Photocatalytic Removal of Microbiological Consortium and Organic Matter in Greywater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Prepared Greywater Samples
2.2. Degradation of Organic Matter:UV254 and DOC Removal
2.3. Bacterial Inactivation
2.4. Kinetic Considerations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Synthetic Greywater Samples
3.2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
3.3. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLF | Black Light Fluorescent |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| FC | Fecal Coliform |
| FS | Fecal Streptococci |
| H1 | High organic matter load grey water with low anion content |
| H2 | High organic matter load grey water with high anion content |
| H3 | High load organic matter grey water with low anion content and bacteria |
| HA | Humic acid |
| L1 | Low organic matter load grey water with low anion content |
| L2 | Low organic matter load grey water with high anion content |
| L3 | Low load organic matter grey water with low anion content and bacteria |
| OM | organic matter |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TC | Total Coliform |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
References
- Eriksson, E.; Auffarth, K.; Henze, M.; Ledin, A. Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water 2002, 4, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourlier, F.; Masse, A.; Jaouen, P.; Lakel, A.; Gerente, C.; Faur, C.; Le Cloirec, P. Formulation of synthetic grey water as an evaluation tool for wastewater recycling technologies. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Leal, L.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buismann, C.J.N. Characterization and anaerobic biodegradability of grey water. Desalination 2011, 270, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Hadari, M. Economic feasibility of on-site grey water reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination 2006, 190, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyas, H.; Choromanski, P.; Muellin, N.; Furmanska, M. Toward chemical-free reclamation of biologically pretreated greywater: Solar photocatalytic oxidation with powdered activated carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghunmi, L.A.; Zeeman, G.; Fayyad, M.; van Lier, J.B. Grey water treatment systems: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 657–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wichmann, K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.T.; Rao, N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Maldonado, M.I.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, K.G.; Conroy, R.M.; Mosler, H.-J.; du Preez, M.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P. Solar water disinfection (SODIS): A review from bench-top to roof-top. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, T.A. The Influence of surface alumina and silica on the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Catalysts 2013, 3, 338–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, R.; Hara, M.; Ishiguro, H.; Yao, Y.; Ochiai, T.; Nakata, K.; Murakami Kajioka, J.; Sunada, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; et al. Broad spectrum microbicidal activity of photocatalysis by TiO2. Catalysts 2013, 3, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kettleson, E.; An, W.-J.; Tang, Y.J.; Biswas, P. Inactivation of E. coli in water using photocatalytic, nanostructured films synthesized by aerosol routes. Catalysts 2013, 3, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, M.; Ramachandran, K.; Ananthapadmanabhan, P.V.; Nalini, B.; Pillai, B.C.; Bondioli, F.; Manivannan, A.; Narendhirakannan, R.T. Photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by reactive plasma processed nanocrystalline TiO2 powder. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marugán, J.; van Grieken, R.; Pablos, C.; Satuf, M.L.; Cassano, A.E.; Alfano, O.M. Photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli aqueous suspensions in a fixed-bed reactor. Catal. Today 2015, 252, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adán, C.; Marugán, J.; Mesones, S.; Casado, C.; van Grieken, R. Bacterial inactivation and degradation of organic molecules by titanium dioxide supported on porous stainless steel photocatalytic membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, M.A.; Varghese, S.; Nair, S.S. Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: Recent updates. Catalysts 2012, 2, 572–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibhadon, A.O.; Fitzpatrick, P. Heterogeneous Photocatalysis: Recent Advances and Applications. Catalysts 2013, 3, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyas, H.; Argáez, A.S.O.; Kong, F.; Liriano Jorge, C.; Eggers, S.; Otterpohl, R. Combining activated carbon adsorption with heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation: Lack of synergy for biologically treated greywater and tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Nanny, M.A.; Butler, E.C. Photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia in model gray waters. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I. Photocatalytic oxidation of grey water over titanium dioxide suspensions. Desalination 2010, 262, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyas, H.; Jain, H.B.; Susanto, A.L.; Malekpur, M.; Harasiuk, K.; Krawczyk, I.; Choromanski, P.; Furmanska, M. Solar photocatalytic oxidation of Pretreated wastewaters: Laboratory scale generation of design data for technical-scale double-skin sheet reactors. Environ. Technol. 2004, 26, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wandruszka, R. Humic acids: Their detergent qualities and potential uses in pollution remediation. Geochem. Trans. 2000, 1, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Becker, W.C.; Wattier, K.L. Surrogate parameters for monitoring organic matter and THM precursors. J. AWWA 1985, 77, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Uyguner, C.S.; Bekbolet, M. Evaluation of humic acid photocatalytic degradation by UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. Catal. Today 2005, 101, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Leal, M.; Li, Q. Degradation of natural organic matter by TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation and its effect on fouling low-pressure membranes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin-hui, Z. Research on UV/TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of organic matter in drinking water and its influencing factors. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, C.; van Grieken, R.; Marugán, J.; Moreno, B. Photocatalytic inactivation of bacteria in a fixed-bed reactor: Mechanistic insights by epifluorescence microscopy. Catal. Today 2011, 161, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Gerardin, F.; André, J.-C.; Pons, M.-N.; Zahraa, O. Study of photocatalytic damages induced on E. coli by different photocatalytic supports (various types and TiO2 configurations). J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 222, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolet, M.; Araz, C.V. Inactivation of Escherichia coli by photocatalytic oxidation. Chemosphere 1996, 32, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolet, M. Photocatalytic bactericidal activity of TiO2 in aqueous suspensions of E. coli. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolet, M. Photocatalytic Inactivation of Microorganisms in Drinking Water. In Control of Disinfection By-Products in Drinking Water Systems; Nikolau, A., Selcuk, H., Rizzo, L., Eds.; NOVA Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, A.; Li, Y.; Yip, H.Y.; An, T.; Li, G.; Jin, P.; Wang, P.-K. Photocatalytic inactivation of Escherichia coli by natural sphalarite suspension: Effect of spectrum, wavelength and intensity of visible light. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marugán, J.; van Grieken, R.; Pablos, C.; Sordo, C. Analogies and differences between photocatalytic oxidation of chemicals and photocatalytic inactivation of microorganisms. Water Res. 2010, 44, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Yu, L.E.; Ray, M.B.V. Photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using fluorescent light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2007, 186, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grieken, R.; Marugán, J.; Pablos, C.; Furones, L.; López, A. Comparison between the photocatalytic inactivation of Gram-positive E. faecalis and Gram-negative E. coli faecal contamination indicator microorganisms. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 100, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 175, 13–886. [Google Scholar]
- Uyguner, C.S.; Bekbolet, M. Application of photocatalysis for the removal of natural organic matter in simulated surface and ground waters. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2009, 12, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Uyguner-Demirel, C.S.; Birben, C.; Bekbolet, M. Key role of common anions on the photocatalytic degradation profiles of molecular size fractions of humic acids. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolet, M.; Boyacioglu, Z.; Ozkaraova, B. The influence of solution matrix on the photocatalytic removal of color from natural waters. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Low, G.K.-W.; Matthews, R.W. Effects of common inorganic anions on rates of photocatalytic oxidation of organic carbon over illuminated titanium dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, A.-G.; Pulgarin, C. Effect of pH, inorganic anions, organic matter and H2O2 on E. coli K12 photocatalytic inactivation by TiO2: Implications in solar water disinfection. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 51, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgarin, C.; Kiwi, J.; Nadtochenko, V. Mechanism of photocatalytic bacterial inactivation on TiO2 films involving cell-wall damage and lysis. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 128, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christl, I.; Kretzschmar, R. Relating ion binding by fulvic and humic acids to chemical composition and molecular size. Proton binding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carp, O.; Huisman, C.L.; Reller, A. Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Solid State Phenom. 2004, 32, 33–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolet, M.; Suphandag, A.S.; Uyguner, C.S. An investigation of the photocatalytic efficiencies of TiO2 powders on the decolourisation of humic acids. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2002, 148, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christova-Boal, D.; Eden, R.E.; McFarlane, S. An investigation into greywater reuse for urban residential properties. Desalination 1996, 106, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Grey water reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings-over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water 1999, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.M.; Butler, D.; Fewkes, A. Guidelines for grey water reuse: Health issues. J. CIWEM 1999, 13, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kerc, A.; Bekbolet, M.; Saatci, A.M. Effects of oxidative treatment techniques on molecular size distribution of humic acids. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
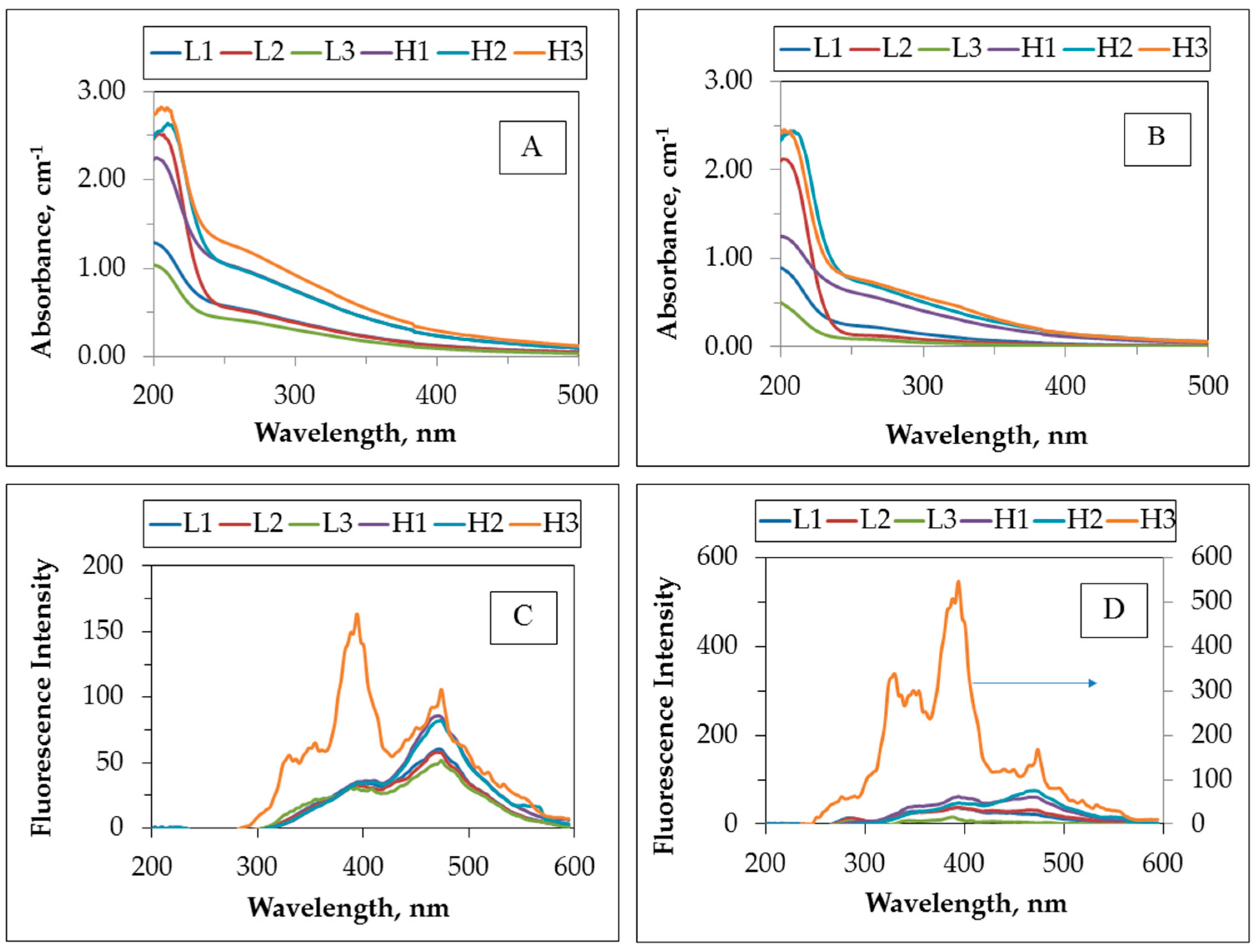
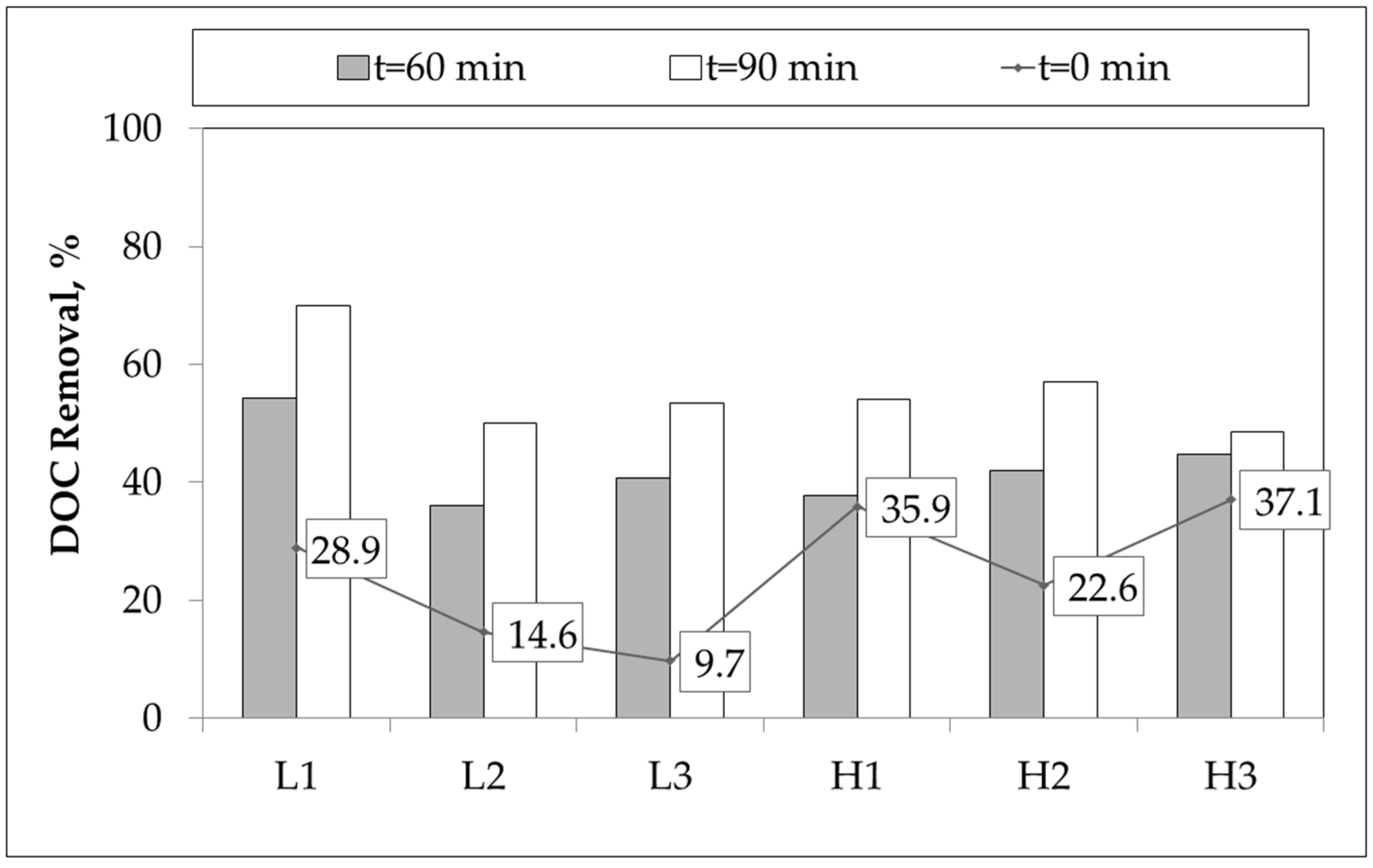
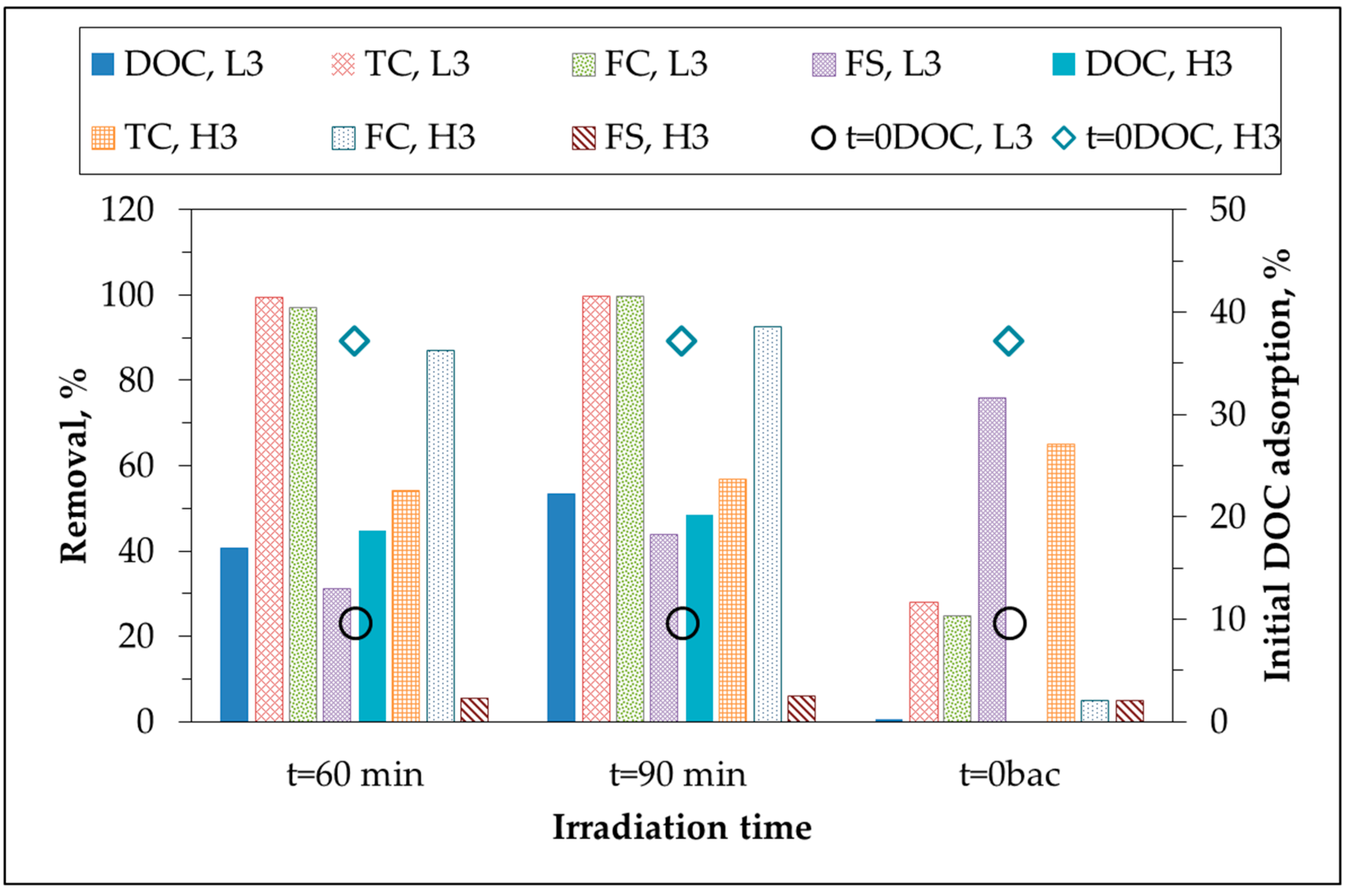
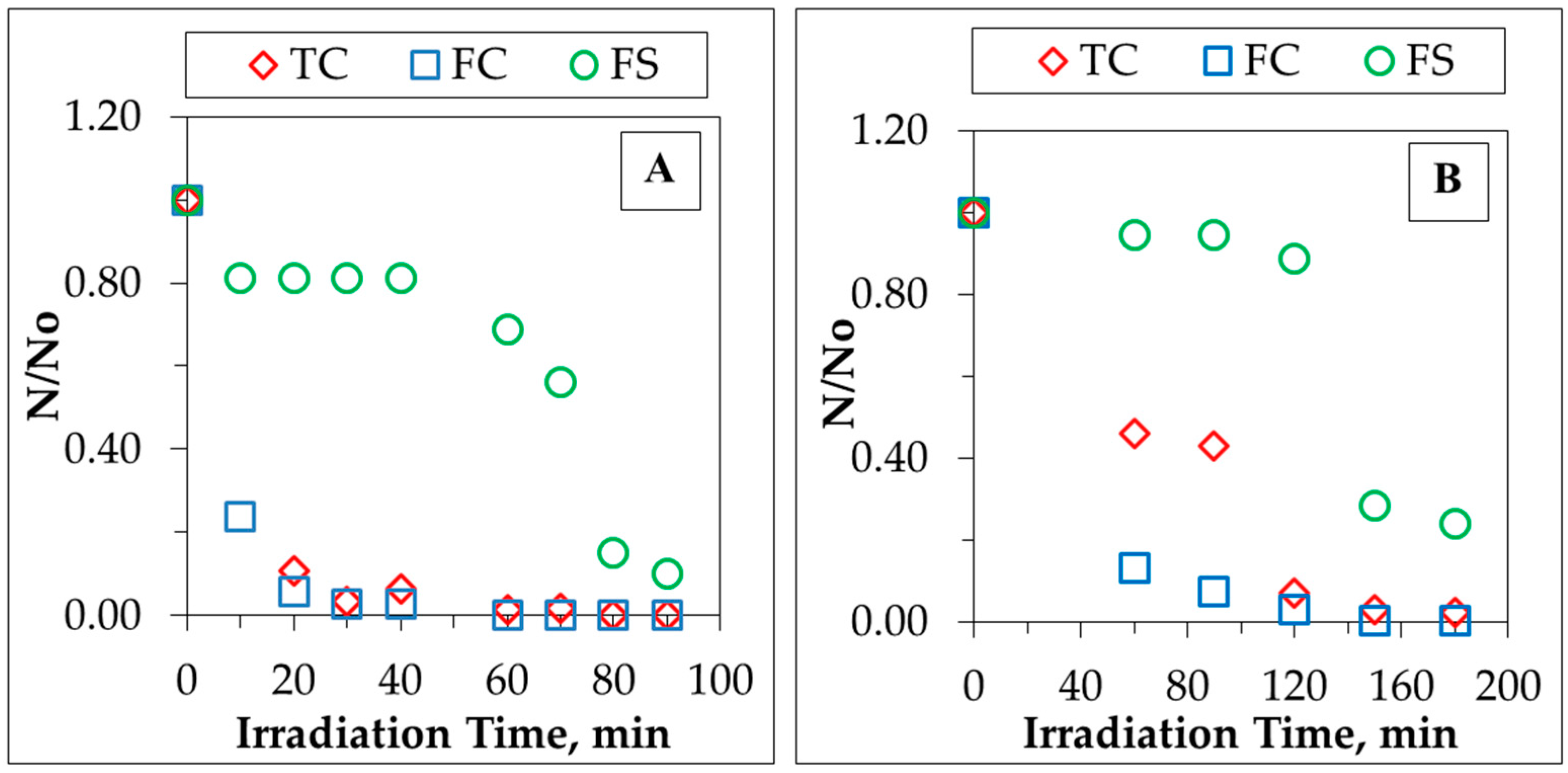
| Greywater | DOC, mg·L−1 | UV254, m−1 | FIsyn | SUVA254 m−1·mg−1·L | SFIsyn | Bacterial Content CFU/100 mL × 104 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | FC | FS | |||||||||||||
| L1 | 6.72 | 56.38 | 60.6 | 8.39 | 8.95 | - | - | - | |||||||
| L2 | 6.44 | 54.74 | 57.8 | 8.50 | 8.98 | - | - | - | |||||||
| L3 | 6.80 | 42.60 | 48.96 | 6.26 | 7.20 | 5.4 | 3.1 | 1.6 | |||||||
| H1 | 13.0 | 103.5 | 85.61 | 7.96 | 6.59 | - | - | - | |||||||
| H2 | 12.9 | 102.6 | 81.55 | 7.95 | 6.32 | - | - | - | |||||||
| H3 | 16.6 | 126.9 | 93.28 | 7.65 | 5.62 | 7.2 | 5.4 | 1.8 | |||||||
| Anions, mg·L−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Greywater | F− | Cl− | Br− | NO2− | NO3− | SO42− | H2PO4−/HPO42− | ||||||||
| L1, L3, H1, H3 | 0.0431 | 0.402 | 0.982 | 0.534 | 0.214 | 0.292 | 0.405 | ||||||||
| L2, H2 | 0.341 | 3.621 | 9.56 | 6.36 | 2.14 | 2.08 | 3.95 | ||||||||
| Molecular Size Fractions | Low OM | High OM |
|---|---|---|
| DOC | ||
| <100 kDa and >30 kDa | 59% | 41% |
| <30 kDa and >3 kDa | 31% | 49% |
| <3 kDa | 10% | 10% |
| UV254 | ||
| <100 kDa and >30 kDa | 62% | 43% |
| <30 kDa and >3 kDa | 35% | 51% |
| <3 kDa | 3% | 6% |
| Greywater | UV254 | DOC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k × 10−2 min−1 | R m−1·min−1 | t1/2 min | k × 10−2 min−1 | R mg·L−1·min−1 | t1/2 min | |
| L1 | 1.29 | 0.727 | 54 | 1.21 | 0.0801 | 57 |
| L2 | 2.18 | 1.19 | 32 | 0.724 | 0.0464 | 97 |
| L3 | 3.12 | 1.33 | 22 | 0.833 | 0.0903 | 83 |
| H1 | 0.853 | 0.880 | 82 | 0.741 | 0.0972 | 94 |
| H2 | 0.791 | 0.811 | 88 | 0.852 | 0.110 | 81 |
| H3 | 0.552 | 0.703 | 125 | 0.574 | 0.0752 | 122 |
| Greywater | TC | FC | FS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k × 10−2 min−1 | R CFU100 mL−1·min−1 | t1/2 min | k × 10−2 min−1 | R CFU100 mL−1·min−1 | t1/2 min | k × 10−2 min−1 | R CFU100 mL−1·min−1 | t1/2 min | |
| L3 | 8.83 | 4.77 × 103 | 8 | 6.54 | 2.03 × 103 | 11 | 5.6 | 0.896 × 103 | 12 |
| H3 | 2.26 | 1.63 × 103 | 31 | 3.23 | 1.74 × 103 | 21 | 0.8 | 0.14 × 103 | 87 |
| Abbreviation | Grey Water Sample |
|---|---|
| L1 | Low OM load grey water with low anion content |
| L2 | Low OM load grey water with high anion content |
| L3 | Low OM load grey water with low anion content and bacteria |
| H1 | High OM load grey water with low anion content |
| H2 | High OM load grey water with high anion content |
| H3 | High OM load grey water with low anion content and bacteria |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birben, N.C.; Uyguner-Demirel, C.S.; Bekbolet, M. Photocatalytic Removal of Microbiological Consortium and Organic Matter in Greywater. Catalysts 2016, 6, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060091
Birben NC, Uyguner-Demirel CS, Bekbolet M. Photocatalytic Removal of Microbiological Consortium and Organic Matter in Greywater. Catalysts. 2016; 6(6):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060091
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirben, Nazmiye Cemre, Ceyda Senem Uyguner-Demirel, and Miray Bekbolet. 2016. "Photocatalytic Removal of Microbiological Consortium and Organic Matter in Greywater" Catalysts 6, no. 6: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060091
APA StyleBirben, N. C., Uyguner-Demirel, C. S., & Bekbolet, M. (2016). Photocatalytic Removal of Microbiological Consortium and Organic Matter in Greywater. Catalysts, 6(6), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060091







