Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Aging-Induced Pd Sintering: The Primary Catalyst Deactivation Mode
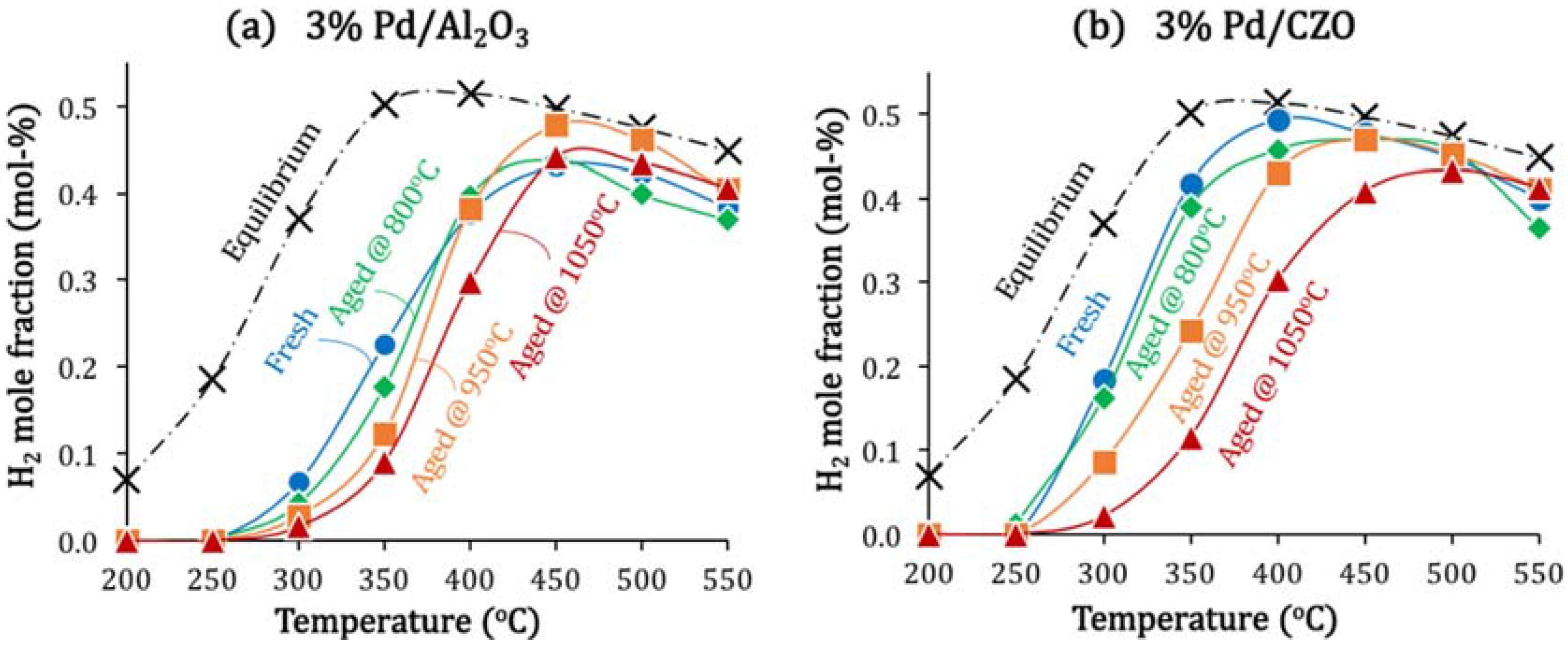
| Catalyst | Fresh | After Aging in Air for 5 min at Different T | After Attempted Regeneration * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 °C | 950 °C | 1050 °C | |||
| 0.5% Rh/Al2O3 | 375 | 415 | 460 | 470 | 375 |
| 0.5% Rh/CZO | 334 | 365 | 431 | 435 | 330 |
| 3% Pd/Al2O3 | 360 | 367 | 375 | 390 | 390 |
| 3% Pd/CZO | 315 | 320 | 355 | 387 | 370 |


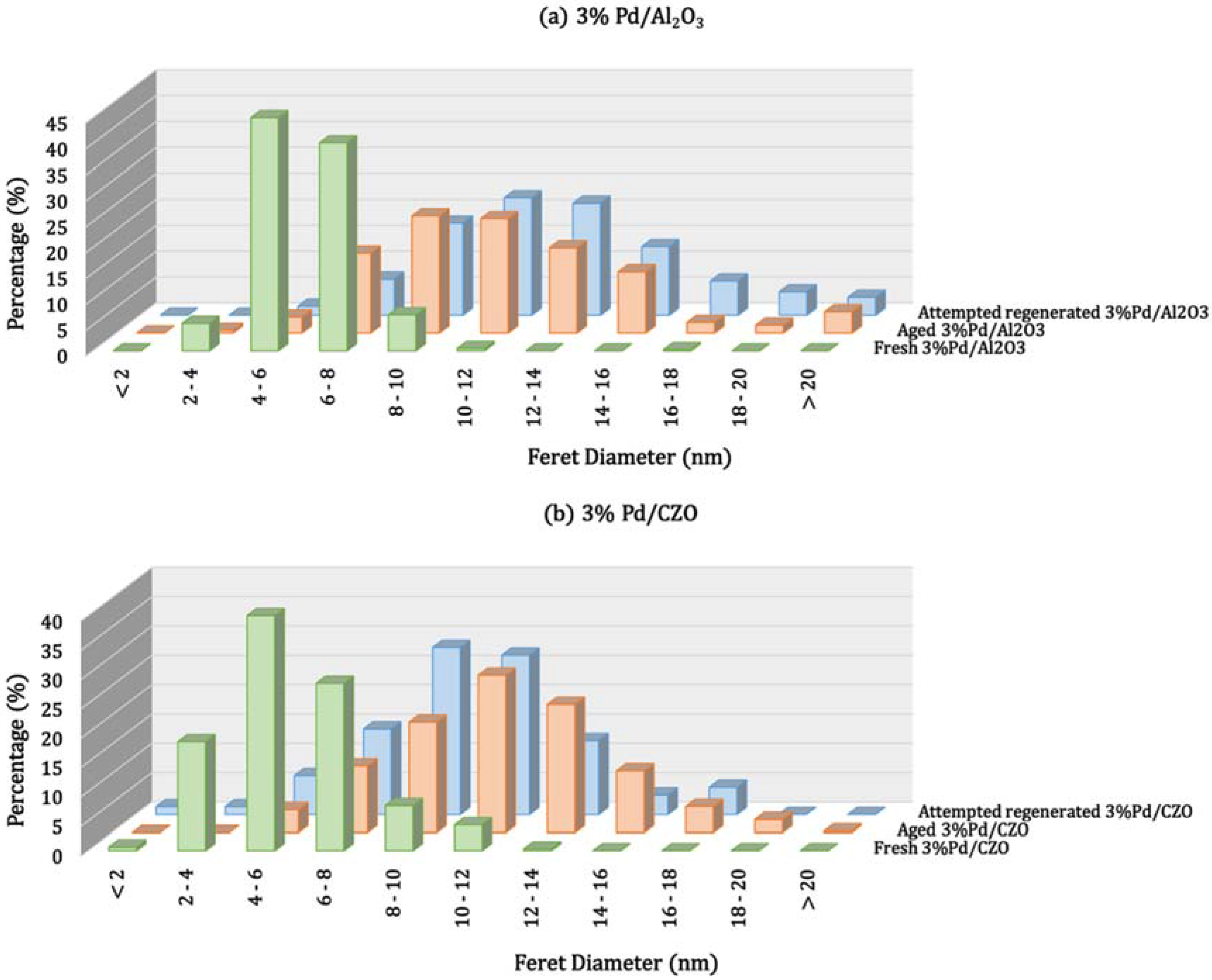
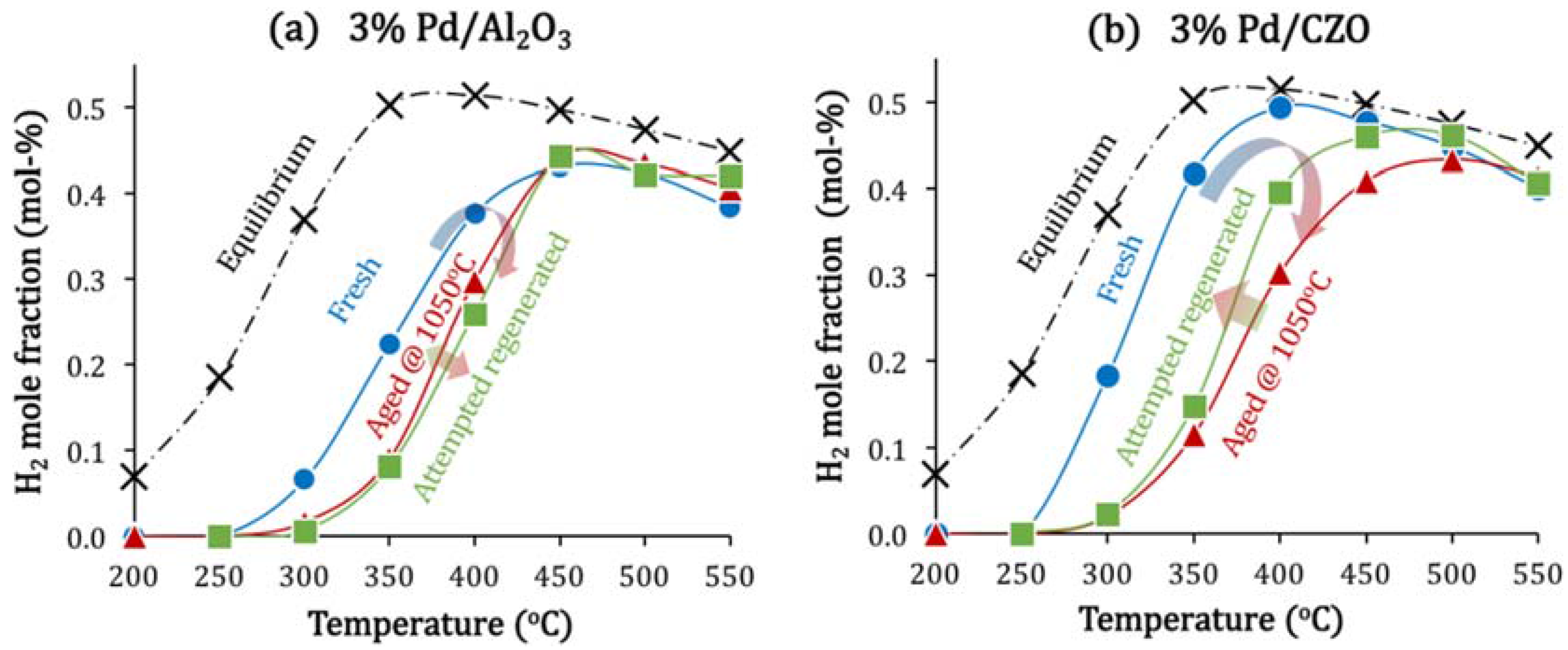
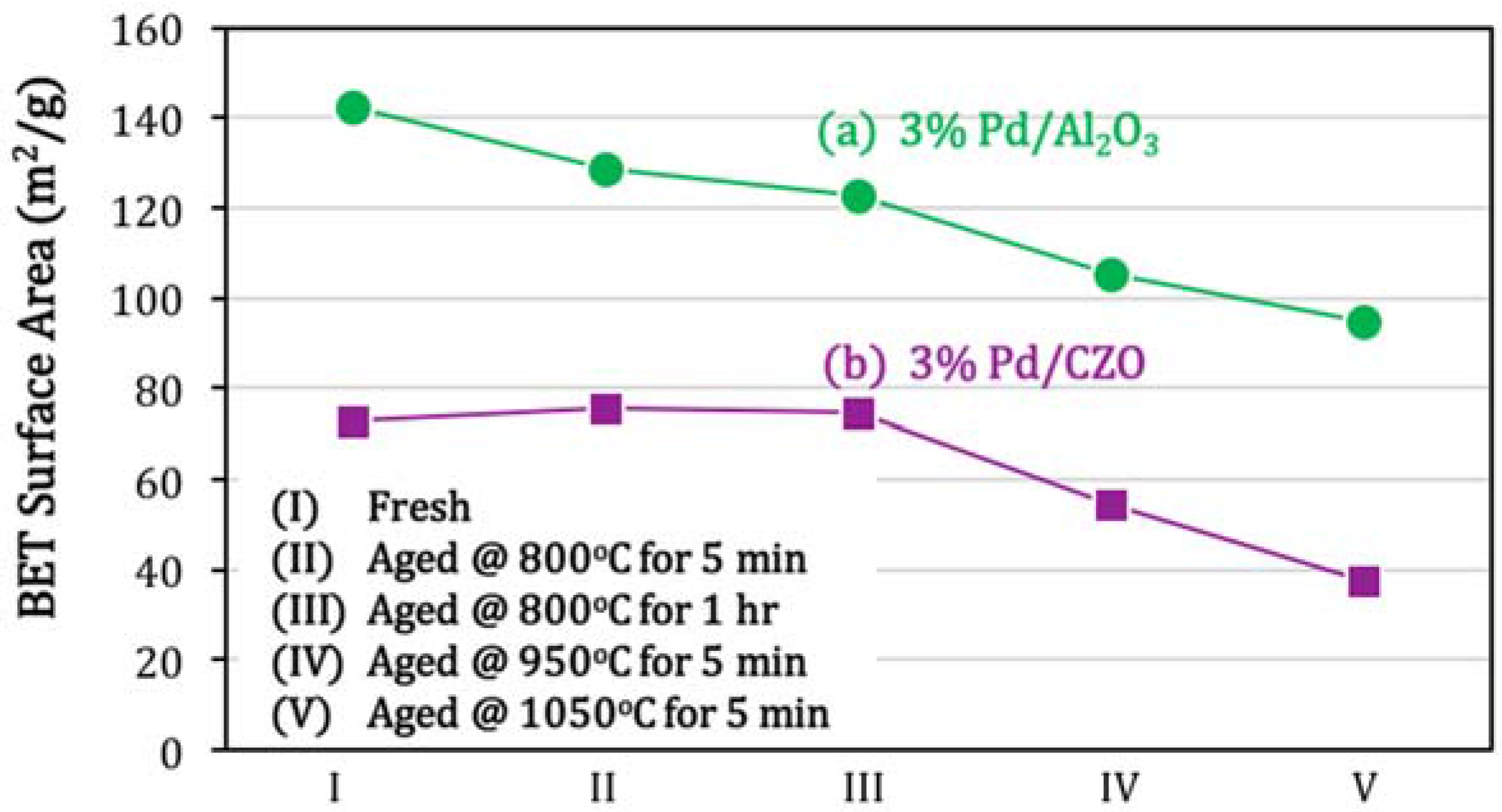
2.2. Support Sintering and Pd-Support Interaction: Other Catalyst Deactivation Modes

| Catalyst | Metal Crystallite Size (nm) | Support Crystallite Size (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | TEM | XRD | TEM | ||
| Fresh 3% Pd/Al2O3 | Fresh | -- | 4.1 | 7.2 | 7.0 |
| Aged | 10.3 | 11.3 | 7.7 | 7.4 | |
| Fresh 3% Pd/CZO | Fresh | -- | 5.7 | 7.3 | 6.5 |
| Aged | 12.9 | 11.2 | 12.6 | 12.0 | |
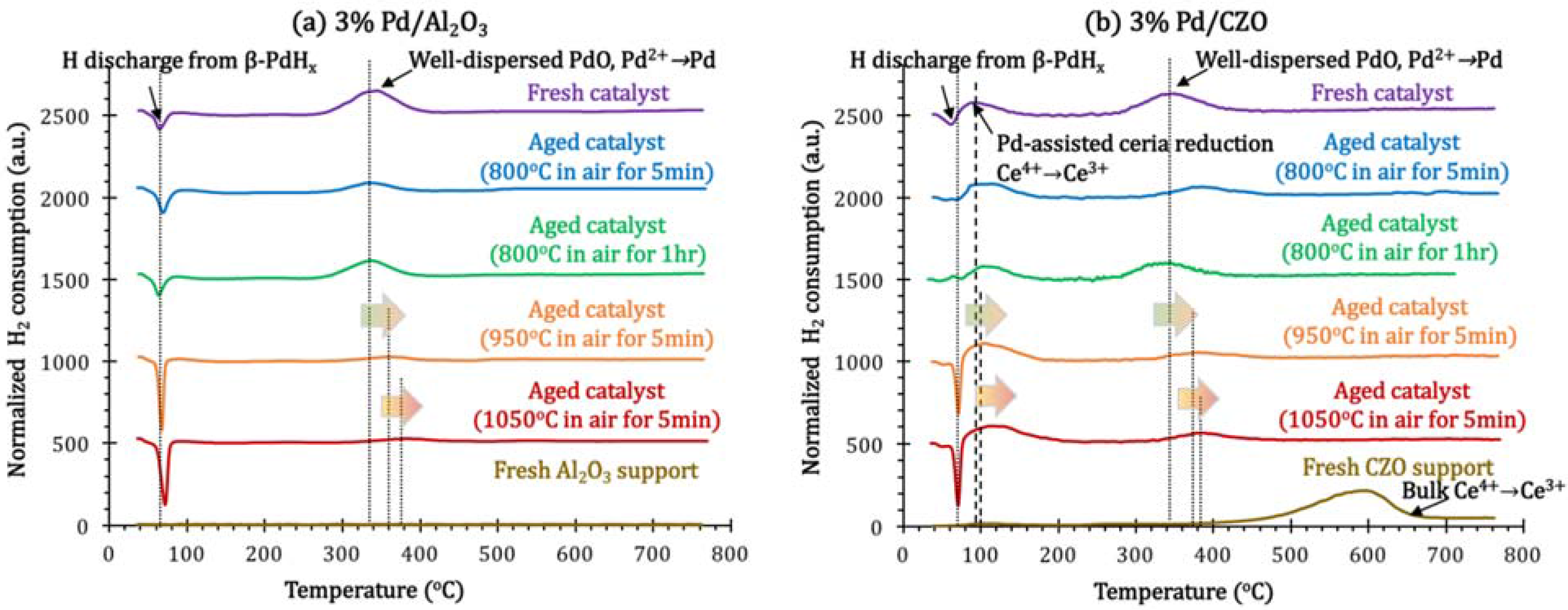
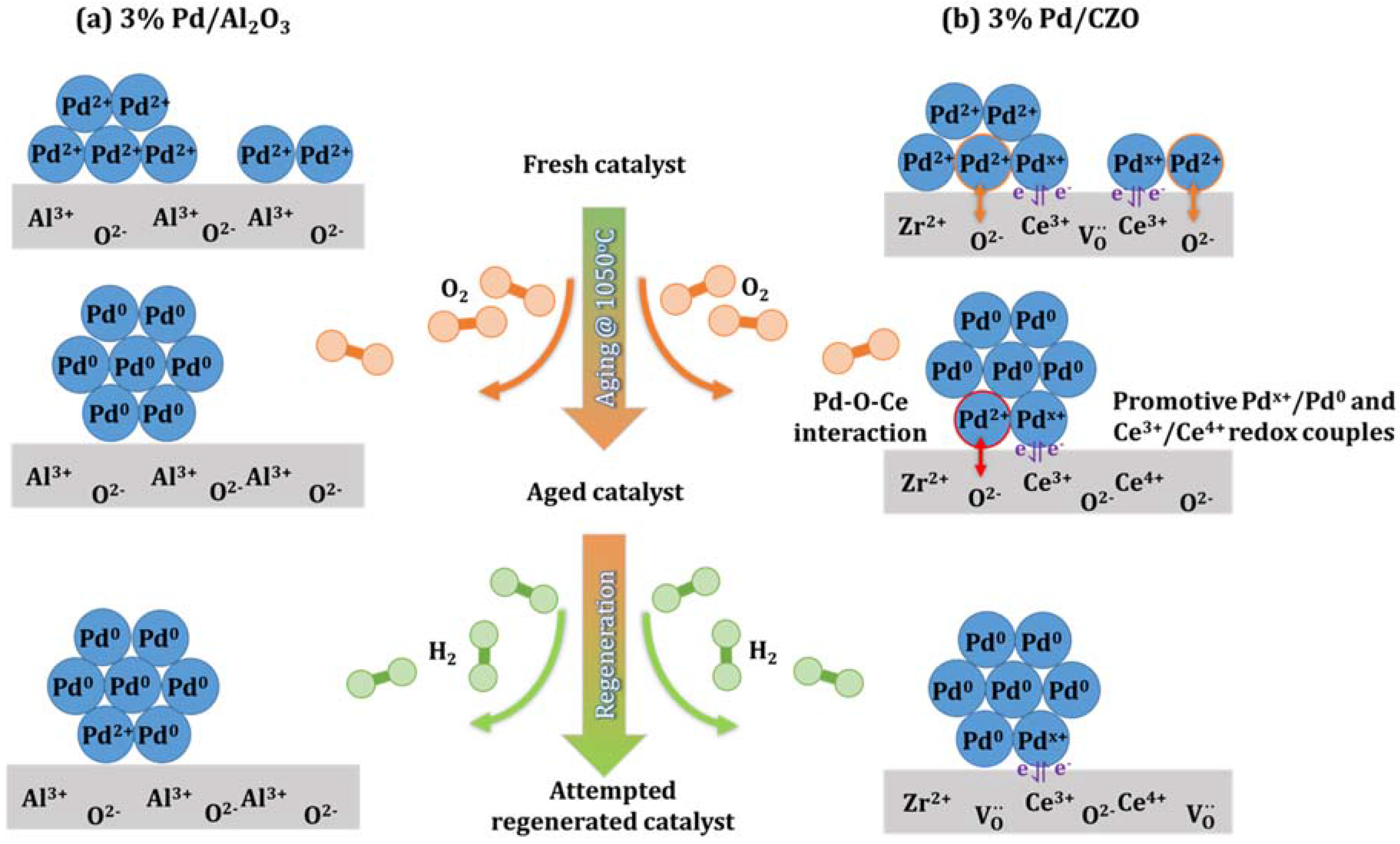
3. Experimental Section
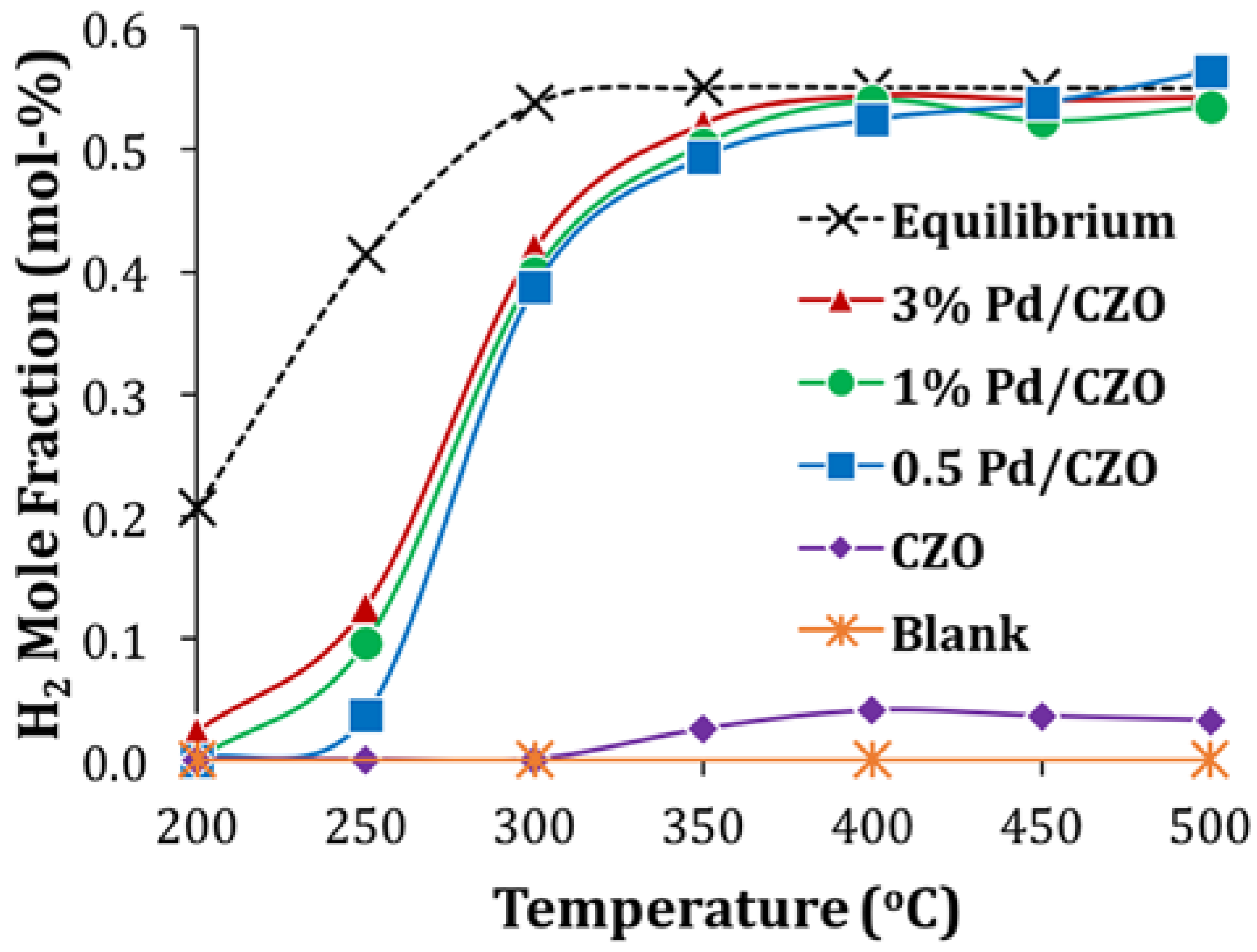
3.1. Catalyst Materials
3.2. Catalyst Activity Tests after Aging and Attempted Regeneration
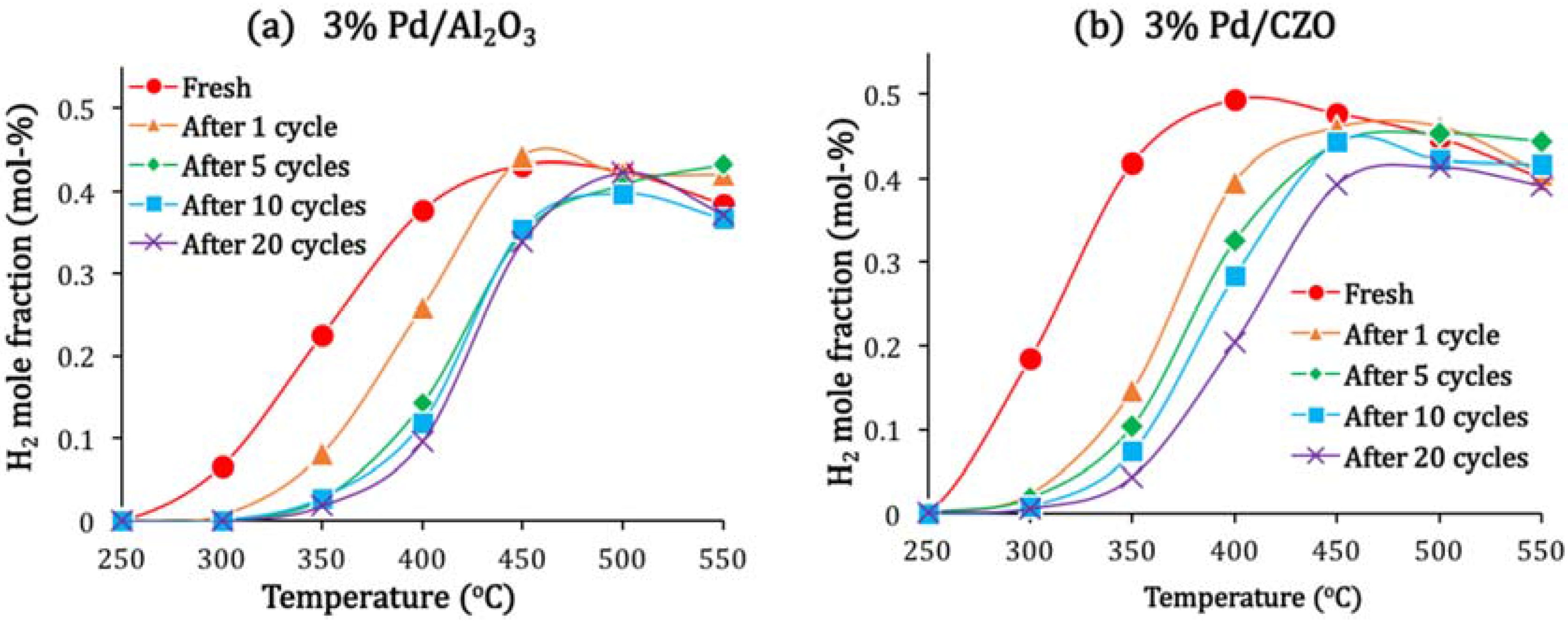
3.3. Catalyst Stability during Aging-Attempted Regeneration Cycle Tests
3.4. Catalyst Characterization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Attempted in situ regeneration, through H2 generation via catalytic steam reforming (SR), although effective for Rh catalysts, could not reverse the deactivation of Pd/Al2O3 due to the severe metal sintering, but allowed a slight recovery of catalyst activity for Pd/CZO. For the latter catalyst, the enhanced redox between Pdx+/Pd0 and Ce3+/Ce4+ couples were likely promoting the catalytic SR regeneration.
- (2)
- Severe aging conditions also led to support sintering and some metal-support interactions for Pd–O–Ce. The metal support interaction had little effect on performance.
- (3)
- Metal re-dispersion by PdO reformation when cooled in air did not significantly occur due to the high degree of Pd sintering that occurred at 1050 °C.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, H.; Lu, J.; Stair, P.C.; Elam, J.W. Alumina over-coating on Pd nanoparticle catalysts by Atomic Layer Deposition: Enhanced stability and reactivity. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Arias, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Hungría, A.B.; Anderson, J.A.; Conesa, J.C.; Soria, J. Influence of thermal sintering on the activity for CO–O2 and CO–O2–NO stoichiometric reactions over Pd/(Ce,Zr)Ox/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2002, 38, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Arias, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Hungría, A.B.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Duncan, K.; Smith, R.; Anderson, J.A.; Conesa, J.C.; Soria, J. Effect of thermal sintering on light-off performance of Pd/(Ce,Zr)Ox/Al2O3 three-way Catalysts: Model gas and engine tests. J. Catal. 2001, 204, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.S.; Slavinskaya, E.M.; Gulyaev, R.V.; Zaikovskii, V.I.; Stonkus, O.A.; Danilova, I.G.; Plyasova, L.M.; Polukhina, I.A.; Boronin, A.I. Metal-support interactions in Pt/Al2O3 and Pd/Al2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 97, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Garcia-Vargas, J.M.; Liotta, L.F.; Pantaleo, G.; Ousmane, M.; Retailleau, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic oxidation of propene over Pd catalysts supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn). Catalysts 2015, 5, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. Influence of transition metals (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni) on the methane combustion over Pd/Ce-Zr/Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5820–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiban, L.; Sorbier, L.; Pichon, C.; Pham-Huu, C.; Drillon, M.; Ersen, O. 3D-TEM investigation of the nanostructure of a σ-Al2O3 catalyst support decorated with Pd nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narui, K.; Yata, H.; Furuta, K.; Nishida, A.; Kohtoku, Y.; Matsuzaki, T. Effects of addition of Pt to PdO/Al2O3 catalyst on catalytic activity for methane combustion and TEM observations of supported particles. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 179, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, M.; Vedrine, J. (Eds.) Characterization of Solid Materials and Heterogeneous Catalysts: From Structure to Surface Reactivity; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Chapter 16; p. 664.
- Hansen, T.W.; Delariva, A.T.; Challa, S.R.; Datye, A.K. Sintering of catalytic nanoparticles: Particle migration or Ostwald Ripening. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Seo, C.Y.; Schwank, J.W.; McCabe, R.W. Aging, re-dispersion, and catalytic oxidation characteristics of model Pd/Al2O3 automotive three-way catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 163, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrauto, R.J.; Hobson, M.C.; Kennelly, T.; Waterman, E.M. Catalytic chemistry of supported palladium for combustion of methane. Appl. Catal. A 1992, 81, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datye, A.K.; Bravo, J.; Nelson, T.R.; Atanasova, P.; Lyubovsky, M.; Pfefferle, L. Catalyst microstructure and methane oxidation reactivity during the Pd↔PdO transformation on alumina supports. Appl. Catal. A 2000, 198, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrauto, R.J.; Lampert, J.K.; Hobson, M.C.; Waterman, E.M. Thermal decomposition and reformation of PdO catalysis: Support effects. Appl. Catal. B 1995, 6, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.C.; Pan, X.Q.; Graham, G.W.; McCabe, R.W.; Schwank, J. Microstructure of Pd/ceria-zirconia catalyst after high-temperature aging. Catal. Lett. 1998, 53, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Kennelly, T.; Farrauto, R.J. Praseodymium-palladium pinary oxide, catalyst compositions containing the same, and methods of use. U.S. Patent WO1992018243 A1, 12 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, R.M.; Farrauto, R.J.; Gulati, S. Catalytic Air Pollution Control: Commercial Technology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 103–176. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Weng, D. The thermal stability and catalytic performance of Ce–Zr promoted Rh-Pd/γ-Al2O3 automotive catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 221, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, M. Performance of dynamic oxygen storage capacity, water-gas shift and steam reforming reactions over Pd-only three-way catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 158, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Wen, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Pd-supported interaction-defined selective redox activities in Pd–Ce0.7Zr0.3O2–Al2O3 model three-wat catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12778–12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinokuma, S.; Fujiii, H.; Okamoto, M.; Ikeue, K.; Machida, M. Metallic Pd nanoparticles formed by Pd–O–Ce interaction: A reason for sintering-induced activation for CO oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6183–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, R.D.; Fornasiero, P.; Kašpar, J.; Rumori, P.; Gubitosa, G.; Graziani, M. Pd/Ce0.6Zr0.4O2/Al2O3 as advanced materials for three-way catlysts-Part 1. Catalyst characterisation, thermal stability and catalytic activity in the reduction of NO by CO. Appl. Catal. B 2000, 24, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, P.; Patil, K.C.; Jayaram, V.; Subbanna, G.N.; Hegde, M.S. Ionic dispersion of Pt and Pd on CeO2 by combustion method: Effect of metal-ceria interaction on catalytic activities for NO reduction and CO and hydrocarbon oxidation. J. Catal. 2000, 196, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauster, S.J. Strong Metal-support interactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 1987, 20, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; de Jonghe, L.C. Sintering of nanophase γ-Al2O3 powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Hu, J.; Lukaski, A.; Kim, D.H.; Szanyi, J.; Peden, C.H.F. Role of pentacoordinated Al3+ ions in the high temperature phase transformation of γ-Al2O3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 9486–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenevey, K.; Valdivieso, F.; Soustelle, M.; Pijolat, M. Thermal stability of Pd or Pt loaded Ce0.68Zr0.32O2 and Ce0.50Zr0.50O2 catalyst materials under oxidizing conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2001, 29, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, D.; Han, X.; Bao, X.; Frandsen, W.; Wang, D.; Su, D. Hydrothermal synthesis of microscale boehmite and gamma nanoleaves alumina. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valecillos, J.; Rodríguez, D.; Méndez, J.; Solano, R.; González, C.; Acosta, T.; Sánchez, J.; Arteaga, G. Propane dehydrogenation over alumina-supported palladium and palladium-tin catalysts. CIENCIA 2006, 14, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhou, R.J. Influence of thermal treatment on catalytic performance of Pd/(Ce,Zr)Ox–Al2O3 three-way catalysts. Alloys Compd. 2010, 494, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieske, H.; Völter, J. Pd redispersion by spreading of PdO in O2 treated Pd/Al2O3. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 1841–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, A.M.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Moro, C.C.; Tonetto, G.M.; Damiani, D.E. NO decomposition on PdMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A 2003, 201, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Chen, J.J.; Yeh, C.T. Temperature-Programmed Reduction and Temperature-Resolved Sorption Studies of Strong Metal-Support Interaction in supported palladium catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 96, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Meng, M.; Xian, H.; Tu, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, T. The nanomorphology-controlled palladium-support interaction and the catalytic performance of Pd/CeO2 catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2009, 133, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matam, S.K.; Otal, E.H.; Aguirre, M.H.; Winkler, A.; Ulrich, A.; Rentsch, D.; Weidenkaff, A.; Ferri, D. Thermal and chemical aging of model three-way catalyst Pd/Al2O3 and its impact on the conversion of CNG vehicle exhaust. Catal. Today 2012, 184, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, H.-W.; Graham, G.W.; Chun, W.; McCabe, R.W.; Cuif, J.-P.; Deutsch, S.E.; Touret, O. Characterization of model automotive exhuast catalysts: Pd on ceria and ceria-zirconia supports. Catal. Today 1999, 50, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Juez, A.; Martí-Arias, A.; Fernández-García, M. Metal-promoter interface in Pd/(Ce,Zr)Ox/Al2O3 catalyst: Effect of thermal aging. J. Catal. 2004, 221, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, R.A.; Christou, S.Y.; Efstathiou, A.M.; Anderson, J.A. Influence of oxychlorination treatments on the tedox and oxygen storage and release properties of thermally aged Pd–Rh/CexZr1−xO2/Al2O3 model three-way catalysts. App. Catal. B 2005, 60, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binet, C.; Jadi, A.; Lavalley, J. Metal-Support Interaction in Pd/CeO2 catalysts: Fourier-transform Infrared Studies of the effects of the reduction temeperature and metal loading: Part 1—Catalysts prepared by the Microemulsion Technique. J. Chem. Soc. 1992, 88, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.C.; Ausen, S.A. Interaction of cerium oxide with noble metals. J. Catal. 1979, 58, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quero, S.; Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Keane, M.A. Effect of Metal Dispersion on the Liquid-Phase Hydrodechlorination of 2,4-Dichlorophenol over Pd/Al2O3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6841–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.H.; Baird, R.J.; Kunz, F.W.; Hoost, T.E. An XRD and TEM investigation of the structure of alumina-supported ceria-zirconia. J. Catal. 2007, 166, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguetto, B.A.; Damyanova, S.; Gouliev, G.; Marques, C.M.P.; Petrov, L.; Bueno, J.M.C. Surface behavior of alumina-supported Pt catalyst modified with cerium as revealed by X-ray Diffraction, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of CO Adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5349–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samain, L.; Jaworski, A.; Edén, M.; Ladd, D.M.; Seo, D.; Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Häussermann, U. Structural analysis of highly porous γAl2O3. J. Sold State Chem. 2014, 217, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Gao, C. A general strategy for the preparation of carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide decorated with PdO nanoparticle in water. Molecules 2010, 15, 4679–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Q.; Farrauto, R.; Deeba, M. Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1797-1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041797
Zheng Q, Farrauto R, Deeba M. Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration. Catalysts. 2015; 5(4):1797-1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Qinghe, Robert Farrauto, and Michel Deeba. 2015. "Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration" Catalysts 5, no. 4: 1797-1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041797
APA StyleZheng, Q., Farrauto, R., & Deeba, M. (2015). Part II: Oxidative Thermal Aging of Pd/Al2O3 and Pd/CexOy-ZrO2 in Automotive Three Way Catalysts: The Effects of Fuel Shutoff and Attempted Fuel Rich Regeneration. Catalysts, 5(4), 1797-1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal5041797







