Abstract
Using the DFT method, an analogue of R,R-t-Bu-BenzP* was tried as a potential ligand for Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation. This ligand contains benzyl groups instead of the t-Bu groups in R,R-t-Bu-BenzP*. Computational results imply that the R,R-Benz-BenzP* ligand (1) is expected to provide excellent enantioselectivity in the Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of 1-phenylethanone oxime. The computed effectiveness of the R,R-Benz-BenzP* ligand is stipulated by its conformational flexibility, which helps stabilize the crucial transition states via a non-bonding interaction between the substrate and the catalyst. R,R-Benz-BenzP* ligands with CN- and OMe-substituted benzyl rings were also computed to possess the same effectiveness.
1. Introduction
Asymmetric hydrogenation is a hot area in modern organic chemistry, enabling the synthesis of optically active compounds using relatively small loadings of chiral catalysts. Numerous hydrogenation products prepared with this method are widely used as pharmaceuticals [1], agrochemicals [2], or chiral synthons in the chemical industry [3]. The efficiency of asymmetric hydrogenation largely depends on the catalysts employed, particularly the structure of the ligand, which dictates the stereochemical outcome of the reaction [4,5]. Diphosphine ligands, due to their tunable electronic and steric properties, play a crucial role in the development of new catalytic systems [6].
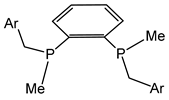
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the design of diphosphine ligands for asymmetric hydrogenation [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Among the numerous chiral diphosphine ligands designed, synthesized and applied in transition metal catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation, the most relevant ones to this work are a series of structurally simple C2 symmetric diphosphines with substituents markedly different in size developed by Imamoto. The most successful ligands of this type are listed in Scheme 1.
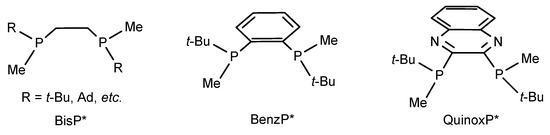
Scheme 1.
Chiral diphosphines designed and synthesized by Imamoto’s group.
The first successful ligand in this series was t-Bu-BisP* [11], in which a combination of the smallest alkyl substituent (Me) and bulky t-Bu group (or a similarly massive alkyl group) allowed creating a well-defined asymmetric environment around the metal atoms in its chelate complexes. These ligands were quite popular in the 2000s since, for example, their Rh complexes provided excellent ee values in asymmetric hydrogenations of a wide range of substrates [11,12,13,14]. Even 25 years later, t-Bu-BisP* remains a frequent subject in catalytic asymmetric reactions. Creative modification of its structure by Imamoto provided QuinoxP* [15] and BenzP* [16] ligands, which have been used much more frequently recently due to their higher stabilities, catalytic performance and wider range of the substrates. The synthetic potential of BenzP* and QuinoxP* ligands in Rh-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation was demonstrated in a comprehensive paper in 2012 [17]. In the next decade, both ligands were widely used in numerous asymmetric catalytic reactions [10,18], including Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation [19,20].
Being interested in the asymmetric hydrogenation catalyzed by diphosphine complexes of Earth-abundant metals and the mechanism of asymmetric hydrogenation, we decided to develop a protocol for computational screening of prospective diphosphine ligands for Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation via computing the important parts of the catalytic cycles and estimating the expected optical yields of the products.
2. Results and Discussion
We decided to modify the t-Bu substituents in the BenzP* ligand. Originally, it was supposed that the physical difference in size between the t-Bu and the Me groups stipulates the high stereoinduction characteristic for the ligands shown in Scheme 1 and structurally similar compounds.
From that point of view, the t-Bu group seems to be a hardly improvable ideal for achieving the perfect optical yields in various catalytic transformations. Indeed, only the evident change in the adamantyl substituent led to comparable efficiency, whereas attempts to make these groups even “bulkier” yielded inferior results, probably due to the lack of spherical symmetry [12]. Moreover, the first prototype of the BisP* ligand with phenyl groups instead of t-butyls was notably less effective [21,22].
On the other hand, recently, the importance of weak non-bonding interactions (NBIs) in the intricate process of chirality induction has been recognized. From this point of view, the importance of the t-Bu groups in the ligands of the BisP* row is based not on their physical size but the 9 C-H bonds capable of effective C-H-X (X = H, O, N, etc.) interactions with the substituents and functional groups of the substrates.
We assumed that although the phenyl group is also capable of participating in weak non-covalent interactions, its position in the place of the t-Bu group in, for example, BenzP* ligand lacks flexibility, which probably prevents the achievement of a configuration appropriate for building numerous stabilizing contacts. Thus, we decided to compute the stereoselective stage in a representative Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation catalyzed by ligand 1 (Benz-BenzP*), which contains benzylic groups instead of t-Bu groups in the BenzP*.
Another reason why Benz-BenzP* 1 could be practically useful in Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation is its expected high affinity to hydrogen due to the electron-donating properties of the benzylic groups. Thus, diphosphine 2 (Scheme 2) was reported to have extremely strong affinity to hydrogen; its Rh complex yielded solvate dihydrides quantitatively and irreversibly [23]. This is not helpful for Rh-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation, since reversibility of most stages of the catalytic cycle is an essential requirement for high enantioselectivities. Nevertheless, in the case of the Ni complex, this high affinity to dihydrogen can be beneficial if it may lead to the possibility to apply lower pressures instead of the usual values of 30–40 atm H2.

Scheme 2.
Chiral diphosphine 1 used in our computations and the known diphosphine 2 [23] containing benzylic fragments.
According to recent publications, we assumed that the stereo-determining step in asymmetric hydrogenation catalyzed by cationic Ni-H 3 with 1-phenylethanone oxime 4 is the approach of the double bond of 4 from encounter complex 5 toward reactive configuration 6, in which the double bond is coplanar to the P-Ni-H unit. This process is followed by migratory insertion, which results in a monohydride agostc intermediate 7 (Scheme 3).
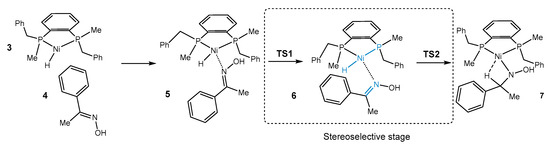
Scheme 3.
Steps of the catalytic cycle important to the stereoselection computed in this work. The level of theory was ωB97XD/6-31G**/SMD(2,2,2-trifluoroethanol). Blue color emphasizes the importance of the proper way of coordination of the double bond.
The computed profiles of the Gibbs free energy for the consequence of reactions converting encounter complex 5 to the monohydride agnostic intermediate 7 for the R and S pathways is shown in Figure 1.
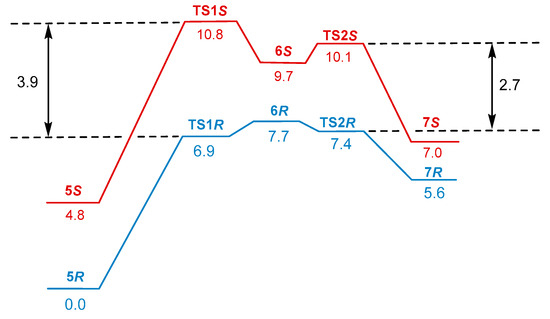
Figure 1.
Profiles of relative Gibbs free energies (kcal/mol) for the R (blue) and S (red) routes of the catalytic cycle leading from the encounter complex 5 to the agostic monohydride iintermediate 7. The intermediate 6R was 2.4 kcal/mol more stable than TS1R, as was proven by IRC analysis. It becomes slightly less stable than TS1R in terms of the Gibbs free energy.
Computations demonstrated that throughout the whole transformation from 5 to 7, the R pathway remained lower in the free energy than the S pathway. The difference in Gibbs free energies between TS1R and TS1S was 3.9 kcal/mol, corresponding to >99% ee (R). In analyzing the structural reasons for the different stabilities of TSR and TSS, we compared the non-bonding interactions between the catalyst and the substrate in these structures (Figure 2, top). These transition states have two CH…O close contacts and one C-H…H-C each. In addition, TSS had only one C-H…π interaction. On the other hand, in TSR, all six carbon atoms of the phenyl ring of the substrate had close contacts in the range of 2.78–2.95 Å with the ortho-proton of the appropriately positioned benzylic group of the catalyst. This structural feature was additionally illustrated through graphical NCI analysis (Figure 2, bottom), displaying a symmetrical round area of stabilizing NCI in the TS1R corresponding to 6 CH–π interactions.
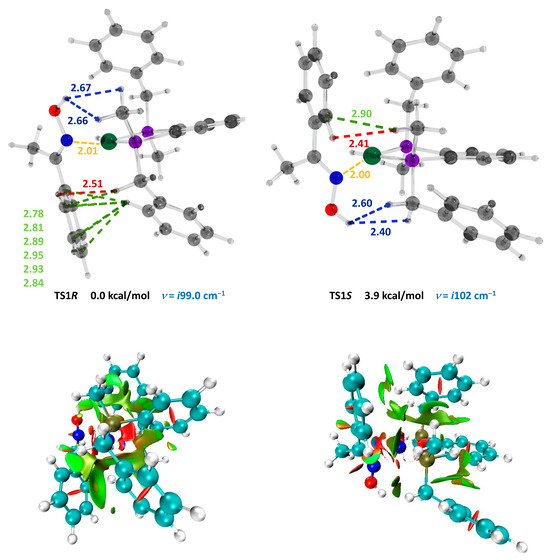
Figure 2.
(top) Optimized structures, relative energies, imaginary frequencies and interatomic distances (Å, in the range of 2.0–3.0 Å) between the catalyst and the substrate of the transition states TS1R and TS1S computed at the ωB97XD/6-31G** level of theory, accounting for a non-specific solvation (SMD, 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol). Atoms: C = gray, H = white, O = red, N = blue, Ni = green, and P = violet. Non-bonding contacts: C-H…H-C = red, O…H-C = blue, C-H…π = lime, and Ni-N = yellow. (bottom) Non-covalent interactions (NCIs) method analysis. The symmetrical round area of stabilizing NCIs in the TS1R, corresponding to 6 CH–π interactions, shown in the upper part of the figure, is noteworthy.
Please note that the imaginary frequencies for TS1R and TS1S correspond to the intramolecular movement of the double bond toward its coordination in a configuration appropriate for the practically barrierless migratory insertion through TS2R and TS2S.
We also computed the difference in the Gibbs free energies of the corresponding transition states for the ligands with strong withdrawing (CN) and donating (OMe) substituents (Figure 3, Table 1). In both TS1R CN and TS1R OMe, the ortho-proton of one of the benzylic units of the catalyst formed close contacts with the phenyl ring of the substrate in the same fashion as that seen in TS1R. The steady decrease in the stereoregulating ΔΔG from the cyano-substituted substrate to the methoxy-substituted one following the decrease in the relative number of stabilizing NCI in the TS1R compared with TS1S is noteworthy.
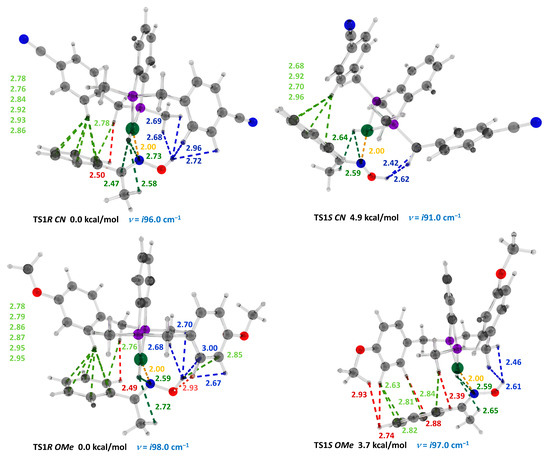
Figure 3.
Optimized structures, relative energies, imaginary frequencies and interatomic distances (Å, in the range of 2.0–3.0 Å) between the catalyst and the substrate of the transition states TS2R and TS2S, computed at the ωB97XD/6-31G** level of theory, accounting for a non-specific solvation (SMD, 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol). Atoms: C = gray, H = white, O = red, N = blue, and P = violet, green: Ni. Non-bonding contacts: C-H…H-C = red, O…H-C = blue, C-H…π = lime, Ni-H…H-C = green, and Ni-N = orange.

Table 1.
Number of NCI and Ni-N distances and computed differences in Gibbs free energies for the transition states of the C-N bond formation and migratory insertion stages for three substrates with different electronic properties.
Also of interest is the absence of a similar dependence in the case of TS2R and TS2S (Table 1). In these transition states, the Ni-N bond is already formed, combining the catalyst and the substrate in one molecule, and the interactions between the former catalyst and substrate sub-units are involved in the network of the stabilizing NCI of the whole molecule.
3. Materials and Methods
Computational Details
Geometry optimizations were performed without any symmetry constraints (C1 symmetry) using the ωB97XD functional [24] as implemented in the Gaussian16 software package [25]. Frequency calculations were undertaken to confirm the nature of the stationary points, yielding one imaginary frequency for all transition states (TSs) and zero for all minima. Constrained energy hypersurface scans were conducted to investigate the molecular reactivity and locate viable reaction channels. Where low-lying barriers were estimated, frequency calculations were performed at the crude saddle points, and the obtained force constants were used to optimize the transition-state structures by employing the Berny algorithm [26]. All atoms were described using the 6-31G** basis set [27,28,29,30,31,32] for geometry optimization and frequency calculation. Non-specific solvation was introduced using the SMD continuum model [33] (2,2,2-trifluoroethanol). We have significant and successful experience in modeling Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation with the wB97XD/6-31G** level for all atoms, including Ni [19,34,35,36,37,38]. These computations provided reasonable geometries and gave correct predictions for the sense and level of enantioselectivity.
Cartesian coordinates of all optimized intermediates and transition states are given in the Supplementary Materials.
4. Conclusions
Modeling a Ni-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of 1-phenylethanone oxime with the newly designed Benz-BenzP* ligand 1 via DFT computations showed that the difference in free energy between the R and S pathways predicted >99% ee for the hydrogenation product. Aside from this, the Ni complex of 1 was expected to have an increased affinity for dihydrogen, which might be beneficial for adjusting milder hydrogenation conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15040352/s1. Cartesian coordinates of all computed transition states and stationary points.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.D.G., J.C. and W.Z.; methodology, I.S.G.; investigation, E.V.P. and I.S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.V.P. and I.S.G.; writing—review and editing, I.D.G., J.C. and W.Z.; supervision, I.D.G. and J.C.; project administration, I.D.G.; funding acquisition, I.D.G., J.C. and W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (grant number 24-43-00011), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2023YFA1506400) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22361132533, 21991112 and 22471157).
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in the manuscript and the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, Y.; Krska, S.; Shultz, C.S.; Tellers, D.M. Enabling asymmetric hydrogenation for the design of efficient synthesis of drug substances. In Asymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale: Challenges, Approaches and Solutions, 2nd ed.; Blaser, H.U., Fesersel, H.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 331–376. [Google Scholar]
- Kuremoto, T.; Yasukawa, T.; Kobayashi, S. Hydrogenation for the synthesis of an (S)-Metolachlor intermediate using catalysts immobilized on a core/shell-type support. Adv. Synth. Cat. 2024, 366, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biosca, M.; Diégues, M.; Zanotti-Gerosa, A. Asymmetric hydrogenation in industry. Adv. Cat. 2021, 68, 341–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gridnev, I.D.; Dub, P.A. Enantioselection in Asymmetric Catalysis; Boca Raton CRC Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bayat, P.; Karami, K.; Gallagher, J.F.; Sillanpää, M. Factors controlling asymmetric hydrogenation reactions catalyzed by complexes of phospholanes, and investigation in to the correlation of molecular and electronic structure from 1991 until 2020. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1286, 135538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, P.; Riera, A.; Verdaguer, X. Bulky P-stereogenic ligands. A success story in asymmetric catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 489, 215192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamoto, T. Development of P-Chirogenic Phosphine Ligands Based on Chemistry of Phosphine–Boranes: Searching for Novelty and Utility in Synthetic Organic Chemistry. TCImail 2017. Available online: https://www.tcichemicals.com/assets/cms-pdfs/174drE_1.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Burke, A.J.; Federsel, H.J.; Hermann, G.J. Recent Advances in Asymmetric Hydrogenation Catalysis Utilizing Spiro and Other Rigid C-Stereogenic Phosphine Ligands. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 87, 1898–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobereiner, G.E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Phosphine ligand development for homogeneous asymmetric hydrogenation. In Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry IV, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 13, pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto, T. P-Stereogenic phosphorus ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 8657–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamoto, T.; Watanabe, J.; Wada, Y.; Masuda, H.; Yamada, H.; Tsuruta, H.; Natsukawa, S.; Yamaguchi, K. P-Chiral bis(trialkylphosphine) ligands and their use in highly enantioselective hydrogenation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1635–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridnev, I.D.; Yamanoi, Y.; Higashi, N.; Tsuruta, H.; Yasutake, M.; Imamoto, T. Asymmetric hydrogenation catalyzed by (S,S)-bisp*-Rh and (R,R)-miniphos-Rh complexes: Scope, limitations and mechanism. Adv. Synth. Cat. 2001, 343, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, M.; Gridnev, I.D.; Higashi, N.; Imamoto, T. Highly enantioselective hydrogenationof (E)-β-(acylamio)acrylates catalyzed by Rh(I)-complexes of electron-rich P-chirogenic diphosphines. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridnev, I.D.; Yasutake, M.; Imamoto, T.; Beletskaya, I.P. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of α,β-umsaturated phosphonates with Rh-BisP* and Rh-MiniPHOS catalysts: Scope and mechanism of the reaction. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5385–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamoto, T.; Sugita, K.; Yoshida, K. An air-stable P-chiral phosphine ligand for highly enantioselective transition-metal-catalyzed reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11934–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamoto, T.; Tamura, K.; Zhang, Z.; Horiuchi, Y.; Sugiya, M.; Yoshida, K.; Yanagisawa, A.; Gridnev, I.D. Rigid P-chiral phosphine ligands with tert-butylmethylphosphino groups for rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of functionalized alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1754–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Sugiya, M.; Yoshida, K.; Yanagisawa, A.; Imamoto, T. Enantiopure 1,2-bis(tert-butylmethylphosphino)benzene as a highly efficient ligand in rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation. Org. Lett. 2010, 13, 4400–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamoto, T.; Nishimura, M.; Koide, A.; Yoshida, K. t-Bu-QuinoxP* ligand: Applications in asymmetric Pd-catalyzed allylic substitution and Ru-catalyzed hydrogenation. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 72, 7413–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of N-sulfonyl imines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7329–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Xie, C.; Guo, Q.; Zi, G.; Hou, G.; Huang, Y. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation ofγ-keto acids, esters, and amides to chiralγ-lactones andγ-hydroxy acid derivatives. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muci, A.R.; Campos, K.R.; Evans, D.A. Enantioselective Deprotonation as a Vehicle for the Asymmetric Synthesis of C2-Symmetric P-Chiral Diphosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9075–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maienza, F.; Spindler, F.; Thommen, M.; Pugin, B.; Malan, C.; Mezzetti, A. Exploring stereogenic phosphorus: Synthetic strategies for diphosphines containing bulky highly symmetric substituents. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 5239–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridnev, I.D.; Higashi, N.; Imamoto, T. Formation of a stable rhodium(I) dihydride complex and its reactions with prochiral substrates of asymmetric hydrogenation. Organometallics 2001, 21, 4542–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-D.; Head-Gordon, M. Long-Range Corrected Hybrid Density Functionals with Damped Atom–Atom Dispersion Corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaussian 16; Revision A.03; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016.
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchfield, R.; Hehre, W.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-Consistent Molecular-Orbital Methods. IX. An Extended Gaussian-Type Basis for Molecular-Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self-Consistent Molecular Orbital Methods. XII. Further Extensions of Gaussian-Type Basis Sets for Use in Molecular Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.C.; Pople, J.A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies. Theor. Chim. Acta 1973, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francl, M.M.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J.; Binkley, J.S.; Gordon, M.S.; DeFrees, D.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XXIII. A polarization-type basis set for second-row elements. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, M.S.; Binkley, J.S.; Pople, J.A.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J. Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods. Small split-valence basis sets for second-row elements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 2797–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassolov, V.A.; Pople, J.A.; Ratner, M.A.; Windus, T.L. 6-31G * basis set for atoms K through Zn. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Nickel-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of 2-Amidoacrylates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5371–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of alpha-Substituted Vinylphosphonates and Diarylvinylphosphine Oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Enantioselective Synthesis of Chiral β2-Amino Phosphorus Derivatives via Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, H.; Gridnev, I.D.; Zhang, W. Weak Attractive Non-Covalent Interactions in Metal-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202425589. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).