Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 1H NMR
2.2. 13C NMR
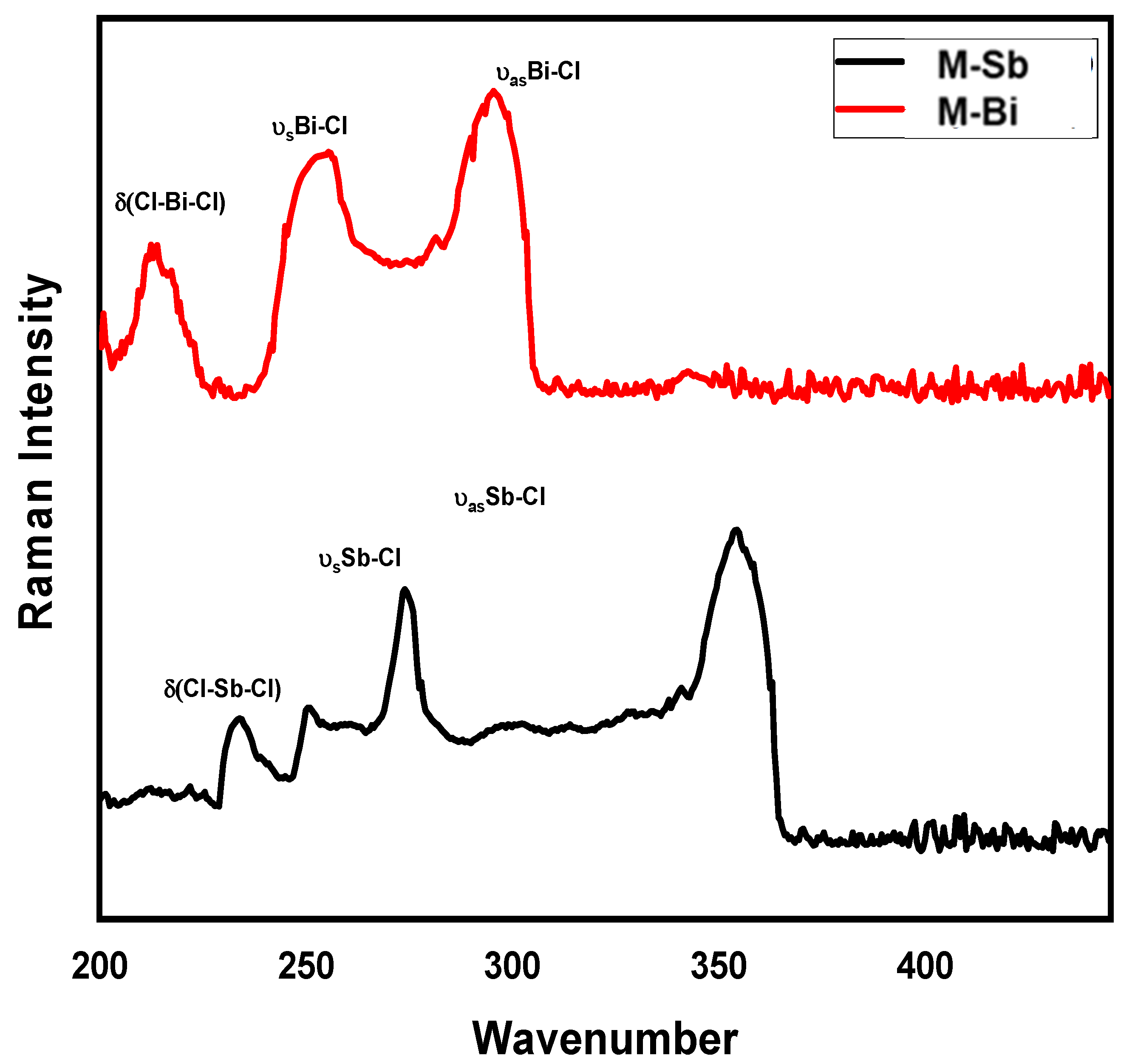
2.3. Raman Spectra
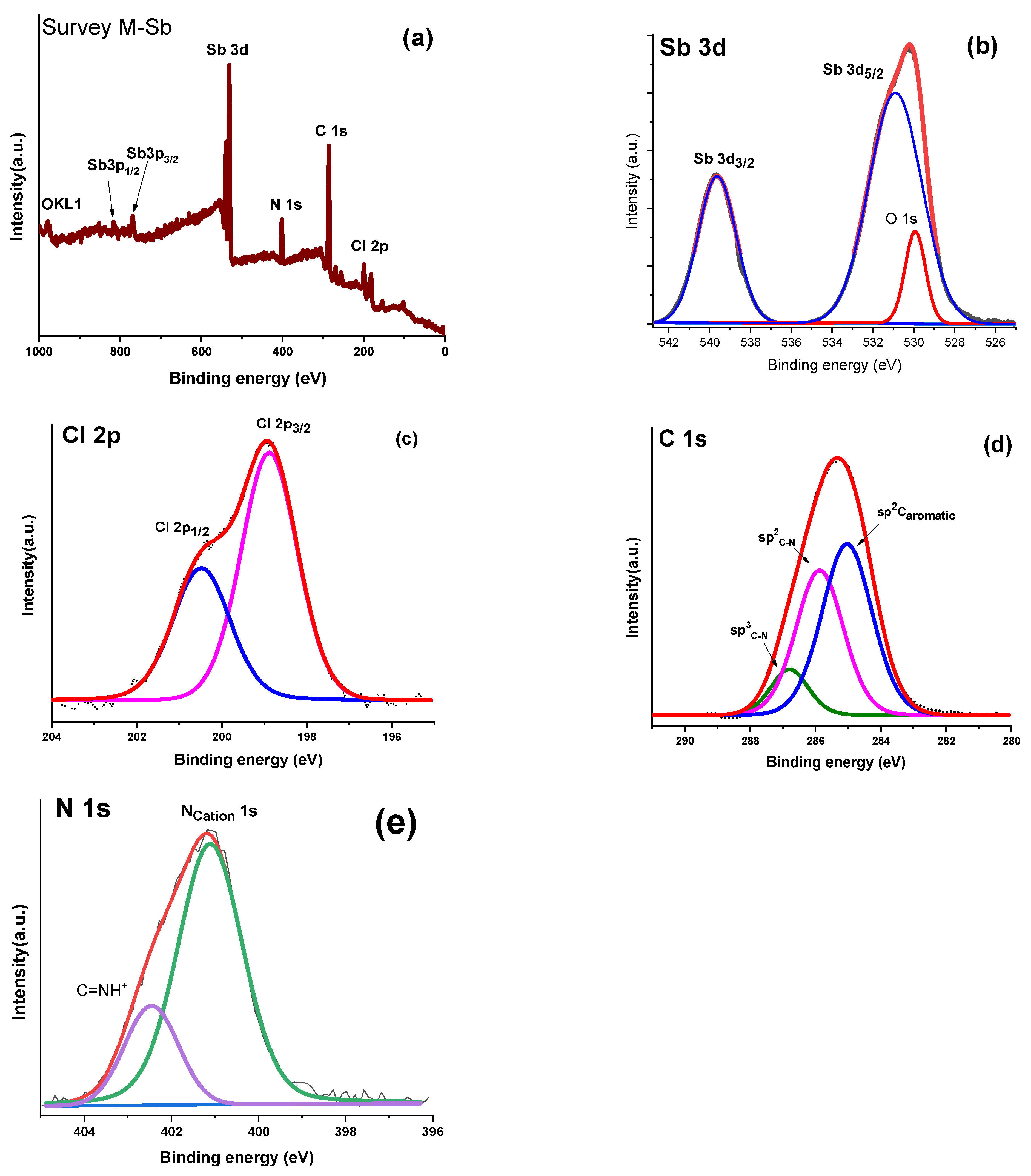
2.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
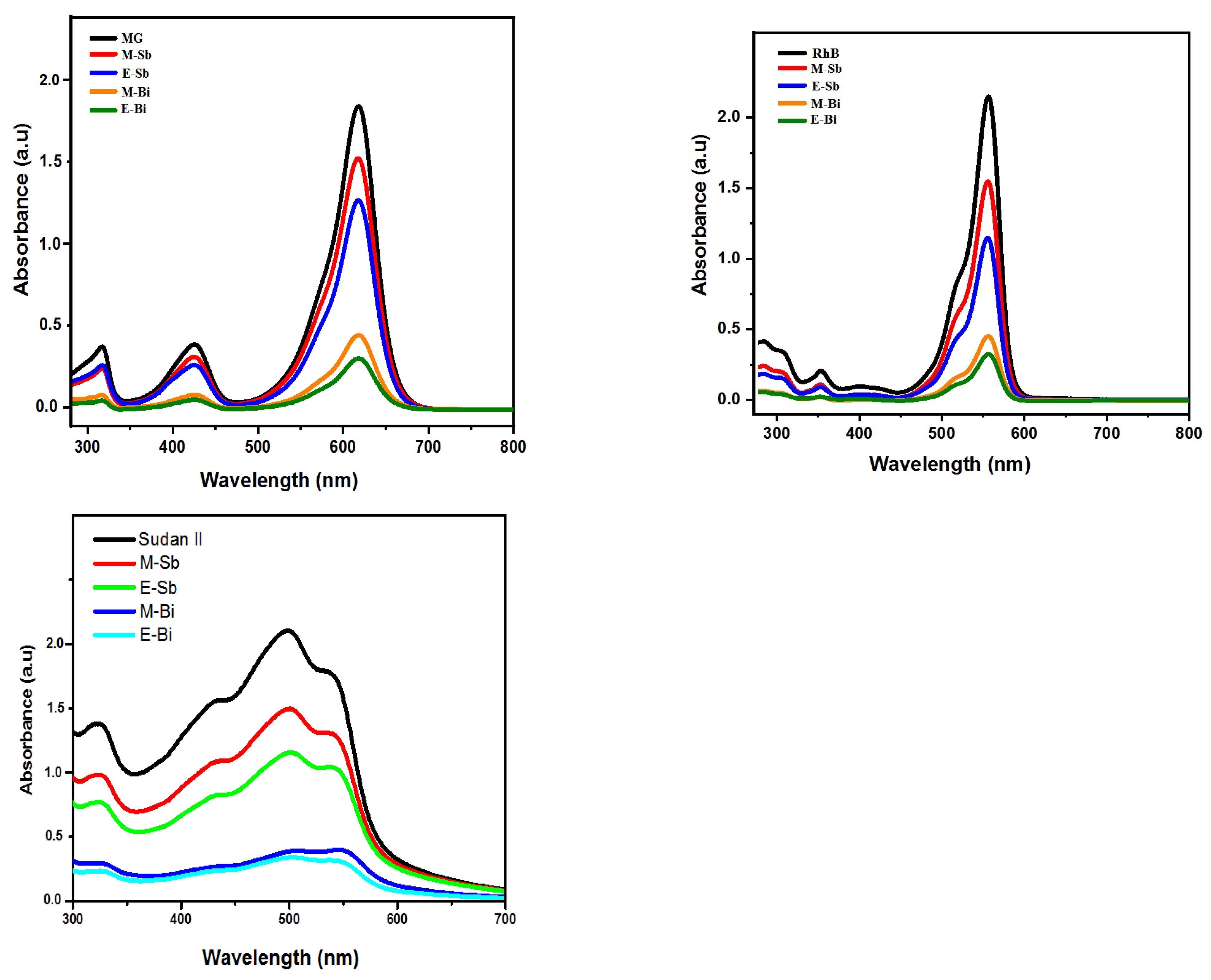
2.5. Adsorption Studies for MG, RhB and Sudan II Dyes
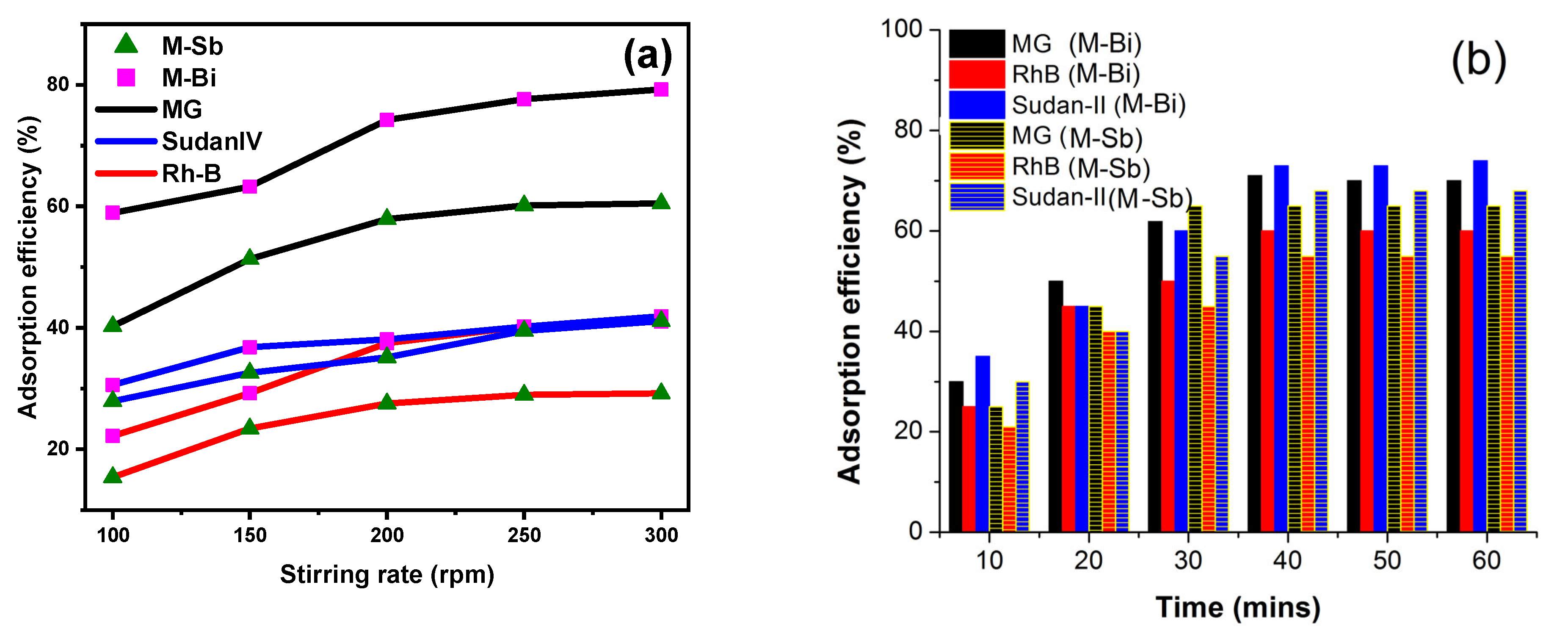
2.6. Optimization of Parameters for Adsorption Process
2.7. Stirring Rate Effect
2.8. Effect of Time
2.9. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
2.10. Effect of Dye Concentration
2.11. Effect of Metal and Alkyl Chain Length
2.12. Kinetic Studies
2.13. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics
2.14. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics
2.15. Elovich Plot
2.16. Adsorption Isotherm Models
2.17. Langmuir Isotherm
2.18. Freundlich Isotherm
2.19. Thermodynamic Studies
2.20. Comparison with the Literature
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Isotherm Model | Reaction Kinetics | Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated slag | MG | Langmuir | - | 74.2 | [63] |
| Waste apricot | MG | Langmuir Model | - | 116.3 | [64] |
| Self-assembled ionic liquid-based organosilica (SAIBO) | MG | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.01 | 19.23 | [65] |
| [BMIM][PF6] | MG | - | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.056 | 84 | [41] |
| Chitosan-based ionic liquids | MG | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.055 | 9.20 | [66] |
| [PC6C6C6C14] [Tf2N] | MG | - | - | 150 | [67] |
| Rice Husk | MG | Freundlich Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.032 | 17.98 | [68] |
| M-Sb | MG | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.00014 | 217.36 | This work |
| M-Bi | MG | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.00077 | 230.18 | This work |
| Sago waste activated carbon | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order | 16.12 | [69] |
| Hyper cross-linked polymeric adsorbent | Rhodamine B | Freundlich Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.0002 | 2.1 | [70] |
| Fly ash | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | - | 10.0 | [61] |
| Mango leaf powder | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-1st Order k1 = 0.053 | 3.31 | [62] |
| Duo-lite C-20 resin | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-1st Order k1 = 0.069 | 28.57 | [71] |
| M-Sb | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.00006 | 62.21 | This work |
| M-Bi | Rhodamine B | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order k2 = 0.00013 | 64.94 | This work |
| Organoclays MCNTS | Sudan IV | Freundlich Model | Pseudo-2nd Order | 22.7 | [72] |
| Coastal soil | Sudan IV | - | - | 0.43–4.6 | [73] |
| M-Sb | Sudan II | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order | 162.3 | This Work |
| M-Bi | Sudan II | Langmuir Model | Pseudo-2nd Order | 170.1 | This Work |
2.21. Regeneration and Recyclability of Adsorbents/ILs
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentations
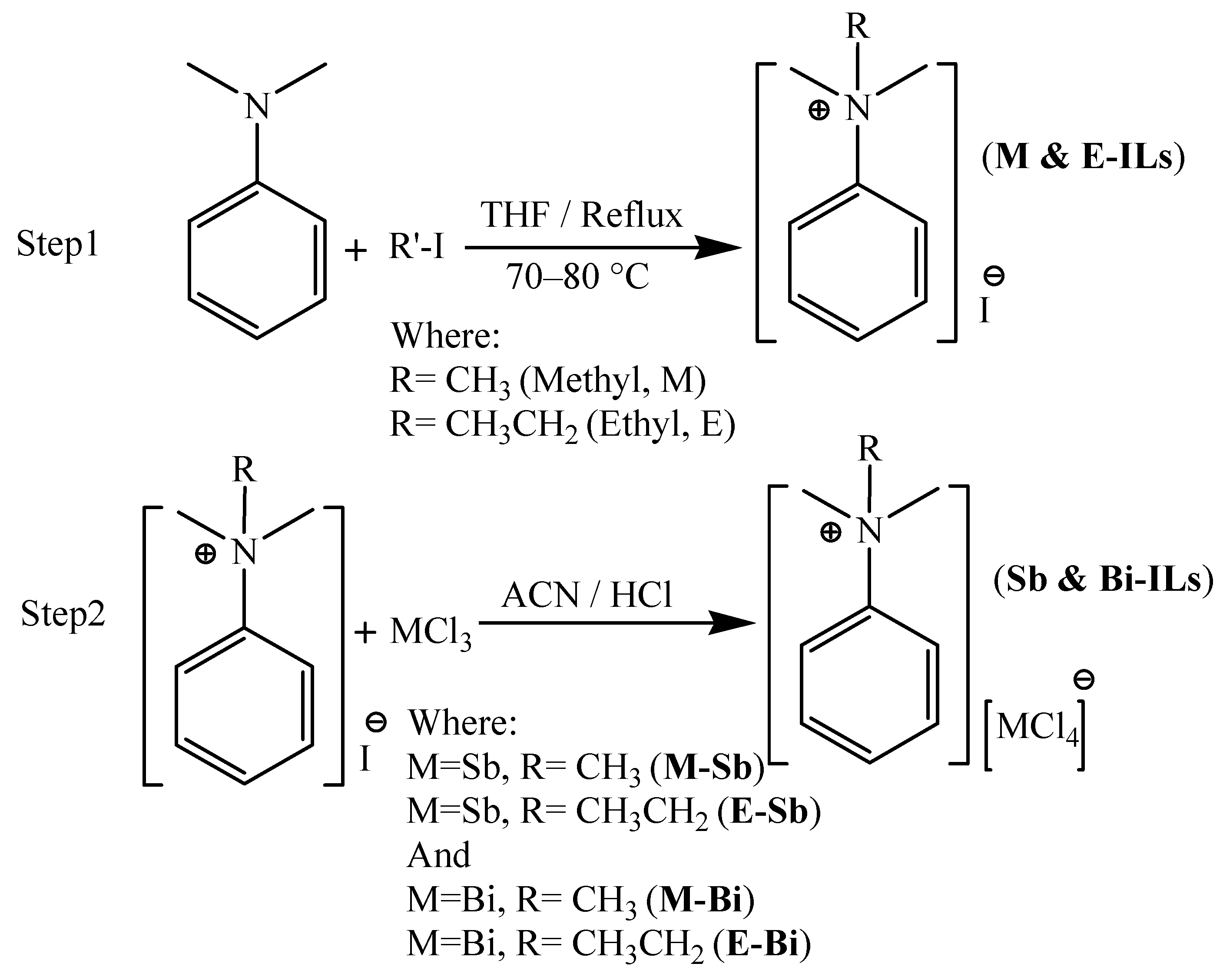
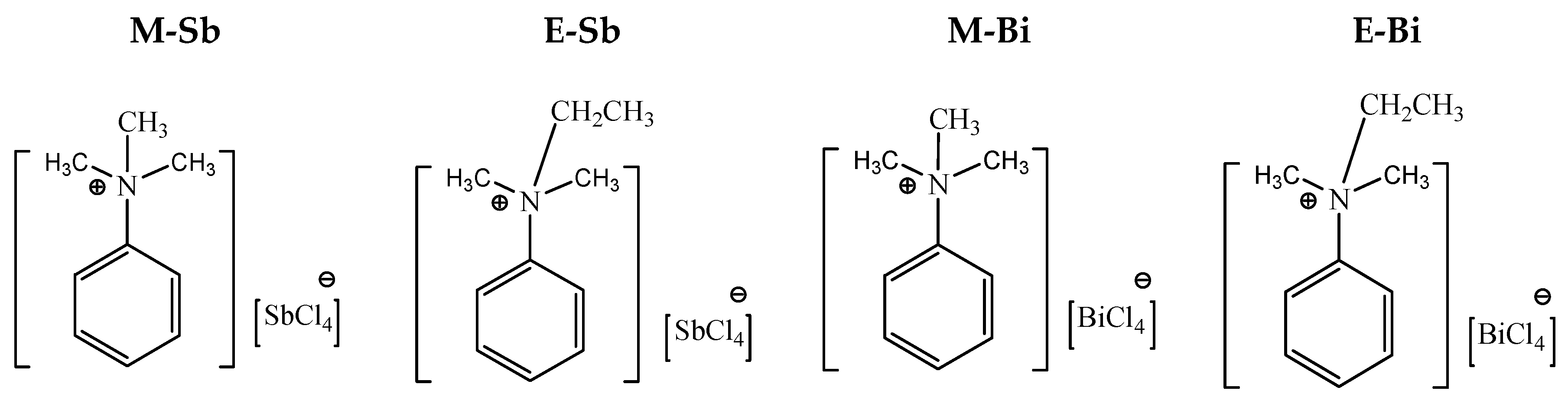
3.3. Synthesis of Adsorbent
3.4. Ionic Liquids Having Iodide as Anion (M- and E-ILs)
3.5. Dye Adsorption
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics
3.7. Adsorption Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent Advances on the Removal of Dyes from Wastewater Using Various Adsorbents: A Critical Review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcu, A.R.; Lazar, C.A.; Rogozea, E.A.; Olteanu, N.L.; Meghea, A.; Mihaly, M. Nonionic Microemulsion Systems Applied for Removal of Ionic Dyes Mixtures from Textile Industry Wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances for Dyes Removal Using Novel Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M. Synthetic Dyes: A Threat to the Environment and Water Ecosystem. In Textiles and Clothing; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Austin, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A Critical Review on Textile Wastewater Treatments: Possible Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Jain, C.K.; Malik, D.S. Toxic Characterization of Textile Dyes and Effluents in Relation to Human Health Hazards. J. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2014, 3, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; Onyancha, R.B.; Okundaye, B.; Pal, K.; Osibote, O.A.; Esiekpe, E.L.; Kusuma, H.S.; Darmokoesoemo, H. A Facile Review on the Sorption of Heavy Metals and Dyes Using Bionanocomposites. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 8030175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; El Nemr, A.; Hassaan, A. Health and Environmental Impacts of Dyes: Mini Review. Am. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, J.; Sharma, M. Impact of Textile Dyes on Human Health and Environment. In Impact of Textile Dyes on Public Health and the Environment; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, G.; Thakur, A. Distinct Approaches of Removal of Dyes from Wastewater: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandisa, R.V.; Saibaba, K.V.N.; Shaik, K.B.; Gopinath, R. Dye Removal by Adsorption: A Review. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2016, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaykhaii, M.; Sasani, M.; Marghzari, S. Removal of Dyes from the Environment by Adsorption Process. Chem. Mater. Eng. 2018, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, S.; Shaw, R.; Tiwari, S.; Tiwari, S.K. Adsorption Dynamics of Congo Red Dye Removal Using ZnO Functionalized High Silica Zeolitic Particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeb, A.; Yousaf, T.; Murtaza, M.; Zahra, M.; Zafar, M.I.; Waseem, A. Green Photocatalyst Cu/NiO Doped Zirconia for the Removal of Environmental Pollutants. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Munir, M.; Nafees, M.; Shah, S.S.A.; Ullah, H.; Waseem, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Silylation Based Grafted Bentonites for the Removal of Sudan Dyes: Isothermal, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 291, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of Pollutants in Wastewater via Biosorbents, Nanoparticles and Magnetic Biosorbents: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Ajmal, M.; Shah, A.; Akhter, M.S.; Ullah, H.; Waseem, A. Modified Clays as an Efficient Adsorbent for Brilliant Green, Ethyl Violet and Allura Red Dyes: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3831–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, T.; Areeb, A.; Murtaza, M.; Munir, A.; Khan, Y.; Waseem, A. Silane-Grafted MXene (Ti3C2TX) Membranes for Enhanced Water Purification Performance. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 19502–19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yahyaoui, S.; Hanafy, H.; Seliem, M.K.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Sellaoui, L.; Li, Q. Effective Adsorption of Dyes on an Activated Carbon Prepared from Carboxymethyl Cellulose: Experiments, Characterization and Advanced Modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Tang, A.Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Kan, C.W. Effect of Reverse Micelle-Encapsulated Reactive Dyes Agglomeration in Dyeing Properties of Cotton. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 161, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikri, R.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; Maguana, Y. Efficiency of Sawdust as Low-Cost Adsorbent for Dyes Removal. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Savio, N.; Srivastava, R.K. A Comprehensive Review on the Production and Application of Sludge Biochar for Water and Soil Remediation. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 2021, 4, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal through Graphene Oxide-based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.; Kaur, Y.; Umar, A.; Chaudhary, G.R. Ionic Liquid and Surfactant Functionalized ZnO Nanoadsorbent for Recyclable Proficient Adsorption of Toxic Dyes from Waste Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Imtiaz-Ud-Din.; Ahmed, S.; Bučar, D.K.; Tahir, M.N.; Palgrave, R.G. Synthesis, Structural Analysis, Electrochemical and Magnetic Properties of Tetrachloroferrate Ionic Liquids. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 13429–13440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.N.; Xing, Y.L.; Xia, C.L.; Sun, H.M.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Ionic iron (III) complexes of bis (phenol)-functionalized imidazolium cations: Synthesis, structures and catalysis for aryl Grignard cross-coupling of alkyl halides. Dalton Trans. 2012, 38, 11597–11607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, S.S.; Filho, R.M. Are Ionic Liquids Eco-Friendly? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic Liquids Toxicity—Benefits and Threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.S.; Tjong, T.C.; Chew, J.W.; Hu, X. Techniques for Recovery and Recycling of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjala, L.K.S.; Kundu, D.; Dutta, D.; Kumar, A.; Bal, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, E.; Mishra, R.; Kumar, S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Advances in Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Environmental Remediation and Reusability. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 396, 123896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, A.O.; Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Demulsification of Stable Seawater/Arabian Heavy Crude Oil Emulsions Using Star-like Tricationic Pyridinium Ionic Liquids. Fuel 2021, 304, 121436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, S.L.; Kar, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Matuszek, K.; Pringle, J.M. Ionic Liquids for Renewable Thermal Energy Storage-a Perspective. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anceschi, A.; Riccardi, C.; Patrucco, A. The Role of Ionic Liquids in Textile Processes: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, A.; Mezzetta, A.; Nowicki, J.; Łuczak, J.; Guazzelli, L. Betaine and L-Carnitine Ester Bromides: Synthesis and Comparative Study of Their Thermal Behaviour and Surface Activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 115988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Shi, E.; Wei, X.; Hou, Z. Ionic Liquid-Stabilized Metal Oxoclusters: From Design to Catalytic Application. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 5127–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.; Leal, B.C.; Lozano, P.; Monteiro, A.L.; Migowski, P.; Scholten, J.D. Ionic Liquids in Metal, Photo-, Electro-, and (Bio) Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 5227–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Qazi, A.B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Metal-Based Ionic Liquids in Oxidative Desulfurization: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.F.; Neumann, J.; Thoming, J. Regeneration, Recovery and Removal of Ionic Liquids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2011, 15, 1992–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.L.; Ahn, K.; Koo, Y.-M. Methods for Recovery of Ionic Liquids—A Review. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Palgrave, R.G.; Muhammad, H. Physico-Chemical Properties of Magnetic Dicationic Ionic Liquids with Tetrahaloferrate Anions. ChemistryOpen 2023, 12, e202200229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Bustam, M.A.; Man, Z.; Khan, A.S. Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Separation of Dye from Aqueous Solution. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Wang, J. Association of Ionic Liquids with Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution: A Thermodynamic Study. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 47, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Evans, T.; Palgrave, R.G.; Imtiaz-ud-Din. An XPS Study of Bridged Dicationic Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Res. 2022, 46, 174751982210929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabar, G.; Saeed, M.; Khoso, S.; Zafar, A.; Saggu, J.I.; Waseem, A. Development of Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Novel Nanocomposites for Green and Efficient Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuel Oil. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2022, 12, 18479804221106321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Batool, S.; Palgrave, R.G.; Yousuf, S. Deep Extractive and Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuels by Using Iron (Iii) Based Dication Ionic Liquids. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 15731–15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.; Lovelock, K.R.J.; Hunt, P.A. Bi (III) Halometallate Ionic Liquids: Interactions and Speciation. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, A. The Aqueous Chloride Complexes of Antimony (III) and Lanthanum (III) from 25 C up to 300 C by Raman Spectroscopy; University of Guelph: Guelph, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Cai, T.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xing, W.; Yan, Z. Multivalent Cationic and Anionic Mixed Redox of an Sb 2 S 3 Cathode toward High-Capacity Aluminum Ion Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 10829–10836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sahoo, R.K.; Shinde, N.M.; Yun, J.M.; Mane, R.S.; Chung, W.; Kim, K.H. Asymmetric Faradaic Assembly of Bi2O3 and MnO2 for a High-Performance Hybrid Electrochemical Energy Storage Device. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32154–32164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.S.; Byard, S.J.; Seaton, C.C.; Sadiq, G.; Davey, R.J.; Schroeder, S.L.M. Proton Transfer and Hydrogen Bonding in the Organic Solid State: A Combined XRD/XPS/ssNMR Study of 17 Organic Acid–Base Complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Malek, N.N.; Jawad, A.H.; Ismail, K.; Razuan, R.; ALOthman, Z.A. Fly Ash Modified Magnetic Chitosan-Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend for Reactive Orange 16 Dye Removal: Adsorption Parametric Optimization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagotia, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S. A Review on Modified Sugarcane Bagasse Biosorbent for Removal of Dyes. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129309. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Fernandes, A.M.; Freire, M.G. Complete Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Media Using Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, V.; Begum, K.M.M.S.; Anantharaman, N. Studies on Removal of Phenol Using Ionic Liquid Immobilized Polymeric Micro-Capsules. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, M.; Shemirani, F. A Novel Method for Dye Removal: Ionic Liquid-Based Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Extraction (IL-DLLE). Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, M.; Singh, P.K.; Srivastav, A.L. A Review of Bismuth-Based Sorptive Materials for the Removal of Major Contaminants from Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17492–17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Mustafa, F.S. Bismuth-Based Nanostructured Photocatalysts for the Remediation of Antibiotics and Organic Dyes. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 291–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Nafees, M.; Iqbal, F.; Awan, M.S.; Shah, A.; Waseem, A. Adsorption Kinetics of Malachite Green and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions Using Surfactant-Modified Organoclays. Acta Chim. Slov. 2017, 64, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savara, A. Standard States for Adsorption on Solid Surfaces: 2D Gases, Surface Liquids, and Langmuir Adsorbates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15710–15715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Gomes, A.A.; Tran, H.N. Comparison of the Nonlinear and Linear Forms of the van’t Hoff Equation for Calculation of Adsorption Thermodynamic Parameters (∆ S° And∆ H°). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Wang, K.-S.; Li, H.-C.; Wey, M.-Y.; Chou, J.-D. Enhancement of Rhodamine B Removal by Low-Cost Fly Ash Sorption with Fenton Pre-Oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Sharma, S.; Ali, I. Adsorption of Rhodamine B Dye from Aqueous Solution onto Acid Activated Mango (Magnifera Indica) Leaf Powder: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2011, 3, 286–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Mittal, J.; Kurup, L.; Singh, A.K. Process Development for the Removal and Recovery of Hazardous Dye Erythrosine from Wastewater by Waste Materials—Bottom Ash and de-Oiled Soya as Adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, C.A. Applicability of the Various Adsorption Models of Three Dyes Adsorption onto Activated Carbon Prepared Waste Apricot. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhamifar, D.; Shojaeipoor, F.; Roosta, M. Self-Assembled Ionic-Liquid Based Organosilica (SAILBO) as a Novel and Powerful Adsorbent for Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseeruteen, F.; Hamid, N.S.A.; Suah, F.B.M.; Ngah, W.S.W.; Mehamod, F.S. Adsorption of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution by Using Novel Chitosan Ionic Liquid Beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thasneema, K.K.; Dipin, T.; Thayyil, M.S.; Sahu, P.K.; Messali, M.; Rosalin, T.; Elyas, K.K.; Saharuba, P.M.; Anjitha, T.; Hadda, T. Ben Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals, Phenolic Compounds and Textile Dyes from Industrial Waste Water Using Phosphonium Based Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mishra, R.; Saha, P.; Kushwaha, P. Adsorption Thermodynamics, Kinetics and Isosteric Heat of Adsorption of Malachite Green onto Chemically Modified Rice Husk. Desalination 2011, 265, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Karthika, C.; Vennilamani, N.; Pattabhi, S. Activated Carbon from Industrial Solid Waste as an Adsorbent for the Removal of Rhodamine-B from Aqueous Solution: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-H.; Huang, K.-L.; Liu, S.-Q.; Wang, A.-T.; Yan, C. Adsorption of Rhodamine B and Methyl Orange on a Hypercrosslinked Polymeric Adsorbent in Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 330, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, S.M.; Al-Gaid, A.A. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption Behavior of Rhodamine B Dye on Duolite C-20 Resin. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous Removal of 2, 4-Dichlorophenol and Pb (II) from Aqueous Solution Using Organoclays: Isotherm, Kinetics and Mechanism. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 22, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zhou, Q. Adsorption Behavior of Sudan I-IV on a Coastal Soil and Their Forecasted Biogeochemical Cycles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10749–10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


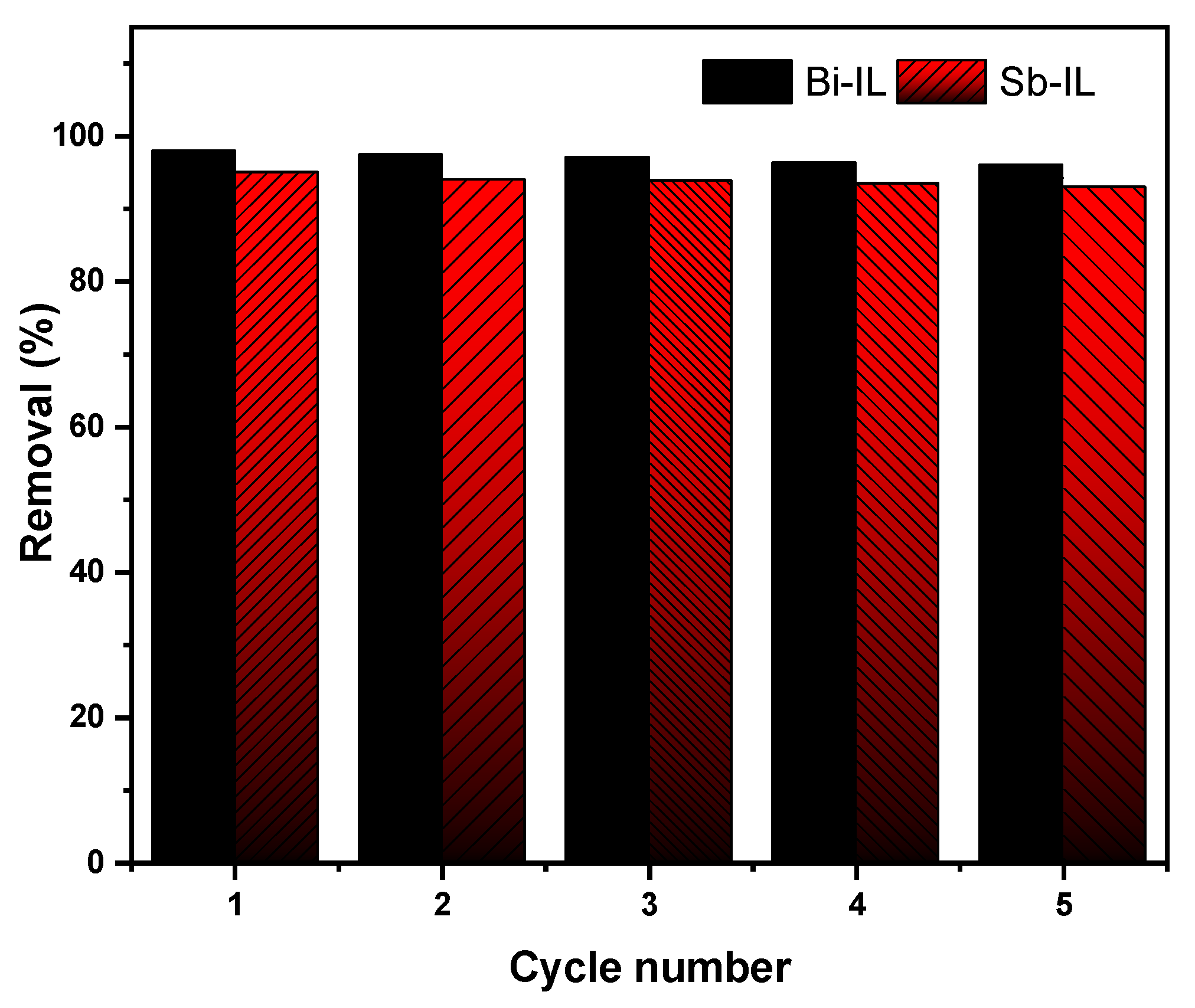
| Adsorbent | Dyes | Pseudo-1st-Order Kinetics | Pseudo-2nd-Order Kinetics | Elovich Plot | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg·g−1) | R2 | k2 (min−1) | qe (mg·g−1) | R2 | α (mg·g−1 .min−1) | β (g.mg−1) | R2 | ||
| M-Sb | MG | 0.225 | 8.1 | 0.972 | 0.00077 | 146.41 | 0.991 | 1.007 | 0.029 | 0.989 |
| RhB | 0.114 | 7.64 | 0.946 | 0.00139 | 56.49 | 0.998 | 1.03 | 0.084 | 0.995 | |
| Sudan II | 0.0306 | 42.52 | 0.75 | 0.00012 | 165.56 | 0.98 | 18.77 | 0.038 | 0.965 | |
| M-Bi | MG | 0.204 | 36.59 | 0.929 | 0.00015 | 56.08 | 0.989 | 2.26 | 0.033 | 0.984 |
| RhB | 0.05 | 4.55 | 0.96 | 6.1E-05 | 85.47 | 0.985 | 5.48 | 0.193 | 0.983 | |
| Sudan II | 0.0202 | 14.53 | 0.91 | 0.0009 | 134.95 | 0.99 | 39.16 | 0.035 | 0.97 | |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg·g−1) | qm (mg·g−1) | KL (L.mg−1) | R2 | n | KF (mg·g−1) | R2 | ||
| M-Sb | MG | 217.1 | 246.2 | 0.278 | 0.995 | 1.99 | 4.09 | 0.98 |
| RhB | 62.94 | 66.45 | 0.176 | 0.99 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 0.97 | |
| Sudan II | 162.1 | 176.67 | 0.761 | 0.92 | 2.46 | 63.43 | 0.982 | |
| M-Bi | MG | 230.1 | 261 | 2.63 | 0.997 | 2.48 | 4.71 | 0.98 |
| RhB | 64.21 | 78.57 | 0.078 | 0.99 | 1.84 | 3.68 | 0.97 | |
| Sudan II | 170.4 | 187.96 | 1.19 | 0.866 | 2.08 | 51.41 | 0.942 | |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | ΔS° (J·mol−1·K−1) | ΔG° (J·mol−1) | ΔH° (J·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-Sb | MG | 566.5 | −1920.0 | −46,660.0 |
| RhB | 651.9 | −3350.0 | −45.34 | |
| Sudan II | 478.7 | −3580.0 | −16,840.0 | |
| M-Bi | MG | −1.619 | −3420.0 | −20,340.0 |
| RhB | 471.4 | −4110.0 | −3.13 | |
| Sudan II | 475.1 | −3420.0 | −16,480.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, A.; Rafique, N.; Batool, S.; Saleem, M.; Alhodaib, A.; Waseem, A. Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes. Catalysts 2025, 15, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050492
Zafar A, Rafique N, Batool S, Saleem M, Alhodaib A, Waseem A. Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes. Catalysts. 2025; 15(5):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050492
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Anham, Nouman Rafique, Saadia Batool, Muhammad Saleem, Aiyeshah Alhodaib, and Amir Waseem. 2025. "Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes" Catalysts 15, no. 5: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050492
APA StyleZafar, A., Rafique, N., Batool, S., Saleem, M., Alhodaib, A., & Waseem, A. (2025). Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes. Catalysts, 15(5), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050492







