L-Cysteine Enhanced Degradation of Chlorobenzene in Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
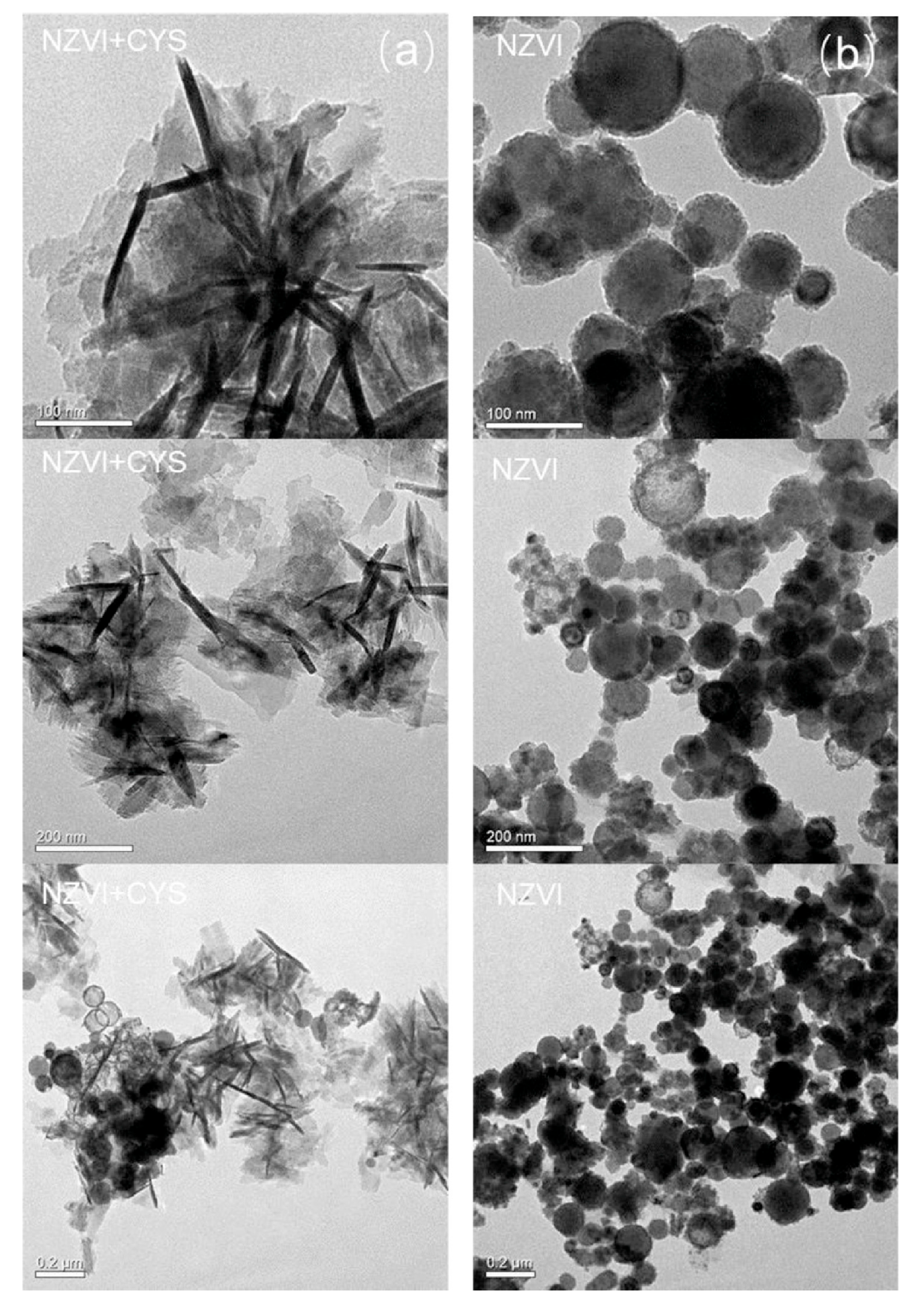
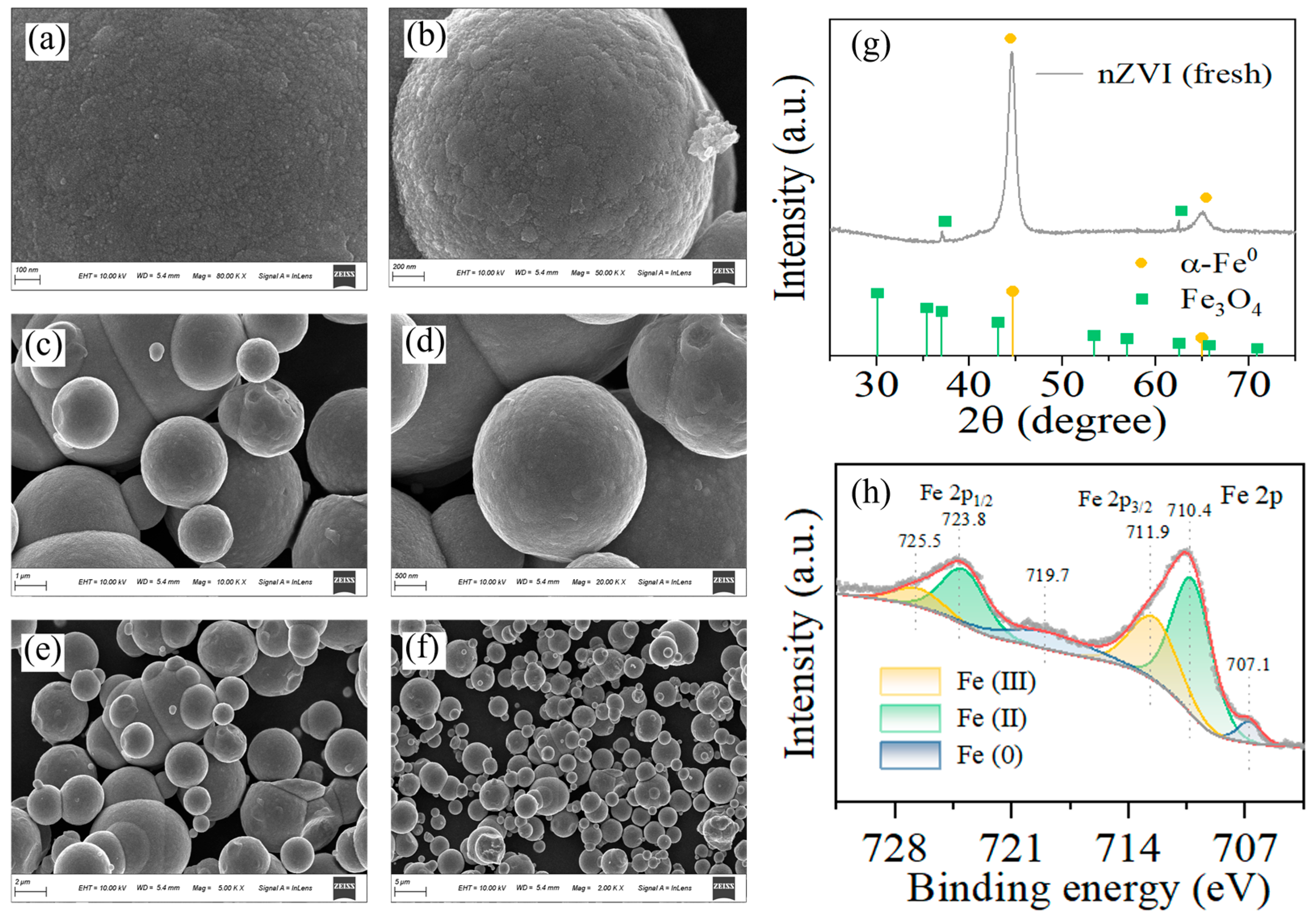
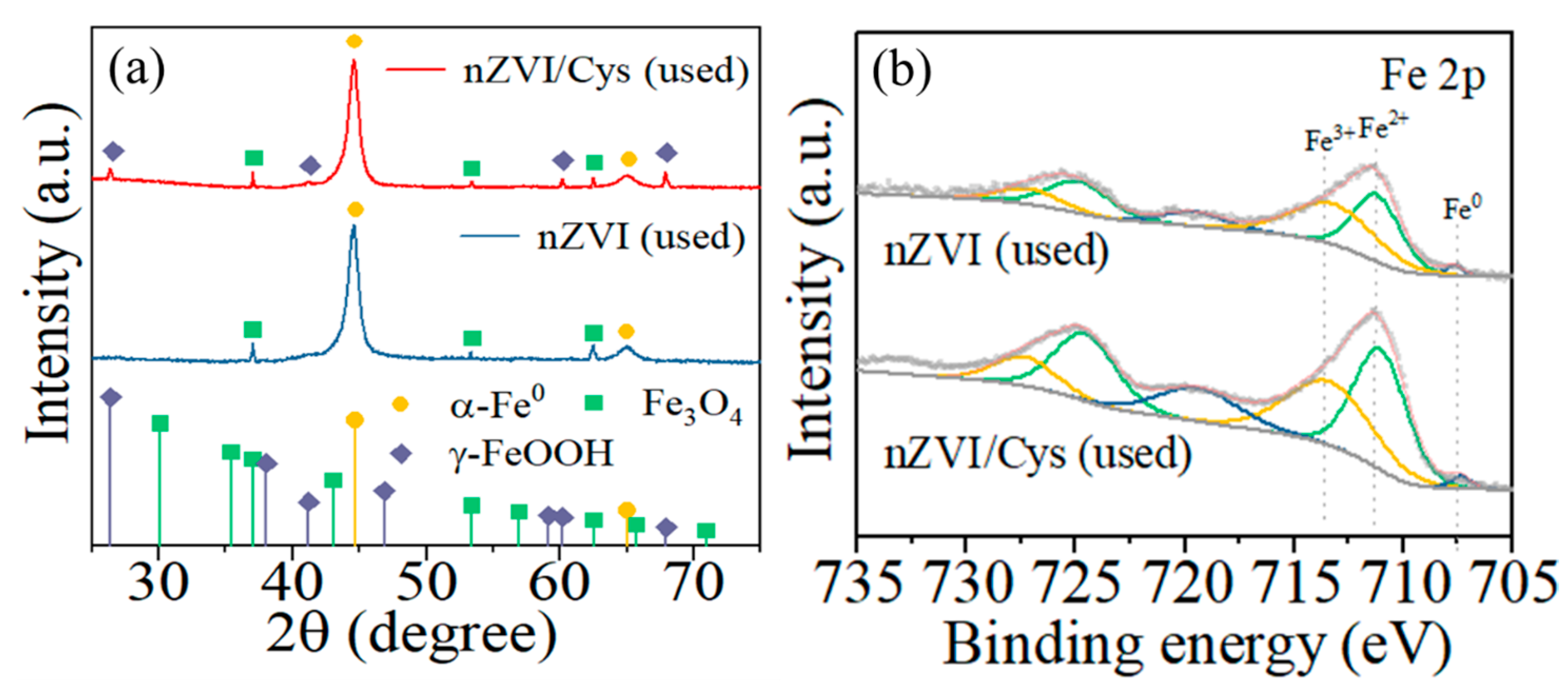
2.1. Characterization of nZVI
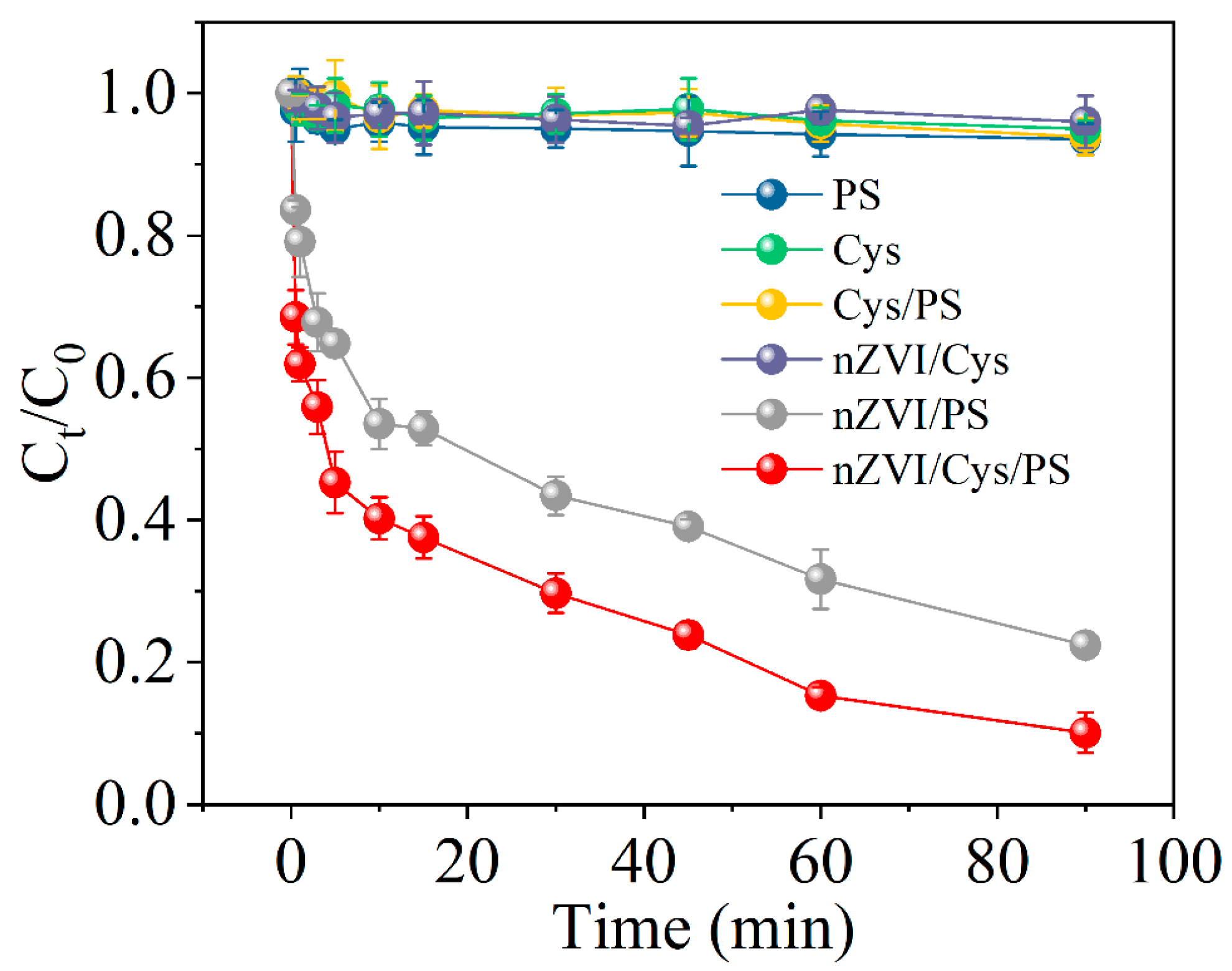
2.2. Reductive Degradation of MCB by Different Systems
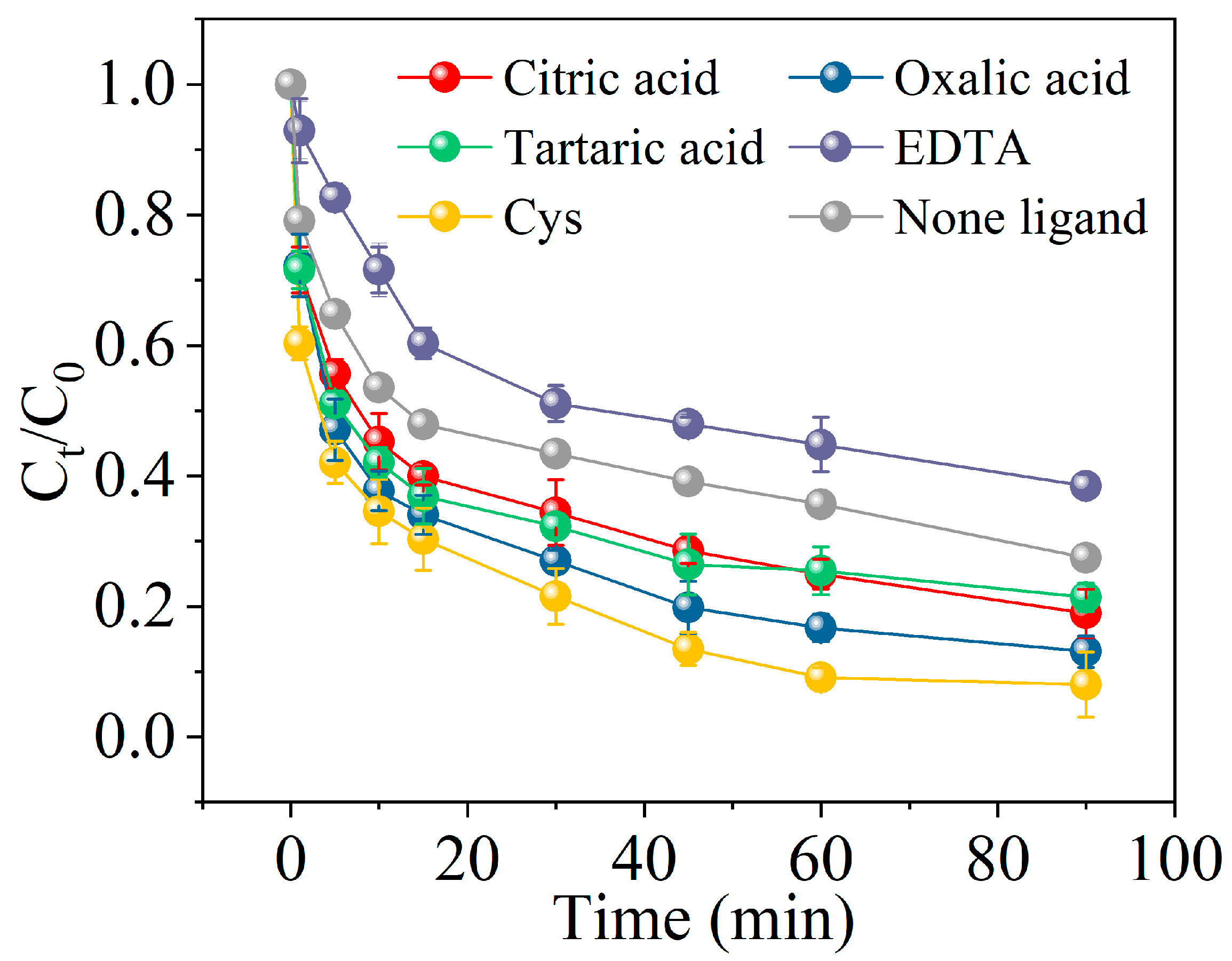
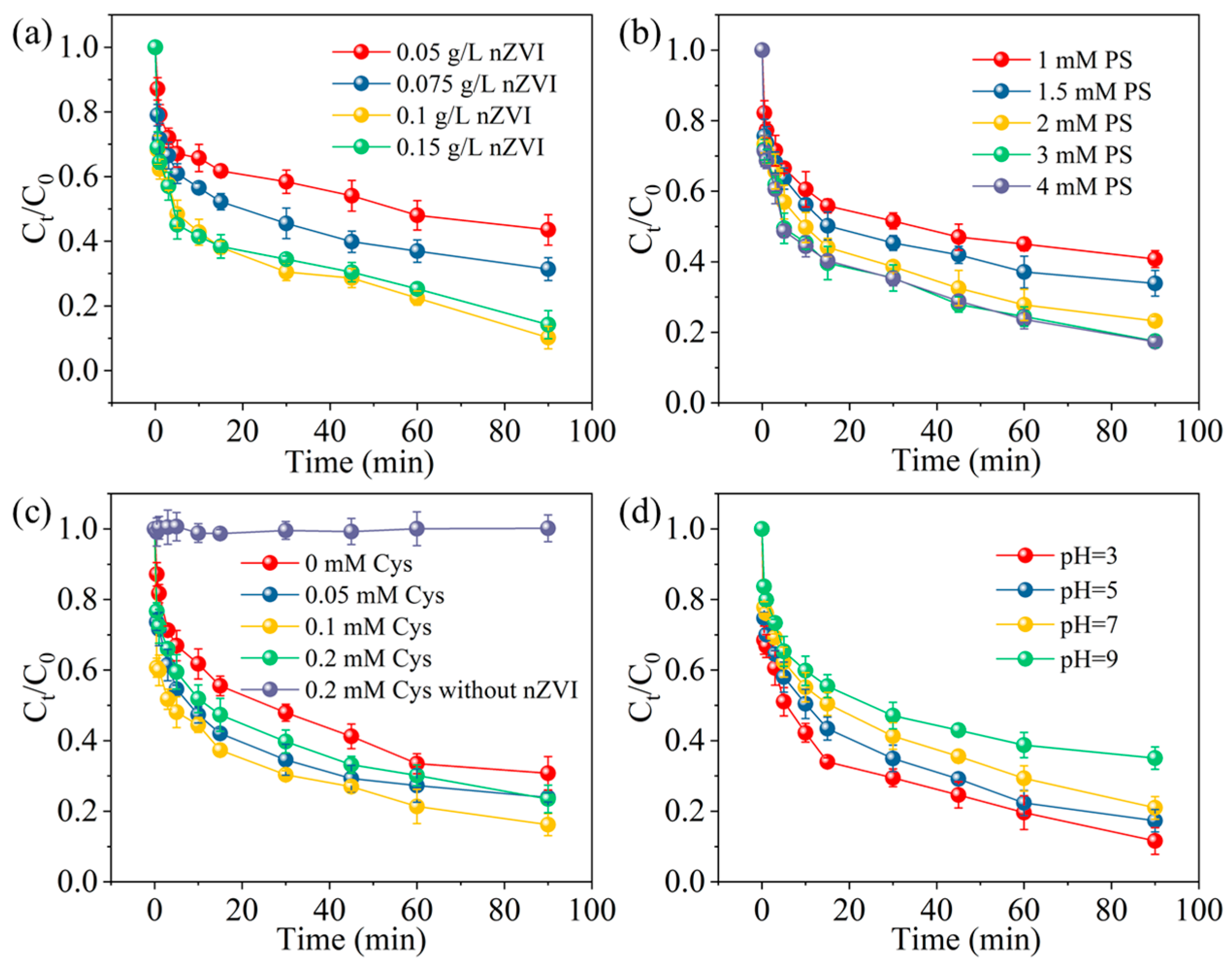
2.3. The Effect of Different Ligands Enhancing the nZVI/PS System on MCB Degradation
2.4. The Influence of Different Reaction Conditions on MCB Degradation
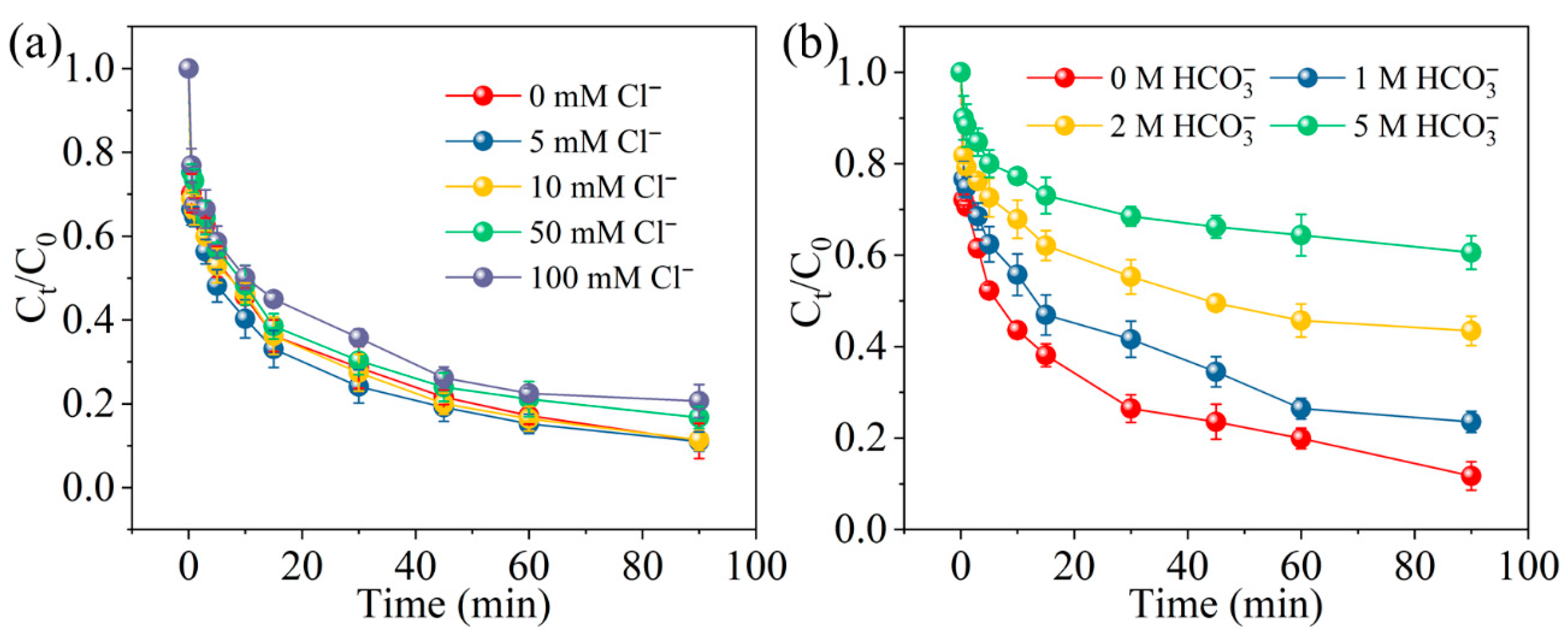
2.5. The Influence of Coexisting Ions in Water on the Degradation of MCB
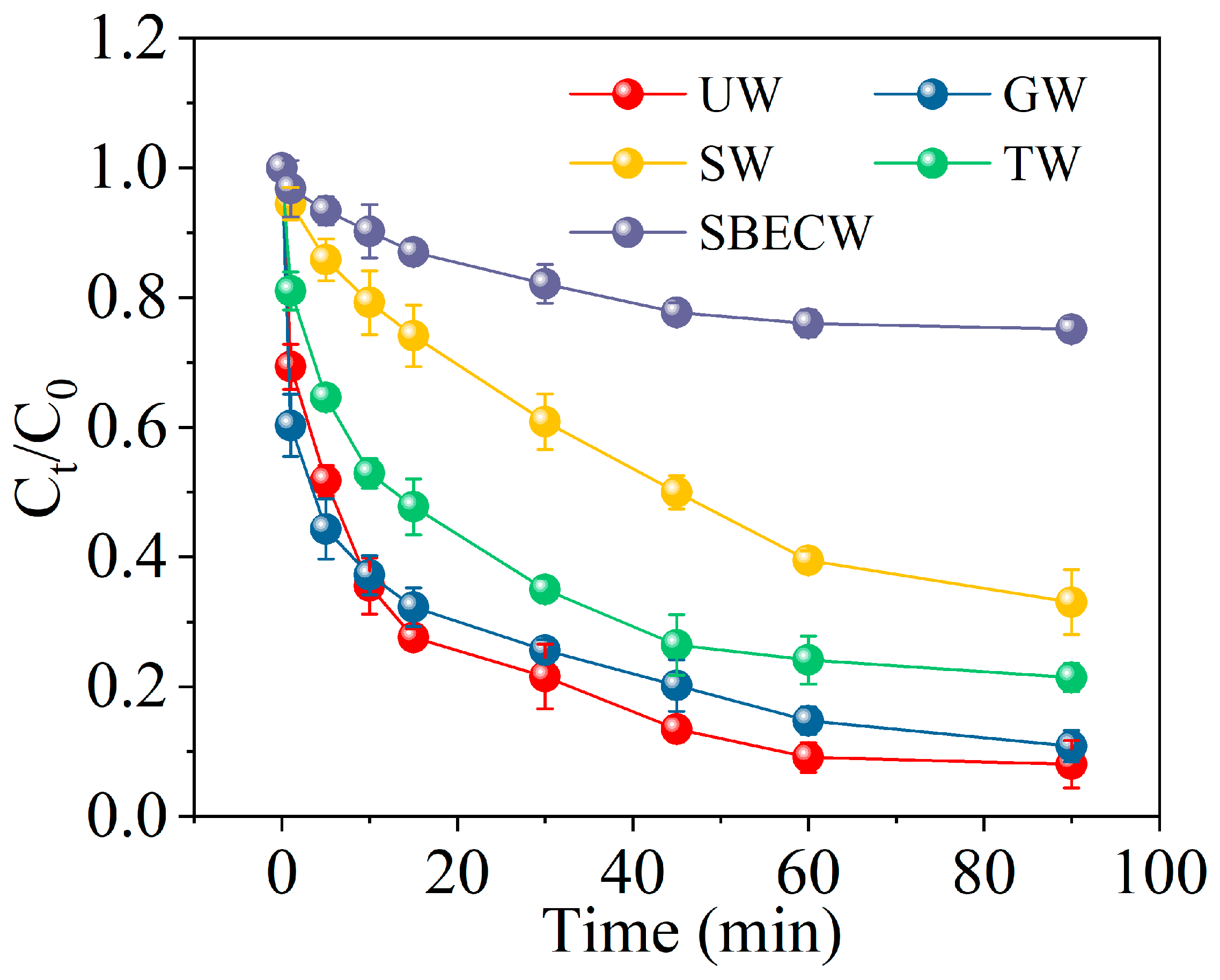
2.6. Efficiency of nZVI/Cys/PS System in Degrading MCB in Different Actual Water Environments
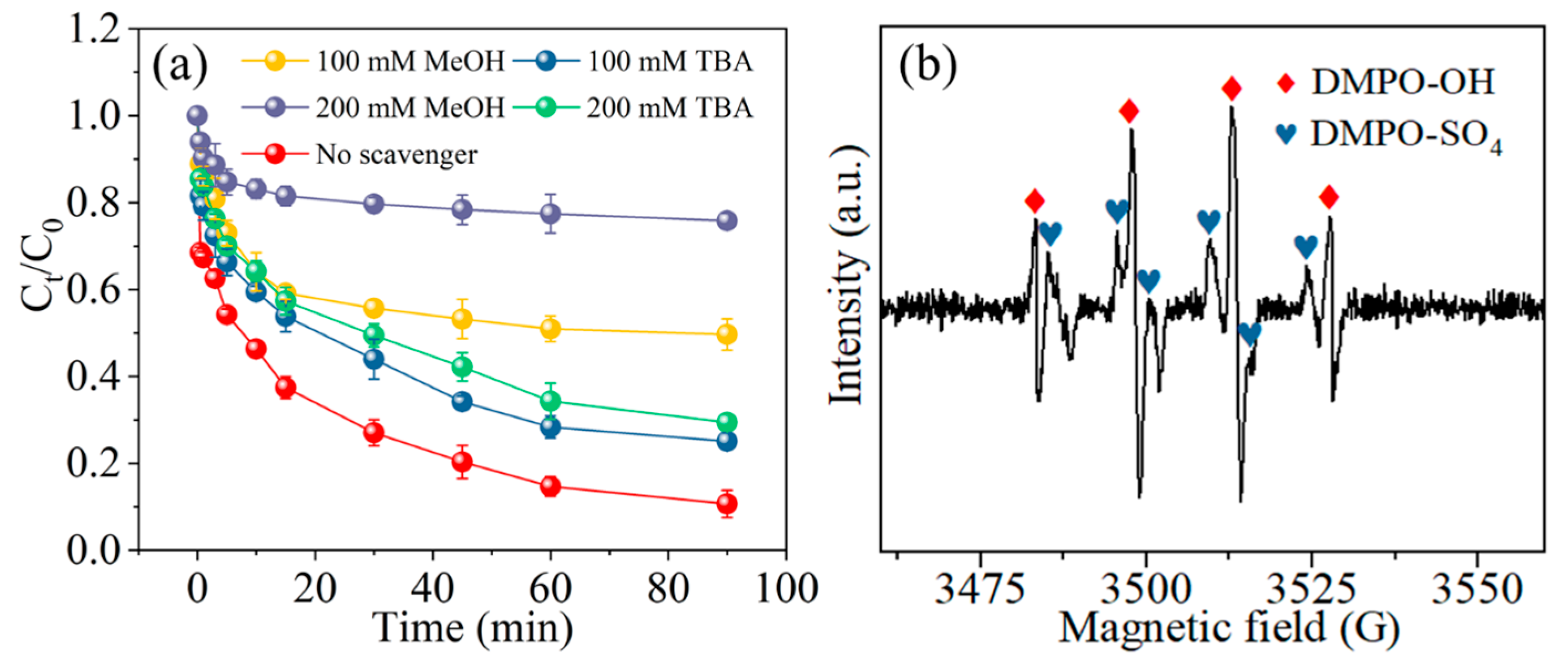
2.7. Analysis of Active Substances in the Degradation of MCB in Water by nZVI/Cys/PS System
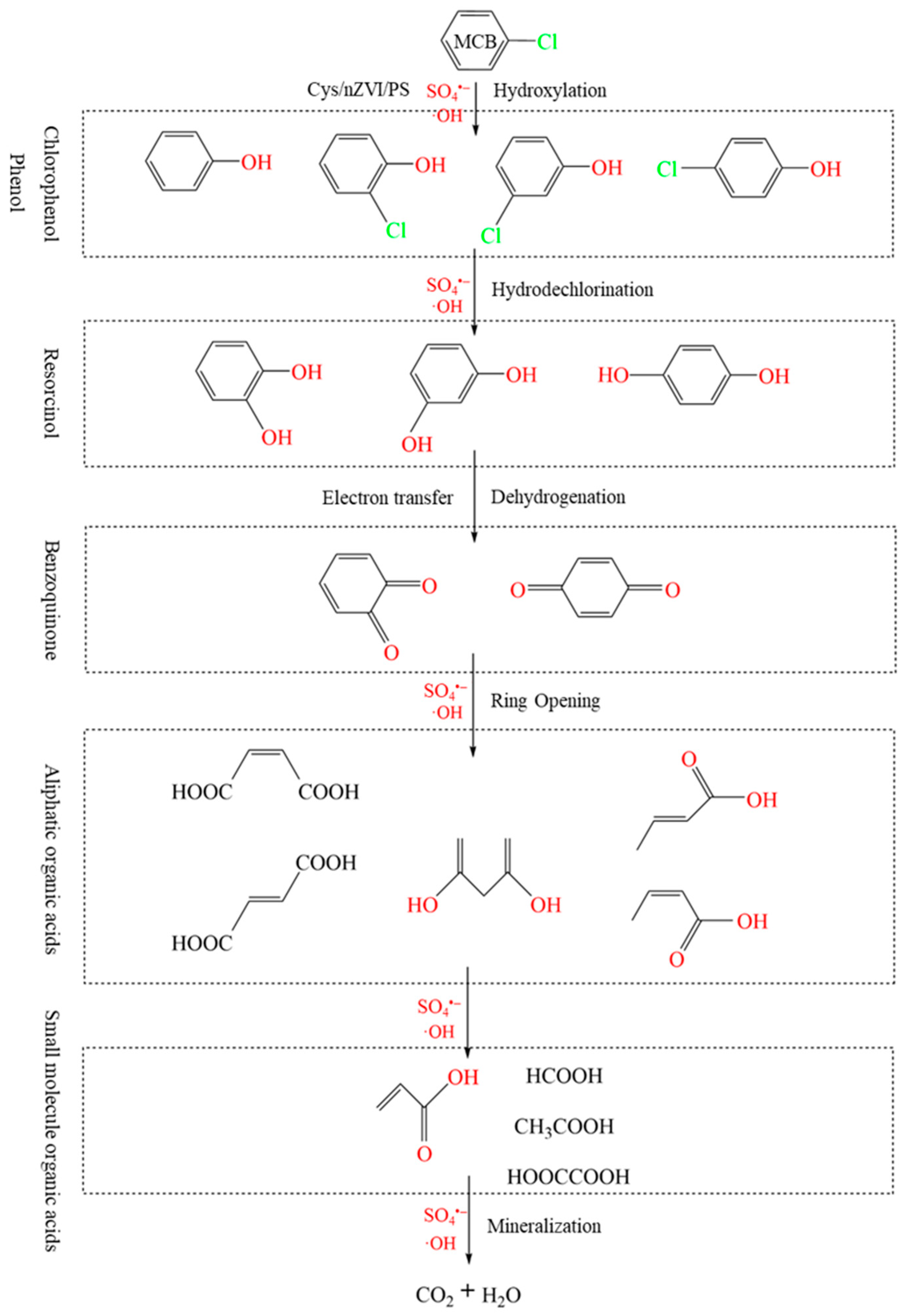
2.8. Proposed Intermediates and Pathways for MCB Degradation
2.9. Mechanism of Cys Enhanced the Degradation of MCB by nZVI/PS System
2.10. Formatting of Mathematical Components
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
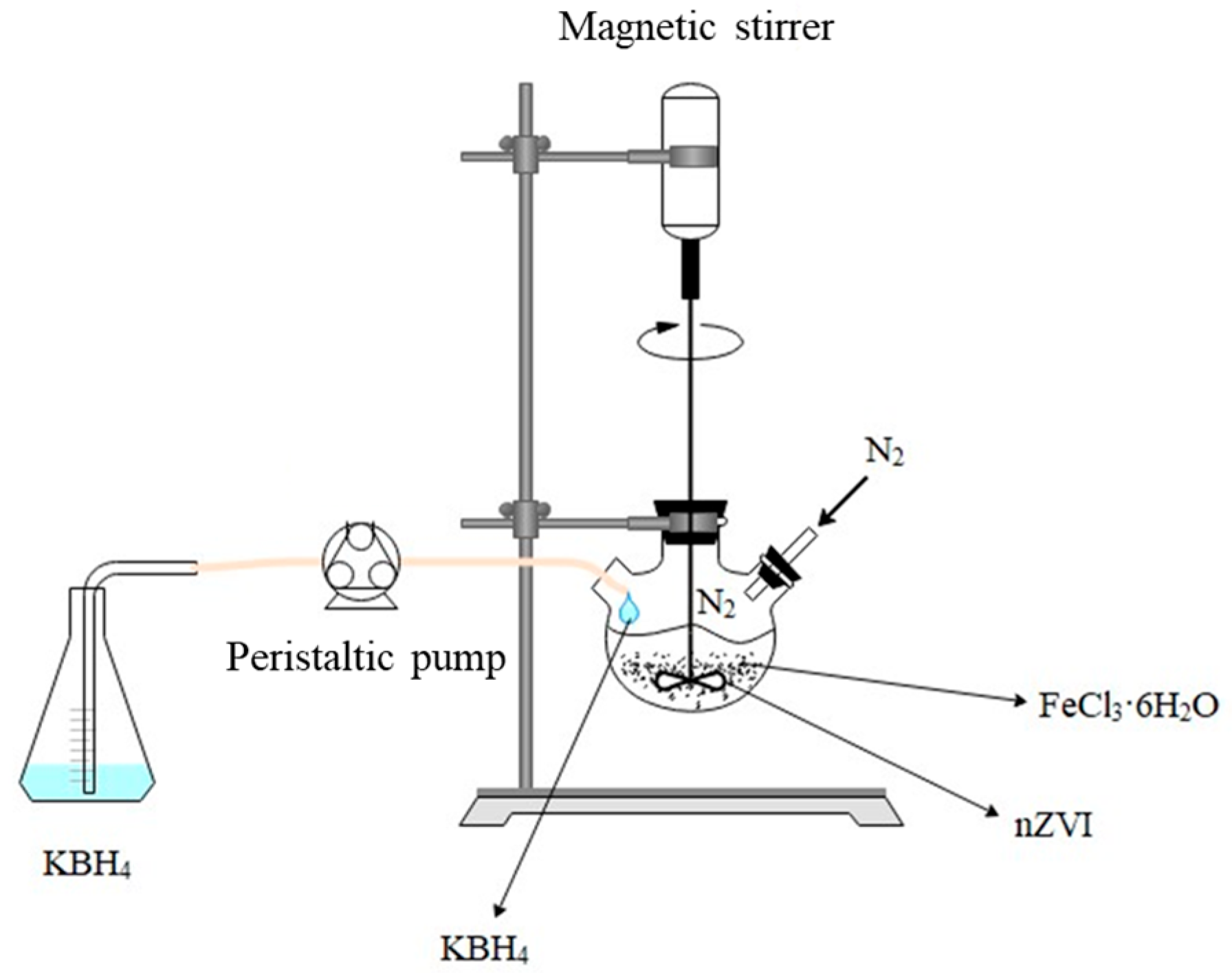
3.2. Synthesis of Nano Zero-Valent Iron
3.3. Degradation Experiments MCB
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| nZVI | Nano zero-valent iron |
| SR-AOPs | Sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes |
| MCB | Mono-chlorobenzene |
| PS | Persulfate |
| Cys | L-cysteine |
| Cy | L-cystine |
| SO4•− | Sulfate radicals |
| •OH | Hydroxyl radicals |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| UW | Ultrapure water |
| GW | Groundwater |
| TW | Tap water |
| SW | Surface water |
| SBECW | Secondary biochemical effluent of coking wastewater |
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Z.; Ning, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, G. Enhanced degradation of monochlorobenzene in groundwater by ferrous iron/persulfate process with cysteine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Ning, Y.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S.; Li, Y. Fe-Mn bimetallic sulfide enhanced persulfate activation for monochlorobenzene degradation in groundwater: Performance, mechanism and applicability. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.M.; Prosser, J. Intrinsic bioremediation of trichloroethylene and chlorobenzene: Field and laboratory studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 69, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, A.M.; Dahshan, H.; Abd-El-Kader, M.A.; Abd-Elall, A.M.M.; Elbana, M.H.; Nabawy, E.; Mahmoud, H.A. Polychlorinated Biphenyls Water Pollution along the River Nile, Egypt. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 389213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Xu, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Mao, Y.; Xing, M.; Li, P.; Han, Q.; Pan, H.; et al. Ceramsite catalyst derived from printed circuit board sludge for catalytic ozonation treatment of coking wastewater: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 497, 139613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.; Dong, Z.; Lim, T. Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: Current development, challenges and prospects. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 194, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, W.; Jia, F.; Wang, S.; Liao, X.; Zhang, L. Rapid Aerobic Inactivation and Facile Removal of Escherichia coli with Amorphous Zero-Valent Iron Microspheres: Indispensable Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species and Iron Corrosion Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitonaki, A.; Petri, B.; Crimi, M.; Mosbaek, H.; Siegrist, R.L.; Bjerg, P.L. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Gong, H.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, X.; Han, Q.; Guo, F. Cysteine controlled Fe2+/PS system to efficiently treat coking wastewater and recover magnetic products simultaneously. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 379, 134987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X. Degradation of azo dye Orange G in aqueous solutions by persulfate with ferrous ion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Guo, Y. Mass transfer and chemical oxidation of naphthalene particles with zerovalent iron activated persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8203–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Du, X. Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kang, S.; Chiu, P.C. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3464–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Lo, I.M.C.; He, D.; Dong, H. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 75, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Shao, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, A.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, S. Oxalate-enhanced reactivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron under different conditions of O2, N2 or without aeration. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, A.H.B.; Queiroz, R.; Temperini, M.L.A.; Sumodjo, P.T.A. Investigation of the electrochemical behavior of l-cysteine in acidic media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 765, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaden, J.; Galushko, A.S.; Schink, B. Cysteine-mediated electron transfer in syntrophic acetate oxidation by cocultures of Geobacter sulfurreducens and Wolinella succinogenes. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Yin, X.; Lin, H.; Rao, B.; Brooks, S.C.; Liang, L.; Gu, B. Why Dissolved Organic Matter Enhances Photodegradation of Methylmercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Shao, J.; Liu, S.; Gu, J. High efficient removal of tetracycline from solution by degradation and flocculation with nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, Y.R.; Liu, H.J. The preparation, surface modification, and characterization of metallic α-Fe nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. 1999, 60, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, A.H.; Asker, M.S.; Abdelhamid, S.A. Bacteriostatic impact of nanoscale zero-valent iron against pathogenic bacteria in the municipal wastewater. Biologia 2021, 76, 2785–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Ren, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yue, D.; Han, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhao, Y. Visible Light Assisted Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Degradation of Organic Pollutant via alpha-FeOOH/Mesoporous Carbon Composites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3993–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Lee, W. Inhibition of nZVI reactivity by magnetite during the reductive degradation of 1, 1, 1-TCA in nZVI/magnetite suspension. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 96, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Pi, Z.; Yao, F.; Wu, B.; He, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Yang, Q. A critical review on the mechanisms of persulfate activation by iron-based materials: Clarifying some ambiguity and controversies. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, N.; Wang, W.; Kang, S.; Xu, J.; Xiang, H.; Yin, D. Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water. Ultrason. Sonochem 2018, 49, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Yin, J.J. Core–Shell Structure Dependent Reactivity of Fe@Fe2O3 Nanowires on Aerobic Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5344–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, E.R.; Friesner, R.A. A Self-Consistent Charge-Embedding Methodology for ab Initio Quantum Chemical Cluster Modeling of Ionic Solids and Surfaces: Application to the (001) Surface of Hematite (α-Fe2O3). J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 8136–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemos Ramos, M.D.; Sousa, L.A.; Aguiar, A. Effect of cysteine using Fenton processes on decolorizing different dyes: A kinetic study. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, P.; Thiruppathi, D.; Ganesan, M.; Rajendran, T.; Rajagopal, S.; Sivasubramanian, V.K. Iron (III)–salen ion catalyzed s-oxidation of l-cysteine and s-alkyl-l-cysteines by H2O2: Spectral, kinetic and electrochemical study. Polyhedron 2019, 159, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Nabi, M.; Tao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. L-cysteine addition enhances microbial surface oxidation of coal inorganic sulfur: Complexation of cysteine and pyrite, inhibition of jarosite formation, environmental effects. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagbi, Y.; Sarswat, A.; Tiwari, S.; Mohan, D.; Pandey, A.; Solanki, P.R. Synthesis of l-cysteine stabilized zero-valent iron (nZVI) nanoparticles for lead remediation from water. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroz, S.; Muhammad, N.; Ratnayake, J.; Dias, G. Keratin-Based materials for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, G.; Du, L.; Zhou, W.; Huang, H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, L. The synergy of Fe0 core and FeSe2 shell with Se vacancy in peroxide-oxidants activation by selenidated nano zero-valent iron for enhanced water decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 515, 163286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Lai, M. Trichloroethylene Degradation by Zero Valent Iron Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauch, A.; Ayoub, G.; Naim, S. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by persulfate assisted micrometric Fe0 in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Su, H. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Zhou, D. Sulfate radical-based degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls: Effects of chloride ion and reaction kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darsinou, B.; Frontistis, Z.; Antonopoulou, M.; Konstantinou, I.; Mantzavinos, D. Sono-activated persulfate oxidation of bisphenol A: Kinetics, pathways and the controversial role of temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gu, X.; Lyu, S. The performance of chlorobenzene degradation in groundwater: Comparison of hydrogen peroxide, nanoscale calcium peroxide and sodium percarbonate activated with ferrous iron. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cui, C.; Yang, C.; Lyu, S. Application of recyclable nano zero-valent iron encapsulated L-cysteine catalytic cylinder product for degradation of BTEX in groundwater by persulfate oxidation. Water Supply 2022, 22, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ji, Y.; Kong, D.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, X. Simultaneous removal of bisphenol A and phosphate in zero-valent iron activated persulfate oxidation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Thao, T.T.; Kim, J.; Hwang, I. Effects of the formation of reactive chlorine species on oxidation process using persulfate and nano zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennedsen, L.R.; Muff, J.; Søgaard, E.G. Influence of chloride and carbonates on the reactivity of activated persulfate. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Feng, X.; Guo, F.; Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Reducing agent-enhanced printed circuit board sludge-based Fenton process for the efficient treatment of coking wastewater: Performance, optimization and mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yin, R.; Sun, J.; An, T.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wong, P.K. Natural magnetic pyrrhotite as a high-Efficient persulfate activator for micropollutants degradation: Radicals identification and toxicity evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Yu, L.; Qian, Z.; Liao, W.; Li, C. Degradation of the earthy and musty odorant 2,4,6-tricholoroanisole by persulfate activated with iron of different valences. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, I.; Bang, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.G.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, W. Selenate removal by zero-valent iron in oxic condition: The role of Fe (II) and selenate removal mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Cao, H.; Qi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, D.; Zhou, S.; Yang, B. L-cysteine boosted Fe (III)-activated peracetic acid system for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of L-cysteine and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doong, R.; Schink, B. Cysteine-mediated reductive dissolution of poorly crystalline iron (III) oxides by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, S.; He, H. Enhanced degradation of organic contaminants by Fe (III)/peroxymonosulfate process with l-cysteine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xie, P.; Ma, J. Strongly enhanced Fenton degradation of organic pollutants by cysteine: An aliphatic amino acid accelerator outweighs hydroquinone analogues. Water Res. 2016, 105, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Mu, Y.; Xue, C.; Chen, A.; Peng, L.; Wu, H.; Luo, S. Cysteine-enhanced reductive degradation of nitrobenzene using nano-sized zero-valent iron by accelerated electron transfer. J. Environ. Sci.—China 2021, 100, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, F.; Zhu, G.; Huang, H.; Feng, X.; Feng, Z.; Han, Q.; Guo, F.; Chang, T.; Wang, M. L-Cysteine Enhanced Degradation of Chlorobenzene in Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System. Catalysts 2025, 15, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090911
Jiang F, Zhu G, Huang H, Feng X, Feng Z, Han Q, Guo F, Chang T, Wang M. L-Cysteine Enhanced Degradation of Chlorobenzene in Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System. Catalysts. 2025; 15(9):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090911
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Fengcheng, Guangyi Zhu, He Huang, Xixi Feng, Zhi Feng, Qiao Han, Fayang Guo, Tianjun Chang, and Mingshi Wang. 2025. "L-Cysteine Enhanced Degradation of Chlorobenzene in Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System" Catalysts 15, no. 9: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090911
APA StyleJiang, F., Zhu, G., Huang, H., Feng, X., Feng, Z., Han, Q., Guo, F., Chang, T., & Wang, M. (2025). L-Cysteine Enhanced Degradation of Chlorobenzene in Water Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System. Catalysts, 15(9), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15090911





