Niobium-Enhanced Kinetics of Tantalum Phosphate in Catalytic Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
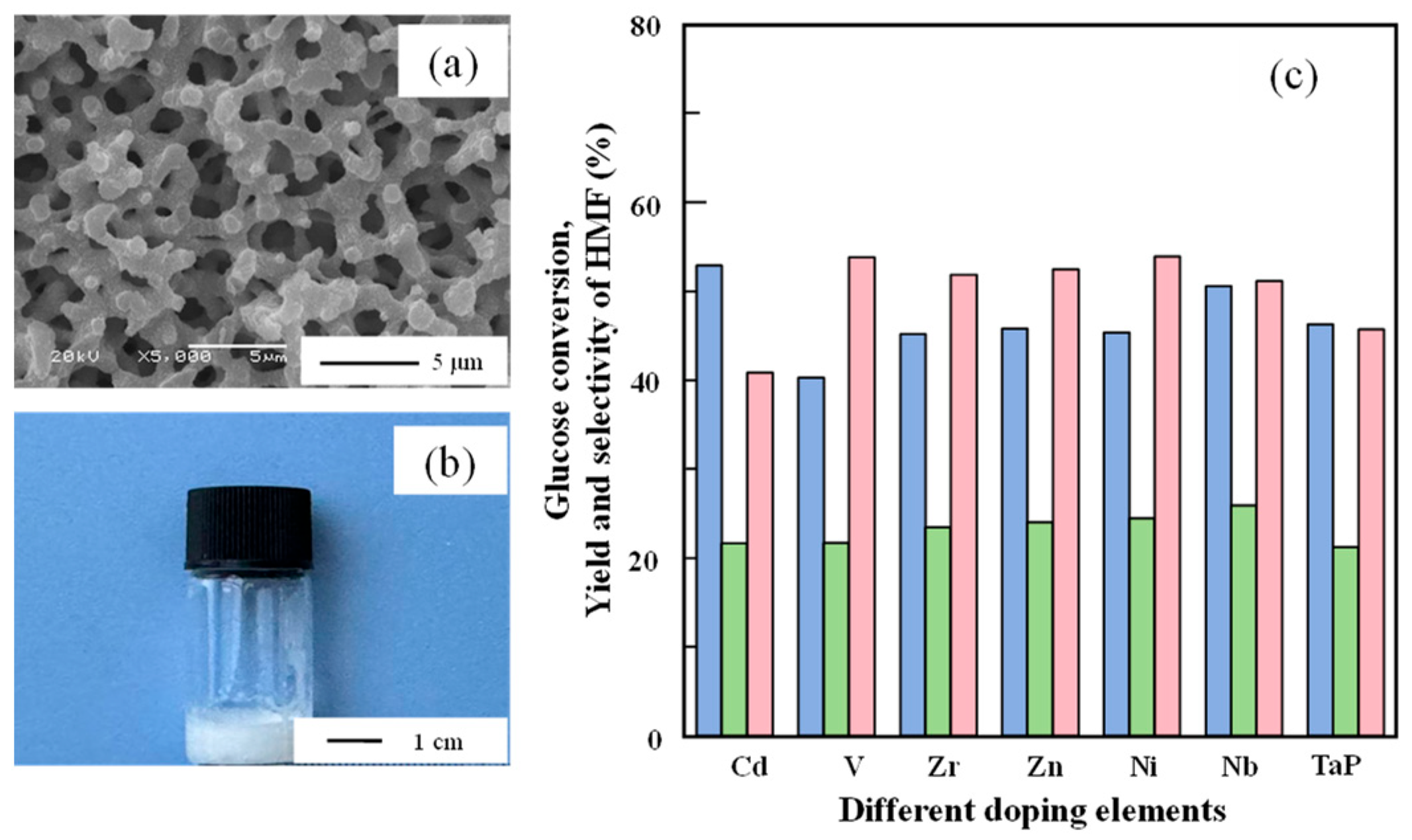
2.1. Synthesis of Metal-Doped Tantalum Phosphate and Catalytic Performance Screening
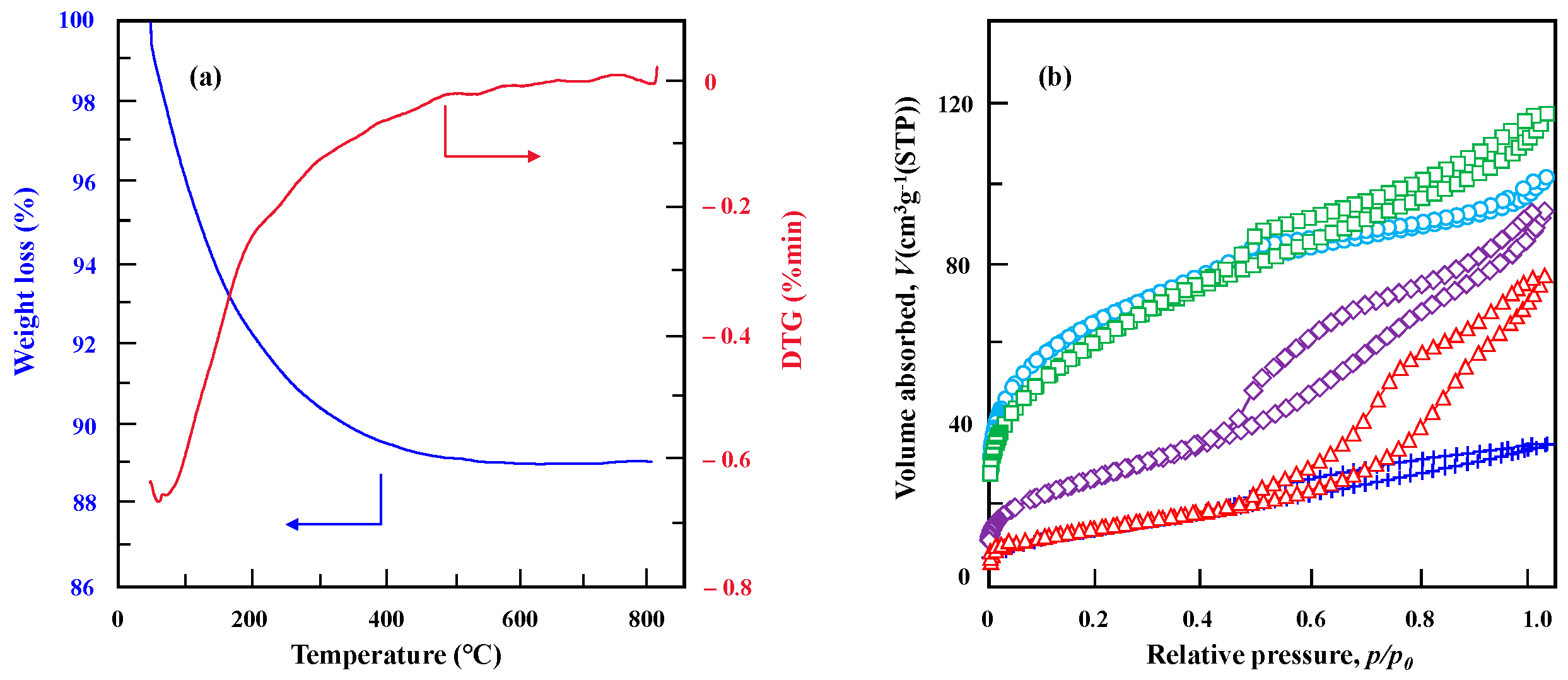
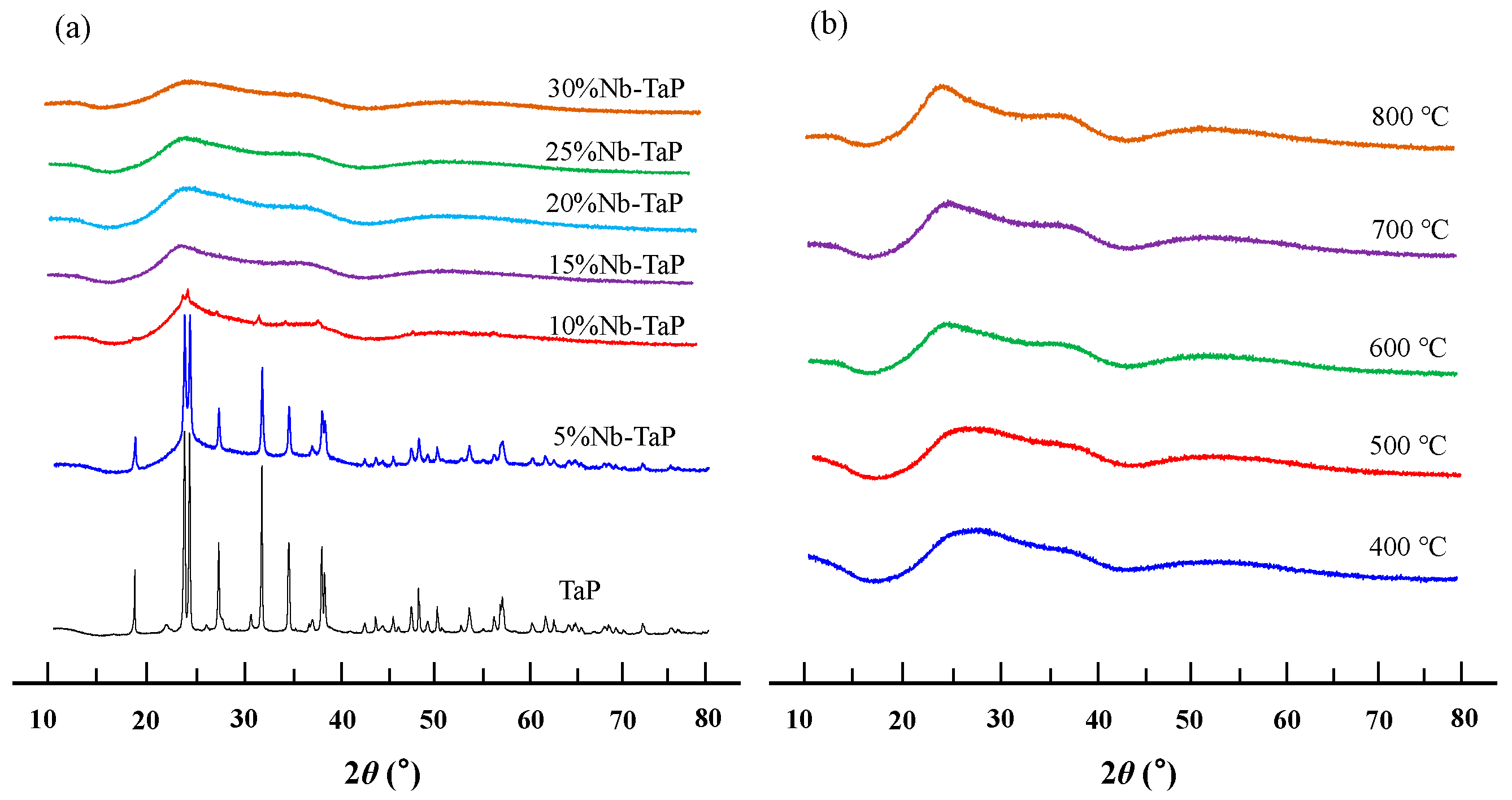
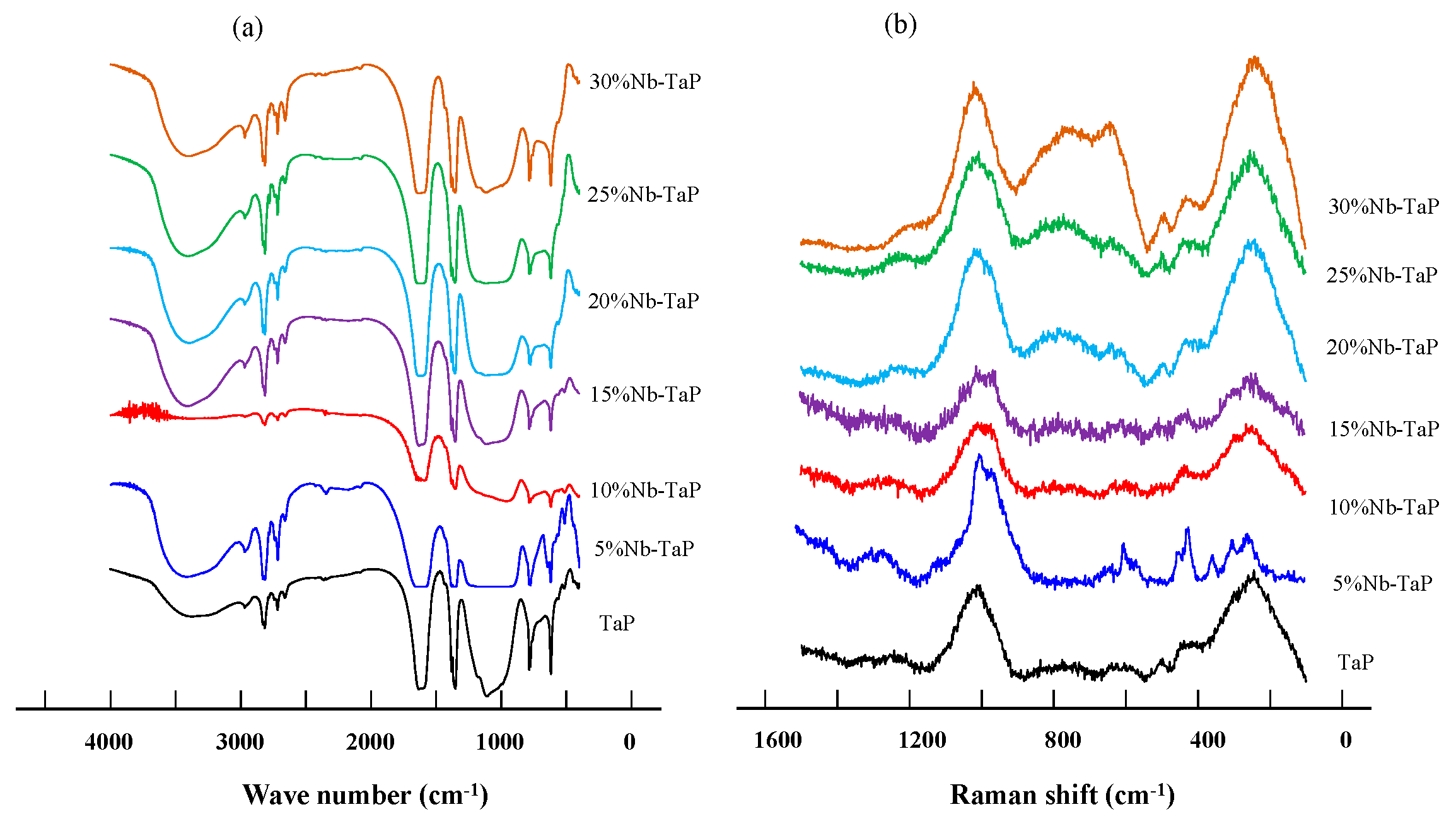
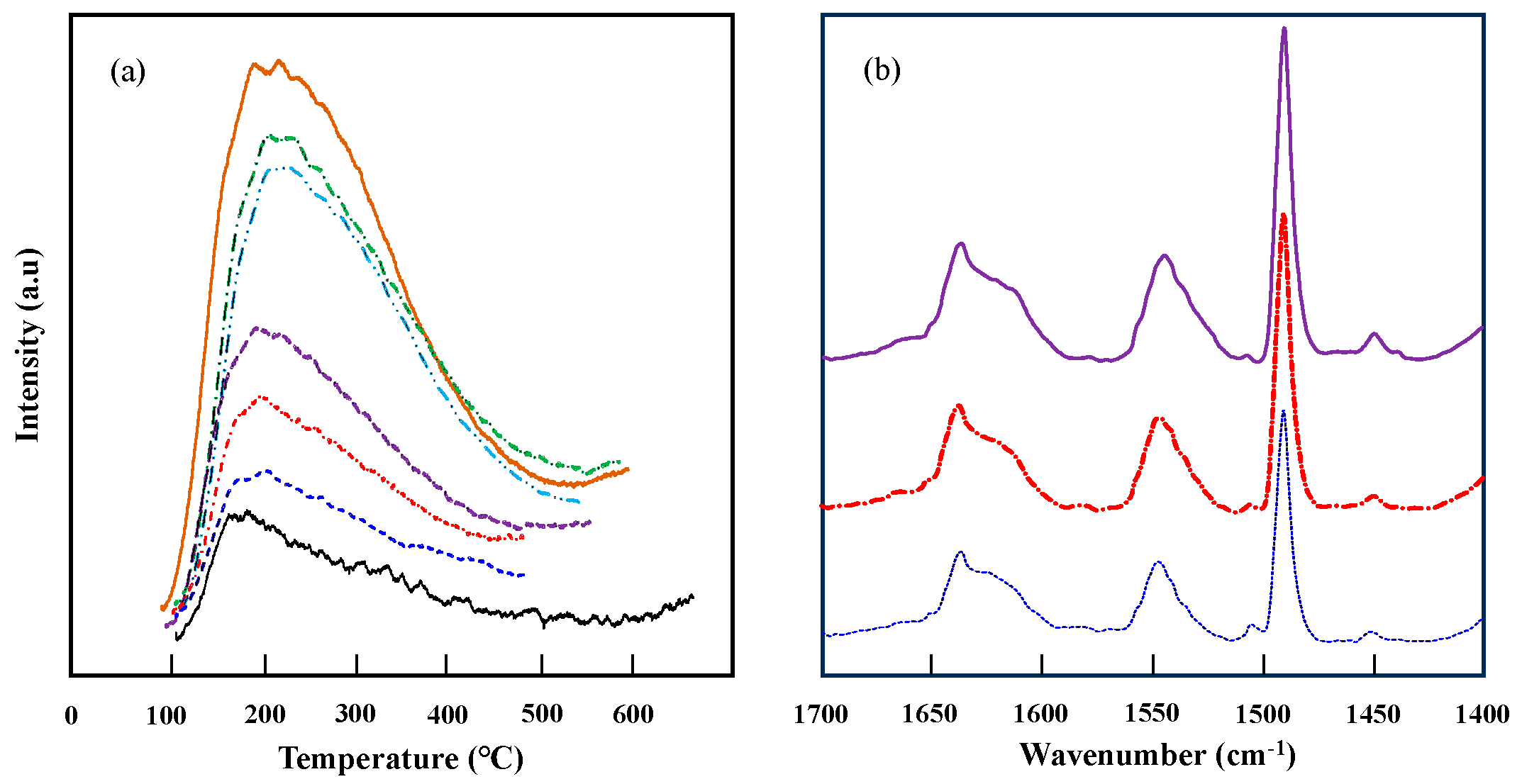
2.2. Structure and Surface Properties of Niobium-Doped Tantalum Phosphate
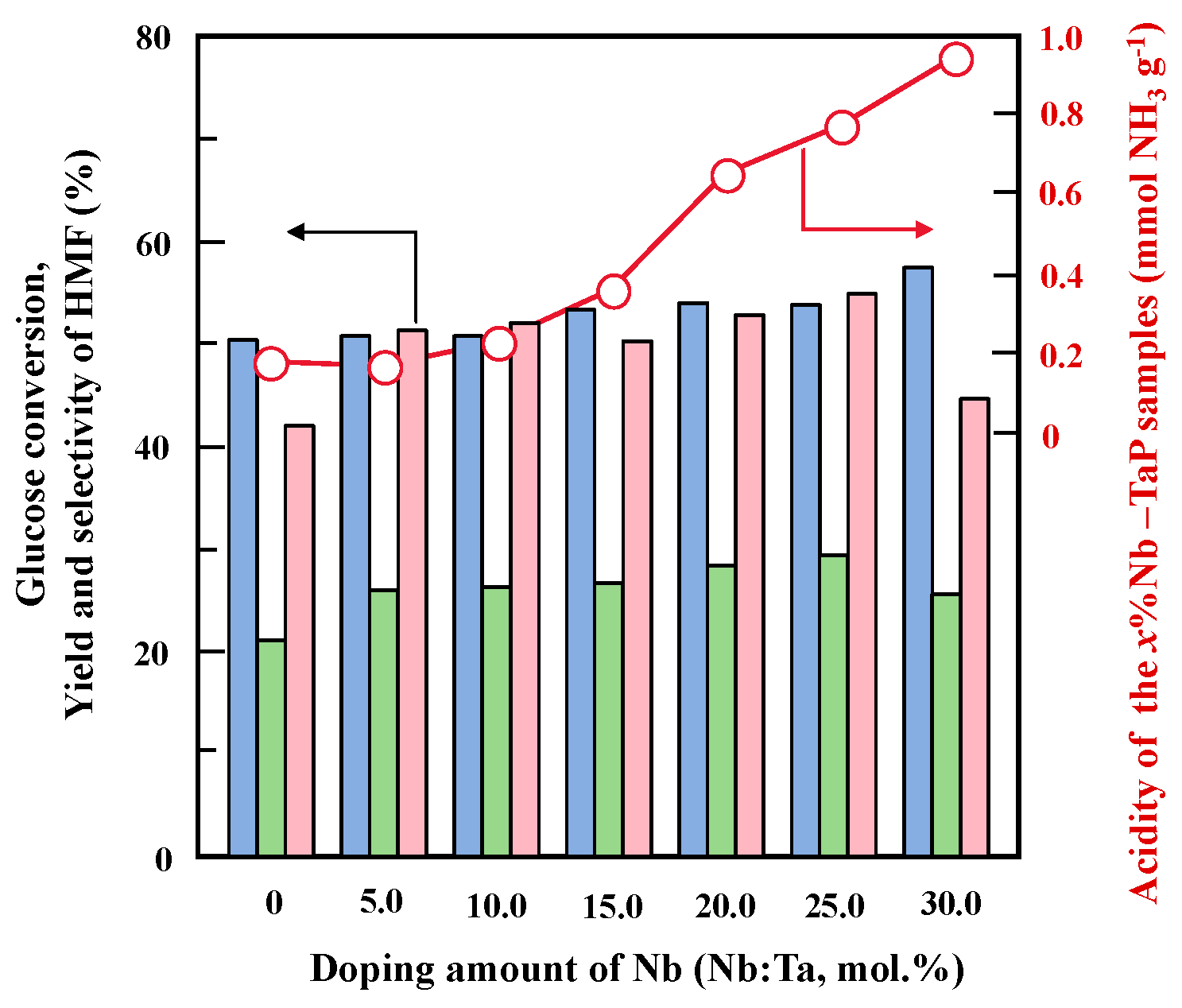
2.3. Catalytic Performance of Nb-Doped TaP in Glucose Dehydration
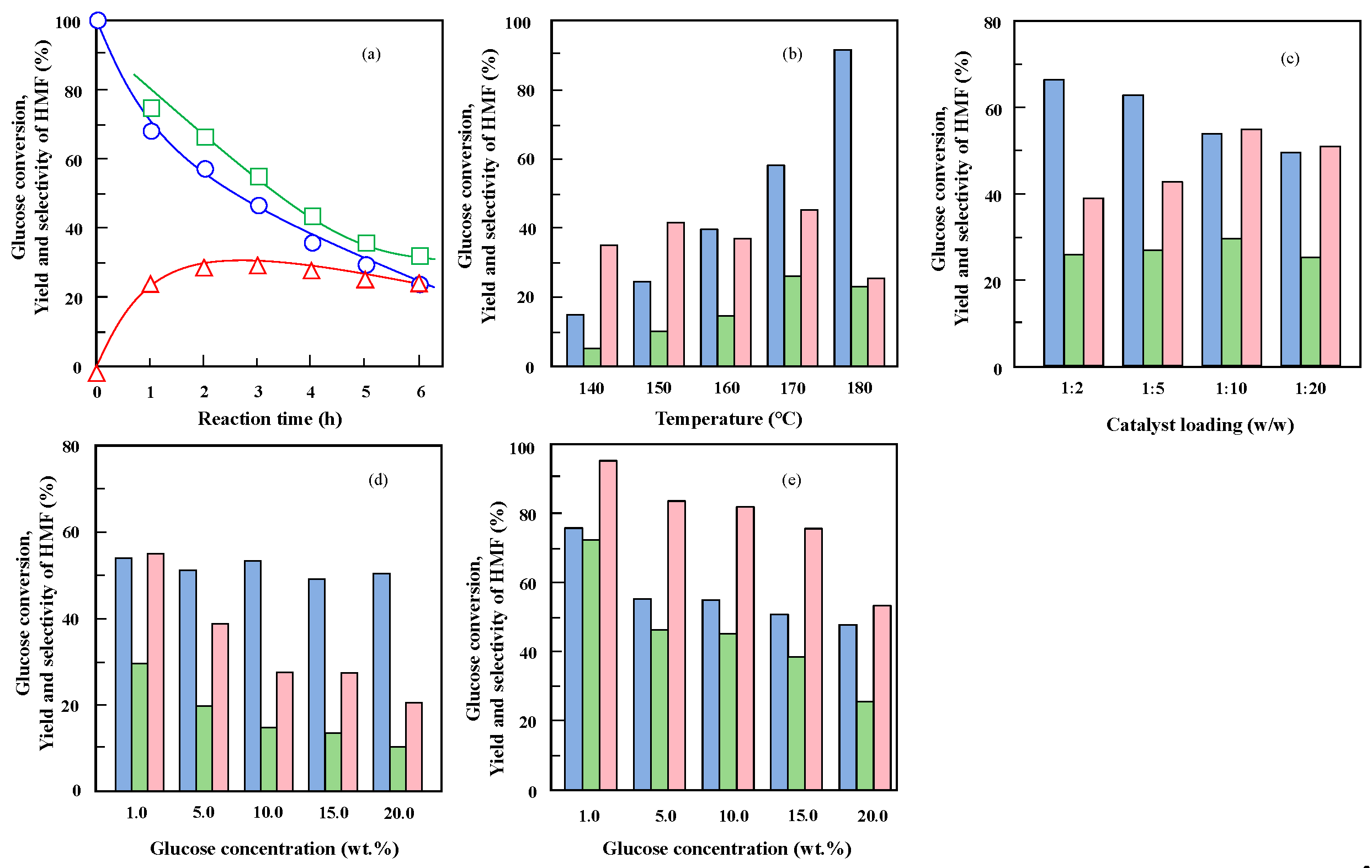
2.4. Dehydration of Glucose in a Water/MIBK Biphasic System
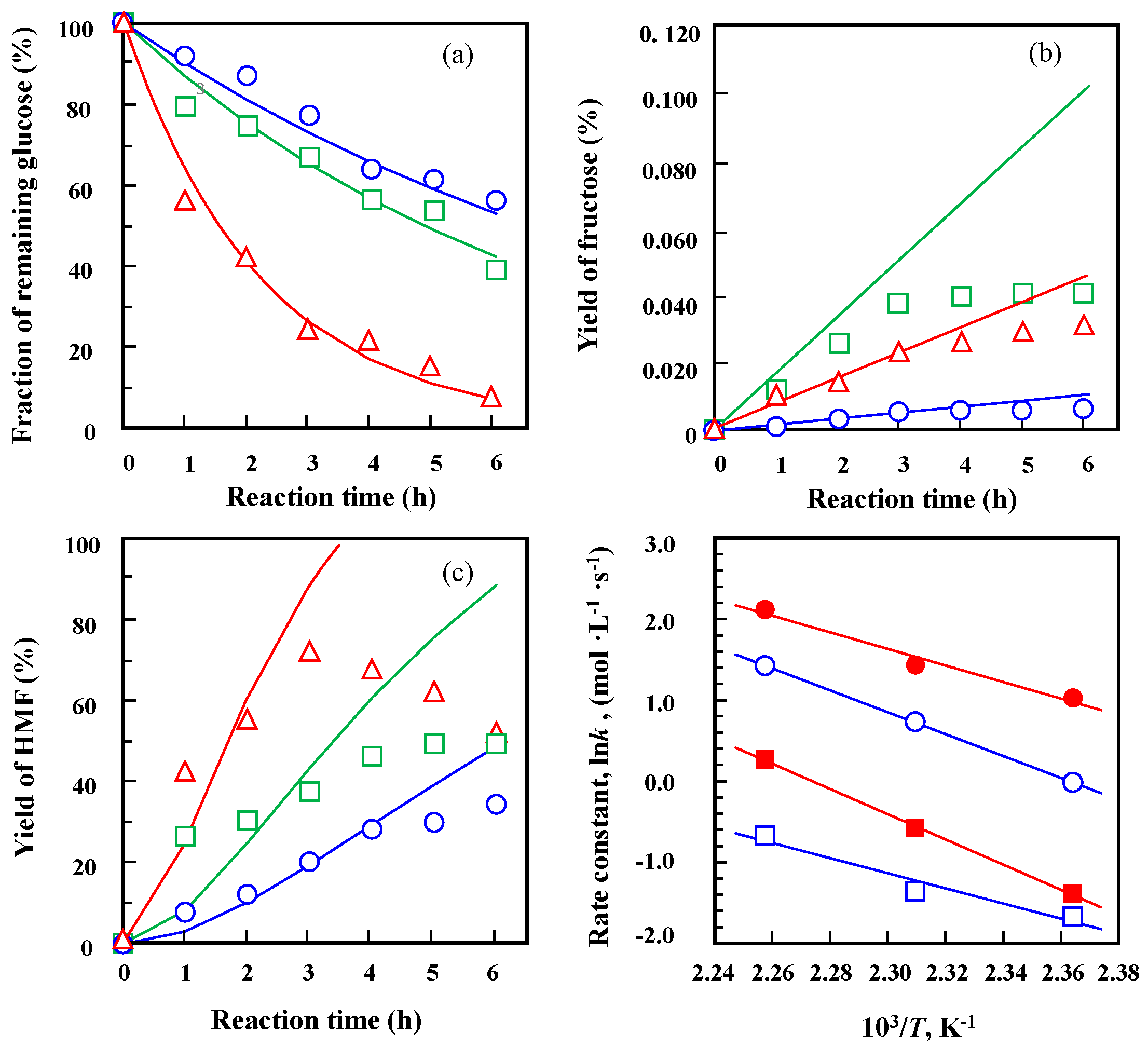
2.5. Kinetic Analysis of Glucose Dehydration over 25%Nb-TaP
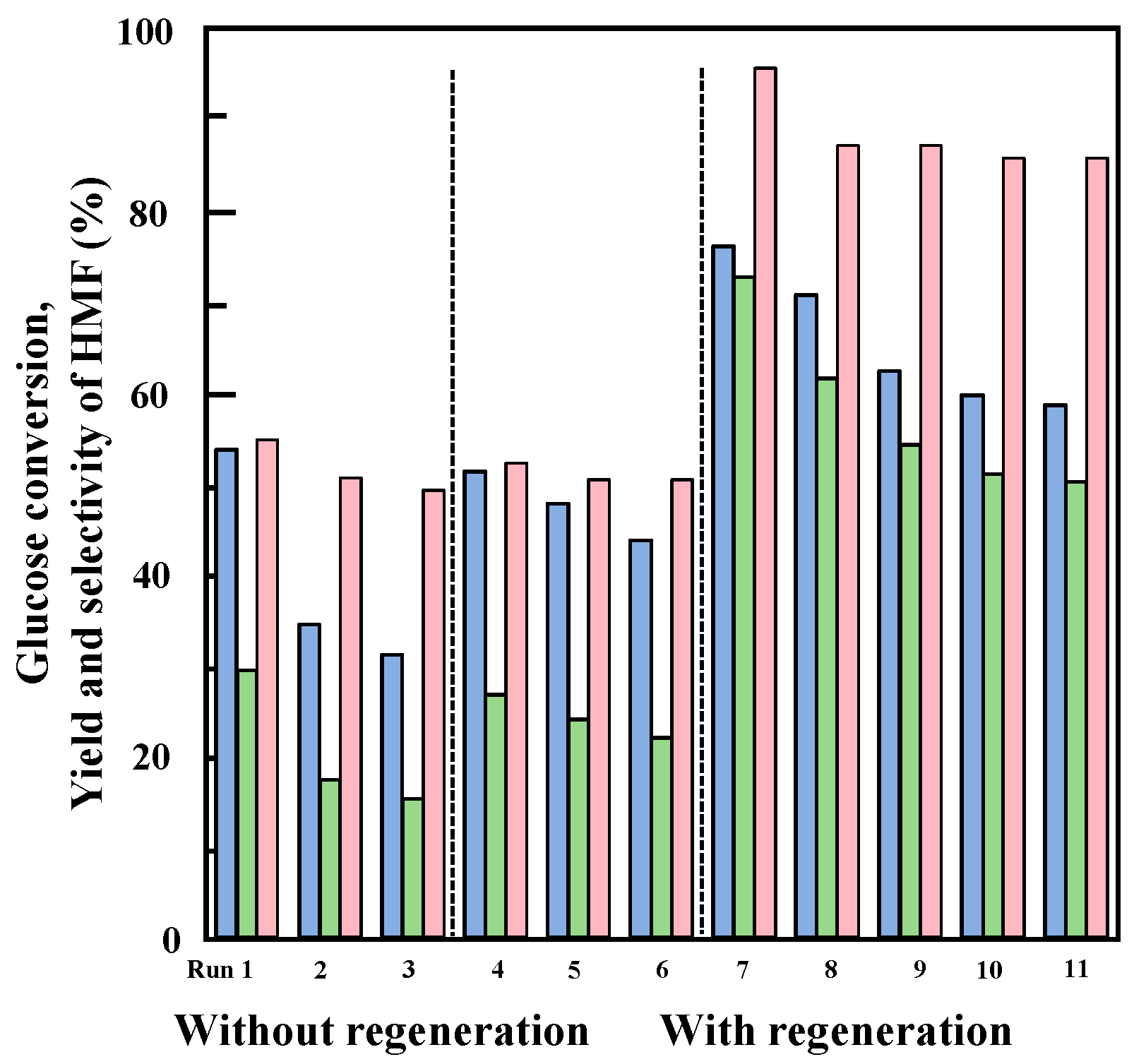
2.6. Deactivation and Reuse of the 25%Nb-TaP Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the Hierarchically Porous Tantalum Phosphate and Transition Metal-Doped Tantalum Phosphate
3.3. Structure and Surface Property of the Ion-Doped Tantalum Phosphate
3.4. Catalytic Performance and Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMF | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural |
| MIBK | methyl isobutyl ketone |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| MOFs | metal-organic frameworks |
| PEO | polyethylene oxide |
| TaP | tantalum phosphate |
References
- Zhu, L.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, C. Controlling the reaction networks for efficient conversion of glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 4812–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Tian, X. Development of different pretreatments and related technologies for efficient biomass conversion of lignocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 202, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiana, S.; Azhari, N.J.; Ilmi, T.; Kadja, G.T. Hierarchical zeolite for biomass conversion to biofuel: A review. Fuel 2022, 309, 122119–122145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X. Fructose decomposition kinetics in organic acids-enriched high temperature liquid water. Biomass Bioenerg. 2009, 33, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Watanabe, M.; Aida, T.M.; Smith, R.L., Jr. Catalytic dehydration of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by ion-exchange resin in mixed-aqueous system by microwave heating. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabanko, V.E.; Chernyak, M.Y.; Nepomnyashchiy, I.V.; Smirnova, M.A. High temperature 5-hydroxymethylfural synthesis in a flow reactor. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2006, 14, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.; Dutta, S.; Saha, B. Microwave assisted conversion of carbohydrates and biopolymers to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with aluminium chloride catalyst in water. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Cui, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhu, Y. Conversion of carbohydrates into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by ZnCl2 in water. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5494–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, L.; Fu, X.; Dai, J.; Guo, X.; Hu, C. Insights into the kinetics and reaction network of aluminum chloride-catalyzed conversion of glucose in NaCl–H2O/THF biphasic system. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, C.; Patrono, P.; Galletti, A.M.R.; Sbrana, G. Heterogeneous catalysts based on vanadyl phosphate for fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 275, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.-M.; Zhao, B.-H.; Liu, H.-C.; Morisato, K.; Kanamori, K.; He, Z.-Y.; Zeng, M.-M.; Wu, H.-P.; Chen, J.; Nakanishi, K. Synthesis of a hierarchically porous niobium phosphate monolith by a sol-gel method for fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfral. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3675–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.W.; Floyd, A.J.; Kinsman, R.G.; Roshan-Ali, Y.J. Dehydration reactions of fructose in non-aqueous media. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1982, 32, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, F.; Carlini, C.; Patrono, P.; Galletti, A.M.R.; Sbrana, G.; Massucci, M.A.; Galli, P. Heterogeneous zirconium and titanium catalysts for the selective synthesis of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde from carbohydrates. Appl. Catal. A 2000, 193, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, K.; Hosoya, T.; Miyafuji, H. High-yield production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from d-fructose, d-glucose, and cellulose by its in situ removal from the reaction system. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadula, S.; Oesterling, O.; Nardone, A.; Dinkelacker, B.; Saha, B. One-pot integrated processing of biopolymers to furfurals in molten salt hydrate: Understanding synergy in acidity. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3888–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, E.-W.; Mao, M.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.-M.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y. The direct conversion of cellulose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with CrCl3 composite catalyst in ionic liquid under mild conditions. Chem. Select. 2019, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Qiu, M.; Qi, X. Mechanochemical-assisted production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from high concentration of cellulose. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3013–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, J.; Hasunuma, T.; Ogino, C.; Kondo, A. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural production from salt-induced photoautotrophically cultivated Chlorella sorokiniana. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 142, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, C.M.; Rajabbeigi, N.; Tsapatsis, M. One-pot synthesis of 5-(ethoxymethyl)furfural from glucose using Sn-BEA and amberlyst catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 52, 5364–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Yasuda, T.; Hatanaka, T.; Hamahiga, K.; Matsuda, N.; Ueshima, M.; Nakai, K. In situ UV–VIS spectrophotometry within the second time scale as a research tool for solid-state catalyst and liquid-phase reactions at high temperatures: Its application to the formation of HMF from glucose and cellulose. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K. Surface and catalytic properties of ZrO2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1985, 13, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanziano, C.A.S.; Moya, S.F.; Barrett, D.H.; Teixeira-Neto, E.; Guirardello, R.; da Silva, F.S.; Rinaldi, R.; Rodella, C.B. Hybrid organic–inorganic anatase as a bifunctional catalyst for enhanced production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from glucose in water. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesfeld, J.J.; Gaquere, R.; Hensen, E.J.M. Mesoporous doped tungsten oxide for glucose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7552–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Cen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, W. Ordered mesoporous Nb-W oxides for the conversion of glucose to fructose, mannose and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Ye, L.; Tang, G.; Zhang, L.; Yue, B.; Tsang, S.C.E.; He, H. Effect of Brønsted/Lewis acid ratio on conversion of sugars to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over mesoporous Nb and Nb-W oxides. Chin. J. Chem. 2017, 35, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesfeld, J.J.; Sommerdijk, N.; Hensen, E.J.M. Early transition metal doped tungstite as an effective catalyst for glucose upgrading to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Protonated and layered transition metal oxides as solid acids for dehydration of biomass-based fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Pérez, G.E.; Torres-Torres, G.; Ortiz-Chi, F.; Godavarthi, S.; Silahua-Pavon, A.A.; Izquierdo-Colorado, A.; Da Costa, P.; Hernandez-Como, N.; Aleman, M.; Espinosa-Gonzalez, C.G. Effect of acid-basic sites ratio on the catalytic activity to obtain 5-HMF from glucose using Al2O3-TiO2-W catalysts. Chem. Select. 2018, 3, 12854–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolla, E.; Roman-Leshkov, Y.; Moliner, M.; Davis, M.E. “One-Pot” synthesis of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural from carbohydrates using Tin-Beta zeolite. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candu, N.; El Fergani, M.; Verziu, M.; Cojocaru, B.; Jurca, B.; Apostol, N.; Teodorescu, C.M.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Coman, S.M. Efficient glucose dehydration to HMF onto Nb-BEA catalysts. Catal. Today 2019, 325, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oozeerally, R.; Pillier, J.; Kilic, E.; Thompson, P.B.; Walker, M.; Griffith, B.E.; Hanna, J.V.; Degirmenci, V. Gallium and tin exchanged Y zeolites for glucose isomerisation and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural production. Appl. Catal. A 2020, 605, 117798–117808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, E.; Keçeci, M.E.; Akmaz, S.; Koc, S. NHeterogeneous Cr-zeolites (USY and Beta) for the conversion of glucose and cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Cellulose 2019, 26, 9035–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, W.; Chebude, Y.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Díaz, I.; Sastre, E. Comparison of glucose conversion to 5-HMF using different modified mordenites in ionic liquid and biphasic media. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Recio, M.; Santamaría-González, J.; Maireles-Torres, P. Brönsted and Lewis acid ZSM-5 zeolites for the catalytic dehydration of glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, P.H.; Dat, N.M.; Cuong, T.D.; Tung, D.T. Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) from rice-straw biomass using a HSO3-ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst under assistance of sonication. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13489–13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivhare, A.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, R. Metal phosphate catalysts to upgrade lignocellulose biomass into value-added chemicals and biofuels. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3818–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ni, W.; Hou, Z. Conversion of biomass to chemicals over zirconium phosphate-based catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jing, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y. NbO x-based catalysts for the activation of C-O and C-C bonds in the valorization of waste carbon resources. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, A.; Gupta, D.; Patra, A.K.; Saha, B.; Bhaumik, A. Synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurural from carbohydrates using large-pore mesoporous Tin phosphate. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.T.V.; Souzanchi, S.; Yuan, Z.; Ray, M.B.; Xu, C. (Charles) Simple and green route for preparation of tin phosphate catalysts by solid-state grinding for dehydration of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48501–48511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, S.; Bae, J.W. Aqueous Phase Synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from glucose over large pore mesoporous zirconium phosphates: Effect of calcination temperature. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Pan, D.; Li, W.; Shen, P.; Wu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, N.; Gao, L.; Xiao, G. Direct conversion of biomass-derived carbohydrates to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using an efficient and inexpensive manganese phosphate catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, D.; Zhu, L.; Hu, C. Solvent effects on degradative condensation side reactions of fructose in its initial conversion to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, I.J.; Teckchandani-Ortiz, A.; Santamaría-González, J.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Jiménez-López, A. Selective dehydration of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on acidic mesoporous tantalum phosphate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, H.-C.; Gao, D.-M. Establishing a kinetic model of biomass-derived disaccharide hydrolysis over solid acid: A case study on hierarchically porous niobium phosphate. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132756–132765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Huhe, T.; Liu, H.; Gao, D.-M.; Zhai, Y. Synthesis of hierarchically porous tantalum phosphate catalysts by a sol-gel method for transformation of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2025, 15, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.-X.; Bi, J.-Q.; Sun, K.-N.; Li, A.-M.; Mao, J.-J. Competition and neutralization: Thermally induced crystallization and phase evolution of amorphous calcium phosphate with cosubstitution of larger and smaller divalent cations. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7602–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Morales, I.; Santamaría-González, J.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Jiménez-López, A. Mesoporous tantalum phosphate as acidic catalyst for the methanolysis of sunflower oil. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 123, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Yu, D.-H.; Zhao, J.-B.; Zhang, W.-G.; Dong, Y.-H.; Huang, H. The effect of P/Ta ratio on sorbitol dehydration over modified tantalum oxide by phosphoric acid. Catal. Commun. 2014, 43, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Morales, I.; Moreno-Recio, M.; Santamaría-González, J.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Jiménez-López, A. Mesoporous tantalum oxide as catalyst for dehydration of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 154, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Ren, J.-W.; Liu, X.-H.; Li, X.-C.; Xia, Y.-J.; Lu, G.-Z.; Wang, Y.-Q. Mesoporous niobium phosphate: An excellent solid acid for the dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.-R.; Yan, B.; Yuan, Z.-F.; Sun, K.-Q. Mesoporous tantalum phosphates: Preparation, acidity and catalytic performance for xylose dehydration to produce furfural. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59081–59090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, A.; Barik, S.K.; Krishnan, R.V.; Chakraborty, S.; Jena, H. Studies on synthesis, structural and thermal properties of sodium niobium phosphate glasses for nuclear waste immobilization applications. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigstedt, P.; Keskiväli, J.; Leskelä, M.; Repo, T. The role of salts and Brønsted acids in Lewis acid-catalyzed aqueous-phase glucose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delidovich, I.; Palkovits, R. Catalytic activity and stability of hydrophobic Mg-Al hydrotalcites in the continuous aqueous-phase isomerization of glucose into fructose. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 4322–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girisuta, B.; Janssen, L.; Heeres, H.J. Green Chemicals: A kinetic study on the conversion of glucose to levulinic acid. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2006, 8, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordomsky, V.V.; Sushkevich, V.L.; Schouten, J.C.; van der Schaaf, J.; Nijhuis, T.A. Glucose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over phosphate catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 300, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.T.V.; Souzanchi, S.; Yuan, Z.-S.; Xu, C.-B. One-pot sol–gel synthesis of a phosphated TiO2 catalyst for conversion of monosaccharide, disaccharides, and polysaccharides to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12483–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordomsky, V.V.; van der Schaaf, J.; Schouten, J.C.; Nijhuis, T.A. The effect of solvent addition on fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in biphasic system over zeolites. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Morales, I.; Moreno-Recio, M.; Santamaría-González, J.; Maireles-Torres, P.; Jiménez-López, A. Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from glucose using aluminium doped MCM-41 silica as acid catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 164, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Temperature (°C) | SBET (m2·g−1) | VP (cm3·g−1) | DP (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 240 | 0.16 | 2.6 |
| 500 | 225 | 0.18 | 3.2 |
| 600 | 101 | 0.14 | 5.7 |
| 700 | 55 | 0.12 | 8.6 |
| 800 | 54 | 0.056 | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, D.-M.; Huang, K.; Zheng, J.; Gong, L.; Ren, J.; Fujino, H.; Liu, H. Niobium-Enhanced Kinetics of Tantalum Phosphate in Catalytic Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Catalysts 2025, 15, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121095
Gao D-M, Huang K, Zheng J, Gong L, Ren J, Fujino H, Liu H. Niobium-Enhanced Kinetics of Tantalum Phosphate in Catalytic Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Catalysts. 2025; 15(12):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121095
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Da-Ming, Kai Huang, Jianxing Zheng, Lei Gong, Junli Ren, Hidemi Fujino, and Haichao Liu. 2025. "Niobium-Enhanced Kinetics of Tantalum Phosphate in Catalytic Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural" Catalysts 15, no. 12: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121095
APA StyleGao, D.-M., Huang, K., Zheng, J., Gong, L., Ren, J., Fujino, H., & Liu, H. (2025). Niobium-Enhanced Kinetics of Tantalum Phosphate in Catalytic Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Catalysts, 15(12), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121095








