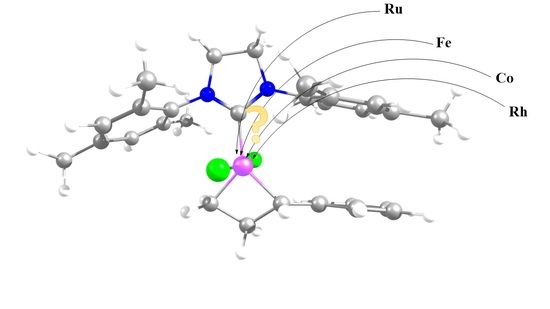
In Silico Switch from Second- to First-Row Transition Metals in Olefin Metathesis: From Ru to Fe and from Rh to Co
Abstract
:1. Introduction
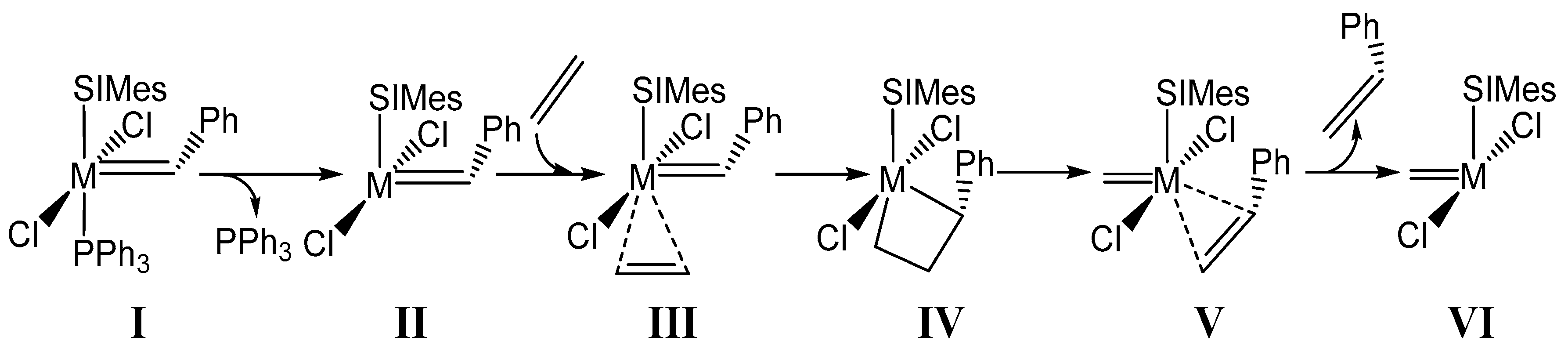
2. Results and Discussion
3. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lutz, E.F. Shell Higher Olefins Process. J. Chem. Educ. 1986, 63, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, B.; Wittcoff, H. The SHOP process an example of industrial creativity. J. Chem. Educ. 1988, 65, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckelsberg, L.F.; Banks, R.L.; Bailey, G.C. A tungsten oxide on silica catalyst for phillips triolefin process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1968, 7, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosebrugh, L.E.; Ahmed, T.S.; Marx, V.M.; Hartung, J.; Liu, P.; López, J.G.; Houk, K.N.; Grubbs, R.H. Probing stereoselectivity in ring-opening metathesis polymerization mediated by cyclometalated ruthenium-based catalysts: A combined experimental and computational study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, M.; Ding, S.; Lee, C.W.; Grubbs, R.H. Synthesis and activity of a new generation of ruthenium-based olefin metathesis catalysts coordinated with 1,3-dimesityl-4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene ligands. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, R.R. Olefin metathesis by molybdenum imido alkylidene catalysts. Tetrahedron 1999, 1999, 8141–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, Y. Olefin metathesis: The early days (Nobel Lecture 2005). Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérisson, J.L.; Chauvin, Y. Catalyse de transformation des olefins par les complexes du tungstène. Makromol. Chem. 1971, 141, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantreil, X.; Poater, A.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Bidal, Y.D.; Falivene, L.; Randall, R.A.M.; Cavallo, L.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cazin, C.S.J. Synthesis and reactivity of ruthenium phosphite indenylidene complexes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7415–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouen, M.; Queval, P.; Borré, E.; Falivene, L.; Poater, A.; Berthod, M.; Hugues, F.; Cavallo, L.; Baslé, O.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; et al. Selective metathesis of α-olefins from bio-sourced Fischer–Tropsch feeds. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7970–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetto, A.; Costabile, C.; Longo, P.; Grisi, F. Ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts with frozen NHC ligand conformations. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2747–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A. Moving from classical Ru-NHC to neutral or charged Rh-NHC based catalysts in olefin metathesis. Molecules 2016, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castarlenas, R.; Esteruelas, M.A.; Oñate, E. N-heterocyclic carbine-osmium complexes for olefin metathesis reactions. Organometallics 2005, 24, 4343–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Pump, E.; Cavallo, L. Comparing Ru and Fe-catalyzed olefin metathesis. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 11216–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Pump, E.; Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Cavallo, L. The activation mechanism of Fe-based olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 610–611, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A. Olefin metathesis and beyond. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeilts, A.L.; Cefalo, D.R.; Bonitatebus, P.J., Jr.; Houser, J.H.; Hoveyda, A.H.; Schrock, R.R. A readily available and user-friendly chiral catalyst for efficient enantioselective olefin metathesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 113, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmeiser, M.R. Homogeneous metathesis polymerization by well-defined group VI and group VIII transition-metal alkylidenes: Fundamentals and applications in the preparation of advanced materials. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1565–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trnka, T.M.; Grubbs, R.H. The development of L2X2Ru=CHR olefin metathesis catalysts: An organometallic success story. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Bahri-Laleh, N.; Cavallo, L. Rationalizing current strategies to protect N-heterocyclic carbene-based ruthenium catalysts active in olefin metathesis from C-H (de)activation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6674–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Cavallo, L. A comprehensive study of olefin metathesis catalyzed by Ru-based catalysts. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodall, B.L.; McIntosh, L.H., III; Rhodes, L.F. New catalysts for the polymerization of cyclic olefins. Macromol. Symp. 1995, 89, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E. Ecotoxicology and Chemistry Applications in Environmental Management; CRC Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Manzini, S.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Poater, A.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cavallo, L.; Nolan, S.P. From Olefin Metathesis Catalyst to Alcohol Racemization Catalyst in One Step. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pump, E.; Poater, A.; Zirngast, M.; Torvisco, A.; Fischer, R.; Cavallo, L.; Slugovc, C. Impact of electronic modification of the chelating benzylidene ligand in cis-dichloro configured 2nd generation Olefin Metathesis catalysts on their activity. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, S.; Poater, A.; Nelson, D.J.; Cavallo, L.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P. Insights into the decomposition of olefin metathesis pre-catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8995–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, J.I.; van Sittert, C.G.C.E.; Vosloo, H.C.M. Metal carbenes in homogeneous alkene metathesis: Computational investigations. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 738, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xu, X.; Dong, X.; Keitz, B.K.; Herbert, M.B.; Grubbs, R.H.; Houk, K.N. Z-selectivity in olefin metathesis with chelated Ru catalysts: Computational studies of mechanism and selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vougioukalakis, G.C.; Grubbs, R.H. Ruthenium-based heterocyclic carbene-coordinated olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1746–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliu, M.; Arduengo, A.J., III; Dixon, D.A. Role of electronegative substituents on the bond energies in the Grubbs metathesis catalysts for M = Fe, Ru, Os. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 13563–13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Ragone, F.; Correa, A.; Cavallo, L. Comparison of different ruthenium–alkylidene bonds in the activation step with N-heterocyclic carbene Ru-catalysts for olefins metathesis. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 11066–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Solans-Monfort, X.; Clot, E.; Copéret, C.; Eisenstein, O. DFT calculations of d0 M(NR)(CHtBu)(X)(Y) (M = Mo, W; R = CPh3, 2,6-iPr–C6H3; X and Y = CH2tBu, OtBu, OSi(OtBu)3) olefin metathesis catalysts: Structural, spectroscopic and electronic properties. Dalton Trans. 2006, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Solans-Monfort, X.; Clot, E.; Copéret, C.; Eisenstein, O. Understanding d0-olefin metathesis catalysts: Which metal? Which ligands? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8207–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becke, A. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behaviour. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P. Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 8822–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P. Erratum: Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. A new local density functional for main-group thermochemistry, transition metal bonding, thermochemical kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Poater, A.; Pump, E.; Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Cavallo, L. The right computational recipe for olefin metathesis with Ru-based catalysts: The whole mechanism of ring-closing olefin metathesis. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 4442–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Smit, W.; Foscato, M.; Occhipinti, G.; Törnroos, K.W.; Jensen, V.R. Loss and reformation of ruthenium alkylidene: Connecting olefin metathesis, catalyst deactivation, regeneration, and isomerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16609–16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falivene, L.; Poater, A.; Cazin, C.S.J.; Slugovc, L.; Cavallo, L. Energetics of the ruthenium–halide bond in olefin metathesis (pre)catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Poater, A.; Lebl, T.; Manzini, S.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cavallo, L.; Nolan, S.P. The activation mechanism of Ru—Indenylidene complexes in olefin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7073–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitgeb, A.; Abbas, M.; Fischer, R.C.; Poater, A.; Cavallo, L.; Slugovc, C. A latent ruthenium based olefin metathesis catalyst with a sterically demanding NHC ligand (pre)catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1640–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Leitgeb, A.; Slugovc, C.; Bantreil, X.; Clavier, H.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Nolan, S.P. Olefin metathesis featuring ruthenium indenylidene complexes with a sterically demanding NHC ligand. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 5045–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Brito Sá, E.; Rodríguez-Santiago, L.; Sodupe, M.; Solans-Monfort, X. Toward olefin metathesis with iron carbene complexes: Benefits of tridentate σ-donating ligands. Organometallics 2016, 35, 3914–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falivene, L.; Credendino, R.; Poater, A.; Petta, A.; Serra, L.; Oliva, R.; Scarano, V.; Cavallo, L. SambVca 2. A web tool for analyzing catalytic pockets with topographic steric maps. Organometallics 2016, 35, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Falivene, L.; Urbina-Blanco, C.A.; Manzini, S.; Nolan, S.P.; Cavallo, L. How does the addition of steric hindrance to a typical N-heterocyclic carbene ligand affect catalytic activity in olefin metathesis? Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7433–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Poater, A.; Childers, M.I.; Widger, P.C.B.; LaPointe, A.M.; Lobkovsky, E.B.; Coates, G.W.; Cavallo, L. Enantioselective polymerization of epoxides using biaryl-linked bimetallic cobalt catalysts: A mechanistic study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18901–18911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Cavallo, L. Comparing families of olefin polymerization precatalysts using the percentage of buried volume. Dalton Trans. 2009, 2009, 8878–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, A.; Huber, C.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusermann, U.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Accuracy of energy-adjusted quasirelativistic ab initio pseudopotentials. Mol. Phys. 1993, 78, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuechle, W.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for the actinides. Parameter sets and test calculations for thorium and thorium monoxide. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 7535–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leininger, T.; Nicklass, A.; Stoll, H.; Dolg, M.; Schwerdtfeger, P. The accuracy of the pseudopotential approximation. II. A comparison of various core sizes for indium pseudopotentials in calculations for spectroscopic constants of InH, InF, and InCl. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 105, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comp. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, V.; Cossi, M. Quantum calculation of molecular energies and energy gradients in solution by a conductor solvent model. J. Phys. Chem. A 1988, 102, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.; Persico, M. Molecular interactions in solution: An overview of methods based on continuous distributions of the solvent. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2027–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Cosenza, B.; Correa, A.; Giudice, S.; Ragone, F.; Scarano, V.; Cavallo, L. SambVca: A web application for the calculation of buried volumes of N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, H.; Correa, C.; Poater, A.; Costabile, C.; Cavallo, L. Understanding the M (SIMes) (SIMes = N-heterocyclic carbene) bond. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R.G.; von Szentpaly, L.; Liu, S. Electrophilicity index. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poater, A.; Gallegos, A.; Carbó-Dorca, R.; Poater, J.; Solà, M.; Cavallo, L.; Worth, A.P. Modelling the structure-property relationships of nanoneedles: A journey towards nanomedicine. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poater, A.; Credendino, R.; Slugovc, C.; Cavallo, L. Exploring new generations of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts: The reactivity of a bis-ylidene ruthenium complex by DFT. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7271–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.P.; Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Falivene, L.; Nolan, S.P.; Cavallo, L.; Solà, M.; Poater, A. In silico olefin metathesis with Ru-based catalysts containing N-heterocyclic carbenes bearing C60 fullerenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6617–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wappel, J.; Fischer, R.C.; Cavallo, L.; Slugovc, C.; Poater, A. Simple activation by acid of latent Ru-NHC-based metathesis initiators bearing 8-quinolinolate co-ligands. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
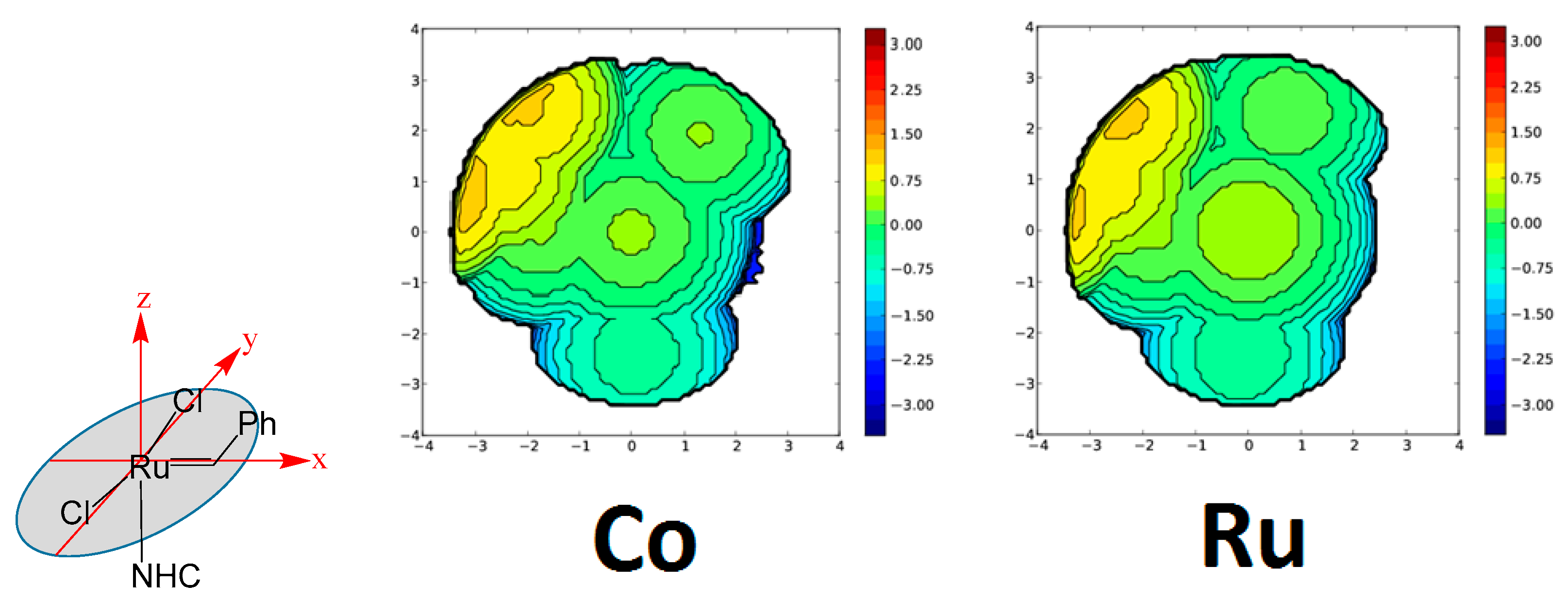
| Ru | Rh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | BP86-D3BJ/TZVP | BP86-D3BJ/TZVP | M06L/TZVP | M06/TZVP | BP86-D3BJ/TZVP | BP86-D3BJ/TZVP | M06L/TZVP | M06/TZVP | ||
| m | Gg | Gs | Gs | Gs | m | Gg | Gs | Gs | Gs | |
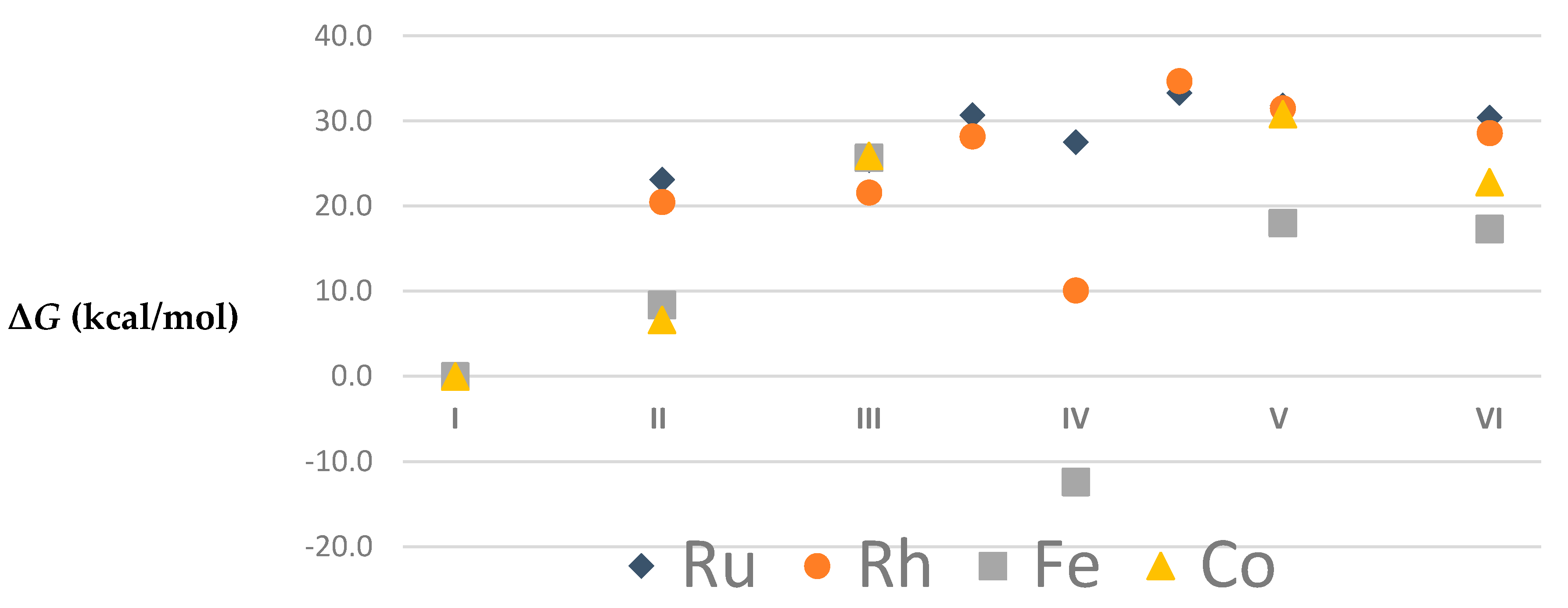
| I | 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| II | 1 | 26.5 | 23.1 | 5.6 | 8.1 | 2 | 25.8 | 20.5 | 5.7 | 9.7 |
| III | 1 | 26.0 | 25.4 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 2 | 22.0 | 21.6 | 11.0 | 11.6 |
| III–IV | 1 | 30.7 | 30.7 | 15.4 | 13.5 | 2 | 29.2 | 28.2 | 19.9 | 21.0 |
| IV | 1 | 27.4 | 27.5 | 10.8 | 9.3 | 2 | 11.0 | 10.1 | −3.9 | −4.6 |
| IV–V | 1 | 34.2 | 33.3 | 17.6 | 15.3 | 2 | 36.3 | 34.7 | 24.0 | 24.2 |
| V | 1 | 32.2 | 31.8 | 16.1 | 14.1 | 2 | 32.4 | 31.5 | 20.0 | 18.6 |
| VI | 1 | 34.5 | 30.4 | 8.9 | 11.4 | 2 | 35.3 | 28.6 | 10.3 | 12.5 |
| Fe | Co | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | m | Eg | Gg | Es | Gs | m | Eg | Gg | Es | Gs |
| I | 1 | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 5.1 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 4 | 11.4 | 11.7 | 13.8 | 14.2 | |
| 5 | 18.0 | 12.0 | 17.3 | 11.3 | 6 | 43.1 | 37.0 | 45.8 | 39.7 | |
| II | 1 | 43.3 | 20.6 | 36.8 | 14.1 | 2 | 35.7 | 15.2 | 27.1 | 6.6 |
| 3 | 38.4 | 17.5 | 29.3 | 8.4 | 4 | 44.1 | 26.9 | 36.1 | 18.9 | |
| 5 | 41.3 | 20.6 | 33.2 | 12.6 | ||||||
| III | 1 | 34.0 | 31.2 | 30.0 | 27.2 | 2 | 32.9 | 29.2 | 29.6 | 25.9 |
| 3 | 35.3 | 30.9 | 30.1 | 25.7 | ||||||
| 5 | 36.3 | 32.8 | 30.0 | 26.5 | 6 | 65.5 | 54.6 | 63.2 | 52.4 | |
| IV | 1 | 26.5 | 25.4 | 23.2 | 22.1 | |||||
| 3 | 18.0 | 11.4 | 14.8 | 8.2 | ||||||
| 5 | 3.5 | −6.3 | −2.6 | −12.4 | ||||||
| 7 | 36.5 | 27.5 | 29.5 | 20.6 | ||||||
| V | 1 | 26.3 | 23.8 | 22.6 | 20.1 | 2 | 37.9 | 32.8 | 35.9 | 30.8 |
| 3 | 25.5 | 22.0 | 21.5 | 18.0 | ||||||
| 5 | 29.9 | 30.7 | 25.6 | 26.4 | 6 | 78.1 | 66.2 | 76.0 | 64.1 | |
| VI | 1 | 55.5 | 32.0 | 48.2 | 24.6 | 2 | 53.9 | 31.7 | 45.0 | 22.8 |
| 3 | 52.7 | 27.0 | 42.9 | 17.3 | 4 | 54.0 | 30.6 | 49.5 | 26.1 | |
| 5 | 58.0 | 31.0 | 48.8 | 21.8 | ||||||
| Fe | Ru | Co | Rh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond | Distance | MBO | Distance | MBO | Distance | MBO | Distance | MBO | ||||
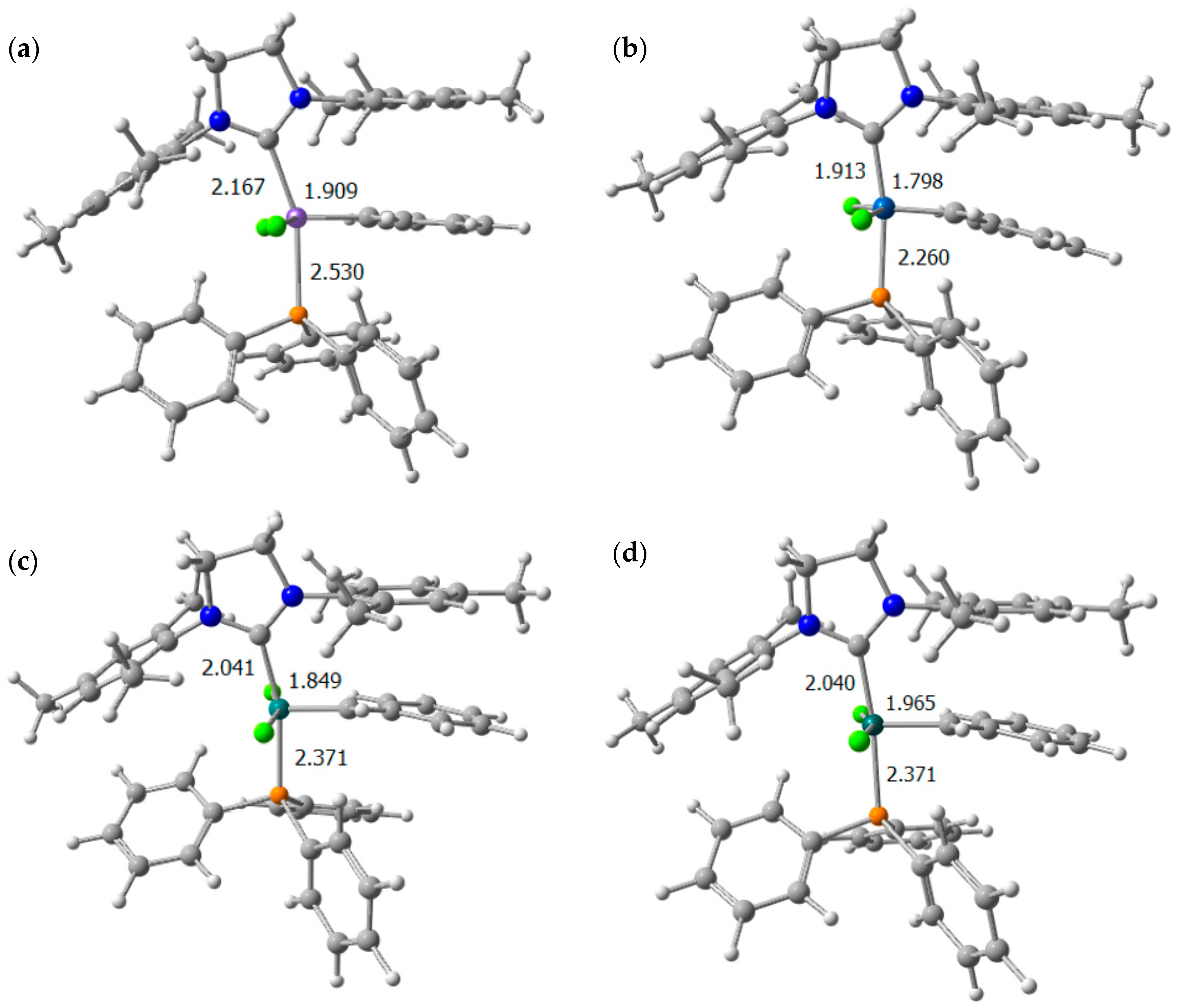
| M–CSIMes | I | 1.931 | 0.94 | I | 2.041 | 0.93 | I | 1.913 | 0.92 | I | 2.040 | 0.83 |
| M=C | 1.747 | 1.74 | 1.849 | 1.75 | 1.798 | 1.44 | 1.965 | 1.01 | ||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.311 | 1.19 | 2.426 | 1.05 | 2.415 | 0.85 | 2.385 | 1.17 | ||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.285 | 1.05 | 2.422 | 0.91 | 2.352 | 0.92 | 2.364 | 0.89 | ||||
| M–P | 2.272 | 0.99 | 2.371 | 0.84 | 2.260 | 0.97 | 2.371 | 0.90 | ||||
| M–CSIMes | II | 2.102 | 0.74 | II | 1.918 | 1.32 | II | 1.867 | 1.03 | II | 1.956 | 1.06 |
| M=C | 1.770 | 1.40 | 1.843 | 1.67 | 1.756 | 1.31 | 1.901 | 1.30 | ||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.205 | 1.36 | 2.316 | 1.03 | 2.184 | 1.26 | 2.360 | 0.92 | ||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.262 | 1.07 | 2.324 | 1.02 | 2.283 | 0.99 | 2.328 | 0.92 | ||||
| M–CSIMes | III | 1.922 | 0.97 | III | 1.994 | 1.02 | III | 1.892 | 0.93 | III | 2.004 | 0.87 |
| M–C | 2.306 | 0.48 | 2.304 | 0.46 | 2.169 | 0.50 | 2.283 | 0.48 | ||||
| M=C | 1.753 | 1.67 | 1.870 | 1.62 | 1.869 | 1.10 | 1.993 | 0.97 | ||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.335 | 1.17 | 2.406 | 1.17 | 2.337 | 1.07 | 2.375 | 1.18 | ||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.311 | 1.12 | 2.410 | 1.02 | 2.338 | 1.00 | 2.370 | 1.03 | ||||
| M–CSIMes | IV | 2.120 | 0.91 | IV | 2.001 | 1.17 | IV | Not located | IV | 1.969 | 1.01 | |
| M–C | 1.980 | 0.86 | 1.982 | 0.95 | 2.068 | 0.89 | ||||||
| M=C | 2.067 | 0.74 | 1.996 | 0.99 | 2.354 | 0.29 | ||||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.246 | 1.20 | 2.408 | 0.92 | 2.375 | 1.05 | ||||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.243 | 1.17 | 2.406 | 0.91 | 2.372 | 1.15 | ||||||
| M–CSIMes | V | 1.914 | 1.06 | V | 2.031 | 0.92 | V | 1.925 | 0.73 | V | 1.997 | 0.87 |
| M–C | 1.725 | 1.89 | 1.826 | 1.77 | 1.743 | 1.76 | 1.962 | 1.08 | ||||
| M=C | 2.284 | 0.45 | 2.282 | 0.47 | 2.493 | 0.17 | 2.353 | 0.39 | ||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.314 | 1.15 | 2.434 | 0.99 | 2.244 | 1.09 | 2.376 | 1.00 | ||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.295 | 1.11 | 2.428 | 1.06 | 2.246 | 1.08 | 2.391 | 1.10 | ||||
| M–CSIMes | VI | 2.092 | 0.77 | VI | 1.923 | 1.39 | VI | 1.869 | 1.00 | VI | 1.954 | 1.04 |
| M–C | 1.722 | 1.80 | 1.810 | 1.86 | 1.716 | 1.78 | 1.866 | 1.40 | ||||
| M–Cl (F) | 2.227 | 1.14 | 2.318 | 0.90 | 2.260 | 0.99 | 2.342 | 0.92 | ||||
| M–Cl (R) | 2.198 | 1.20 | 2.316 | 0.94 | 2.168 | 1.14 | 2.339 | 0.94 | ||||
| Complex | HOMO | LUMO | η | ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-I | −0.204 | −0.091 | 0.113 | 0.096 |
| Fe-II | −0.216 | −0.104 | 0.112 | 0.114 |
| Fe-III | −0.160 | −0.119 | 0.041 | 0.237 |
| Fe-IV | −0.158 | −0.124 | 0.034 | 0.292 |
| Fe-V | −0.165 | −0.115 | 0.050 | 0.196 |
| Fe-VI | −0.241 | −0.114 | 0.127 | 0.124 |
| Ru-I | −0.145 | −0.099 | 0.046 | 0.162 |
| Ru-II | −0.169 | −0.105 | 0.064 | 0.147 |
| Ru-III | −0.156 | −0.112 | 0.044 | 0.204 |
| Ru-IV | −0.154 | −0.100 | 0.054 | 0.149 |
| Ru-V | −0.158 | −0.099 | 0.059 | 0.140 |
| Ru-VI | −0.174 | −0.094 | 0.080 | 0.112 |
| Co-I | −0.137 | −0.117 | 0.020 | 0.403 |
| Co-II | −0.166 | −0.126 | 0.040 | 0.266 |
| Co-III | −0.141 | −0.124 | 0.017 | 0.516 |
| Co-V | −0.158 | −0.121 | 0.037 | 0.263 |
| Co-VI | −0.178 | −0.123 | 0.055 | 0.206 |
| Rh-I | −0.118 | −0.098 | 0.021 | 0.282 |
| Rh-II | −0.149 | −0.128 | 0.021 | 0.456 |
| Rh-III | −0.130 | −0.109 | 0.021 | 0.343 |
| Rh-IV | −0.160 | −0.138 | 0.022 | 0.505 |
| Rh-V | −0.134 | −0.102 | 0.032 | 0.215 |
| Rh-VI | −0.158 | −0.127 | 0.031 | 0.326 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luque-Urrutia, J.A.; Gimferrer, M.; Casals-Cruañas, È.; Poater, A. In Silico Switch from Second- to First-Row Transition Metals in Olefin Metathesis: From Ru to Fe and from Rh to Co. Catalysts 2017, 7, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120389
Luque-Urrutia JA, Gimferrer M, Casals-Cruañas È, Poater A. In Silico Switch from Second- to First-Row Transition Metals in Olefin Metathesis: From Ru to Fe and from Rh to Co. Catalysts. 2017; 7(12):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120389
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuque-Urrutia, Jesús Antonio, Martí Gimferrer, Èric Casals-Cruañas, and Albert Poater. 2017. "In Silico Switch from Second- to First-Row Transition Metals in Olefin Metathesis: From Ru to Fe and from Rh to Co" Catalysts 7, no. 12: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120389
APA StyleLuque-Urrutia, J. A., Gimferrer, M., Casals-Cruañas, È., & Poater, A. (2017). In Silico Switch from Second- to First-Row Transition Metals in Olefin Metathesis: From Ru to Fe and from Rh to Co. Catalysts, 7(12), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7120389