Kinetics of Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Methyl Glycolate on an Activated Carbon-Supported Copper Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
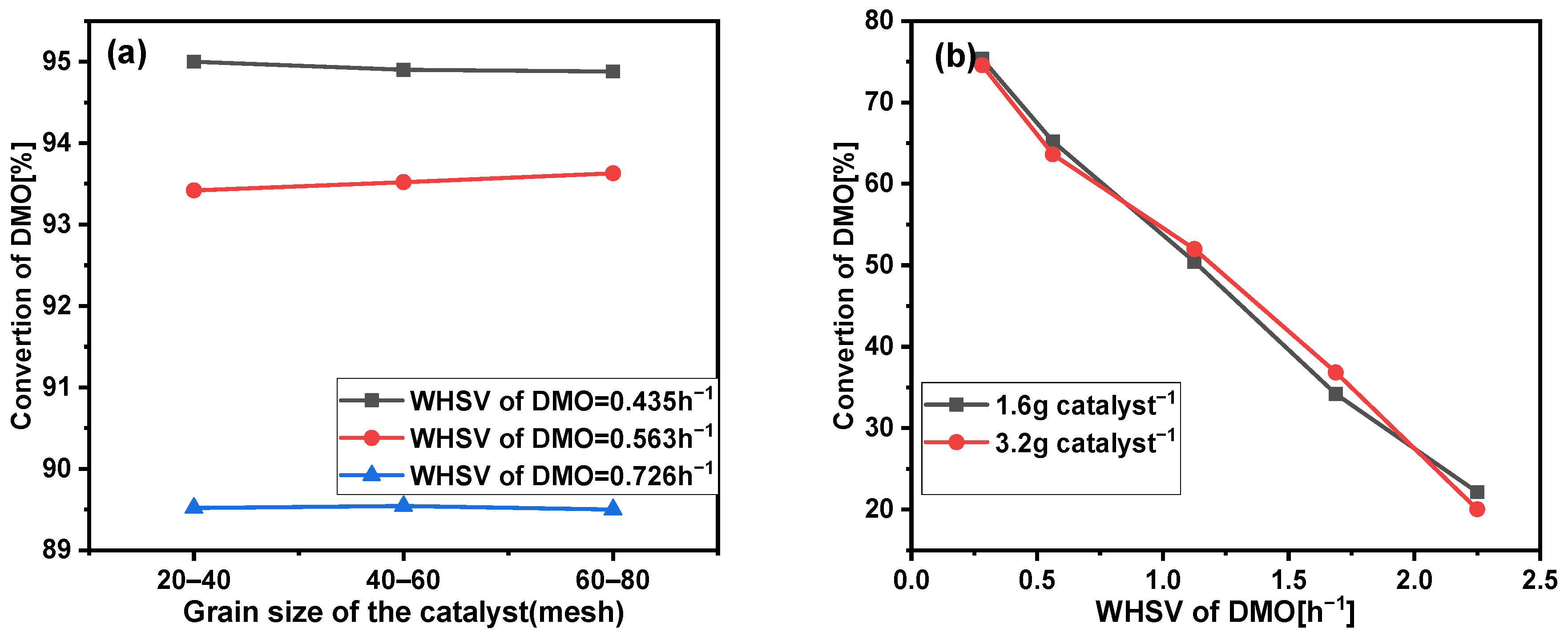
2.1. Elimination of Diffusion Effect
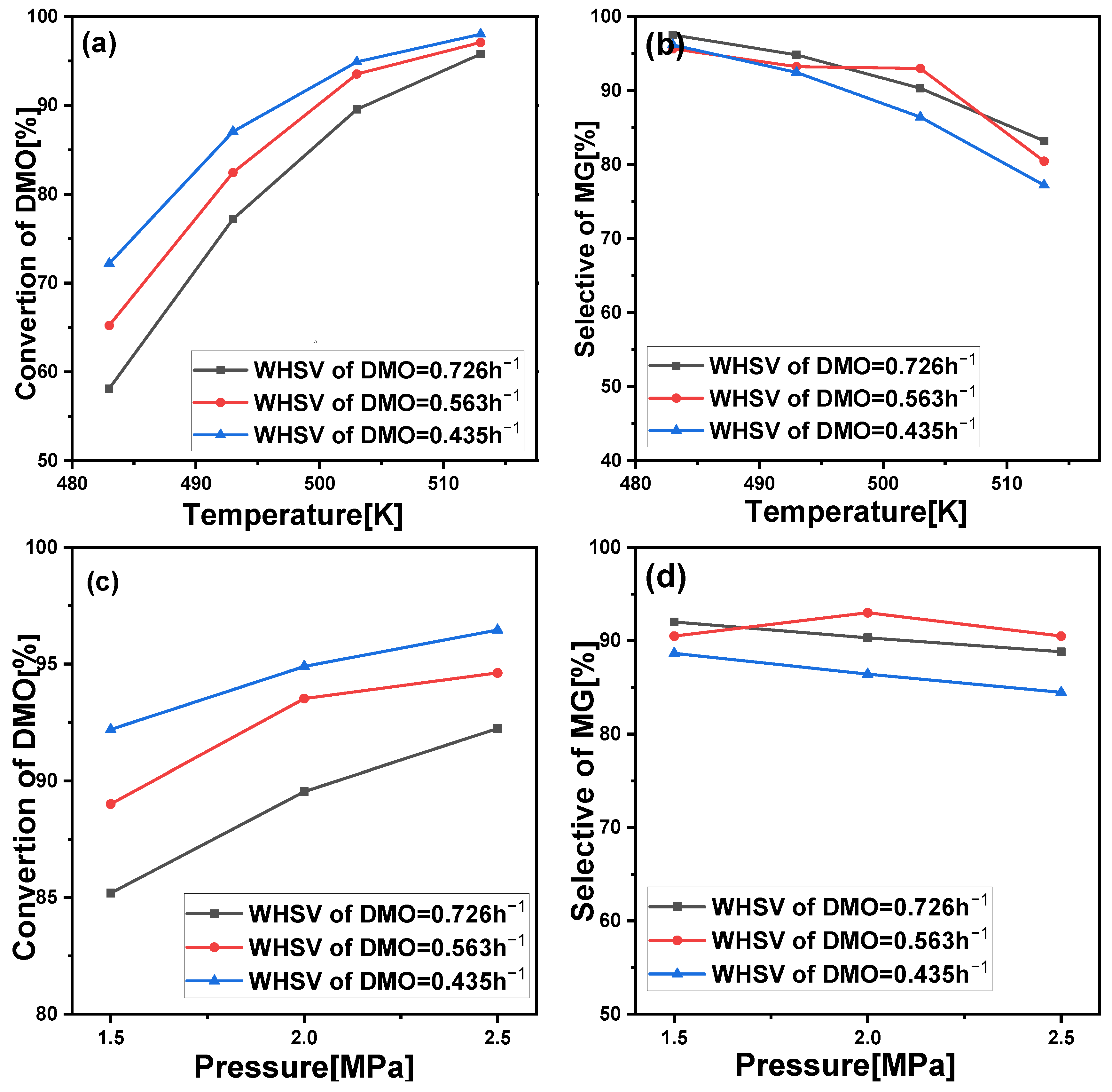
2.2. Reaction Performance
2.3. Reaction Mechanism and Kinetic Modeling
- The adsorption of ester and hydrogen occurs at two different active sites (double active sites).
- The adsorption type of ester is dissociative adsorption or non-dissociative adsorption.
- All the active sites are equal, and the change in catalyst surface coverage does not affect the adsorption activation energy and desorption activation energy.
- The adsorption or surface reaction of reactants is the rate-controlling step of the reaction.
2.4. Parameter Estimation
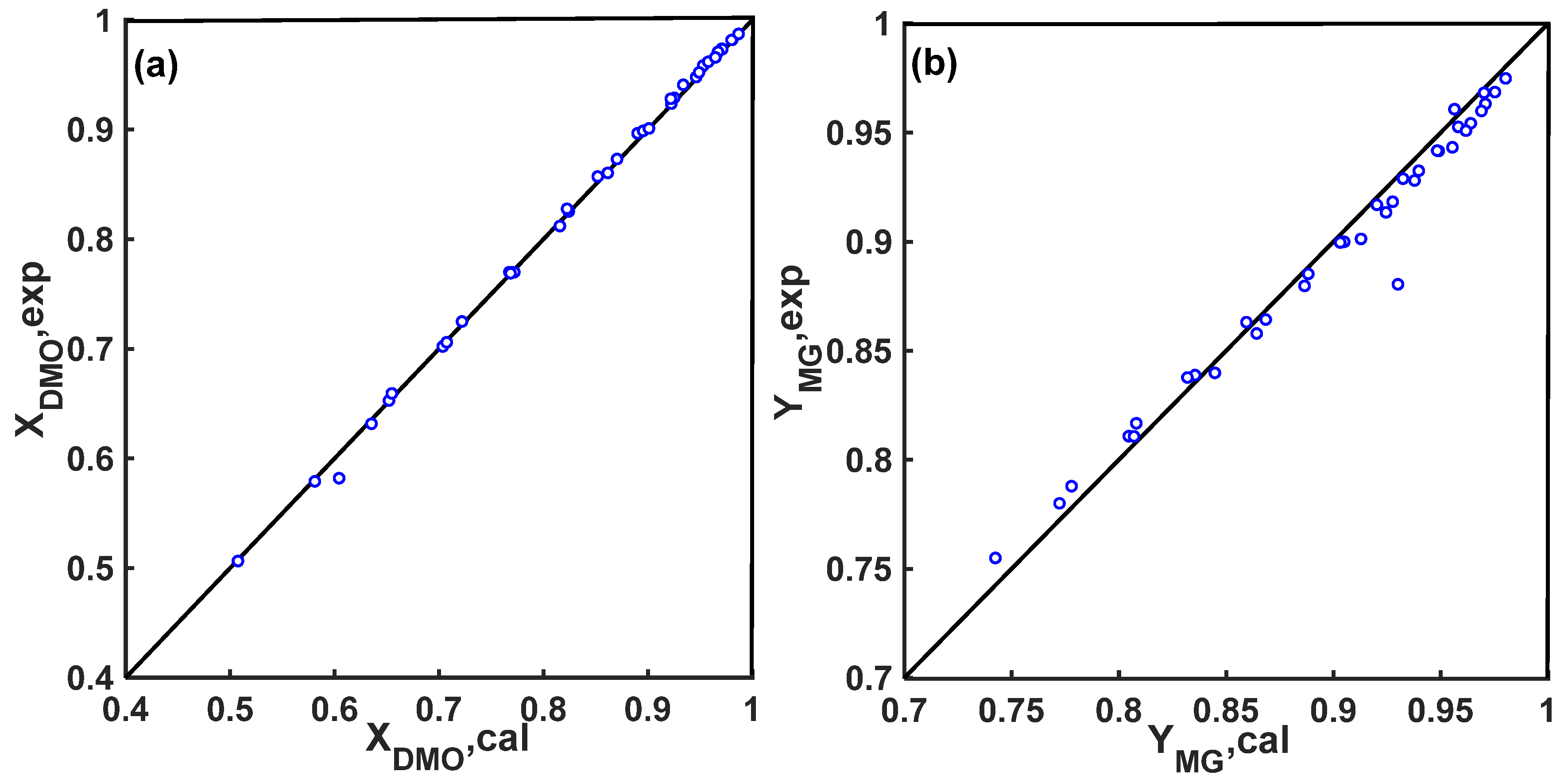
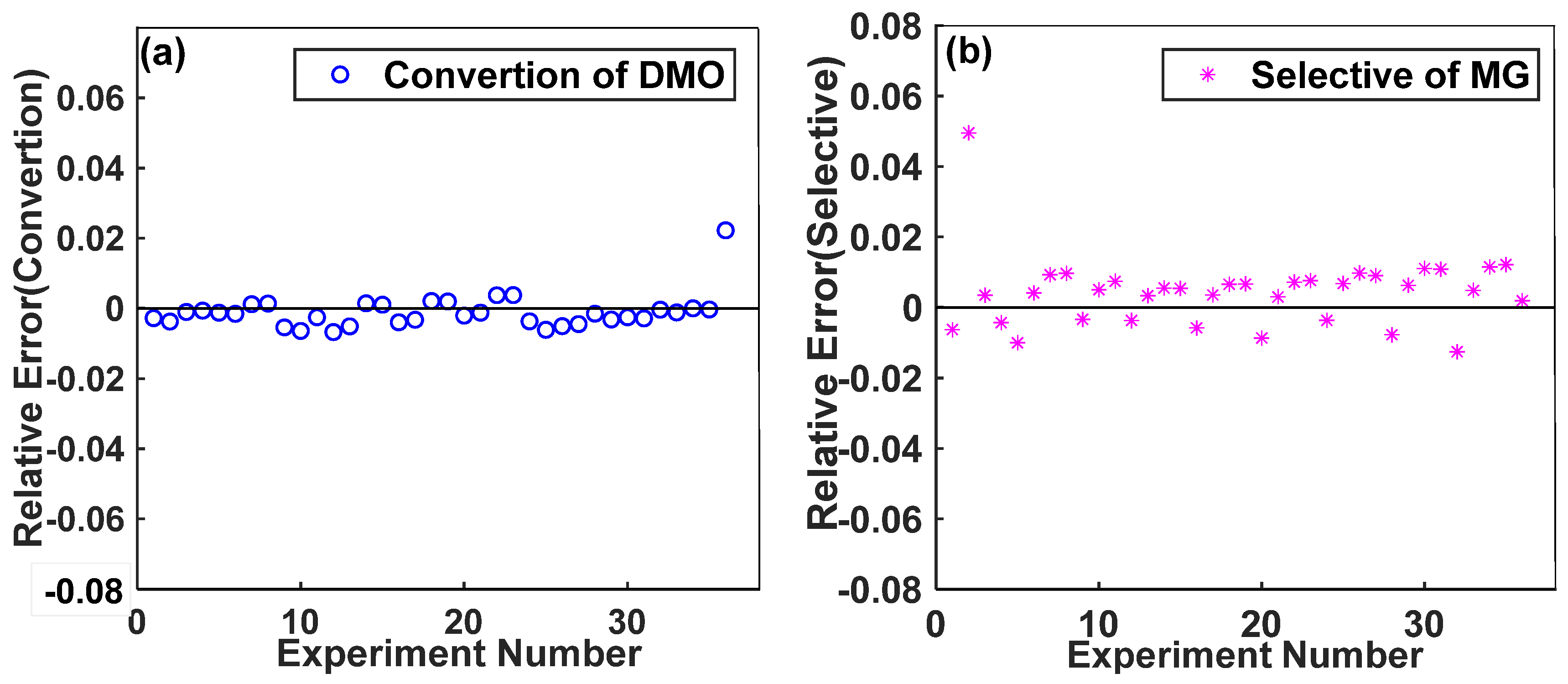
2.5. Model Testing
2.6. Discussion of Reaction Mechanism
3. Experiment
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Kinetic Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMO | dimethyl oxalate |
| MG | methyl glycolate |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| MeOH | methanol |
Symbols Used
| Eai [kJ·mol−1] | activation energy of R1 and R2 |
| Fi [mol h−1] | molar flow of substance i |
| ΔHi [kJ·mol−1] | heat of adsorption of substance i |
| k1, k2 [-] | reaction rate constant of R1 and R2 |
| k1,0, k2,0 [-] | pre-exponential factor of reaction rate constant of R1 and R2 |
| Ki [MPa−1] | adsorption equilibrium constant of substance i |
| Ki,0 [MPa−1] | pre-exponential factor of adsorption equilibrium constant of substance i |
| Kp1, Kp2 [-] | reaction equilibrium constant of R1 and R2 |
| m [g] | catalyst loading |
| N [-] | number of experiments |
| Np [-] | number of parameters |
| P [MPa] | pressure |
| pi [MPa] | partial pressure of substance i |
| r1 [mol gcat−1h−1] | reaction rate of DMO to MG |
| r2 [mol gcat−1h−1] | reaction rate of MG to EG |
| R [J mol−1K−1] | universal gas constant |
| R2 [-] | coefficient of determination |
| Sg [J mol−1K−1] | entropy of gas |
| ΔS [J mol−1K−1] | adsorption entropy |
| T [K] | temperature |
| WHSV [g gcat−1h−1] | weight hourly space velocity |
| XDMO [%] | conversion of DMO |
| Xexp [%] | experimental conversion |
| Xcal [%] | calculated conversion |
| y [-] | experimental value |
| ȳ [-] | average of experimental values |
| ŷ [-] | calculated value |
| YEG [%] | selectivity of EG |
| Yexp [%] | experimental selectivity |
| Ycal [%] | calculated selectivity |
| Sub- and superscripts | |
| cal | calculated value |
| cat | catalyst |
| exp | experimental value |
References
- Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Tan, Y.; Ding, Y. Synthesis of methyl glycolate by hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate with a P modified Co/SiO2 catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 1958–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Dong, G.; Cao, Y.; Hu, S.; Ye, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, X. Regulating mesopore structures of support toward enhanced selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate on Ag catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cao, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, T.; Hu, W.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y. Nanoporous Ni3P evolutionarily structured onto a Ni Foam for highly selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37635–37643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Ai, P.; Guo, Q.; Jin, H.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W. The effect of nitrogen doping on hydrogenation capability and stability of Cu-based catalyst in ester hydrogenation to methyl glycolate. Fuel 2023, 351, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, H.; Si, J.; Nie, Q.; Meng, C.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. High-Performance Ni3P/meso-SiO2 for gas-phase hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16719–16729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Q. Condensation of formaldehyde and methyl formate to methyl glycolate and methyl methoxy acetate using heteropolyacids and their salts. Catal. Today 1999, 51, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, F.E.; Lawrence, H.; Bell, A.T. Synthesis of precursors to ethylene glycol from formaldehyde and methyl formate catalyzed by heteropoly acids. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 288, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z. Highly effective synthesis of methyl glycolate with heteropolyacids as catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Zong, B.; Dai, W. Reaction temperature controlled selective hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate and ethylene glycol over copper-hydroxyapatite catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. Insight into the balancing effect of active Cu species for hydrogenation of carbon–oxygen bonds. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6200–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, F.S.; Syed Sulaiman, S.H.; Aziz, N. Multivariable optimisation of hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate for maximising productivity of ethylene glycol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 30882–30890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Highly dispersed, ultra-small and noble metal-free Cu nanodots supported on porous SiO2 and their excellent catalytic hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10290–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Yu, F.; Dai, B. Highly active and stable ZrO2-SiO2-supported Cu–Catalysts for the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 4823–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, B.; Wen, C.; Chen, X.; Dai, W. Investigation of activated-carbon-supported copper catalysts with unique catalytic performance in the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Wu, S.; Yin, S.; Zhao, J.; Ren, J. Highly stable Cu catalyst embedded in N-doped carbon microsphere for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2024, 677, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Shen, W.; Fang, Y. Alkaline earth modified activated carbon supported Cu catalysts with enhanced selectivity in the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11849–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.P.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Ding, D.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, P.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Adidharma, H.; Radosz, M.; et al. Perspectives on the Active Sites and Catalyst Design for the hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate. ACS Catal. 2020, 1, 4465–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Jing, Y.; Li, X. Organic compound modified Cu-based catalysts for the hydrogenation of esters. ChemCatChem 2025, 17, e202401597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strekalova, A.; Shesterkina, A.; Kustov, L. Recent progress in hydrogenation of esters on heterogeneous bimetallic catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 7229–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, H. Simulation of radial reactor for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol. Nat. Gas Chem. Ind. 2019, 44, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Qian, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, W. Study on precursors of Cu/SiO2 catalyst for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate. J. East China Univ. Technol. 2004, 20, 613–617. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Study on Catalyst for Gas Phase Hydrogenation of Diethyl Oxalate to Ethylene Glycol. Master’s Theis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.J.; Wehrli, J.T.; Wainwright, M.S.; Trimm, D.L.; Cant, N.W. Hydrogenolysis of diethyl oxalate over copper-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1992, 86, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. Kinetics of the hydrogenation of diethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X. Kinetics study of hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate over Cu/SiO2 Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, G.H.; Veldsink, J.W.; Beenackers, A.M. Intrinsic kinetics of 9-monoenic fatty acid methyl ester hydrogenation over nickel-based catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Tsubaki, N. New synthesis method of ethanol from dimethyl ether with a synergic effect between the zeolite catalyst and metallic catalyst. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2843–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, R.; Chaudhari, S.T.; Rode, C.V.; Chaudhari, R.V.; Mills, P.L. Hydrogenation of diethyl adipate in a catalytic fixed-bed reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, W. Ultra-stable Cu-based catalyst for dimethyl oxalate hydrogenation to ethylene glycol. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 60, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Lin, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, Y. synthesis of robust MOF-derived Cu/SiO2 catalyst with low copper loading via sol–gel method for the dimethyl oxalate hydrogenation reaction. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3382–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poling, B.E.; Prausnitz, J.M.; O’Connell, J.P. The Properties of Gases and Liquids; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 707p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B. Comparative thermodynamic analysis of hydrogenation reaction of diethyl oxalate and dimethyl oxalate. Shiyou Huagong/Petrochem. Technol. 2011, 40, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Vannice, M.A.; Hyun, S.H.; Kalpakci, B.; Liauh, W.C. Entropies of adsorption in heterogeneous catalytic reactions. J. Catal. 1979, 56, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, Y.B.; Ponamar’yenko, A.T.; Rozovsky, A.Y. Determination of kinetics of heterogeneous catalytic reactions, based on the critical ignition conditions. J. Catal. 1967, 7, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wan, S.; Xia, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wen, J.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, L. Efficient synthesis of diethyl oxalate from transesterification of dimethyl oxalate and ethanol using alkaline catalysts and kinetic studies of transesterification. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 5510–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitthisa, S.; Sooknoi, T.; Ma, Y.; Balbuena, P.B.; Resasco, D.E. Kinetics and mechanism of hydrogenation of furfural on Cu/SiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 2011, 277, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.V.; Jaganathan, R.; Vaidya, S.H.; Chaudhari, S.T.; Naik, R.V.; Rode, C.V. Hydrogenation of diethyl maleate in a fixed-bed catalytic reactor: Kinetics, reactor modelling and pilot plant studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 3643–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.A.N.; Sánchez-Castillo, M.A.; Cortright, R.D.; Dumesic, J.A. Catalytic reduction of acetic acid, methyl acetate, and ethyl acetate over silica-supported copper. J. Catal. 2000, 193, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, I.B.; Jeon, W.; Park, M.; Suh, Y.W.; Suh, D.J.; Lee, C.H. Kinetic studies of vapor-phase hydrogenolysis of butyl butyrate to butanol over Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 387, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Cant, N.W.; Wainwright, M.S.; Trimm, D.L. Catalytic hydrogenolysis of esters: A comparative study of the reactions of simple formates and acetates over copper on silica. J. Mol. Catal. 1987, 43, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Ma, X.; Gong, J. An alternative synthetic approach for efficient catalytic conversion of syngas to ethanol. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Substrate | Product | Temperature /°C | Pressure /Mpa | Hydrogen Ester Ratio | LHSV of DMO /h | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMO | MG | 220 | 2.5 | 200 | 0.257 | [12] |
| DMO | MG | 230 | 2.5 | 100 | 0.4 | [13] |
| DMO | MG | 220 | 2.5 | 120 | 0.18 | [14] |
| DMO | MG | 220 | 3 | 80 | 0.6 | [15] |
| DMO | MG | 240 | 2 | 80 | 0.9 | [16] |
| DMO | MG | 230 | 2.5 | 100 | 0.6 | [17] |
| DMO | EG | 190 | 3 | 100 | 0.6 | [18] |
| DMO | EG | 185 | 2 | 100 | 1.2 | [19] |
| No. | Adsorption Type of Ester | RDS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | ||
| 1 | non-dissociation | adsorption | adsorption |
| 2 | non-dissociation | adsorption | surface reaction |
| 3 | non-dissociation | surface reaction | adsorption |
| 4 | non-dissociation | surface reaction | surface reaction |
| 5 | dissociation | adsorption | adsorption |
| 6 | dissociation | adsorption | surface reaction |
| 7 | dissociation | surface reaction | adsorption |
| 8 | dissociation | surface reaction | surface reaction |
| Model | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | 0.1376 | 0.1835 | 0.1549 | 0.1372 | 0.0385 | 0.1446 | 0.1458 | 0.1714 |
| R2 (for X) | 0.9893 | 0.9817 | 0.9827 | 0.9876 | 0.9990 | 0.9804 | 0.9897 | 0.9642 |
| R2 (for Y) | 0.9689 | 0.9538 | 0.9589 | 0.9682 | 0.9751 | 0.9523 | 0.9685 | 0.9589 |
| No. | Temp. [K] | n(H2)/n(DMO) | WHSV of DMO | Con. exp [%] | Con. cal of Model 1/5 [%] | Con. Relative Error of Model 1/5 [%] | Sel. exp [%] | Sel. cal of Model 1/5 [%] | Sel. Relative Error of Model 1/5 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 503 | 80 | 0.375 | 99.88 | 95.38/98.18 | 4.51/1.70 | 82.38 | 84.32/80.77 | 2.35/1.95 |
| 2 | 493 | 80 | 0.375 | 91.18 | 93.99/89.49 | 3.08/1.85 | 89.43 | 90.41/87.69 | 1.95/1.10 |
| 3 | 483 | 80 | 0.375 | 72.64 | 75.94/74.56 | 4.54/2.64 | 92.42 | 94.42/93.79 | 2.16/1.48 |
| T [K] | Kp1 | Kp2 |
|---|---|---|
| 493 | 27.1 | 2.27 |
| 503 | 20.3 | 2.10 |
| 513 | 15.1 | 1.96 |
| 523 | 9.9 | 1.82 |
| Parameters | Pre-Exponential Factor | Activation Energy/Heat of Adsorption |
|---|---|---|
| ki,0 [mol gcat−1h−1)] | Eai [kJ·mol−1] | |
| k1 | 3.59 × 109 | 127.29 |
| k2 | 4.95 × 108 | 130.51 |
| Ki,0 [MPa−1] | ΔHi [kJ·mol−1] | |
| KDMO | 5.72 × 10−3 | −50.02 |
| KMG | 3.08 × 10−3 | −54.62 |
| KEG | 1.02 × 10−3 | −40.35 |
| KMeOH | 1.80 × 10−3 | −18.93 |
| KH2 | 6.0 × 10−4 | −12.14 |
| Substrate | Catalyst | Ea1 /kJ·mol−1 | Ea2 /kJ·mol−1 | ΔHDMO /kJ·mol−1 | ΔHMG /kJ·mol−1 | ΔHEG /kJ·mol−1 | ΔHMeOH /kJ·mol−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMO | Cu/SiO2 | 51.2 | 73.2 | −32.38 | −69.26 | −75.07 | −27.04 | [20] |
| DMO | Cu/SiO2 | 36.38 | 44.84 | −56.28 | −48.09 | −34.09 | −74.42 | [25] |
| DMO | Cu-Ca/AC | 127.29 | 130.51 | −50.02 | −54.62 | −40.35 | −18.93 | our study |
| Substance | ΔS | Sg [J mol−1 K−1] | 51 − 0.0014ΔH |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMO | −42.09 | 364.84 | −121.03 |
| MG | −43.18 | 345.12 | −127.47 |
| EG | −93.05 | 323.55 | −107.49 |
| MeOH | −73.12 | 239.7 | −77.485 |
| H2 | −46.00 | 130.6 | −51.84 |
| Substrate | Catalyst | Adsorption Type of Ester | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| furfural | Cu/SiO2 | non-dissociation | [36] |
| diethyl maleate | copper chromite | non-dissociation | [37] |
| ethyl acetate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [38] |
| butyl butyrate | Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 | dissociation | [39] |
| formate/acetate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [40] |
| dimethyl oxalate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [21] |
| dimethyl oxalate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [23] |
| dimethyl oxalate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [25] |
| dimethyl oxalate | Cu/SiO2 | dissociation | [41] |
| dimethyl oxalate | Cu-Ca/AC | dissociation | our study |
| Elementary Reaction Steps |
|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, P.; Shen, W.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y. Kinetics of Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Methyl Glycolate on an Activated Carbon-Supported Copper Catalyst. Catalysts 2025, 15, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070624
Shao P, Shen W, Wang J, Fang Y. Kinetics of Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Methyl Glycolate on an Activated Carbon-Supported Copper Catalyst. Catalysts. 2025; 15(7):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070624
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Pan, Weihua Shen, Junyou Wang, and Yunjin Fang. 2025. "Kinetics of Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Methyl Glycolate on an Activated Carbon-Supported Copper Catalyst" Catalysts 15, no. 7: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070624
APA StyleShao, P., Shen, W., Wang, J., & Fang, Y. (2025). Kinetics of Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Methyl Glycolate on an Activated Carbon-Supported Copper Catalyst. Catalysts, 15(7), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15070624







