1. Introduction
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) has become a cornerstone material across industrial manufacturing, architectural engineering, and consumer products due to its exceptional cost-effectiveness, chemical stability, mechanical durability, and thermoplastic processability [
1]. This escalation in material demand strongly correlates with rapid urbanization and GDP growth trajectories, driving sustained expansion in global PVC consumption alongside other engineering plastics. The traditional disposal methods for PVC waste are mainly landfilling, mechanical recycling and incineration [
2]. In China, landfilling constitutes 36.0% of total PVC waste, followed by mechanical recycling (25.5%) and incineration (9.3%), with merely 0.8% undergoing chemical recycling [
3,
4]. However, PVC’s high chlorine content (56%) induces groundwater contamination through landfill leaching, while incineration releases HCl and toxic chlorinated aromatics (e.g., dioxins) [
5,
6], leading to serious environmental problems. These systemic limitations underscore the urgent need for advanced PVC waste valorization strategies integrating dechlorination and resource recovery. As a synthetic plastic polymer, PVC has a high energy content (15–40 MJ‧kg
−1) that can be converted to useable fuel through resource recycling [
7,
8,
9]. Therefore, the recycling of waste PVC will reflect its high environmental and economic value if the chlorine in PVC can be removed during resource recycling process or through pre-treatment processes.
In recent years, many experts and scholars have conducted in-depth research on the removal of chlorine in PVC, and the specific dechlorination methods can be summarized as mechanical ball milling, low-temperature pyrolysis, microwave heating and hydrothermal carbonization. Mechanical ball milling and microwave irradiation exhibit relatively low dechlorination efficiencies and involve multiple processing steps [
10,
11,
12]. The reaction temperature of pyrolysis is high (above 300 °C), leading to relatively high energy consumption and the difficult separation of pyrolysis products [
13]. The wet treatment of PVC waste often employs various solvents, including water, subcritical/supercritical fluids, and organic solvents. Additionally, diverse additives and reaction media—such as alkaline agents, metal oxides, and biomass—are frequently introduced to improve dechlorination efficiency [
14,
15,
16]. Compared with other methods, wet treatment has obvious advantages: the reaction temperature is relatively low, and hydrogen chloride and other chlorine-containing compounds can be easily dissolved in the liquid phase and separated from dechlorinated PVC [
17,
18]. The wet treatment methodology can be systematically classified into three distinct categories: solvent-thermal processing, hydrothermal treatment, and co-hydrothermal carbonization (co-HTC), depending on the type of additives and reaction media.
Co-HTC is a thermochemical process where binary or multi-component feedstocks are co-treated hydrothermally, enabling the formation of carbonaceous products via synergistic interactions between intermediates from each feedstock under subcritical aqueous conditions. Considering that PVC waste is widely used in industry, agriculture, and medical care, it is more likely to be mixed with other waste, such as metal, glass, carbon fiber, rubber, and biomass, forming a complex and diverse waste mixture [
19]. Co-HTC presents remarkable advantages in treating PVC waste mixtures by eliminating the need for drying the feedstock and for sorting and separating the composite material before treatment, thereby reducing operating costs and energy consumption. Moreover, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC also can be improved when PVC is treated in co-HTC [
20,
21]. Xiu et al. studied the co-hydrothermal treatment of PVC and used a liquid crystal display (LCD) in a one-pot process at low temperatures [
22]. In the optimum conditions (220 °C, 90 min, PVC-to-LCD ratio of 4:1, PVC-to-H
2O ratio of 1:30 g/mL), the dechlorination rate of PVC could reach up to 100%. The study’s result revealed that the LCD contained a variety of metal oxides such as SiO
2, Fe
2O
3, CaO, K
2O, and MgO. The oxygen in the metal oxide lattice could provide sufficient oxygen element and was excited to form the hydroxyl radical, participating in multiple substitution reactions of the C-Cl bond in PVC, hence promoting the dechlorination of PVC. Xu et al. studied the co-hydrothermal treatment of PVC and waste concrete, and PVC dechlorination efficiency could be enhanced to as high as 95.04% by introducing waste concrete [
23].
Numerous proofs have shown that the co-hydrothermal treatment of PVC and biomass can effectively promote the removal of the chlorine element. Wei et al. studied the co-hydrothermal dechlorination of pomelo peel and PVC at 220 °C in the presence of lemon acid [
9]. A maximum dechlorination efficiency of 93.50% was achieved under optimal conditions. Lu et al. studied the co-HTC of corncob and PVC [
7]. It was revealed that the synergistic effects of corncob and PVC in co-HTC could effectively improve the dechlorination efficiency of PVC. The maximum dechlorination rate of 95.20% was obtained at 260 °C, with a corncob/PVC mixing ratio of 5:5 and pH = 5 with citric acid.
Although numerous studies have demonstrated that the co-hydrothermal treatment of PVC with lignocellulosic biomass effectively achieves the removal of organochlorine, the dechlorination mechanism—particularly under alkaline catalysis—remains unclear. In this study, a co-hydrothermal treatment strategy for polyvinyl chloride and lignin using a one-pot method at low temperatures is proposed to improve the dechlorination efficiency of PVC and prepare high-energy hydrothermal carbon. The synergistic dechlorination mechanism governing polyvinyl chloride (PVC) during co-HTC through ammonium carbonate and lignin was investigated, with reaction pathways being explored.
2. Results and Discussion
Lignin was mixed with PVC, and ammonium carbonate was used as a supplementary additive to establish the co-hydrothermal (HT-CO) system. To further explore the effects of ammonium carbonate and lignin on PVC dechlorination, three additional experiments in different hydrothermal systems were also conducted, following the same experimental procedure as HT-CO: a hydrothermal system (HT, only PVC and water were present in the reactor), a hydrothermal system with lignin (HT-PL, where lignin was added), and a hydrothermal system with ammonium carbonate (HT-PN, with ammonium carbonate added). Meanwhile, blank control experiments were also conducted for the above three systems (HT-CO-CG, HT-PN-CG, and HT-PL-CG, without the addition of PVC).
2.1. Effect of Reaction Temperature on PVC Dechlorination Efficiency
As shown in
Figure 1, the effect of temperature on the efficiency of the hydrothermal dechlorination of PVC varied among the HT-PL, HT-PN, and HT-CO systems. Overall, the hydrothermal dechlorination of PVC in all three systems was poor at low temperatures. However, as the temperature rose, the efficiency significantly improved, with notable differences among the systems. In the HT-PN and HT-CO systems, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC markedly increased at 200 °C, reaching 58.86% and 87.01%, respectively. In the HT-PL system, a significant improvement in the dechlorination efficiency of PVC started at 220 °C, reaching 39.04%, and it further increased to 87.34% at 240 °C. This indicated that the dechlorination of PVC was significantly enhanced in the presence of ammonium carbonate, which may have been due to its alkaline nature, promoting the dechlorination process [
24]. Additionally, at high temperatures, ammonia was produced, enhancing the system’s alkalinity [
25]. The escape of ammonia created pores within the PVC, increasing its contact area with additives [
26]. Therefore, the effectiveness of dechlorination was further boosted. At 240 °C or higher, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC in the HT-PN system was less than in the HT-PL system, which might have been due to the decomposition of lignin into phenolic compounds that adhered to undissolved lignin or polyaromatic carbons, preventing PVC aggregation, increasing its interaction with water, and promoting the conversion of organic chlorine to inorganic chlorine [
27]. In the HT-PN system, the ammonia release from ammonium carbonate was nearly complete at 220 °C, so at higher temperatures, the increase in dechlorination efficiency with increasing temperature was no longer significant.
In the 180–260 °C range, as shown in
Figure 1, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC in the HT-CO system consistently outperformed that in the HT-PL and HT-PN systems. At 200 °C, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC reached 87.01% in the HT-CO system, far exceeding 17.60% in HT-PL and 58.86% in HT-PN. When the temperature was raised to 220 °C, the difference in dechlorination efficiency reached its maximum, with 99.43% for HT-CO, 76.87% for HT-PN and 39.04% for HT-PL. This indicated the synergistic effect of lignin and ammonium carbonate in the HT-CO system. The presence of lignin resulted in the better dispersion of PVC particles. At the same time, the ammonium carbonate further increased the solution’s alkalinity, which jointly promoted the lowering of the reaction temperature and improved the dechlorination. Additionally, the lignin in the hydrothermal system improved the chemical composition and microstructure of the hydrothermal carbon, enhancing its quality.
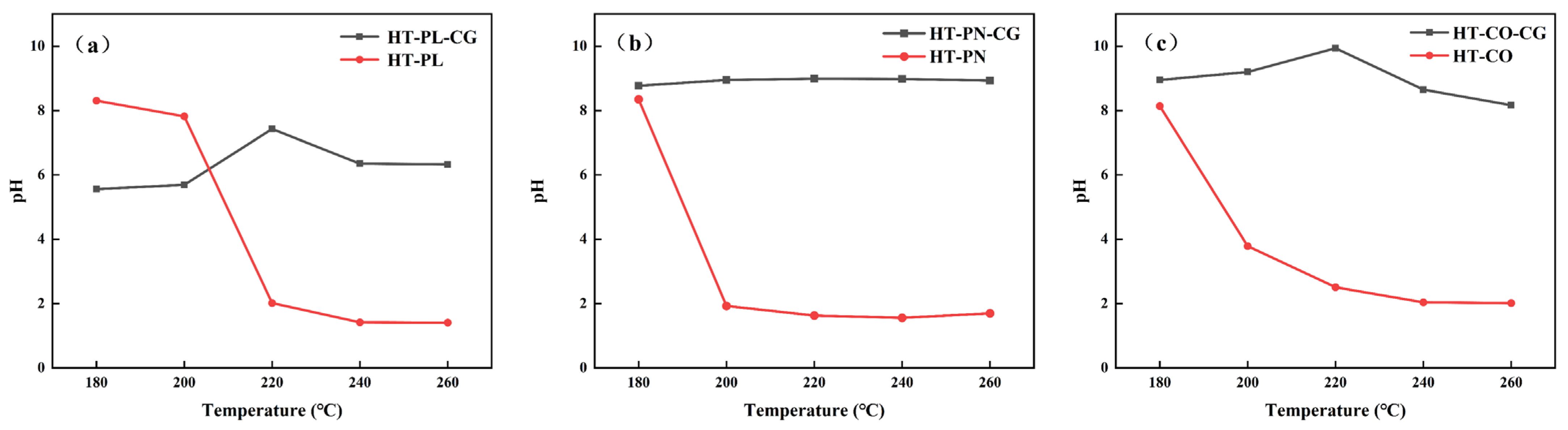
2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature on the PH Value of the System
To further investigate the reason for differences in PVC dechlorination efficiency across hydrothermal systems, blank experiments were conducted for the three systems (HT-PL, HT-PN, and HT-CO) in which the same experimental conditions were applied but no PVC was added. Following 240 min of dechlorination and blank experiments for all three systems, the pH values of the solutions were measured, with the results presented in
Figure 2.
Figure 2a illustrates the pH variations with temperature in the PVC dechlorination experiment within the HT-PL system and the blank experiment (HT-PL-CG). The pH value of HT-PL-CG was around 6 at 180 °C, slightly increasing with temperature but suddenly rising to 7.43 at 220 °C due to lignin depolymerization under hydrothermal conditions, releasing phenolic substances and OH
− and thus increasing solution alkalinity. However, as the temperature rose to 240 °C, the lignin further broke down into organic acids and alcohols [
28], causing a decrease in the pH within HT-PL-CG. As for the PVC dechlorination process in HT-PL, the pH value drastically dropped to 2.02 at 220 °C due to the production of HCl during the dechlorination process, which resulted in a decrease in the pH value of the system.
Figure 2b illustrates the pH changes with temperature in the blank experiment (HT-PN-CG) and the PVC dechlorination process in the HT-PN system. The PH maintained a stable value of around 9 at different temperatures in HT-PN-CG due to the presence of ammonium carbonate. However, the pH sharply dropped to 1.93 at 200 °C in the PVC dechlorination process and remained stable when the reaction temperature was further increased. This pH trend matched the dechlorination efficiency trend of the HT-PN system in
Figure 2, indicating that ammonium carbonate can effectively promote the dechlorination of PVC at lower temperatures and that further increases in reaction temperature cannot significantly improve the dechlorination efficiency of PVC.
Compared with the HT-PL-CG and HT-PN-CG systems, as shown in
Figure 2c, the pH of the HT-CO-CG system was close to the average pH of the other two blank systems at corresponding temperatures, indicating no significant interaction between the lignin and ammonium carbonate in the HT-CO system. In the PVC dechlorination experiments in the HT-CO system, the pH significantly decreased after the reaction at 200 °C and continued to drop with increasing temperature, consistent with the dechlorination efficiency trend of the HT-CO system shown in
Figure 2.
In general, the pH of all three systems decreased as temperature increased during PVC dechlorination. When the temperature exceeded 240 °C, the pH values of the three systems tended to stabilize, indicating that the dechlorination process was largely completed. Notably, at temperatures above 200 °C, especially at 220 °C, the pH of the HT-CO system was significantly higher than that of the HT-PL and HT-PN systems. This suggests that the simultaneous presence of lignin and ammonium carbonate created a more alkaline environment that positively affected the dechlorination of PVC and contributed to the efficiency of the HT-CO system.
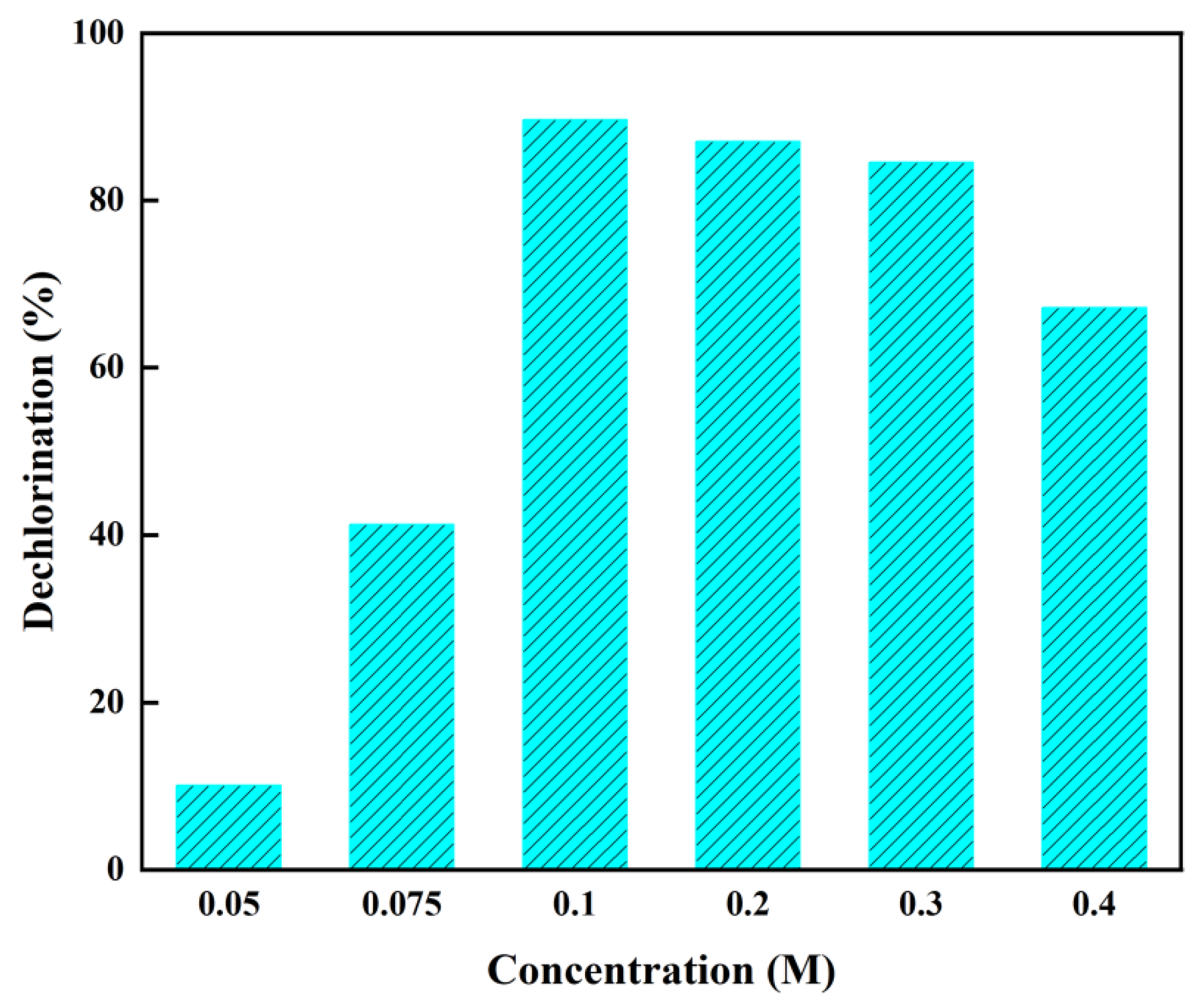
2.3. Effect of Ammonium Carbonate Concentration on Dechlorination Efficiency of PVC
To investigate the impact of ammonium carbonate concentration on PVC dechlorination efficiency in the HT-CO system, experiments were conducted with concentrations ranging from 0.05 to 0.4 M at 200 °C. As shown in
Figure 3, the dechlorination efficiency was only about 10% when the concentration of ammonium carbonate was 0.05 M. When the concentration increased to 0.1 M, the efficiency reached 89.10%. However, further increases in concentration led to a decrease in dechlorination efficiency from 89.10% at 0.1 M to 67.13% at 0.4 M. This indicates that increasing the concentration of ammonium carbonate within a certain range improved the dechlorination efficiency, whereas excess ammonium carbonate inhibited the dechlorination reaction due to the higher viscosity of the alkaline liquid, which covered a larger number of active centers and promoted the polymerization of polyvinyl chloride [
29]. Therefore, the optimal ammonium carbonate concentration for PVC dechlorination is 0.1 M.
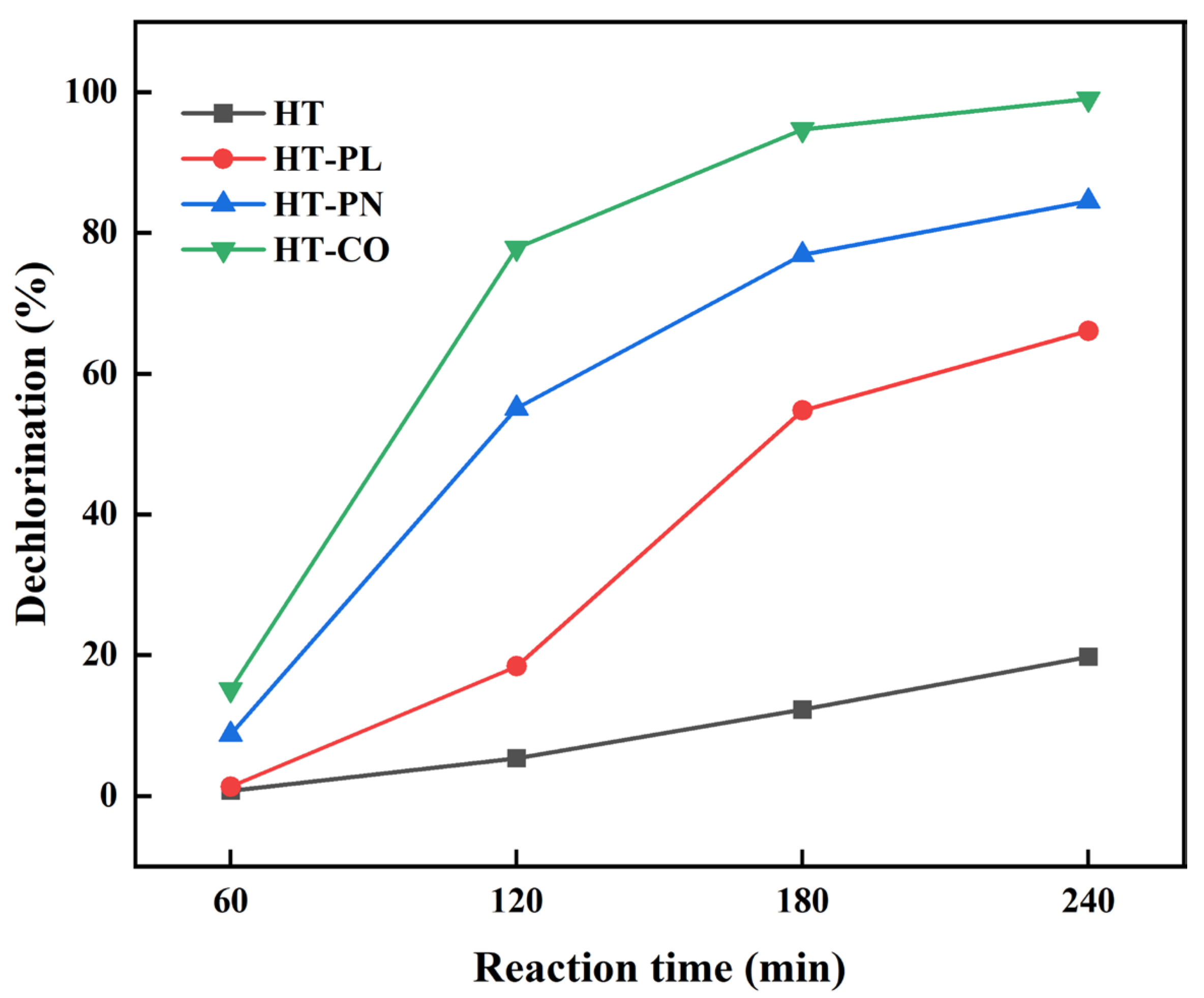
2.4. Effect of Reaction Time on Dechlorination Efficiency of PVC
Four reaction times, 60, 120, 180, and 240 min, were set to investigate the effect of reaction time on the dechlorination of PVC, and the results are shown in
Figure 4. As shown in
Figure 4, the PVC dechlorination efficiency increased over reaction time at 220 °C across all systems, which indicates that reaction time is a crucial factor in determining PVC dechlorination efficiency. At each reaction time, the PVC dechlorination efficiencies in all four systems, in ascending order, were HT < HT-PL < HT-PN < HT-CO. The dechlorination of PVC in the HT system was the lowest, only 19.75% at the longest reaction time, which indicates that PVC is difficult to dechlorinate itself via a hydrothermal reaction without adding any auxiliary reagents. After co-hydrothermalization with lignin in the HT-PL system, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC was improved and reached 60.10% after 240 min of reaction. In the HT-PN system, adding ammonium carbonate greatly improved the dechlorination efficiency of PVC, and the dechlorination efficiency reached 84.48% at 240 min. In the HT-CO system, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC reached nearly 80% at 120 min, and after 240 min, the Cl in PVC was almost completely removed. The improvement of PVC dechlorination efficiency in HT-CO was due to a combination of lignin depolymerization, increased PVC porosity from the ammonia generated by the ammonium carbonate, and carbonate‘s catalytic action. The trend of PVC dechlorination efficiency with time in the HT-CO system was similar to that of the HT-PN system, indicating that the ammonium carbonate had a greater effect on PVC dechlorination than the lignin in the HT-CO co-hydrothermal dechlorination system. This might have been because lignin depolymerizes slowly at low temperatures and short times while ammonium carbonate dissolves well in water, generating ammonia and carbonate to accelerate the initial dechlorination reaction [
16]. However, the dechlorination efficiency of PVC in the HT-PN system with ammonium carbonate only was much lower than that in the HT-CO system, which highlights the significant synergistic effect of lignin and ammonium carbonate to significantly improve dechlorination efficiency.
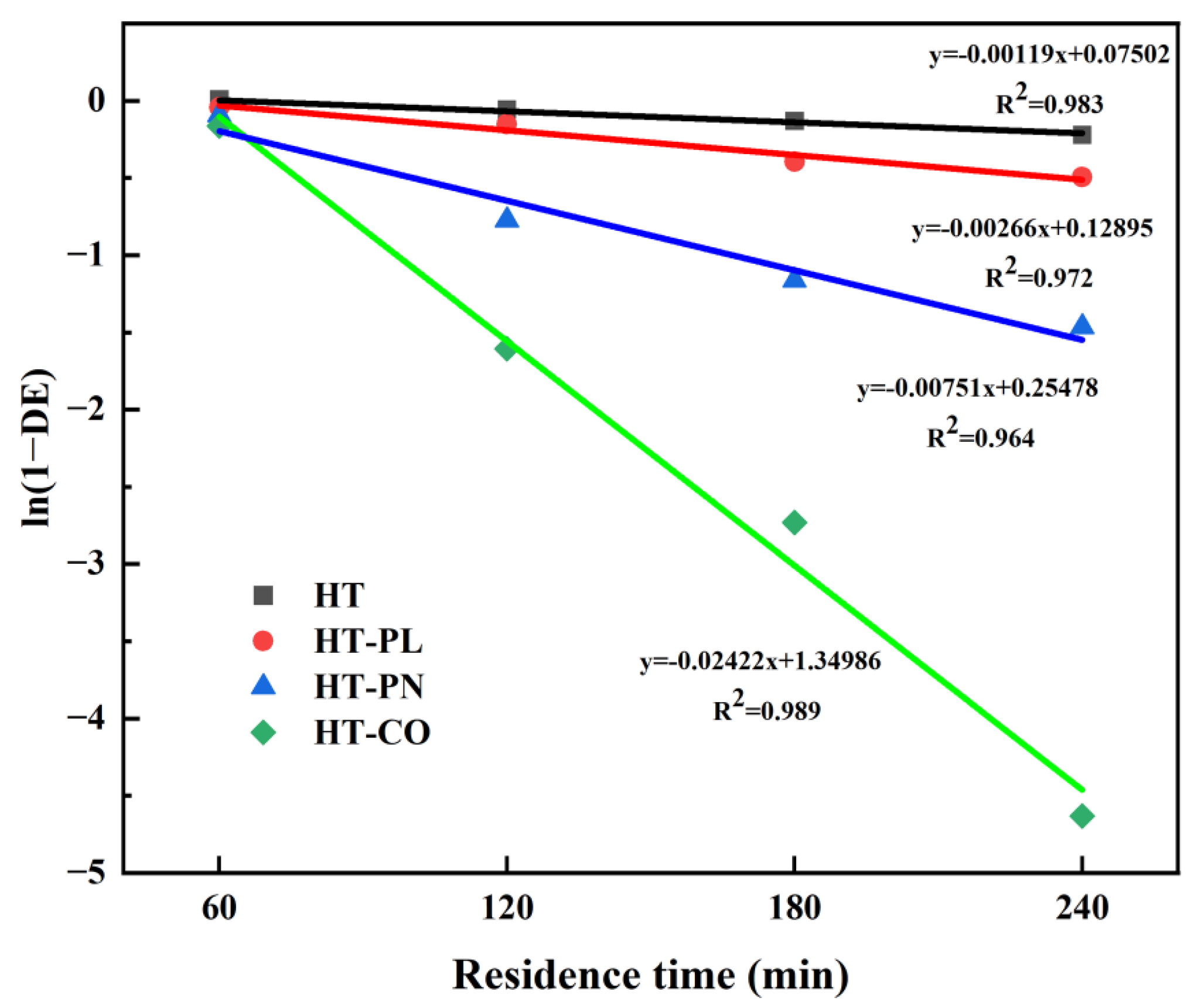
2.5. Kinetic Characterization of Co-Hydrothermal Dechlorination of PVC
To better understand the impact of the additives on the process and rate of PVC hydrothermal dechlorination, the dechlorination kinetics in each hydrothermal system were studied for this article.
In the hydrothermal dechlorination reaction of PVC, since the dechlorination reaction rate is related to the chlorine content in PVC, the kinetic equation can be described as
where
t is reaction time,
k is apparent rate constant, and
X is the residual chlorine content in PVC during the reaction, calculated as 1 − DE (%).
Shin et al. found that the PVC hydrothermal carbonization process is first order [
30]; therefore, Equation (1) for the dechlorination reaction can be rewritten as
The first-order plot of the dehydrochlorination for PVC at 220 °C in the four systems is shown in
Figure 5. As shown in
Figure 5, the correlation coefficients (R
2) for all four lines were greater than 0.95, indicating that all the dechlorination of PVC in the different systems followed a first-order kinetic model. The reaction rate constant for the HT-PL and HT-PN systems were 2.66 × 10
−3 min
−1 and 7.51 × 10
−3 min
−1, respectively, which were 2.3 and 6.3 times higher than that of the HT system (1.19 × 10
−3 min
−1). This indicates that the addition of ammonium carbonate had a more significant impact on the dechlorination rate of PVC compared with lignin. The PVC dechlorination rate constant for the HT-CO system was 2.42 × 10
−2 min
−1, which was 20 times that of the HT system and also significantly higher than those for the HT-PL and HT-PN systems. These results align with previous findings that the synergistic effect of lignin and ammonium carbonate greatly enhances the dechlorination of PVC.
2.6. Characterization and Analysis of Solid Products
2.6.1. SEM
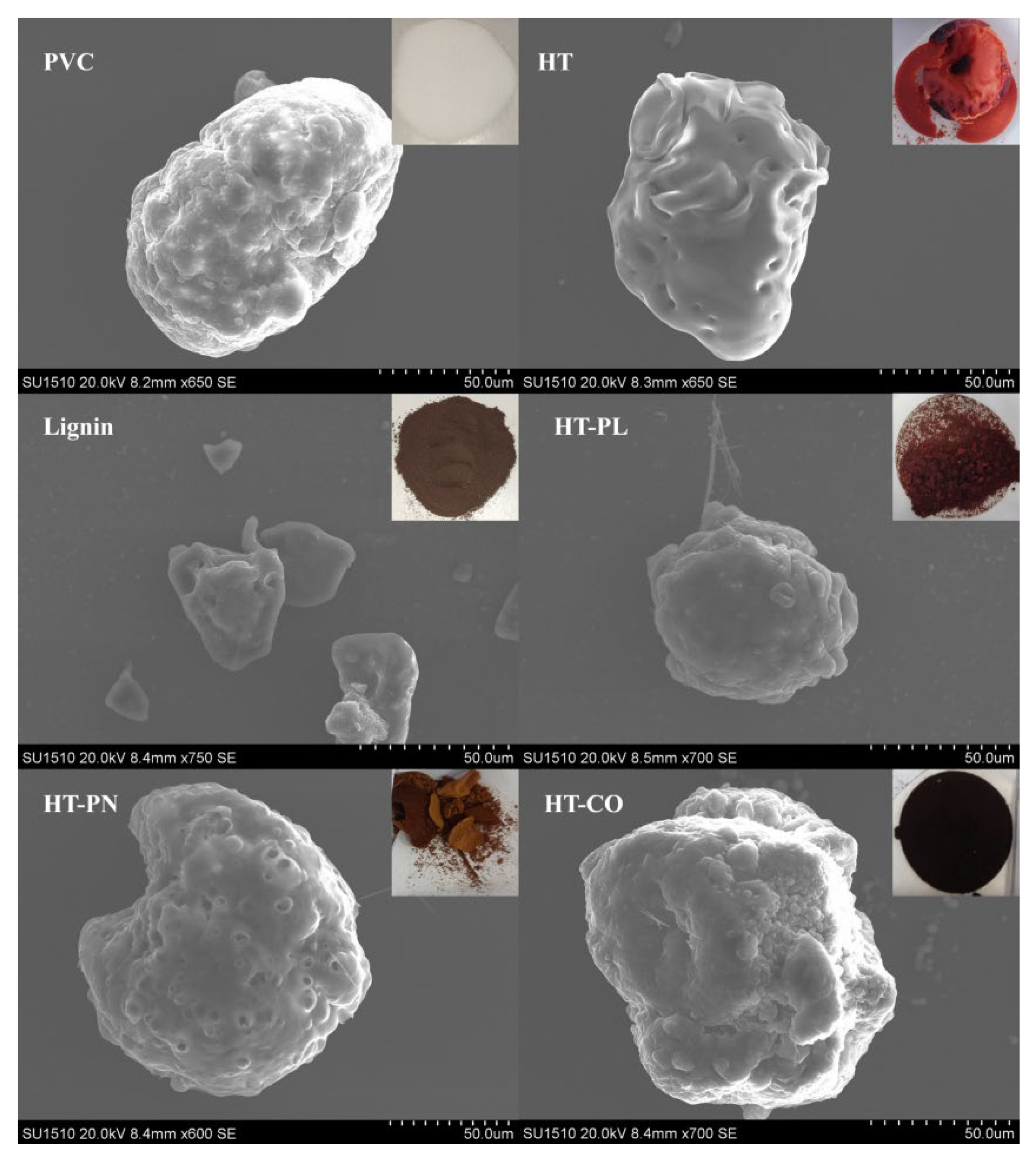
Figure 6 shows the appearance of the products from the hydrothermal reaction of PVC in different systems (HT, HT-PL, HT-PN, and HT-CO) at 220 °C for 240 min, along with that of the raw PVC material and lignin. As shown in
Figure 6, the raw PVC material particles were relatively smooth with tiny pores, while the HT carbon was smoother and showed signs of clumping. The lignin particles were small and homogeneous in texture. Compared with the HT carbon, the HT-PL carbon showed significantly reduced clumping, indicating that lignin helps prevent the aggregation of solid particles [
27]. The surface of the HT-PN charcoal appeared to have more and larger holes, and the overall structure was loose and porous. This was attributed to the continuous escape of CO₂, ammonia, and HCl generated by the ammonium carbonate and PVC during the reaction, and these escape channels changed the structure and morphology of the dechlorinated product, resulting in a loose and porous overall structure.
The appearance color of the HT-CO carbon was darker than that of the HT-PN carbon, indicating a higher degree of carbonization. From the SEM images, it can be seen that the structure of the HT-CO carbon was more compact, suggesting that the dechlorination process in HT-CO was more thorough. This is probably because adding the lignin significantly improved the agglomeration of the PVC. At the same time, the ammonium carbonate selectively catalyzed and accelerated the progress of the dechlorination reaction. Under the synergistic effect of the two, the PVC particles achieved a better dechlorination effect.
2.6.2. FT-IR Analysis
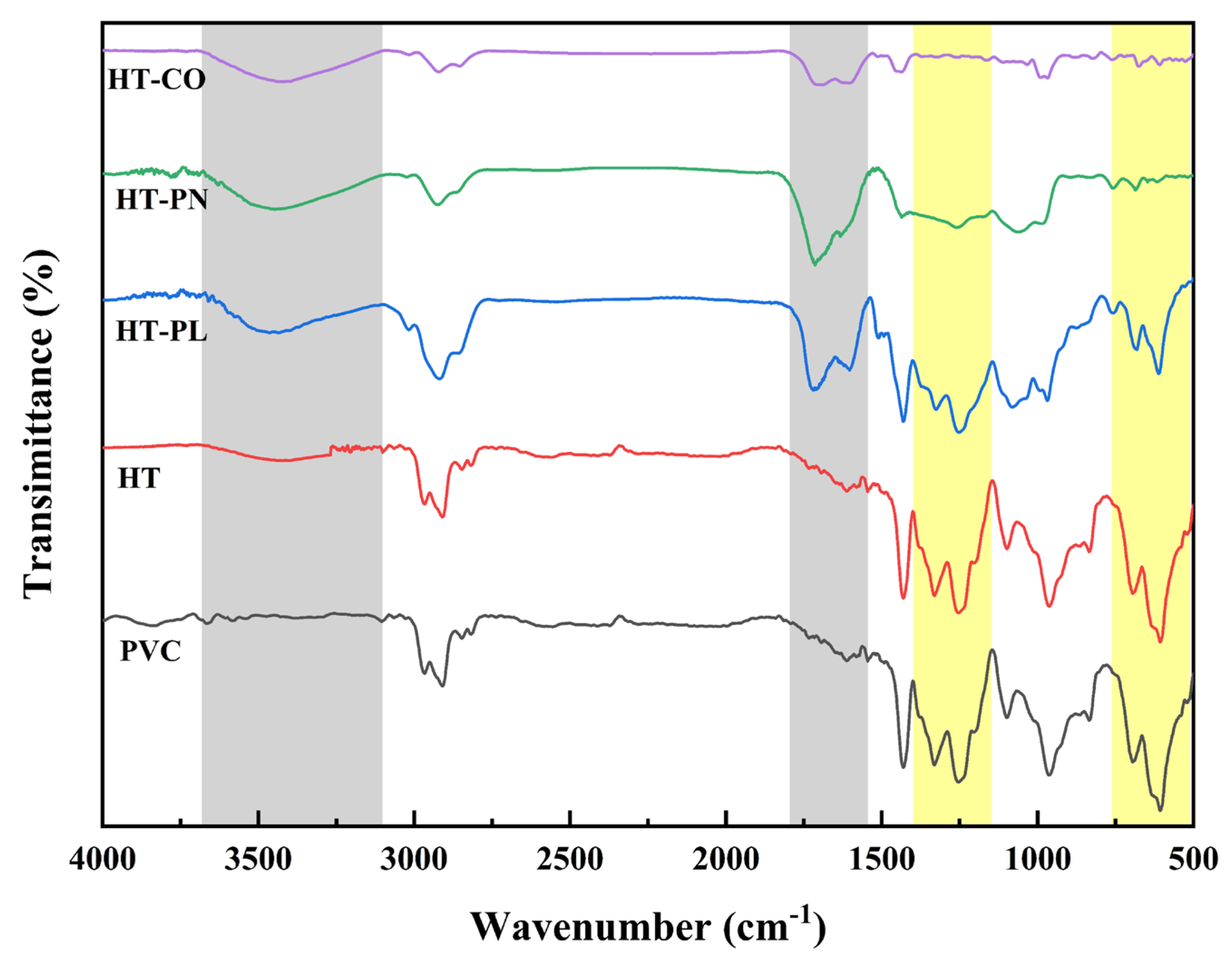
FT-IR analysis was carried out on the raw PVC particles and their hydrothermal reaction products generated under specific conditions (220 °C, 240 min) in four systems (HT, HT-PL, HT-PN, HT-CO), aiming to analyze the changes in the functional groups of PVC during the hydrothermal reaction. As shown in the infrared spectra in
Figure 7, there were noticeable chemical bond differences between hydrothermal carbons and PVC at 3500 cm
−1. The peak at 3500 cm
−1 generally corresponds to the stretching vibrations of hydroxyl (−OH) groups. Compared with PVC and the HT carbon, the carbons produced by the other three reaction systems exhibited a significant broad peak at 3500 cm
−1, indicating a substantial substitution of hydroxyl groups during the reaction. The infrared spectrum of the PVC particles shows two groups of distinct Cl-containing peaks: the stretching vibrations of C-H in -CHCl at 1324 cm
−1 and 1249 cm
−1 and the double peaks at 698 cm
−1 and 603 cm
−1 caused by C-Cl [
31]. The HT carbon shows peaks of chlorine-containing functional groups almost identical to those of the raw PVC particles. This indicates that chlorine in PVC was difficult to remove in the HT system. However, the peak intensities in the HT-PL carbon slightly decreased at these positions with the addition of lignin. When ammonium carbonate was added into the HT system, the Cl-containing peaks in the product (HT-PN carbon) significantly reduced. This aligns with the dechlorination efficiency data from measuring the Cl content in liquid-phase products. When lignin and ammonium carbonate were added simultaneously, the peaks at these positions in the product, the HT-CO carbon, almost disappeared, indicating that the chlorine in the PVC was nearly completely removed in the HT-CO system.
All the hydrothermal carbons of HT-PL, HT-PN, and HT-CO showed prominent peaks at 1700 cm
−1, indicating the formation of C=O bonds in the hydrothermal reaction of PVC. Additionally, peaks corresponding to C=C bonds at 1600 cm
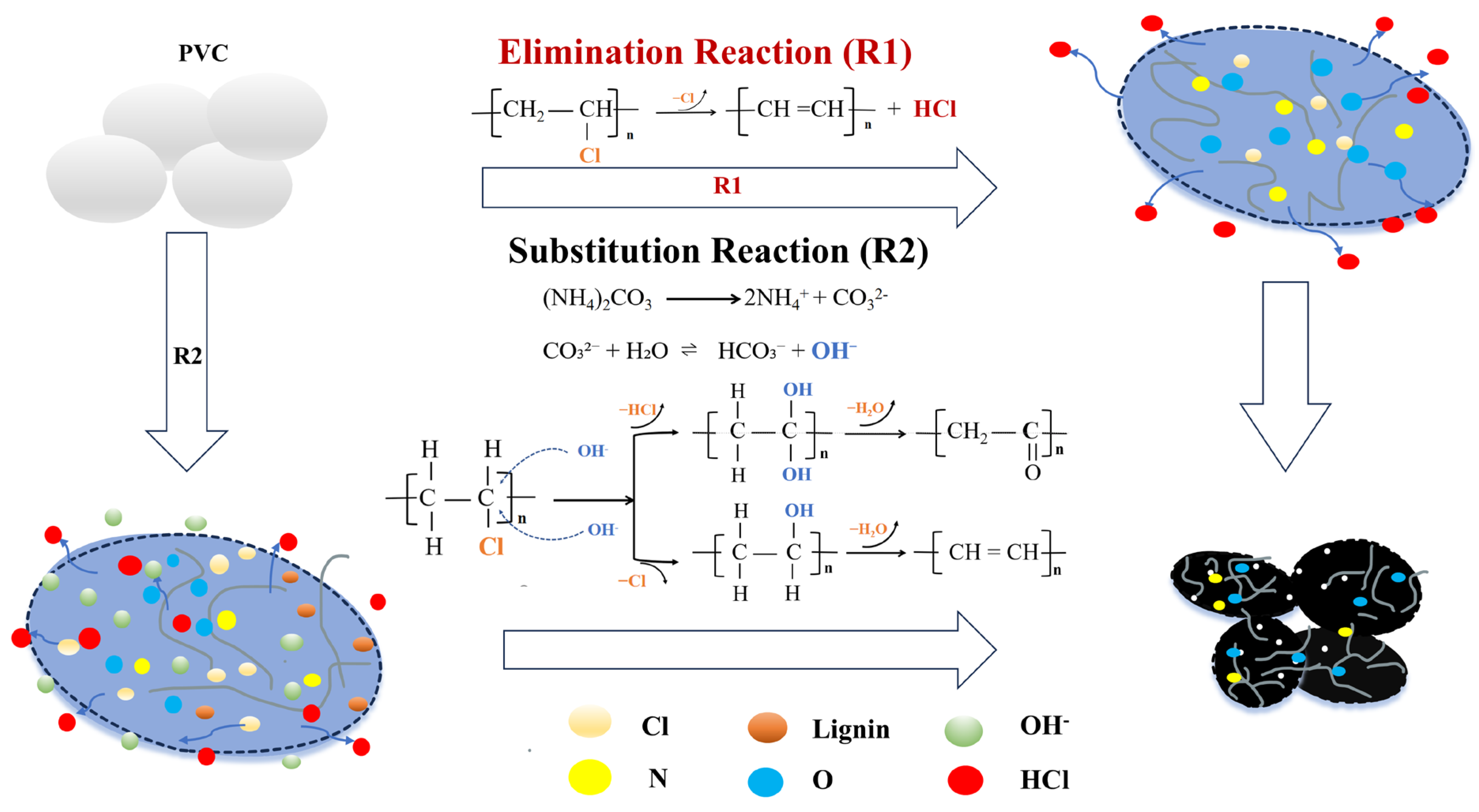
−1 also appeared in all of these three hydrothermal carbons. The appearance of these two peaks was due to the existence of two main dechlorination mechanisms, namely the elimination reaction and the substitution reaction, during the hydrothermal process. The possible dechlorination reaction pathways of PVC during the co-hydrothermal process of lignin and PVC assisted by ammonium carbonate are shown in
Figure 8. As depicted in
Figure 8, during the elimination reaction (R1), the PVC underwent condensation to form an olefin structure. This formation was evidenced by the peak appearing at 1600 cm⁻
1 in the IR spectrum. Simultaneously, chlorine atoms were detached from the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) molecules in the form of HCl and entered the aqueous phase, causing the pH value of the system to decrease (
Figure 2). In the system where ammonium carbonate existed, the ammonium carbonate underwent hydrolysis to produce carbonate ions, which further hydrolyzed to generate OH
−. When the C chain on PVC was attacked by OH
−, a substitution reaction (R2) occurred. One or two OH
− could substitute the −Cl or, simultaneously, the −H and −Cl on the carbon, generating unstable intermediate products. Subsequently, the intermediate products underwent intermolecular or intramolecular dehydration, leading to the formation of C=C and C=O functional groups, which was confirmed by both the IR spectrum and the C1s XPS spectrum.
Both lignin and ammonium carbonate have an influence on the dechlorination process of PVC, the dechlorination efficiency, and the formation of functional groups in a hydrothermal carbon product, but their action mechanisms are different. Lignin is polymerized from various aromatic ring substances, and it contains C=C bonds in itself, which are manifested in HT-PL carbon. Lignin can hydrolyze into phenolic compounds (like catechol and phenol) and OH−, preventing PVC from aggregating and increasing its contact area with water. OH− can also attack the C-Cl bonds, enhancing substitution reactions. Dechlorination efficiency is improved in the above two ways. As to ammonium carbonate, it dissociates into carbonate ions in water, and these ions hydrolyze to produce more OH−, making the C-Cl bonds more susceptible to attack and thus promoting substitution reactions and the formation of C=O bonds. Accordingly, the peak intensity of the HT-PN carbon at 1700 cm⁻1 was relatively high, but since it did not provide C=C bonds by itself, the peak intensity at 1600 cm⁻1 was relatively low. In the HT-CO carbon, the intensities of the C=O and C=C peaks were both weakened. This could be attributed to the significant release of Cl during the hydrothermal process, as hydrochloric acid in water can facilitate the partial decomposition of lignin, thereby leading to a decrease in the contribution of lignin during the carbon formation process and weakening the peak intensities at these two positions.
2.6.3. Changes in Chemical Element Composition and Chlorine Migration
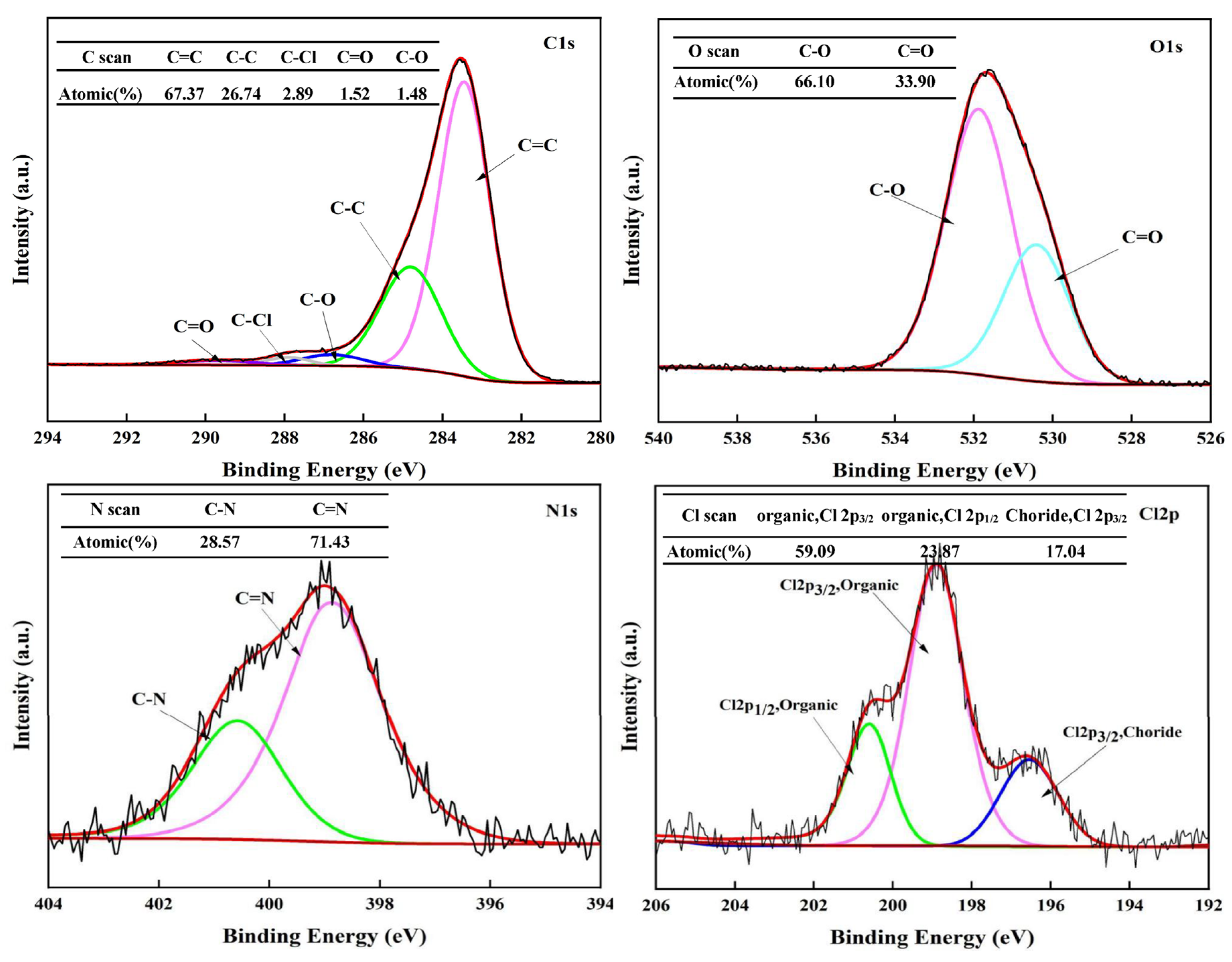
To investigate the formation mechanism of solid products and the migration behavior of chlorine during the hydrothermal process, XPS was employed to analyze the content and bonding states of C, O, N, and Cl on the surface of the HT-CO carbon with the optimal dechlorination effect.
Figure 9 represents the full XPS spectrum of the hydrothermal carbon obtained after polyvinyl chloride (PVC) underwent a reaction in the HT-CO system at a temperature of 220 °C for a duration of 240 min, encompassing the peaks of C1s, O1s, N1s, and Cl2p.
The C1s, O1s, N1s, and Cl2p XPS spectra of the HT-CO carbon are shown in
Figure 10, and the proportion of each element derived from the XPS spectrum is listed in
Table 1. The results indicate that after the ammonium carbonate-assisted co-hydrothermal reaction of lignin and PVC, the hydrothermal carbon contained very little Cl, indicating that the Cl in the PVC was effectively removed.
It can be seen from the Cl2p spectrum that the HT-CO carbon contained 82.96% organic chlorine and 17.04% inorganic chlorine. In combination with the total XPS spectrum and dechlorination efficiency, it was found that 99.53% of the Cl in PVC had been transformed into inorganic Cl and most of this inorganic Cl had been transferred to the liquid phase. Both the FT-IR analysis (
Figure 7) and XPS analysis (
Figure 9) indicated that there were C=C, C-O, and C=O bonds in the hydrothermal carbon, and their relative contents, derived from the C1s spectrum, were 67.37%, 2.89%, and 1.48%, respectively. The peak of the C=C bond in the HT-CO carbon was the largest, and there are be three possible reasons: Firstly, lignin itself has an aromatic ring structure, and part of the structure is retained in the hydrothermal carbon during the hydrothermal process; secondly, PVC may form C=C bonds through dechlorination via the elimination reaction; thirdly, the carbon structure of PVC may be damaged during the hydrothermal reaction, and aromatization may occur within the molecule, forming an aromatic hydrocarbon structure [
32]. As shown in
Figure 10, elemental O in the HT-CO carbon mainly existed in the form of C–O and C=O, and the ratio of C-O to C=O was approximately 2:1, which is relatively low [
33]; this can be attributed to ammonium carbonate’s presence promoting the conversion of some carbon–oxygen single bonds to carbon–oxygen double bonds. The N1s spectrum shows that N elements existed in the HT-CO carbon as C-N and C=N due to the generation of ammonia from the ammonium carbonate in the water, which participated in the reaction and introduced N into the HT-CO carbon.
2.6.4. Combustion Characteristics
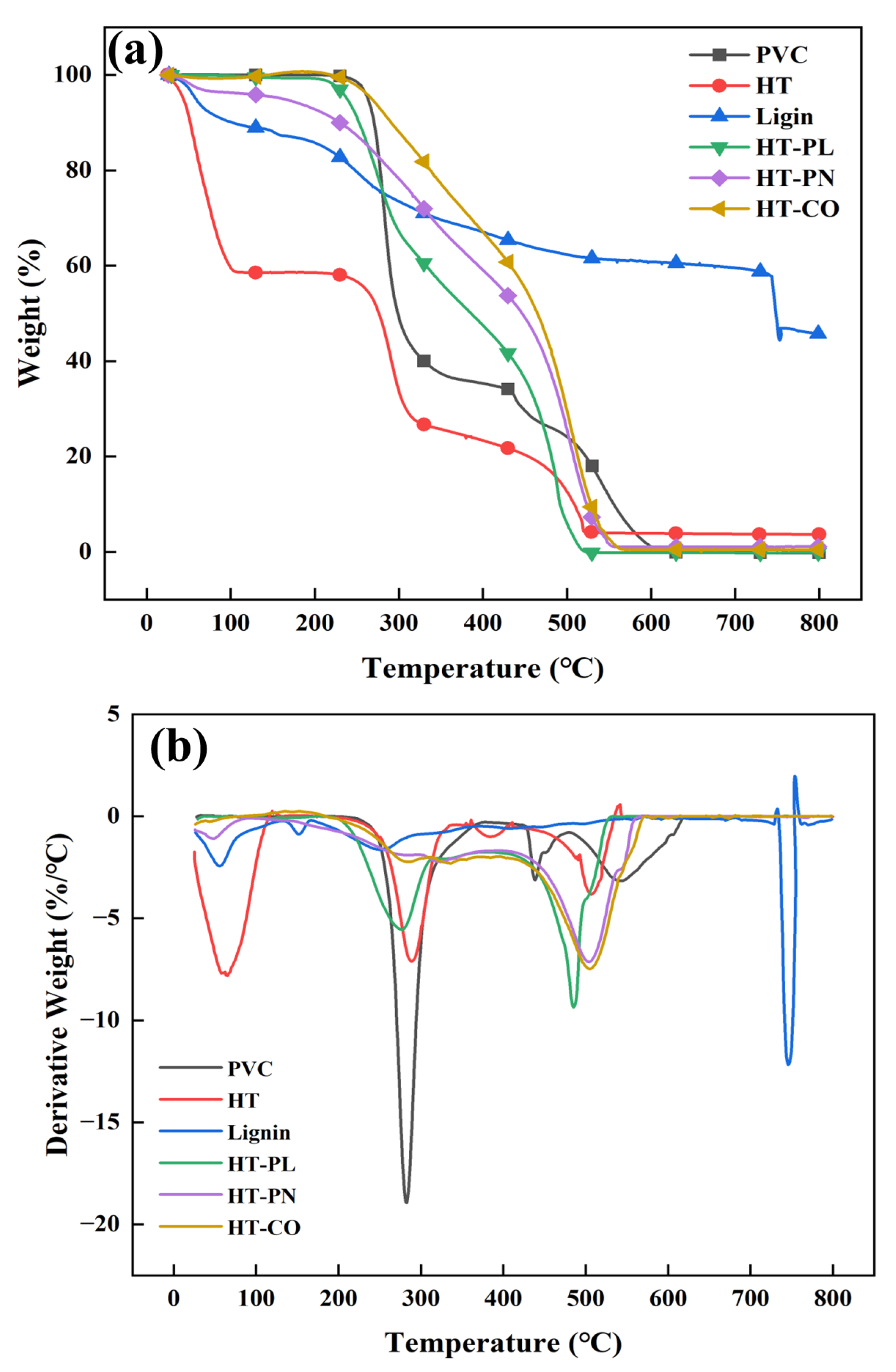
To assess the utilization potential of hydrothermal carbons, the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the PVC, lignin, and hydrothermal carbons was performed under air conditions, and the combustion characteristics of the hydrothermal carbons were thoroughly examined.
Figure 11 illustrates the thermogravimetric (TG) and derivative thermogravimetric (DTG) curves for six samples. It can be seen from
Figure 11 that the thermal weight loss of the PVC was mainly divided into three stages. The first stage was from 220 °C to 340 °C, and the maximum weight loss rate occurred at around 290 °C. In this stage, the weight loss was about 60%, mainly attributed to the chlorine element’s removal (in the form of HCl and chlorine-containing organic substances) and the partial decomposition of PVC. The second stage was between 340 °C and 460 °C, and the maximum weight loss rate occurred around 450 °C. The final stage was from 460 °C to 620 °C, with the maximum weight loss peak at around 540 °C. The residues in the PVC were completely burned out during this stage [
34].
As for the HT carbon, there was a noticeable weight loss between 30 and 100 °C, mainly due to water evaporation. A significant weight loss peak similar to that of PVC was observed around 300 °C, implying that most of the Cl was retained in the HT carbon. The weight loss peak at 300 °C for the HT-CO carbon showed significant changes compared with the PVC, the TG peak became more gradual, and the DTG peak was greatly weakened, indicating a considerable reduction in the weight loss rate. This suggests that chlorine was effectively removed from the PVC during the HT-CO hydrothermal process, and the observed weight loss at this stage was likely due to the decomposition and combustion of some volatile components in the hydrothermal carbon.
The temperature corresponding to the second maximum weight loss rate in the DTG curve of the HT-CO carbon (500 °C) was lower than the temperature corresponding to the last maximum weight loss rate of the PVC particles (550 °C), and the burnout temperature of the HT-CO carbon (550 °C) was also lower than that of the PVC (600 °C). This comparison highlights that the HT-CO carbon could achieve complete combustion at a lower combustion temperature and in a shorter time, thus demonstrating better combustion performance. Meanwhile, a significant amount of chlorine was removed during the co-hydrothermal process, substantially reducing the formation of Cl-containing species during HT-CO combustion and thereby minimizing environmental impacts.
2.6.5. Elemental Composition Analysis and Higher Heating Value (HHV) Estimation
To assess the potential of HT-CO carbon as a fuel source, elemental analysis, proximate analysis, and a calculation of the higher heating value (HHV) for the PVC and HT-CO carbon were conducted and compared. The HHV of the PVC and HT-CO charcoal was estimated according to the Chang model [
35], Equation (4). The specific method substitutes the mass composition of the C, H, N, O, and Cl elements into the following model formula:
where H, N, O, and Cl are the sample’s mass percentages of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and chlorine, respectively.
Table 2 displays the results obtained from the ultimate analysis, proximate analysis, and determination of HHV. As quantitatively shown in
Table 2, the synergistic dechlorination process achieved a dramatic reduction in chlorine content—from an initial 56.8% to 0.79%—accompanied by significant increases in oxygen (0% to 20.50%) and carbon (38.40% to 71.80%) concentrations. These results align with the infrared and XPS (C 1s, O 1s) spectra, which indicated the formation of abundant C=O, C–O, and C=C functional groups in the HT-CO system. Notably, the higher heating value (HHV) of the HT-CO carbon was 31.07 MJ/kg, substantially higher than that of raw PVC (17.87 MJ/kg), underscoring its considerable potential as a fuel source. The high chlorine content in PVC usually leads to the formation of toxic chlorine-containing compounds and causes equipment corrosion during utilization as fuel. By contrast, the hydrothermal carbon produced via the HT-CO dechlorination process removes over 99% of the chlorine, effectively preventing the generation of hazardous chlorinated byproducts during its use and thereby mitigating environmental and equipment-related risks. In addition, during the hydrothermal process, abundant oxygen-containing functional groups, such as C=C, −OH and C=O, are formed on the surface of hydrothermal carbon. This enables hydrothermal carbon, when mixed with traditional fossil fuels like coal, to lower the ignition temperature and improve the combustion efficiency [
36].
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the dechlorination efficiency of PVC in three hydrothermal systems (HT-PN, HT-PL, and HT-CO) and assessed the properties of the resulting hydrothermal carbon products. The effects of hydrothermal system type, reaction temperature, reaction time, and ammonium carbonate concentration on PVC dechlorination were systematically examined. Under optimal conditions of 220 °C for 240 min with 0.1 M ammonium carbonate, the lignin–PVC co-hydrothermal system assisted by ammonium carbonate achieved a dechlorination efficiency of 99.43%.
Based on analyses of the elemental composition, surface functional groups, surface morphology, and combustion performance of HT-CO carbon, the following conclusions are drawn: In the HT-CO system, the lignin and ammonium carbonate exhibited a significant synergistic effect on PVC dechlorination. The lignin improved the dispersion of PVC particles, while the ammonium carbonate dissolved in water to generate carbonate ions that hydrolyzed to produce hydroxide ions (OH−), increasing solution alkalinity. This enhanced the nucleophilic attack of OH− on chlorine atoms (-Cl) in the PVC, promoting substitution reactions. Under their synergistic action, the reaction temperature decreased and dechlorination efficiency was notably improved.
The hydrothermal carbon produced by the HT-CO system had a chlorine content of less than 1% and abundant functional groups on its surface, and it had a high calorific value of 31.07 MJ/kg, which gives it a better utilization value and ensures that no chlorine-containing substances are released during utilization.