Abstract
Carbon xerogels were prepared by the polycondensation of resorcinol and formaldehyde using three different solution pH values and the gels were carbonized at three different temperatures. Results show that it is possible to tailor the pore texture of carbon xerogels by adjusting the pH of the initial solution and the carbonization temperature. Materials with different textural properties were obtained and used as catalysts for NO oxidation at room temperature. The NO conversions obtained with carbon xerogels were quite high, showing that carbon xerogels are efficient catalysts for NO oxidation. A maximum of 98% conversion for NO was obtained at initial concentration of NO of 1000 ppm and 10% of O2. The highest NO conversions were obtained with the samples presenting the highest surface areas. The temperature of reaction has a strong influence on NO oxidation: the conversion of NO decreases with the increase of reaction temperature.
1. Introduction
The emission of nitrogen oxides in fuel combustion from stationary sources—primarily from power stations, industrial heaters and cogeneration plants [1]—represents a major environmental problem. NOx is blamed for the formation of ozone in the troposphere [2], the production of acid rains and respiratory problems to mankind [3,4,5].
Combustion modification and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) methods are probably the most widely used techniques for the control of NOx emissions [1,6]. Increasingly stricter environmental regulations concerning the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) have forced the development of more efficient technologies to reduce the discharge of this pollutant by industrial facilities.
NO oxidation into NO2 attracts some interest because it can function in air at room temperature and the NO2 produced is captured by water as nitric acid. Activated carbons and activated carbon fibers have been recognized as effective catalysts for this reaction [7,8,9,10,11,12] as well as for SO2 oxidation and NO-NH3 reaction [13]. However, carbon materials in the form of monoliths or membranes are required for more advanced applications. This has led to a growing interest in polymer derived porous carbons, such as carbon xerogels [14].
Carbon xerogels possess excellent characteristics such as high surface area (400–1200 m2 g−1), high porosity, controllable pore size, high density (0.6–0.8 g cm−3), high conductivity and can be prepared in the desired form (monoliths, thin film or powder) [15,16,17].
The textural and structural properties of carbon xerogels can be controlled according to the synthesis and processing conditions (e.g., pH of preparation, drying conditions and carbonization temperature); thus, the main advantage of carbon xerogels is the possibility for tailoring their properties to fit specific applications [18,19,20,21,22,23]. For this reason, carbon xerogels are used in a wide range of applications, including catalysis [24,25], adsorption [26,27] and energy storage [28,29,30].
In the present work, carbon xerogels were synthesized by the conventional sol-gel approach using formaldehyde and resorcinol at three different pH values and were carbonized at three different temperatures, leading to carbon xerogels with different textural properties.
The carbon materials prepared were subjected to subsequent oxidation treatments (oxidation in gas phase with 5% of oxygen and oxidation in liquid phase with nitric acid) and a treatment with nitrogen precursor (urea). The influence of the textural and chemical properties of carbon xerogels on NO removal efficiency will be evaluated.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Carbon Xerogels
Carbon xerogels were prepared as follows: 40 mL of distilled water were added to 25 g of resorcinol under stirring. When the resorcinol was dissolved, a few drops of NaOH 2 M were added in order to bring the pH to 5.3, 6.0 and 6.9. Then, 34 mL of formaldehyde were added under stirring and the pH was adjusted to 5.3, 6.0 and 6.9 by adding a few drops of HCl 0.1 M. The gelation was accomplished in a water bath at 85 °C for three days. The gel was crushed and dried in an oven during 4 days (1st day at 60 °C, 2nd day at 80 °C, 3rd day at 100 °C and 4th day at 120 °C). The dried gel was carbonized under nitrogen flow (100 cm3 min−1) at 500 °C (700 °C and 900 °C) in a tubular furnace. The carbonization protocol comprised the following sequential steps, all at the same heating rate of 2 °C min−1: (1) up to 200 °C and hold for 2 h; (2) up to 300 °C and hold for 1 h; (3) up to 500 °C (700 °C and 900 °C) and hold for 2 h [21]. The materials prepared were designated as CX followed by the respective pH and carbonization temperature.
2.2. Chemical Modification of Carbon Xerogels
The treatments outlined below were carried out in order to obtain materials with different surface chemistries. All these treatments were performed on the carbon xerogels that presented the highest surface area in each range of pH.
2.2.1. Oxidation in Liquid Phase with HNO3 5 M
The oxidation with nitric acid was performed using a Soxhlet extraction apparatus. Thus, 200 cm3 of 5 M nitric acid solution was introduced into a 250 cm3 Pyrex round-bottom flask and heated to boiling temperature with a heating mantle. The Soxhlet (250 cm3) with 2 g of carbon xerogels was connected to boiling temperature flask and to the condenser. The reflux was stopped after 6 h. The sample was washed with distilled water to neutral pH and dried in an air convection oven at 110 °C for 24 h. These materials were designated as CX followed by the respective pH, carbonization temperature and HNO3.
2.2.2. Oxidation in Gas Phase with 5% O2
About 3 g of sample was placed in the oven and heated at 10 °C min−1 until 500 °C, passing only a N2 flow (75 cm3 min−1). When this temperature was reached, 25 cm3 min−1 of air was added. After 3 h the sample was cooled down in an inert atmosphere. These materials were designated as CX followed by the respective pH, carbonization temperature and O2.
2.2.3. Treatment with Urea
A 2 g of sample was impregnated with urea solution (1M) by stirring it for 24 h. Then it was heated in nitrogen flow by raising the temperature at 10 °C min−1 to 600 °C for 1 h. The samples obtained by this treatment were designated as CX followed by the respective pH, carbonization temperature and U.
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
2.3.1. Textural Characterization
The textural characterization of the samples was based on the nitrogen adsorption isotherms at −196 °C, which were determined using a Quantachorome Nova 4200e instrument. The specific volume of micropores (Vmicro) and the specific area of mesopores (Smeso) were calculated by the t-method, using the appropriate standard isotherm. The specific surface area of carbon xerogels was calculated by the BET method (SBET).
2.3.2. Chemical Characterization
Temperature programmed desorption (TPD) was performed in an AMI-200 Catalyst Characterization Instrument (Altamira Instruments), equipped with a quadrupole mass spectrometer (Dymaxion, Ametek). The catalyst sample was placed in a U-shaped quartz tube inside an electrical furnace and heated at 5 °C min−1 up to 1100 °C using a constant flow rate of helium (25 cm3 min−1). The masses monitored for all samples were: 2 (H2), 18 (H2O), 28 (CO) and 44 (CO2) [31].
To determine the point of zero charge of the samples (pHpzc), 20 cm3 of NaCl 0.01 M were placed in closed vessels and the pH was adjusted to values between 2 and 12, by adding 0.1 M solutions of NaOH or HCl. Then, 0.05 g of sample was added to each vessel. The suspensions were kept under stirring at room temperature for 48 h and then the final pH was recorded. The pHpzc of each sample was determined by the intersection of the curve pHfinalvs pHinitial with the line pHfinal = pHinitial. Blank experiments were carried out, and the pHinitial used in each case was that corresponding to the pHfinal of the blank test [32].
The chemical composition (C, H, N, S and O) of the carbon xerogels was analysed using an EA 1108 Elemental Analyser (Carlo Erba instruments).
Thermal analysis (TG) was performed on the xerogel samples in order to obtain information about the loss of water and carbonaceous residues involved in the carbonization step. Thermal analyses were done in a Netzsch STA 409 PC Luxx instrument.
2.4. Oxidation of NO
Reaction of NO with O2 on carbon xerogels was carried out in a fixed bed U-shaped flow type reactor. The sample weight, catalyst size, the flow rate, the O2 concentration, the NO concentration in He and the reaction temperature were 0.2 g, 0.2–0.3 mm, 100 cm3 min−1, 2–20%, 1000 ppm and 25–150 °C, respectively.
The concentrations of NO and NO2 at the outlet of the reactor were measured continuously by a NOx analyser (Model 42i-HL Thermo Scientific).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
3.1.1. Textural Characterization
Figure 1 shows the nitrogen adsorption isotherms of carbon xerogels. It is noticeable that the textural properties of carbon xerogels were affected by the synthesis pH and by the carbonization temperature.
The isotherms are typical of materials with micro and mesoporosity, except in the case of xerogels synthesized at pH = 6.9, which show very little or no microporosity. When the pH is high, polymerization is retarded and the formation of a cross-linked network is prevented [33,34], leading to a weak pore structure that cannot withstand carbonization at the higher temperatures (700 and 900 °C), resulting in the collapse of the nanostructure.
The isotherms of the materials prepared at pH = 5.3, independently of the carbonization temperature, exhibit a large increase in the amount of nitrogen adsorbed at relative pressures above 0.9, indicating the presence of very large pores.
Table 1 collects the textural properties of the materials prepared.
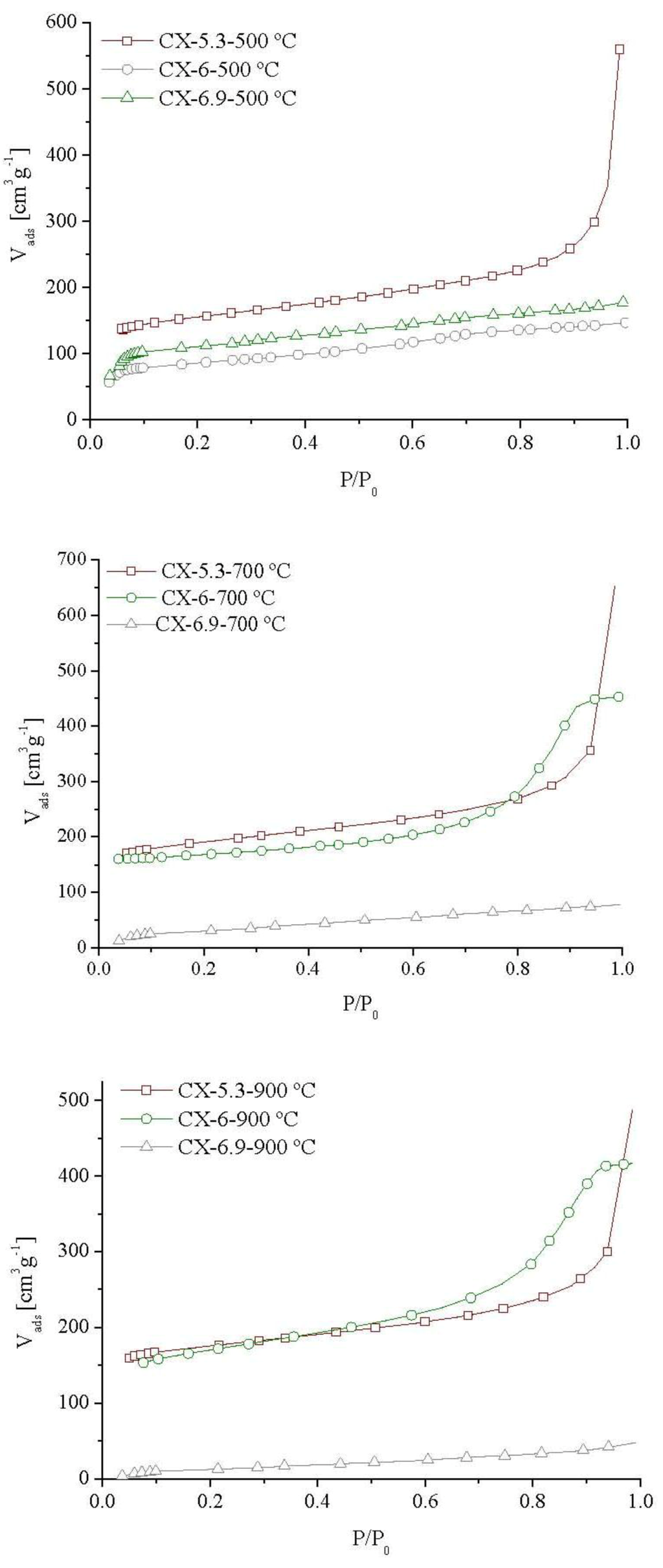
Figure 1.
Nitrogen adsorption isotherms at −196 °C of carbon xerogels prepared at different pHs (5.3, 6.0 and 6.9) and carbonized at different temperatures (500 °C, 700 °C and 900 °C).

Table 1.
Textural properties of carbon xerogels.
| Sample | SBET [m2 g-1] | Vmicro [cm3 g-1] | Smeso [m2 g-1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CX-5.3-500 °C | 583 | 0.14 | 230 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C | 707 | 0.20 | 226 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-HNO3 | 634 | 0.18 | 184 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-O2 | 628 | 0.23 | 136 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-U | 714 | 0.19 | 266 |
| CX-5.3-900 °C | 661 | 0.19 | 189 |
| CX-6-500 °C | 367 | 0.07 | 156 |
| CX-6-700 °C | 625 | 0.19 | 167 |
| CX-6-700 °C-HNO3 | 677 | 0.17 | 277 |
| CX-6-700 °C-O2 | 1049 | 0.29 | 342 |
| CX-6-700 °C-U | 708 | 0.19 | 246 |
| CX-6-900 °C | 567 | 0.07 | 380 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C | 486 | 0.10 | 174 |
| CX-6.9-500°C-HNO3 | 641 | 0.05 | 514 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-O2 | 618 | 0.08 | 236 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-U | 526 | 0.10 | 200 |
| CX-6.9-700 °C | 149 | 0.01 | 110 |
| CX-6.9-900 °C | 87 | 0 | 87 |
In the case of carbon xerogels prepared at pH = 5.3 and pH = 6.0, the maximum BET surface area and micropore volume correspond to the materials carbonized at 700 °C. The largest mesopore surface area corresponds to sample CX-6-900 °C.
These results confirm that it is possible to control the texture of the carbon xerogels by adjusting the pH of the initial solution and the carbonization temperature.
The effect of pH on the surface area and micropore volume of carbon xerogels carbonized at 700 °C is shown in Figure 2.
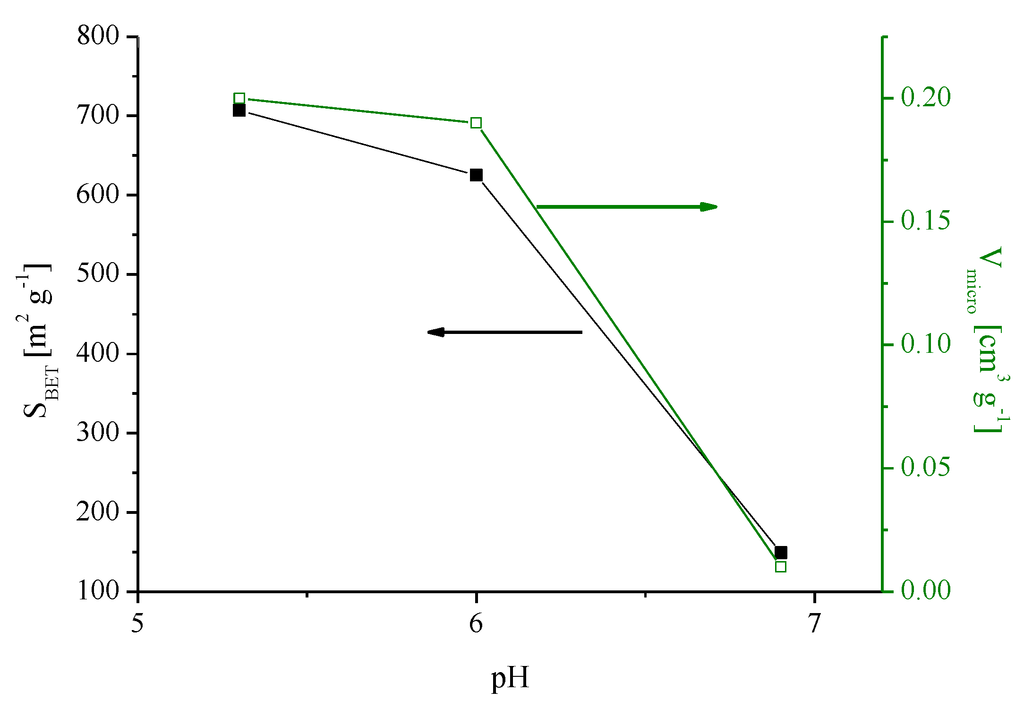
Figure 2.
Effect of the initial pH of the solution of resorcinol and formaldehyde on the surface area and micropore volume of the xerogels carbonized at 700 °C.
It is clear that the micropore volume and the surface area of carbon xerogels are very low at high pH. When the pH decreases from 6.9 to 6.0, there is a large increase of micropore volume and surface area. With further decrease to pH = 5.3, there is not much change in the textural properties.
The effect of pH on the porosity of carbon xerogels can be explained by the polymerization mechanism between resorcinol and formaldehyde, as described in the literature [34].
The subsequent treatments performed on the carbon xerogels were intended to modify their surface chemical properties, but additional changes in the textural properties also occur [31]. In general, the BET surface area increases upon treatment with nitric acid and with oxygen in the gas phase. The development of the porosity of the materials probably occurs by the widening of existing pores and/or creation of new pores by selective gasification of structural components, or by the opening of some of the previously inaccessible pores.
3.1.2. Thermal Analysis (TG)
Figure 3 shows the TG curves for the organic xerogels (RF) synthesized at different pHs. All the TG curves have a common behavior; the different initial pH values do not lead to any major difference.
Two peaks of mass loss were detected during the carbonization process: one at 200 °C and another at 300 °C. The first peak probably corresponds to the extraction of the remaining solvent and/or the elimination of H2O formed by the condensation of –OH groups [34]. The second peak is observed when the remaining hydrogen and oxygen atoms included in the polymer network are eliminated as CO2, CH4 or other organic molecules [34].
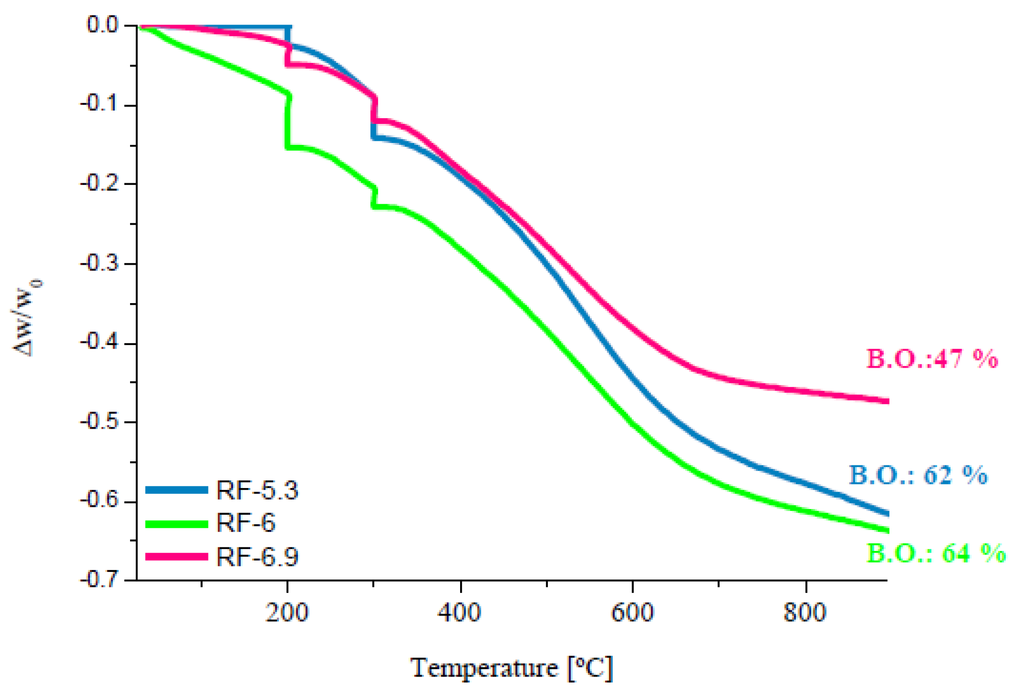
Figure 3.
Thermal Analysis (TG) curves of organic xerogels.
3.1.3. Elemental Analysis
The results of elemental analysis of the original and modified carbon xerogels are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Elemental analysis of the original and modified carbon xerogels.
| Sample | N [wt.%] | C [wt.%] | H [wt.%] | O [wt.%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX-5.3-500 °C | - | 79.9 | 2.5 | 17.6 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C | - | 92.4 | 1.1 | 6.5 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-HNO3 | 0.3 | 89.5 | 1.2 | 9.0 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-O2 | - | 90.8 | 1.3 | 7.9 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-U | 0.4 | 94.5 | 1.6 | 3.5 |
| CX-5.3-900 °C | - | 95.0 | 0.4 | 4.6 |
| CX-6-500 °C | - | 83.9 | 3.1 | 13.0 |
| CX-6-700 °C | - | 90.2 | 2.8 | 7.0 |
| CX-6-700 °C-HNO3 | 0.4 | 87.2 | 0.4 | 12.0 |
| CX-6-700 °C-O2 | - | 82.7 | 1.3 | 16.0 |
| CX-6-700 °C-U | 0.7 | 91.2 | 0.3 | 7.8 |
| CX-6-900 °C | - | 94.9 | 0.5 | 4.6 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C | - | 82.6 | 2.4 | 15.0 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-HNO3 | 0.2 | 80.9 | 0.9 | 18.0 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-O2 | - | 77.7 | 3.3 | 19.0 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-U | 0.3 | 89.6 | 1.5 | 8.6 |
| CX-6.9-700 °C | - | 98.5 | 1.4 | 0.10 |
| CX-6.9-900 °C | - | 98.9 | 1.0 | 0.10 |
The process of pyrolysis, development of the surface area and generation of new pores, leads to an increase in the content of carbon, and a significant decrease in the content of hydrogen and oxygen.
The oxidative treatments with nitric acid in liquid phase and with 5% of oxygen in gas phase introduce a large amount of oxygen groups on the surface of carbon xerogels. For example, sample CX-6-700°C has 7% of oxygen and after the treatment in the gas phase presents 16% of oxygen.
The treatment with nitric acid, in addition to introducing large amounts of oxygen groups in the carbon xerogels, also introduces some nitrogen groups. Larger amounts of nitrogen groups are introduced by the treatment with urea. The incorporation of nitrogen from urea occurs by derivatization, predominantly of the carboxylic oxygen species, and in general leads to a decrease of the oxygen content.
3.1.4. TPD and pHpzc
The total amount of the various oxygen surface groups present on the carbon xerogels (carboxylic acids, carboxylic anhydrides, lactones, phenols and carbonyls or quinones) can be determined by the TPD spectra, since these groups are decomposed into CO and/or CO2 upon heating.
The total amounts of CO and CO2 released are presented in Table 3.
The ratio of CO/CO2 released, included in Table 3, can be regarded as a measure of the surface acidity and basicity. Low values of the ratio correspond to strong surface acidity while high values of this parameter correspond to strong surface basicity [31]. The samples treated with HNO3 show the lowest CO/CO2 ratio, indicating that the surface chemistry of these samples is acidic in character, since this treatment introduces large amounts of acid groups (carboxylic acids) onto the surface of carbon materials. This result is consistent with the lowest values of pHpzc exhibited by these samples.
All the other materials showed neutral or basic properties (pHpzc ~ 6.9–8.1) independently of the pH used in their preparation.
The carbon xerogels carbonized at 500 °C present large amounts of surface oxygenated groups, which are partially explained by the relatively low temperature used during their preparation. Most of the CO and CO2 released above 500 °C is still the result of the xerogel matrix carbonization. The amount of oxygen-containing surface groups decreases as the carbonization temperature increases.

Table 3.
Amounts of CO and CO2 obtained from the TPD spectra and pHpzc values of carbon xerogels.
| Sample | pHpzc | CO [μmol g-1] | CO2 [μmol g-1] | CO/CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CX-5.3-500 °C | 7.0 | 2989.2 | 548.4 | 5.5 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C | 7.6 | 865.3 | 550.8 | 1.6 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-HNO3 | 6.2 | 907.6 | 1714.4 | 0.5 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-O2 | 7.1 | 3178.7 | 317.5 | 10.0 |
| CX-5.3-700 °C-U | 7.6 | 1003.6 | 122.6 | 8.2 |
| CX-5.3-900°C | 8.1 | 231.6 | 464.4 | 0.5 |
| CX-6-500 °C | 6.9 | 1137.6 | 912.0 | 1.2 |
| CX-6-700 °C | 6.9 | 614.4 | 446.4 | 1.4 |
| CX-6-700 °C-HNO3 | 6.2 | 1640.4 | 3465.6 | 0.5 |
| CX-6-700 °C-O2 | 7.2 | 2944.6 | 805.0 | 3.7 |
| CX-6-700 °C-U | 7.5 | 1843.2 | 653.5 | 2.8 |
| CX-6-900 °C | 6.9 | 583.2 | 184.3 | 3.2 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C | 7.0 | 1226.0 | 444.0 | 2.8 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-HNO3 | 6.5 | 1353.6 | 5373.9 | 0.3 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-O2 | 7.5 | 1482.0 | 376.2 | 3.9 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C-U | 7.5 | 1791.3 | 482.3 | 3.7 |
| CX-6.9-700 °C | 7.3 | 855.8 | 421.3 | 2.0 |
| CX-6.9-900 °C | 7.3 | 720.6 | 311.5 | 2.3 |
In general, the samples treated with urea have higher values of pHpzc than the samples treated with oxygen. This is due to the introduction of nitrogen groups, which increase the basicity of the carbon materials, namely pyridine and pyrrole groups which are Lewis bases.
3.2. Catalytic Tests
3.2.1. Influence of O2 Concentration on NO Oxidation
Figure 4 shows the influence of O2 concentration on NO conversion at 25 °C.
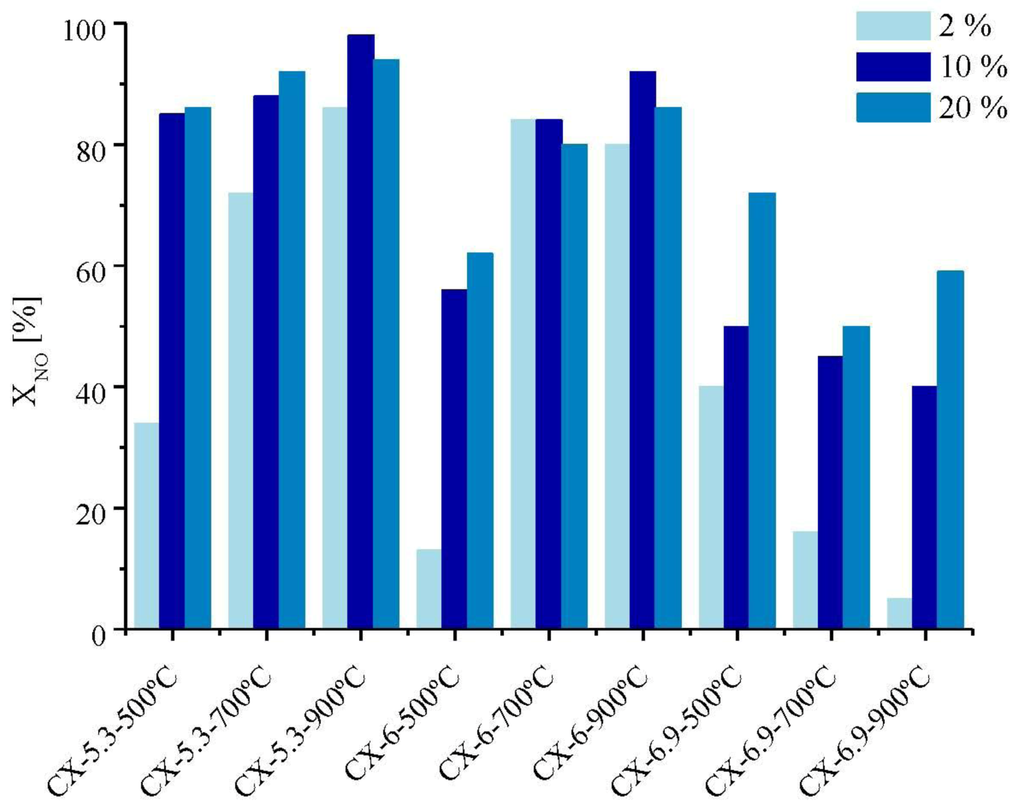
Figure 4.
Influence of O2 concentration on NO conversion at 25 °C.
In the presence of oxygen, the carbon materials catalytically oxidize NO with rates larger than those of the homogeneous oxidation (XNO: 36% for 20% O2).
The oxidation of NO to NO2 increases with the increase of O2 concentration from 2% to 10%. Further increase of oxygen concentration from 10% to 20% does not affect so much the conversion. Even in the presence of 2% oxygen, the NO conversion can reach 86% with sample CX-5.3-900 °C.
In some cases, the maximum NO conversion was obtained when 10% of oxygen was used. It seems that there is an optimum oxygen concentration above which the NO conversion levels off due to saturation of the adsorption sites with atomic oxygen. The highest NO conversion was obtained on sample CX-5.3-900 °C with 10% of O2 (XNO: 98%).
In the experiments with carbon xerogels that have micropores, it was observed that no NO2 is detected at the reactor outlet during the initial stages of the experiment. The NO2 produced during the first minutes of reaction is retained in the micropores of the carbon xerogel. Thereafter, the concentration of NO2 in the gas phase increases and reaches a plateau (steady state conversion). In the case of sample CX-6.9-900 °C, NO2 is detected from the beginning of the reaction, because this sample has no micropores.
At steady state, the micropores are occupied with NO2 adsorbed, so only the mesopore surface area is available for reaction. Smeso will thus subsequently normalize the rates.
The effect of oxygen in the removal of NO has been reported in many studies [7,8,9,10,12]. In the absence of oxygen, NO passes through the carbon xerogel bed unreacted.
There is virtually no NO adsorption when oxygen is absent, indicating that oxygen is needed for the process. These observations suggest that NO2, rather than NO, is the adsorbed molecule, possibly because of its higher polarity.
The strong dependence of NO conversion on the oxygen concentration leads to the conclusion that oxygen is first adsorbed on the surface of carbon xerogels, and then it reacts with NO to form adsorbed NO2. Then, NO2 can desorb to the gas phase. A simplified scheme of this process is represented in Figure 5.
The highest NO conversions were obtained with the samples which presented the highest surface areas (CX-5.3-500 °C, CX-5.3-700°C, CX-5.3-900 °C, CX-6-700 °C and CX-6-900 °C). In addition, the lowest NO conversions were obtained with the samples which presented the lowest surface areas (CX-6-500 °C, CX-6.9-500 °C, CX-6.9-700 °C and CX-6.9-900 °C).
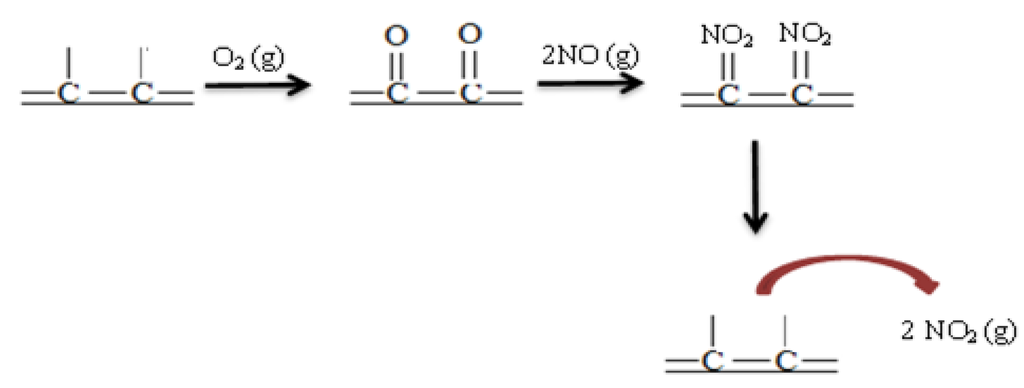
Figure 5.
Simplified scheme of NO oxidation on carbon xerogels.
Therefore, the surface area determines the number of sites available for NO oxidation, showing that the surface of carbon xerogels is fully accessible and has a uniform distribution of active sites.
There are many contradictions about the influence of the texture of the carbon materials on NO oxidation. Shimizu et al. [35], Illan-Gómez et al. [36] and Jan et al. [37] reported a correlation between the activity of carbon materials for NO reduction and their surface area. Mochida et al. [38] found no relationship between surface area of the carbon materials and the removal of NO; however, the carbon materials used in this case were treated with sulphuric acid, and it is difficult to separate the effect of surface area and the effect of oxygen groups in the catalytic activity of carbon materials. Using nitrogen-doped carbon materials, the present authors did not find any correlation between NO conversion and surface area [8,39]. The carbon materials used in these works contained large amounts of nitrogen groups, which are known to enhance the activity of carbon materials in oxidation reactions [40,41,42].
Thus, the catalytic activity of carbon materials is conditioned both by their textural and chemical properties. Chemical functionalities existing on the carbon surface, such as oxygen groups with an acid or basic character, and heteroatoms (mainly nitrogen functionalities) are responsible for the catalytic activity of the carbon materials. In this sense, the textural properties contribute to the catalytic activity only as long as the surface of carbon materials does not suffer any modification, and in this case the most important textural property is the surface area.
Therefore, the surface area of the carbon xerogels is a key factor in determining their activity for NO oxidation.
3.2.2. Influence of Surface Chemistry of the Carbon Xerogels on NO Oxidation
In each range of pH, the carbon xerogels that presented the highest surface area were subjected to three different treatments (oxidation with 5% of oxygen in gas phase, oxidation with nitric acid 5 M in liquid phase and treatment with a 1 M urea solution at room temperature).
In the previous section, it was noted that the increase of oxygen concentration in the gas phase increases NO conversion. The treatments with nitric acid in liquid phase and with oxygen in gas phase were intended to introduce oxygen groups on the surface of the carbon xerogels and to evaluate their effect on the catalytic activity for NO oxidation. The oxygen groups introduced by these treatments are different. The treatment with nitric acid introduces mainly carboxylic acid groups, while the treatment with oxygen in gas phase introduces mainly phenol and carbonyl/quinone surface groups.
The role of nitrogen in catalysis is usually linked to its basicity and ability to activate oxygen via formation of O2− superoxide, which has tremendous effects on oxidation reactions [40,41,42].
This section is also intended to evaluate the effect of nitrogen groups introduced by post-treatment and to compare with N-doped carbon xerogels (where nitrogen is incorporated during the synthesis) [39]. Treatment with a urea solution at room temperature was performed in order to introduce nitrogen groups on the surface of the carbon xerogels. According to the literature [42,43,44], such treatment should introduce amide groups on the surface. Upon heating to 600 °C, these are converted into more stable nitrogen groups, such as pyridine and pyrrole [45].
The NO conversions obtained with the original materials and with the materials chemically modified are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
NO conversion with the original and modified carbon xerogels. NO: 1000 ppm, O2: 20% and Temp: 25 °C.
| Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | -HNO3 | -U | -O2 | |
| Sample | XNO [%] | |||
| CX-5.3-700 °C | 92 | 85 | 92 | 86 |
| CX-6-700 °C | 80 | 88 | 93 | 87 |
| CX-6.9-500 °C | 72 | 72 | 66 | 64 |
Since these treatments also modified the textural properties of the carbon xerogels, Figure 6 shows the rate of NO converted per unit of (mesopore) surface area as a function of the amount of nitrogen, for the urea treated samples.
Although there are only three data points, there is a clear relationship between the rate of NO conversion and the amount of nitrogen. This is in agreement with our previous report [39], where the presence of nitrogen groups on carbon xerogels was shown to enhance the oxidation of NO to NO2.
To assess the influence of surface oxygen groups on NO oxidation, the rate of NO converted per unit surface area was plotted as a function of the oxygen content (Figure 7).
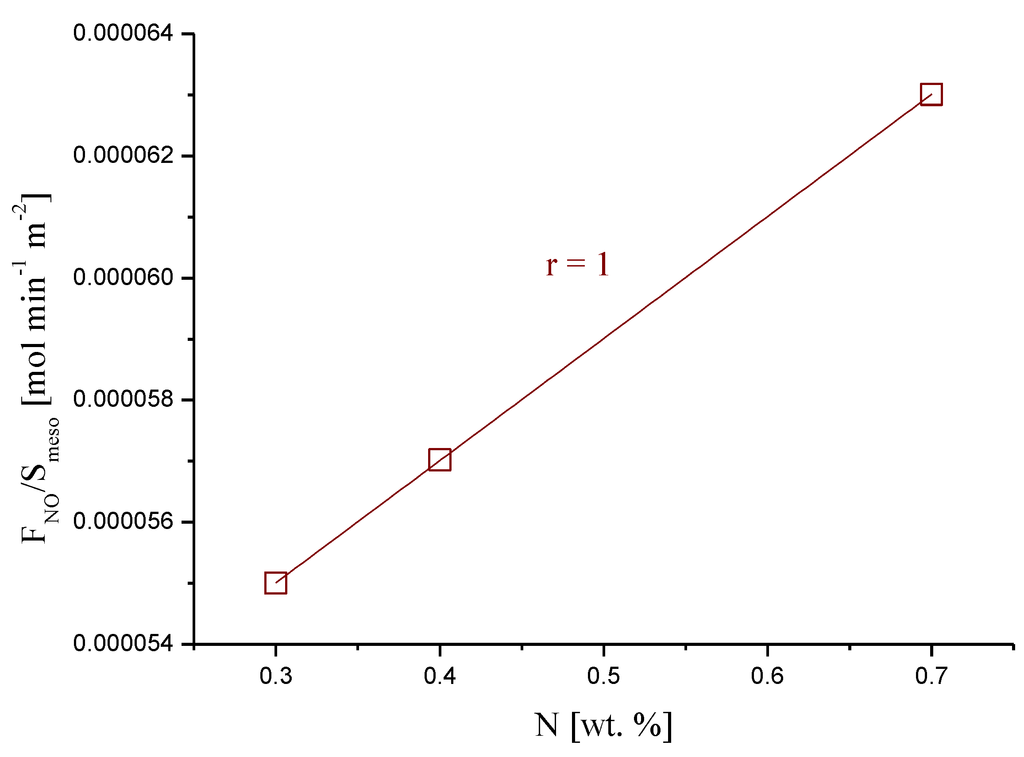
Figure 6.
Rate of NO converted vs. the amount of nitrogen present in the carbon xerogels treated with urea.
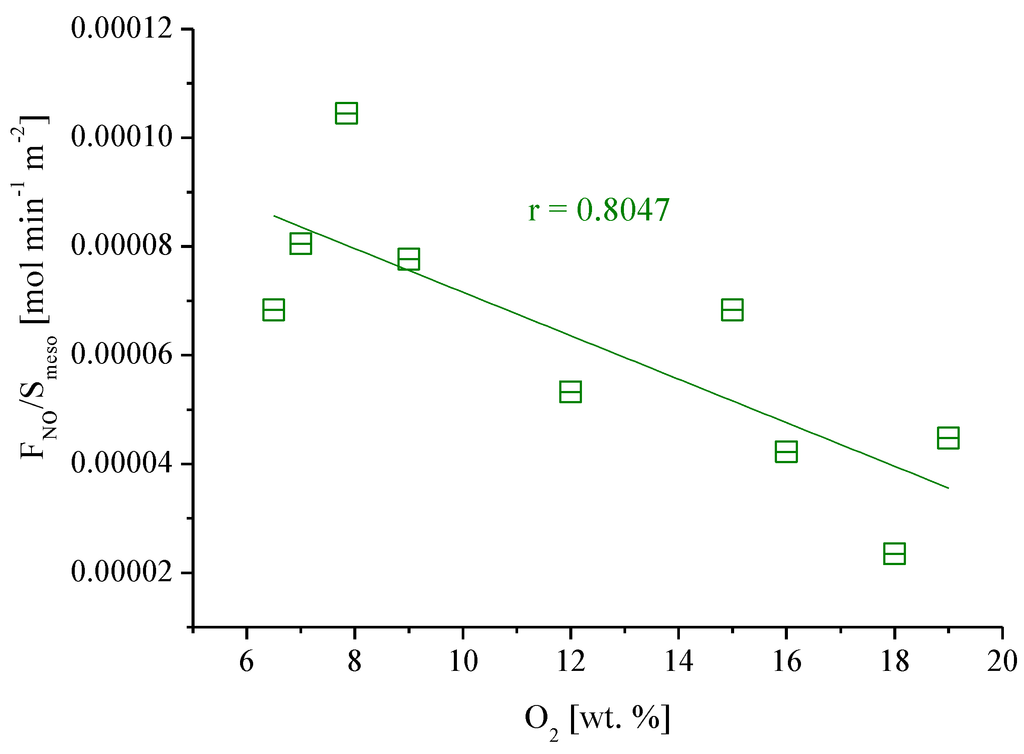
Figure 7.
Rate of NO converted vs. the amount of oxygen present in the original and modified carbon xerogels (CX-5.3-700 °C, CX-5.3-700 °C-O2, CX-5.3-700 °C-HNO3, CX-6-700 °C, CX-6-700 °C-O2, CX-6-700 °C-HNO3, CX-6.9-500 °C, CX-6.9-500 °C-O2, CX-6.9-500 °C-HNO3).
It appears that the oxidative treatment of carbon xerogels, which produced a carbon surface largely covered by oxygen groups (Table 3), inhibits the oxidation of NO at low temperatures. The oxygen complexes formed during the treatments with nitric acid and with oxygen in gas phase are not active sites for the NO oxidation. These oxygen groups are stable under the reaction conditions, and so they occupy active centers of the carbon xerogels, decreasing the activity for NO oxidation.
The treatment with nitric acid introduces small amounts of nitrogen, but not in the form of pyrrole or pyridine (as does the urea treatment). On the other hand, it introduces very large amounts of oxygen groups, especially carboxylic acids. Therefore, the inhibitive effect of the oxygen groups offsets any beneficial effect that might be due to the presence of nitrogen.
3.2.3. Influence of CO and CO2 on NO Oxidation
In the context of the practical application of this process for the abatement of NOx in flue gases of combustion systems, it is important to know the influence of other compounds such as CO and CO2. The experiments were conducted with 1000 ppm NO, 20% O2, 4% CO (CO2) and at room temperature over samples CX-5.3-900 °C and CX-6-900 °C.
The NO conversions obtained over these samples in the presence of CO or CO2 are equal to those obtained when the reaction was realized only with NO and O2, so it may be concluded that the presence of CO (or CO2) does not affect NO oxidation. It appears that CO and CO2 do not compete with oxygen for the catalyst active sites.
3.2.4. Stability of the Sample CX-5.3-900 °C for NO Oxidation
The stability of a catalyst is an important aspect in the global evaluation of its performance. So, an experiment was carried out during one week with the purpose of evaluating the stability of carbon xerogels as catalysts for NO oxidation. The reaction was carried out with 1000 ppm of NO and 10% of oxygen over the most efficient catalyst (CX-5.3-900 °C). The results are shown in Figure 8. The steady-state conversion is reached after 26 h of reaction (XNO: 98%), and does not change thereafter.
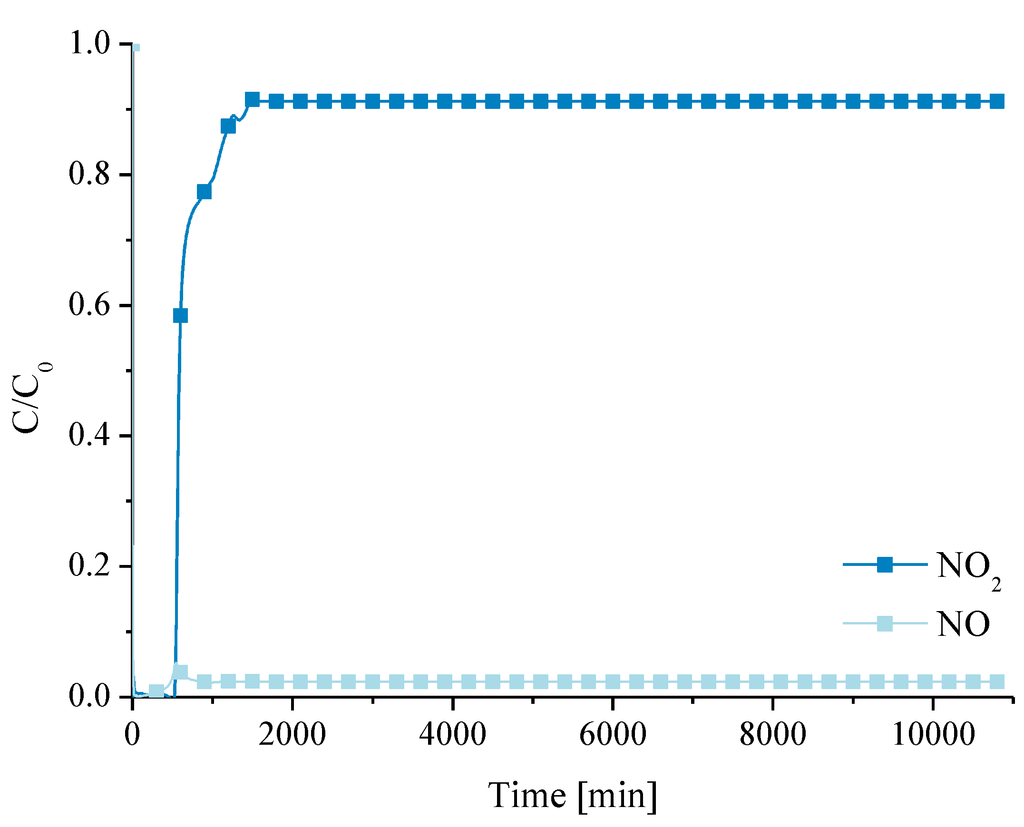
Figure 8.
Evolution of profiles of NO and NO2 during one week of reaction with sample CX-5.3-900 °C.
3.2.5. Influence of Reaction Temperature on NO Oxidation
The dependence of the NO conversion on the reaction temperature was studied with sample CX-5.3-900 °C. The experiments were carried out with 1000 ppm of NO, 10% of O2 and in the temperature range 25–150 °C. Figure 9 shows the profiles of NO oxidation at different reaction temperatures.
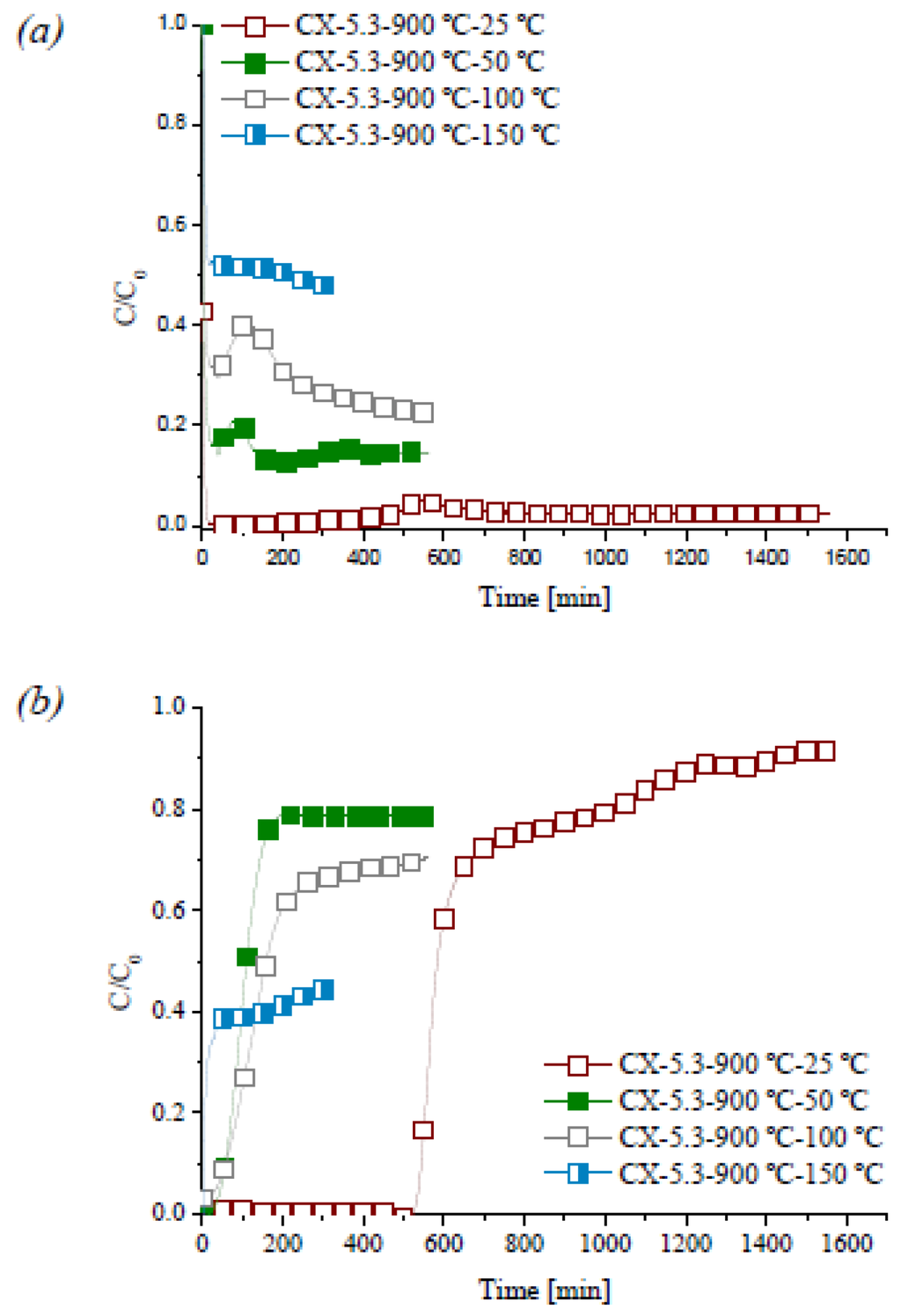
Figure 9.
Evolution of profiles of NO (a) and NO2 (b) at different reaction temperatures.
A conversion of 98% was obtained at 25 °C, but decreased to 86% at 50 °C, to 77% at 100 °C, and to 53% at 150 °C. Thus, reaction at room temperature was found to be favorable for the maximum oxidation of NO.
The carbon surface can act as a catalyst for oxidation of NO to NO2, which then may remain adsorbed. Inspection of Figure 9 shows that no NO2 is detected at the outlet during 523 min, at 25 °C. The NO2 produced is completely retained on the carbon xerogel in this period. By increasing the reaction temperature, the induction time of NO2 (time interval during which the NO2 produced is retained) is shortened, because the adsorption of NO2 decreases. So, at room temperature there are two phenomena, reaction and adsorption, but the latter becomes negligible at higher reaction temperatures.
4. Conclusions
A range of carbon xerogels with different textural properties was prepared. The textural properties of the carbon xerogels depend on the pH of preparation and carbonization temperature. The removal of NO by catalytic oxidation of NO to NO2 on carbon xerogels is feasible at low temperatures. NO conversion increases with the oxygen concentration in the gas phase. The highest NO conversions were obtained with the samples that presented the highest surface areas. In a steady state, the micropores are occupied with NO2 adsorbed, so only the mesopore surface area is available for reaction.
The oxidative treatments had a negative effect on the performance of the carbon xerogels in NO oxidation, while the treatment with urea enhanced the catalyst activity.
The temperature of reaction has a strong influence on NO oxidation: the conversion of NO decreases with the increase of reaction temperature.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) and FEDER through Program COMPETE (FCT Pest-C/EQB/LA0020/2011) and research fellowship SFRH/BD/45720 /2008 (JPSS).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Forzatti, P. Present status and perpectives in de-NOx SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 222, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pârvulescu, V.I.; Grange, P.; Delmon, B. Catalytic removal of NO. Catal. Today 1998, 46, 233–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-García, M.A.; Pitchon, V.; Kiennemann, A. Pollution by nitrogen oxides: an approach to NOx abatement by using sorbing catalytic materials. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska, K.; Miller, J.S.; Ledakowicz, S. Trends in NOx abatement: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3976–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Philip, L. Integrated System for the Treatment of Oxides of Nitrogen from Flue Gases. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2006, 40, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzki, J.; Wiśniewski, M. Adsorption and decomposition of NO on carbon and carbon-supported catalysts. Carbon 2002, 40, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Kisamori, S.; Hironaka, M.; Kawano, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Yoshikawa, M. Oxidation of NO into NO2 over Active Carbon Fibers. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.P.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Catalytic oxidation of NO to NO2 on N-doped activated carbons. Catal. Today 2011, 176, 383–387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Rabiei, S.; Bagreev, A.; Zhuang, M.S.; Rasouli, F. Study of NO adsorption on activated carbons. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 83, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-X.; Huang, Z.-H.; Shimohara, T.; Kang, F.; Liang, K. NO removal by electrospun porous carbon nanofibers at room temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanmore, B.R.; Tschamber, V.; Brilhac, J.F. Oxidation of carbon by NOx, with particular reference to NO2 and N2O. Fuel 2008, 87, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, W.; Rincón, S. Adsorption and reaction of NO on activated carbon in the presence of oxygen and water vapour. Fuel 2007, 86, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Hsu, Y.-F.; Tu, Y.-T. Reduction of NO with NH3 over carbon catalysts—the influence of carbon surface structures and the global kinetics. Appl. Catal. B 1999, 20, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, N.; Silva, A.R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freire, C.; Castro, B.; Figueiredo, J.L. Anchoring of a [Mn(salen)Cl] complex onto mesoporous carbon xerogels. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 311, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, P.V.; Gonçalves, F.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Surface activation of a polymer based carbon. Carbon 2004, 42, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Sabatier, F.; Pirard, J.-P.; Crine, M.; Léonard, A. Towards the production of carbon xerogel monoliths by optimizing convective drying conditions. Carbon 2006, 44, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Synthesis, pore texture and surface acid–base character of TiO2/carbon composite xerogels and aerogels and their carbonized derivatives. Appl. Catal. A 2000, 203, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhatat, A.M.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A. Advances in Tailoring Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Organic and Carbon Gels. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2887–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Preparation and Properties of Resorcinol–Formaldehyde Organic and Carbon Gels. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Théry, A.; René, P.; Marien, J.; Kocon, J.L.; Rouzaud, J.-N.; Béguin, F.; Pirard, J.-P. Carbon aerogels, cryogels and xerogels: Influence of the drying method on the textural properties of porous carbon materials. Carbon 2005, 43, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Pirard, R.; Marien, J.; Pirard, J.-P. Porous carbon xerogels with texture tailored by pH control during sol–gel process. Carbon 2004, 42, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, A.; Job, N.; Blacher, S.; Pirard, J.-P.; Crine, M.; Jomaa, W. Suitability of convective air drying for the production of porous resorcinol–formaldehyde and carbon xerogels. Carbon 2005, 43, 1808–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubizarreta, L.; Arenillas, A.; Pirard, J.-P.; Pis, J.J.; Job, N. Tailoring the textural properties of activated carbon xerogels by chemical activation with KOH. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 115, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Heinrichs, B.; Ferauche, F.; Noville, F.; Marien, J.; Pirard, J.-P. Hydrodechlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane on Pd–Ag catalysts supported on tailored texture carbon xerogels. Catal. Today 2005, 102–103, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Job, N.; Heinrichs, B.; Lambert, S.; Pirard, J.-P.; Colomer, J.-F.; Vertruyen, B.; Marien, J. Carbon xerogels as catalyst supports: Study of mass transfer. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.; Zhang, Y.; Haji, S.; Erkey, C. Dynamics of removal of organosulfur compounds from diesel by adsorption on carbon aerogels for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.Y.; Lee, B.I.; Lee, J.S. Hydrogen adsorption on nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels. Carbon 2009, 47, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frackowiak, E.; Béguin, F. Carbon materials for the electrochemical storage of energy in capacitors. Carbon 2001, 39, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Binder, L. A modified activated carbon aerogel for high-energy storage in electric double layer capacitors. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, N.; Marie, J.; Lambert, S.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Achard, P. Carbon xerogels as catalyst supports for PEM fuel cell cathode. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes on activated carbons with different surface chemistries. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, C.; Gálvez, M.E.; Sebastián, D.; Moliner, R.; Lázaro, M.J. Influence of Synthesis pH on Textural Properties of Carbon Xerogels as Supports for Pt/CXs Catalysts for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Int. J. Electrochem. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ritter, J.A. Effect of synthesis pH on the structure of carbon xerogels. Carbon 1997, 35, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Sazawa, Y.; Adschiri, T.; Furusawa, T. Conversion of char-bound nitrogen to nitric oxide during combustion. Fuel 1992, 71, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illan-Goméz, M.J.; Linares-Solano, A.; de Lecea, C.S.M.; Calo, J.M. Nitrogen oxide (NO) reduction by activated carbons. 1. The role of carbon porosity and surface area. Energy Fuels 1993, 7, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, E.J. Formation and reduction of nitrogen oxides in fluidized-bed combustion. Fuel 1994, 73, 1398–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, I.; Ogaki, M.; Fujitsu, H.; Komatsubara, Y.; Ida, S. Reduction of nitric oxide with activated PAN fibres. Fuel 1985, 64, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.P.S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. NO oxidation over nitrogen doped carbon xerogels. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H.P. Catalytic Properties of Nitrogen-Containing Carbons. In Carbon Materials for Catalysis; Serp, P., Figueiredo, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Chapter 7. [Google Scholar]
- Stöhr, B.; Boehm, H.P.; Schlögl, R. Enhancement of the catalytic activity of activated carbons in oxidation reactions by thermal treatment with ammonia or hydrogen cyanide and observation of a superoxide species as a possible intermediate. Carbon 1991, 29, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Hulicova-Jurcakova, D.; Lu, G.Q.; Bandosz, T.J. Surface functional groups of carbons and the effects of their chemical character, density and accessibility to ions on electrochemical performance. Carbon 2008, 46, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangun, C.L.; Benak, K.R.; Economy, J.; Foster, K.L. Surface chemistry, pore sizes and adsorption properties of activated carbon fibers and precursors treated with ammonia. Carbon 2001, 39, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pels, J.R.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A.; Zhu, Q.; Thomas, K.M. Evolution of nitrogen functionalities in carbonaceous materials during pyrolysis. Carbon 1995, 33, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, R.; Hävecker, M.; Wrabetz, S.; Blume, R.; Lerch, M.; McGregor, J.; Parrot, E.P.J.; Zeitler, J.A.; Gladden, L.F.; Knop-Gericke, A.; et al. Tuning the Acid/Base Properties of Nanocarbons by Functionalization via Amination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 33, 9616–9630. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).