Reactive Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Bismuth Tungstate Coatings for Water Treatment Applications under Natural Sunlight
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Coatings Overview
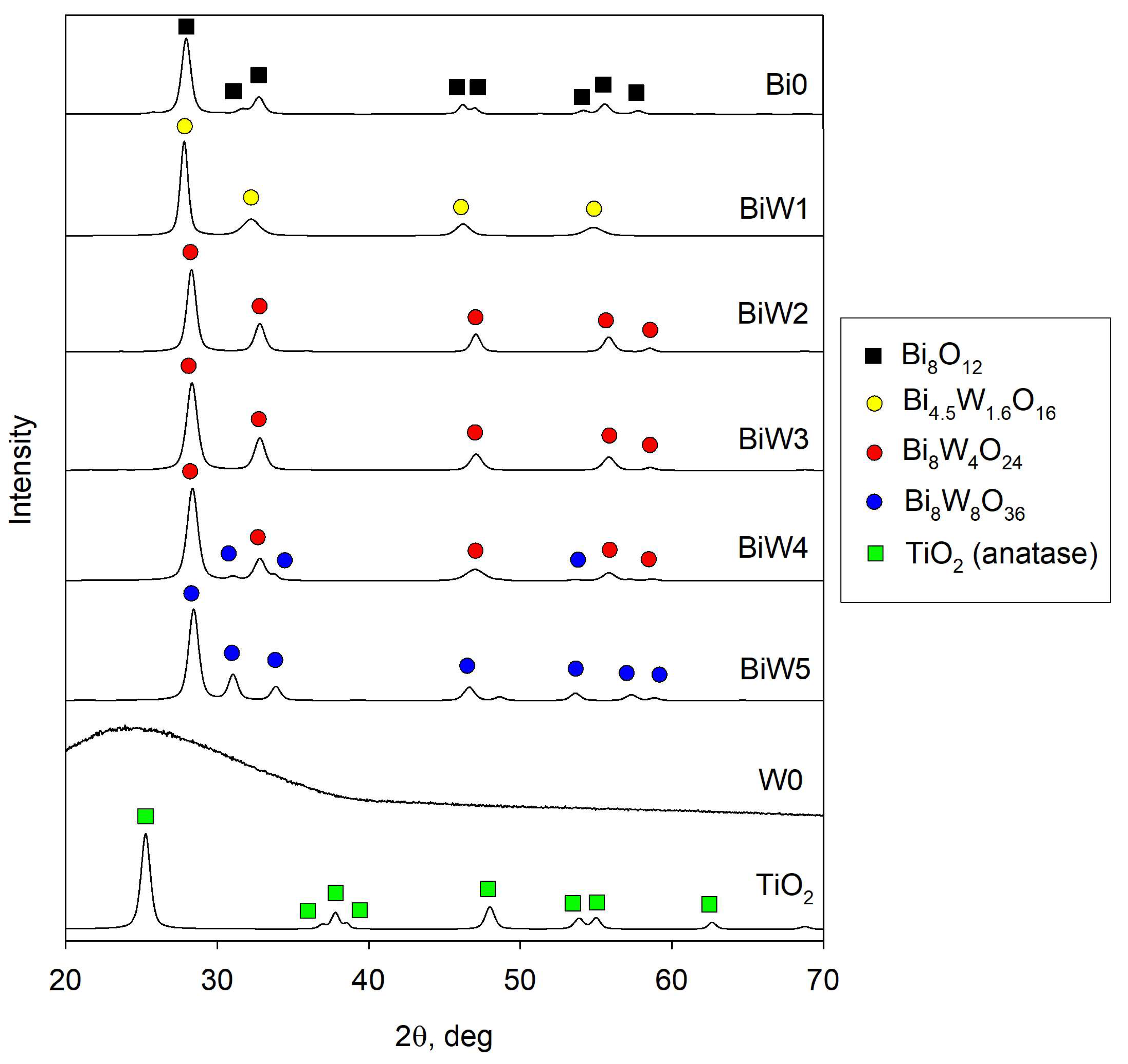
2.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Results
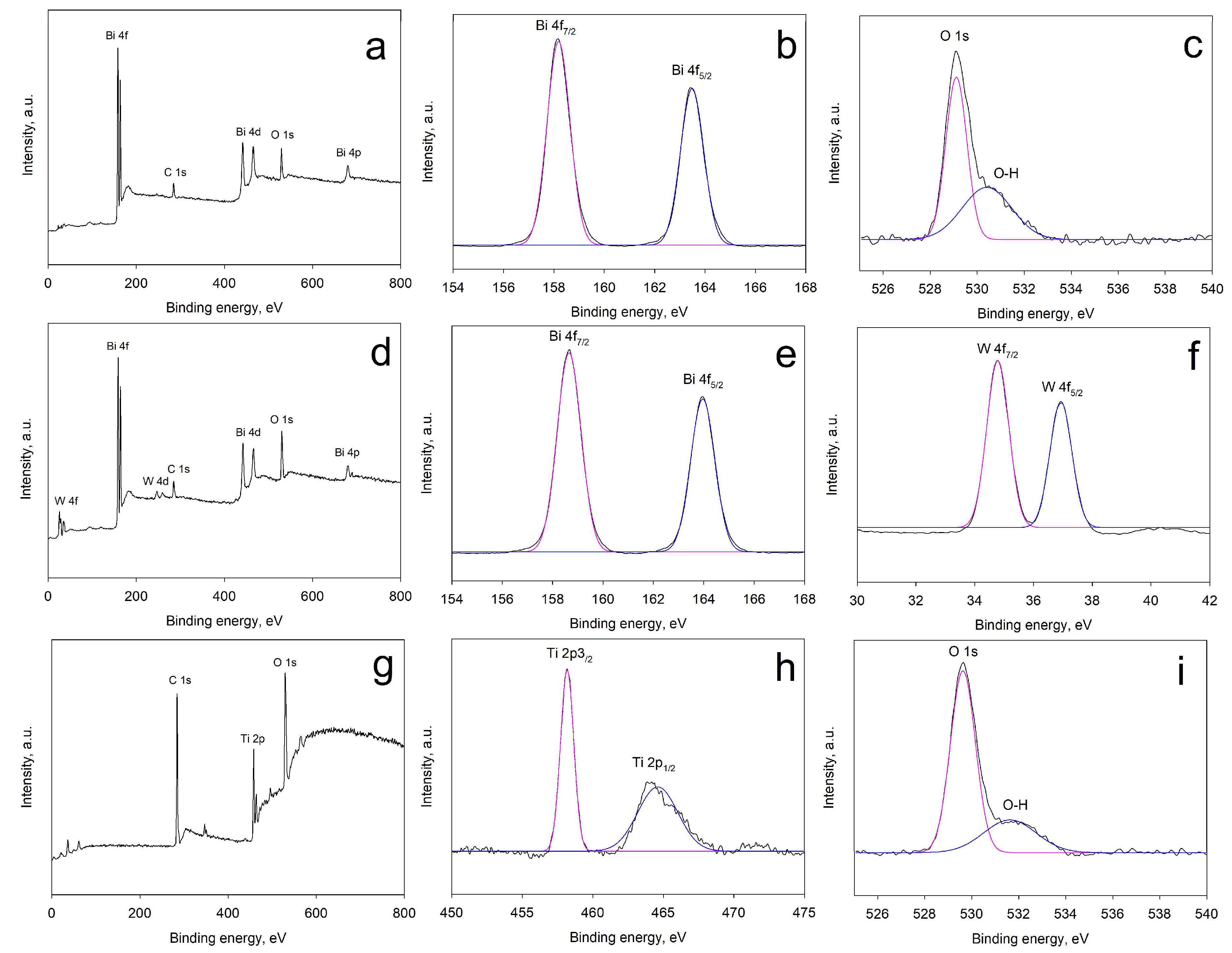
2.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Results
2.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Results
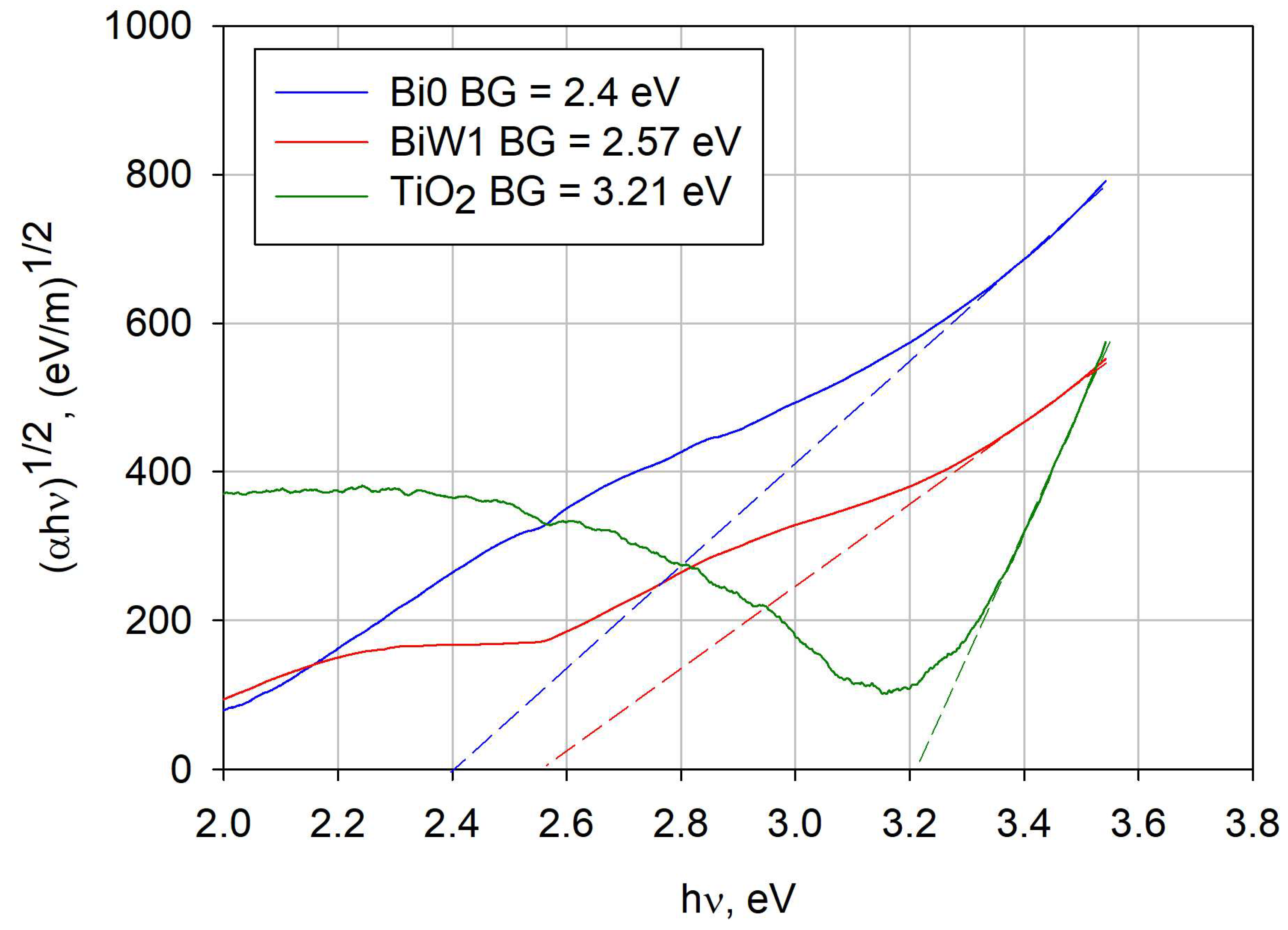
2.5. Optical Properties (Band Gap Calculation)
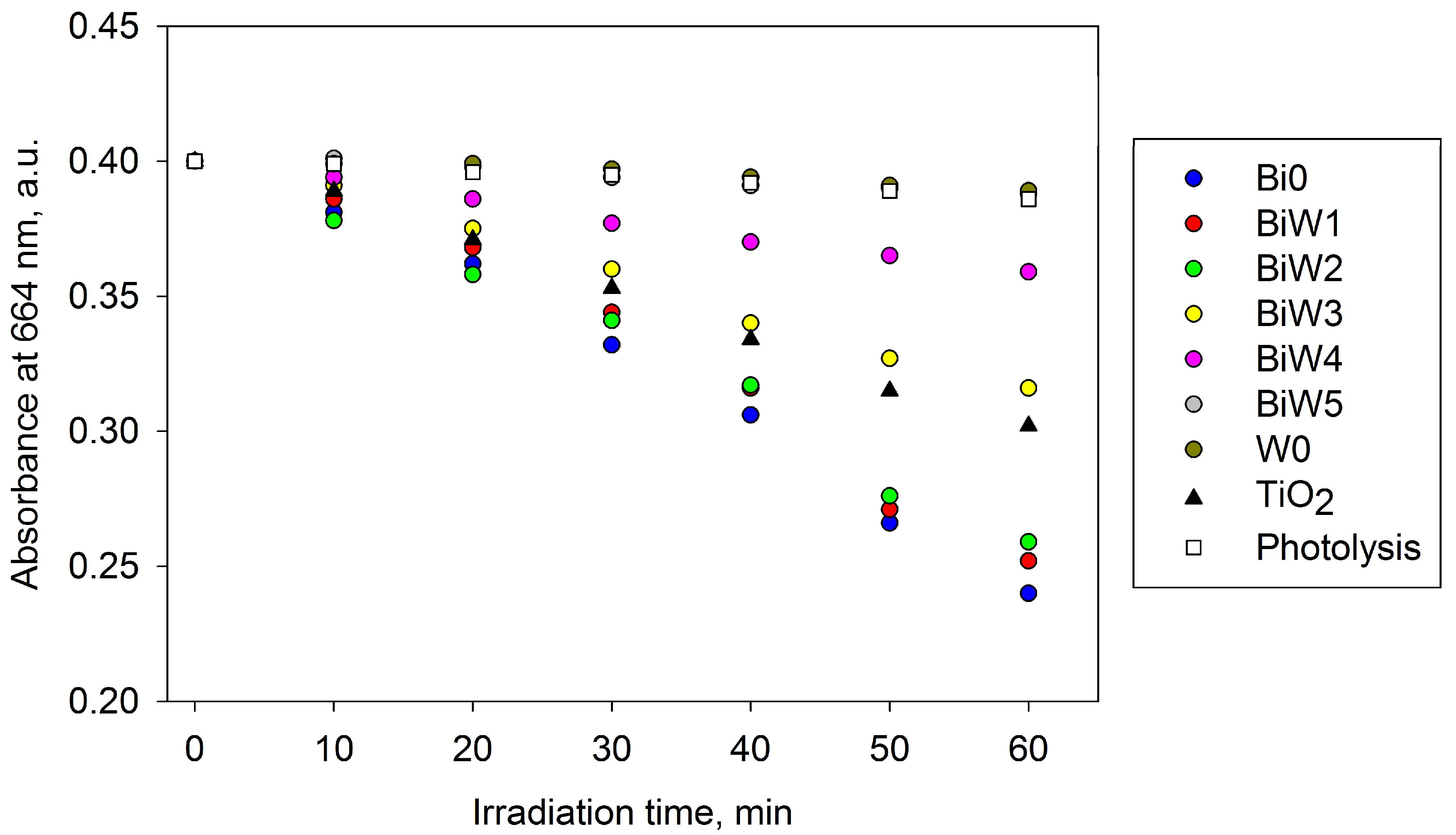
2.6. Photocatalytic Activity Assessment
2.6.1. Indoor Assessment (Fluorescent Light Source)
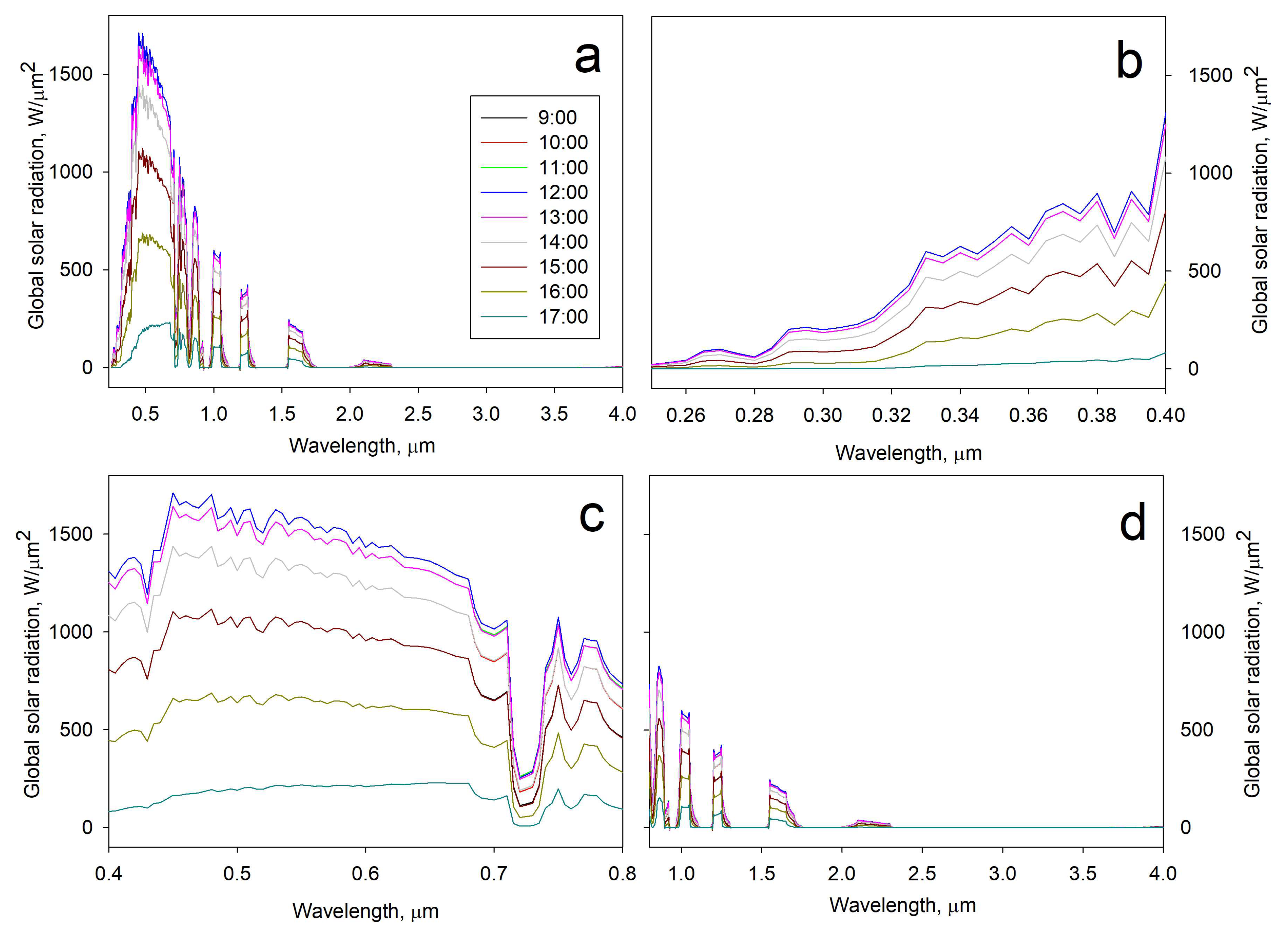
2.6.2. Outdoor Assessment (Direct Solar Irradiation)
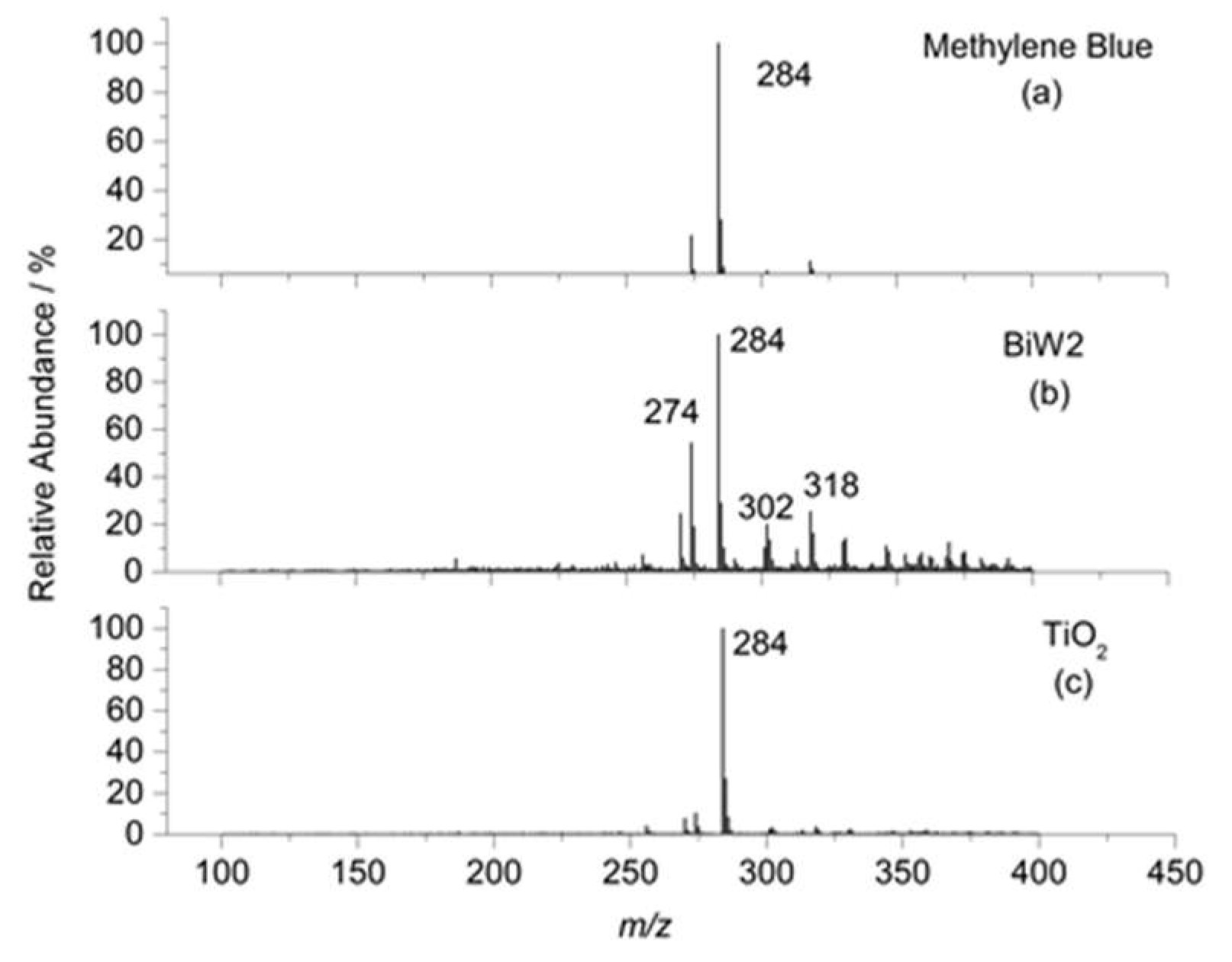
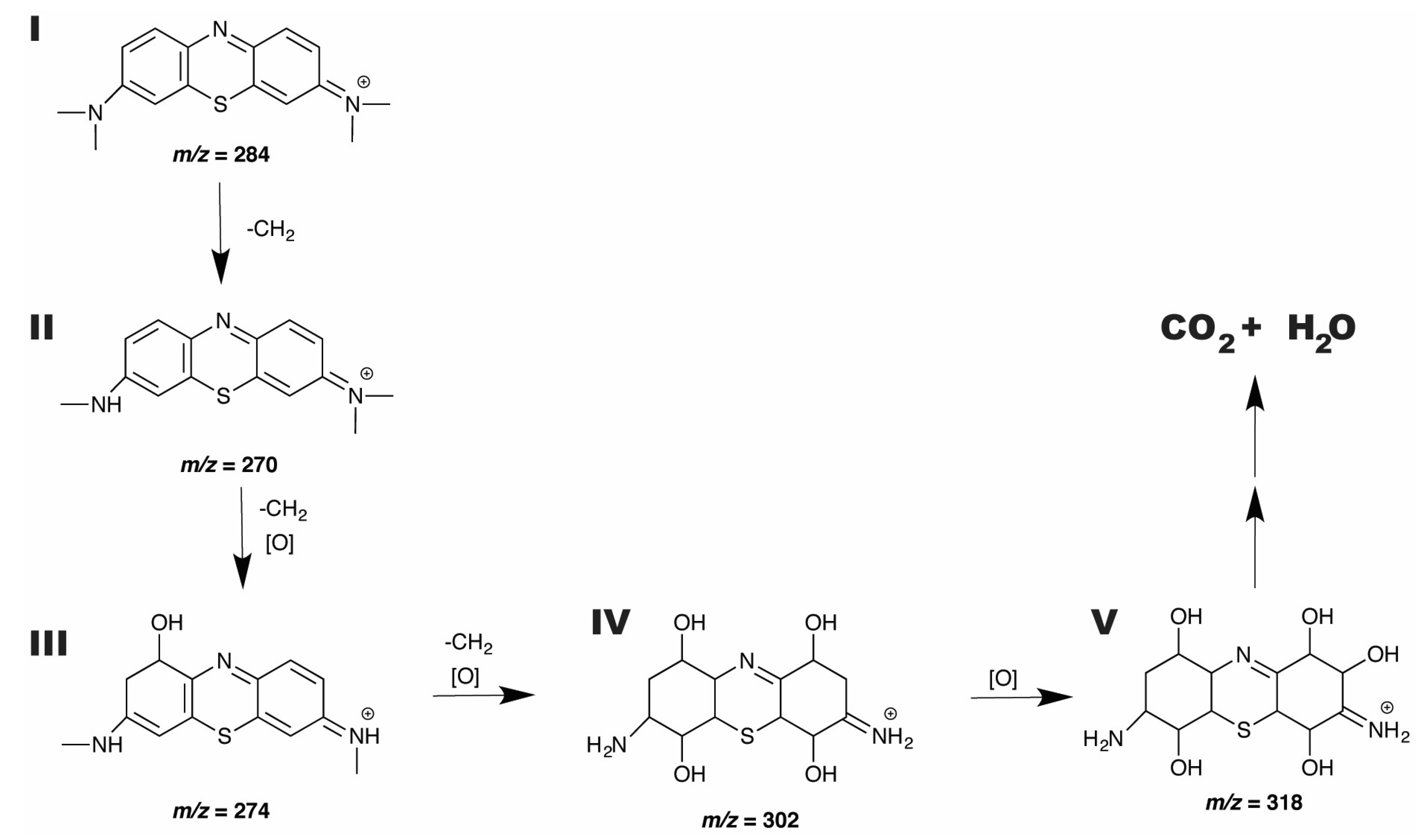
2.6.3. ESI-MS Study of MB Degradation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Deposition Process
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Photocatalytic Activity Assessment
3.3.1. Laboratory Assessment (Fluorescent Irradiation Source)
3.3.2. Outdoor Assessment (Direct Solar Irradiation)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K.-I.; Kikuchi, S.-I. Photosensitized electrolytic oxidation on semiconducting n-type TiO2 electrode. Kogyo Kagaku Zasshi 1969, 72, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chu, J.-W. NOx photocatalytic degradation on active concrete road surface: from experiment to real-scale application. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Poon, C.-S. Photocatalytic construction and building materials: From fundamentals to applications. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likodimos, V.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Falaras, P. Clean water: Water detoxification using innovative photocatalysts. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2010, 9, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Feng, J.; Fan, M.; Pi, Y.; Hu, L.; Han, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, J. Recent developments in heterogeneous photocatalytic water treatment using visible light-responsive photocatalysts: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14610–14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, A. Direct growth of F-doped TiO2 particulate thin films with high photocatalytic activity for environmental applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2008, 195, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Kambala, V.S.R.; Srinivasan, M.; Rajarathnam, D.; Naidu, R. Tailored titanium dioxide photocatalysts for the degradation of organic dyes in wastewater treatment: A review. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 359, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekakis, P.A.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Mantzavinos, D. Treatment of textile dyehouse wastewater by tio2 photocatalysis. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Alonso, M.D.; Fresno, F.; Suarez, S.; Coronado, J.M. Development of alternative photocatalysts to TiO2: Challenges and opportunities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 1231–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Wei, W.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, M.; Dai, Y.; Huang, B. Effects of oxygen vacancy and N-doping on the electronic and photocatalytic properties of Bi2MO6 (M=Mo, W). J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 187, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Yao, W.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-F. Synthesis of porous Bi2WO6 thin films as efficient visible-light-active photocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2008, 21, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Zhai, H.; Wang, Q.; Chang, L. Controllable synthesis and photocatalytic activity of spherical, flower-like and nanofibrous bismuth tungstates. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 188, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Shan, G.; Chang, C.; Fu, Y.; Yue, L.; Zhu, L. Effective degradation of tetracycline by mesoporous Bi2WO6 under visible light irradiation. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratova, M.; West, G.T.; Kelly, P.J. Photocatalytic visible-light active bismuth tungstate coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2015, 115, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kang, S.; Yang, Y.; Qin, H.; Ni, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, X. Facile synthesis of Bi/ Bi2WO6 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 196, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helali, S.; Polo-López, M.I.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Ohtani, B.; Amano, F.; Malato, S.; Guillard, C. Solar photocatalysis: A green technology for E.Coli contaminated water disinfection. Effect of concentration and different types of suspended catalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2014, 276, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, Y.; Han, Z. Heterogeneous photocatalytic treatment of wastewater in ultraviolet light irradiation—photocatalyst Bi2WO6 microsphere with high repeatability. Front. Optoelectron. 2012, 5, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Arnell, R.D. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratova, M.; Kelly, P.; West, G.; Tosheva, L. A novel technique for the deposition of bismuth tungstate onto titania nanoparticulates for enhancing the visible light photocatalytic activity. Coatings 2016, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratova, M.; Kelly, P.J.; West, G.T.; Tosheva, L.; Edge, M. Reactive magnetron sputtering deposition of bismuth tungstate onto titania nanoparticles for enhancing visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 392, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Shi, M.; Song, L. Preparation of Bi2WO6 by electrospinning: Researching their synthesis mechanism and photocatalytic activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2011, 22, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, B.; Goutham, R.; Badri Narayan, R.; Ramprasath, A.; Gopinath, K.P.; Sankaranarayanan, A.R. Recent advancements in supporting materials for immobilised photocatalytic applications in waste water treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karches, M.; Morstein, M.; Rudolf von Rohr, P.; Pozzo, R.L.; Giombi, J.L.; Baltanás, M.A. Plasma-CVD-coated glass beads as photocatalyst for water decontamination. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaor, D.A.H.; Sorrell, C.C. Sand supported mixed-phase TiO2 photocatalysts for water decontamination applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratova, M.; Kelly, P.; West, G.; Xia, X.; Gao, Y. Deposition of visible light active photocatalytic bismuth molybdate thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering. Materials 2016, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seah, M.P.; Clifford, C.A.; Green, F.M.; Gilmore, I.S. An accurate semi-empirical equation for sputtering yields i: For argon ions. Surf. Interface Anal. 2005, 37, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.C.; Leung, M.K.H. An efficient bismuth tungstate visible-light-driven photocatalyst for breaking down nitric oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4276–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L.; Chang, J.; Sheng, W.; Hu, C.; Cao, S. C-doped hollow TiO2 spheres: In situ synthesis, controlled shell thickness, and superior visible-light photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 165, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, F.; Nogami, K.; Ohtani, B. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of bismuth-tungsten mixed oxides for oxidative decomposition of acetaldehyde under visible light irradiation. Catal. Commun. 2012, 20, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Hill, C.; Robertson, P.K.J. Overview of the current iso tests for photocatalytic materials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2012, 237, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidong, H.; Wei, Q.; Xiaohong, W.; Xianbo, D.; Long, C.; Zhaohua, J. The photocatalytic properties of bismuth oxide films prepared through the sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 5362–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirota, B.; Reyes-Cuellar, J.; Kohli, P.; Wang, L.; McCarroll, M.E.; Aouadi, S.M. Bismuth oxide photocatalytic nanostructures produced by magnetron sputtering deposition. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 6118–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Maldonado, M.I.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratova, M.; Kelly, P.J.; West, G.T.; Iordanova, I. Enhanced properties of magnetron sputtered photocatalytic coatings via transition metal doping. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228, S544–S549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratório de energia solar-labsol. 2017. Available online: http://www.solar.ufrgs.br (accessed on 20 August 2017).
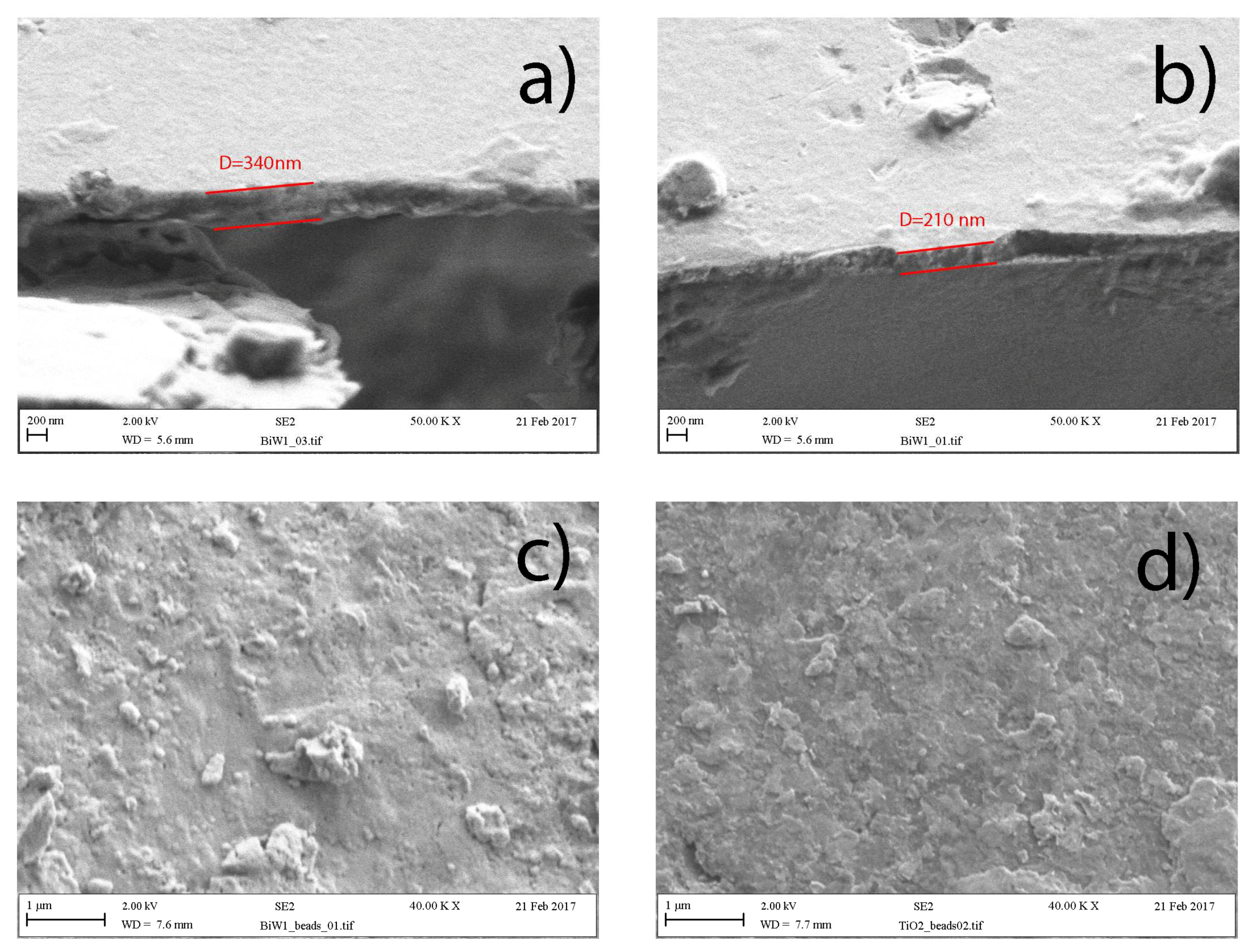




| Sample ID | Bi Power, W | W Power, W | Power Ratio | Bi Content, atomic % | W Content, atomic % | Atomic % Ratio | Coating Thickness, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0 | 600 | 0 | --- | 100 | 0 | --- | 340 |
| BiW1 | 300 | 300 | 1/1 | 73 | 27 | 2.7/1 | 210 |
| BiW2 | 200 | 400 | 1/2 | 65 | 35 | 1.8/1 | 160 |
| BiW3 | 150 | 450 | 1/3 | 57 | 43 | 1.3/1 | 130 |
| BiW4 | 120 | 480 | 1/4 | 52 | 48 | 1.1/1 | 110 |
| BiW5 | 100 | 500 | 1/5 | 44 | 56 | 1/1 | 100 |
| W0 | 0 | 600 | --- | 0 | 100 | --- | 70 |
| TiO2 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | 90 |
| Sample ID | Major Crystal Phase | Surface Roughness Ra, nm | Surface Area Sa, µm2 | Band Gap, eV | Absorption Edge, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0 | Bismuth oxide | 8.3 | 904 | 2.40 | 516.7 |
| BiW1 | Russelite Bi4.5W1.6O16 | 6.6 | 902 | 2.57 | 482.5 |
| BiW2 | Russelite Bi8W4O24 | 7.3 | 903 | 2.64 | 469.7 |
| BiW3 | Russelite Bi8W4O24 | 6.4 | 902 | 2.68 | 462.7 |
| BiW4 | Russelite Bi8W4O24/bismuth tungstate Bi8W8O36 | 4.5 | 902 | 2.75 | 450.9 |
| BiW5 | Bismuth tungstate Bi8W8O36 | 3.8 | 901 | 2.83 | 438.2 |
| W0 | None (amorphous) | 5.5 | 901 | 2.97 | 417.5 |
| TiO2 | Anatase | 4.8 | 900 | --- | 388.7 |
| Sample ID | Round 1 kapp, min−1 | Round 2 kapp, min−1 | Round 3 kapp, min−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0 | 0.0134 | 0.0130 | 0.0103 |
| BiW1 | 0.0121 | 0.0118 | 0.0101 |
| BiW2 | 0.0128 | 0.0126 | 0.0103 |
| TiO2 | 0.0085 | 0.0079 | 0.0077 |
| Photolysis | 0.0087 | 0.0081 | 0.0084 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratova, M.; Marcelino, R.B.P.; De Souza, P.P.; Amorim, C.C.; Kelly, P.J. Reactive Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Bismuth Tungstate Coatings for Water Treatment Applications under Natural Sunlight. Catalysts 2017, 7, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100283
Ratova M, Marcelino RBP, De Souza PP, Amorim CC, Kelly PJ. Reactive Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Bismuth Tungstate Coatings for Water Treatment Applications under Natural Sunlight. Catalysts. 2017; 7(10):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100283
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatova, Marina, Rafaela B. P. Marcelino, Patterson P. De Souza, Camila C. Amorim, and Peter J. Kelly. 2017. "Reactive Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Bismuth Tungstate Coatings for Water Treatment Applications under Natural Sunlight" Catalysts 7, no. 10: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100283
APA StyleRatova, M., Marcelino, R. B. P., De Souza, P. P., Amorim, C. C., & Kelly, P. J. (2017). Reactive Magnetron Sputter Deposition of Bismuth Tungstate Coatings for Water Treatment Applications under Natural Sunlight. Catalysts, 7(10), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7100283