An Efficient Approach for β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder Through High-Temperature Gelatinization and Enzymatic Conversion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
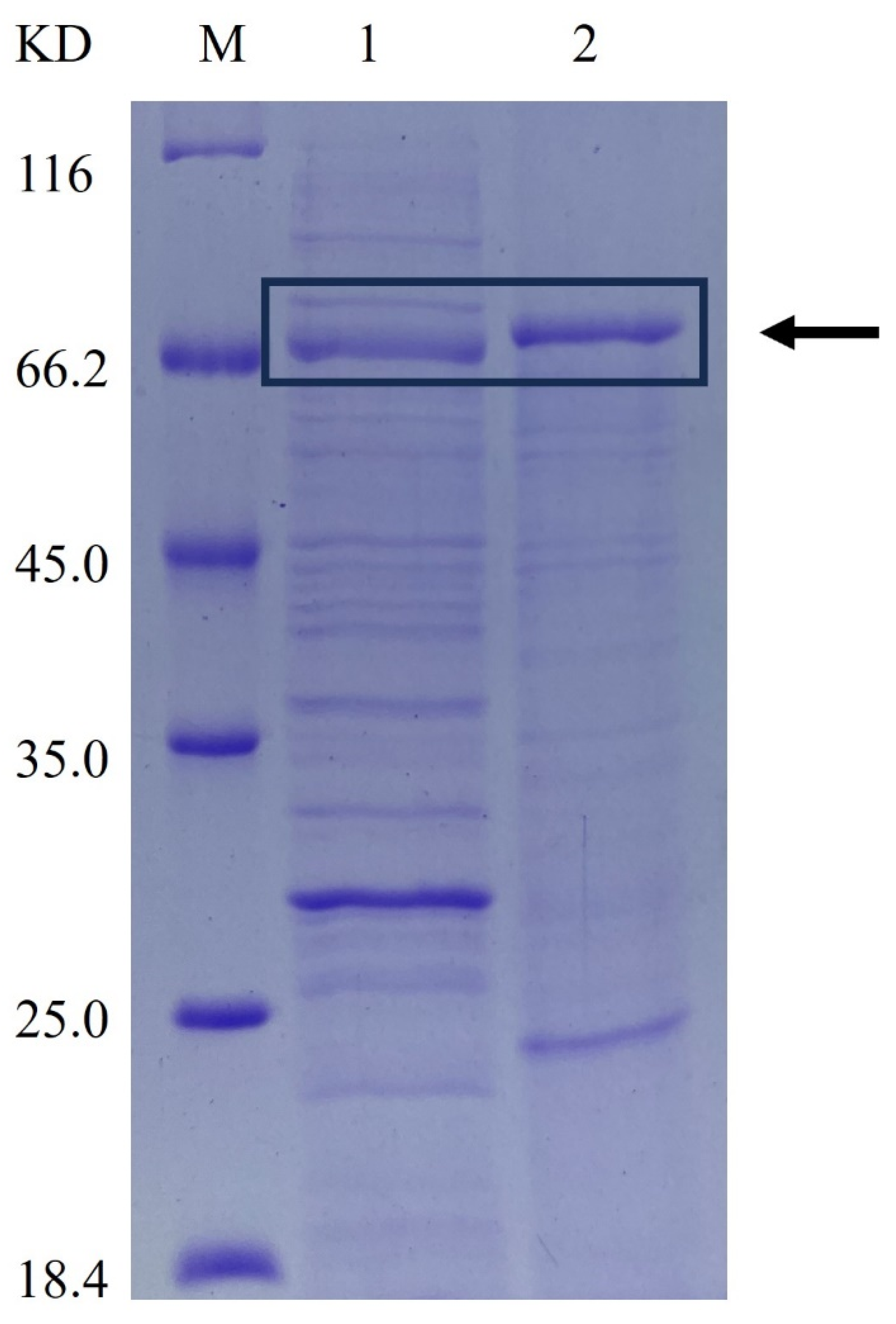
2.1. Extracellular Expression of β-CGTase in E. coli BL21(DE3) and B. subtilis WB600
2.2. Effect of Substrate and Pretreatment Methods on the Preparation of Cyclodextrins from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder
2.2.1. Feasibility of β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Materials
2.2.2. Effect of Pretreatment Schemes on the Preparation of β-Cyclodextrin
2.3. Effect of Pretreatment Schemes on the Physicochemical Properties of Ginkgo Starch
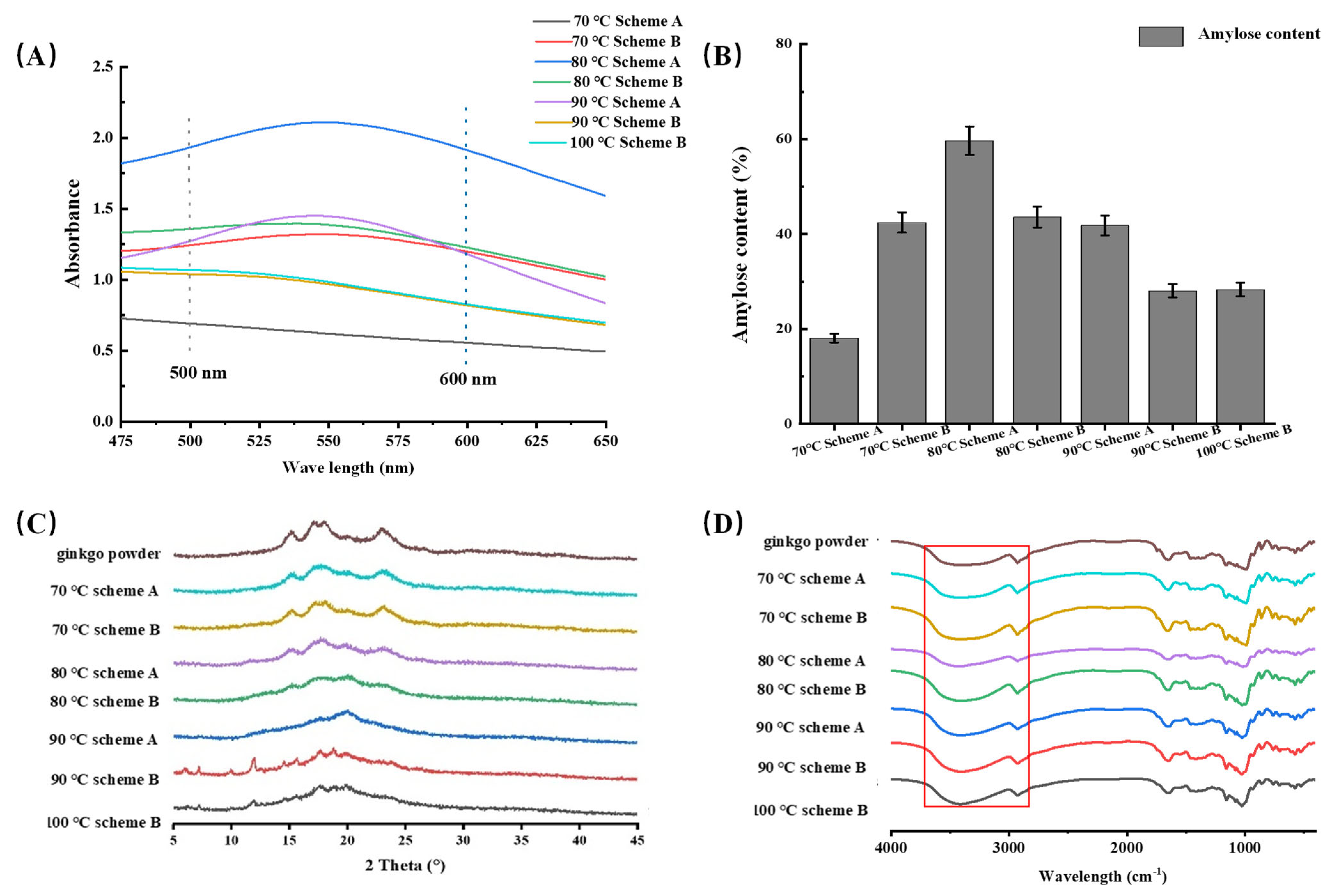
2.3.1. Viscosity Analysis
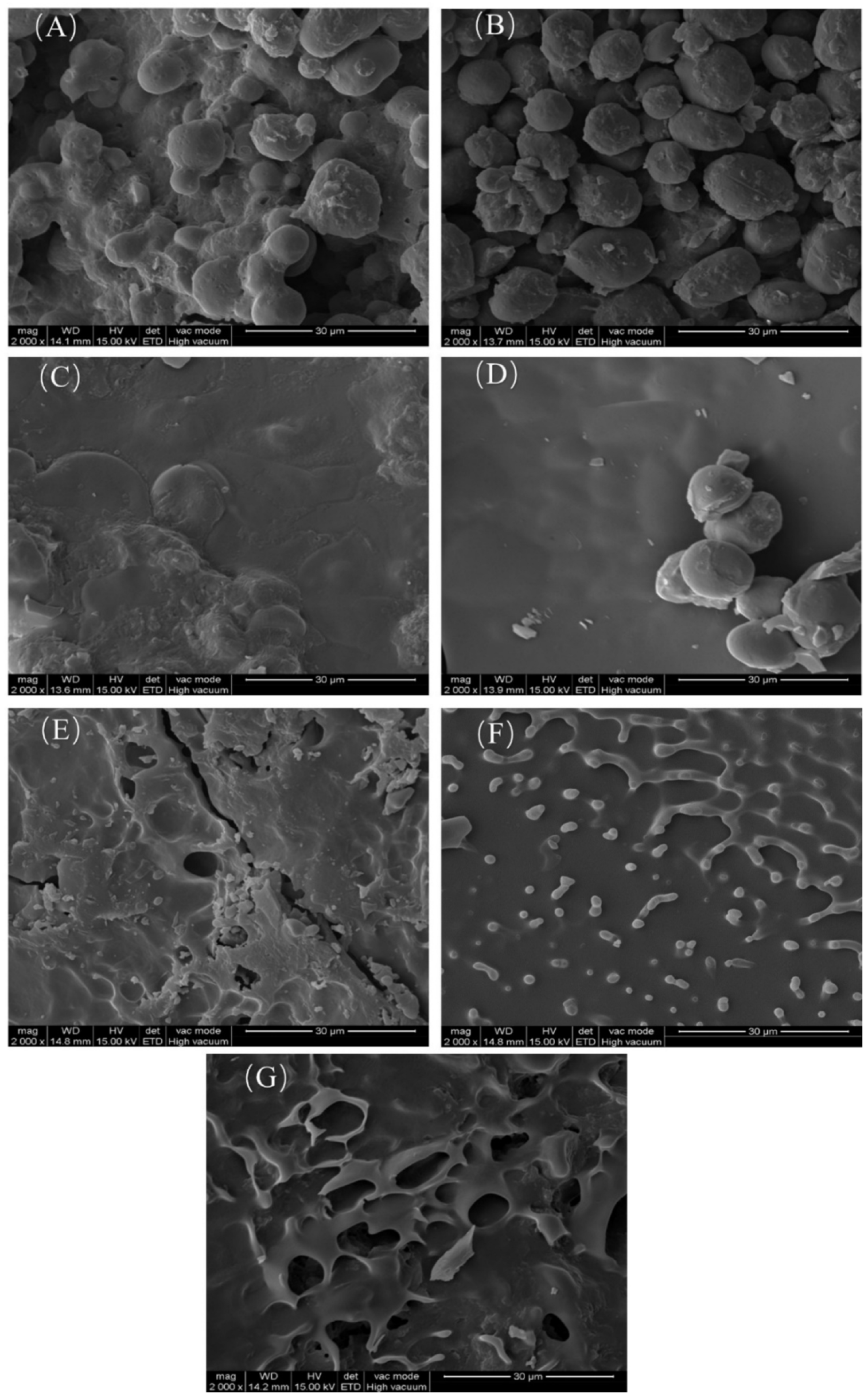
2.3.2. Starch Structure Morphology Analysis
2.3.3. Characterization of Amylopectin and Amylose Composition
2.3.4. XRD Analysis
2.3.5. FTIR Analysis
2.4. Optimization of β-Cyclodextrin Conversion Process
2.4.1. Effect of Substrate Concentration
2.4.2. Effect of Liquefaction Time
2.4.3. Effect of the Amount of Enzyme Added
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Construction of Expression Vector
3.3. Production and Assay of β-CGTase
3.4. Assay Activity of β-CGTase
3.5. Preparation of Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder
3.6. Determination of Moisture and Starch Content of Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder
3.7. Pretreatment of Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder
3.8. Enzymatic Conversion of Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder to β-Cyclodextrin
3.9. Rapid Visco Analyzer (RVA) Analysis
3.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.11. Amylopectin and Amylose Composition Analysis
3.12. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.13. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.14. Determination of Cyclodextrin Content
3.15. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Gong, H.; Cao, F. Ginkgo biloba extracts-loaded starch nano-spheres: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro release kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Yu, W.; Cui, Q.; Lu, X.; Du, P.; An, L. Hair-growth promoting effect and anti-inflammatory mechanism of Ginkgo biloba polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Shen, F.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Ye, S. Preparation and functional characteristics of protein from Ginkgo endophytic Pseudomonas R6 and Ginkgo seed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Che, F.; Shen, N.; Cui, Y. Leaves, seeds and exocarp of Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae): A comprehensive review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, resource utilization and toxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Studies on nutritional intervention of ginkgo starch-lauric acid complex in obese rats induced by a high-fat diet. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalajahi, S.G.; Malekjani, N.; Samborska, K.; Akbarbaglu, Z.; Gharehbeglou, P.; Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M. The enzymatic modification of whey-proteins for spray drying encapsulation of Ginkgo-biloba extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Labreche, F.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Shi, H.; Ye, C. Preparation and aroma analysis of flavonoid-rich ginkgo seeds fermented using rice wine starter. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Shi, R.; Qayum, A.; Bilawal, A.; Gantumur, M.-A.; Hussain, M.A.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, B. Comparison in bioactivity and characteristics of Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharides from four extract pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Channab, B.-E.; El Idrissi, A.; Zahouily, M.; Motamedi, E. A comprehensive review on starch: Structure, modification, and applications in slow/controlled-release fertilizers in agriculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, Y.S.; Manas, N.H.A.; Jaafar, N.R.; Rahman, R.A.; Puspaningsih, N.N.T.; Illias, R.M. Combined cross-linked enzyme aggregates of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and maltogenic amylase from Bacillus lehensis G1 for maltooligosaccharides synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Rafe, M.R. Cyclodextrin: A prospective nanocarrier for the delivery of antibacterial agents against bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knegtel, R.M.; Strokopytov, B.; Penninga, D.; Faber, O.G.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystallographic studies of the interaction of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251 with natural substrates and products. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29256–29264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Luan, S. Efficient secreted expression of natural intracellular β-galactosidase from Bacillus aryabhattai via non-classical protein secretion pathway in Bacillus subtilis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jailani, N.; Jaafar, N.R.; Rahman, R.A.; Illias, R.M. Robust cross-linked cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from Bacillus lehensis G1 aggregates using an improved cross-linker and a new co-aggregant for the production of cyclodextrins. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 169, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenelon, V.C.; Miyoshi, J.H.; Mangolim, C.S.; Noce, A.S.; Koga, L.N.; Matioli, G. Different strategies for cyclodextrin production: Ultrafiltration systems, CGTase immobilization and use of a complexing agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Manna, K.; Dey, S.; Pal, S. Chemical modification of β-cyclodextrin towards hydrogel formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Luo, Y.; Barba, F.J.; Wu, Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, S.; Lyu, Q.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y. Effect of β-cyclodextrins on the physical properties and anti-staling mechanisms of corn starch gels during storage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.X.; Donner, E.; Liu, Q.; Smith, D.C.; Ravenelle, F. Potentiometric titration for determination of amylose content of starch—A comparison with colorimetric method. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1142–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, B.; Cui, S.W.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, T. Structure and functional properties of starches from Chinese ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) nuts. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.; Chen, Y.; Lee, L.; McPherson, A.; Wong, K.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Holler, T.P.; Li, C. Leu600 mutations decrease product inhibition of the beta-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans STB01. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Ji, H.; Svensson, B.; Bai, Y. Improved production of gamma-cyclodextrin from high-concentrated starch using enzyme pretreatment under swelling condition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavent-Gil, Y.; Rosell, C.M.; Gilbert, E.P. Understanding CGTase action through the relationship between starch structure and cyclodextrin formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M. Effects of maltogenic α-amylase treatment on the proportion of slowly digestible starch and the structural properties of pea starch. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Tong, Y.; Shi, Y.-C. Partial swelling of granules enables high conversion of normal maize starch to glucose catalyzed by granular starch hydrolyzing enzyme. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ji, H.; Bai, Y.; Jin, Z. Development of pullulanase mutants to enhance starch substrate utilization for efficient production of beta-CD. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yao, C.; Hu, L.; Peng, Y.; Shen, J. Study on physicochemical and in-vitro enzymatic hydrolysis properties of ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dura, A.; Rosell, C.M. Physico-chemical properties of corn starch modified with cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Zhu, F. Impact of long-term ultrasound treatment on structural and physicochemical properties of starches differing in granule size. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Cui, C.; Gao, L.; Qin, Y.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Shi, R.; Sun, Q. A review of starch swelling behavior: Its mechanism, determination methods, influencing factors, and influence on food quality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, C. Relationship between structure and physicochemical properties of ginkgo starches from seven cultivars. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 125082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Herbuger, K.; Petersen, B.L.; Cui, Y.; Blennow, A.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. High-pressure pasting performance and multilevel structures of short-term microwave-treated high-amylose maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Chatakanonda, P.; Sriroth, K. Internal unit chain composition in amylopectins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, N.R.; Ahmad, R.a.A.; Nawawi, N.N.; Abd Rahman, N.H.; Shamsul Annuar, N.A.; Rahman, R.A.; Illias, R.M. Synergistic action of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and maltogenic amylase improves the bioconversion of starch to malto-oligosaccharides. Process Biochem. 2021, 103, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, E. Effects of amylose and amylopectin chain-length distribution on the kinetics of long-term rice starch retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S.; Tang, P.; Zou, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of ginseng starches under citric acid-autoclaving treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 131031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maarel, M.J.; Leemhuis, H. Starch modification with microbial alpha-glucanotransferase enzymes. Carbohydr Polym. 2013, 93, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Karkalas, J.; Qi, X. Starch—Composition, fine structure and architecture. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorndech, W.; Sagnelli, D.; Meier, S.; Jansson, A.M.; Lee, B.H.; Hamaker, B.R.; Rolland-Sabate, A.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Tongta, S.; Blennow, A. Structure of branching enzyme- and amylomaltase modified starch produced from well-defined amylose to amylopectin substrates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yao, C.; Zhang, H. The optimization of isoamylase processing conditions for the preparation of high-amylose ginkgo starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liang, D.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, W. Investigation of the role of sodium chloride on wheat starch multi-structure, physicochemical and digestibility properties during X-ray irradiation. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 139012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, D.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhu, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Tang, N. Structural, physicochemical and digestive properties of rice starch modified by preheating and pullulanase treatments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Maior, L.; Bach, D.; Demiate, I.M.; Lacerda, L.G. Impact of cyclic and continuous dry heat modification on the structural, thermal, technological, and in vitro digestibility properties of potato starch (Solanum tuberosum L.): A comparative study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Characterizing digestibility of potato starch with cations by SEM, X-ray, LF-NMR, FTIR. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Qi, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, B. Potential relation between starch granule-associated proteins and retrogradation properties of buckwheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, F.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Flanagan, B.M. Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterise starch ordered structure—A joint FTIR–ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninga, D.; van der Veen, B.A.; Knegtel, R.M.; van Hijum, S.A.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Dijkhuizen, L. The raw starch binding domain of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 32777–32784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, J. Enhanced production of gamma-cyclodextrin by optimization of reaction of gamma-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase as well as synchronous use of isoamylase. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3072–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Korpela, T.; Laakso, S. Colorimetric determination of beta-cyclodextrin: Two assay modifications based on molecular complexation of phenolphtalein. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1987, 14, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Hao, Y.; Fang, H.; Xiong, Z. Separation and purification of amylose and amylopectin from cassava starch and content determination by dual-wavelength spectrophotometry. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 123–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Substrate Type | β-CD Conversion Rate Using Different Raw Materials (%) | β-CD Conversion Rate Using Different Starches (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ginkgo | 38.96 ± 1.52 | 53.41 ± 1.37 |
| Corn | 31.30 ± 3.27 | 39.91 ± 2.56 |
| Potato | - | 75.40 ± 4.31 |
| Temperature (°C) | β-CD Conversion Rate by Scheme A (%) | β-CD Conversion Rate by Scheme B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | 1.57 ± 0.07 | 38.97 ± 1.38 |
| 80 | 51.27 ± 2.65 | 56.47 ± 2.47 |
| 90 | 53.43 ± 3.21 | 64.04 ± 3.38 |
| 100 | - | 61.83 ± 2.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ding, Y. An Efficient Approach for β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder Through High-Temperature Gelatinization and Enzymatic Conversion. Catalysts 2025, 15, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020108
Duan X, Fan Y, Liu Q, Ding Y. An Efficient Approach for β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder Through High-Temperature Gelatinization and Enzymatic Conversion. Catalysts. 2025; 15(2):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Xuguo, Yucheng Fan, Qianqian Liu, and Yucheng Ding. 2025. "An Efficient Approach for β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder Through High-Temperature Gelatinization and Enzymatic Conversion" Catalysts 15, no. 2: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020108
APA StyleDuan, X., Fan, Y., Liu, Q., & Ding, Y. (2025). An Efficient Approach for β-Cyclodextrin Production from Raw Ginkgo Seed Powder Through High-Temperature Gelatinization and Enzymatic Conversion. Catalysts, 15(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020108






