Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using Polycrystalline Phosphorus-Doped Diamond Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
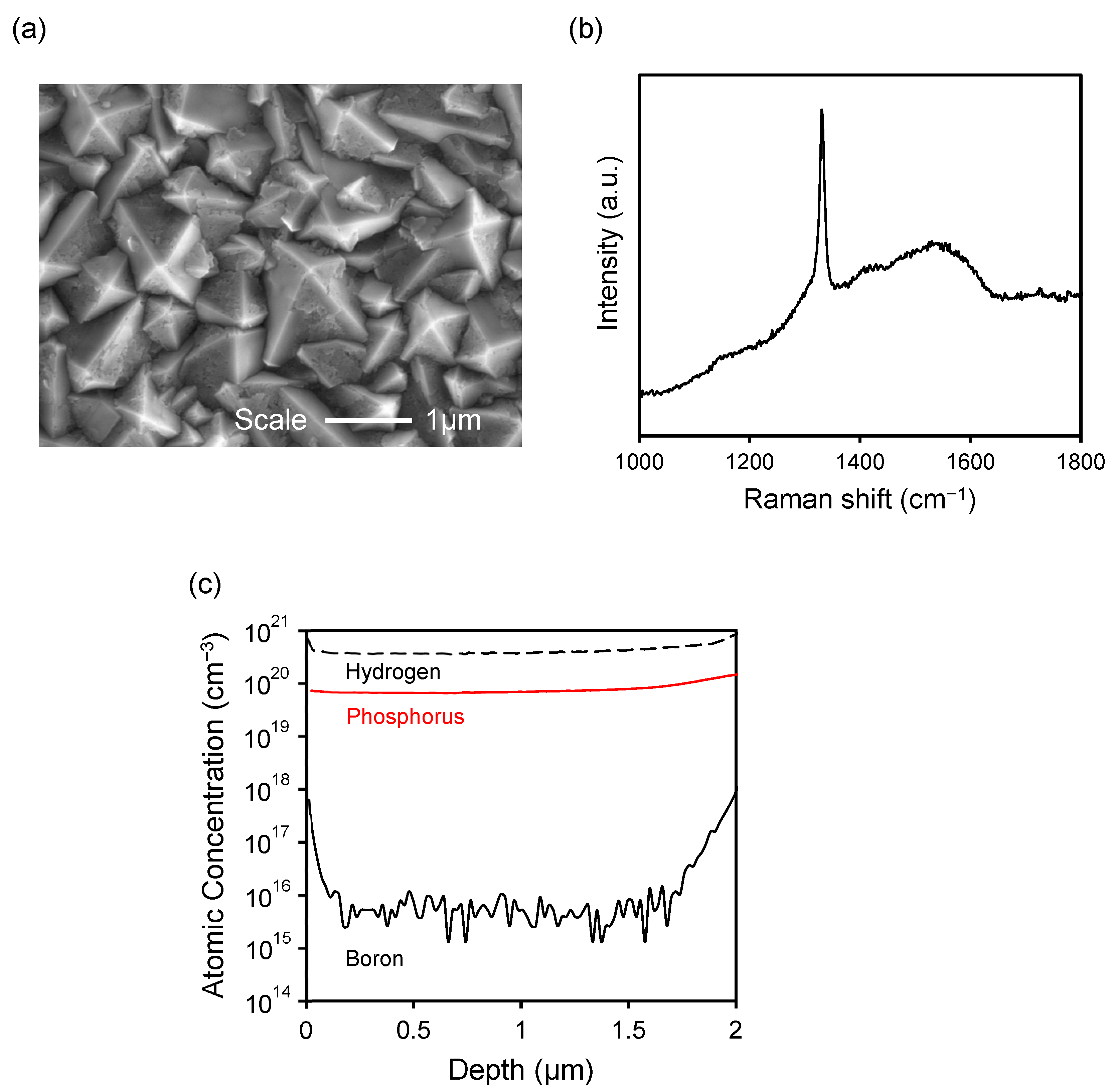
2.1. Characterization of the PDD Electrode
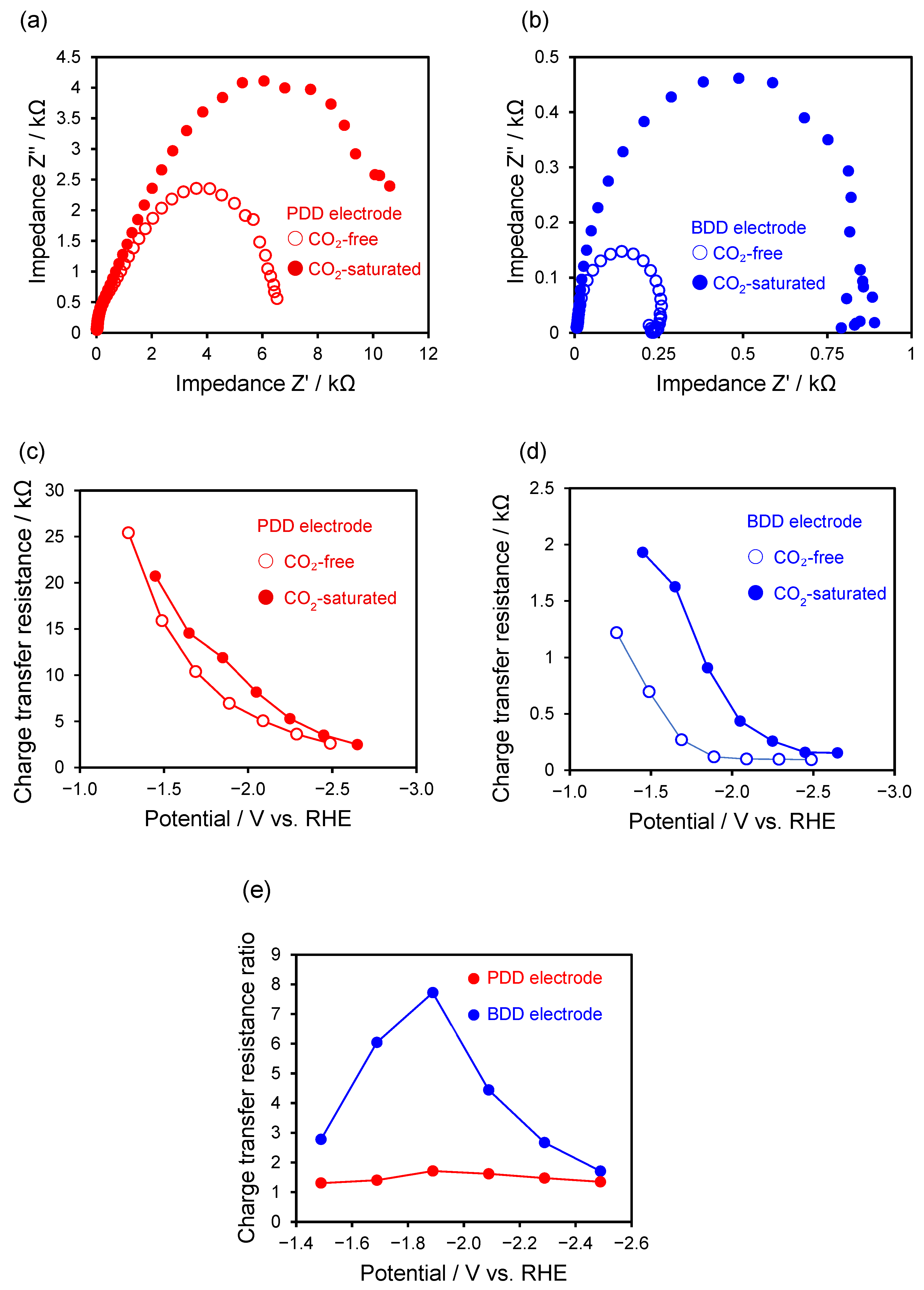
2.2. Electrochemical Properties
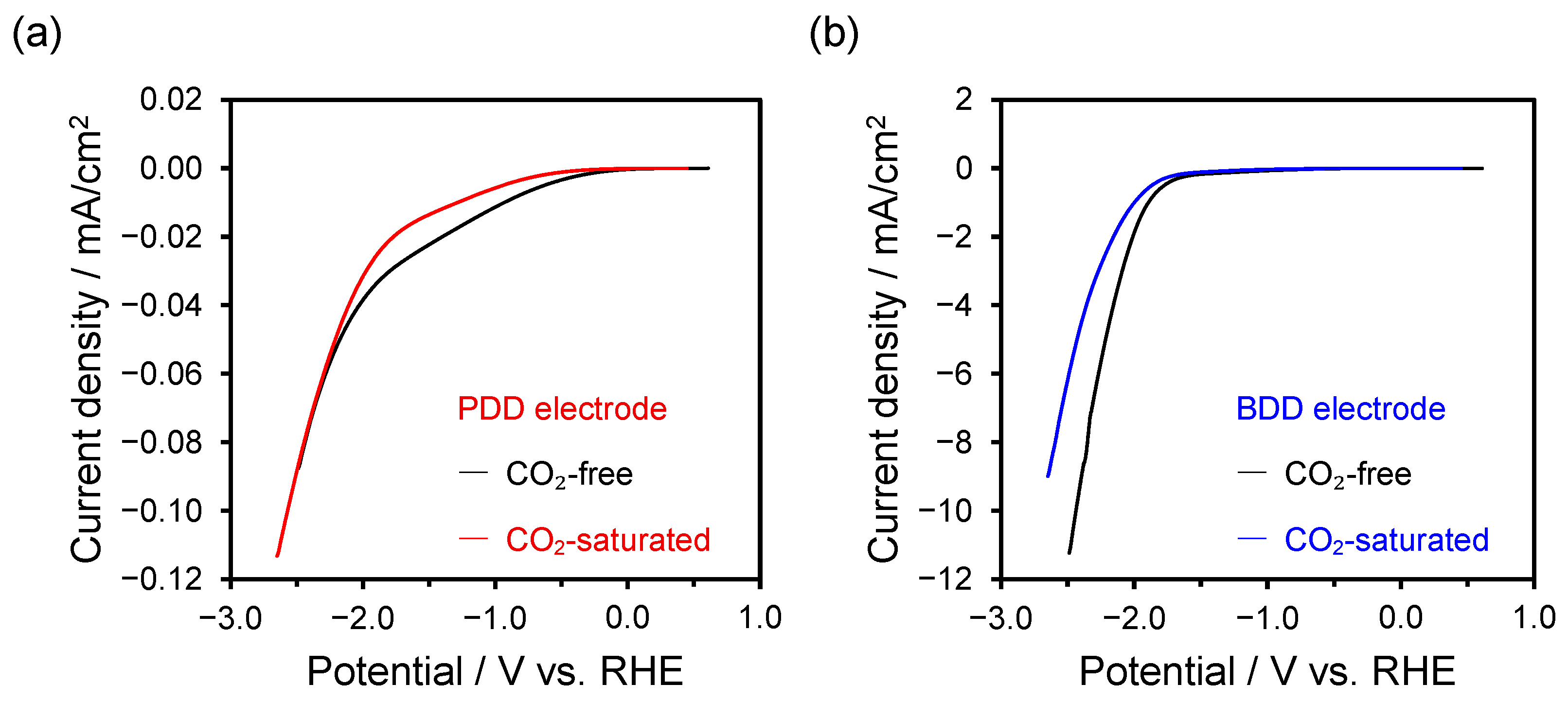
2.3. LSV Measurements Before and After CO2 Bubbling
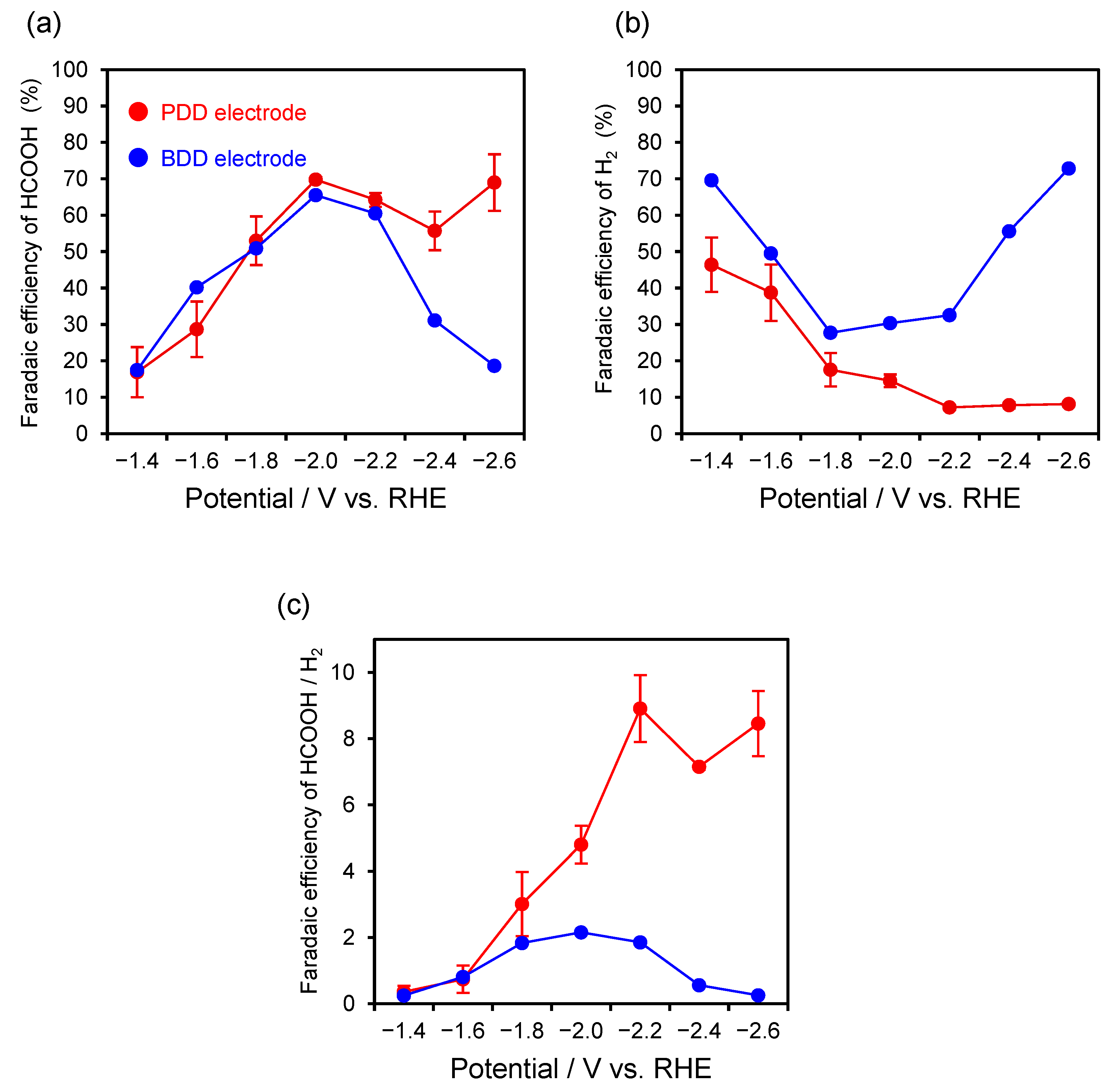
2.4. Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using PDD Electrode
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of PDD Electrode
- (1)
- Plasma stabilization and nucleationCH4:H2 = 0.5:200 sccm; gas pressure: 50 torr; microwave power: 0.6 kW; substrate temperature: 700 °C; synthesis time: 30 min
- (2)
- Deposition of PDDCH4:H2 = 0.5:500 sccm; gas pressure: 75 torr; microwave power: 1.0 kW; substrate temperature: 930 °C; synthesis time: 8 h; heating temperature of red phosphorus: 390 °C
3.2. Electrochemical Properties of PDD Electrode
3.3. Materials and Reagents
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDD | boron-doped diamond |
| PDD | phosphorus-doped diamond |
| HER | hydrogen evolution reaction |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| SIMS | secondary ion mass spectrometry |
| CV | cyclic voltammetry |
| LSV | linear sweep voltammetry |
| EIS | electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
References
- Gong, E.; Ali, S.; Hiragond, C.B.; Kim, H.S.; Powar, N.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; In, S.-I. Solar fuels: Research and development strategies to accelerate photocatalytic CO2 conversion into hydrocarbon fuels. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 880–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.; Fiorani, G.; Kleij, A.W. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Preparation of Cyclic Organic Carbonates. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1353–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Wakebe, H.; Tsukamoto, T.; Koga, O. Electrocatalytic process of CO selectivity in electrochemical reduction of CO2 at metal electrodes in aqueous media. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einaga, Y. Application of Boron-doped Diamond Electrodes: Focusing on the Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. Electrochemistry 2022, 90, 101002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Akram, M.Z.; Ghouri, M.D.; Hussain, S.; Kanade, S.; Kale, B.B.; Gautam, M. Recent Progress on Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: A Mini-review. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 10445–10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsui, K.; Iwakawa, H.; Ikemiya, N.; Nakata, K.; Einaga, Y. Stable and Highly Efficient Electrochemical Production of Formic Acid from Carbon Dioxide Using Diamond Electrodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irkham; Nagashima, S.; Tomisaki, M.; Einaga, Y. Enhancing the Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 by Controlling the Flow Conditions: An Intermittent Flow Reduction System with a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5298–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Einaga, Y. Semipermanent Continuous Formic Acid Production from CO2 by Controlling Ion Transport Using Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchová, S.; Sung, K.-d.; Weiss, Z.; Kopeček, J.; Fekete, L.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Mortet, V. Unveiling the microstructure and promising electrochemical performance of heavily phosphorus-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochimica Acta 2024, 499, 144696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukuda, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Ueda, A.; Nishibayashi, Y.; Einaga, Y. Electrochemical properties of phosphorus doped diamond. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 179, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Uchida, A.; Hunge, Y.M.; Shitanda, I.; Itagaki, M.; Kondo, T.; Yuasa, M.; Uestuska, H.; Terashima, C. Enhanced growth rates of N-type phosphorus-doped polycrystalline diamond via in-liquid microwave plasma CVD. Solid State Sci. 2024, 155, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, R. On the substitutional nitrogen donor in diamond. Solid State Commun. 1969, 7, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, S.; Teraji, T.; Kanda, H. Phosphorus-doped chemical vapor deposition of diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2000, 9, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Makino, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Okushi, H. n-type diamond growth by phosphorus doping on (0 0 1)-oriented surface. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 6189–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, S.; Kamo, M.; Sato, Y.; Mita, S.; Sawabe, A.; Reznik, A.; Uzan-Saguy, C.; Kalish, R. Growth and characterization of phosphorus doped n-type diamond thin films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1998, 7, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, N.; Weiss, Z.; Klimša, L.; Kopeček, J.; Gedeonová, Z.; Hubík, P.; Mortet, V. Highly phosphorus-doped polycrystalline diamond growth and properties. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 125, 108964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.-d.; Irimiciuc, S.A.; Novotný, M.; Weiss, Z.; Hubík, P.; Kopeček, J.; Vondráček, M.; Mortet, V. Advanced perspective on heavily phosphorus-doped diamond layers via optical emission spectroscopy. APL Mater. 2025, 13, 011118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, T.; Tomisaki, M.; Sato, S.; Nakamura, J.; Yamada, H.; Einaga, Y. Fabrication of polycrystalline phosphorus-doped diamond electrodes from red phosphorus. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 14825–14831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naragino, H.; Saitoh, Y.; Honda, K. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in an aqueous solution using phosphorus-doped polycrystalline diamond electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 134, 107164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebel, C.E. Photocatalysis: A source of energetic electrons. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Einaga, Y. Effect of sp2 species in a boron-doped diamond electrode on the electrochemical reduction of CO2. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 115, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Shao, J.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Demir, M.; Al Mesfer, M.K.; Danish, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, X. High-performance CO2 adsorption with P-doped porous carbons from lotus petiole biomass. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, H.; Bi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M. Efficient electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO enhanced by the synergistic effect of N,P on carbon aerogel. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 6439–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
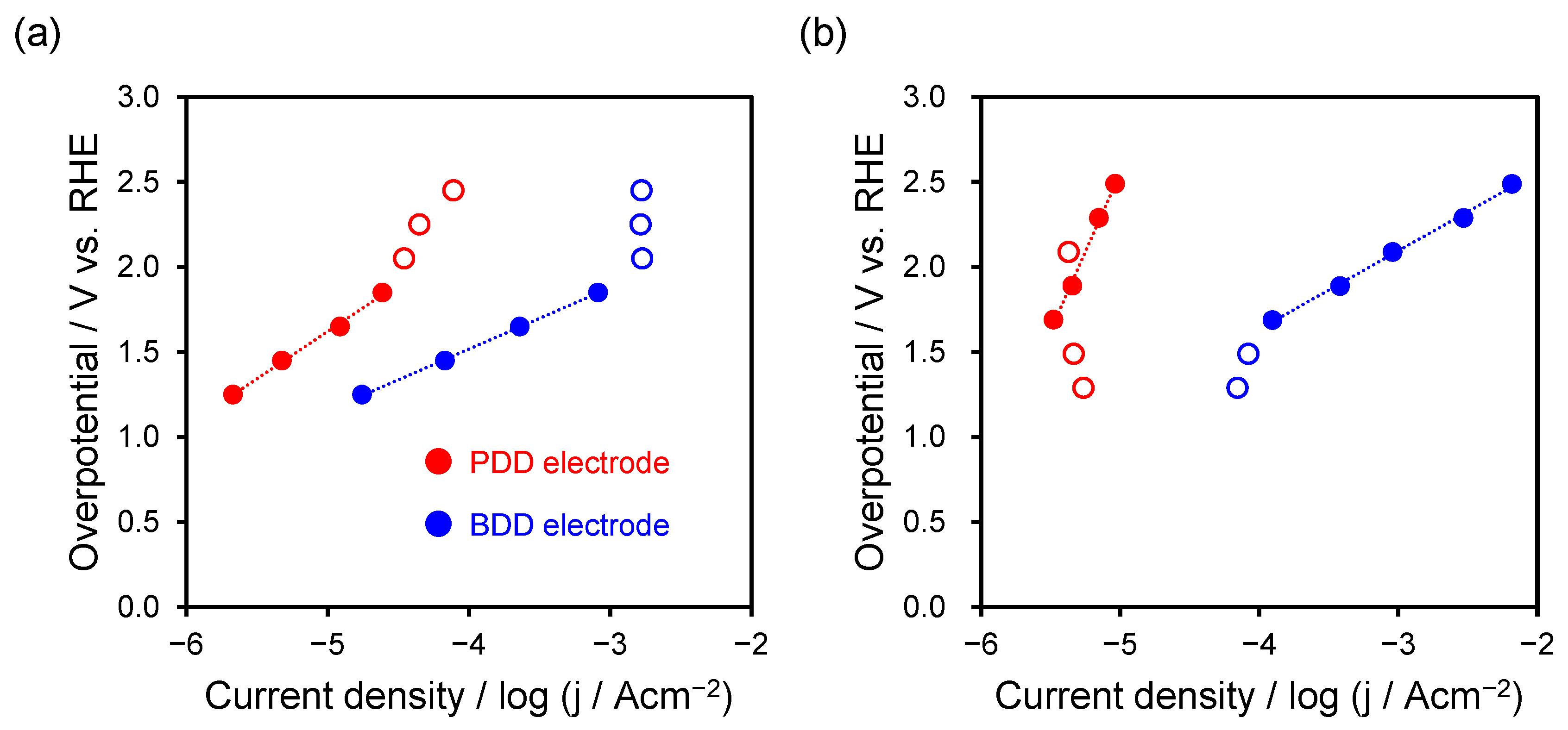
| Reaction & Electrode | Tafel Equation (η = a + b log10 j0) | Potential Range | b (V/dec) | a (V) | α | j0 [A/cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formic acid (PDD) | η = 4.41 + 0.556 log10(j0) | −1.2~−1.8 | 0.556 | 4.41 | 0.053 | 1.2 × 10−8 |
| Formic acid (BDD) | η = 2.96 + 0.361 log10(j0) | 0.361 | 2.96 | 0.082 | 6.3 × 10−9 | |
| Hydrogen (PDD) | η = 11.81 + 1.850 log10(j0) | −1.6~−2.4 | 1.85 | 11.81 | 0.016 | 4.2 × 10−7 |
| Hydrogen (BDD) | η = 3.48 + 0.461 log10(j0) | 0.461 | 3.48 | 0.0642 | 2.8 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Moriguchi, T.; Einaga, Y. Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using Polycrystalline Phosphorus-Doped Diamond Electrode. Catalysts 2026, 16, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal16010054
Moriguchi T, Einaga Y. Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using Polycrystalline Phosphorus-Doped Diamond Electrode. Catalysts. 2026; 16(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal16010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoriguchi, Tomokiyo, and Yasuaki Einaga. 2026. "Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using Polycrystalline Phosphorus-Doped Diamond Electrode" Catalysts 16, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal16010054
APA StyleMoriguchi, T., & Einaga, Y. (2026). Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 Using Polycrystalline Phosphorus-Doped Diamond Electrode. Catalysts, 16(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal16010054






