Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of Supernatants
2.2. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Non-Disintegrated Sewage Sludge
2.3. Crystallization Kinetics of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Non-Disintegrated Sewage Sludge
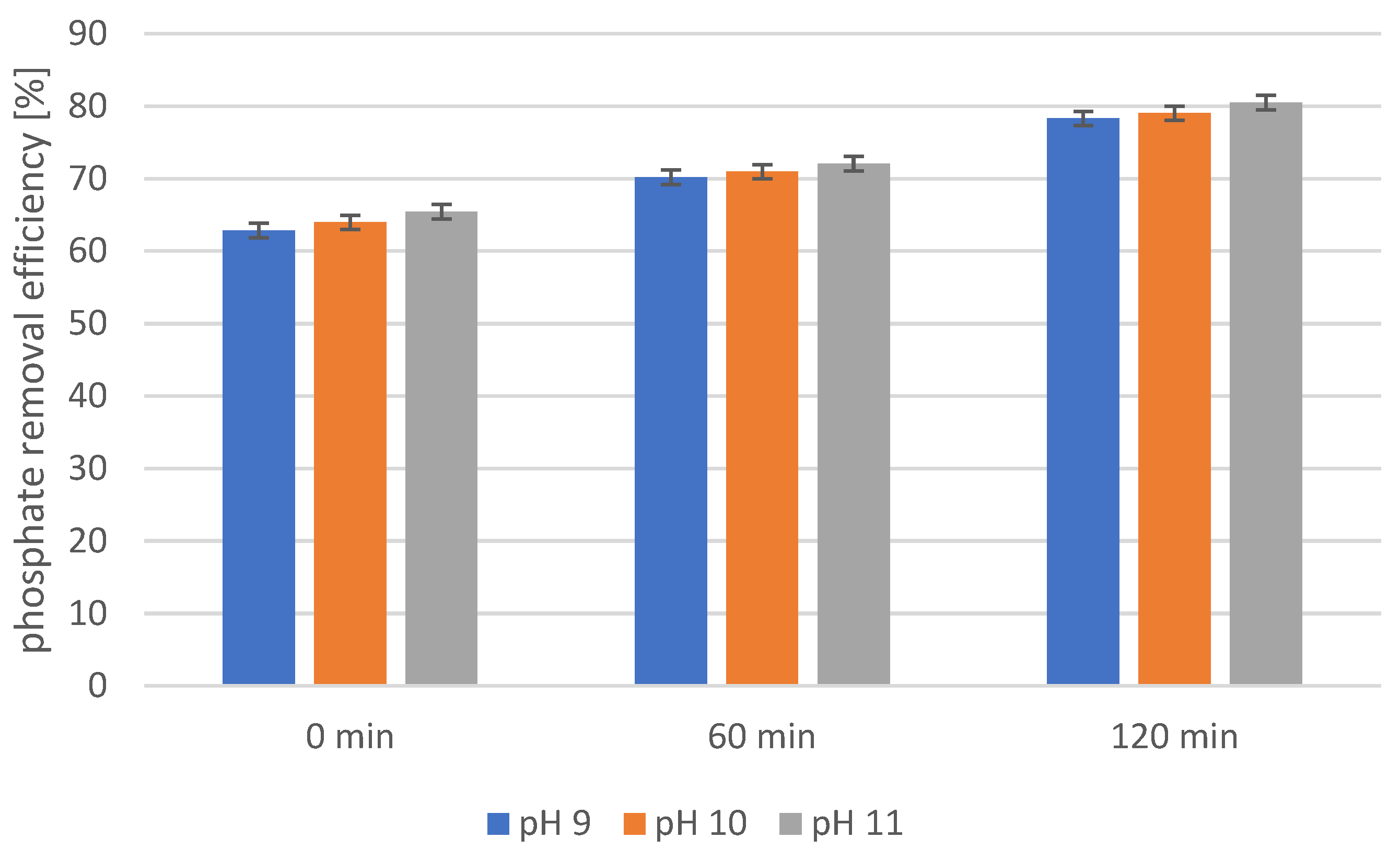
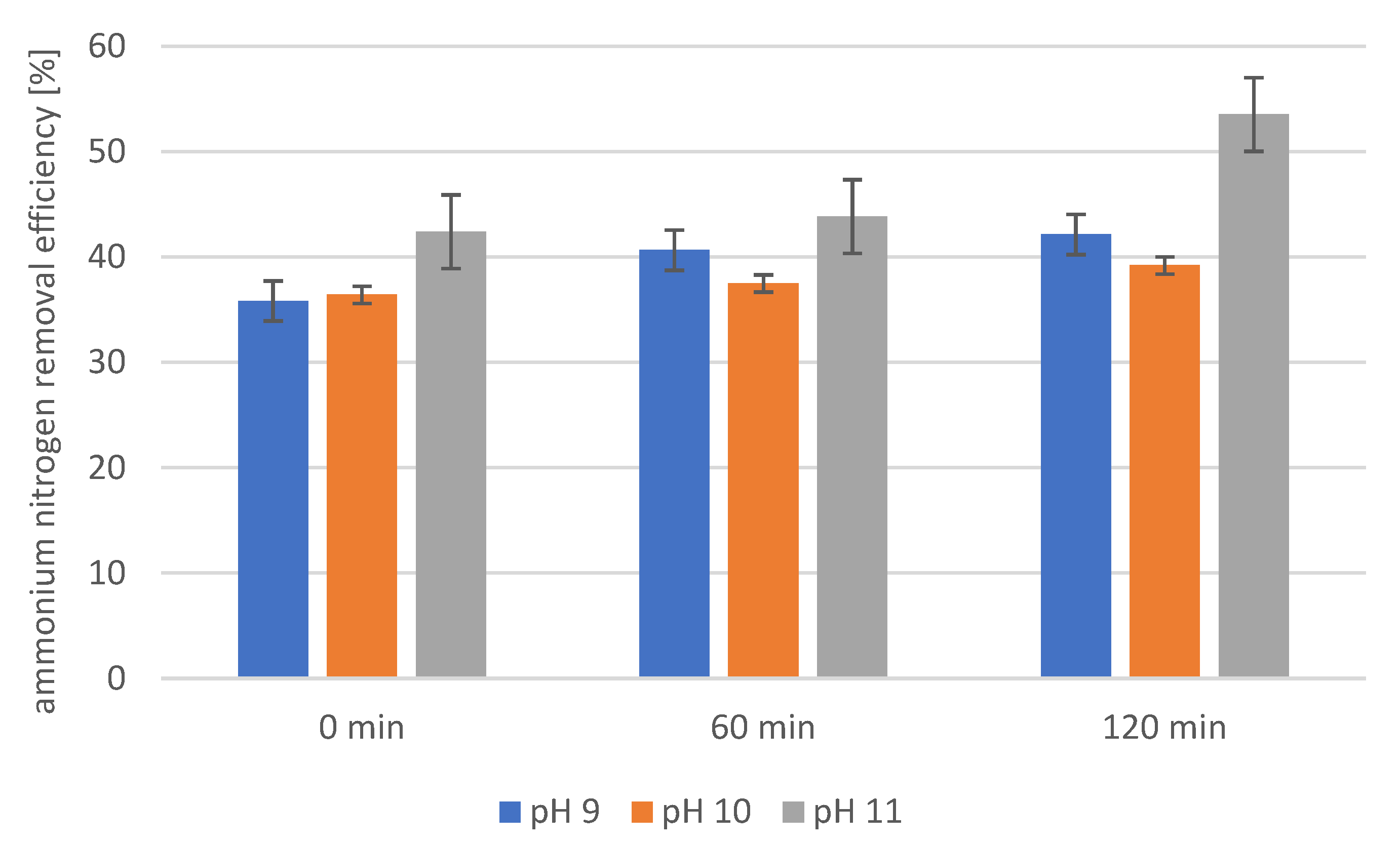
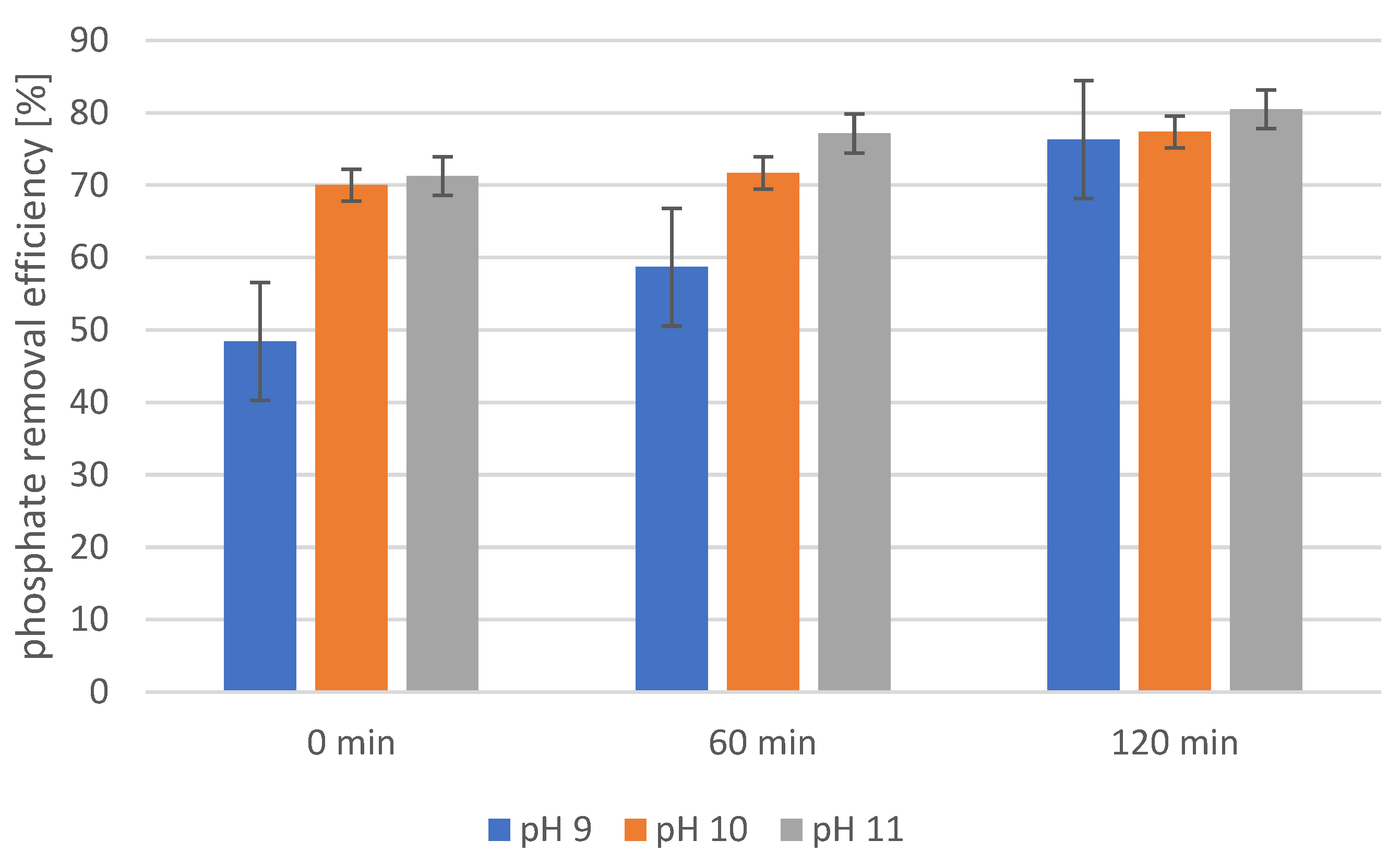
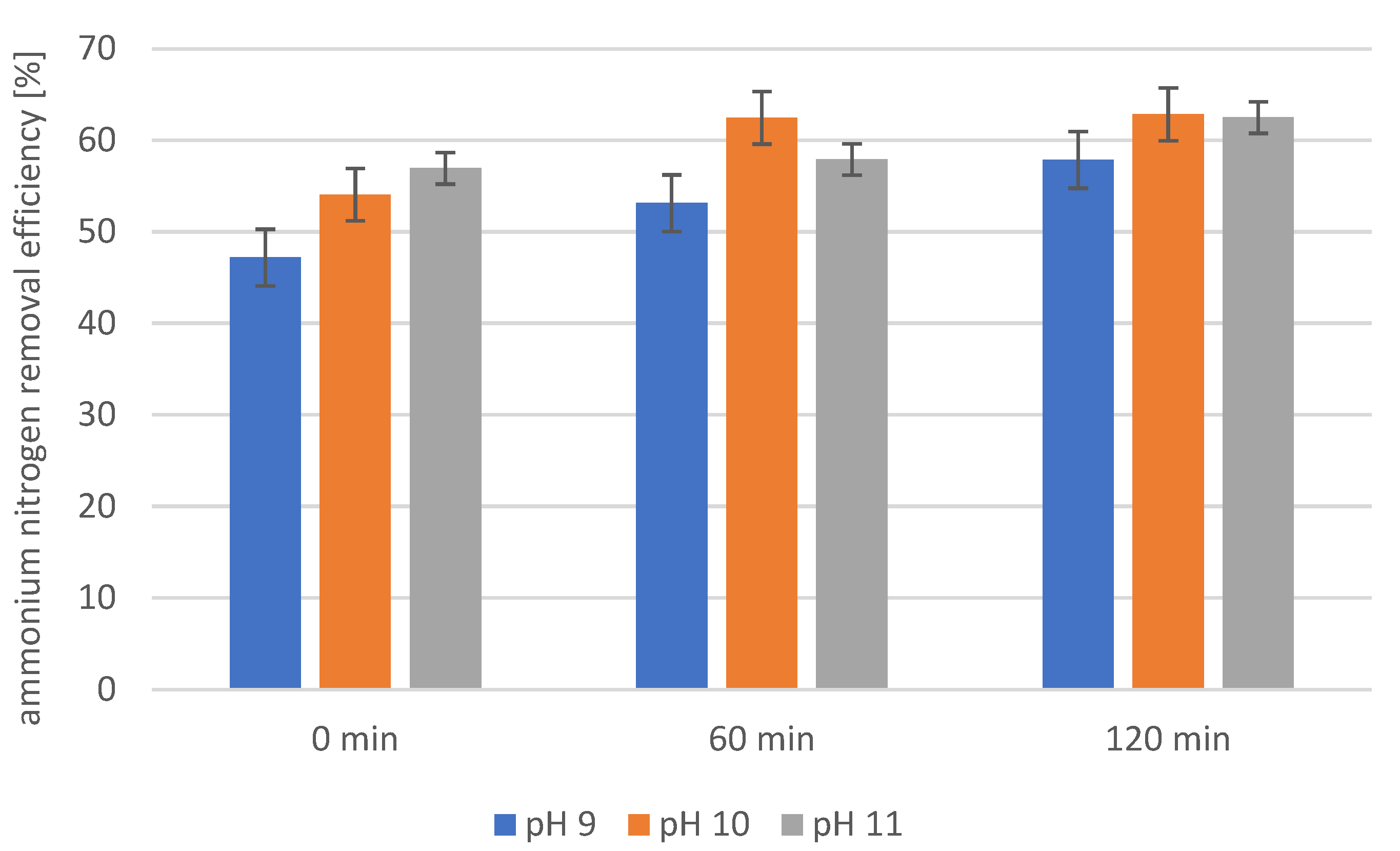
2.4. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Disintegrated Sewage Sludge with 1% Papain Enzyme
2.5. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Disintegrated Sewage Sludge with 2% Papain Enzyme
2.6. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Disintegrated Sewage Sludge with 3% Papain Enzyme
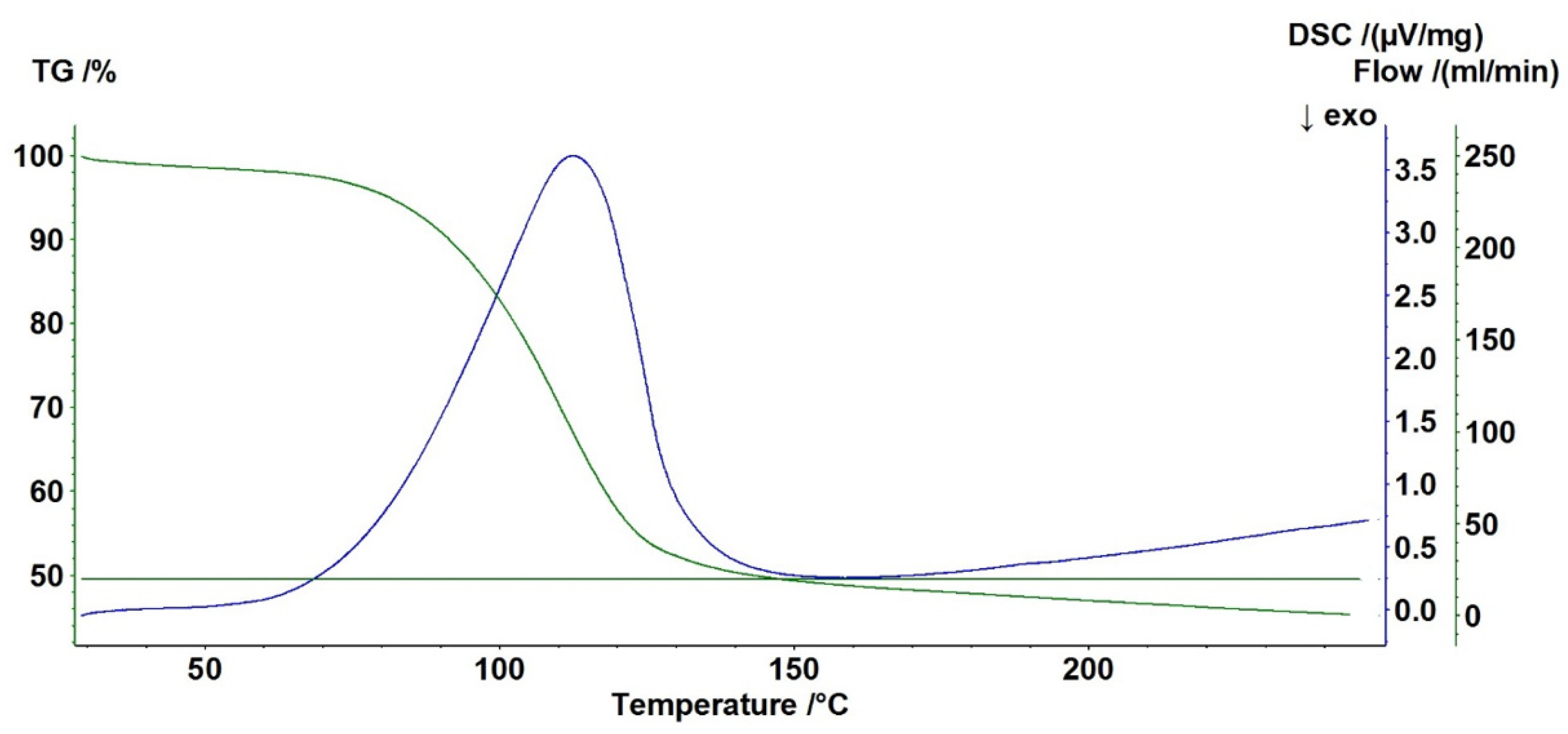
2.7. DSC/TGA Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Precipitation of Struvite
3.3. Course of Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daneshgar, S.; Cecconet, D.; Capsoni, D.; Capodaglio, A.G. Side-stream phosphorus recovery in activated sludge processes. Water 2022, 14, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M.; Osiak, M.; Pietrzak, A.; Bień, B.; Poniatowska, A. Comparative efficiency of phosphorus removal from supernatants by coagulation process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 301, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.S.; Back, Y.J.; Kim, K.C.; Cha, R.; Jeong, T.Y.; Chung, H.K. Optimization for the removal of orthophosphate from aqueous solution by chemical precipitation using ferrous chloride. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.H.; Takdastan, A.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Mogadam, M.A.; Mengelizadeh, N. Removal of orthophosphate from municipal wastewater using chemical precipitation process in Ahvaz wastewater treatment plant, Iran. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufahl, P.K.; Groat, L.A. Sedimentary and igneous phosphate deposits: Formation and exploration: An invited paper. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 483–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, R.W.; Wellmer, F.W. Approaching a dynamic view on the availability of mineral resources: What we may learn from the case of phosphorus? Global Environ. Change 2013, 23, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowska, J.; Malarski, M.; Siwiec, T. Modelling of sediment precipitation containing struvite from aqueous solutions on the inner walls of steel pipelines. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2019, 45, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Miao, Y.; Jia, F.; Du, R.; Peng, Y. Biological nitrogen removal from sewage via anammox: Recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouropoulos, N.C.; Koutsoukos, P.G. Spontaneous precipitation of struvite from aqueous solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 213, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineyard, D.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Barak, P. BioWin modeling of CalPrex phosphorus recovery from wastewater predicts substantial nuisance struvite reduction. Environments 2024, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Molinari, R. Advances in struvite precipitation technologies for nutrients removal and recovery from aqueous waste and wastewater. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, J.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Hermana, B.; García, J. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge as struvite. Water 2023, 15, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Ou, R.; Zeng, G. A review of struvite crystallization for nutrient source recovery from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater by struvite crystallization: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 433–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshgar, S.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Buttafava, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. Optimization of P compounds recovery from aerobic sludge by chemical modeling and response surface methodology combination. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchi, F.; Cavinato, C. Smart approaches to food waste final disposal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jóźwiak, T.; Kowalkowska, A.; Filipkowska, U.; Struk-Sokołowska, J.; Bolozan, L.; Gache, L.; Ilie, M. Recovery of phosphorus as soluble phosphates from aqueous solutions using chitosan hydrogel sorbents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.; Chang, H.; Jang, Y.; Lim, H.; Jung, J.; Kim, W. Prediction of adequate pH and Mg2+ dosage using an empirical MgO solubility model for struvite crystallization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavhungu, A.; Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Mbaya, R.; Tekere, M.; Kortidis, I.; Chatzisymeon, E. Advocating circular economy in wastewater treatment: Struvite formation and drinking water reclamation from real municipal effluents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.T.; Zhang, R.; Teter, S.; McGarvey, J.A. The effect of enzyme addition on anaerobic digestion of Jose Tall Wheat Grass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4564–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamadony, M. Enrich waste activated sludge digestibility via natural enzyme supplementation. E3S Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2019, 83, 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Pesante, S.; Venegas, M.; Vidal, G. Developments in pre-treatment methods to improve anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 173–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, I.V.; de Almeida, R.; Cammarota, M.C. A review of sludge pretreatment methods and co-digestion to boost biogas production and energy self-sufficiency in wastewater treatment plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszograj, S.; Płuciennik-Koropczuk, E. Thermal disintegration of sewage sludge as a method of improving the biogas potential. Energies 2023, 16, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjenbruch, M.; Kopplow, O. Enzymatic, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment of surplus sludge. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B. Effects of Enzymatic Disintegration on the Decomposition of Organic Compounds During Methane Fermentation of Sewage Sludge. Catalysts 2025, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B.; Popowska-Nowak, E.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M.; Bień, B.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M. Intensification of Energy Production in the Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge Using Enzymatic Disintegration. Energies 2025, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Pulse electric field technology for wastewater and biomass residues’ improved valorization. Processes 2021, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montusiewicz, A. Impact bioaugmentation on nutrient release in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Proc. ECOpole 2015, 9, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, A.D.; Larson, M.A. Theory of Particulate Processes; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hulburt, H.M.; Katz, S. Some problems in particle technology: A statistical mechanical formulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1964, 19, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, C.L. Crushing & Grinding Process Handbook; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Stanclik, A. Precipitation and Crystallization of Struvite from Aqueous Solutions Similar in Chemical Composition to Municipal and Industrial Sewage. (Wytrącanie i Krystalizacja Struwitu z Roztworów Wodnych Zbliżonych Składem Chemicznym do Ścieków Komunalnych i Przemysłowych). Retrieved from Atlas Zasobów Otwartej Nauki. July 2024. Available online: https://zasobynauki.pl/zasoby/wytracanie-i-krystalizacja-struwitu-z-roztworow-wodnych-zblizonych-skladem-chemicznym-do-sciekow-kom,78497 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Hövelmann, J.; Stawski, T.M.; Besselink, R.; Freeman, H.M.; Dietmann, K.M.; Mayanna, S.; Pauw, B.R.; Benning, L.G. A template-free and low temperature method for the synthesis of mesoporous magnesium phosphate with uniform pore structure and high surface area. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6939–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, A.; de Sario, S.; Attanasio, A.; Di Capua, F.; Gorgoglione, A.; Fratino, U.; Mascolo, M.C.; Pirozzi, F.; Trancone, G.; Spasiano, D. Phosphorus recovery as struvite and hydroxyapatite from the liquid fraction of municipal sewage sludge with limited magnesium addition. J. Environ. Qual. 2023, 52, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trancone, G.; Spasiano, D.; Race, M.; Luongo, V.; Petrella, A.; Pirozzi, F.; Fratino, U.; Piccinni, A.F. A combined system for asbestos-cement waste degradation by dark fermentation and resulting supernatant valorization in anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



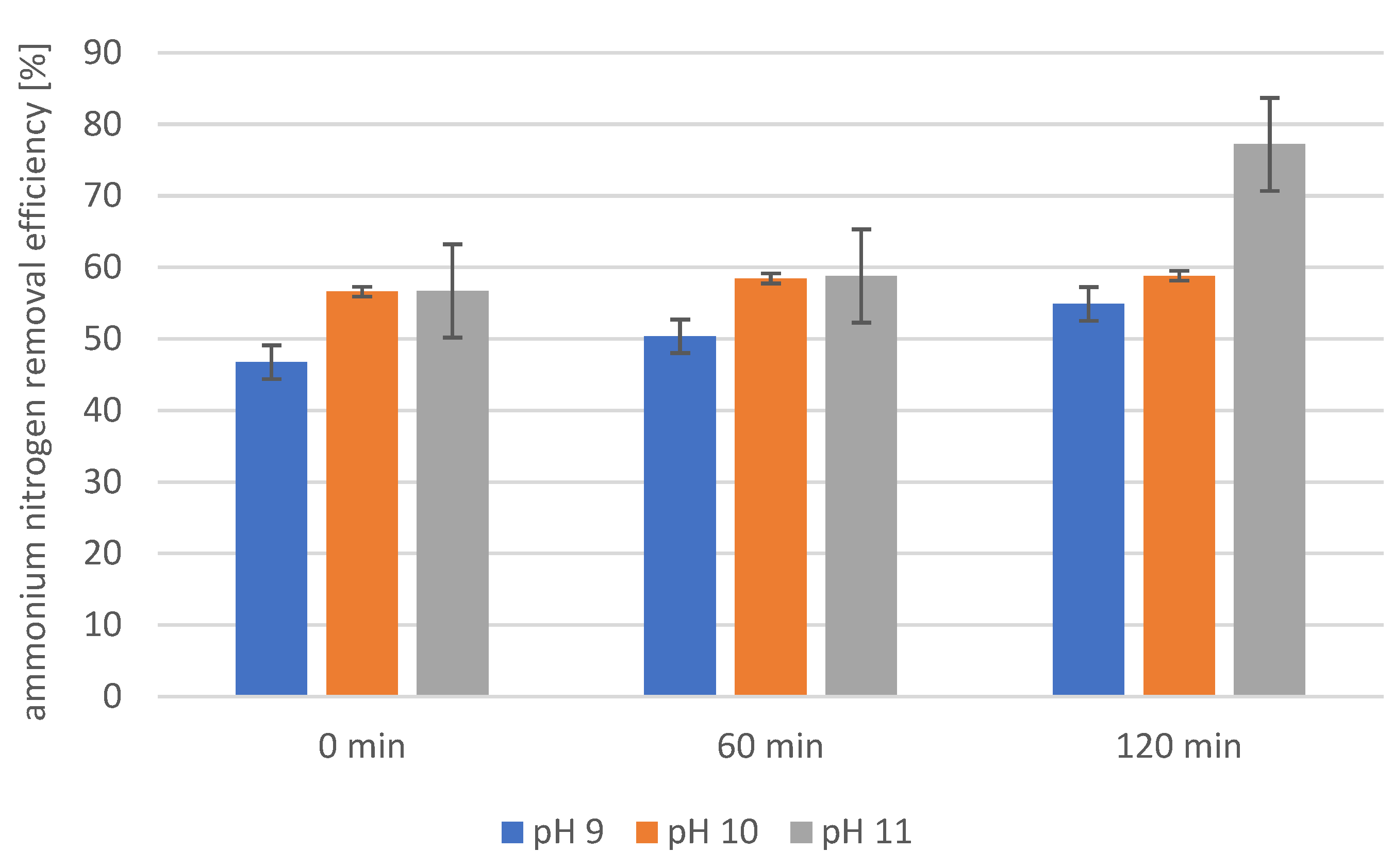


| Indicator | Stage I 0% | Stage II 1% | Stage III 2% | Stage IV 3% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphates, mg PO43−/L | 27.2 | 47.7 | 78.4 | 92.4 |
| Phosphorus, mg P−/L | 8.9 | 15.6 | 25.6 | 30.2 |
| Ammonium nitrogen, mg N-NH4+/L | 685.8 | 667.7 | 660.0 | 655.5 |
| COD, mgO2/L | 1800 | 1900 | 1900 | 2000 |
| pH | t [s] | G [m/s] | B [1/(s·m3)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 900 | 2.07 × 10−8 | 3.7 × 107 |
| 9.0 | 3600 | 7.68 × 10−9 | 4.3 × 106 |
| 10.0 | 900 | 1.67 × 10−8 | 5.3 × 107 |
| pH | t [s] | Mkexp [mg/L] | Mk [mg/L] | RE [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 3600 | 359.3 | 336.3 | 6.4 |
| 7200 | 373.5 | 380.0 | 1.7 | |
| 10 | 3600 | 336.1 | 339.6 | 1.0 |
| 7200 | 356.5 | 418.0 | 17.2 | |
| 11 | 3600 | 347.8 | 342.7 | 1.5 |
| 7200 | 468.4 | 459.8 | 1.8 |
| Temperature Range | Loss of Weight [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Pure Struvite | |
| 30 °C do 150 °C | 49.22 | 46.89 |
| Temperature Range | Amount of Papain [%] | Loss of Weight [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 9 | pH = 10 | pH = 11 | ||
| 30 °C do 150 °C | 0 | ~30 | ~30 | ~35 |
| 30 °C do 150 °C | 1 | ~30 | ~30 | ~35 |
| 30 °C do 150 °C | 2 | ~40 | ~40 | 49.65 |
| 30 °C do 150 °C | 3 | 48.10 | 48.70 | 49.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macherzyński, B.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M.; Gierycz, P.; Kraj, A. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge. Catalysts 2025, 15, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040361
Macherzyński B, Wszelaka-Rylik M, Gierycz P, Kraj A. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge. Catalysts. 2025; 15(4):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040361
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacherzyński, Bartłomiej, Małgorzata Wszelaka-Rylik, Paweł Gierycz, and Aleksandra Kraj. 2025. "Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge" Catalysts 15, no. 4: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040361
APA StyleMacherzyński, B., Wszelaka-Rylik, M., Gierycz, P., & Kraj, A. (2025). Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge. Catalysts, 15(4), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15040361







