Abstract
High performance catalysts for carbon monoxide (CO) oxidation were obtained through thermal activation of a CuBTC (BTC: 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid) metal–organic framework (MOF) in various atmospheres. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photonelectron spectroscopy (XPS), N2 adsorption–desorption measurement, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) were adopted to characterize the catalysts. The results show that thermal activation by reductive H2 may greatly destroy the structure of CuBTC. Inert Ar gas has a weak influence on the structure of CuBTC. Therefore, these two catalysts exhibit low CO oxidation activity. Activating with O2 is effective for CuBTC catalysts, since active CuO species may be obtained due to the slight collapse of CuBTC structure. The highest activity is obtained when activating with CO reaction gas, since many pores and more effective Cu2O is formed during the thermal activation process. These results show that the structure and chemical state of coordinated metallic ions in MOFs are adjustable by controlling the activation conditions. This work provides an effective method for designing and fabricating high performance catalysts for CO oxidation based on MOFs.
1. Introduction
Catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide (CO) has drawn much research attention due to its significance in fundamental research and practical applications in pollution air purification, vehicle exhaust removal, and CO preferential oxidation in hydrogen-rich gas [1,2,3,4,5]. Noble metal catalysts, including supported Au, Pd, Pt, etc., exhibit excellent CO oxidation activity [6,7,8]. However, due to their relatively high cost, large-scale applications are limited. To solve this problem, supported bimetallic catalysts (such as Pd–Cu) [9,10] and transition-metal oxides [11,12,13,14] have been investigated. However, the activities are relatively lower, and there still exists the problem of the aggregation of metal nanoparticles. If supported non-noble metal catalysts with high CO oxidation activity can be fabricated, it will have great theoretical value and practical significance.
Recently, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been proven efficient for CO oxidation at ambient pressure and elevated temperatures [15,16,17]. MOFs are a new kind of porous material that have highly porous structures and unique properties [18], and have been used in catalysis [19], sensors [20], and gas adsorption, separation [21,22], and storage [23,24]. The use of MOFs as catalysts has especially aroused much research interest. For instance, MOFs can be engineered to build catalysts with the active sites of the ligands [25] and the metals [26,27], or simply adopted as the host matrices [28,29]. Catalytic oxidation of CO over MOFs materials has also drawn much research attention. For MOFs-based catalysts, MOFs generally play the role of supports for noble metals like Au, Ag, and Pd [30,31,32], or as the hosts for the synthesis of active metal oxides such as Co3O4 [33] and CuO [34,35].
An activation process for MOFs is generally essential for the aforementioned applications, to remove both pore-filling guest molecules and pre-coordinating solvent molecules from the open coordination sites [36]. Various activation methods have been developed, including thermal activation [37,38,39], solvent exchange [40,41,42], freeze-drying [43,44], supercritical CO2 exchange [45], and chemical treatment [46,47]. Among these, thermal activation is most commonly used for its simplicity and efficiency. In general, the thermal activation of MOFs is conducted in inert gas or vacuum, and temperature is the only concerned parameter for researchers. For example, Qiu et al. [17] investigated the effect of activation temperature on CO oxidation activity over CuBTC (BTC: 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid). Zhang et al. [34] also proved that thermal treatment temperature of CuBTC would significantly influence the performance of resulted CuO catalysts. Moreover, thermal activation of CuBTC within the CO reaction gas (mixture of CO, O2, and balance gas) has been studied recently, and the results showed that active CuO species were obtained, which may facilitate CO oxidation [28]. However, although these studies have shown that both the temperature and the atmosphere are crucial influencing factors in the thermal activation process, no research focused on the atmosphere has been reported. Furthermore, to meet the requirement of heterogeneous reaction in the previous works, the activated MOFs need to be supported or made into pellets. As far as the thermal activation of pure MOFs is concerned, the high pressure of tableting and the following crushing process may destroy the structure of the MOFs, which are also important for their structure and properties.
In this work, CuBTC MOF was tableted and thermally activated in various atmospheres. CO oxidation activity test, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), field emission SEM (FESEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) characterizations were conducted to investigate the activity and structure of the CuBTC. The influence of the tableting on the structure and properties of the CuBTC are discussed. The results confirmed that the activation atmosphere profoundly affected the structure and performance of CuBTC catalysts. The influence may be attributed to the change of the chemical composition of CuBTC tuned by thermal activation, which provides important guiding significance for synthesizing high-performance CO oxidation catalysts from CuBTC.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Crystalline Phase Structure of CuBTC and the Effects of Tableting
As we know, it is difficult to apply the CuBTC catalysts for gas phase reaction if they existed in the form of powder. Therefore, the CuBTC powder was tableted and crushed into pellets, and the effects of tableting were investigated. XRD patterns of as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC were observed and are shown in Figure 1. Their XRD patterns are similar to previous work [25]. The characteristic diffraction peaks of CuBTC can be observed for both the as-prepared and tableted samples, indicating that the as-prepared blue crystals possess a crystalline phase structure of CuBTC. Besides, the process of tableting did not change the crystalline phase structure of CuBTC, except for a slight decrease in its intensity according to the XRD characterization.
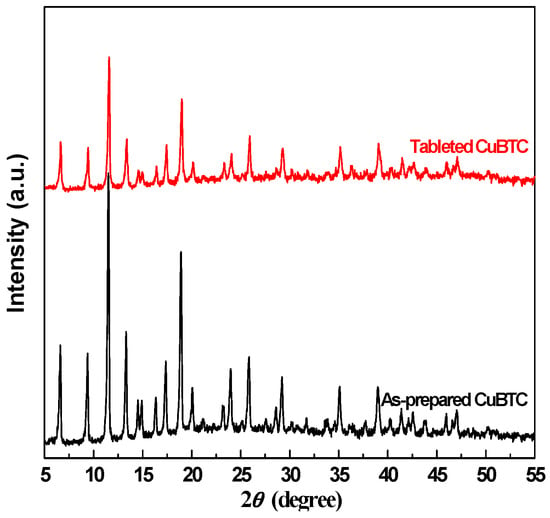
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC.
The N2 sorption isotherms and pore size distributions of as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC were measured and are shown in Figure S1. The pore diameters (Dp), pore volumes (Vp), and specific surface areas (SBET) of as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC are summarized in Table 1. The as-prepared CuBTC exhibited a high specific surface area (1102.9 m2·g−1), with the pore diameter and pore volume of 3.84 nm and 0.412 cm3·g−1, respectively. No obvious change of pore diameter was observed after tableting. However, the pore volume and specific surface area for tableted CuBTC decreased to 0.266 cm3·g−1 and 616.7 m2·g−1, respectively. This indicates that some pores in CuBTC were crushed with tableting, which may be mainly due to the high-pressure tableting process. This is consistent with the decrease of the characteristic diffraction peaks for CuBTC in XRD patterns. Although the structure of CuBTC is partly destroyed after tableting, the crystal structure is kept and the specific surface area is still high enough.

Table 1.
The pore diameters (Dp), pore volumes (Vp), specific surface areas (SBET), and 50% and 100% CO conversion temperatures (T50% & T100%) of as-prepared CuBTC, tableted CuBTC (denoted as CuBTC) and CuBTC activated under various atmospheres at 240 °C (G-240).
To further disclose the influence of tableting on the structure of CuBTC, the morphology of the as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC samples was observed using field emission scanning electron microscopy, as shown in Figure 2. Figure 2a reveal that the as-prepared CuBTC crystals show an octahedral shape, with a size of about 10 μm, which is similar to previous work [17]. However, the octahedral shape has been changed into sheets (Figure 2b after tableting. The morphological transformation is consistent with the XRD and BET results, indicating that tableting process has significant effects on the morphology of CuBTC materials.
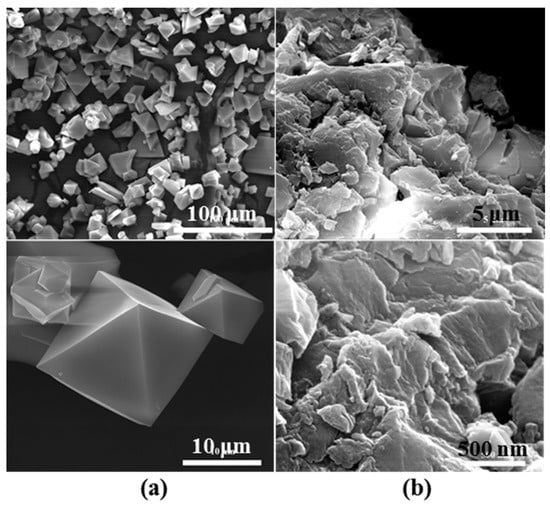
Figure 2.
Typical field emission SEM (FESEM) images of (a) the as-prepared CuBTC; and (b) the tableted CuBTC.
In this study, we aimed to prepare high performance catalysts for CO oxidation by the thermal activation of CuBTC. Therefore, the effect of tableting on the performance of CuBTC before and after tableting was also investigated, and presented in Figure S2. CO oxidation over the samples indicated that there was no obvious difference between the as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC.
2.2. Effect of Activating Atmosphere on CuBTC Catalysts
Catalysts from thermal activation of CuBTC samples at 240 °C under different atmospheres, including Ar, H2, O2, and CO reaction gas were obtained firstly. The catalysts are accordingly noted as G-240 (G for Ar, H2, O2, and CO reaction gas). Their catalytic activities over CO oxidation were then studied, and the results are illustrated in Figure 3, and the 50% and 100% CO conversion temperatures (T50% and T100%) for the G-240 samples are summarized Table 1.
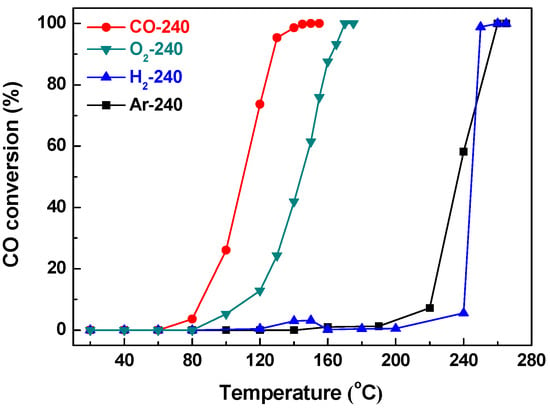
Figure 3.
CO conversion over G-240 samples.
The results show that the order of the catalytic activities of all G-240 samples was as follows: CO-240 > O2-240 > Ar-240 > H2-240, with a T100% temperature of 145 °C, 170 °C, 255 °C, and 255 °C, respectively. The CO-240 sample mentioned above still showed the highest activity, and the activity of the O2-240 sample was a little bit lower than CO-240, but higher than CO-260 (T100% = 200 °C). This indicates that O2atmosphere is also effective in enhancing the activity of CuBTC, as proven by previous work [31]. The Ar-240 and H2-240 samples, however, were less effective and show almost no activity for CO oxidation below 200 °C. Notably, previous work [17] has shown that CuBTC activated at 250 °C in N2 atmosphere is highly active for CO oxidation (T100% = 170 °C); this may be due to the higher activation temperature and the double amount of catalysts (100 mg) for the activity test compared to our study.
XRD patterns of G-240 samples were also observed and are shown in Figure 4, from which we may see that part of Cu2+ ions in H2-240 were reduced to metallic Cu (JCPDS file of No. 040836) due to the strong reduction ability of H2 gas at high temperature. In addition, new diffraction peaks were observed at the 2θ range of 5°–30°, which may be attributed to the collapse of CuBTC structure. The O2-240 samples activated in the O2 atmosphere should generate CuO species, according to the literature [31]. However, the phenomenon was not observed from the XRD patterns shown in Figure 4, which may be ascribed to a lower thermal treatment temperature (240 °C) than the literature (250 °C). For the Ar-240 sample, the XRD pattern still showed the characteristic peaks of CuBTC, which was also observed when activated in N2 gas [17].
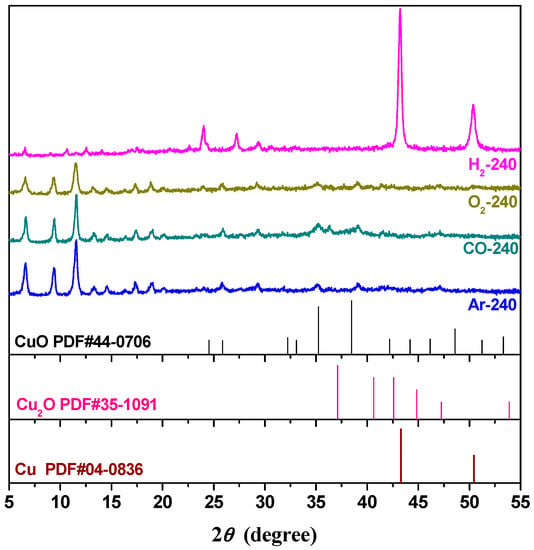
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of G-240 samples.
To further investigate the chemical composition of the CuBTC catalysts and the valence states of copper in them, XPS survey spectra and the corresponding high-resolution spectra of C1s, Cu2p, and O1s in the G-240 samples were recorded and are presented in Figure 5. As shown in the XPS survey spectra (Figure 5a), Cu2p, O1s, and C1s were detected in the samples. Figure 5b indicates that the C1s spectra in the samples were composed of two contributions: the binding energy at 284.6 eV arises from the carbon atoms in the aromatic rings and carbon contamination from the XPS instrument, while the 288.5 eV signal is attributed to the carboxyl groups. There is no obvious difference between them. Cu2p XPS spectra (Figure 5c) present the main peaks of copper, and the satellite peaks corresponding to copper (II) were observed in all four samples [48]. The Cu2p3/2 spectra in CO-240 can be deconvoluted into two peaks at 933.7 eV and 933.0 eV, corresponding to Cu (II) and Cu (I) due to the reduction of CO. In addition, three peaks may be fitted from Cu2p in H2-240 at 933.7 eV, 933.0 eV, and 932.4 eV, respectively, corresponding to Cu (II), Cu (I), and metallic Cu due to the strong reduction of H2. According to the Cu2p XPS spectra, the percentages of copper in different valence states were calculated. Cu (II) and Cu (I) in CO-240 were 73.5% and 26.5%, while Cu (II), Cu (I), and metallic Cu in H2-240 were 43.1%, 14.1%, and 42.8%. O1s XPS spectra for the samples were also recorded and are illustrated in Figure 5d. The peaks at 529.6 eV were attributed to the copper (II) species, and no other peaks could be deconvoluted for O1s in O2-240 and Ar-240, in line with the results of Cu2p XPS spectra in Figure 5c. Corresponding to the results of Cu2p XPS spectra for CO-240 and H2-240 in Figure 5c, the O1s spectra could be fitted with two peaks at 529.6 eV and 530.7 eV, respectively, attributed to CuO and Cu2O, which are in line with the results of Figure 5c.
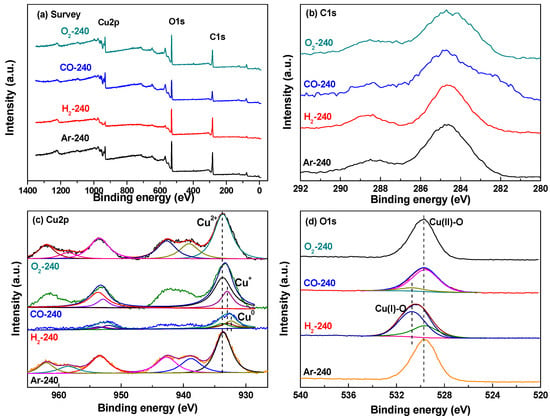
Figure 5.
(a) XPS survey spectra and the corresponding high-resolution spectra of (b) C1s, (c) Cu2p, and (d) O1s in the G-240 samples.
The values of BET specific surface area of the samples obtained by the data taken from Figure S3 (Table 1) follow the order of Ar-240 (759.4 m2·g−1) > O2-240 (385.6 m2·g−1) > CO-240 (253.4 m2·g−1) > H2-240 (2.0 m2·g−1). This demonstrates that when activated at 240 °C, the pore structure of CuBTC is more prone to be collapsed in reductive atmosphere. O2 and CO reaction gas are relatively moderate for G-240 samples, whereas H2 exhibits powerful reduction and thus results in the formation of Cu and the complete break of CuBTC structure.
Typical FESEM images of the G-240 samples were also obtained and are shown in Figure 6. The morphology of Ar-240, O2-240, and CO-240 samples showed no significant changes, except that more pores can be seen from the images of the CO-240 sample, while a special rod-like crystal and the aggregation particles can be clearly observed for H2-sample. This may correspond to the observed diffraction peaks of Cu and unknown crystalline phase in the XRD pattern shown in Figure 4. The energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images of the tableted CuBTC and CO-240 were also observed (Figure S4). EDS mapping images revealed that copper species were uniformly distributed in the samples before and after thermal activation in CO reaction gas. In addition, part of the oxygen species was removed due to the thermal activation. The disordered distribution of the oxygen and carbon may be attributed to the contamination of conductive plastic and the effect of the test environment.
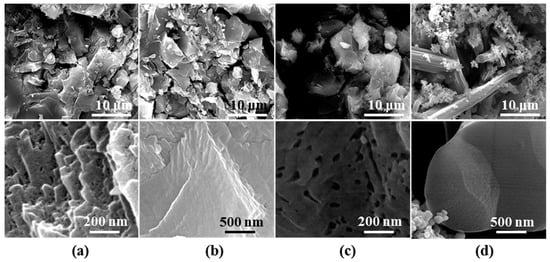
Figure 6.
Typical FESEM images of (a) Ar-240; (b) O2-240; (c) CO-240; and (d) H2-240.
Long-term catalytic activity is an important factor for high-performance catalysts. The most efficient CuBTC catalyst (CO-240) obtained by thermal activation during CO reaction gas was selected to perform the long-term catalytic activity experiment at its 100% CO conversion temperature (145 °C), and the result is illustrated in Figure 7. Although 36 h is not long enough for practical application, it is still meaningful for testing of the catalytic stability. As shown in Figure 7, 100% CO conversion was kept at 145 °C for 36 h, indicating a high catalytic stability for the CO-240 catalyst. Interestingly, 100% CO conversion temperature for CO-240 was 5 °C lower than that for the TiO2-supported Pd catalyst (0.8 wt % loading amount) reported in previous work [49].
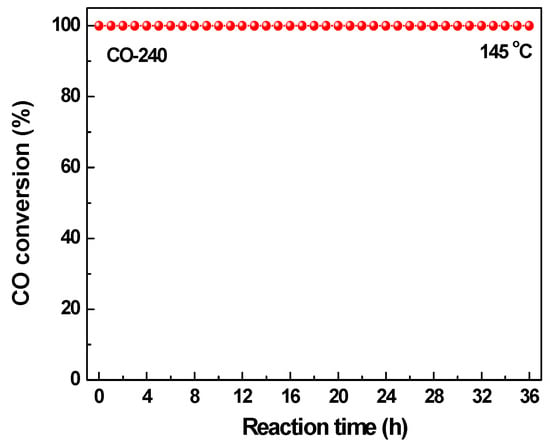
Figure 7.
Long-term catalytic stability for CO-240 at 145 °C.
In conclusion, the thermal activation atmosphere has a significant influence on the structure and performance of CuBTC. Ar is one kind of inert gas, and has little effect on the structure of CuBTC when activated at 240 °C; therefore, the Ar-240 catalyst exhibited poor CO oxidation activity. The H2 atmosphere would completely destroy the CuBTC structure and result in the formation of ineffective Cu, both of which decreased the catalytic activity. Activating with O2 is effective for CuBTC catalysts, as active CuO species can be obtained over the slight collapse of CuBTC structure. Additionally, the activity is better when activating with CO reaction gas since more pores were formed on the surface of CO-240 and more effective Cu2O was formed during the thermal activation. Therefore, high-performance CO oxidation catalysts may be obtained by thermal activation of CuBTC under appropriate atmosphere (CO reaction gas).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Copper (II) nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, 99%), ethanol (EtOH, 99.7%), and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 99.5%) were obtained from Tianjin Bodi Chemical Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China. 1,3,5-benzene tricarboxylic acid (BTC, 98%) was purchased from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All chemicals were used as received.
3.2. Preparation and Thermal Activation of the CuBTC Catalysts
CuBTC was prepared according to the low-temperature synthesis method of previous work [26], with some modification. Briefly, 1.0 g BTC was dissolved in a 1:1 mixture of EtOH-DMF (30 mL), while 2.077 g Cu(NO3)2·3H2O was dissolved in deionized water (15 mL). The solutions were stirred until the solutes were absolutely dissolved, and then they were mixed and stirred for another 10 min. After that, they were transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and kept at 100 °C for 12 h. The resulting blue crystals were isolated by filtration and washed by DMF and EtOH three times, respectively. Subsequently, they were dried at 60 °C for 5 h in a vacuum oven, and CuBTC MOF was obtained.
Prior to thermal activation, the as-prepared CuBTC was tableted to pellets under the pressure of 16 MPa for 5 min, and then crushed and sieved into 40–60 mesh particles. Multiple CuBTC catalysts were then obtained from thermal activation of the tableted CuBTC samples within various atmospheres and at different temperatures. Typically, 50 mg CuBTC were placed in a quartz tube (i.d. 4 mm) reactor, blocked with silica wools at both ends of the samples. Then, the quartz tube loaded with samples was heated in an oven at 240 °C under 20 mL·min−1 of certain gases (Ar, O2, H2, or CO reaction gas; i.e., 1.0 vol. % CO, 20.0 vol. % O2, and N2 balance) for 3 h.
3.3. Catalysts Characterization
The crystalline phase composition of as-prepared CuBTC, tableted CuBTC, and G-240 samples was examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Dandong Haoyuan, DX-2700, Dandong, China. The applied radiation wavelength was 1.54 Å generated from Cu Kα1 at 40 kV and 30 mA. A NOVA 2200e gas sorption analyzer (Quantachrome Corp., Syosset, NY, USA) was employed to test the pore size distributions (Dp) and specific surface areas (SBET), and pore volumes (Vp) were measured by nitrogen adsorption/desorption. Prior to adsorption analysis, the samples were outgassed at 200 °C for 5 h in the degas port of the analyzer. A field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Quanta 200F, Hillsboro, OR, USA) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV was used to investigate the morphology of the samples. The chemical compositions of the samples and the valence states of copper were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, ESCALAN250 Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with monochromatized AlKα (1486.6 eV) X-ray radiation. All binding energies were referenced to the carbon 1s binding energy set at 284.6 eV.
3.4. CO Oxidation Activity Test
CO oxidation activity over tableted CuBTC and G-240 samples was evaluated in a quartz tube (i.d. 4 mm) loaded with 50 mg catalyst. The reaction was carried out in a flowing CO/O2 mixture (1.0 vol % CO, 20.0 vol % O2, N2 balance) with a flow rate of 20 mL·min−1. The outlet concentrations of CO and CO2 were analyzed on-line by an infrared absorption spectrometer (S710, Sick-Maihak, Reute, Germany). CO conversion was calculated according to the following equation:
where and are the CO concentrations of inlet and outlet, respectively.
4. Conclusions
In this study, thermal activation was proven to be significant in enhancing CO oxidation activity over CuBTC. Tableting the CuBTC had no significant influence on their CO oxidation activity. The influence of activation atmospheres was investigated. Thermal activation in inert Ar gas had little effect on the structure of CuBTC, and the catalyst exhibited low CO oxidation activity. Thermal activation of CuBTC in reductive H2 may greatly destroy the structure of CuBTC. Activating with O2 is effective for CuBTC catalysts, since active CuO species can be obtained over the slight collapse of CuBTC structure. The highest activity is obtained when activating CuBTC in CO reaction gas since more pores and effective Cu2O is formed during thermal activation.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/7/4/106/s1, Figure S1: (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of as-prepared CuBTC and tableted CuBTC, Figure S2: CO oxidation activity over (a) the as-prepared CuBTC and (b) the tableted CuBTC, Figure S3: (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of the G-240 samples, Figure S4: The EDS mapping images of (a) the tableted CuBTC and (b) CO-240.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21673026, 11505019, 21173028), and Dalian Youth Science and Technology Project (Grant No. 2015R089).
Author Contributions
Xiuling Zhang conceived and designed the experiments; Zhibin Zhan and Zhuang Li performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Xiuling Zhang and Lanbo Di provided the concept of this research and managed all the experimental and writing process as the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Haruta, M.; Tsubota, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kageyama, H.; Genet, M.J.; Delmon, B. Low-temperature oxidation of CO over gold supported on TiO2, α-Fe2O3, and Co3O4. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.M.; Hackenberg, S.; Van Veen, A.C.; Muhler, M.; Plzak, V.; Behm, R.J. CO oxidation over supported gold catalysts—“Inert” and “Active” support materials and their role for the oxygen supply during reaction. J. Catal. 2001, 197, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Fukumoto, K.; Ishima, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Sano, M.; Miyake, T. Preparation of copper-containing mesoporous manganese oxides and their catalytic performance for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 89, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, P.S.; Di Benedetto, A.; Landi, G.; Lisi, L. CuO/CeO2 based monoliths for CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich streams. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Garcia, I.; Navlani-Garcia, M.; Garcia-Aguilar, J.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Lozano-Castello, D.; Cazorla-Amoros, D. Capillary microreactors based on hierarchial SiO2 monoliths incorporating noble metal nanoparticles for the preferential oxidation of CO. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Duan, D.; Zhang, X.; Qi, B.; Zhan, Z. Effect of TiO2 crystal phase and preparation method on the catalytic performance of Au/TiO2 for CO oxidation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhan, Z.; Di, L.; Zhang, X. Enhanced activity for CO oxidation over Pd/Al2O3 catalysts prepared by atmospheric-pressure cold plasma. Catal. Today 2015, 256, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasilp, A.; Gulari, E. Selective CO oxidation over Pt/alumina catalysts for fuel cell applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 37, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, A.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Mou, C.Y.; Zhang, T. Au-Cu Alloy nanoparticles confined in SBA-15 as a highly efficient catalyst for CO oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2008, 27, 3187–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.B.; Xu, W.J.; Zhan, Z.B.; Zhang, X.L. Synthesis of alumina supported Pd-Cu alloy nanoparticles for CO oxidation via a fast and facile method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71854–71858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Haruta, M.; Shen, W.J. Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 2009, 458, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.M.; Rao, K.N.; Bharali, P. Copper promoted cobalt and nickel catalysts supported on ceria-alumina mixed oxide: Structural characterization and CO oxidation activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8478–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Takei, T.; Ohashi, H.; He, H.; Zhang, X.L.; Haruta, M. Pretreatments of Co3O4 at moderate temperature for CO oxidation at −80 °C. J. Catal. 2009, 267, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgouropoulos, G.; Ioannides, T. Selective CO oxidation over CuO-CeO2 catalysts prepared via the urea–nitrate combustion method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 244, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.Q.; Sakurai, H.; Han, S.; Zhong, R.Q.; Xu, Q. Probing the lewis acid sites and CO catalytic oxidation activity of the porous metal-organic polymer [Cu (5-methylisophthalate)]. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8402–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.Y.; Liu, C.J. Cu3(BTC)2: CO oxidation over MOF based catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.G.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.Q.; Zhan, Z.C.; Zi, X.H.; Zhang, G.Z.; Wang, R.; He, H. Effect of activation temperature on catalytic performance of CuBTC for CO oxidation. Chin. J. Catal. 2012, 33, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowsell, J.L.C.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal-organic frameworks: A new class of porous materials. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2004, 73, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.J.; Farha, O.K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K.A.; Nguyen, S.T.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–organic framework materials as chemical sensors. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 1105–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.R.; Kuppler, R.J.; Zhou, H.C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Chua, Y.S.; Krungleviciute, V.; Tyagi, M.; Chen, P.; Yildirim, T.; Zhou, W. Unusual and highly tunable missing-linker defects in zirconium metal–organic framework UiO-66 and their important effects on gas adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10525–10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.S.; Dailly, A.; Yaghi, O.M.; Long, J.R. Impact of preparation and handling on the hydrogen storage properties of Zn4O (1,4-benzenedicarboxylate)3 (MOF-5). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14176–14177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Langmi, H.W.; North, B.C.; Mathe, M.; Bessarabov, D. Modulated synthesis of zirconium-metal organic framework (Zr-MOF) for hydrogen storage applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaerts, L.; Séguin, E.; Poelman, H.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Jacobs, P.A.; De Vos, D.E. Probing the Lewis Acidity and Catalytic Activity of the Metal-Organic Framework [Cu3(BTC)2] (BTC = Benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate). Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 7353–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xamena, F.X.L.I.; Casanova, O.; Tailleur, R.G.; Garcia, H.; Corma, A. Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalysts: A combination of Cu2+ and Co2+ MOFs as an efficient catalyst for tetralin oxidation. J. Catal. 2008, 255, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens, P.; Vermoortele, F.; De Vos, D. Metal-organic frameworks as catalysts: The role of metal active sites. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamaro, J.M.; Pérez, N.C.; Miró, E.E.; Casado, C.; Seoane, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. HKUST-1 MOF: A matrix to synthesize CuO and CuO-CeO2 nanoparticle catalysts for CO oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösler, C.; Fischer, R.A. Metal–organic frameworks as hosts for nanoparticles. Crystengcomm 2015, 17, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Liu, B.; Akita, T.; Haruta, M.; Sakurai, H.; Xu, Q. Au@ZIF-8: CO oxidation over gold nanoparticles deposited to metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11302–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, C.L.; Liu, C.J. Enhanced CO oxidation over thermal treated Ag/Cu-BTC. Catal. Commun. 2013, 38, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.C.; Jiang, G.Y.; Duan, A.J. Pd Nanoparticles deposited on metal-organic framework of MIL-53(Al) an active catalyst for CO oxidation. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2014, 30, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.X.; Li, Y.W.; Zhang, R.J.; He, D.H.; Liu, H.J.; Liao, S.J. Metal-organic framework as a host for synthesis of nanoscale Co3O4 as an active catalyst for CO oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2012, 12, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Xiao, W.M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, N. CuO/CeO2 catalysts with well-dispersed active sites prepared from Cu3(BTC)2 metal–organic framework precursor for preferential CO oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2012, 26, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Pachfule, P.; Banerjee, R.; Poddar, P. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticle synthesis from metal organic frameworks (MOFs): Finding the border of metal and metal oxides. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondloch, J.E.; Karagiaridi, O.; Farha, O.K.; Hupp, J.T. Activation of metal–organic framework materials. Crystengcomm 2013, 15, 9258–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; Groy, T.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Establishing microporosity in open metal-organic frameworks: Gas sorption isotherms for Zn(BDC) (BDC = 1, 4-benzenedicarboxylate). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 8571–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.C.; Culp, J.T.; Natesakhawat, S.; Bockrath, B.C.; Zande, B.; Sankar, S.G.; Garberoglio, G.; Johnson, J.K. Experimental and theoretical studies of gas adsorption in Cu3(BTC)2: An effective activation procedure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 9305–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shukla, P.; Wang, S.; Rudolph, V.; Chen, X.M.; Zhu, Z. Significant improvement of surface area and CO2 adsorption of Cu–BTC via solvent exchange activation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17065–17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jin, A.; Xie, Z.; Lin, W. Freeze drying significantly increases permanent porosity and hydrogen uptake in 4, 4-connected metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohe, M.R.; Rose, M.; Kaskel, S. Metal–organic framework (MOF) aerogels with high micro-and macroporosity. Chem. Commun. 2009, 40, 6056–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.P.; Farha, O.K.; Mulfort, K.L.; Hupp, J.T. Supercritical processing as a route to high internal surface areas and permanent microporosity in metal-organic framework materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 131, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, W.; Volosskiy, B.; Demir, S.; Gándara, F.; McGrier, P.L.; Furukawa, H.; Cascio, D.; Stoddart, J.F.; Yaghi, O.M. Synthesis, structure, and metalation of two new highly porous zirconium metal-organic frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 6443–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Yun, W.S.; Kim, M.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Jeong, N.C. A chemical route to activation of open metal sites in the copper-based metal–organic framework materials HKUST-1 and Cu-MOF-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10009–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Duan, D.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, X. Gas-liquid cold plasma for synthesizing copper hydroxide nitrate nanosheets with high adsorption capacity. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Li, Z.; Lee, B.; Park, D.-W. An alternative atmospheric-pressure cold plasma method for synthesizing Pd/P25 catalysts with the assistance of ethanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).