Abstract
With the booming development of natural anticancer agents, icaritin has been widely used in clinical liver cancer treatment due to the smaller number of side effects. Among them, enzymes as catalysts for producing icaritin have attracted considerable attention. Industrial production remains in its infancy due to the poor reusability of free enzymes, despite enzymes possessing favorable efficiency and green catalytic effects. The present study investigated two immobilization methods, including cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) and magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs). The optimal temperature and pH for the two hydrolases were determined, followed by characterization using VSM, XRD, FT-IR, and TEM techniques. The experiments have demonstrated that MCLEAs eradicate the need for ultrafiltration; MCLEAs are beneficial for enhancing fixation efficiency. Additionally, MCLEAs exhibited significantly higher catalytic activity, which raised the catalytic activity by approximately 30% compared with CLEAs. Moreover, after 10 consecutive reuse cycles, the catalytic activity of MCLEAs remained above 70%, maintaining a conversion rate of epimedin C at 61.59%. To summarize, MCLEAs offer an efficient strategy for enzyme immobilization. MCLEAs not only significantly enhanced both the enzyme’s ability to catalyze and resist but also eliminated the necessity for ultrafiltration as well as enabled rapid product separation.
1. Introduction
Globally, hepatocellular carcinoma is ranked as the sixth most common cancer and holds the fourth position in terms of causing mortality related to cancer [1]. The predominant strategy for most cancer management is chemotherapy, which relies on the potent cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents against malignant cells. However, the inherent limitations and significant side effects of conventional chemotherapy drugs have consistently been demonstrated [2]. In an endeavor to mitigate the side effects and adverse reactions associated with chemotherapeutic medications, researchers are currently exploring the potential of harnessing natural anticancer compounds derived from diverse botanical origins and organisms. Their primary objective is to attain optimal efficacy while minimizing toxicity levels [3]. Epimedium, a well-known herbal medicine in China, is frequently used as a tonic and treatment for rheumatism [4]. Icaritin (ICT), a primary flavone compound with an 8-prenyl group, has been identified as a significant component found in medicinal plants belonging to the Epimedium genus. Its effectiveness in cancer treatments has been demonstrated through mechanisms associated with apoptosis [5]. In the year 2022, a molecular-level immunomodulatory drug in the form of an icaritin soft capsule was introduced to the market, offering a viable therapeutic option for individuals suffering from hepatocellular carcinoma and unfavorable prognosis. Icaritin soft capsules significantly improved the standard of life in individuals diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma [6]. Icaritin showed satisfactory clinical performance and possessed great global market prospects; thus, icaritin has attracted widespread attention from both academia and medicine.
Due to the significantly limited presence of icaritin (less than 1%) in epimedium, the direct extraction method is considerably tough to prepare icaritin on a large scale. In addition, the synthesis of icaritin through chemical means is inefficient because of the costly catalysts, harsh conditions, intricate procedure, and complex byproducts [7,8]. Natural enzymes as green catalysts are a promising method for producing icaritin. At present, the enzymes have been used to prepare icaritin, mainly including glucosidase, rhamnosidase, snail enzyme, cellulase, pectinase, and naringinase [9,10,11].
As the majority of published research used icariin as a substrate, while the extraction method of icariin is complicated, and the yield is not high. In contrast to icariin, epimedin C is more abundant in epimedium, so the cost of preparing icaritin can be greatly decreased by using epimedin C as a substrate [12,13]. Although epimedin C is present at a relatively high content level, its hydrolysis is hindered by the two rhamnose molecules at the C3 position, making it a less explored target. Recently, Xie et al. were the first to report the use of β-glucosidase and α-rhamnosidase to achieve the stepwise hydrolysis of epimedin C, ultimately yielding icaritin [9]. β-glucosidase (G4, MT779019) causes the hydrolysis of epimedin C by clearing the glycosidic bond at the C7 position. Additionally, α-rhamnosidase (R2, MT779021) possesses the ability to remove rhamnose moieties at the C3 position. The icaritin production from epimedin C uses R2 and G4 by a two-step catalysis. However, the reusability and operational stability of free enzymes were relatively restricted, which limited their potential industrial application [14]. Therefore, it is imminent to find a suitable approach to immobilization [15].
The immobilization of enzymes has gained significant attention because of its benefits in overcoming the demerits of free enzymes [16]. The past few decades have witnessed a growing body of investigation into the immobilization of enzyme methods, for example, carrier-bound immobilization methods including entrapment, adsorption, and covalence, which have several demerits [17]. In contrast, the benefits of the carrier-free immobilization approach were more obvious. Particularly, cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) technology had arose as a viable option due to its reusability, ease of preparation, and capability to be detached from reactions in industrial applications [18]. Thus, it offers significant technical and economic benefits.
Application of CLEAs is constrained by certain limitations, which hinder its further implementation. One of the reasons is that the enhanced size (clumping phenomenon) of CLEAs clusters occurs as a result of their separation from a mixture of reactions through centrifugation or filtration. This phenomenon may potentially impair the mass transfer efficiency of enzymes, and such an effect is more prominent when enzymes act on macromolecular substrates [19]. The mechanical instability of CLEAs poses another concern, as it leads to the loss of enzyme activity during filtration and centrifugation [20].
To overcome this, iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have attracted much interest. The immobilization of CLEAs using MNPs has been extensively employed in numerous studies to prepare magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs) [21].
In addition to the added advantage of facile separation and recovery from reaction media, MNPs lower operating costs compared to traditional methods like filtration and centrifugation [22]. The aforementioned nanomaterials exhibit distinctive characteristics of biocompatibility and non-toxicity. MNPs are superior supports for enzyme immobilization, offering a substantial area on the surface for potentially elevated enzyme loading [23]. The choice of a cross-linking agent plays a vital role in the formation of enzyme aggregates [24]. Glutaraldehyde, known for its remarkable versatility, high reactivity, and stability, is widely used as a cross-linking agent to immobilize various types of enzymes [25]. Through covalent bonds formed by cross-linking, it has the potential to decrease thermal oscillation and limit conformational adaptability, thereby mitigating the denaturation and unfolding of enzymes [26]. To summarize, these magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs) have demonstrated enhanced stability against pH and temperature variations, reduced inhibition effects, and high activity levels [27]. This makes them an indispensable strategy in improving enzymatic processes.
This study investigated various immobilization techniques for glycosidases, including the synthesis of cross-linked enzymatic aggregates (CLEAs) and magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs). CLEAs were prepared by ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, glutaraldehyde cross-linking, and centrifugation. For MCLEAs, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were used, and the aggregates were collected by magnetic separation after (NH4)2SO4 precipitation and glutaraldehyde cross-linking (without ultrafiltration, Scheme 1).
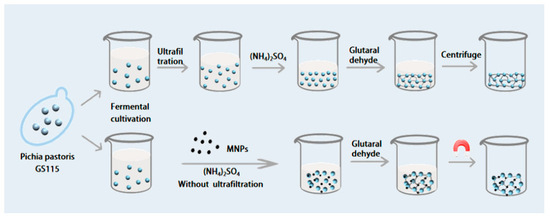
Scheme 1.
Flow chart of the two preparation routes.
The optimization of preparation conditions for immobilizing R2 and G4 was conducted by factors such as precipitation, cross-linking conditions, and preparation pH on activity recovery. Furthermore, a systematic comparison was made between the enzyme properties of CLEAs and MCLEAs.
2. Results
2.1. Optimization and Characterization of CLEAs
The addition of salts to aqueous protein solutions resulted in the precipitation of physical aggregates, which remained together due to non-covalent bonding without causing any disruption to their tertiary structure [28]. The precipitation of enzymes using ammonium sulfate is a widely employed purification method. Thus, the precipitant chosen for the subsequent experiment was saturated ammonium sulfate. The correct dosage of precipitant was determined by investigating various volume ratios of ammonium sulfate. As shown in Figure 1A, the ratio gradient of the fermentation broth to ammonium sulfate was from 1:0.25 to 1:3. The highest enzyme activity recovery was achieved when the ratio reached 1:2. As ammonium sulfate continued to increase, the enzyme activity gradually decreased. A reduced dosage will result in ineffective enzyme precipitation, while an increased dosage may lead to enzyme denaturation due to the removal of the hydration layer, resulting in the loss of enzymatic activity [29].
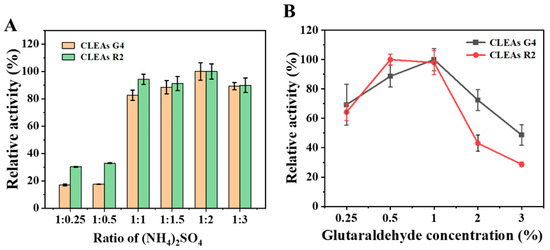
Figure 1.
Optimization of CLEAs preparation. Impact of different concentrations of (NH4)2SO4 (A) and glutaraldehyde (B) on enzyme.
Glutaraldehyde is a powerful cross-linking agent due to its cost-effectiveness, ready availability in large quantities for commercial purposes, and status as one of the most popular reagents in biocatalytic design [30]. When utilized at various concentrations (0.25–2%) to form CLEAs, the activity recovery of CLEAs increased most substantially as the GA concentration was elevated to 1% (Figure 1B). Nevertheless, with further increases in the GA concentration, we observed a sharp decline in activity recovery, which may be owing to the infiltration of GA into the protein core, resulting in an adverse interaction with crucial catalytic amino acids [31,32]. The other factors contributing to the decrease in enzymatic activity at elevated GA concentrations may be the diminishment of enzyme flexibility or more compact CLEAs, which result in the limited diffusion of coarse substrates to the catalytic site [32,33].
The CLEAs can form either regular spherical aggregates (type 1) or asymmetric cross-linked aggregates (type 2) [34]. To investigate the structure of the CLEAs, SEM was used to capture micrographs. As depicted in Figure S1A, CLEAs G4 exhibited a relatively uniform structure comprising numerous small globular particles. This spherical morphology offers an increased specific surface area and a higher catalytic site per unit area, thereby facilitating their application as biocatalysts [10]. Conversely, CLEAs R2 (Figure S1B) displayed a less spherical morphology where proteins interlinked to create porous networks resembling type II structures. Furthermore, both types of CLEAs exhibited highly porous network structures, which enhance the connection between substrates and the active sites of enzymes for improved efficiency [35].
To further investigate the interaction between free enzymes and CLEAs, the secondary structure of CLEAs was analyzed using FT-IR spectroscopy, which was a crucial technique for monitoring the reconfiguration of protein conformational alterations in protein structures [16]. As shown in Figure S2, the characteristic peaks observed at 1510 cm−1 and 1560 cm−1 are attributed to the protein amide II band, which results from the coupled vibrations of C=N stretching and N–H bending [36]. The absorption at 1150 cm−1 is associated with C–O stretching vibrations originating from amino acid residues [37]. Additionally, the broad spectral feature in the 3400–3300 cm−1 region corresponds to O–H stretching vibrations, likely introduced by glutaraldehyde-mediated cross-linking [38]. Together, these spectral signatures provide clear evidence for the successful immobilization of glycosidases onto the magnetic nanoparticle support.
2.2. Optimization and Characterization of MCLEAs
The requirement for centrifugation to recover the immobilized enzyme remains one of the drawbacks associated with conventional CLEAs [39]. To solve this issue, we introduced magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as cores, which were co-precipitated with the aggregated enzyme and then cross-linked, thus achieving the results of recycling with a magnet [40]. The magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregate comprises an enzyme aggregate and a surface-functionalized magnetic particle, which are cross-linked together by glutaraldehyde [28]. The preparation method is to mix the enzyme solution and the surface-functionalized magnetic particles evenly, then add ammonium sulfate to make the enzyme form an enzyme aggregate, and finally add glutaraldehyde, serving as a cross-linking agent to cross-link the enzyme aggregate and the surface-functionalized magnetic particles to form the magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregate [41]. In this experiment, we used 4 mg of carboxylated ferric oxide with 0.2U of R2 and G4 to prepare magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates.
First, we optimized the preparation conditions. Compared to CLEAs, MNPs offer a multitude of surface regions for enhanced enzyme loading, thereby obviating the need for ultrafiltration. MCLEAs were prepared by initially physically aggregating enzymes using precipitants and subsequently establishing chemical bonds between them through cross-linking agents. The optimization of the ammonium sulfate concentration is also crucial, as it can induce varying degrees of enzyme aggregation during precipitation. As shown in Figure 2A, when the volume fraction of the precipitant increased, the precipitated protein increased, and the enzyme activity recovery gradually increased. However, after reaching a certain ratio (1:3), even though the content of ammonium sulfate exhibited a continuous increase, the recovery of enzyme activity did not increase but began to decrease. High concentrations of ammonium sulfate enriched the solution with hydroxyl groups, which adversely affected the protein’s tertiary structure and resulted in the reduced catalytic activity of glycosidases [42,43].
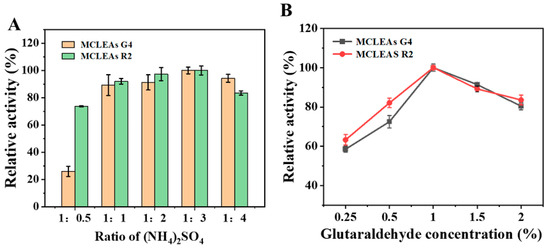
Figure 2.
Optimization of MCLEAs preparation. Impact of different concentrations of (NH4)2SO4 (A) and glutaraldehyde (B) on enzyme.
The concentration of GA is an important factor affecting the recovery of MCLEAs activity as well. At lower cross-linker concentrations, inadequate cross-linking occurs, releasing the enzyme into the reaction medium as a consequence of unstable CLEAs and MCLEAs [41]. The relative activity of MCLEAs was the highest at a final glutaraldehyde concentration of 1% (Figure 2B). However, when the glutaraldehyde concentration continued to improve, the relative activity of MCLEAs began to decrease. The reason for this is that elevated concentrations of glutaraldehyde can induce conformational changes in the active sites of enzymes [44]. Furthermore, in high concentrations of glutaraldehyde, the increased rigidity of enzymes lead to the loss of flexibility of the enzymes; therefore, the catalytic activity decreases [45].
The formation of MCLEAs was verified by performing TEM on carboxyl-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles and MCLEAs. Panel A shows the magnetic nanoparticles, panel B shows the G4 on magnetic nanoparticles (MCLEAs G4), and the TEM of MCLEAs R2 is shown in the Figure S3. The electron beam in TEM analysis passes through a thin sample, and the contrast between denser and less dense regions is formed by the variation in electron density of the elements present in the sample, resulting in darker contrasts for higher electron densities [46]. As shown in Figure S3A, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are granular, uniformly dispersed, smooth, clearly delineated, and bright. In contrast, as shown in Figure S3B, after MCLEAs G4 formation, the contours were not clear, and overall transmittance decreased due to the encapsulation of surface proteins, proving that proteins were successfully attached to the MNPs surface.
The FTIR analysis (Figure S4) confirmed the presence of MNPs within the structure of MCLEAs, but the presence of proteins gives identifiable differences in their characteristic peaks. The absorption peaks observed at 570 cm−1 in the FT-IR spectrum of MCLEAs correspond to the stretching vibrations of Fe–O bonds, providing evidence for MNP incorporation into MCLEAs [47,48]. The confirmation of the enzyme’s presence was established through the characteristic peak of the N-H bond at 3145 cm−1 and the characteristic peak of the C-O bond at 1082 cm−1 [49,50]. There are characteristic peaks at 1395 cm−1 and 1554 cm−1, which are mainly formed by the amide bond after enzyme cross-linking [21,46]. Thus, the successful immobilization of enzymes onto magnetic nanoparticles can be confirmed.
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique was commonly employed to investigate the crystalline arrangement of magnetic nanoparticles, both prior to and subsequent to the immobilization process [51]. As depicted in Figure S5, the powder XRD patterns of the synthesized samples exhibited a close match in terms of the peak positions and relative intensities with the reference magnetite Fe3O4 pattern (JCPDS card 19-0629) [52,53]. These findings indicate that the cross-linking steps did not induce any structural alterations in MNPs.
The nanoparticles used in this study have the added advantage of easy separation. The magnetic behavior was assessed through VSM analysis (Figure S6). Based on the findings, it was observed that MNPs exhibit a saturation magnetization value of 62.88 emu/g, indicating their super magnetic property [48]. Additionally, the saturation magnetization values of MCLEAs G4 and MCLEAs R2 were measured to be 41.54 emu/g and 33.45 emu/g, respectively. The decline in the saturation magnetization value of MNPs indicates successful enzyme loading on MNPs. Despite the decline in the magnetic saturation value following immobilization, the prepared MCLEAs are quickly attracted towards the applied magnet.
2.3. Assays of the Optimal pH and Temperature
After determining the optimal cross-linking conditions, we investigated the optimal pH and temperature changes in MCLEAs and CLEAs. The activity of MCLEAs and CLEAs was investigated across a broad temperature range (30–80 °C) and pH range (3.0–7.0). Relative activity was achieved by establishing the maximum activity at 100%.
As shown in Figure 3A, G4 demonstrated its highest level of activity when the pH value was set at 4.0, and the optimum pH value remained unchanged before and after fixation. However, at pH 5.0 to 7.0, the relative activity of CLEAs G4 was above 20%, while the catalytic activity of the free G4 was significantly reduced, indicating that immobilized enzymes had a wider pH adaptability. Meanwhile, Figure 3B shows that the activity of R2 was the highest at pH 4.5, and the optimal pH did not change before and after fixation; however, the activity of immobilized enzymes was higher than free enzymes across various pH conditions. The alteration of the pH in the enzyme solution may induce subunit dissociation of the multimeric enzyme, thereby exerting a significant impact on its enzymatic activity [54]. At extreme pH, CLEAs can maintain greater activity than free enzymes because cross-linking enhanced the stability of enzyme structures and protected enzyme subunits from dissociation [55]. Next, we compared the change in the optimal temperature of the two enzymes before and after immobilization. As shown in Figure 3C, at a temperature of 55 °C, CLEAs R2 exhibited the greatest relative activity as the free enzyme. CLEAs R2 retained above 30% of its relative enzyme activity at various temperatures from 65 °C to 80 °C, indicating that CLEAs R2 has good thermal adaptability. For CLEAs G4, the optimum temperature was elevated to 10 °C compared to that of free G4, and its catalytic activity was still above 50% even at 75 °C. After immobilization, the enzyme exhibits enhanced rigidity and reduced molecular mobility, which is crucial for protecting the enzyme structure under harsh acidic and alkaline conditions [56]. In addition, the application of elevated temperatures can enhance the solubility of the substrate, which helps to accelerate the hydrolysis reaction and reduce the production cost [57].
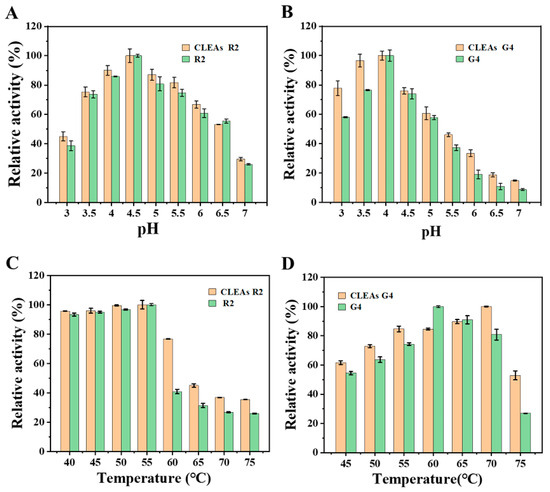
Figure 3.
Effect of pH (A,B) and temperature (C,D) on free enzymes and CLEAs. The relative activity was expressed as the percentage of control activity.
In general, although the enzymatic properties of CLEAs are better than those of free enzymes, they do not perform particularly well. In contrast, MCLEAs has a better performance. The enzyme activity of MCLEAs was significantly improved under the extreme conditions of pH 3.0 and 7.0, as shown in Figure 4. In terms of the optimal temperature, MCLEAs also have a relatively good performance. This may be due to covalent binding to carboxylated ferric oxide, which may limit conformational changes and thus lead to higher relative activity over a wide pH range [40,58].The optimum temperature of R2 was raised from 55 °C to 60 °C. Under an extremely high temperature of 75 °C, the activity of free G4 was less than 30%, while that of MCLEAs G4 was nearly 60%, indicating that the enzyme activity was significantly increased. The observed enhancement may be attributed to the presence of nanoparticle pores that trap water molecules, thereby preserving their structure and improving enzyme stability [55].
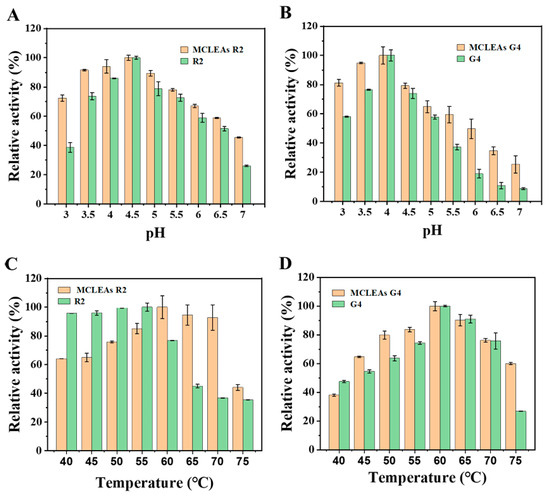
Figure 4.
Effect of pH (A,B) and temperature (C,D) on MCLEAs and free enzymes. The relative activity was expressed as the percentage of control activity.
2.4. Stability and Reusability
Inactivation of enzymes under harsh conditions posed a crucial limitation to their widespread implementation in the industry. We conducted an investigation into the stability of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs), magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs), and free enzymes under varying pH conditions.
The residual activity of MCLEAs and CLEAs remained stable and did not exhibit a significant decrease across the tested pH range (Figure 5A,B) following a 2 h incubation. The incubation at a high temperature of 65 °C for 30–90 min, as depicted in Figure 5C,D, immobilized enzymes exhibited a significantly greater level of activity compared to free enzymes; however, MCLEAs demonstrated superior stability when compared to CLEAs. The significant residual activity in MCLEAs could potentially be ascribed to the sufficient cross-linking of the enzyme with MNPs [59]. The process of cross-linking increased the rigidity of the enzymes, resulting in a prominent improvement in protein’s tolerance to its surrounding environment. The reusability of biocatalysts is a crucial element deciding industrial applicability, serving as a significant indicator of the effectiveness of immobilized enzymes.
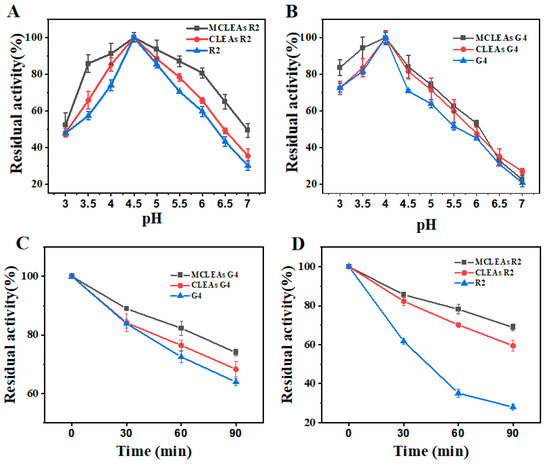
Figure 5.
Evaluation of enzyme stability at different pH and high-temperature conditions. (A) Residual activity of R2 under different pH conditions. (B) Residual activity of G4 under different pH conditions. (C) Residual activity of G4 incubated at 65 °C for different times. (D) Residual activity of R2 incubated at 65 °C for different times.
Figure 6 indicated that CLEAs had only 20% activity after six cycles of utilization. However, MCLEAs retained above 70% activity after 10 cycles of utilization. For MCLEAs G4, residual activity reached 83% for 10 consecutive batches, indicating good reusability. The above results indicate that MCLEAs are more conducive to improving the stability of the enzyme.
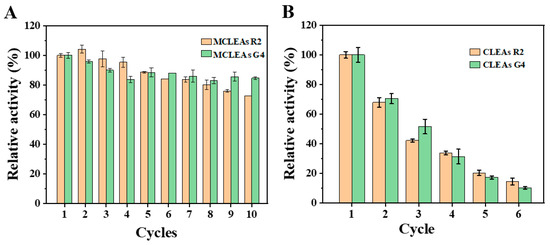
Figure 6.
Reusability of MCLEAs (A) and CLEAs (B) in buffer.
2.5. Application in Icaritin Biosynthesis
As shown in Figure 7, 0.2U G4 can completely hydrolyze 1mg/mL of epimedin C within 30 min. Compared with free enzymes, MCLEAs G4 are significantly improved and can reach 129.71% of free enzymes, while the activity of CLEAs (98.27%) is basically the same as that of free enzymes. At 20 min, the conversion rate of G4 reached 80%, while MCLEAs G4 were already close to saturation. For R2, the enzyme activity was not significantly increased after fixation but decreased to a certain extent. In the optimal preparation conditions, enzyme activity recovery rates of CLEAs R2 and MCLEAs R2 were 62.93% and 92.56%, respectively. It may be owing to the relatively small pore size of rhamnosidase during immobilization, which may lead to the difficult access of macromolecular substrates and limited diffusion, resulting in decreased catalytic efficiency [41].
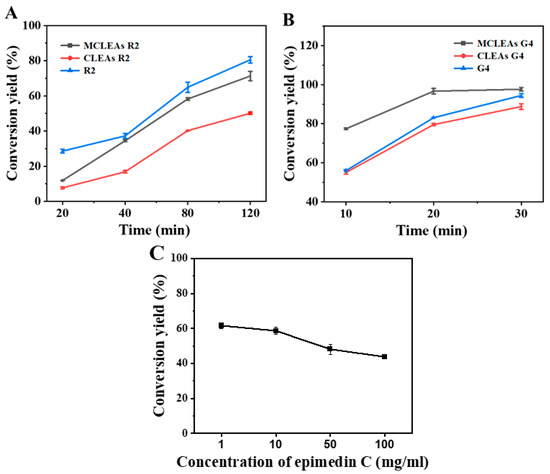
Figure 7.
Conversion of epimedin C with free enzymes, CLEAs, and MCLEAs (A,B). Conversion of various concentrations of epimedin C (C).
The one-pot biosynthesis of icaritin was achieved by adding MCLEAs R2 and MCLEAs G4 to the optimal reaction system in a ratio of 2:1 based on the molar ratio of glucose residues and rhamnose residues present in icaritin, resulting in the conversion rate of epimedin C at 61.59%. This approach exhibits significant advantages compared to those reported in the other literature. Wang et al. utilized crude glycosidase derived from Aspergillus, strain y848, for the synthesis of icaritin from icariin, achieving a weight yield of 50.4% under optimized conditions [60]. A whole-cell catalytic experiment demonstrated that Escherichia coli, strain WPE4, exhibited an efficiency of 46.4% in converting kaempferol to icaritin [61]. Xie et al., after incubating a reaction mixture containing 1 g/L epimedin C and TpeRha at a temperature of 90 °C for 100 min, introduced Tpebgl1 into the mixture and further incubated it for an additional 50 min. Ultimately, with optimal conditions, the conversion rate of 1 g/L epimedin C reached 0.4337 g/L [9]. The efficiency of icaritin production by MCLEAs at different concentrations of epimedin C is illustrated in Figure 7C. There was no apparent substrate inhibition observed with the increasing substrate concentration.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Epimedin C was obtained through Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (PNPG) and p-nitrophenyl-α-rhamnopyranoside (PNPR) were obtained though Beijing Solarbio Science&Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. Glutaraldehyde (GA), FeCl2⋅4H2O, and FeCl3⋅6H2O were obtained from Macklin. Ammonium sulfate was purchased from Beijing Chemical Works (Beijing, China). The reagents employed in the subsequent experiment were of analytical purity.
3.2. Expression of Rhamnosidase and Glucosidase
In Pichia pastoris, rhamnosidase (R2) and glucosidase (G4) were overexpressed. pPIC9K-R2 and pPIC9K-G4, recombinant plasmids, were electroporated into P. pastoris GS115, followed by cultivation of the resulting recombinant cells in buffered glycerol-complex medium at 30 °C for 24 h. Enzyme expression was carried out in buffered methanol-complex medium at 30 °C by providing a daily addition of 1% methanol for 5 days, ultimately leading to the collection of R2 and G4 through centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 10 min. The enzymes were obtained from the strains cultivated and stored in our laboratory in previous work.
3.3. Enzyme Activity Assay
The enzymatic activity of R2 and G4 was assessed using 1 mg/mL PNPG or pNPR as substrate in 50 mM buffer (pH 5.0) at 55 °C. The reaction system was pre-incubated at the target temperature before the enzyme was added to initiate the timing. The reaction was conducted for 30 s and terminated by adding an equal volume of sodium carbonate solution. The absorbance of the released p-nitrophenol (pNP) was measured at 405 nm. One unit (U) of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μmol of pNP per minute.
The concept of relative activity was introduced to provide a more accessible approach for assessing the catalytic activity of enzymes. It was quantified using the following equation: relative activity = (where A0 represents the highest activity within a specific group, and Ax denotes the activities of other groups).
3.4. Preparing Carboxyl-Functionalized Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
On this basis, some modifications were made to prepare carboxyl-functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles [62]. We dissolve 1.195 g of FeCl2⋅4H2O and 3.25 g of FeCl3⋅6H2O in 50 mL of deionized water, which was transferred into a three-necked, round-bottomed flask with a volume of 100 mL, heating to 50 °C with vigorous agitation for a duration of 30 min. When the temperature was elevated to 75 °C, 6.25 mL of NH3⋅H2O was added into the system and mixed for an hour. When the system temperature was raised to 85 °C, the system was supplemented with 6.25 mL (1.5 mol/L) trisodium citrate. The reaction continued for 90 min with continuous stirring until the completion of the preparation. Magnetic nanoparticles were magnetically immobilized and subsequently subjected to multiple washes with saturated sodium chloride, deionized water, and pure ethanol. Ultimately, magnetic nanoparticles were stored in 20% ethanol solution at low temperature until use.
3.5. Preparation of CLEAs and MCLEAs
CLEAs are prepared in two steps. Beforehand, the collected fermentation broth was concentrated with an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (Solarbio Science, Beijing, China, 50 mL, and 30 kDa), and its unit activity was determined for subsequent experiments. In the first step, protein was precipitated by the addition of saturated ammonium sulfate solution in different volume ratios to form enzyme aggregates. In detail, the crude enzyme solution containing 0.25U remained at 4 °C for 2–5 h with saturated ammonium sulfate solutions in different ratios. In the subsequent phase, different glutaraldehyde concentrations were added to the formed enzyme aggregates to gain water-insoluble cross-linked enzyme aggregates. The CLEAs R2 and CLEAs G4 were finally obtained by adding glutaraldehyde to an ultimate concentration from 0.2% to 3% and cross-linking for 3 h at 16 °C.
The MCLEAs were prepared with Fe3O4 using the same strategy of CLEAs, but one can just use fermentation broth instead of ultrafiltrate. A total of 200 μL of fermentation broth (0.4 U/mL) and 4 mg of Fe3O4 were mixed with different volume ratios of saturated (NH4)2SO4 solution; mixture was incubated at a temperature of 4 °C for a duration of 2–5 h. Eventually, different concentrations of GA were utilized to cross-link Fe3O4 and enzymes for a duration of 3 h at a temperature of 16 °C. The resulting precipitate was separated by magnet, then washed three times with phosphate-buffered solution (pH 5, 20 mM) to eliminate unfixed glycosidases, and stored at 4 °C.
3.6. Stability Evaluation of Free Enzymes and Immobilized Enzymes
To assess stability of pH and thermal stability, phosphate buffers with pH gradients from 3 to 7 and temperature gradients from 40 °C to 75 °C were prepared. Immobilized enzymes and free enzymes were incubated for 2 h in this phosphate buffer described above, and the residual activities of both the free enzymes and immobilized enzymes were assessed. Reusability of MCLEAs and CLEAs was investigated by determining the relative activity following hydrolysis of epimedin C. After every determination, MCLEAs and CLEAs were recovered through magnet or centrifugation and washed with 20 mmol/L phosphate buffer at pH 5.0.
3.7. Characterizations
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) was utilized to document the morphologies and dimensions of CLEAs, and observation of MCLEAs was conducted using transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL-JEM 2100F, JEOL-JEM 2100F) on samples that were coated with a layer of gold via sputter-coating. The magnetic properties of the samples were determined though vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, Lake Shore 8600, Lake Shore Cryotronics, Westerville, OH, USA) under a magnetic field ranging from −15 kOe to 15 kOe at 25 °C. Participating in the immobilization process of free enzymes, CLEAs, MCLEAs, and MNPs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR, Shimadzu IRAffinity-1, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) in the gradients of 4000–400 cm−1. The identification of phases was conducted using X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD, Shimadzu XRD-6000, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). The diffracting angles 2θ were scanned from 3° to 90° with a step size of 10° and a measurement time of 10 min per step.
4. Conclusions
This study systematically evaluated two immobilization techniques, cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) and magnetic cross-linked enzyme aggregates (MCLEAs), for the enzymatic hydrolysis of epimedin C. The MCLEA system demonstrated a superior catalytic performance relative to CLEAs. Specifically, the activity of MCLEAs G4 reached 129.71%, representing a 1.4-fold increase over that of CLEAs G4 (98.27%). Similarly, the activity of R2 increased from 62.53% in CLEAs to 92.56% in MCLEAs, corresponding to a 1.56-fold enhancement. Under the optimized MCLEAs conditions, a hydrolysis conversion rate of 61.59% for epimedin C was achieved, leading to a markedly improved yield of the target product icaritin. Moreover, the immobilized enzymes exhibited enhanced operational stability and reusability, along with facile separation from the reaction system. These findings support MCLEAs as an efficient and practical strategy for the biocatalytic production of high-value natural products such as icariin.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15111034/s1, Figure S1: SEM photos of CLEAs; Figure S2: FT-IR spectra of free enzyme and CLEAs; Figure S3: TEM photos of MNPs(A), MCLEAs G4(B) and MCLEAs R2(C); Figure S4: FT-IR spectra of free enzyme and MCLEAs; Figure S5: XRD patterns of MNPs and MCLEAs; Figure S6: XRD patterns of MNPs and MCLEAs.
Author Contributions
Y.Z.: Methodology, Investigation, and Writing—original draft. W.Z.: Investigation. Y.L.: Supervision, Writing—review and editing. W.F.: Investigation. H.L.: Methodology, Supervision, and Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC2102800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22078014), the Major Science and Technology Projects of Beijing Polytechnic (2024X005-KXD), the Supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (NO. 7254488).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, L.; Wei, X.; Gu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H. Human Liver Cancer Organoids: Biological Applications, Current Challenges, and Prospects in Hepatoma Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 555, 216048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.-Y.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Cheng, S.-X.; Rong, L.; Zhang, X.-Z. Drug Self-Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 112, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ion, D.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Păduraru, D.N.; Andronic, O.; Mușat, F.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bolocan, A. An Up-to-Date Review of Natural Nanoparticles for Cancer Management. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunoregulatory Effects of Icariin and Icaritin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Son, N.T. Icaritin: A Phytomolecule with Enormous Pharmacological Values. Phytochemistry 2023, 213, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, B.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Qu, L.; Yin, Y.; Wei, Y. Advancements in the Biotransformation and Biosynthesis of the Primary Active Flavonoids Derived from Epimedium. Molecules 2023, 28, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-F.; Li, Y.-P.; Ou, T.-M.; Huang, S.-L.; Gu, L.-Q.; Huang, M.; Huang, Z.-S. Synthesis and Antimultidrug Resistance Evaluation of Icariin and Its Derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4237–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wei, B.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Liang, H. Co-Immobilizing Two Glycosidases Based on Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates to Enhance Enzymatic Properties for Achieving High Titer Icaritin Biosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11631–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Tong, X.; Wu, T.; Pei, J.; Zhao, L. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Hyperthermophilic α-l-Rhamnosidase from Thermotoga petrophila and Its Application in Production of Icaritin from Epimedin C with a Thermostable β-Glucosidase. Process Biochem. 2020, 93, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, C.; Xu, J.; Pei, J.; Zhao, L. Immobilization of Thermostable β-Glucosidase and α-l-Rhamnosidase from Dictyoglomus Thermophilum DSM3960 and Their Cooperated Biotransformation of Total Flavonoids Extract from Epimedium into Icaritin. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 2950–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, R.; Peng, J.; Qu, D.; Huang, M.; Chen, Y. Enhanced Hydrolysis and Antitumor Efficacy of Epimedium Flavonoids Mediated by Immobilized Snailase on Silica. Process Biochem. 2019, 86, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yin, H.; Tam, J.P.; Yang, H.; Jia, X. Construction of a Novel Catalysis System for Clean and Efficient Preparation of Baohuoside I from Icariin Based on Biphase Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, J. Simultaneous Preparation and Comparison of the Osteogenic Effects of Epimedins A–C and Icariin from Epimedium Brevicornu. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.L.; Albuquerque, B.F.; Nunes, M.A.P.; Ribeiro, M.H.L. Exploring Magnetic and Imprinted Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Rhamnopyranosidase in Microbioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Smith, S.R. Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregate (CLEA) Preparation from Waste Activated Sludge. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, F. Preparation, Activity and Structure of Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (CLEAs) with Nanoparticle. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 107, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ji, D.; Deng, Y.; Agyei, D. Preparation and Assessment of Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (CLEAs) of β-Galactosidase from Lactobacillus Leichmannii 313. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 124, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaarani, S.M.; Jahim, J.M.; Rahman, R.A.; Idris, A.; Murad, A.M.A.; Illias, R.M. Silanized Maghemite for Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Recombinant Xylanase from Trichoderma Reesei. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 133, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, S.; Ghodake, V.; Ghotage, T.; Rathod, P.; Deshmukh, P.; Nadar, S.; Mulla, M.; Ladole, M. Novel Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (Magnetic CLEAs) of Alpha Amylase. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Porous Cross-Linked Aggregates of Tramates Versicolor MTCC 138 Laccase for the Efficient Removal of Pentachlorophenol from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, G.N.; dos Santos, C.C.; Pinto, G.C.; Piazza, R.D.; Guedes, W.N.; Jafelicci Júnior, M.; de Paula, A.V.; Marques, R.F.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregate and Its Evaluation of the Alternating Magnetic Field (AMF) Effects in the Catalytic Activity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 516, 167326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante Morales, L.K.; Sengar, P.; Dorado Baeza, A.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Chauhan, K. Enhanced Laccase Activity and Stability as Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates on Magnetic Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles for Biotechnological Processes. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202301071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhamid, M.B.; Hero, J.S.; Zamora, M.; Gómez, M.I.; Navarro, M.C.; Romero, C.M. Effect of the Biological Functionalization of Nanoparticles on Magnetic CLEA Preparation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, K.; Zhai, X.; Fang, B.; Liu, K.; Zulekha; Li, D. A Comparison of Dual-Enzyme Immobilization by Magnetic Nanoparticles and Magnetic Enzyme Aggregates for Cascade Enzyme Reactions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 204, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Apetrei, C. Tyrosinase Immobilization Strategies for the Development of Electrochemical Biosensors—A Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Pu, S.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Yang, C.; Naseer, S.; Li, D. Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Geniposide Directly Acts as Cross-Linking Agent for Enzyme Immobilization. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguerra, O.M.; Wahab, R.A.; Huyop, F.; Al-Fakih, A.M.; Mahmood, W.M.A.W.; Mahat, N.A.; Sabullah, M.K. An Overview of Crosslinked Enzyme Aggregates: Concept of Development and Trends of Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 5711–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R. CLEAs, Combi-CLEAs and ‘Smart’ Magnetic CLEAs: Biocatalysis in a Bio-Based Economy. Catalysts 2019, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Wahab, M.K.H.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Bakar, F.D.A.; Murad, A.M.A.; Jahim, J.M.; Illias, R.M. Improvement of Cross-Linking and Stability on Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregate (CLEA)-Xylanase by Protein Surface Engineering. Process Biochem. 2019, 86, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Glutaraldehyde in Bio-Catalysts Design: A Useful Crosslinker and a Versatile Tool in Enzyme Immobilization. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Q.; Wang, M.; Qi, W.; Su, R.; He, Z. Preparation of β-Mannanase CLEAs Using Macromolecular Cross-Linkers. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, D.; Kaira, G.S.; Kapoor, M. Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (CLEAs) and Magnetic Nanocomposite Grafted CLEAs of GH26 Endo-β-1,4-Mannanase: Improved Activity, Stability and Reusability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. Magnetic Macromolecular Cross Linked Enzyme Aggregates (CLEAs) of Glucoamylase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 83, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoevaart, R.; Wolbers, M.W.; Golubovic, M.; Ottens, M.; Kieboom, A.P.G.; van Rantwijk, F.; van der Wielen, L.A.M.; Sheldon, R.A. Preparation, Optimization, and Structures of Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (CLEAs). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, G.; Cao, L.; Ren, G.; Kong, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, G.; Liu, Y.-H. Characterization of the Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of a Novel β-Galactosidase, a Potential Catalyst for the Synthesis of Galacto-Oligosaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, A.G.; Tiwari, P.; Shaily, J.; Tiwari, S. Stabilizing Effect of Quercetin upon Bovine Serum Albumin as a Model Protein. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 252, 114663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazary, A.E.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.-H. Biochemical Studies on Native and Cross-Linked Aggregates of Aspergillus Awamori Feruloyl Esterase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatik, A.G.; Jain, A.K.; Muley, A.B. Preparation, Characterization and Stability of Cross Linked Nitrilase Aggregates (Nitrilase–CLEAs) for Hydroxylation of 2-Chloroisonicotinonitrile to 2-Chloroisonicotinic Acid. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1559–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.E.; Mary, P.R.; Haritha, K.V.; Panwar, D.; Kapoor, M. Soluble and Cross-Linked Aggregated Forms of α-Galactosidase from Vigna Mungo Immobilized on Magnetic Nanocomposites: Improved Stability and Reusability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, H.; Liang, H. Enhancing Stability and By-Product Tolerance of β-Glucuronidase Based on Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 210, 112241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifko, D.; Vasić, K.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. (Magnetic) Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Cellulase from T. Reesei: A Stable and Efficient Biocatalyst. Molecules 2023, 28, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Cui, G.; Abdulrazaq, M.A.; Yan, Y. Enhancing Enzyme Activity and Enantioselectivity of Burkholderia Cepacia Lipase via Immobilization on Melamine-Glutaraldehyde Dendrimer Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Cao, M.; Wen, H.; Tan, Z.; Jia, S.; Cui, J. Biodegradation of Polyvinyl Alcohol Using Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Degrading Enzymes from Bacillus Niacini. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in Aqueous Solution, Reaction with Proteins, and Application to Enzyme Crosslinking. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Li, X.; Lu, L. Preparation and Synthetic Dye Decolorization Ability of Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Laccase from Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, G.N.; dos Santos, C.C.; Pinto, G.C.; da Rocha, C.O.; Brandt, J.V.; de Paula, A.V.; Jafelicci Júnior, M.; Marques, R.F.C. Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates (MCLEAs) Applied to Biomass Conversion. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, S.; Joshi, A.; Kambale, S.; Jadhav, S.; Nadar, S.; Ladole, M. A Tri-Enzyme Magnetic Nanobiocatalyst with One Pot Starch Hydrolytic Activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. Combined Effect of Enzyme Co-Immobilized Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) and Ultrasound for Effective Extraction and Purification of Curcuminoids from Curcuma Longa. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Badhe, P.S.; Adivarekar, R.; Ladole, M.R.; Pandit, A.B. Synthesis of Glycinamides Using Protease Immobilized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 12, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Rakshit, K.; Rathee, S.; Angmo, S.; Kaushal, S.; Garg, P.; Chung, J.H.; Sandhir, R.; Sangwan, R.S.; Singhal, N. Metallic/Bimetallic Magnetic Nanoparticle Functionalization for Immobilization of α-Amylase for Enhanced Reusability in Bio-Catalytic Processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.E.; Fellows, B.; Mefford, O.T. Best Practices for Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14159–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-F.; Lu, B.-Y.; Lin, M.-G.; Wang, T.-F.; Lin, L.-L. Magnetic Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates of a Transpeptidase-Specialized Variant (N450D) of Bacillus Licheniformis γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase: An Efficient and Stable Biocatalyst for l-Theanine Synthesis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X. Laccase Immobilized on Chitosan-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Reusable Biocatalyst for Degradation of Chlorophenol. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1220, 128769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, U.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Wojcieszyńska, D. Immobilization as a Strategy for Improving Enzyme Properties-Application to Oxidoreductases. Molecules 2014, 19, 8995–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawawi, N.N.; Hashim, Z.; Manas, N.H.A.; Azelee, N.I.W.; Illias, R.M. A Porous-Cross Linked Enzyme Aggregates of Maltogenic Amylase from Bacillus Lehensis G1: Robust Biocatalyst with Improved Stability and Substrate Diffusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Hadi Razavi, S. Green Construction of Recyclable Amino-Tannic Acid Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles: Application for β-Glucosidase Immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Ryan, M.P.; Walsh, G. Purification and Characterization of a Novel β-Galactosidase From the Thermoacidophile Alicyclobacillus Vulcanalis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 1190–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Pi, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Song, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles-Based Lactate Dehydrogenase Microreactor as a Drug Discovery Tool for Rapid Screening Inhibitors from Natural Products. Talanta 2020, 209, 120554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgın, S.; Salgın, U. Bioconjugation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates: Characterization and Comparison of CLEAs and Magnetic CLEAs. Curr. Nanosci. 2017, 13, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Wu, B.; Huai, B.; Zhuang, Z.; Sun, C.; Xu, L.; Jin, F. Icaritin Preparation from Icariin by a Special Epimedium Flavonoid-Glycosidase from Aspergillus Sp.Y848 Strain. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Complete Biosynthesis of the Potential Medicine Icaritin by Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liang, H. Thermostable Enzyme-Immobilized Magnetic Responsive Ni-Based Metal–Organic Framework Nanorods as Recyclable Biocatalysts for Efficient Biosynthesis of S-Adenosylmethionine. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).