Scalable Preparation of High-Performance Sludge Biochar with Magnetic for Acid Red G Degradation by Activating Peroxymonosulfate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
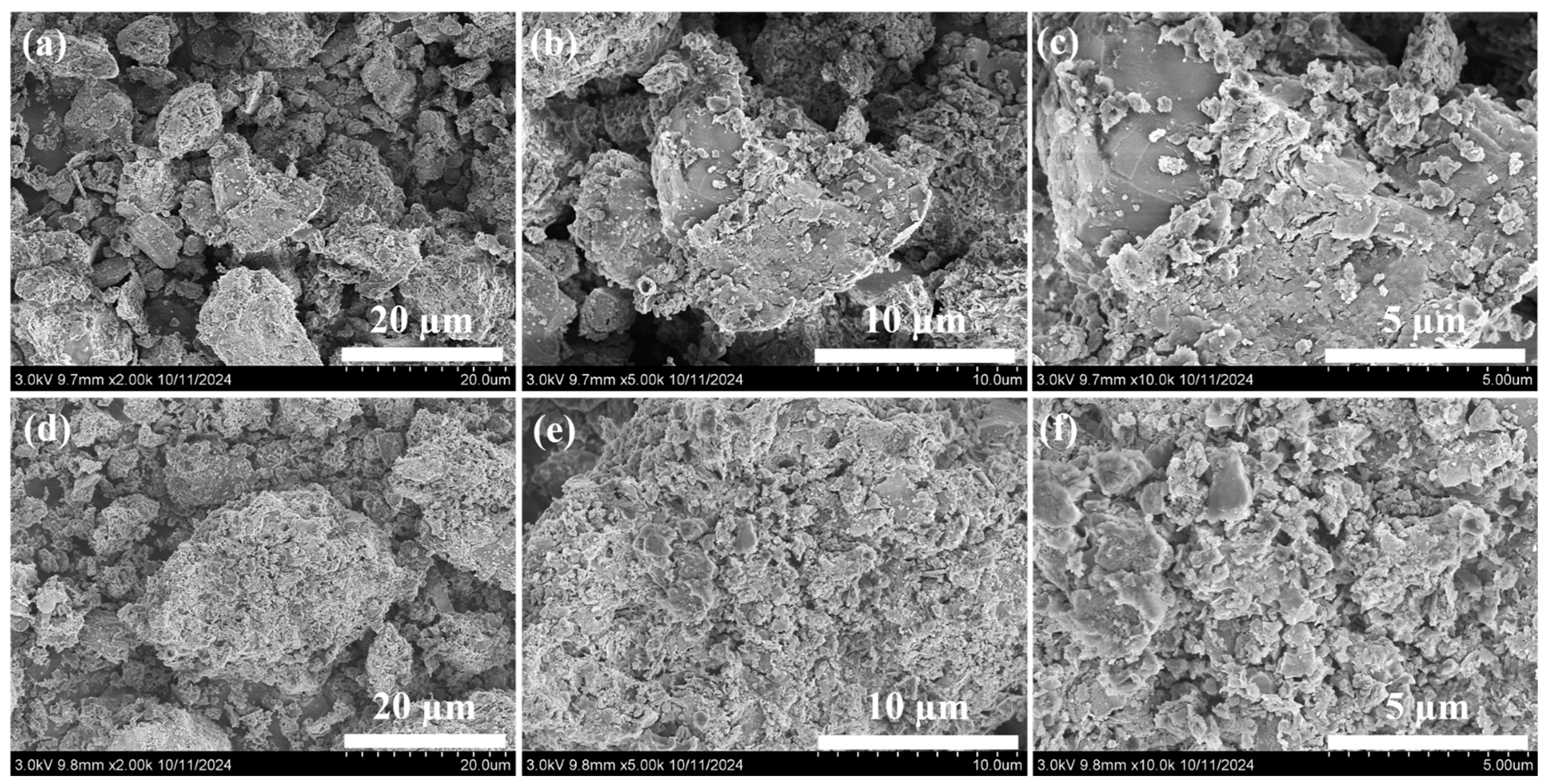
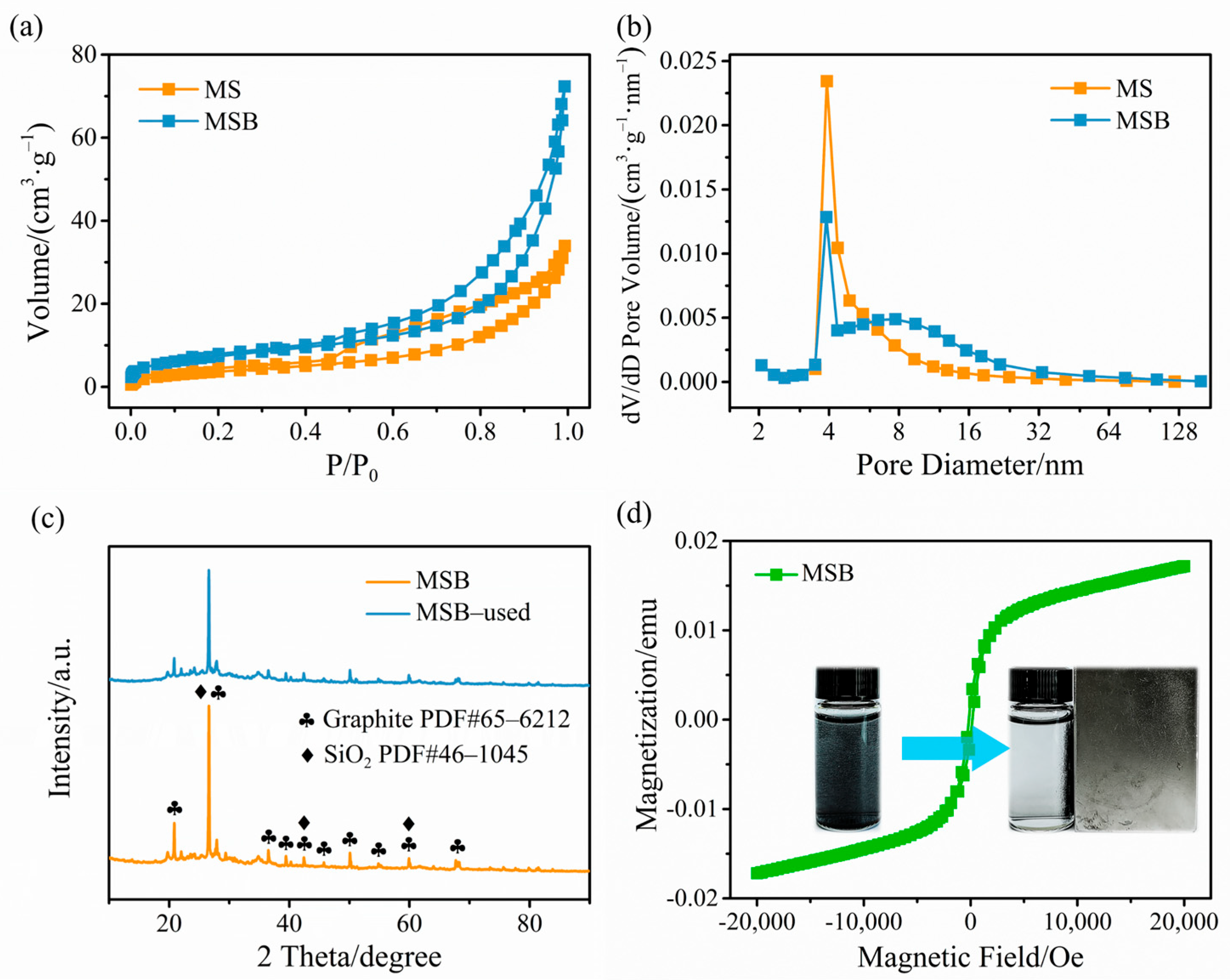
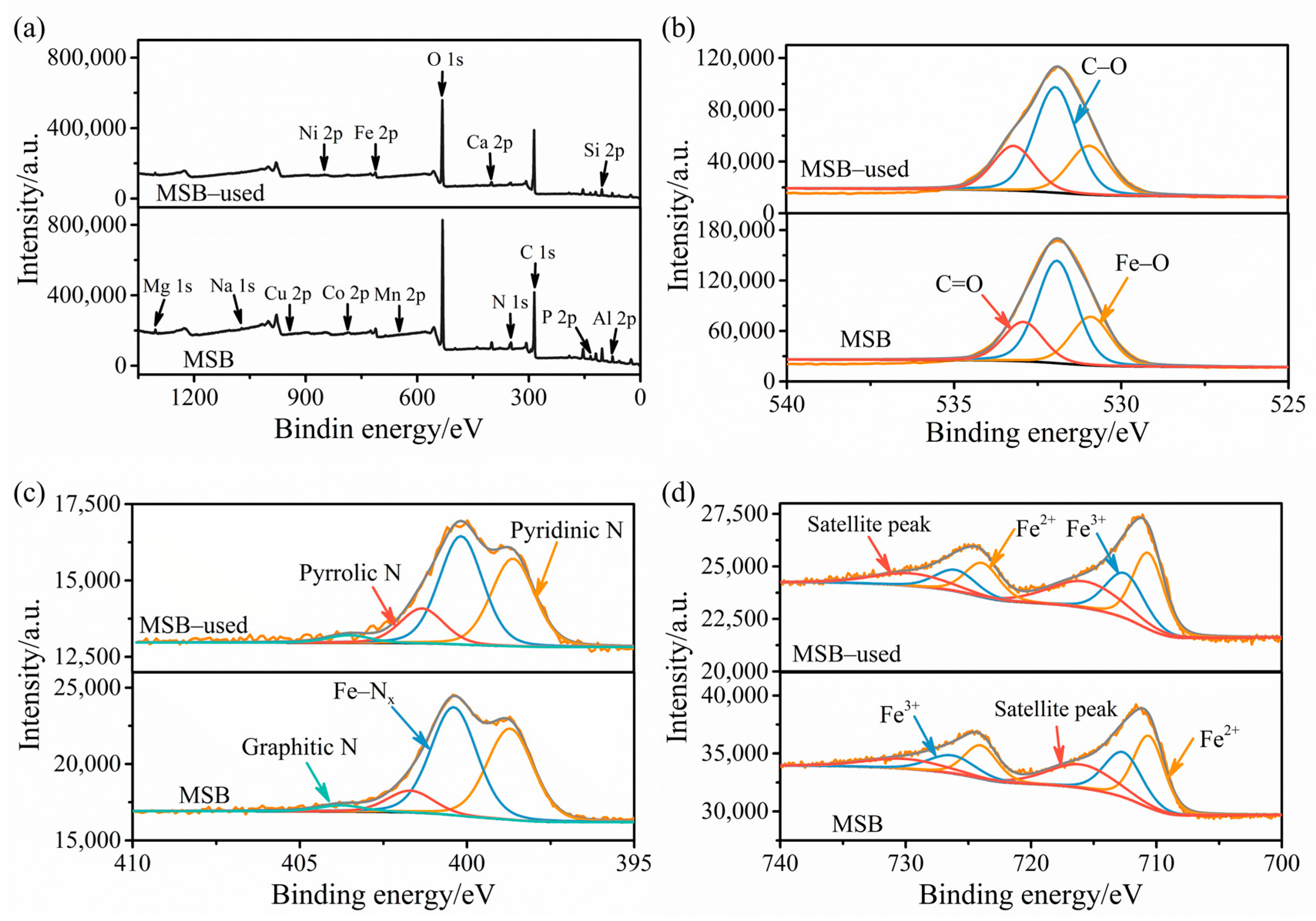
2.1. Characterization of MSB
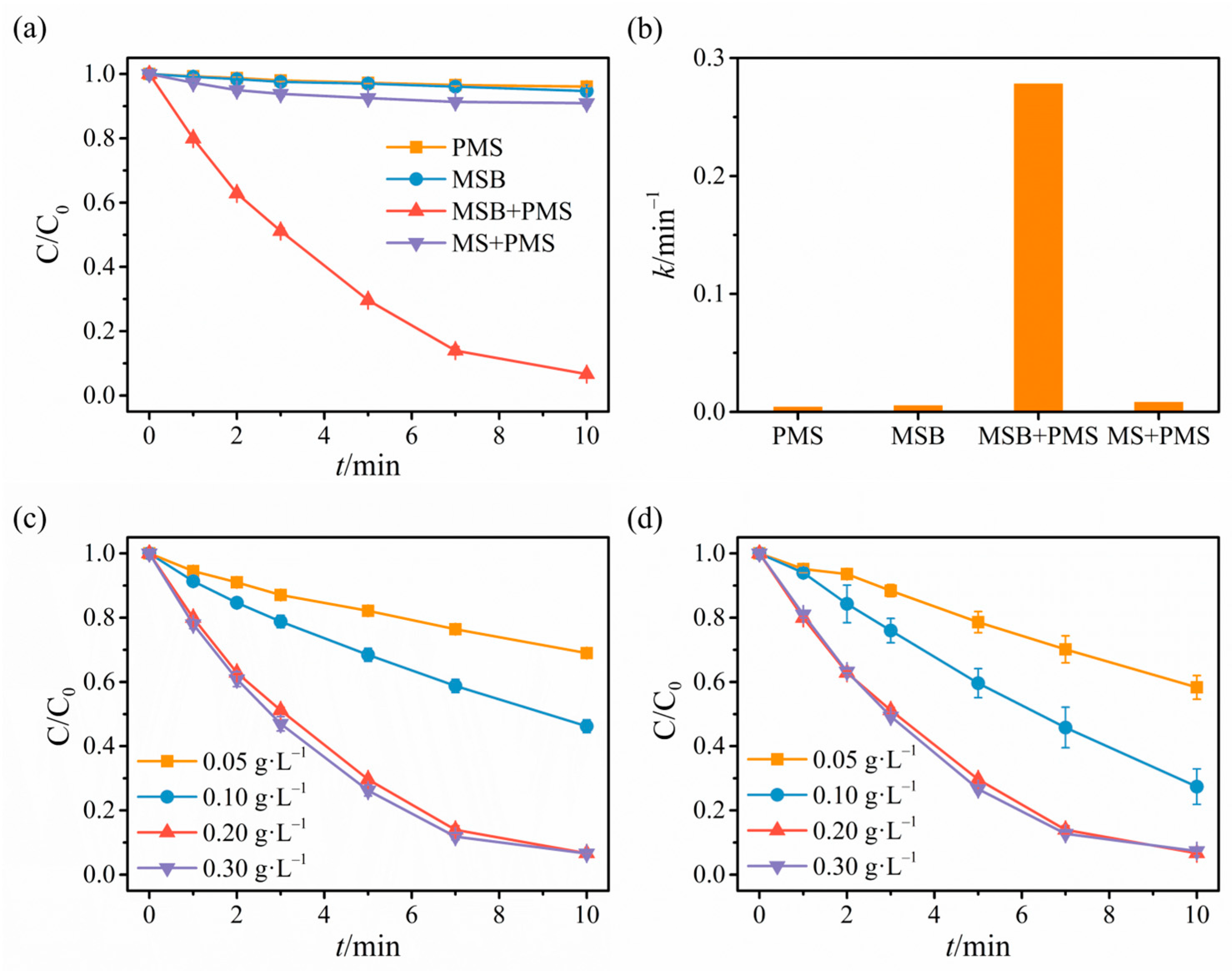
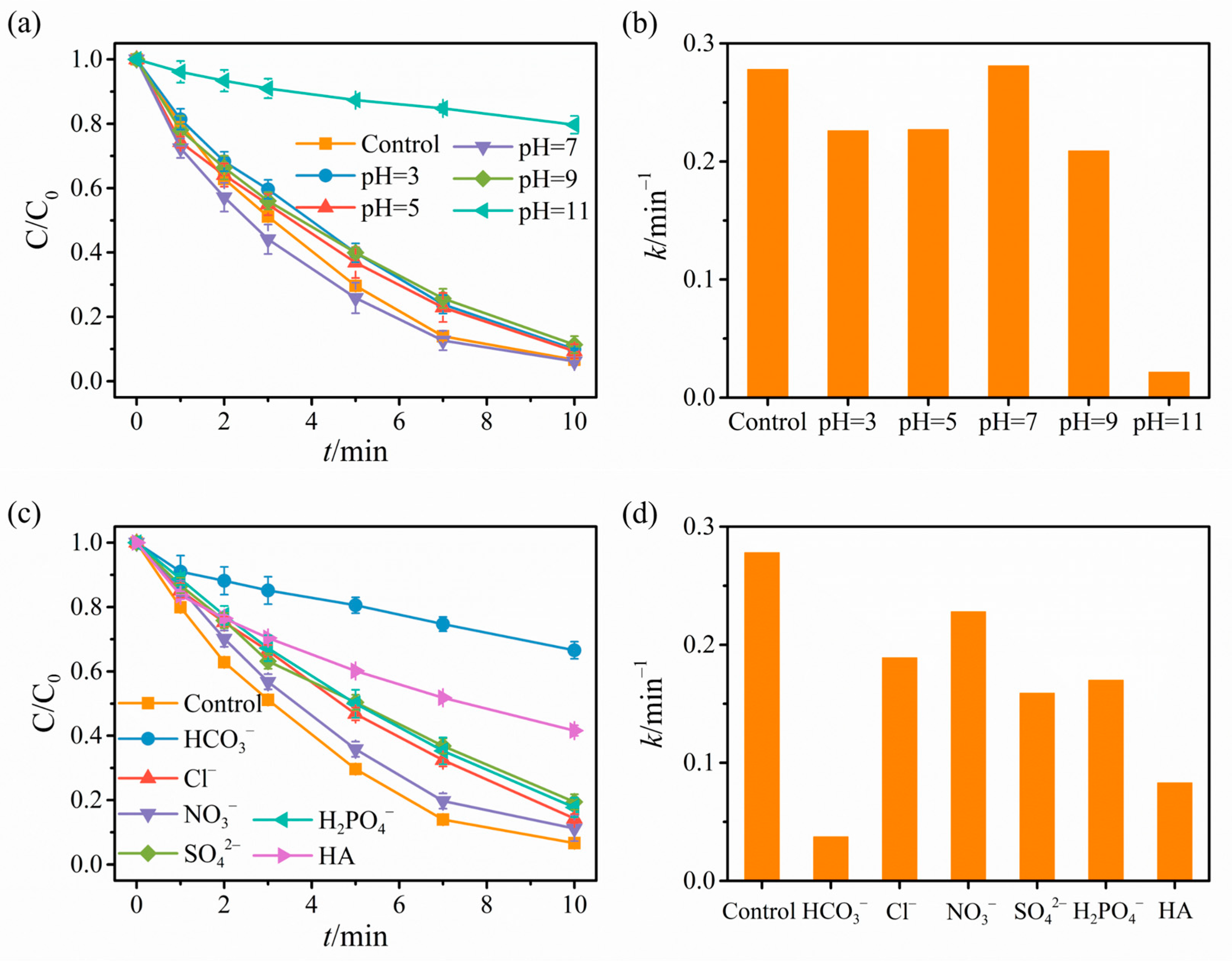
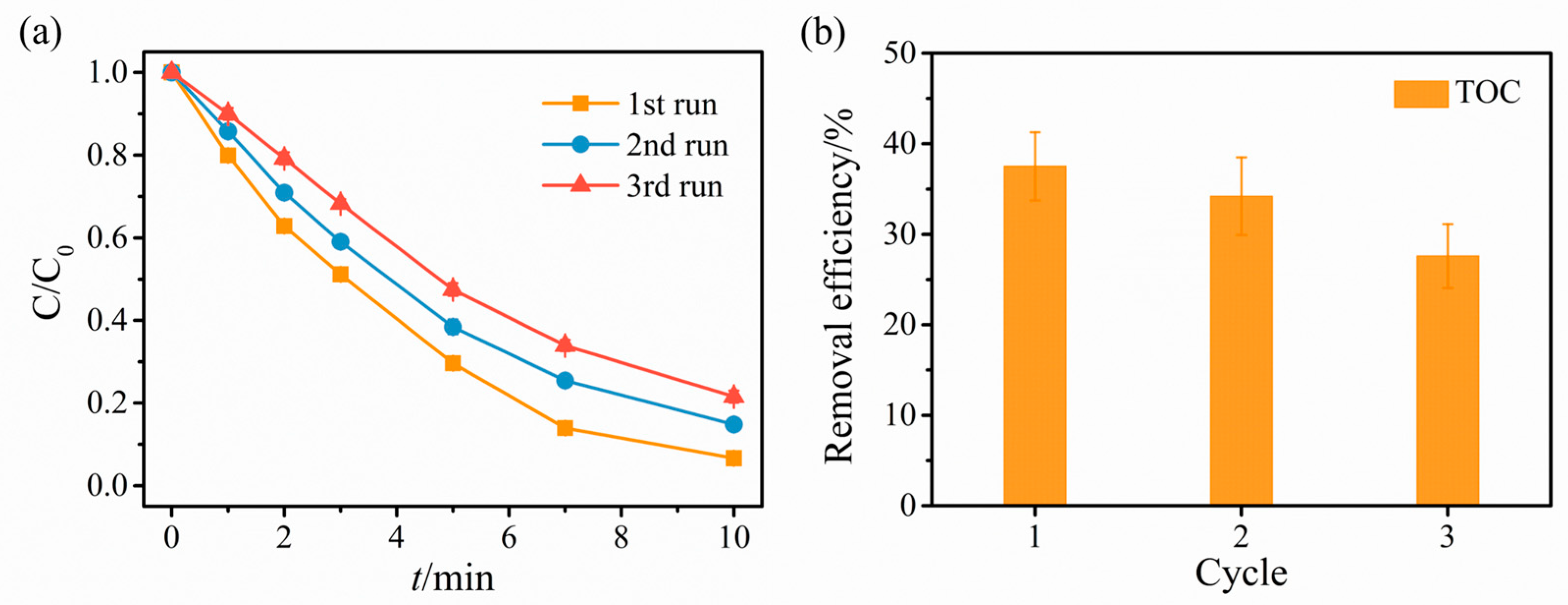
2.2. Catalytic Degradation Results
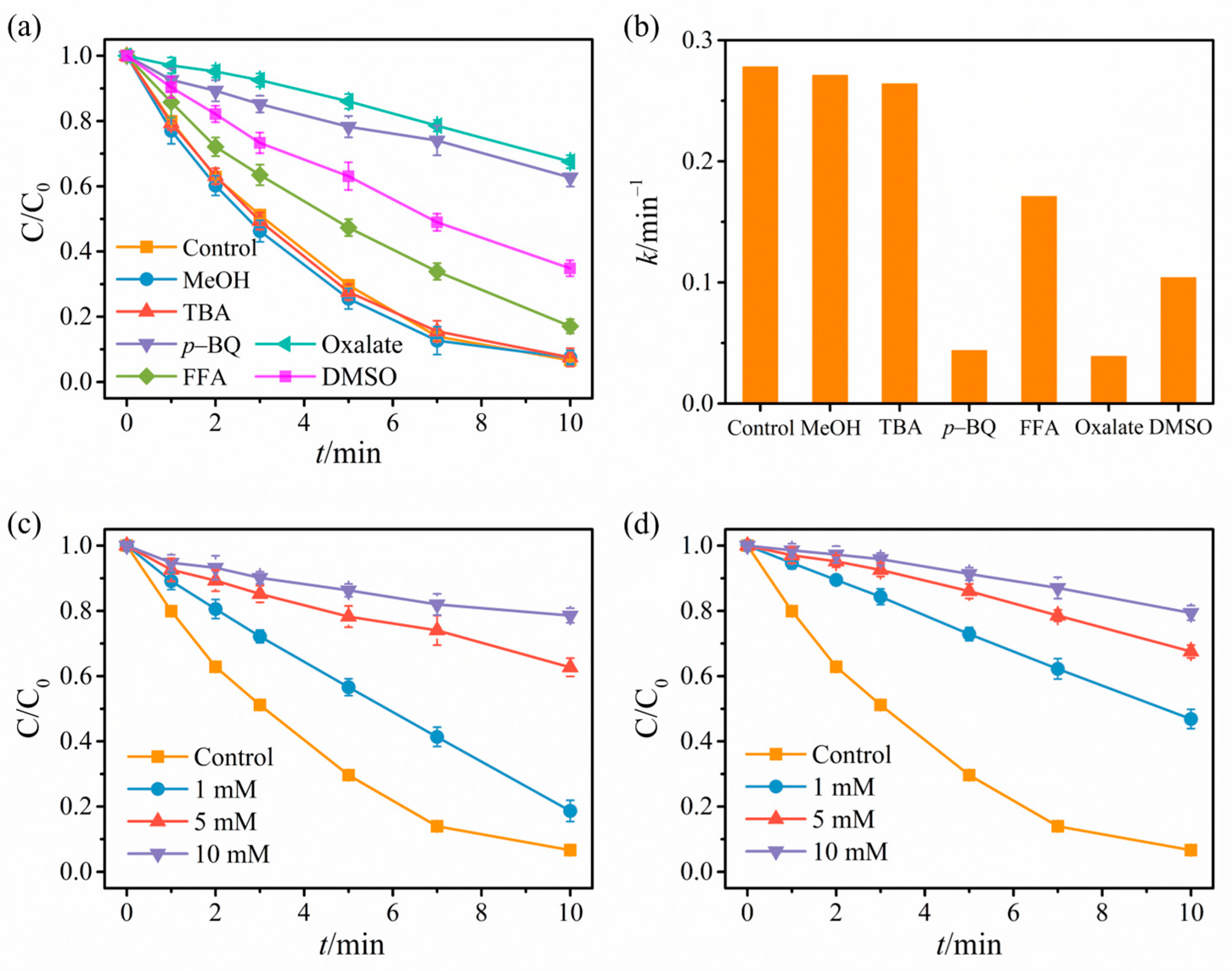
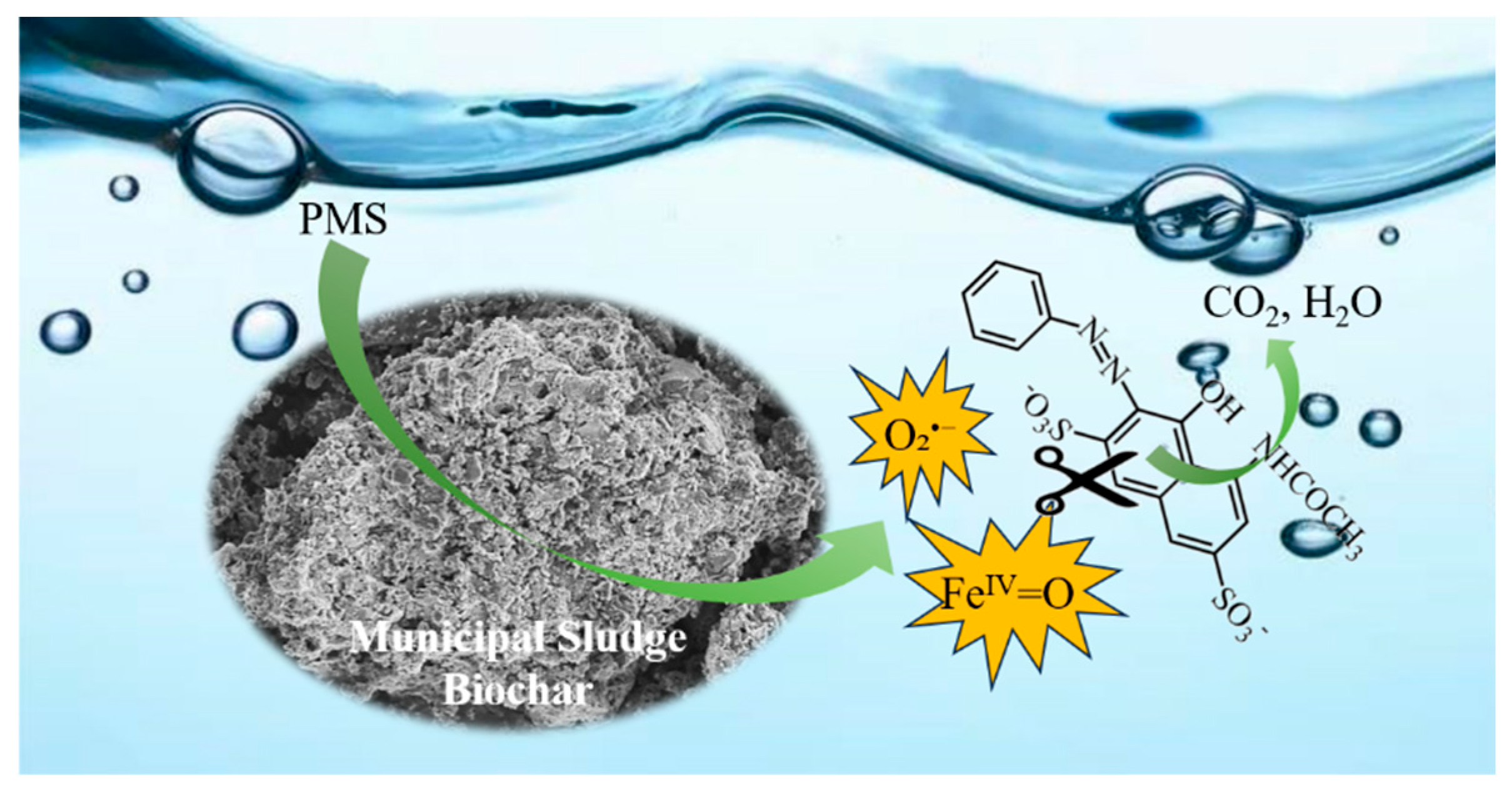
2.3. Revelation of Reactive Substances and Catalyst Mechanism
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of Sludge Biochar
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Catalytic Degradation of ARG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, Z.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, C.; Xu, G. Study on the process technology of energy saving and consumption reducing for municipal sludge-based biochar. Renew. Energ. 2024, 220, 119606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s characteristics and speciation and environmental risks of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochars. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2022, 26, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; An, B.; Liang, Z. Phosphate Removal by Ca-Modified Magnetic Sludge Biochar Prepared by a One-Step Hydrothermal Method. Catalysts. 2023, 13, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Zeng, S.; Liu, L. Potential removals of tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole by iron-loaded sludge biochar. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 103962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Khan, M.T.; Zubair, M.; Bilal, M.; Sajid, M. Removal of pharmaceuticals from water using sewage sludge-derived biochar: A review. Chemosphere. 2022, 289, 133196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Yao, X.; Tian, T.; Zhao, C.; Tao, S.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, M. Large-Scale Preparation of Granular Sludge@MOF-Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon Catalysts for Advanced Oxidation Process: Preparation Process and Intrinsic Degradation Mechanism. Catalysts. 2025, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Zhou, H.; Liang, S.; Lei, X.; Deng, X. Sludge-derived biochar applied in peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation: Regulation of active sites and synergistic production of reaction oxygen species. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 171, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Lins, P.V.d.S.; Oliveira, L.M.T.d.M.; Sepulveda, P.; Ighalo, J.O.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Meili, L. Sewage sludge-derived biochar for the adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Fang, W.; Liang, Q.; Xing, Y.; Sun, M.; Luo, H. Synthesis of Fe-doped sludge biochar from Fenton sludge for efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate in tetracycline hydrochloride degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wei, L.; Ning, C.; Zhang, F.; Cui, J.; Xiangli, P. Highly-efficient persulfate activation by nitrogen-doped biochar derived from dewatered sewage sludge for 2,4-dichlorophenol removal: Process and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xue, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Y. Enhanced removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics by peroxydisulfate activated with N-doped sludge biochar: Performance, mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zou, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Hao, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived magnetic biochar for pollutant removal: Performance, applicability, and synergetic mechanism of iron species and carboxylated biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C. Periodate activation by a Fenton sludge biochar for enhanced tetracycline degradation: Identification of key factors through machine learning. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 176, 114295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, F.; Liang, L.; Li, N.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H. Enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge via peroxymonosulfate activation process initiated by magnetic biochar derived from iron-rich sludge. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 39, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Cao, S.; Dou, J.; Chen, R.; Hu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Li, M.; et al. Sludge-based biochar preparation: Pyrolysis and co-pyrolysis methods, improvements, and environmental applications. Fuel. 2024, 373, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Shi, W. Iron and nitrogen modified sludge biochar efficiently activated persulfate for mineralization of sulfamethoxazole in groundwater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Yang, R.; Liu, M.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, W. A highly-efficient peroxymonosulfate activator using a sewage sludge derived biochar supported cobalt oxide: Mechanism and characteristics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 192, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, R.; Kong, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H. Preparation of magnetically recyclable hierarchical porous sludge-pine needle derived biochar loaded CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for rapid degradation of tetracycline by activated PMS. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, D.; Cheng, M.; Wei, Z.; Du, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.; Lei, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, R. Application of sludge biochar nanomaterials in Fenton-like processes: Degradation of organic pollutants, sediment remediation, sludge dewatering. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xu, F. Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by porous Co-doped LaFeO3 for organic pollutants degradation in water. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 297, 122077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Ma, F.; Xu, F. Green synthesis of poly(pyrrole methane) for enhanced adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2021, 590, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Si, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, N. Sludge-derived biochar as efficient persulfate activators: Sulfurization-induced electronic structure modulation and disparate nonradical mechanisms. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 279, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M. Degradation of tetracycline by peroxydisulfate activation on sludge-derived biochar modified with tannin extract. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 173, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G. Green synthesis of poly(pyrrole methane)-based adsorbent for efficient removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Fang, K.; Liu, H.; Pan, X.; Jin, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L. Facile synthesis of carbon nitride nanotube confined nano Fe0 for boosting activation of peroxymonosulfate towards tetracycline removal. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2025, 38, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Shan, Z.; Tang, L.; Chen, C.; Lan, Y.; Li, W. Fabrication of magnetic cobalt-iron composite moored on carbon derived from cigarette butts (Co-Fe@CCB) for peroxymonosulfate activation to efficiently degrade Rhodamine B. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xin, Y.; Lv, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Z. In-situ construction of mesoporous CuCo2O4 decorated CNTs networks as a long-lasting peroxymonosulfate activator for rapid removal of aqueous micropollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, J.; Wu, J.; Miao, L. Mesoporous carbon framework supported Fe-Cu-Mn oxides as an efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for the control of harmful algal blooms: Synergism of Fe-Cu-Mn and role of mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lai, L.; Yu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lo, V.; Roy, A.; Chivers, B.; Zhong, X.; Wei, L.; et al. Carbon/iron by-product from catalytic methane decomposition as recyclable Fenton catalyst for pollutant degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Song, W.; Ying, Y.; Liang, S.; Miao, L.; Cao, J.; Lv, W.; et al. M−N3 Configuration on Boron Nitride Boosts Singlet Oxygen Generation via Peroxymonosulfate Activation for Selective Oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2024, 63, e202402669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.L.; He, C.S.; Lai, L.D.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.L.; Xiong, Z.K.; Mu, Y.; Pan, Z.C.; Yao, G.; et al. Activating peroxymonosulfate by N and O co-doped porous carbon for efficient BPA degradation: A re-visit to the removal mechanism and the effects of surface unpaired electrons. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 314, 121390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Akiyama, K.; Bingham, P.A.; Kubuki, S. Elucidating the Mechanistic Origin of a Spin State-Dependent FeNx-C Catalyst toward Organic Contaminant Oxidation via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M. Rapid removal of ofloxacin with peroxymonosulfate activation process mediated by Co3O4/Sludge-derived biochar composite: Unveiling the enhancement of biochar. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, W.; Ma, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, H.; Shi, F. Efficient tetracycline hydrochloride degradation via peroxymonosulfate activation by N doped coagulated sludge based biochar: Insights on the nonradical pathway. Environ. Res. 2025, 266, 120554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Gao, M.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, P.; Ma, D. Activation of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt embedded in layered delta-MnO2 for degradation of dimethyl phthalate: Mechanisms, degradation pathway, and DFT calculation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 130901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Guo, X.; Lu, X.; Li, R.; Hu, H.; Nie, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, R.; Zhu, M.; Hei, S.; et al. Boosting peroxymonosulfate activation by a novel bifunctional core-shell nanoreactor MnFe2O4@HZO for nitrilotris-methylenephosphonic acid removal. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 330, 122508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, S.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X. Aluminum-based layered metal oxides activating peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol A degradation via surface-bound sulfate radicals and singlet oxygen. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y. Co3O4/C-PC composite derived from pomelo peel-loaded ZIF-67 for activating peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to degrade ciprofloxacin. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ji, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Cui, N.; Guan, S.; Li, J.; et al. Boron amplifies the cation vacancy effect to enhance multi-pathway degradation of organic pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 371, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Guo, Y.; Du, S.; Sui, M. Ultrafast Fenton-like reaction using a peroxymonosulfate-mediated confined-Fe0 catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 358, 124442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; You, Y.; Zhong, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, R.; Huang, Z. Green synthesis of manganese-cobalt-tungsten composite oxides for degradation of doxycycline via efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shan, C.; Pan, B. Fe(III)-Doped g-C3N4 Mediated Peroxymonosulfate Activation for Selective Degradation of Phenolic Compounds via High-Valent Iron-Oxo Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, W.; Miao, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. Generation of FeIV=O and its Contribution to Fenton-Like Reactions on a Single-Atom Iron-N-C Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2023, 62, e202218510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Constructing carbon nitride embedded Fe0 for efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate towards organic pollutants degradation in water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.W.; Guo, P.C.; Yu, H.Q. Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn1.8Fe1.2O4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12611–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | SBET a/(m2/g) | Sexter b/(m2/g) | Vtotal c/(cm3/g) | Vmicro d/(cm3/g) | Vmeso e/(cm3/g) | D f/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 14.19 | 18.03 | 0.036 | 0 | 0.036 | 10.11 |
| MSB | 27.04 | 27.97 | 0.067 | 0 | 0.067 | 9.93 |
| Sample | K | O | C | Si | Al | N | Fe | Mg | P | Ca | Na | Cu | Ni | Co | Mn | V | Cr | Zn | As | Cd | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS a | 0.94 | - | - | 7.92 | 4.62 | - | 5.31 | 0.39 | - | 0.14 | 0.087 | 0.007 | ND | 0.001 | 0.077 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.069 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.005 |
| MSB a | 1.34 | - | - | 9.05 | 6.09 | - | 7.94 | 0.46 | - | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.13 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.097 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | 0.007 |
| MS b | 0.12 | 39.89 | 40.11 | 5.57 | 4.50 | 4.56 | 1.41 | 0.43 | 1.67 | 1.09 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| MSB b | 0.32 | 36.68 | 39.09 | 7.77 | 6.07 | 4.52 | 1.67 | 0.74 | 1.09 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.14 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| MSB-used b | 0 | 32.18 | 52.23 | 4.92 | 3.92 | 2.82 | 1.09 | 0.66 | 1.08 | 0.67 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.13 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Sample | Reaction Parameters | t/min | Removal Efficiency/% | k/min−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sewage sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 5 g/L, [PS] = 2 mM, T = 25 °C, [2,4-DCP] = 100 mg/L | 120 | 100 | 0.119 | [10] |
| CoFe2O4/ sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.5 g/L, [PMS] = 0.977 mM, T = 25 °C, [TC] = 20 mg/L | 30 | 99.8 | - | [18] |
| Fe-doped sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.1 g/L, [PMS] = 0.05 g/L, T = 25 °C, [TC] = 10 mg/L | 30 | 90.9 | 0.3619 | [9] |
| Paper mill sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.3 g/L, [PMS] = 0.6 mM, T = 25 °C, [4-CP] = 20 mg/L | 60 | 100 | 0.1165 | [7] |
| Co3O4@sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.1 g/L, [PMS] = 0.975 mM, T = 25 °C, [OFL] = 20 mg/L | 10 | 99 | 0.4991 | [33] |
| Co3O4@sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.2 g/L, [PMS] = 0.5 mM, T = 20 °C, [TC] = 0.1 mM | 60 | 93.2 | 0.126 | [17] |
| Microplastics coagulated aluminum sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.1 g/L, [PMS] = 0.2 g/L, T = 25 °C, [TC] = 20 mg/L | 30 | 84.7 | 0.086 | [34] |
| N-Fe co-doped sludge biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.4 g/L, [PDS] = 0.4 g/L, T = 25 °C, [SMX] = 20 mg/L | 120 | 99% | 0.0288 | [16] |
| Tannin extract-sludgederived biochar | [Catalyst] = 0.15 g/L, [PDS] = 0.1 g/L, T = 25 °C, [TC] = 20 mg/L | 120 | 90% | 0.0178 | [23] |
| MSB | [Catalyst] = 0.2 g/L, [PMS] = 0.2 g/L, T = 25 ± 2 °C, [ARG] = 20 mg/L | 10 | 93.34 | 0.278 | This work |
| Element | Active Group | MSB | MSB-Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| N 1s | Pyridinic N | 38.13% | 37.74% |
| Fe-Nx | 47.54% | 44.46% | |
| Pyrrolic N | 11.62% | 14.84% | |
| Graphitic N | 2.71% | 2.96% | |
| O 1s | Fe-O | 25.55% | 24.54% |
| C-O | 52.80% | 53.01% | |
| C=O | 21.64% | 22.45% | |
| Fe 2p | Fe2+ | 57.54% | 56.70% |
| Fe3+ | 42.46% | 43.30% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Ji, Y.; Yu, L.; Ma, M.; Ma, D.; Wei, J. Scalable Preparation of High-Performance Sludge Biochar with Magnetic for Acid Red G Degradation by Activating Peroxymonosulfate. Catalysts 2025, 15, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070637
Xu F, Ji Y, Yu L, Ma M, Ma D, Wei J. Scalable Preparation of High-Performance Sludge Biochar with Magnetic for Acid Red G Degradation by Activating Peroxymonosulfate. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070637
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Feiya, Yajun Ji, Lu Yu, Mengjie Ma, Dingcan Ma, and Junguo Wei. 2025. "Scalable Preparation of High-Performance Sludge Biochar with Magnetic for Acid Red G Degradation by Activating Peroxymonosulfate" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070637
APA StyleXu, F., Ji, Y., Yu, L., Ma, M., Ma, D., & Wei, J. (2025). Scalable Preparation of High-Performance Sludge Biochar with Magnetic for Acid Red G Degradation by Activating Peroxymonosulfate. Catalysts, 15(7), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070637






