Immobilization and Kinetic Properties of ß-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium oxalicum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Kinetic Properties of Hex
2.2. Kinetic and Mass Transfer Effects in Particles with Immobilized Enzyme
2.3. Inhibition Study of Hex
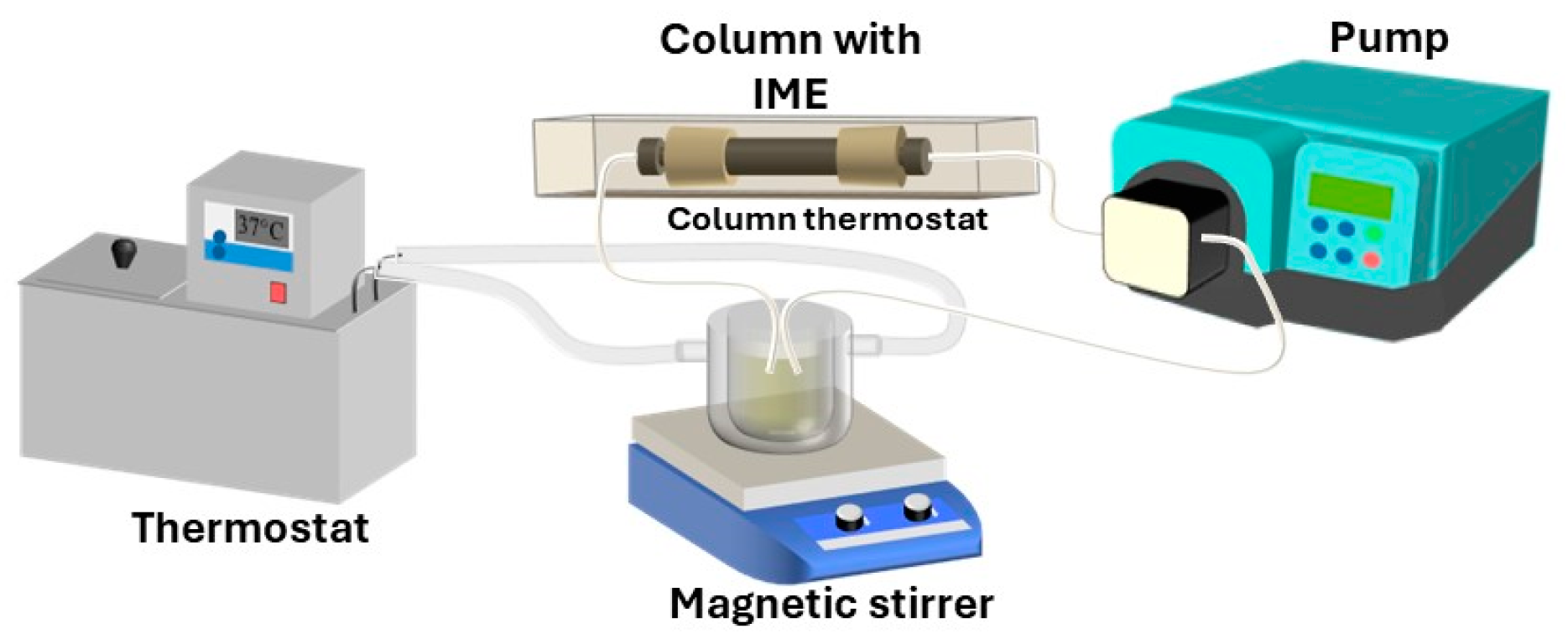
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Hex
3.3. Immobilization of Hex
3.4. Activity Assay and Kinetics of Soluble Hex
3.5. Activity Assay and Kinetics of Immobilized Hex
3.5.1. Measurement of Kinetics in a Batch System
3.5.2. Inhibition Studies in a Continuous Flow System
3.5.3. Crushed Particles of Immobilized Hex
3.6. Mathematical Modeling
3.6.1. Kinetics of Hex
3.6.2. Kinetic Modeling of Reaction with Immobilized Hex
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.R. Immobilized Enzymes: A Comprehensive Review. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo-Young, M. Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 9780080885049. [Google Scholar]
- Konopka, J.B. N-Acetylglucosamine Functions in Cell Signaling. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 489208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmölzer, K.; Weingarten, M.; Baldenius, K.; Nidetzky, B. Correction: Lacto-N-Tetraose Synthesis by Wild-Type and Glycosynthase Variants of the β-N-Hexosaminidase from Bifidobacterium Bifidum. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, S.; Li, T.; Jiang, Z. Production of Lacto-N-Triose II and Lacto-N-Neotetraose from Chitin by a Novel β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase Expressed in Pichia Pastoris. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 15466–15474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, S. Directed Evolution of a β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Haloferula sp. for Lacto-N-Triose II and Lacto-N-Neotetraose Synthesis from Chitin. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2023, 164, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarová, P.; Kulik, N.; Slámová, K.; Hubálek, M.; Kotik, M.; Cvačka, J.; Pelantová, H.; Křen, V. Selective β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Aspergillus Versicolor—A Tool for Producing Bioactive Carbohydrates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Laborda, P.; Lu, A.M.; Wang, M.; Duan, X.C.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. Chemo-Enzymatic Approach to Access Diastereopure α-Substituted GlcNAc Derivatives. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2016, 35, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.N., II; William, H.; Baricos, Y.-T.L.; Chambers, R.P.; Cohen4, W. Characterization of Immobilized β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase. Anal. Lett. 1977, 10, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.-K.; Owen, A.J.; Dain, J.A. Effect of Immobilization on Stability and Properties of N-Acetyl-β-d-Hexosaminidase from Turbo Cornutus. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 75, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Uchiyama, T.; Matahira, Y.; Nanjo, F. Immobilization of Chitinolytic Enzymes and Continuous Production of N-Acetylglucosamine with the Immobilized Enzymes. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1991, 72, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzic, L.; Bolivar, J.M.; Nidetzky, B. Glycosynthase Reaction Meets the Flow: Continuous Synthesis of Lacto-N-Triose II by Engineered β-Hexosaminidase Immobilized on Solid Support. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hronská, H.; Štefuca, V.; Ondrejková, E.; Bláhová, M.; Višňovský, J.; Rosenberg, M. Chemo-Enzymatic Production of 4-Nitrophenyl-2-Acetamido-2-Deoxy-α-D-Galactopyranoside Using Immobilized β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase. Catalysts 2022, 12, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryšlavá, H.; Kalendová, A.; Doubnerová, V.; Skočdopol, P.; Kumar, V.; Kukačka, Z.; Pompach, P.; Vaněk, O.; Slámová, K.; Bojarová, P.; et al. Enzymatic Characterization and Molecular Modeling of an Evolutionarily Interesting Fungal β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.G.; Thomas, P.; Westwood, J.H. The Purification and Properties of a Beta-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Trichomonas Foetus. Biochem. J. 1975, 151, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Lee, K.M.; Kumagai, H.; Tochdcura, T. Purification and Characterization of β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium Oxalicum. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C.; Li, Y.-T. Studies on the Glycosidases of Jack Bean Meal. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 5153–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Copa-Patino, J.L.; Reyes, F.; Pérez-Leblic, M.I. A Β-N-acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium Oxalicum Implicated in Its Cell-wall Degradation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 19, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škerlová, J.; Bláha, J.; Pachl, P.; Hofbauerová, K.; Kukačka, Z.; Man, P.; Pompach, P.; Novák, P.; Otwinowski, Z.; Brynda, J.; et al. Crystal Structure of Native β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase Isolated from Aspergillus Oryzae Sheds Light onto Its Substrate Specificity, High Stability, and Regulation by Propeptide. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 580–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Miller, L.; Gao, W.; Gross, R.A. Imaging the Distribution and Secondary Structure of Immobilized Enzymes Using Infrared Microspectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefuca, V.; Gemeiner, P. Investigation of Catalytic Properties of Immobilized Enzymes and Cells by Flow Microcalorimetry. In Thermal Biosensors, Bioactivity, Bioaffinitty; Bhatia, P.K., Danielsson, B., Gemeiner, P., Grabley, S., Lammers, F., Mukhopadhyay, A., Ramanathan, K., Saleemuddin, M., Scheper, T., Stefuca, V., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 69–99. ISBN 978-3-540-49811-7. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, D.A.; Caon, N.B.; Alberton, M.D.; Vitali, L.; Parize, A.L.; Micke, G.A. Immobilized Acetylcholinesterase in Magnetic Nanoparticles for In-Line Inhibition Studies Using a Capillary Electrophoresis System. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1275, 341566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdeira Ferreira, L.M.; da Costa, E.T.; do Lago, C.L.; Angnes, L. Miniaturized Flow System Based on Enzyme Modified PMMA Microreactor for Amperometric Determination of Glucose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajić, M.; Plazl, I.; Stloukal, R.; Žnidaršič-Plazl, P. Development of a Miniaturized Packed Bed Reactor with ω-Transaminase Immobilized in LentiKats®. Process Biochem. 2017, 52, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, P.C.O.; Lessa, R.C.; Ceroullo, M.S.; Wegermann, C.A.; De Moraes, M.C. On-Flow Enzymatic Inhibitor Screening: The Emerging Success of Liquid Chromatography-Based Assays. Front. Anal. Sci. 2022, 2, 1004113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekrathok, P.; Stubbs, K.A.; Aunkham, A.; Kaewmaneewat, A.; Kardkuntod, A.; Bulmer, D.M.; van den Berg, B.; Suginta, W. NAG-Thiazoline Is a Potent Inhibitor of the Vibrio Campbellii GH20 β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4982–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, K.A.; Zhang, N.; Vocadlo, D.J. A Divergent Synthesis of 2-Acyl Derivatives of PUGNAc Yields Selective Inhibitors of O-GlcNAcase. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, G.E.; Macauley, M.S.; Stubbs, K.A.; Dennis, R.J.; Taylor, E.J.; Davies, G.J.; Greig, I.R.; Vocadlo, D.J. Analysis of PUGNAc and NAG-Thiazoline as Transition State Analogues for Human O-GlcNAcase: Mechanistic and Structural Insights into Inhibitor Selectivity and Transition State Poise. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Vocadlo, D.; Gao, Z.; Kirk, B.; Lou, J.; Withers, S.G. NAG-Thiazoline, An N-Acetyl-β-Hexosaminidase Inhibitor That Implicates Acetamido Participation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6804–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plíhal, O.; Sklenář, J.; Hofbauerová, K.; Novák, P.; Man, P.; Pompach, P.; Kavan, D.; Ryšlavá, H.; Weignerová, L.; Charvátová-Pišvejcová, A.; et al. Large Propeptides of Fungal β-N-Acetylhexosaminidases Are Novel Enzyme Regulators That Must Be Intracellularly Processed to Control Activity, Dimerization, and Secretion into the Extracellular Environment. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 2719–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huňková, Z.; Křen, V.; Ščigelová, M.; Weignerová, L.; Scheel, O.; Thiem, J. Induction of β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase in Aspergillus Oryzae. Biotechnol. Lett. 1996, 18, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slámová, K.; Bojarová, P.; Gerstorferová, D.; Fliedrová, B.; Hofmeisterová, J.; Fiala, M.; Pompach, P.; Křen, V. Sequencing, Cloning and High-Yield Expression of a Fungal β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase in Pichia Pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyahia, F.; O’Neill, K.E. Enhanced Voidage Correlations for Packed Beds of Various Particle Shapes and Sizes. Part. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Gnanasekaran, P.; Allgeier, A.M.; Weatherley, L.R. Study and Deployment of Methacrylate-Based Polymer Resins for Immobilized Lipase Catalyzed Triglyceride Hydrolysis. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.R.; Chang, P. Correlation of Diffusion Coefficients in Dilute Solutions. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
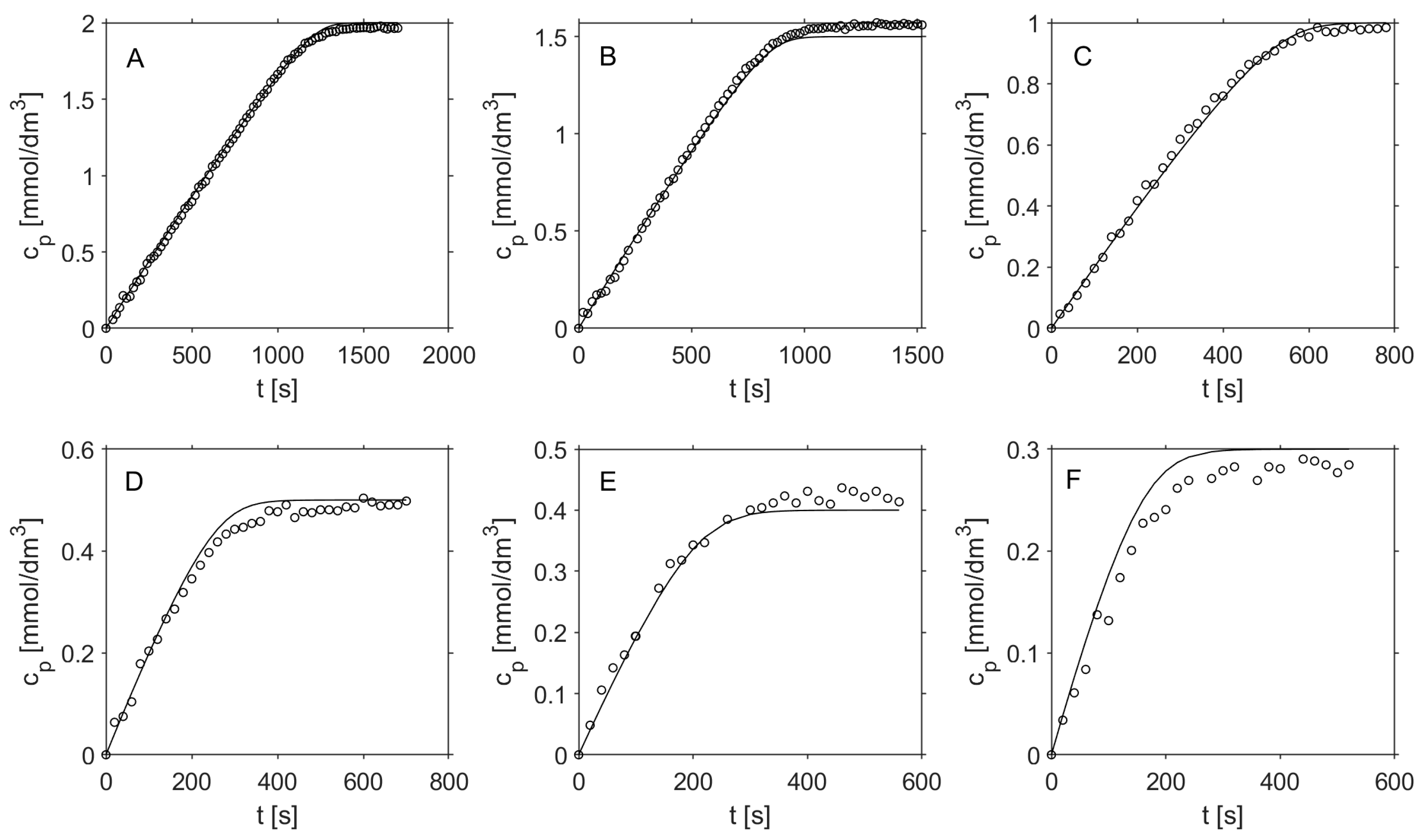

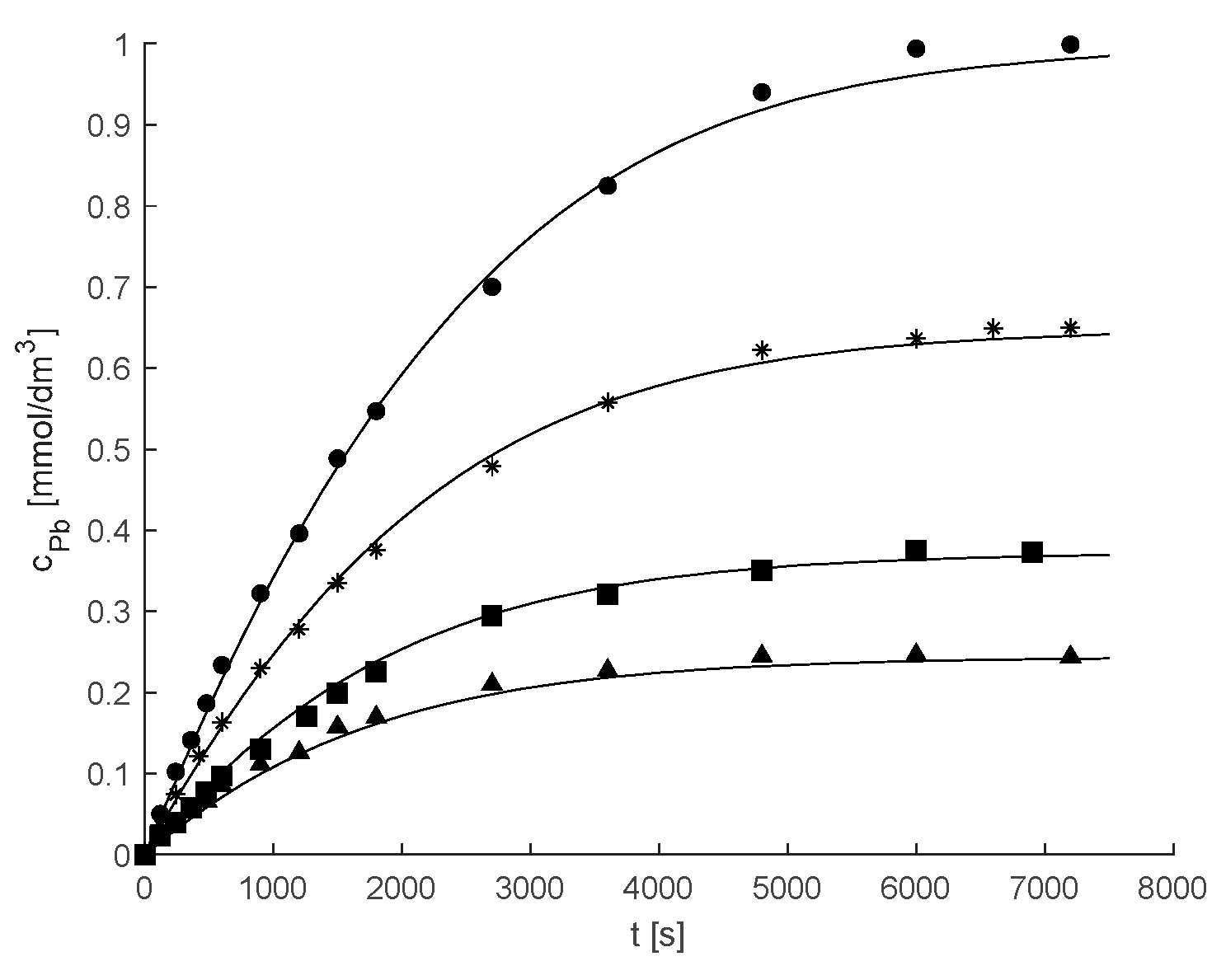

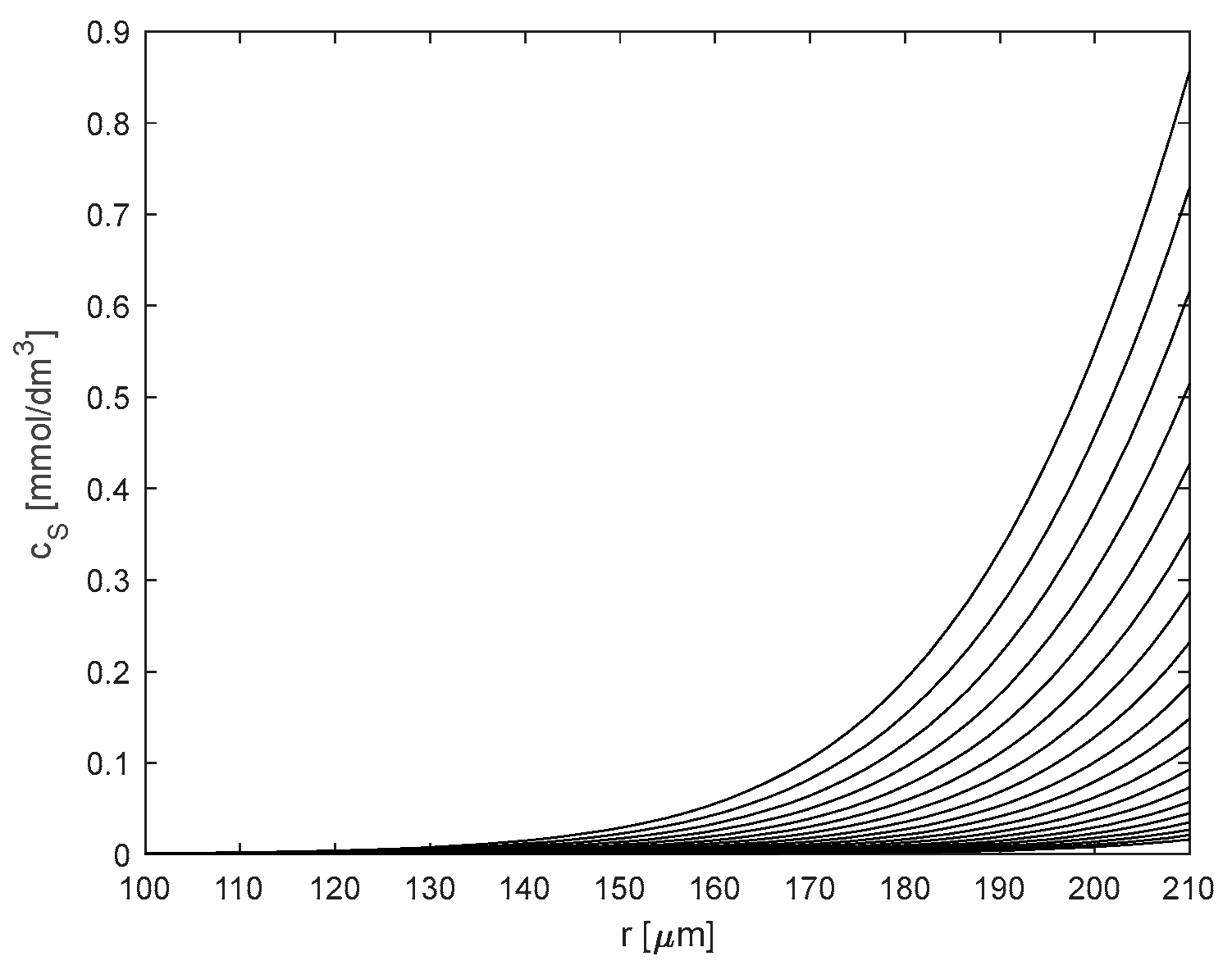
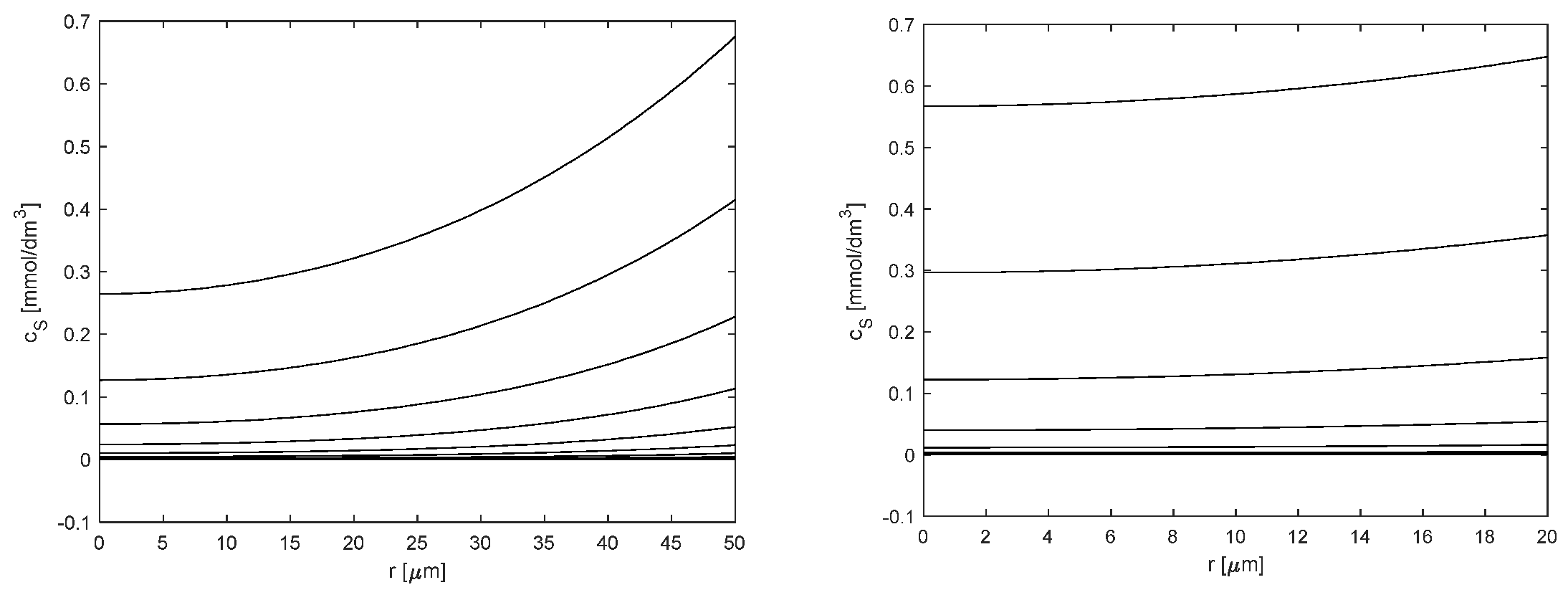

| Model | Vmax (×10−3 mM/s) | Km (mM) | Kis (mM) | Kip (mM) | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M–M | 1.7452 ± 0.0002 | 0.0560 ± 0.0001 | - | - | 1.395 |
| M–M with substrate inhibition | 4.1187 ± 0.0024 | 0.4876 ± 0.0008 | 1.2157 ± 0.0021 | - | 0.454 |
| M–M with uncompetitive substrate and non-competitive product inhibition | 4.1441 ± 0.0024 | 0.4105 ± 0.0024 | 6.8619 ± 0.0060 | 1.3611 ± 0.0014 | 0.175 |
| M–M with uncompetitive substrate and competitive product inhibition | 3.7795 ± 0.0026 | 0.3263 ± 0.0005 | 2.5736 ± 0.0042 | 1.4210 ± 0.0018 | 0.248 |
| Model | Vmax (mM/s) | Km (mM) | Kis (mM) | Kip (mM) | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M–M | (7.431 ± 0.016) × 10−3 | 0.5249 ± 0.0031 | - | - | 0.0158 |
| M–M with substrate inhibition | (1.452 ± 0.023) × 10−3 | 1.362 ± 0.027 | 2.018 ± 0.063 | - | 0.0087 |
| M–M with uncompetitive substrate and non-competitive product inhibition | (1.448 ± 0.022) × 10−3 | 1.326 ± 0.025 | 31.4 ± 1.7 | 2.074 ± 0.062 | 0.0081 |
| M–M with uncompetitive substrate and competitive product inhibition | (1.425± 0.022) × 10−3 | 1.300 ± 0.026 | 23.9 ± 1.7 | 2.090 ± 0.064 | 0.0083 |
| Enzyme Preparation | Mathematical Model Used | Km (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| Free enzyme | M–M | 0.4105 ± 0.0004 |
| Immobilized Hex–crushed particles | M–M | 0.5249 ± 0.0031 |
| Immobilized Hex–intact particles | M–M | 1.168 ± 0.014 |
| Immobilized Hex–intact particles | Mass transfer + M–M | 0.3493 ± 2.5 × 10−7 |
| Model | Vmax (mM/s) | Km (mM) | Kis (µM) | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUGNAc competitive | 0.68 | 6.15 | 0.91 | 7.032 |
| PUGNAc non-competitive | 0.78 | 7.31 | 1.13 | 7.129 |
| NAG-thiazoline competitive | 0.32 | 2.47 | 189 | 2.628 |
| NAG-thiazoline non-competitive | 0.35 | 2.80 | 298 | 2.534 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štefuca, V.; Bláhová, M.; Hronská, H.; Rosenberg, M. Immobilization and Kinetic Properties of ß-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium oxalicum. Catalysts 2024, 14, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100725
Štefuca V, Bláhová M, Hronská H, Rosenberg M. Immobilization and Kinetic Properties of ß-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium oxalicum. Catalysts. 2024; 14(10):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100725
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtefuca, Vladimír, Mária Bláhová, Helena Hronská, and Michal Rosenberg. 2024. "Immobilization and Kinetic Properties of ß-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium oxalicum" Catalysts 14, no. 10: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100725
APA StyleŠtefuca, V., Bláhová, M., Hronská, H., & Rosenberg, M. (2024). Immobilization and Kinetic Properties of ß-N-Acetylhexosaminidase from Penicillium oxalicum. Catalysts, 14(10), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14100725







