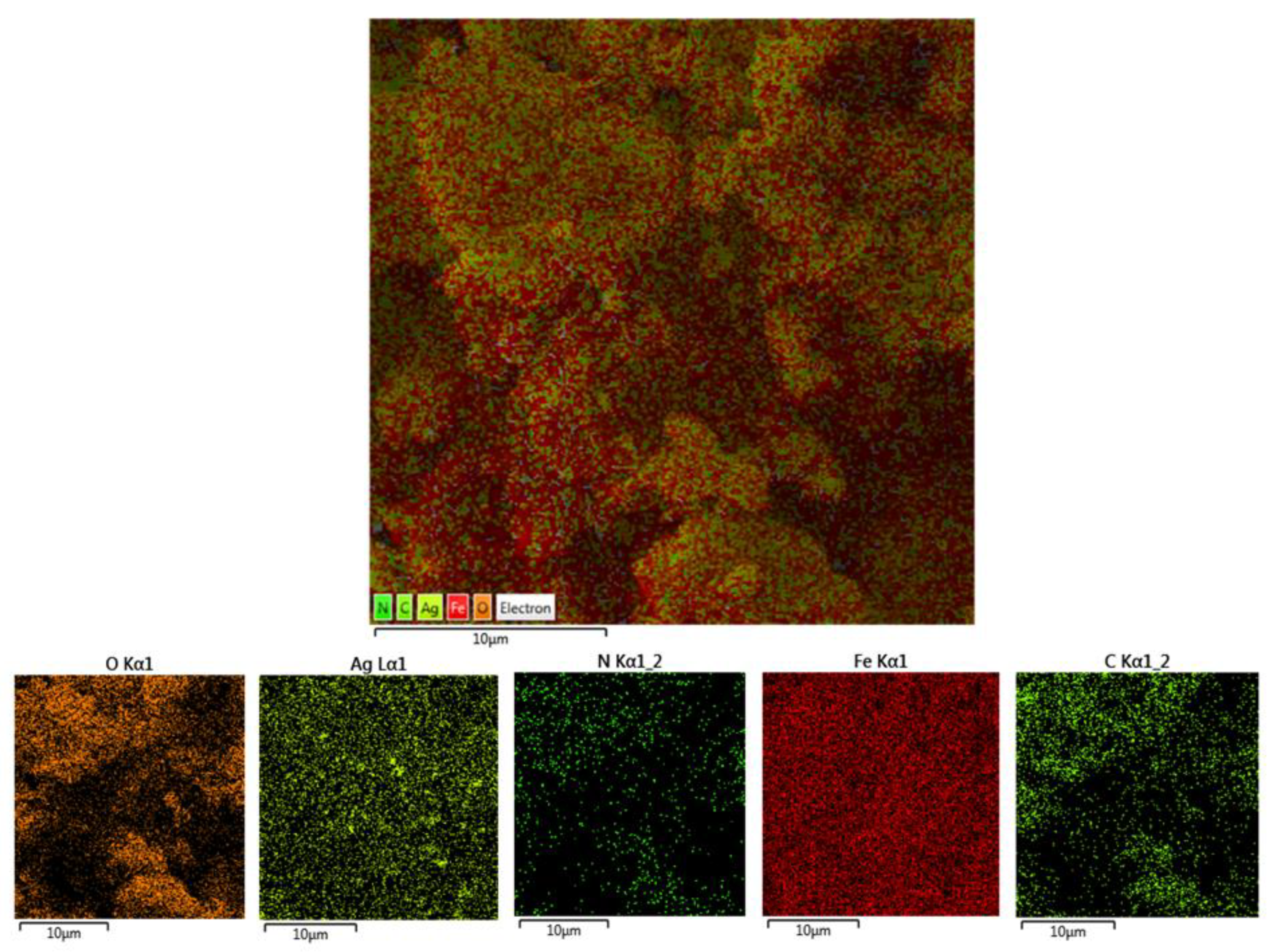
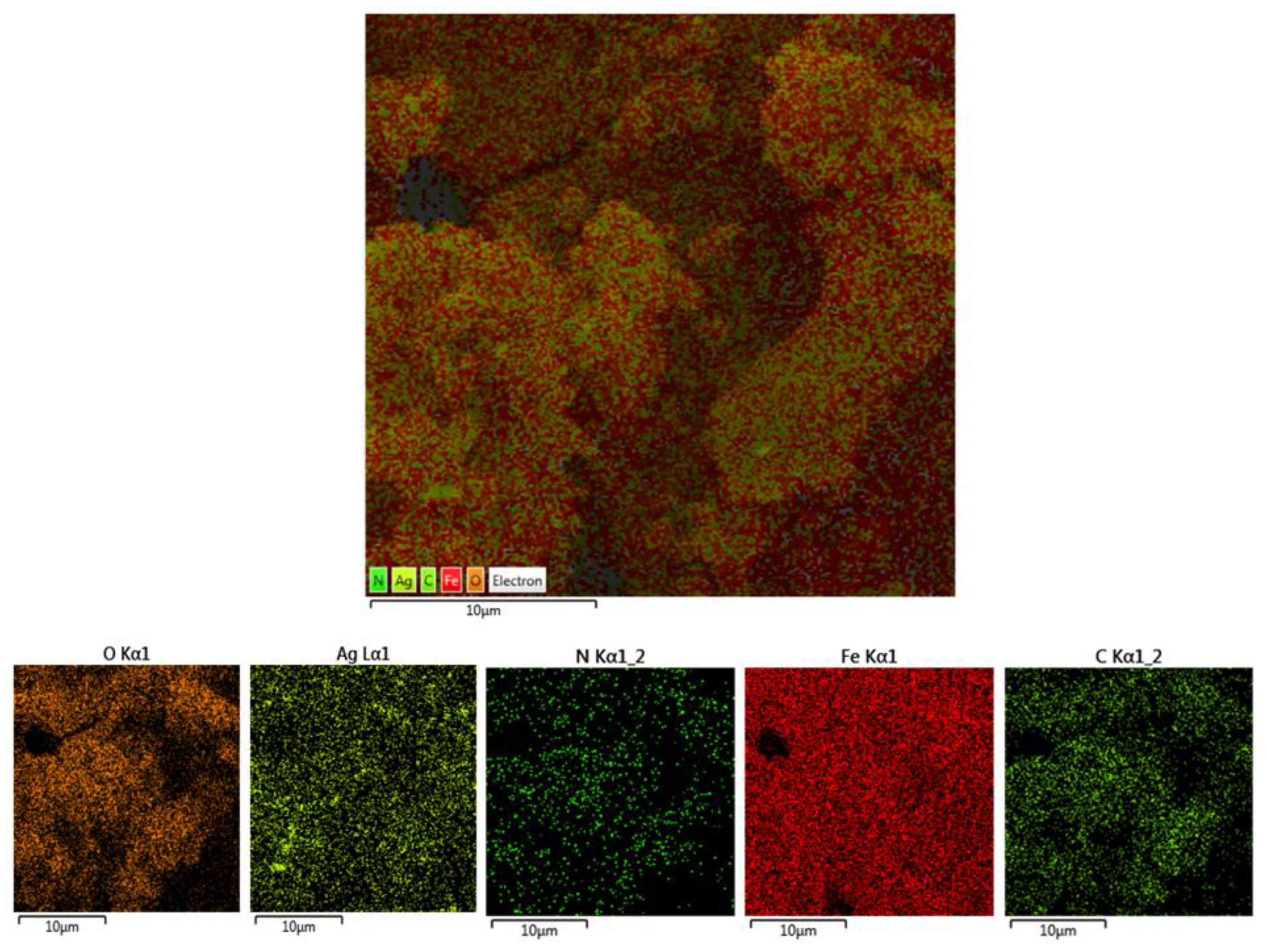
2.1. Characterization
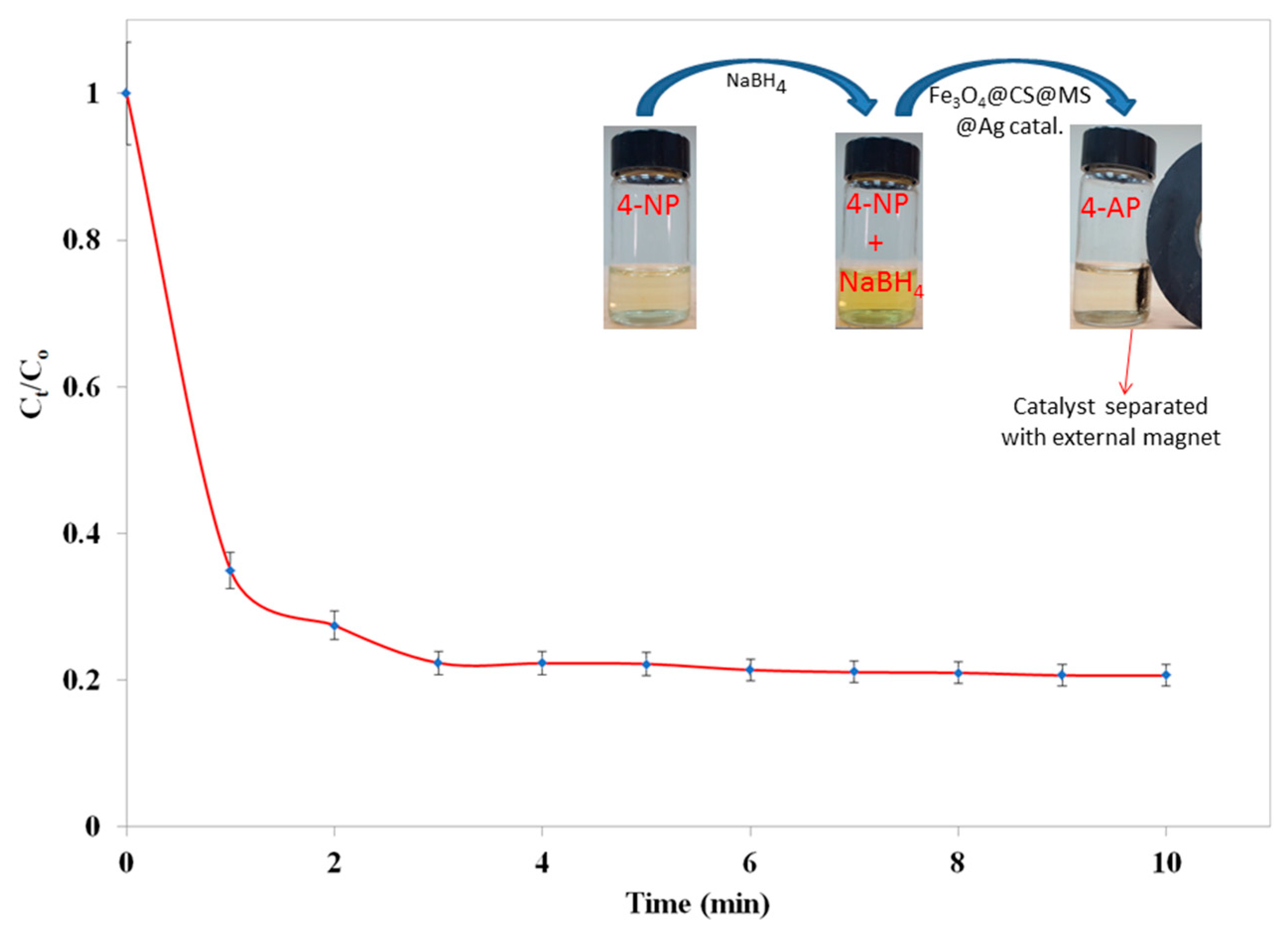
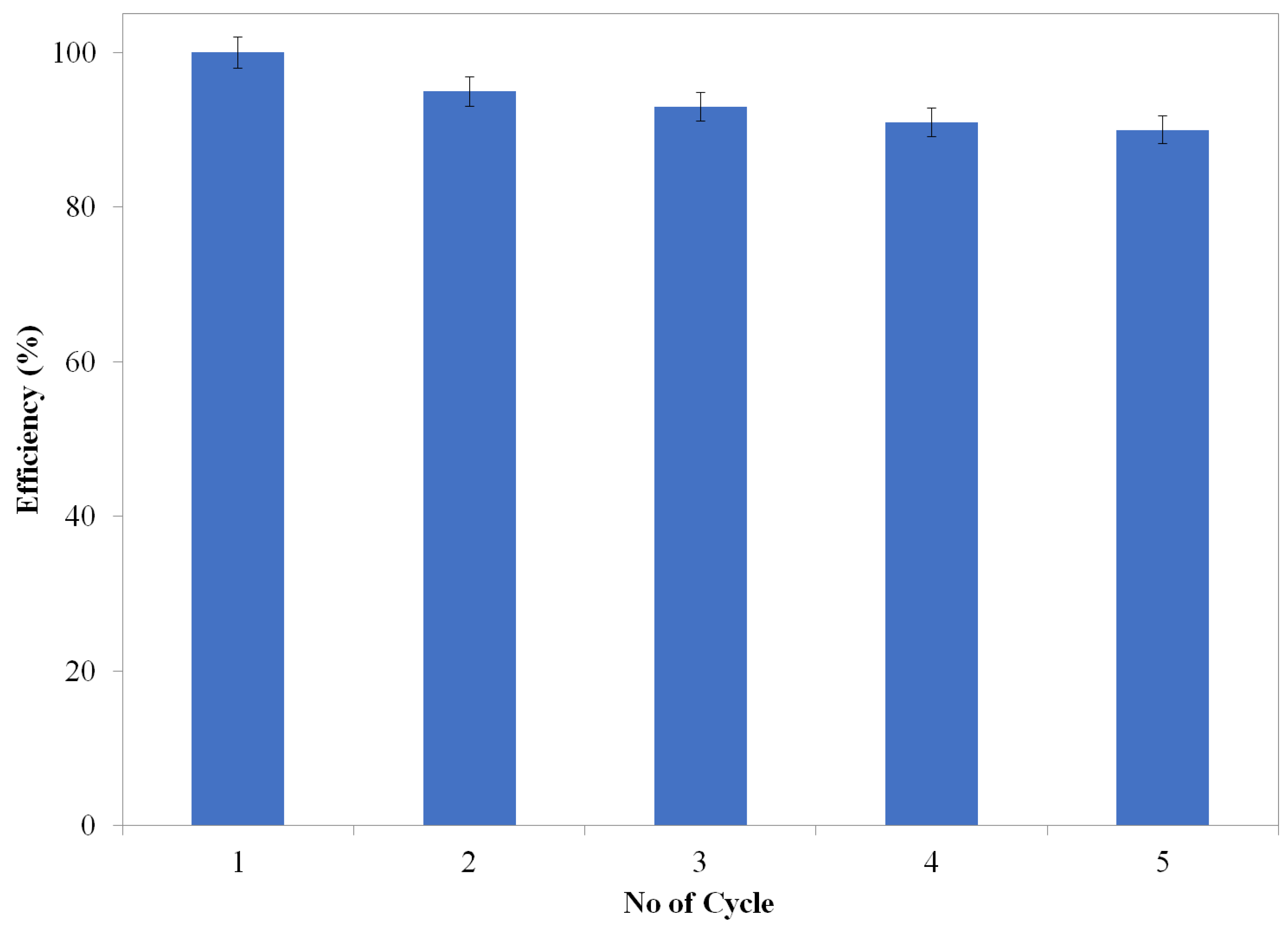
2.2. Reduction of the 4-Nitrophenol (4-NP)
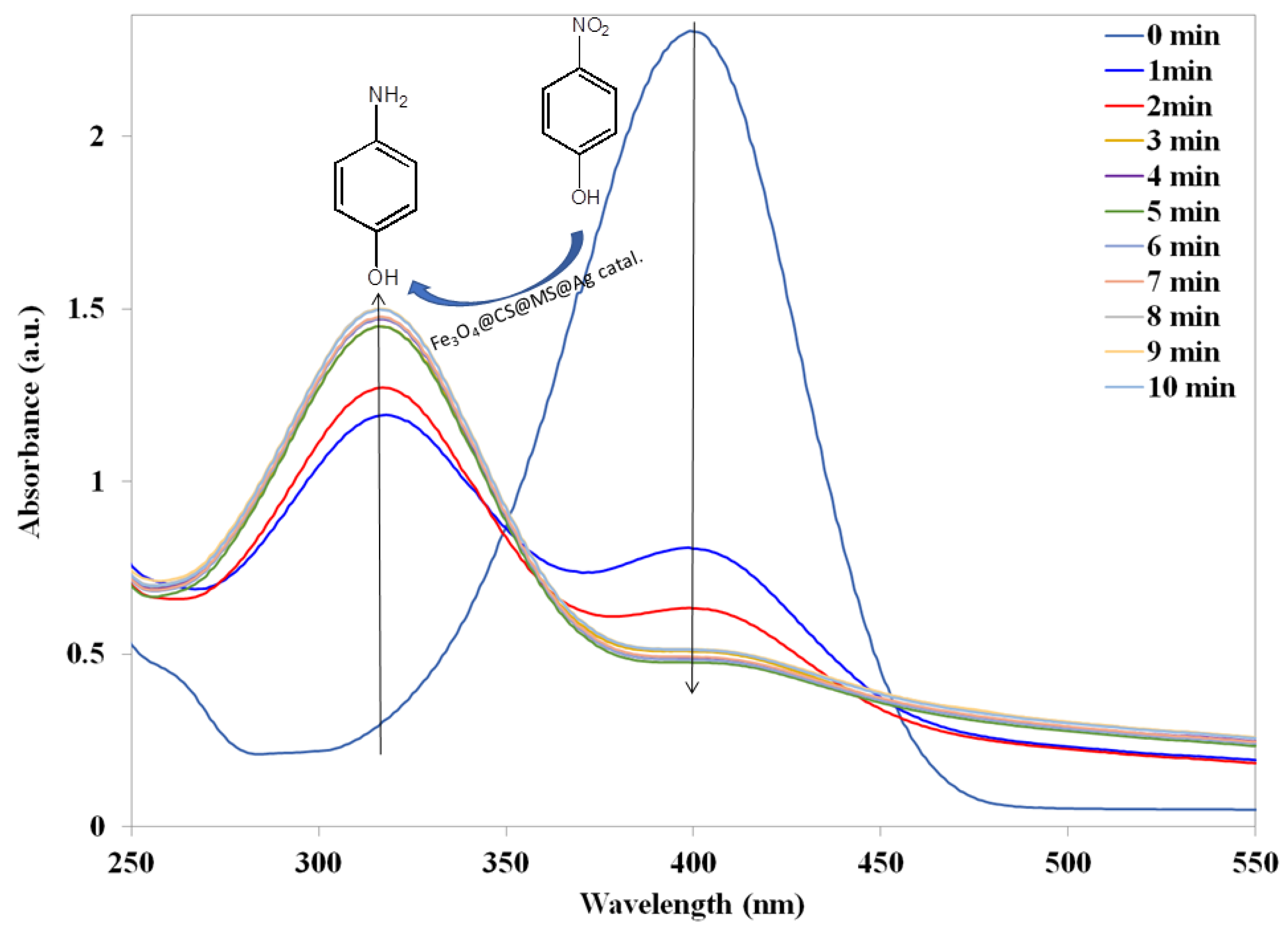
 violet color spectrum). When a freshly prepared NaBH4 solution was added to the 4-NP solution, immediately the color of the reaction mixture changed from light yellow to bright yellow, and the position of absorption maximum (λmax) shifted to 400 nm. This color change indicates the formation of nitrophenolate ions in presence of alkaline NaBH4 solution (Figure 7;
violet color spectrum). When a freshly prepared NaBH4 solution was added to the 4-NP solution, immediately the color of the reaction mixture changed from light yellow to bright yellow, and the position of absorption maximum (λmax) shifted to 400 nm. This color change indicates the formation of nitrophenolate ions in presence of alkaline NaBH4 solution (Figure 7;  black color spectrum). The absorption (λmax) remained unchanged over time (30 min) and even after adding an additional amount of NaBH4 solution. It clearly proves that reduction of 4-NP does not proceed by using only NaBH4 solution.
black color spectrum). The absorption (λmax) remained unchanged over time (30 min) and even after adding an additional amount of NaBH4 solution. It clearly proves that reduction of 4-NP does not proceed by using only NaBH4 solution. red color spectrum). However, when silver nanoparticles deposited surface modified magnetic chitosan catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.5 mg; 1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) was added to the aqueous solution of 4-NP and NaBH4 mixture, immediately the color of the reaction mixture turned to very light yellow. This color change was estimated by UV-Vis absorption (Figure 7;
red color spectrum). However, when silver nanoparticles deposited surface modified magnetic chitosan catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.5 mg; 1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) was added to the aqueous solution of 4-NP and NaBH4 mixture, immediately the color of the reaction mixture turned to very light yellow. This color change was estimated by UV-Vis absorption (Figure 7;  blue color spectrum), indicating the appearance of a new peak at 320 nm for the formation of 4-AP.
blue color spectrum), indicating the appearance of a new peak at 320 nm for the formation of 4-AP.  blue color spectrum). To the best of our knowledge, this is for the first-time the CS decorated Fe3O4 has shown catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP. The experiment was repeated for three times and every time the same result was reproduced. We speculate the reduction occurred via electron relaying mechanism from the donor BH4− to the acceptor 4-NP while both have been adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst. Hydrogen atom generated from hydride by transferring electron to magnetic chitosan surface and then attacking the substrate 4-NP and reducing it to 4-AP. During the reduction process, as concertation of NaBH4 is relatively excessive compared to 4-NP, it has been considered that NaBH4 concentration remains constant. Then, the surface modified magnetic CS by methyl salicylate Fe3O4@CS@MS was examined for the catalytic reduction of 4-NP in the presence of NaBH4 solution (Figure 8;
blue color spectrum). To the best of our knowledge, this is for the first-time the CS decorated Fe3O4 has shown catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP. The experiment was repeated for three times and every time the same result was reproduced. We speculate the reduction occurred via electron relaying mechanism from the donor BH4− to the acceptor 4-NP while both have been adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst. Hydrogen atom generated from hydride by transferring electron to magnetic chitosan surface and then attacking the substrate 4-NP and reducing it to 4-AP. During the reduction process, as concertation of NaBH4 is relatively excessive compared to 4-NP, it has been considered that NaBH4 concentration remains constant. Then, the surface modified magnetic CS by methyl salicylate Fe3O4@CS@MS was examined for the catalytic reduction of 4-NP in the presence of NaBH4 solution (Figure 8;  black color spectrum).
black color spectrum).  red color spectrum).
red color spectrum). 3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4
3.3. Coating of Fe3O4 with Chitosan (Fe3O4@CS)
3.4. Surface Modification of Magnetic Chitosan (Fe3O4@CS@MS)
3.5. Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles on Modified Magnetic Chitosan (Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag)
3.6. Catalytic Reaction
3.7. Instrumentation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chorkendroff, I.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W. Introduction to catalysis. Concepts Mod. Catal. Kinet. 2003, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Coperet, C.; Chabanas, M.; Saint-Arroman, R.P.; Basset, J.-M. Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis: Bridging the gap through surface organometallic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 156–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Rafiaei, S.M.; Abolhosseini, S.; Shokouhimehr, M. Palladium nanocatalysts confined in mesoporous silica for heterogeneous reduction of nitroaromatics. Energy Environ. Focus 2015, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadi, A.; Rostamnia, S.; Panahi, P.; Wilson, L.D.; Kong, Q.; An, Z.; Shokouhimehr, M. Palladium comprising dicationic bipyridinium supported periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO): Pd@Bipy-PMO as an efficient hybrid catalyst for suzuki-miyaura cross-coupling reaction in water. Catalysts 2019, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hong, K.; Suh, J.M.; Lee, T.H.; Kwon, O.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Jang, H.W. Facile synthesis of monodispersed Pd nanocatalysts decorated on graphene oxide for reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous solution. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M.; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Du, X.; Shi, L.; Gao, R. Shape-controlled synthesis and catalytic application of ceria nanomaterials. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 14455–14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V.K.; Lauhon, L.J.; Marks, T.J.; Hersam, M.C. Carbon nanomaterials for electronics, optoelectronics, photovoltaics, and sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2824–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaera, F. Nanostructured materials for applications in heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2746–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; Quinn, S.J.; Giordani, S. Carbon nanomaterials: Multi-functional agents for biomedical fluorescence and Raman imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4672–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, C.; Roy, V.A.L. Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide-semiconductor composite nanomaterials as promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.F.; Tang, J.; Nie, Z.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, L. Preparation and application of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for wastewater purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 68, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-R.; Wu, S.-T.; Tsai, Z.-T.; Wang, J.-J.; Yen, T.-C.; Tsai, J.-S.; Shih, M.-F.; Liu, C.-L. Characterization of quaternized chitosan-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles as a novel potential magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent for cell tracking. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, F.; Su, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Hou, Y. Synthesis and catalysis of oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanocrystals for direct coal liquefaction. Catal. Commun. 2012, 26, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojtahedi, M.M.; Abaee, M.S.; Rajabi, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Bagherpoor, S. Recyclable superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient catalysis of thiolysis of epoxides. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2012, 361, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Sung, Y.-E. Heterogeneous Suzuki cross-coupling reaction catalyzed by magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.W.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Lee, D.J.; Jang, Y.; Park, J.; Hyeon, T. One-pot synthesis of magnetically recyclable mesoporous silica supported acid-base catalysts for tandem reactions. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7821–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Lee, J.E.; Han, S.I.; Hyeon, T. Magnetically recyclable hollow nanocomposite catalysts for heterogeneous reduction of nitroarenes and Suzuki reactions. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4779–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiaei, S.M.; Kim, A.; Shokouhimehr, M. Gadolinium triflate immobilized on magnetic nanocomposites as recyclable Lewis acid catalyst for acetylation of phenols. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2014, 6, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhimehr, M. Magnetically separable and sustainable nanostructured catalysts for heterogeneous reduction of nitroaromatics. Catalysts 2015, 5, 534–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Hong, K.; Lee, T.H.; Moon, C.W.; Hong, S.P.; Zhang, K.; Suh, J.M.; Choi, K.S.; Varma, R.S.; Jang, H.W. Magnetically retrievable nanocomposite adorned with Pd nanocatalysts: Efficient reduction of nitroaromatics in aqueous media. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Wang, S.M.; Huang, J.F.; Zhuo, L.H.; Guo, Y.C. Study on the heterogeneous degradation of chitosan with hydrogen peroxide under the catalysis of phosphotungstic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, A.; Maleki, A. Cellulose sulfuric acid as a bio-supported and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the one-pot three-component synthesis of α-amino nitriles. Appl. Catal. A 2007, 331, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, S.E.S.; Stolle, A.; Ondruschka, B.; Cravotto, G.; De Leo, C.; Jandt, K.D.; Keller, T.F. Chitosan as a support for heterogeneous Pd catalysts in liquid phase catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2010, 379, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Ye, Y.; Jia, X.; Yuan, C.; Qian, W. Chitosan as an active support for assembly of metal nanoparticles and application of the resultant bioconjugates in catalysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, P.; Roy, A.S.; Tuhina, K.; Salam, N.; Mobarak, M. A reusable polymer supported copper catalyst for the C-N and C-O bond cross-coupling reaction of aryl halides as well as arylboronic acids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 696, 4264–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Rajgopal, K.; Maheswari, C.U.; Kantam, M.L. Chitosan hydrogel: A green and recyclable biopolymer catalyst for aldol and Knoevenagel reactions. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekamin, M.G.; Azimoshan, M.; Ramezani, L. Chitosan: A highly efficient renewable and recoverable bio-polymer catalyst for the expeditious synthesis of α-amino nitriles and imines under mild conditions. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.; Basu, S.; Praharaj, S.; Pande, S.; Jana, S.; Pal, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Synthesis and size-selective catalysis by supported gold nanoparticles: Study on heterogeneous and homogeneous catalytic process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spain, J.C. Biodegradation OF nitroaromatic compounds. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 523–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; He, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W. Biodegradation kinetics of picric acid by Rhodococcus sp.NJUST16 in batch reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, M.J.; Kulkarni, S.M.; Chaudhari, R.V. Synthesis of p-Aminophenol by Catalytic Hydrogenation of p-Nitrophenol. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2003, 7, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Luo, Y.; Qin, X.; Lu, W.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Synthesis of Pt nanoparticles decorated 1,5-diaminoanthraquinone nanofibers and their application toward catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7075–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemanashi, M.; Meijboom, R. Synthesis and characterization of Cu, Ag and Au dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles and their application in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 389, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Yan, J. Fabrication of graphene oxide decorated with Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles and its superior catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7384–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. Facile synthesis of Au nanoparticles supported on polyphosphazene functionalized carbon nanotubes for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 5056–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.-H.; Na, H.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.-X. Preparation of Au nanoparticles immobilized cross-linked poly(4-vinylpyridine) nanofibers and their catalytic application for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3909–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamuly, C.; Hazarika, M.; Bordoloi, M. Biosynthesis of Au and Ag-Au bimetallic nanoparticles by pedicellamide for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Bionanosci. 2015, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, P.; Sun, Q.; Jia, Y.; Yan, W.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Q. Au nanoparticle decorated N-containing polymer spheres: Additive-free synthesis and remarkable catalytic behavior for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Chang, W.; Chang, K.; Zhang, H. Synthesis and characterization of ultrafined palladium nanoparticles decorated on 2D magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets and their application for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Cheng, S.; Feng, C.; Shang, N.; Gao, S.; Wang, C. Fabrication of highly dispersed Pd nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Catal. Commun. 2017, 90, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C. Preparation and characterization of core-shell polystyrene/polyaniline/Pd composites and their catalytic properties for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berahim, N.; Basirun, W.J.; Leo, B.F.; Johan, M.R. Synthesis of bimetallic gold-silver (Au-Ag) nanoparticles for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Catalysts 2018, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q. Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles decorated multi-amino cyclophosphazene hybrid microspheres as enhanced activity catalysts for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 207, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Costa, P.; Sousa, C.A.D.; Pereira, C.; Rodriguez-Borges, J.E.; Freire, C. L-serine-functionalized montmorillonite decorated with Au nanoparticles: A new highly efficient catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Catal. 2018, 361, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdankhah, M.; Veisi, H.; Hemmati, S. In situ immobilized palladium nanoparticles (Pd NPs) on fritillaria imperialis flower extract-modified graphene and their catalytic activity for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.-S.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Meng, H.-B.; Feng, J.-J.; Wang, A.-J. One-pot synthesis of highly branched Pt@Ag core-shell nanoparticles as a recyclable catalyst with dramatically boosting the catalytic performance for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.S.; Choi, J.-Y.; Park, C.S.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, K. Facile synthesis and catalytic application of silver-deposited magnetic nanoparticles. Catal. Lett. 2009, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Yue, H.; Jiang, J. Environmentally friendly light-driven synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in situ grown on magnetically separable biohydrogels as highly active and recyclable catalysts for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23447–23453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-C.; Chen, D.-H. Green synthesis and synergistic catalytic effect ofAg/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, J.; Zarnegar, Z.; Sadeghi, M.; Enayati-Najafabadi, A. Dendritic macromolecules supported Ag nanoparticles as efficient catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1125, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamani, F.; Azizian, S. Green and simple synthesis of Ag nanoparticles loaded onto cellulosic fiber as efficient and low-cost catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, H.; Kazemi, S.; Mohammadi, P.; Safarimehr, P.; Hemmati, S. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol over Ag nanoparticles immobilized on Stachys lavandulifolia extract-modified multi walled carbon nanotubes. Polyhedron 2019, 157, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, B.; Hazra, S.; Prasad, V.S.; Ghosh, N.N. Synthesis of Ag nanoparticles within the pores of SBA-15: An efficient catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, J.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; An, S. Ag-deposited silica-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles catalyzed reduction of p-nitrophenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liang, X.; Chen, N.; Tang, J.; Shao, W.; Gao, Q.; Teng, Z. Magnetic separable chitosan microcapsules decorated with silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 507, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Hou, P. Reversible immobilization of glucoamylase onto magnetic chitosan nanocarriers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Boostani, E.; Mohammadsaleh, F. Proline-functionalized chitosan–palladium(ii) complex, a novel nanocatalyst for C–C bond formation in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24742–24748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipour, A.; Fakhri, A. Heterogeneous Fe3O4@chitosan-Schiff base Pd nanocatalyst: Fabrication, characterization and application as highly efficient and magnetically-recoverable catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck–Mizoroki C–C coupling reactions. Catal. Commun. 2016, 73, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, R.; Arun, T.; Manickam, S.T.D. A review on applications of chitosan-based Schiff bases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 615–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Cui, G.; Tian, Y.; Yan, S. Multifunctional magnetic core-shell dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres decorated with tiny Ag nanoparticles as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, J.; Javadian, L. Chitosan decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a magnetic catalyst in the synthesis of phenytoin derivatives. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48973–48979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2782–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Kerdari, H.; Rabbani, M.; Shafiee, M. Synthesis, characterization and adsorbing properties of hollow Zn-Fe2O4 nanospheres on removal of Congo red from aqueous solution. Desalination 2011, 28, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Qin, P.; Lei, M.; Zeng, Q.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Liao, B.; Gu, J. Modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with humic acid for removal of Rhodamine B in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Zhang, F.-W.; Niu, J.-R.; Yang, H.-L.; Li, R.; Ma, J.-T. Pd immobilized on thiol-modified magnetic nanoparticles: A complete magnetically recoverable and highly active catalyst for hydrogenation reactions. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, A.R.; Rezaei, F.; Khorsandi, Z. Pd/Cu-free Heck and Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction by Co nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic chitosan as reusable catalyst. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 violet line), in presence of NaBH4 (
violet line), in presence of NaBH4 (  black line), NaBH4 with Fe3O4 (
black line), NaBH4 with Fe3O4 (  red line) and NaBH4 with 1.5 mg (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) of catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (
red line) and NaBH4 with 1.5 mg (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) of catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (  blue line).
blue line).
 violet line), in presence of NaBH4 (
violet line), in presence of NaBH4 (  black line), NaBH4 with Fe3O4 (
black line), NaBH4 with Fe3O4 (  red line) and NaBH4 with 1.5 mg (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) of catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (
red line) and NaBH4 with 1.5 mg (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) of catalyst Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (  blue line).
blue line).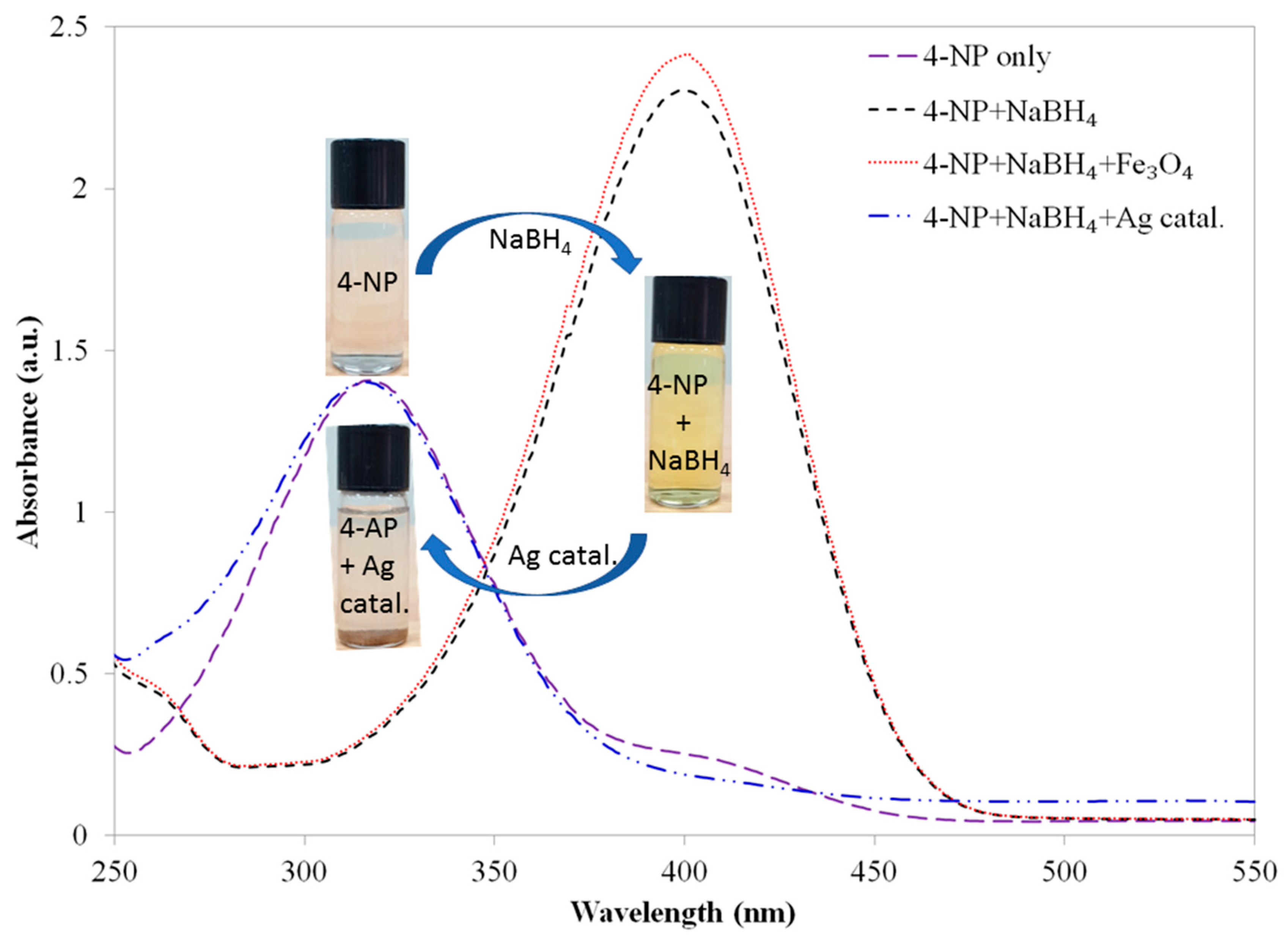
 blue line), Fe3O4@CS@MS (
blue line), Fe3O4@CS@MS (  black line) and Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) (
black line) and Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) (  red line) after 10 min.
red line) after 10 min.
 blue line), Fe3O4@CS@MS (
blue line), Fe3O4@CS@MS (  black line) and Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) (
black line) and Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (1.2 × 10−6 mol Ag) (  red line) after 10 min.
red line) after 10 min.
 blue line) and 0.8 mg (6.5 × 10−7 mol Ag) of Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (
blue line) and 0.8 mg (6.5 × 10−7 mol Ag) of Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (  red line) after 10 min.
red line) after 10 min.
 blue line) and 0.8 mg (6.5 × 10−7 mol Ag) of Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (
blue line) and 0.8 mg (6.5 × 10−7 mol Ag) of Fe3O4@CS@MS@Ag (  red line) after 10 min.
red line) after 10 min.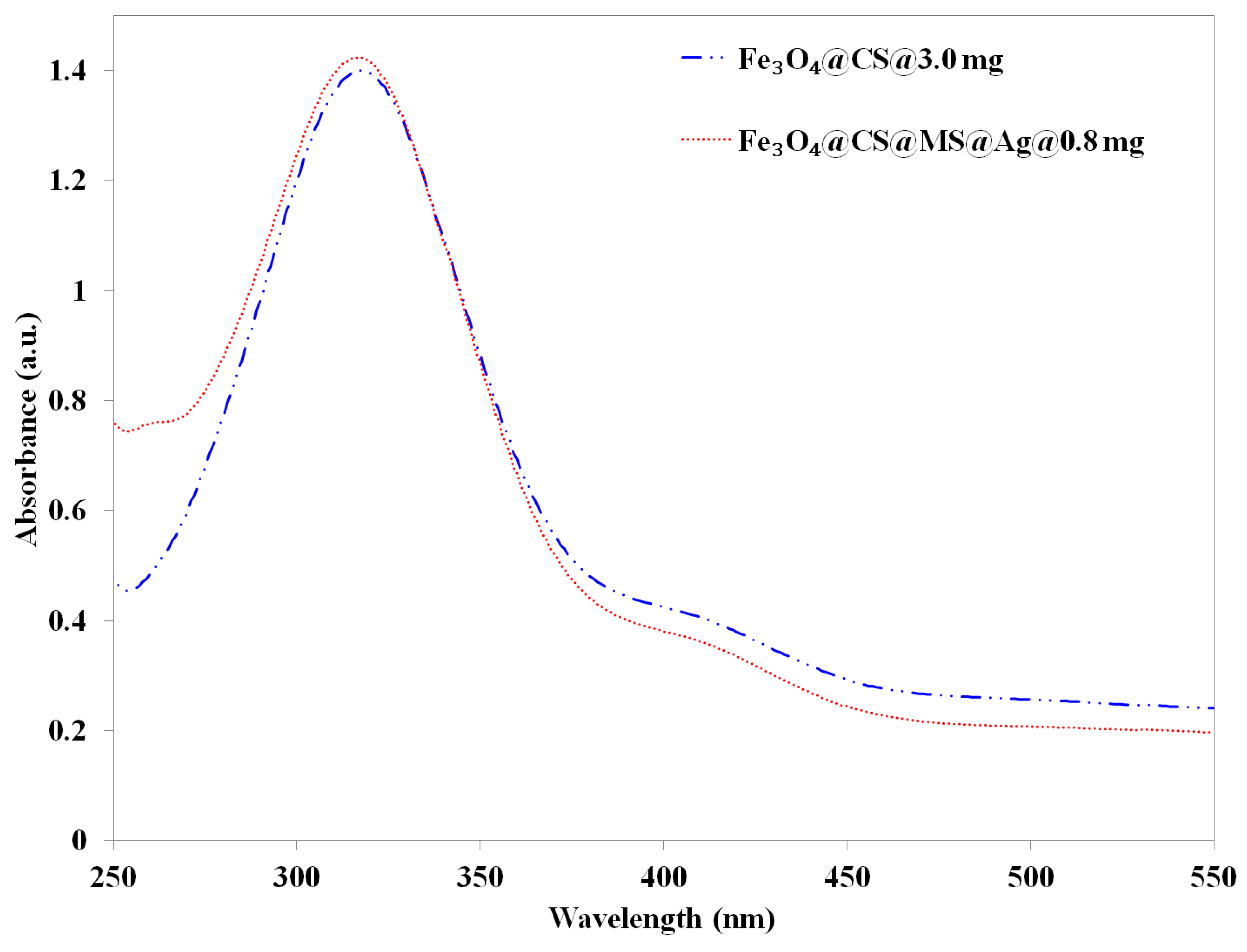
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, K.; Shehadi, I.A.; Al-Bab, N.D.; Elgamouz, A. Magnetic Chitosan-Supported Silver Nanoparticles: A Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Catalysts 2019, 9, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100839
Hasan K, Shehadi IA, Al-Bab ND, Elgamouz A. Magnetic Chitosan-Supported Silver Nanoparticles: A Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Catalysts. 2019; 9(10):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100839
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Kamrul, Ihsan Ahmed Shehadi, Nemat Dek Al-Bab, and Abdelaziz Elgamouz. 2019. "Magnetic Chitosan-Supported Silver Nanoparticles: A Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol" Catalysts 9, no. 10: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100839
APA StyleHasan, K., Shehadi, I. A., Al-Bab, N. D., & Elgamouz, A. (2019). Magnetic Chitosan-Supported Silver Nanoparticles: A Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Catalysts, 9(10), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100839






