Abstract
Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with systemic health risks due to the production of acetaldehyde, a primary carcinogen that not only pollutes the environment but also endangers human health. In this study, a promising bacterial strain for biodegrading both ethanol and acetaldehyde was successfully isolated from the traditional fermented food Jiaosu and identified as Acetobacter ghanensis JN01 based on average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis. Initial ethanol of 1 g/L was completely biodegraded within 4 h, while initial acetaldehyde of 1 g/L was also rapidly removed at 2 or 1 h by whole cells or cell-free extracts (CEs) of JN01, respectively, which indicated that JN01 indeed has a strong ability in the biodegradation of both ethanol and acetaldehyde. Whole-genome sequencing revealed a 2.85 Mb draft genome of JN01 with 57.0% guanine–cytosine (GC) content and the key metabolic genes (adh1, adh2, and aldh) encoding involving alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), co-located with NADH dehydrogenase genes and ethanol-responsive regulatory motifs, supporting the metabolic pathway of transforming ethanol to acetaldehyde, and, subsequently, converting acetaldehyde to acetic acid. Furthermore, selected in vitro safety-related traits of JN01 were also assessed, which is very important in the development of microbial catalysts against both ethanol and acetaldehyde.
1. Introduction
Alcohol consumption remains a major global health concern, contributing to over 3.3 million deaths annually and imposing significant social and economic burdens [1]. In China, the prevalence of alcohol use has increased steadily in recent years, with the adult drinking rate reaching 39.8% in 2018 [2]. Ethanol is primarily metabolized in the liver through a two-step enzymatic process involving alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), producing acetaldehyde as a key intermediate [3]. Acetaldehyde is a highly reactive and toxic compound, classified as a Group 1 carcinogen due to its capacity to form DNA adducts, induce oxidative stress, and impair mitochondrial function [4]. Individuals with the ALDH2*2 allele, common in East Asian populations, exhibit reduced ALDH2 activity and impaired acetaldehyde clearance [5], leading to prolonged exposure to acetaldehyde, which has been associated with a significantly increased risk of esophageal cancer, head and neck cancers, and local carcinogenesis in the oral cavity [6,7,8]. Acute alcohol intoxication can lead to central nervous system suppression due to ethanol accumulation [9], while chronic exposure is associated with hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis [10]. Alcohol-associated liver disease is now one of the leading causes of liver-related mortality worldwide [11]. Oxidative stress and ferroptosis are key contributors to ethanol-induced hepatocellular injury [12]. Although some interventions, such as Angelica sinensis polysaccharides and zinc-glutathione complexes, have shown protective effects on animals, their clinical utility remains limited [13,14].
Current approaches for alcohol detoxification primarily rely on pharmacological and dietary interventions. Metadoxine, the most extensively studied drug for acute alcohol intoxication, enhances ADH and ALDH activities and has demonstrated clinical benefits in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis [15,16]. However, it has limited applicability in individuals with hepatic dysfunction and may cause gastrointestinal side effects [17]. In addition, dietary restrictions are often difficult to maintain over time due to behavioral and cultural barriers, and compliance remains a challenge [18,19]. In recent years, microbial strategies have emerged as a promising alternative. Engineered strains such as Lactococcus lactis expressing human ADH1B have been shown to reduce blood ethanol levels in mice within 2 h [20]. For acetaldehyde, recombinant Bacillus subtilis expressing ALDH variants has demonstrated improved biodegradation efficiency [21]. Several natural strains, including Lactobacillus fermentum, L. casei, and Bifidobacterium breve, also exhibit acetaldehyde-biodegrading activity [22,23]. Similarly, B. velezensis YW01 achieved complete biodegradation of 1 g/L acetaldehyde within 84 h [24], and recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ALDH has been evaluated for potential food applications [25]. However, these strains are generally limited to biodegrading either ethanol or acetaldehyde, and few have been reported to efficiently target both substrates. Safety assessments, including hemolysis, biogenic amine production, and resistance or virulence profiling, are often insufficient or lacking in current studies [26].
In this study, a bacterial strain capable of biodegrading both ethanol and acetaldehyde was isolated from the traditional fermented food Jiaosu and identified as Acetobacter ghanensis JN01. To support its application in microbial alcohol detoxification and probiotic development, we integrated whole-genome sequencing, metabolic gene identification, and phenotypic evaluation of safety traits to systematically evaluate JN01’s probiotic potential. These results provide a basis for the application of JN01 in microbial detoxification of both ethanol and acetaldehyde.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Identification of a Bacterial Strain for Biodegrading Both Ethanol and Acetaldehyde
The single colonies of JN01 were grown on a screening agar plate (Figure 1a), exhibiting creamy-white coloration with circular morphology and semi-transparent edges. Under 1000× magnification, JN01 cells appeared as small and short rods, typically existing as single cells or in pairs (Figure 1b).
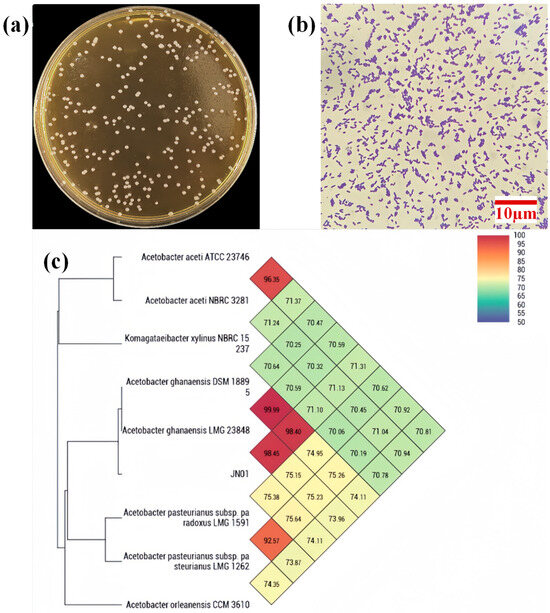
Figure 1.
(a) Single colonies of JN01 were grown on an agar plate; (b) morphology (1000×) of JN01 under the microscope; (c) heatmap generated indicating orthologous average nucleotide identity values calculated among related Acetobacter genera.
Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rDNA sequencing identified JN01 as a member of the Acetobacter genus. Species within the Acetobacter genus are known for their aerobic ethanol oxidation capabilities and have been widely applied in the food industry for acetic acid production [27]. Through average nucleotide identity (ANI), the genome of JN01 has 98.45% homology with the typical genome of A. ghanensis (Figure 1c), which was first described in 2006 [28]. A. ghanensis is a member of the acetic acid bacteria group, which are Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, and morphologically diverse microorganisms commonly found in fruit, insect intestines, and soil [29,30].
A strain of A. ghanensis isolated from Pennisetum showed synergistic effects on other bacterial strains during co-fermentation, significantly improving both the organoleptic properties and preservation quality of the silage. The findings demonstrate its potential as a premium microbial inoculant for forage processing [31]. Previous studies have proved that A. ghanensis can enhance intestinal barrier function by attenuating the modulatory effects of PT-gliadin with immunoregulatory and gluten-digestive properties [32]. A. pasteurianus BP2201 isolated from brewing substrates demonstrated highly efficient ethanol biodegradation capability and probiotic properties [33]. However, no studies have reported on the biodegradation of both ethanol and acetaldehyde by A. ghanensis.
2.2. Biodegradation of Ethanol by Whole Cells and Cell-Free Extracts (CEs) of JN01
Initial ethanol of 1 g/L could be completely biodegraded by whole cells and CEs of JN01 within 4 h (Figure 2). No acetaldehyde was detected during the biodegradation process of ethanol, indicating that its conversion is not the rate-limiting step of the ethanol biodegradation pathway.
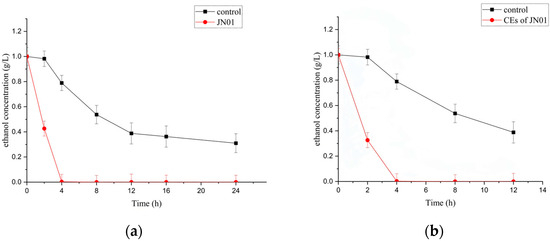
Figure 2.
Biodegradation of ethanol by whole cells (a) and CEs (b) of A. ghanensis JN01. “Control” refers to the same test conditions without whole cells or CEs.
Previous studies of Pediococcus acidilactici RH2712 exhibited a biodegradation efficiency of only 13.38% when incubated with 10% ethanol for 24 h [34]. The selected strain G-1 exhibited approximately 90% biodegradation of 5% ethanol over 24 h [35]. In comparison, recombinant B. subtilis fmb8 co-expressing ADH and ALDH achieved a 33% ethanol biodegradation ratio after 48 h at pH 4.0 [36]. Limosilactobacillus fermentum DACN611 achieved 90.87% biodegradation of 2.5% ethanol over 24 h, with the upregulation of ethanol metabolism-associated genes [37]. Compared with previously reported strains, both whole cells and CEs of JN01 were found to have stronger abilities for the biodegradation of ethanol (Figure 2). Furthermore, no acetaldehyde accumulation was observed, indicating a balanced and efficient ADH-ALDH system was involved, which is particularly significant considering the toxicity of acetaldehyde, a carcinogenic metabolite known to cause cytotoxic and genotoxic effects [38]. The ability to rapidly metabolize ethanol and avoid acetaldehyde accumulation may contribute to reducing ethanol-induced toxicity, suggesting promising applications in alcohol detoxification therapeutics.
2.3. Biodegradation of Acetaldehyde by Whole Cells and CEs of JN01
Initial acetaldehyde of 1 g/L could be completely biodegraded by whole cells and CEs of JN01 within 2 h and 1 h, respectively (Figure 3), demonstrating the strong acetaldehyde-biodegrading ability of JN01.
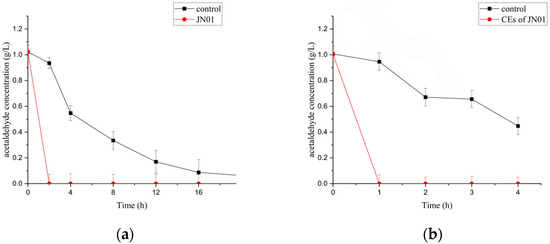
Figure 3.
Biodegradation of acetaldehyde by whole cells (a) and CEs (b) of A. ghanensis JN01. “Control” refers to the same test conditions without whole cells or CEs.
Acetaldehyde of 1 g/L was completely biodegraded by B. velezensis YW01 within 84 h under optimized conditions (pH 7.0, 38 °C) [24]. Similarly, B. velezensis LT-2 showed 89.77 ± 2.33% biodegradation efficiency for 1 g/L acetaldehyde in 22 h under optimized conditions [39]. Recombinant B. subtilis expressing the ALDHS273N mutant achieved 87.34% biodegradation of 100 mM acetaldehyde within 2 h [40]. Compared with that reported above, both whole cells and CEs of JN01 demonstrated markedly faster biodegradation rates. Moreover, the rate for biodegrading acetaldehyde is faster than that of ethanol biodegradation (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The observed biodegradation performance of JN01 and its CEs highlights their potential utility in developing strategies for the detoxification of both ethanol and acetaldehyde.
2.4. Overview of JN01 Genome Analysis
The draft genome of JN01 was assembled to a total length of 2,852,887 bp with an average guanine–cytosine (GC) content of 57.0%. The sequencing reads were assembled into 57 non-overlapping contigs, with the longest contig measuring 710,307 bp. The assembly N50 value was 354,630 bp, indicating that over 50% of the genomic content was contained within contigs of this length or longer. These characteristics are consistent with genome assemblies reported for other Acetobacter species.
A total of 2647 protein-coding genes were annotated in the Non-Redundant Protein Database (NR) (Figure 4a). Functional classification identified 1806 genes annotated in the Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) database (Figure 4b) and 871 genes annotated in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (Figure 4c). Among these, 829 genes were commonly annotated in both COG and KEGG databases, highlighting consistency in predicted metabolic functions. COG annotation revealed that genes were predominantly involved in amino acid transport and metabolism (173 genes), energy production and conversion (147 genes), and coenzyme metabolism (118 genes), reflecting active central metabolism and cofactor utilization. KEGG pathway analysis indicated gene enrichment in amino acid metabolism (150 genes), carbohydrate metabolism (139 genes), and cofactor/vitamin metabolism (134 genes). Genes associated with energy metabolism (120 genes), membrane transport (72 genes), and signal transduction (65 genes) were also identified, supporting the metabolic versatility and environmental adaptability of strain JN01.
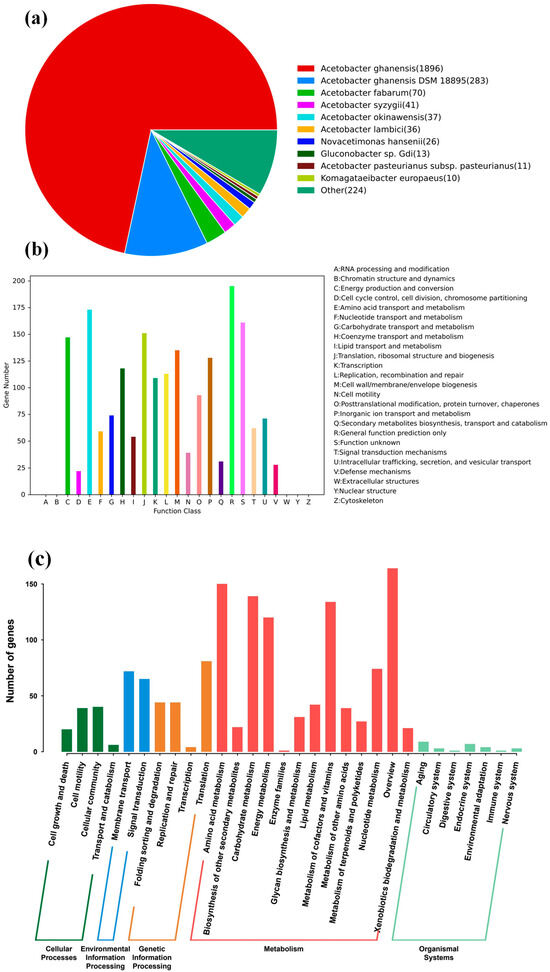
Figure 4.
Statistical legend of gene annotation classification of A. ghanensis JN01. (a) NR function classification; (b) COG function classification; (c) histogram of KEGG.
2.5. Pathway for Biodegrading Both Ethanol and Acetaldehyde by JN01
The genes and enzymes involved in the conversion of both ethanol and acetaldehyde were annotated based on the NR, COG, and KEGG analysis (Table 1). Among the annotated genes, adh1 (adh, ctg00005_01632), adh2 (adhA1, ctg00001_00447), and aldh (ald1, ctg00009_02255) were identified as key candidates encoding enzymes responsible for ethanol metabolism. Specifically, adh1 and adh2 encode ADH, while aldh encodes ALDH. Notably, these genes were localized within a 15 kb genomic region flanked by NADH dehydrogenase genes (ctg00005_01635-01638), suggesting coordinated regulation and efficient NAD+ recycling under ethanol-induced stress. Promoter analysis revealed AlcR-like motifs upstream of these genes, indicating potential inducible expression under ethanol exposure.

Table 1.
Genes and corresponding enzymes involved in the biodegradation of both ethanol and acetaldehyde. In the main text, adh1 refers to adhA1, adh2 to yqhD, and aldh to ald1, based on NR, COG, and KEGG annotations.
The proposed ethanol metabolic pathway is shown in Figure 5. Ethanol is first oxidized to acetaldehyde by ADH (EC 1.1.1.1), using NAD+ or NADP+ as electron acceptors. Acetaldehyde is subsequently converted to acetate by ALDH (EC 1.2.1.-). The resulting acetate can be further converted to acetyl-CoA via acetyl-CoA synthetase and fed into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. This sequential oxidation prevents the accumulation of a toxic intermediate, acetaldehyde. The organization of these genes, flanked by NADH dehydrogenase loci and potential ethanol-responsive elements, suggests coordinated regulation and efficient electron transfer during ethanol metabolism. Experimental results verified that initial ethanol of 1 g/L was completely biodegraded within 4 h (Figure 2), while initial acetaldehyde of 1 g/L was totally removed at 2 or 1 h (Figure 3) by whole cells or CEs of JN01, respectively, which indicated the genomic evidence for biodegrading both ethanol and acetaldehyde by JN01.
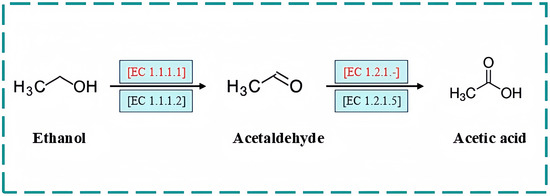
Figure 5.
Pathway for biodegrading both ethanol and acetaldehyde by A. ghanensis JN01. The pathways in red are annotated based on the KEGG analysis. [EC 1.1.1.1], ADH; [EC 1.2.1.-], ALDH.
In addition to the genomic and phenotypic results, the ability of A. ghanensis JN01 to simultaneously biodegrade both ethanol and acetaldehyde is considered to offer potential advantages for microbial detoxification processes. Compared with single-substrate systems, this dual-substrate biodegradation capacity may be more effective in reducing alcohol-derived intermediates in biological treatment or fermentation environments. Further studies are warranted to assess the enzymatic kinetics and stability under industrially relevant conditions.
2.6. Genetic Features of Probiotic Properties of A. ghanensis JN01
To evaluate the probiotic potential of JN01, the presence of key functional genes related to stress resistance, nutrient metabolism, and host interaction was examined based on genome annotation results. A total of 18 genes were identified with predicted roles associated with probiotic functionality (Table 2).

Table 2.
Potential genes related to different probiotic properties from A. ghanensis JN01 genome.
Genes involved in DNA replication and repair, such as dnaA, dnaG, and recA, were detected. These genes may contribute to genomic stability and stress tolerance, particularly during gastrointestinal transit [41]. The identification of the chaperonin gene groS suggests JN01’s capacity to resist acidic or oxidative conditions during gastrointestinal transit [42]. Genes associated with energy metabolism were identified, including, notably, a complete F0F1-ATP synthase operon (atpA, atpB, atpC, atpD, atpF, atpG), spanning contigs ctg00003 and ctg00010. These genes are essential for ATP production under anaerobic conditions, enhancing survival and metabolic activity in the host intestinal environment [43]. The presence of amino acid biosynthesis-related genes such as aspS and argS indicates the strain’s capacity to synthesize essential amino acids and support host nutritional metabolism [44]. Additionally, alsD, involved in the acetolactate pathway, has been associated with acid resistance and aroma compound biosynthesis, which may enhance palatability and survivability of probiotic formulations [45]. Transport-related genes such as satP, encoding a short-chain acid transporter, suggest potential involvement in acetate or lactate uptake, further linking to the strain’s metabolic integration in gut environments [46]. The presence of tyrS, encoding tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, reflects overall translational robustness and cellular homeostasis maintenance, often associated with stress resistance in probiotic strains [47]. Although these genes associated with probiotic functionality were identified in A. ghanensis JN01, its classification as a probiotic remains to be confirmed through further investigation.
2.7. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factor Evaluation
To assess the biosafety-related genomic features of A. ghanensis JN01, comprehensive genome mining was performed using the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) and the Virulence Factor Database (VFDB). No antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) were detected in the genome of JN01. These results are consistent with previous studies demonstrating that Acetobacter species generally lack transferable ARGs, suggesting a low risk of horizontal gene transfer in potential probiotic applications [48].
Genomic analysis using the Virulence Factor Database (VFDB) revealed no detectable genes encoding canonical virulence factors, including hemolysins, adhesins, or type III/IV secretion system components. Although genes related to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biosynthesis were identified, these are commonly found among Gram-negative bacteria and are not directly associated with pathogenicity [49]. The absence of both genotypic and phenotypic virulence markers, combined with the lack of resistance determinants, suggests a low risk of pathogenicity. However, its overall biosafety remains to be further investigated.
2.8. In Vitro Safety Assessment of A. ghanensis JN01
Phenotypic assays were conducted to further evaluate the safety of A. ghanensis JN01. Hemolytic activity was tested on Columbia blood agar with 5% defibrinated sheep blood. After incubation at 37 °C for 48 h, the strain showed no clear or green zones around the colonies (Figure 6a), indicating a γ-hemolytic phenotype. Genomic analysis corroborated this result by revealing the absence of annotated hemolysin-coding genes. Hemolysins are known to disrupt epithelial barriers and contribute to bacterial virulence. The absence of hemolytic activity suggests that JN01 has low pathogenic potential [50,51].

Figure 6.
(a) Hemolysis ability of A. ghanensis JN01; (b) determination of the ability of A. ghanensis JN01 to produce biogenic amines. From left to right are amino acid decarboxylase control broth, ornithine decarboxylase broth, lysine decarboxylase broth, and L-arginine decarboxylase broth.
The strain also tested negative for biogenic amine production. When inoculated into decarboxylase media containing lysine, ornithine, or arginine, no purple color change was observed after 24 h at 37 °C (Figure 6b), suggesting the absence of amino acid decarboxylase activity. Consistently, gene annotation revealed no presence of decarboxylase-related sequences typically responsible for the formation of histamine, tyramine, or putrescine. Biogenic amines such as histamine and tyramine can cause adverse physiological effects, including hypertension and gastrointestinal discomfort [52,53].
In addition, JN01 did not produce gelatinase on the nutrient gelatin medium. No liquefaction or halo formation was observed following treatment with saturated ammonium sulfate, indicating the lack of gelatin hydrolysis. Correspondingly, the genomic analysis did not identify genes encoding gelatinase or related extracellular proteases. Gelatinase is often associated with the degradation of host extracellular matrix components and is considered a virulence factor [54].
Taken together, these results indicate that A. ghanensis JN01 does not exhibit major virulence-related traits based on both in vitro assays and genomic evidence. However, whether the strain qualifies as a probiotic or meets relevant safety requirements remains to be further investigated.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples and Media
The target strain was isolated from Jiaosu, a traditional fermented food obtained from local villagers in Shandong Province, China. Acetaldehyde screening was performed using de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) medium (Solarbio Co., Beijing, China) supplemented with 5% (v/v) anhydrous ethanol (≥99.5%, Sigma-Aldrich, Beijing, China). For subculturing, beef extract–peptone agar medium was used, containing (per liter): beef extract 3.0 g, peptone 10.0 g, NaCl 5.0 g, and agar 15.0 g (pH 7.0). All media were sterilized at 121 °C for 20 min.
3.2. Isolation of Bacterial Strain for Biodegrading Both Ethanol and Acetaldehyde
To screen ethanol-tolerant strains, 1 mL of Jiaosu sample was serially diluted in sterile saline (0.85% NaCl). Aliquots (100 µL) of 10−5 to 10−8 dilutions were spread on ethanol-supplemented MRS agar and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. Colonies exhibiting growth were streaked onto beef extract–peptone agar for purity verification. Pure cultures were preserved in 20% (v/v) glycerol at −80 °C.
3.3. Determination Biodegradation Ability of Both Ethanol and Acetaldehyde by JN01
To investigate the biodegradation capacity of strain JN01, experiments were conducted using both whole cells and cell-free extracts (CEs). Cultures were grown to an OD680 of approximately 1.0, then harvested by centrifugation at 8000× g for 10 min at 4 °C (Pingke PK-16A, Changsha, China) and washed twice with sterile PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4). The final cell suspension was adjusted to approximately 108 CFU/mL based on plate counts. Ethanol or acetaldehyde was added to a final concentration of 1 g/L, and the suspensions were incubated at 30 °C with shaking at 200 rpm. At designated time points (0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h for ethanol; 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 h for acetaldehyde), 0.5 mL aliquots were withdrawn, mixed immediately with 50 μL of 0.1 M HCl to terminate the reaction, and stored at −20 °C until further analysis. Controls included heat-inactivated cells (80 °C for 30 min) and PBS without cells.
For preparation of CEs, cells from 200 mL of culture were collected and resuspended in 20 mL PBS. Cell disruption was performed by ultrasonication on ice using a Scientz JY92-IIDN processor (Ningbo, China) at 360 W for a total of 6 min (8 s on/4 s off, 5 cycles). The lysate was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane. Protein concentration was determined using a BCA assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China), and CEs were standardized to 10 mg/mL total protein. The protein concentrations of the CEs used were 0.77 mg/mL for ethanol and 0.91 mg/mL for acetaldehyde assays, as determined by the BCA assay. Biodegradation assays were conducted under the same conditions as whole-cell assays, and samples were collected at the same time points.
3.4. Analytical Methods
Ethanol concentration was quantified using an enzymatic assay kit (Solarbio Co., Beijing, China). Acetaldehyde was analyzed by HPLC (Shimadzu LC-20AT, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an Agilent ZORBAX SB-Aq column (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm). The mobile phase (acetonitrile: water = 65:35, v/v) flowed at 1.0 mL/min, with detection at 360 nm (column temperature: 30 °C; injection volume: 20 μL). All assays included triplicate biological replicates.
3.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Genome Annotation
Genomic DNA of strain JN01 was isolated using the MagPure Bacterial DNA Kit (D6361-02, Magen, Shanghai, China) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA concentration was measured with a Qubit 4.0 fluorometer (Thermo, Q33226, Waltham, MA, USA), and quality was verified by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The genomic DNA was fragmented randomly to obtain segments of approximately 200–400 bp. These fragments were end-repaired, A-tailed, ligated with adapters, and amplified by PCR to prepare the sequencing library. Magnetic beads were used to purify the library products. Library size was assessed via 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, and concentration was re-evaluated using the Qubit 4.0 fluorometer.
High-throughput sequencing was performed on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). Raw reads were processed using Trimmomatic v0.36 to eliminate adapter sequences and low-quality bases. The clean reads were assembled de novo using SPAdes v3.15, followed by gap closure using GapFiller v1.11. Gene prediction and annotation were carried out with Prokka v1.10. Functional annotation of protein-coding genes was conducted by comparison with the NR, COG, and KEGG databases. Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes were predicted using VFDB (http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs, accessed on 23 November 2024) and CARD (https://card.mcmaster.ca, accessed on 23 November 2024).
3.6. Identification of JN01
To determine the phylogenetic position of strain JN01, both average nucleotide identity (ANI) analysis and 16S rDNA sequence analysis were performed. For ANI analysis, the complete or draft chromosomal sequences of eight related strains were retrieved from the GenBank database. The ANI values between JN01 and these reference strains were calculated using the OrthoANI online tool (https://www.ezbiocloud.net/tools/orthoani, accessed on 19 May 2025). A heatmap was constructed based on the ANI results to visualize genomic similarity and infer evolutionary relationships among the strains. The Whole-Genome Shotgun project was deposited in GenBank under accession JBNZCO000000000.1.
3.7. Safety Assessment
A. ghanensis JN01 and S. aureus were cultivated on Columbia blood agar plates. After incubation at 37 °C for 48 h, signs of β-hemolysis (complete hemolysis), α-hemolysis (incomplete hemolysis), or γ-hemolysis (non-hemolysis) were observed [55].
Gelatinase activity was examined using gelatinase tubes (Hopebio, Qingdao, China). Tubes were inoculated with 100 μL of JN01 suspension (approximately 108 CFU/mL) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Following cooling at 4 °C for 30 min, no liquefaction was observed, indicating the absence of extracellular protease activity.
The biogenic amine production assay of A. ghanensis JN01 was performed using a micro-biochemical identification tube for bacteria (Hopebio, Qingdao, China). In summary, a volume of 100 µL of JN01 cell suspension was inoculated into the amino acid decarboxylase control broth, lysine decarboxylase broth, ornithine decarboxylase broth, and L-arginine decarboxylase broth. Subsequently, 300 µL of sterilized liquid paraffin was added to each tube, and the tubes were then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The color change in the broth was then observed. The presence of purple coloration in the broth indicated the production of the corresponding biogenic amine.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
All the analyses were carried out in three parallel experiments, and the results were expressed as means ± SD. The statistics were analyzed using Excel Office 2021 and Origin 2025.
4. Conclusions
A newly isolated A. ghanensis JN01 from the traditional fermented food Jiaosu exhibited a strong ability in the biodegradation of both ethanol and acetaldehyde. Whole-genome sequencing analysis revealed key genes involved in alcohol metabolism, and, first, ethanol was converted to acetaldehyde catalyzed by ADH (EC 1.1.1.1), and then acetic acid was produced from acetaldehyde catalyzed by ALDH (EC 1.2.1.-), respectively. In addition, in vitro safety assessment results indicated that JN01 had no hemolytic activity and did not possess gelatinase and amino acid decarboxylase activities. Taken together, these findings highlight the catalytic potential of JN01 for ethanol and acetaldehyde detoxification. However, the probiotic classification and safety of both the strain and its CEs remain to be further investigated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.; Methodology, H.L. and J.W.; Software, H.L. and X.D.; Validation, J.W. and K.L.; Investigation, H.L. and J.W.; Resources, J.W. and X.C.; Data Curation, H.L. and J.W.; Formal Analysis, J.W. and X.C.; Writing—Original Draft, H.L. and J.W.; Writing—Review and Editing, Q.X. and H.Y.; Visualization, H.L.; Project Administration, Q.X. and H.Y.; Supervision, Q.X. and H.Y.; Funding Acquisition, H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFE0118800).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Macfarlane, V.F.; Prentice, D.A.; Walsh, M.S. The Auckland alcohol detoxification outcome study: Measuring changes in quality of life in individuals completing a medicated withdrawal from alcohol in a detoxification unit. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 202, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lei, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Ren, J. Impact of changing the prevalence of smoking, alcohol consumption and overweight/obesity on cancer incidence in China from 2021 to 2050: A simulation modelling study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 63, 102215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Guo, H.; Ren, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Pathogenic Mechanisms and Regulatory Factors Involved in Alcoholic Liver Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Arsenic, metals, fibres, and dusts. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100C, 11–465. [Google Scholar]
- Shortall, K.; Djeghader, A.; Magner, E.; Soulimane, T. Insights into aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes: A structural perspective. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 659550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, L. The role of ALDH2 in tumorigenesis and tumor progression: Targeting ALDH2 as a potential cancer treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.C.; Guerrero-Morán, J.D.; González-Espinosa, C. Alcohol: Immunomodulatory Effects and Cancer. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2023, 75, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väkeväinen, S.; Tillonen, J.; Agarwal, D.P.; Srivastava, N.; Salaspuro, M. High salivary acetaldehyde after a moderate dose of alcohol in ALDH2-deficient subjects: Strong evidence for the local carcinogenic action of acetaldehyde. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.B.; Chen, Y.; Lu, K.K. Advancements in nursing research regarding acute alcohol poisoning. Asian J. Surg. 2024, 47, 5205–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, B.; Fu, Y.; Maccioni, L.; Gao, B. Alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, L.; Qian, S.; Chen, Y.; Ya, R.; Ma, N.; Hao, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Hepatic microRNA-320 restrains ferroptosis to mitigate acute-on-chronic alcohol-induced liver injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Deng, S.; Wu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Mei, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide could alleviate the gastrointestinal damage in alcoholic fatty liver disease mice: Regulation of alcohol metabolism and enhancement of short-chain fatty acids utilization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 338, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Ba, T.; Luo, Z.; Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Kang, Y.J. Zinc-glutathione in Chinese Baijiu prevents alcohol-associated liver injury. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirijello, A.; Addolorato, G. Treatment of acute alcohol intoxication: The role of metadoxine. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 110, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-de la Tijera, F.; Servín-Caamaño, A.I.; Cruz-Herrera, J.; Serralde-Zúñiga, A.E.; Abdo-Francis, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Reyes, G.; Pérez-Hernández, J.L. Treatment with metadoxine and its impact on early mortality in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Martínez, M.C.; Díaz Martínez, A.; Villamil Salcedo, V.; Cruz Fuentes, C. Efficacy of metadoxine in the management of acute alcohol intoxication. J. Int. Med. Res. 2002, 30, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberman, Y.; Hajnal, A. Diet, diet access, and metabolic physiology as critically understudied factors in rodent models of alcohol intake: A commentary on Emous et al. (2025). Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2025, 49, 1111–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamurcu Varol, P.; Kaya, E.; Alphan, E.; Yilmaz, Y. Role of intensive dietary and lifestyle interventions in the treatment of lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yan, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, R.; Zheng, K.; Jin, W.; Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, M. Oral Probiotic Expressing Human Ethanol Dehydrogenase Attenuates Damage Caused by Acute Alcohol Consumption in Mice. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0429422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, R.; Fang, Y.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z. Optimal Secretory Expression of Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase from Issatchenkia terricola in Bacillus subtilis through a Combined Strategy. Molecules 2022, 27, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Son, J.H.; Chun, H.N.; Yang, J.O.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, S.K. Effect of Lactobacillus fermentum MG590 on alcohol metabolism and liver function in rats. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 13, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.J.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, E.O.; Lee, S.O.; Chung, Y.J.; Chung, M.J.; Chae, S.W. Regulation of alcohol and acetaldehyde metabolism by a mixture of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species in human. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Song, M.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. Genome analysis of a newly isolated Bacillus velezensis-YW01 for biodegrading acetaldehyde. Biodegradation 2024, 35, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, J.J.; Liu, X.X.; Shi, H.L.; Lu, Y.F.; Shi, J.Y.; Tang, C.D. High-level expression of an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and preliminary evaluation of its potential as a functional food additive. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodmann, T.; Endo, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Vinderola, G.; Kneifel, W.; de Vos, W.M.; Gómez-Gallego, C. Safety of novel microbes for human consumption: Practical examples of assessment in the European Union. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, H.S. Classification of acetic acid bacteria and their acid resistant mechanism. AMB Express 2021, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleenwerck, I.; Camu, N.; Engelbeen, K.; De Winter, T.; Vandemeulebroecke, K.; De Vos, P.; De Vuyst, L. Acetobacter ghanensis sp. nov., a novel acetic acid bacterium isolated from traditional heap fermentations of Ghanaian cocoa beans. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengun, I.Y.; Kilic, G.; Charoenyingcharoen, P.; Yukphan, P.; Yamada, Y. Investigation of the microbiota associated with traditionally produced fruit vinegars with focus on acetic acid bacteria and lactic acid bacteria. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoń, A.; Łepecka, A.; Szymański, P.; Neffe-Skocińska, K. The Effect of the Use of the Beneficial Acetic Acid Bacteria Starter Cultures on the Microbiological and Physicochemical Quality of Raw Ripening Sausages. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhou, X.G.; Peng, S.P.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.Y.; Liu, G.H. Study on the identification of dominant strains and influence on fermentation quality of Pennisetum giganteum silage. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2025, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Doguer, C.; Akalan, H.; Tokatlı Demirok, N.; Erdal, B.; Mete, R.; Bilgen, T. Protective effects of Acetobacter ghanensis against gliadin toxicity in intestinal epithelial cells with immunoregulatory and gluten-digestive properties. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Chu, W. Alcohol degradation, learning, and memory-enhancing effect of Acetobacter pasteurianus BP2201 in Caenorhabditis elegans model. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, P.; Lin, X.M.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, T.T.; Peng, Y.Z. Screening, identification, and anti-alcoholic and anti-drunken efficacy evaluation of ethanol-degrading lactic acid bacteria. China Brew. 2024, 43, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.L.; Jin, Y.; Hu, M.Q.; Zhao, F.L. Screening of ethanol-degrading strains from Siraitia grosvenorii endophytes and optimization of fermentation conditions. China Brew. 2021, 40, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Co-expression of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis for alcohol detoxification. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Song, J.; Suo, H. Degradation effects and mechanisms of Limosilactobacillus fermentum on ethanol. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 10283–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobh, A.; Loguinov, A.; Stornetta, A.; Balbo, S.; Tagmount, A.; Zhang, L.; Vulpe, C.D. Genome-Wide CRISPR Screening Identifies the Tumor Suppressor Candidate OVCA2 As a Determinant of Tolerance to Acetaldehyde. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 169, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.Y.; Yan, R.Y.; Zheng, B.Y.; Yang, K.Y.; Guo, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M.L.; Wu, L.T. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions of an Acetaldehyde-Degrading Bacterium Bacillus velezensis LT-2. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 3345–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, R.; Xia, X.; Zhang, J. Engineered acetaldehyde dehydrogenase for the efficient degradation of acetaldehyde. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, B.M.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Comparative survival of probiotic lactobacilli spray-dried in the presence of prebiotic substances. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Keersmaecker, S.C. Genes and molecules of lactobacilli supporting probiotic action. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 72, 728–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Alegría, Á.; Bron, P.A.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lemos, J.A.; Linares, D.M.; Ross, P.; Stanton, C.; et al. Stress physiology of lactic acid bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 837–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, S.; Malik, K.A.; Kang, S.A.; Kim, H.Y. Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Meng, Z.; Ma, X.L.; Zhao, S.M.; An, Y.; Xiao, Z.J. Characterization and regulation of the acetolactate synthase genes involved in acetoin biosynthesis in Acetobacter pasteurianus. Foods 2021, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douillard, F.P.; de Vos, W.M. Functional genomics of lactic acid bacteria: From food to health. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13 (Suppl. 1), S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, I.; Sybesma, W.; Phothirath, P.; Ananta, E.; Mercenier, A. Application of probiotics in food products—Challenges and new approaches. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Fu, Y.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M. Genomic, Antimicrobial, and Aphicidal Traits of Bacillus velezensis ATR2, and Its Biocontrol Potential against Ginger Rhizome Rot Disease Caused by Bacillus pumilus. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsutani, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Hirakawa, H.; Shiwa, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Okamoto-Kainuma, A.; Ishikawa, M.; Kataoka, N.; Yakushi, T.; Matsushita, K. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Closely Related Acetobacter pasteurianus Strains Provides Evidence of Horizontal Gene Transfer and Reveals Factors Necessary for Thermotolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, e00553-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaadany, K.; El-Sayed, A.I.; Awad, S. Identification, Safety Assessment, and Antimicrobial Characteristics of Cocci Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Traditional Egyptian Dairy Products. Foods 2024, 13, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, Q. In vitro investigation on lactic acid bacteria isolated from Yak faeces for potential probiotics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 984537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, D.M.; del Río, B.; Ladero, V.; Martínez, N.; Fernández, M.; Martín, M.C.; Álvarez, M.A. Factors influencing biogenic amines accumulation in dairy products. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazgan, H.; Kuley, E.; Gökmen, T.G.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, F. The antimicrobial properties and biogenic amine production of lactic acid bacteria isolated from various fermented food products. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanasidou, C.; Asimakoula, S.; Sameli, N.; Fanitsios, C.; Vandera, E.; Bosnea, L.; Koukkou, A.-I.; Samelis, J. Safety Evaluation, Biogenic Amine Formation, and Enzymatic Activity Profiles of Autochthonous Enterocin-Producing Greek Cheese Isolates of the Enterococcus faecium/durans Group. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Park, S.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Wang, M.-H. Isolation and Characterization of Enterococcus faecium from Fermented Korean Soybean Paste with Antibacterial Effects. Fermentation 2023, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).