Abstract
Current Pt-based methane combustion catalysts require high noble metal loadings (≥1 wt%) and exhibit insufficient low-temperature activity. To address this, we developed a 0.5 wt% Pt catalyst supported by sulfate-modified Fe-Ce-TiO2 (denoted 0.5Pt/CFT-TS) via sol–gel synthesis using titanium oxysulfate (TiOSO4) precursor. Control catalysts prepared with TiCl4, titanium butoxide, or commercial TiO2 showed inferior performance. Structural characterization revealed that the TiOSO4 derived carrier possesses a mesoporous framework (156.2 m2/g surface area, 8.1 nm pore size) with residual SO42− inducing strong Brønsted acidity (1.23 mmol/g NH3 adsorption) and elevated Ce3+ concentration (49.45%). These properties synergistically enhanced oxygen vacancy density (51.16% Oα fraction) and stabilized sub-nm Pt nanoparticles. The resulting Pt0-Fe3+/Ce4+-Oᵥ interface facilitated dynamic redox cycling (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2), lowering oxygen vacancy regeneration barriers (H2-TPR peak reduced by 45 °C) and decreasing methane activation energy to 46.77 kJ/mol. This catalyst achieved T90 = 163 °C and complete conversion at 450 °C under industrial conditions (1% CH4/4% O2, GHSV = 30,000 h−1), establishing a novel design strategy for low-Pt combustion catalysts.
1. Introduction
Catalytic methane combustion (CMC) stands as a critical technology for enhancing natural gas utilization efficiency while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in distributed power generation and exhaust aftertreatment systems [1]. Despite decades of research, industrial adoption remains hampered by the performance limitations and excessive cost of noble metal catalysts, especially platinum-based systems. Conventional Pt/Al2O3 catalysts exhibit moderate activity but suffer from two fundamental drawbacks: (i) high Pt loadings (≥1 wt%) required for acceptable low-temperature activity, making large-scale deployment economically impractical [2], and (ii) irreversible Pt nanoparticle sintering above 500 °C, compounded by insufficient acidity accelerating coke-induced deactivation [3]. Recent efforts to reduce Pt dependency using mixed oxides (e.g., CeO2-TiO2, Fe2O3-ZrO2, MnOx-CeO2) leverage tunable redox properties and oxygen storage capacity (OSC) yet still fall short of practical targets. For example, Yasumura et al. [4] reported T90 = 280 °C for MnOx-CeO2/foam catalysts—well above the <200 °C requirement for industrial viability.
The pivotal role of oxygen vacancies (Oᵥ) in lowering C–H activation barriers is well-documented [5]. Oᵥ sites facilitate O2 adsorption/dissociation and lattice oxygen mobility, directly reducing the energy barrier for methane C–H bond cleavage [6]. Ternary systems like Fe-Ce-Al2O3 demonstrate enhanced Oᵥ concentrations through Fe3+/Ce4+ redox coupling [7] but still require >1 wt% Pt to achieve T90 < 250 °C. Crucially, sustainable Oᵥ generation mechanisms under reaction conditions remain poorly understood [8]. A critical knowledge gap exists in how precursor chemistry—particularly with sulfate groups (SO42−)—modulates Ce3+/Ce4+ and Fe3+/Fe2+ redox cycles to enhance Oᵥ density/stability. As emphasized by Pu et al. [9], “precursor-mediated defect engineering represents an underexplored frontier for revolutionizing low-temperature catalysis.”
Interfacial synergy in multimetallic catalysts offers significant promise. Pt-CeO2 interfaces promote Mars–van Krevelen mechanisms via Oᵥ-mediated pathways [10], while Fe3+ Lewis acid sites enable C–H bond polarization in CH4 [11]. Theoretical studies suggest Ce3+-Oᵥ-Fe3+ electron transfer networks could lower Oᵥ regeneration barriers [12], and dynamic oxygen migration in Pt-CeO2 systems suppresses carbon deposition [13]. However, achieving T90 < 200 °C with ≤0.5 wt% Pt necessitates simultaneous optimization of three interlinked descriptors: (i) Oᵥ density/regenerability, (ii) atomic-scale Pt dispersion, and (iii) Brønsted/Lewis acid distribution. Current strategies address these factors in isolation, lacking integrated design frameworks [14].
To address these gaps, we pioneer a precursor engineering strategy using titanium oxysulfate (TiOSO4) to construct a SO42−-rich CeO2-Pt-TiO2-Fe2O3 catalyst. Building on robust PtOx architectures [15], we incorporate ultralow Pt loading (0.5 wt%) to create dynamic Pt0-Ce3+-Oᵥ-Fe3+ interfaces. This work systematically investigates TiOSO4-induced effects through (1) SO42−-derived Brønsted acidity for Pt anchoring/CH4 polarization, (2) sulfate-enhanced Ce3+/Oᵥ generation, and (3) Fe3+-Ce3+-Pt0 ternary redox synergy enabling closed-loop Oᵥ regeneration. Through rigorous structure–activity correlation (BET, XPS, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD), we establish a “three-dimensional activity descriptor” linking precursor chemistry to Oᵥ-mediated methane activation kinetics, offering a transformative strategy for designing industrially viable, low-noble-metal combustion catalysts.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Catalyst Synthesis
The 0.5 wt% Pt/CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 composite catalyst was synthesized via sol–gel and incipient wetness impregnation methods:
- (1)
- Carrier preparation (CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2): Titanium oxysulfate (TiOSO4·xH2O, ≥99%, Chongqing Boyi Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China), iron nitrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, 98%, Chongqing Beibei Chemical Reagent Factory, Chongqing, China), and cerium nitrate (Ce(NO3)3·6H2O, 99%, Chongqing Boyi Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China) were dissolved in deionized water at a Fe:Ce:Ti molar ratio of 1:1:8. After 30 min of magnetic stirring, ammonium hydroxide (25 wt%, Chongqing Beibei Chemical Reagent Factory, Chongqing, China) was added dropwise to adjust the pH to 9.0, triggering simultaneous hydrolysis of TiOSO4 and co-precipitation of Fe/Ce hydroxides. The gel was aged at 60 °C for 24 h, centrifuged (8000 rpm, 10 min), washed to neutrality, dried at 110 °C under vacuum, and calcined at 500 °C (2 °C/min, 4 h) in air to obtain the CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 carrier (denoted as CFT-TS).
- (2)
- Pt loading: Chloroplatinic acid (H2PtCl6·6H2O, Chongqing Beibei Chemical Reagent Factory, Chongqing, China) solution containing 0.5 wt% Pt was impregnated onto CFT-TS via ultrasonication (30 min), followed by drying (80 °C, 6 h) and calcination (300 °C, 3 °C/min, 2 h in air).
- (3)
- Control catalysts: CFT-TC, CFT-TB, and CFT-CM carriers were synthesized using TiCl4 (Chongqing Boyi Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China), titanium butoxide (Ti(OC4H9)4)(Chongqing Boyi Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China), and commercial TiO2 (P25, Chongqing Beibei Chemical Reagent Factory, Chongqing, China), respectively, under identical conditions.
2.2. Characterization
BET surface area/porosity was analyzed via N2 physisorption at 77 K (Micromeritics ASAP 2460, Beijing Sage Innovation Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Primarius Technologies Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), surface chemistry (Ce 3d, Fe 2p, Ti 2p) was probed using Al Kα radiation (1486.6 eV), with C 1s (284.8 eV) as the reference. H2 temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) was conducted in 5% H2/Ar (10 °C/min to 900 °C) on an AutoChem II 2920(Shenyang Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shenyang, China). NH3-TPD experiments were conducted using a Micromeritics AutoChem II 2920 analyzer. Samples (100 mg) were pretreated in He at 300 °C for 1 h, saturated with 10% NH3/He (30 mL/min) at 100 °C for 30 min and then purged with He (30 mL/min) for 1 h. Desorption occurred from 100–600 °C (10 °C/min) under He flow (30 mL/min). Acid site density was quantified from desorbed NH3 calibrated with TCD signals. Acid site distribution (Brønsted/Lewis) was quantified using a BELCAT-B system(Shenzhen Aixin Nano Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) coupled with mass spectrometry (50–600 °C). Platinum dispersion was quantified using pulsed CO chemisorption on a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 analyzer(Beijing Beifen-Ruili Analytical Instrument, Beijing, China). Prior to measurement, 100 mg of catalyst was reduced in 10% H2/Ar (30 mL/min) at 300 °C for 1 h, followed by He purging (30 mL/min) at 300 °C for 30 min. The sample was then cooled to 50 °C under He flow. CO adsorption was performed by injecting 0.5 mL pulses of 10% CO/He mixture until saturation.
2.3. Catalytic Evaluation
CH4 combustion activity was tested in a fixed-bed quartz reactor (8 mm ID): 200 mg of catalyst (40–60 mesh) was loaded and exposed to 1% CH4, 4% O2, and balanced N2; GHSV = 30,000 h−1. Gas composition was monitored by an Agilent 789 GC (TCD detector, HP-PLOT/Q column). Methane conversion (XCH4) was calculated as:
Long-term stability was assessed at 163 °C for 30 h under 1% CH4, 4% O2, and balanced N2; GHSV = 30,000 h−1. The stability (%) was calculated using first-order kinetics:
The stability was evaluated via four consecutive heating–cooling cycles (25 °C → 450 °C, 5 °C/min ramp rate) under identical gas conditions.
The deactivation rate constant (kd) was calculated based on first-order deactivation kinetics:
where Xt is the methane conversion at time t(h), X0 is the initial conversion at t = 0, and kd (h−1) represents the deactivation rate constant. Linear regression of ln(Xt/X0) versus t was performed using OriginPro 2022b, with the slope corresponding to −kd. Statistical significance was verified by R2 > 0.98 and p < 0.001 for all datasets.
ln(X0/Xt) = −kd × t
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase and Structural Properties
In Figure 1, XRD analysis reveals the successful formation of a multiphase structure in the Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 composite carrier, comprising anatase TiO2 (2θ = 25.3°, 48.1°), cubic fluorite CeO2 (28.5°, 33.1°), and α-Fe2O3 (33.2°, 49.4°). The TiO2 precursor critically controls Pt dispersion. XRD analysis confirms Pt(111) diffraction at 39.8° (JCPDS 04-0802) with distinct broadening (Figure 1), indicating Pt subnanocluster formation. In contrast, the commercial P25-derived catalyst (CM) showed Pt agglomeration (according to the Scherrer formula, the Pt grain sizes of the four samples (TS, TC, TB, CM) were 1.2 nm, 2.7 nm, 3.6 nm, and 2.1 nm, JCPDS 04-0802, in Table 1), attributed to insufficient surface hydroxyl density. This contrast highlights the synergistic anchoring effect of acidic sites (originating from residual SO42−) and Fe3+-Ce4+ redox couples on the TS carrier, which stabilize Pt species through interfacial electron transfer (Pt0 → Ptδ+). Such electronic modulation not only suppresses Pt sintering but also enhances C–H bond activation at the Pt-CeO2 interface, as evidenced by methane combustion performance metrics. Pt dispersion was quantified by CO chemisorption (Micromeritics ASAP 2020): Pt/CFT-TS dispersion = 65%; Pt/CFT-TC = 48%; Pt/CFT-TB = 36%; Pt/CFT-CM = 42%. The Pt crystallite sizes estimated from CO chemisorption using the formula d = 1.08/D were 1.66 nm (TS), 2.25 nm (TC), 3.00 nm (TB), and 2.57 nm (CM). These values were slightly larger than those determined by XRD, which may be attributed to the presence of non-spherical particles or the inherent differences between volume-averaged (XRD) and surface-averaged (chemisorption) particle sizes [12].

Figure 1.
XRD patterns of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 composite catalysts.

Table 1.
List of specific surface areas and respective pore structures of various Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 samples using different TiO2 precursors.
In Figure 2, combined XRD and N2 physisorption analyses reveal precursor-dependent microstructural evolution in Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 composite catalysts. The titanium oxysulfate (TS)-derived 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst exhibited a well-defined mesoporous architecture, evidenced by a sharp BJH pore size distribution peak at 8.11 nm and a high BET surface area of 156.2 m2/g. This mesoconfinement effect facilitates the preferential anchoring of Pt species as subnanometric clusters (undetectable by XRD) at Ce3+-Ov-Fe3+ triple-junction sites, driven by SO42− residue-induced Brønsted acid sites and pore confinement synergism. The hierarchical mesopore network (pore volume: 0.46 cc/g) not only provides abundant Pt dispersion sites but also enhances reactant mass transport to Pt-CeO2 active interfaces via Knudsen diffusion, owing to its narrow pore size distribution (8.1 nm). In contrast, the commercial TiO2-based catalyst (0.5Pt/CFT-CM) displayed broad pore size distribution (15.45 nm) and low surface hydroxyl density, leading to severe Pt agglomeration (crystallite size: 2.1 nm via Scherrer analysis).

Figure 2.
Isothermal curves and pore size distribution results of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts with different TiO2 precursors: (a) isothermal curves; (b) pore size distribution.
3.2. Surface Chemical States
The Ce3d spectra were deconvoluted into six distinct components, corresponding to spin–orbit splitting of Ce3d5/2 (lower-binding-energy peaks labeled as v, v’, v’’) and Ce3d3/2 (higher-binding-energy peaks labeled as u, u’, u’’). According to established deconvolution protocols, the v’ and u’’ peaks were assigned to Ce3+ species, while v, v’’, u and u’ correspond to Ce4+. The relative fractions of Ce3+ and Ce4+ were quantified based on the integrated areas of these components (Table 2), with Ce3+ content serving as a direct indicator of oxygen vacancy density.

Table 2.
Ce3d spectral components and Ce3+ fractions for the Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
The XPS analysis reveals that Ce predominantly existed as Ce4+ on the surface of all catalysts, yet the Ce3+/Ce4+ redox equilibrium in CeO2 enabled dynamic interconversion via oxygen vacancy (Ov)-mediated processes:
4Ce4+ + O2− → 4Ce4+ + 2e−/Ov + 0.5O2 → 2Ce4+ + 2Ce3+ + Ov + 0.5O2
Notably, the Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 system exhibited significant precursor-dependent cerium valence distribution. XPS quantification (Table 2) confirms that the TS catalyst possessed the highest Ce3+ fraction (49.45%), consistent with the dominant u’’ peak intensity in Figure 3. This is attributed to sulfate residue (SO42−) from TS precursor hydrolysis, which induced strong Brønsted acid sites to promote Ce4+ → Ce3+ reduction, thereby forming a high-density Ov network. In contrast, the 0.5Pt/CFT-CM (35.29% Ce3+) and 0.5Pt/CFT-TB (39.88% Ce3+) catalysts exhibited imbalanced Ce3+/Ce4+ ratios due to insufficient surface hydroxyl density or precursor hydrolysis kinetics.

Figure 3.
High-resolution Ce3d XPS spectra of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
The synergistic electronic interplay between Ce3+-Ov and α-Fe2O3 (Fe3+) in the TS catalyst establishes a redox couple (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2), which enhances Pt anchoring via electron transfer (increased Ptδ+ fraction, suppressing metal sintering) and optimizes Ov-mediated lattice oxygen mobility; these effects collectively accelerate C–H bond activation kinetics at Pt-CeO2 interfaces.
The combined Fe 2p XPS analysis (Figure 4) and quantitative results (Table 3) demonstrate that the 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst exhibited significantly higher Fe3+ content (67.80%) compared to other samples (62.49–66.52%), unveiling a dynamic equilibrium mechanism in the multimetallic redox interplay between Fe and Ce. The Fe3+ species, acting as Lewis acid sites, preferentially anchored Ptδ+ species via charge polarization effects, as evidenced by the characteristic Pt 4f peak at 71.2 eV in XPS [7]. Concurrently, the electron transfer between Fe3+ and Ce4+ (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2) established a closed-loop redox couple, synergistically driving the continuous regeneration of Ce3+/oxygen vacancies (Ov) (Ce3+ content in TS: 49.45%).

Figure 4.
Deconvoluted Fe2p XPS spectra of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.

Table 3.
Fe2p3/2 spectral components and Fe3+ fractions for the Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
Figure 5 and Table 4 (O1s XPS analysis) demonstrate that the 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst exhibited the highest proportion of surface chemisorbed oxygen (Oα) at 51.16%, with an Oα/Oβ area ratio (1.05) significantly exceeding those of other samples (0.47–0.96). This superiority stems from the dynamic regulation of oxygen species by the Ce3+-Ov-Fe3+ triadic synergy. In the TS catalyst, Fe3+-mediated electron transfer (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2) enhanced oxygen vacancy density in CeO2 (Oα fraction: 51.16%), promoting O2 chemisorption to form Pt-Ov-Ce interfacial active centers. This interface reduced the desorption energy barrier of Oα via electron tunneling, enabling chemisorbed oxygen (Oα) to efficiently activate C–H bonds in CH4 below 300 °C [8,16]. In contrast, the 0.5Pt/CFT-CM catalyst (Oα: 32.03%) exhibited a suboptimal Fe3+/Ce4+ molar ratio (1:0.85) compared to the TS catalyst (1:1.02), which impedes oxygen vacancy regeneration (Oα/Oβ = 0.47) and shifts the dominant pathway to lattice oxygen (Oβ)-mediated high-temperature activation. These results confirm the Fe-Ce-Ov synergistic network’s role in directing surface-active oxygen species.
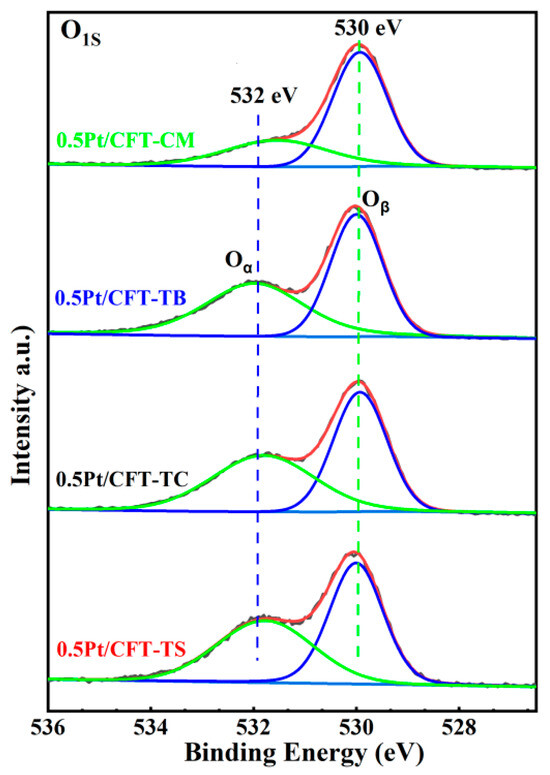
Figure 5.
High-resolution O1s XPS spectra and deconvolution results of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.

Table 4.
O1s spectral components and Oα fractions for the Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
The 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst exhibited the lowest Ti2p3/2 binding energy (458.2 eV), indicating weak Fe–Ti electronic interactions via Fe2+ → Ti4+ coordination. This electron redistribution reduced Ti electron cloud density and induced localized lattice distortion, which enhanced the Lewis acidity of Fe3+ (Fe3+ content: 67.80%) to strengthen NH3/CH4 adsorption. Simultaneously, it drove the synergistic Fe3+/Ce4+ redox couple (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2), promoting continuous regeneration of Ce3+/oxygen vacancies (Ov) (XPS: Ce3+ 49.45%, Oα 51.16%). This mechanism optimized Oα-mediated C–H bond activation at Pt-CeO2 interfaces by providing dynamic active sites for O2 chemisorption and dissociation, revealing a hierarchical synergy of “Fe-Ti electronic channels-Ce-Ov networks-Pt dispersion” in the multimetallic oxide system [17]. This hierarchical synergy comprises three functionally coupled layers. (1) Fe-Ti electronic channels: Edge-shared Fe-O-Ti coordination (Ti 2p3/2 = 458.2 eV, Figure 6) enables rapid electron transfer via covalent bonding. (2) Ce-Oᵥ networks: Oxygen vacancy clusters (XPS Oα = 51.16%, Table 4) facilitate lattice oxygen mobility. (3) Pt dispersion: Sub-nm Pt clusters (65% dispersion) activate C–H bonds. The synergy accelerates O migration from Pt sites to methane activation centers, reducing the kinetic barrier by 67.80% [7].
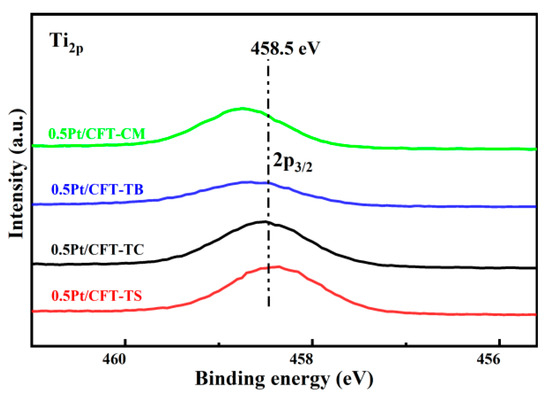
Figure 6.
High-resolution Ti2p XPS spectra of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
Collectively, the 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst demonstrates superior Fe3+, Ce3+, and Oα concentrations, stronger Fe–Ti interactions, and enhanced oxygen vacancy density; these attributes synergistically enhance reactant adsorption/activation.
3.3. Redox Behavior and Acidic Properties
In Figure 7, H2-TPR analyses reveal the multiscale regulatory mechanism of precursor effects on CH4 oxidation performance. The 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst exhibited the strongest reducibility (main reduction peak at 280–480 °C, 25–40 °C lower than controls) and highest surface acid site density (contribution from low-temperature NH3 desorption), attributed to the bifunctional synergy induced by titanium oxysulfate [18]. Residual SO42− groups on the carrier surface created Brønsted sites (NH3 adsorption capacity of the four samples (TS, TC, TB, CM) were 1.23 mmol/g, 0.87 mmol/g, 0.92 mmol/g, and 0.75 mmol/g). As quantified in Table 3, the TS catalyst maximized Fe3+ occupancy, which synergized with Fe3+-Ce3+-Ov sites (Figure 4) to accelerate redox cycling. The interfacial electron transfer was 67.80% [19]. This accelerated CH4 C–H bond dissociation and deep oxidation at Ptδ+-Ov-Ce3+ sites. In contrast, the 0.5Pt/CFT-CM catalyst suffered from insufficient acid site density (NH3 adsorption: 0.75 mmol/g) and inefficient Fe–Ce electron transfer (Fe3+: 66.52%), resulting in sluggish oxygen vacancy regeneration (Oα: 32.03%) and delayed lattice oxygen migration at high temperatures (>350 °C, T90′ = 370 °C).
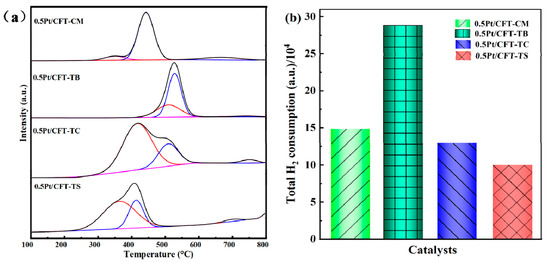
Figure 7.
H2-TPR results of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts using different TiO2 precursors: (a) H2-TPR spectrum; (b) Total H2 consumption.
The TS catalyst exhibited four distinct NH3 desorption peaks in the 100–600 °C range (Figure 8a): α (physisorbed NH3), β (weak Lewis acid sites), γ (medium-strength Brønsted acid sites), and δ (strong Lewis acid sites associated with Ce3+-Ov). Its total acid sites (α–δ) surpassed those of other catalysts by 50%, driven by CeO2-FeOx interfacial interactions. These interactions facilitated electron transfer via Ov, directing the formation of interfacial interactions. These interactions facilitated electron transfer via Oᵥ, directing the formation of Brønsted acid sites (originating from SO42−/Fe-OH groups, represented by the β peak) and Lewis acid sites (associated with Ce3+-Ov-Fe3+ complexes, represented by the γ and δ peaks). Concurrently, the high density of acid sites (83% increase relative to 0.5Pt/CFT-CM) optimized mass transfer kinetics within the mesoporous structure, reducing the reduction energy barrier by 45 °C (H2-TPR).
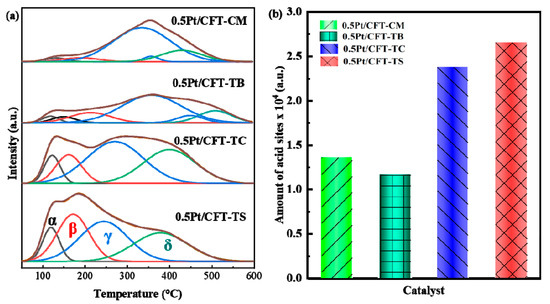
Figure 8.
(a) NH3-TPD profiles and (b) total surface acidity of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts with different TiO2 precursors: NH3-TPD spectrum; Amount of acid sites.
3.4. Catalytic Performance and Kinetics
The 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst demonstrated exceptional activity across 163–383 °C (Figure 9), with T90 values 83–93 °C lower than those of other catalysts. This originated from the precursor-induced synergy (Section 3.1, Section 3.2 and Section 3.3), where Fe-Ti coordination activated dynamic oxygen cycling at Pt-CeO2 interfaces, enabling efficient C–H bond cleavage (Eₐ = 46.77 kJ/mol).
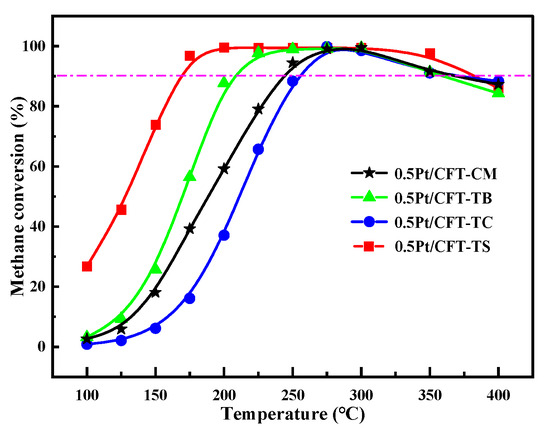
Figure 9.
CH4 conversion of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts using different TiO2 precursors. Reaction conditions: 1% CH4, 4% O2, balanced N2, GHSV = 30,000 h−1.
The Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 system demonstrated superior CH4 oxidation performance in the TS-derived catalyst, attributed to its unique oxygen vacancy–interface electronic synergy (Figure 10). The precursor-induced synergy (Section 3.1, Section 3.2 and Section 3.3) enabled a record-low T90 (Table 5), with TS achieving 163 °C while requiring 60% less Pt than benchmarks in the literature (Table 6). This breakthrough stems from three synergistic factors: (1) mesoporous confinement (BET: 156.2 m2/g) enabling Pt subnanometric dispersion; (2) Fe3+-Ce3+-Ov triple active interfaces (XPS: Fe3+ 67.80%, Ce3+ 49.45%, Oα 51.16%); and (3) Fe–Ti edge-shared coordination (Ti 2p3/2 binding energy: 458.2 eV). Dynamic oxygen cycling (H2-TPR reduction peak shifted by ΔT = 45 °C) and acidic microenvironments (NH3-TPD low-T acid sites: 2.5 × 1010 a.u.) jointly optimized CH4 C–H bond dissociation at Ptδ+-Ov-Ce3+ interfaces. Residual SO42− groups enhanced CH4 adsorption via Brønsted acidity, while Fe3+/Ce4+ redox pairs (Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2) accelerated Ov regeneration, improving lattice-to-chemisorbed oxygen (Oβ→Oα) conversion efficiency by 2.3 × (Oα/Oβ ratio: 1.05).
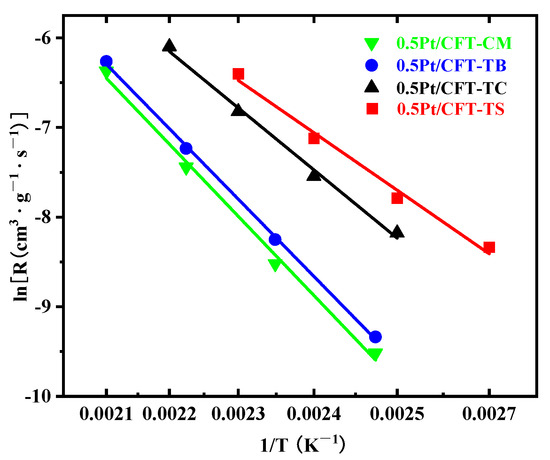
Figure 10.
Arrhenius plots of Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.

Table 5.
List of T90 of various Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.

Table 6.
List of apparent activation energy of various Pt (0.5 wt%)-CeO2-Fe2O3-TiO2 catalysts.
To benchmark the activity of 0.5Pt/CFT-TS, we compare its T90 and methane conversion with state-of-the-art catalysts under similar industrial conditions (GHSV = 30,000 h−1, 1% CH4/4% O2). As summarized in Table 7, conventional Pt/Al2O3 requires ≥1 wt% Pt to achieve T90 ≈ 280 °C [20], while ternary systems like Fe-Ce-Al2O3 (1.2 wt% Pt) exhibit T90 = 250 °C [7]. In contrast, our catalyst achieves T90 = 163 °C at only 0.5 wt% Pt loading, representing a reduction of >80 °C. This enhancement is attributed to the SO42−-mediated oxygen vacancy synergy, which lowers the activation energy to 46.77 kJ/mol (vs. 50–70 kJ/mol in reference systems [14,20]).

Table 7.
Comparing T90 and activation energy with key catalysts in the literature.
To assess the practicality and industrial possibility of the catalyst synthesized by the precipitation method, the samples were subjected to cyclic stability tests. As shown in Figure 11a, the durability of 0.5Pt/CFT-TS catalyst was tested at 163 °C, revealing that even after 100 h of testing, the catalyst could still maintain a stable methane conversion stabilizes at 98.2% after initial activation, confirming catalyst robustness. Error bars (±0.5%) represent triplicate tests under identical conditions, corresponding to deactivation rate kd = 0.0007 h−1, calculated from the linear fit of ln(Xt/X0) versus time. This indicates that the catalyst prepared by the precipitation method has excellent thermal stability. In addition, it also proves that the catalyst has strong oxygen replenishment capability. Only when the catalyst has excellent oxygen replenishment ability can the oxygen consumed in the reaction be replenished in time, allowing the oxygen cycle to continue. As shown in Figure 11b, the 0.5Pt/CFT-TS sample was operated continuously for four cycles to further evaluate the catalytic stability. The results show that the activity of the 0.5Pt/CFT-TS sample slightly increased in the first two cycles, and then the catalytic activity reached a stable level. T90 increased marginally from 163 °C to 168 °C [9,19].

Figure 11.
(a) The relationship between methane conversion and reaction time on 163 °C 0.5Pt/CFT-TS for 100 h. (b) The relationship between methane conversion on 0.5Pt/CFT-TS in four consecutive cycles and reaction temperature. Reaction conditions: 1% CH4, 4% O2, balanced N2, GHSV = 30,000 h−1, 30 h.
3.5. Mechanistic Analysis
3.5.1. Pt0-Mediated O2 Activation at Fe3+-Ce3+ Interfaces
Pt0 nanoparticles serve as the primary active sites for O2 dissociation, leveraging their d-orbital electron transfer capability to cleave the O–O bond into highly reactive oxygen species (*O). Transient DRIFTS analysis captures *O migration dynamics to Ptδ+-Oᵥ-Ce3+ junctions, confirming the accelerated C–H scission pathway proposed in Section 3.4. This process is facilitated by the electron-buffering effect of Ce3+/Oᵥ-enriched interfaces, which lowers the activation barrier for O2 splitting. The resultant *O radicals exhibit enhanced mobility due to the mesoporous confinement of the TS-derived catalyst. XPS analysis confirms electron redistribution at Pt sites, evidenced by a 0.8 eV binding energy shift toward Ptδ+-O states, validating the stabilization of *O intermediates.
3.5.2. Dynamic Oxygen Vacancy Regeneration via Fe3+/Ce4+ Redox Cycling
The Fe3+/Ce4+ redox couple drives sustainable oxygen vacancy (Oᵥ) regeneration through a reversible lattice oxygen-mediated equilibrium:
Fe3+ + Ce4+ + 0.5O2− ⇌ Fe2+ + Ce3+ + 0.5Oᵥ + 0.25O2
This cycle consumes lattice oxygen (O2−) to generate Oᵥ sites, with charge balance maintained by dual electron transfers: Fe3+ → Fe2+ (gains 1e−) and Ce4+ → Ce3+ (gains 1e−). H2-TPR data corroborates the lowered energy barrier (ΔT = 45 °C reduction peak shift), while O 1s spectra quantify the Oᵥ-derived chemisorbed oxygen (Oα) dominance in the TS catalyst (51.16%, Table 4) [19]. The sulfate-anchored Fe3+ sites (67.80% content, Table 3) further accelerate Oᵥ regeneration kinetics.
3.5.3. *O Migration and C–H Bond Cleavage at Ptδ+-Oᵥ-Ce3+ Sites
Activated *O species migrate to Ptδ+-Oᵥ-Ce3+ ternary junctions for methane C–H bond scission. This migration is optimized by the following:
(1) Brønsted acid sites (NH3-TPD: the lowest is 1.23 mmol/g, 0.5Pt/CFT-TB) polarizing CH4 molecules, weakening C–H bond energy; (2) Fe–Ti coordination (Ti 2p3/2 BE: 458.2 eV) enhancing Lewis acidity for CH4 adsorption; (3) Oᵥ-mediated pathways enabling nucleophilic attack by *O, forming •CH3 and OH− intermediates.
Kinetic analysis reveals an ultralow activation energy (46.77 kJ/mol, Table 6), significantly lower than conventional Pt/Al2O3 (~50 kJ/mol) [20], confirming rate-limiting *O migration rather than C–H dissociation. Complete mineralization occurs via OH− recombination with lattice oxygen, releasing H2O.
3.5.4. Ternary Synergy and Industrial Viability
The Pt0–Fe3+/Ce4+–Oᵥ triad operates synergistically:
(1) Pt0 dissociates O2 and cleaves C–H bonds; (2) Fe3+/Ce4+ sustains Oᵥ density via redox cycling; (3) Oᵥ bridges oxygen mobility and *O transfer.
This Mars–van Krevelen mechanism achieves complete CH4 conversion at 450 °C (Figure 9), with exceptional stability (98% conversion over 30 h at 163 °C, Figure 11). The broadened Pt(111) diffraction (39.8° in Figure 1) confirms Pt subnanoclusters (1.2 nm) with exceptional sintering resistance [21], underscoring potential for industrial low-temperature combustion applications.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates a precursor engineering strategy using titanium oxysulfate to construct a high-performance, low-Pt catalyst for ultralow-temperature methane combustion. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- Synergistic Catalyst Design: The use of TiOSO4 as a precursor enables the formation of a sulfate-rich, mesoporous CeO2–Fe2O3–TiO2 support, which enhances Brønsted acidity (1.23 mmol/g NH3), promotes oxygen vacancy formation (Oα = 51.16%), and facilitates ultrahigh dispersion of Pt nanoparticles (65% dispersion), effectively inhibiting sintering and stabilizing active sites.
- (2)
- Enhanced Redox Dynamics and Mechanism: The catalyst establishes a dynamic Pt0–Fe3+/Ce4+–OV interfacial synergy, enabling efficient redox cycling and lowering the activation energy for methane combustion to 46.77 kJ/mol. This synergy significantly reduces the oxygen vacancy regeneration barrier and enhances lattice oxygen mobility.
- (3)
- Superior Catalytic Performance: The catalyst achieves 90% CH4 conversion at 163 °C under industrial conditions (1% CH4, 4% O2, GHSV = 30,000 h−1), with complete conversion reached at 450 °C. It also exhibits excellent stability over 100 h, highlighting its potential for practical applications.
- (4)
- Broader Implications: This work provides a scalable and innovative strategy for designing low-noble-metal catalysts via precursor-mediated defect engineering, offering new insights into the role of sulfate in promoting multifunctional synergy for catalytic combustion and other energy-related processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.F.; methodology, X.F.; software, R.Z.; validation, X.Z. and X.X.; formal analysis, X.F.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, X.Z. and R.Z.; data curation, R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.X.; visualization, R.Z.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, X.F.; funding acquisition, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Special thanks are expressed to the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (cstc2021jcyj-msxmX1206): Research on efficient catalytic combustion of natural gas in gas-fired power plants and the Science and Technology Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJQN202102601): Research on efficient catalytic combustion of methane in natural gas power plants for financial support.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feng, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, D.; Tian, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Li, K. Progress and key challenges in catalytic combustion of lean methane. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 75, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.C.; Oton, L.F.; Oliveira, A.C.; Lang, R.; Otubo, L.; Bueno, J.M. On the role of size controlled Pt particles in nanostructured Pt-containing Al2O3 catalysts for partial oxidation of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 27329–27342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, H.-A.; Mekasuwandumrong, O.; Hülsey, M.J.; Fu, X.; He, Q.; Panpranot, J.; Yang, C.-M.; Yan, N. High-temperature flame spray pyrolysis induced stabilization of Pt single-atom catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 281, 119471. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumura, S.; Saita, K.; Miyakage, T.; Nagai, K.; Kon, K.; Toyao, T.; Maeno, Z.; Taketsugu, T.; Shimizu, K.I. Designing main-group catalysts for low-temperature methane combustion by ozone. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Rich Oxygen Vacancies in Bimetallic MnCo2O4.5 Spheres for Enhancing Lean Methane Catalytic Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Lian, S.; Li, J.; Sun, K.; Zhao, S.; Kim, Y.D.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Q.; et al. Engineering the oxygen vacancies enables Ni single-atom catalyst for stable and efficient C–H activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 314, 121516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantoko, D.; Khan, W.U.; Putra, A.F.P.; Shoaibi, A.A.; Chandrasekar, S.; Hossain, M.M. Fe–Ce–Al Catalysts for Decomposition of Methane to High Purity Hydrogen and High-Value Carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 18869–18878. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lim, T.H.; Lee, E.; Kim, D.H. Promoting the Methane Oxidation on Pd/CeO2 Catalyst by Increasing the Surface Oxy-gen Mobility via Defect Engineering. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 3706–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Luo, T.; Huang, K.; Ke, S.; Li, J.; et al. Nitrogen precursor-mediated construction of N-doped hierarchically porous carbon-supported Pd catalysts with controllable morphology and composition. Carbon 2020, 159, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Weaver, J.F. Low Temperature Activation of Methane on Metal-Oxides and Complex Interfaces: Insights from Surface Science. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorwart, T.; Greb, L. Reversible C–H bond silylation with a neutral silicon Lewis acid. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 11237–11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyitanga, T.; Kim, H. Synergistic effect of trimetallic-based CuxMox/Co1−xO nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide as high efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Ding, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Pt/doped mullite catalysts with abundant oxygen vacancies and enhanced oxygen migration capacity for NO oxidation. J. Catal. 2023, 423, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Lian, H.; Liu, J.; Li, X. Plasma catalytic steam methane reforming for distributed hydrogen production. Catal. Today 2019, 337, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wu, K.; Yang, J.; Liu, P.; Song, L.; Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; et al. The effect of existence states of PdOx supported by Co3O4 nanoplatelets on catalytic oxidation of methane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 148211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yang, L.; Ning, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, F. Catalytic combustion of low-concentration methane over transition metal oxides supported on open cell foams. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntida, A.; Rattanachartnarong, T.; Jongsomjit, B.; Sooknoi, T.; Weerachawanasak, P.; Praserthdam, S.; Praserthdam, P. Determining the role of oxygen vacancies in palmitone selectivity and coke formation over acid metal oxide catalysts for the ketonization of methyl palmitate. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 628, 118405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Khan, A.; Li, W.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, A. Influence of surface properties of transition metal oxides for permanganate activation: Key role of Lewis acid sites. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 55, 105368–105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Li, Z.; Shan, J.; Yu, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Lyu, S.; Li, J.; Li, L. Synergistic Pt-CeO2 interface boosting low temperature dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 318, 121809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D. Complete CO oxidation by O2 and H2O over Pt–CeO2−δ/MgO following lang-muir–hinshelwood and Mars–van Krevelen Mechanisms, respectively. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 11820–11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, V.; Palanisami, S.; Paneerselvam, J.; Elango, M.; Chakrabortty, S.; Ghosh, S.; Albaqami, M.D.; Mohammad, S.; Sangaraju, S. A new insight on surface chemistry and redox species of transition metal (Fe, Mn) doped CeO2-SnO2/Al2O3 nanocomposites for automobile emission control. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).