Understanding the Role of Electrolyte Cations on Activity and Product Selectivity of CO2 Reduction over Cu Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
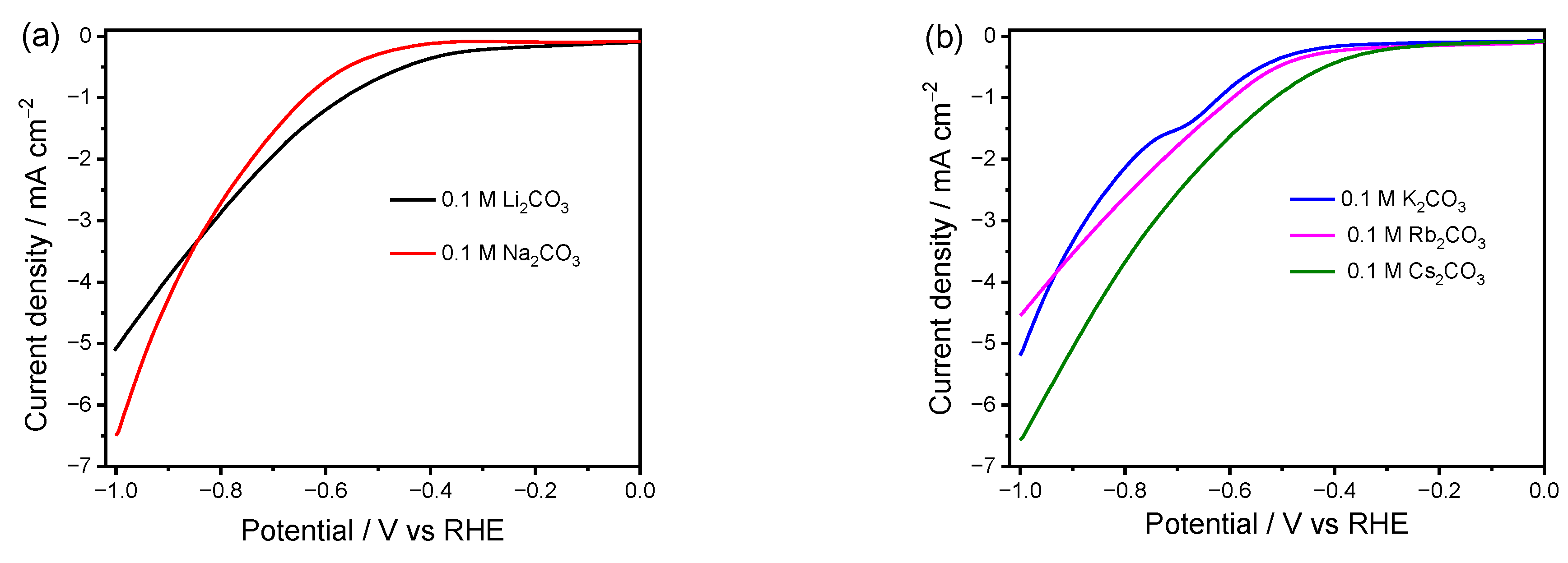
2.1. Linear Scan Voltammetry
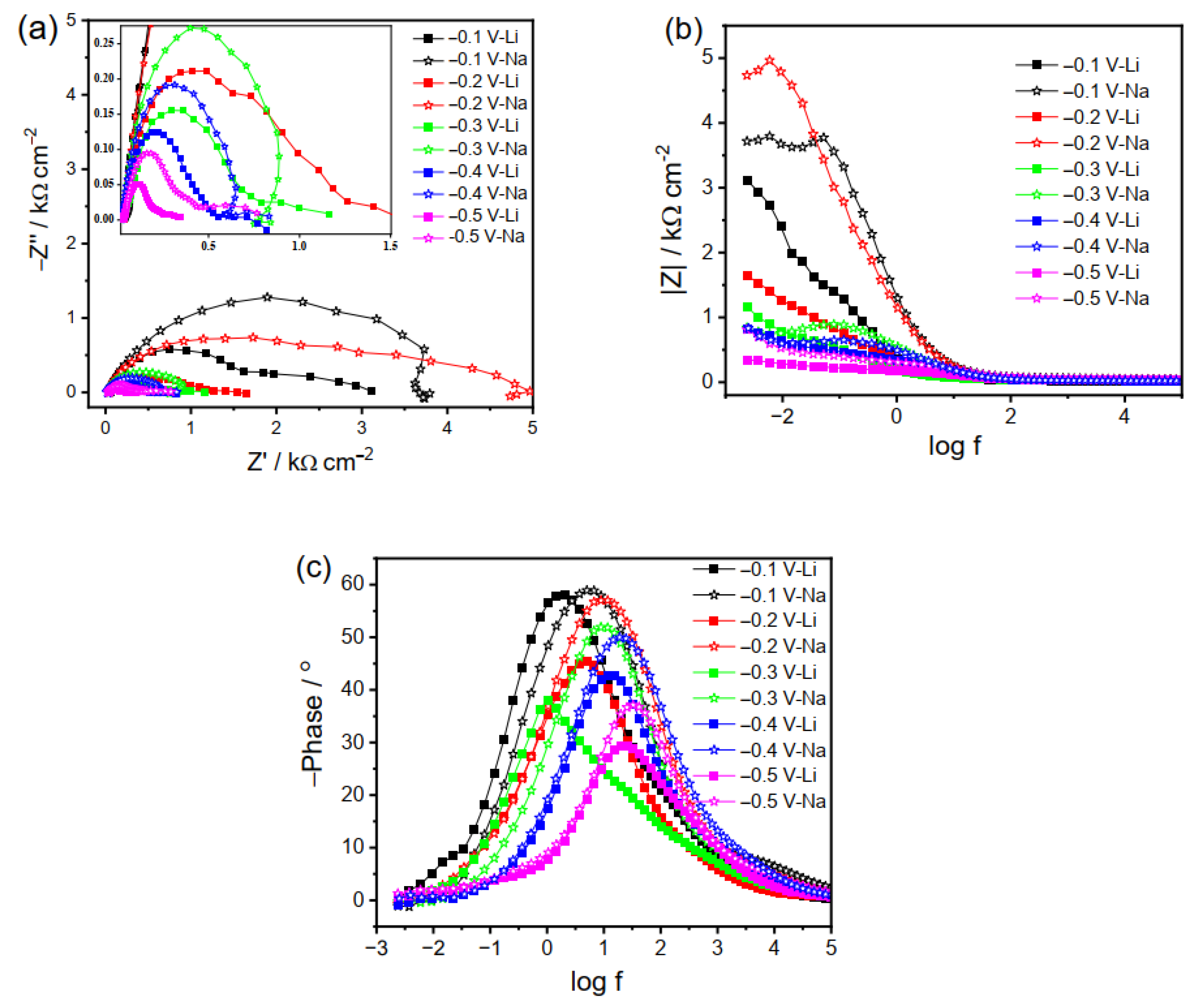
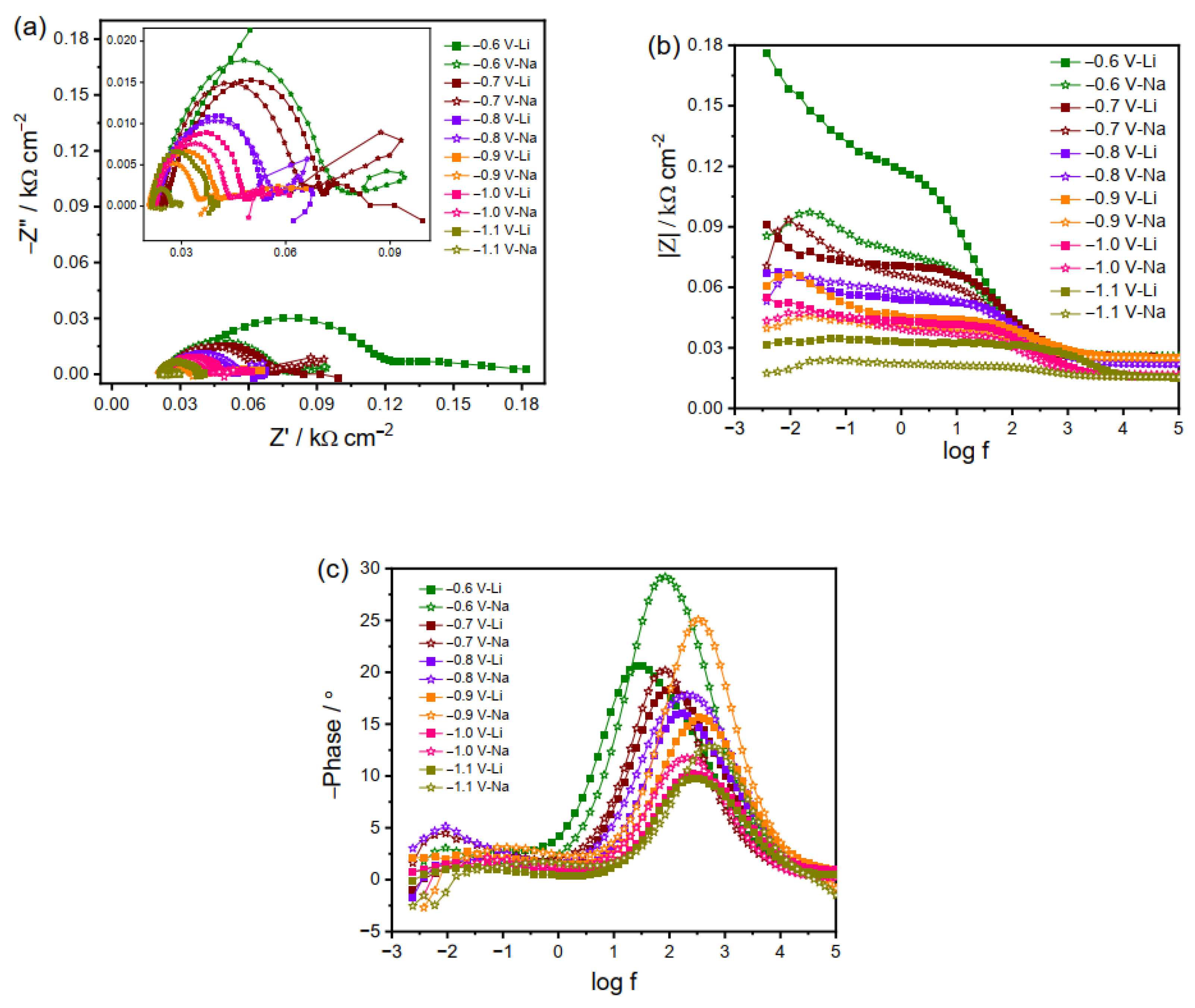
2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
2.2.1. EIS Plots of Cu Electrode in Li2CO3 and Na2CO3 Electrolyte
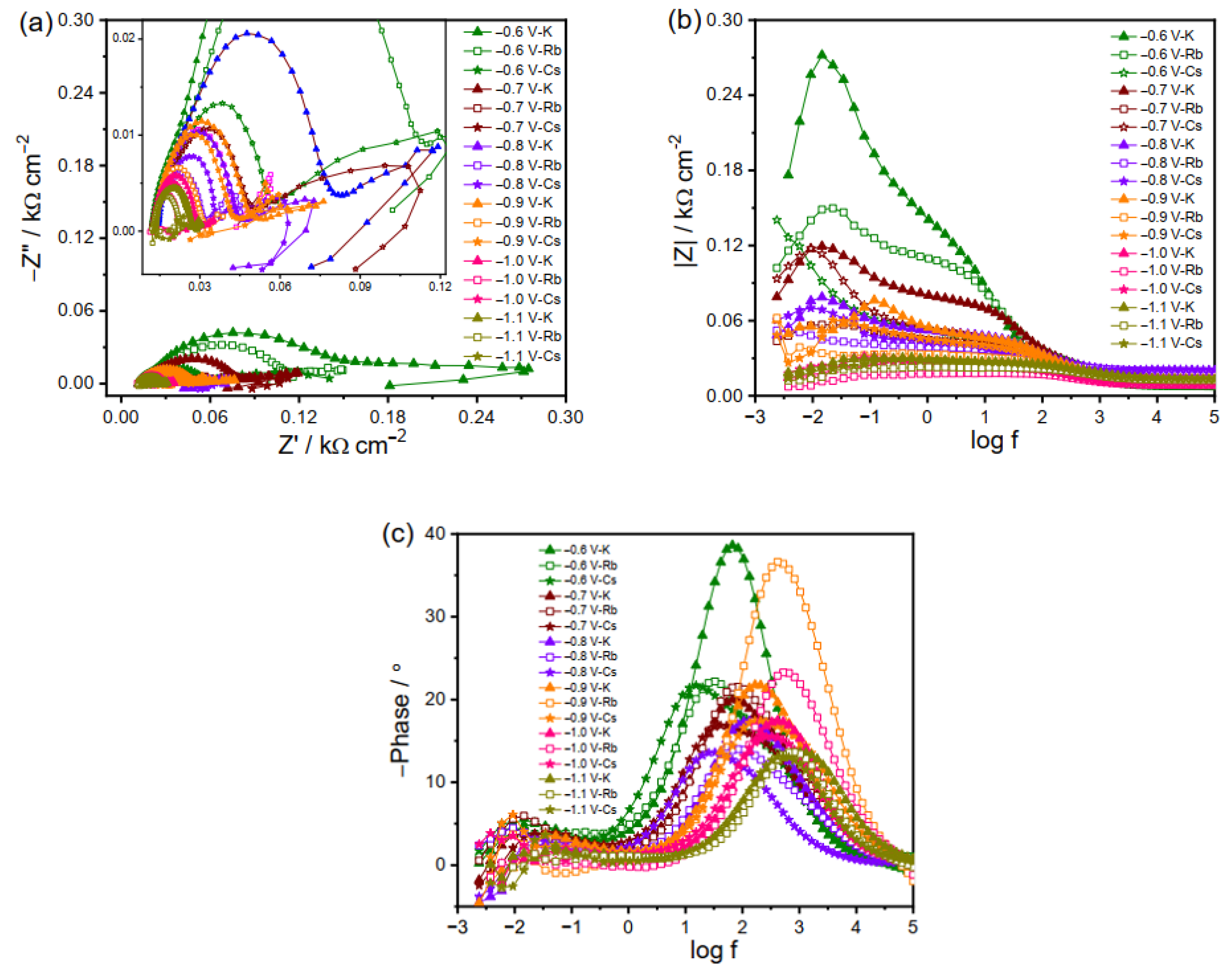
2.2.2. EIS Plots of Cu Electrode in K2CO3, Rb2CO3 and Cs2CO3 Electrolyte
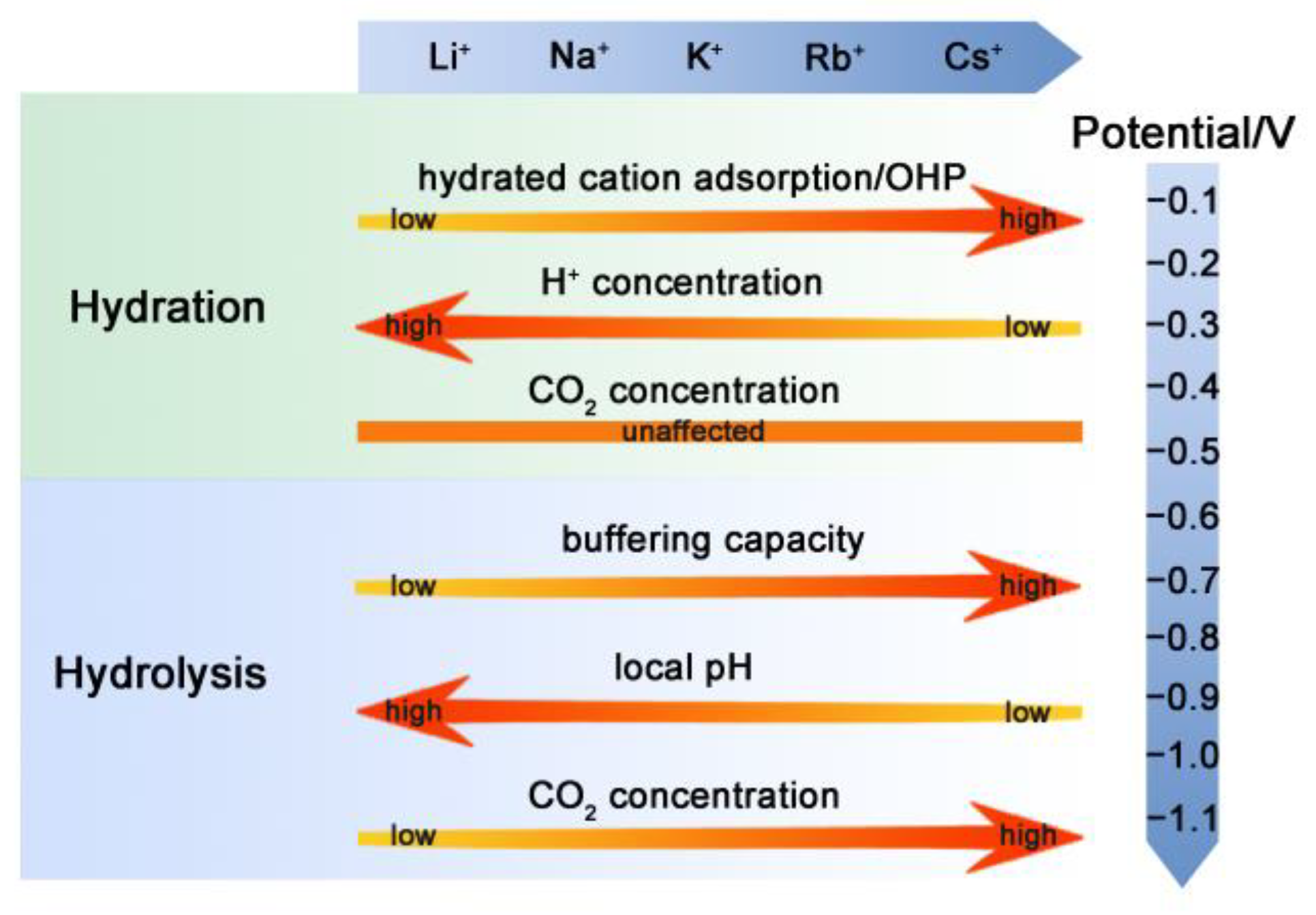
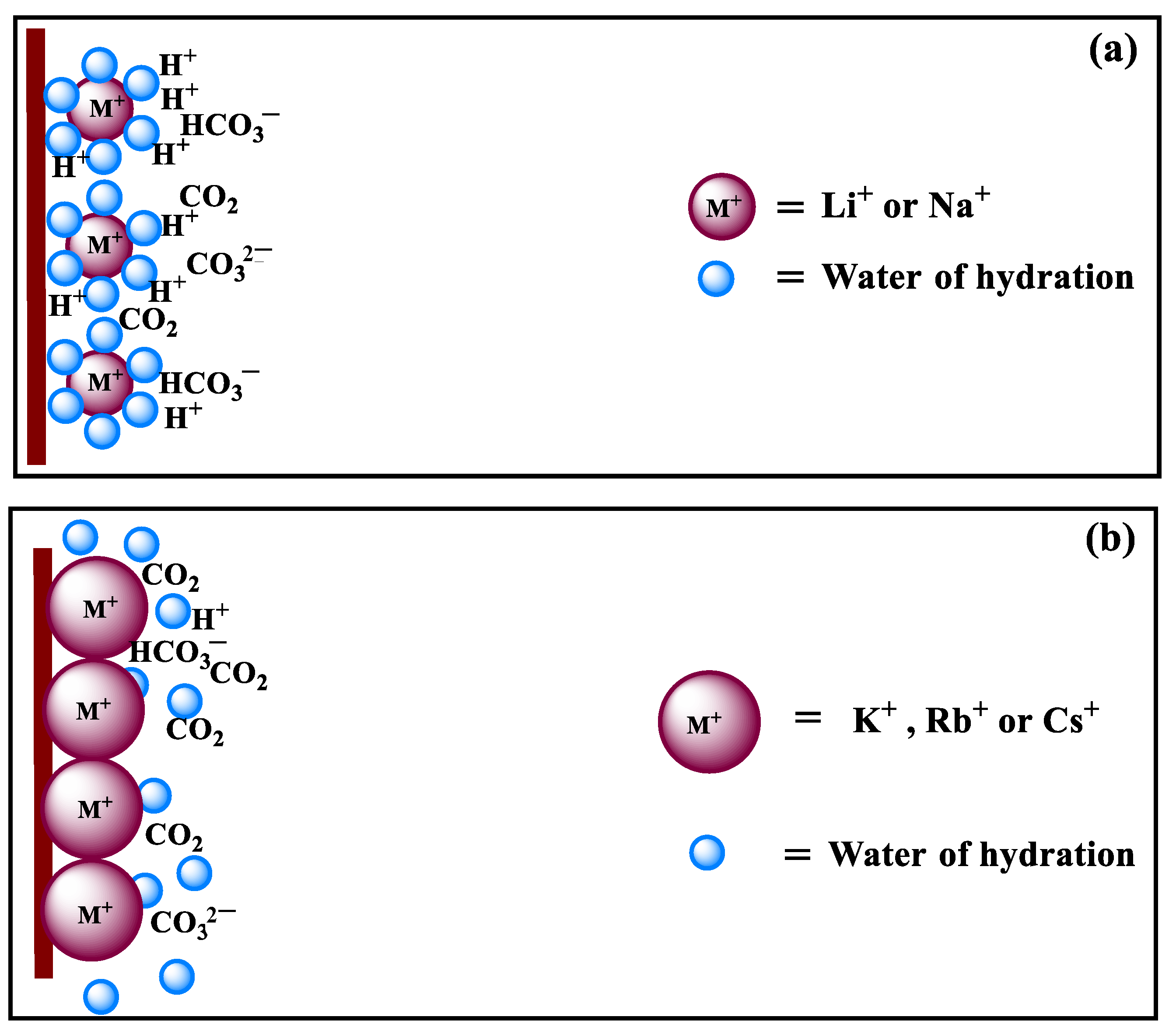
2.3. Mechanism Analysis of Cations Effect on CO2RR
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Electrode and Electrolyte Preparation
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, N.S.; Nocera, D.G. Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15729–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resasco, J.; Chen, L.D.; Clark, E.; Tsai, C.; Hahn, C.; Jaramillo, T.F.; Chan, K.; Bell, A.T. Promoter effects of alkali metal cations on the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11277–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, T.; Jung, K.Y.; Park, K.T. Recent progress in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to pure formic acid using a solid-state electrolyte device. Catalysts 2023, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, K.P.; Hatsukade, T.; Cave, E.R.; Abram, D.N.; Kibsgaard, J.; Jaramillo, T.F. Electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to methane and methanol on transition metal surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14107–14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, Y.; Wakebe, H.; Tsukamoto, T.; Koga, O. Electrocatalytic process of CO selectivity in electrochemical reduction of CO2 at metal electrodes in aqueous media. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarandi, R.F.; Rezaei, B.; Ghaziaskar, H.S.; Ensafi, A.A. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to ethanol using copper nanofoam electrode and 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium bromide as the homogeneous co-catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, K.P.; Cave, E.R.; Abram, D.N.; Jaramillo, T.F. New insights into the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide on metallic copper surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7050–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Y.J.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Na, J.; Lee, U.; Hwang, Y.J. Catalyst-electrolyte interface chemistry for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6632–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.; Hatsukade, T.; Kim, Y.G.; Vailionis, A.; Baricuatro, J.H.; Higgins, D.C.; Nitopi, S.A.; Soriaga, M.P.; Jaramillo, T.F. Engineering Cu surfaces for the electrocatalytic conversion of CO2: Controlling selectivity toward oxygenates and hydrocarbons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5918–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, K.; Fan, S.; Kanan, M.W. A direct grain-boundary-activity Correlation for CO electroreduction on Cu nanoparticles. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raciti, D.; Livi, K.J.; Wang, C. Highly dense Cu nanowires for low-overpotential CO2 reduction. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Raciti, D.; Li, C.; Livi, K.J.T.; Rottmann, P.F.; Hemker, K.J.; Mueller, T.; Wang, C. Mechanistic insights for low-overpotential electroreduction of CO2 to CO on copper nanowires. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8578–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, K.; Zhang, H.; He, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Chen, J.G.; Cheng, M.-J.; Lu, Q. Effectively increased efficiency for electroreduction of carbon monoxide using supported polycrystalline copper powder electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Takahashi, I.; Koga, O.; Hoshi, N. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide at various series of copper single crystal electrodes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 199, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Takahashi, I.; Koga, O.; Hoshi, N. Selective formation of C2 compounds from electrochemical reduction of CO2 at a series of copper single crystal electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 106, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gallent, E.; Marcandalli, G.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Koper, M.T.M. Structure- and potential-dependent cation effects on CO reduction at copper single-crystal electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16412–16419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, T.; Gauthier, J.A.; Dickens, C.F.; Brown, K.S.; Ringe, S.; Chan, K.; Nørskov, J.K. Atomistic insight into cation effects on binding energies in Cu-catalyzed carbon dioxide reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 24765–24775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Hori, Y. Product selectivity affected by cationic species in electrochemical reduction of CO2 and CO at a Cu electrode. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 64, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.R.; Kwon, Y.; Lum, Y.; Ager, J.W., 3rd; Bell, A.T. Hydrolysis of electrolyte cations enhances the electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Ag and Cu. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13006–13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, W.; Andersen, T.N.; Eyring, H. Kinetic studies of the electrolytic reduction of carbon dioxide on the mercury electrode. Electrochim. Acta 1969, 14, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumkin, A.N. Influence of cation adsorption on the kinetics of electrode processes. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1959, 55, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, M.R.; Siil, K.I.; Kenis, P.J.A. Effect of cations on the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 160, F69–F74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneco, S.; Iiba, K.; Katsumata, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ohta, K. Effect of sodium cation on the electrochemical reduction of CO2 at a copper electrode in methanol. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2006, 11, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringe, S.; Clark, E.L.; Resasco, J.; Walton, A.; Seger, B.; Bell, A.T.; Chan, K. Understanding cation effects in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3001–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Risalvato, F.G.; Ke, F.-S.; Pellechia, P.J.; Zhou, X.-D. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide I. effects of the electrolyte on the selectivity and activity with Sn electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, F353–F359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; McCrum, I.T.; Deo, S.; Choi, Y.-W.; Scholten, F.; Wan, W.; Chen, J.G.; Janik, M.J.; Roldan Cuenya, B. Activity and selectivity control in CO2 electroreduction to multicarbon products over CuOx catalysts via electrolyte design. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10012–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Zheng, F.; Gao, G.; Ye, M.; Dong, C.; Du, X.-W.; Wang, L.-W. Distribution of alkali cations near the Cu (111) surface in aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24428–24437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayemoba, O.; Cuesta, A. Spectroscopic evidence of size-dependent buffering of interfacial pH by cation hydrolysis during CO2 electroreduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27377–27382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Co, A.C. Direct evidence of local pH change and the role of alkali cation during CO2 electroreduction in aqueous media. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, P.E.; Jothi, V.R.; Pitchaimuthu, S.; Yi, S.; Anantharaj, S. Alternating current techniques for a better understanding of photoelectrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12763–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a tool to investigate the electroreduction of carbon dioxide: A short review. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köleli, F.; Röpke, T.; Hamann, C.H. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic investigation of CO2 reduction on polyaniline in methanol. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-w.; Li, Q.-y.; Shen, F.-x.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Song, N.; Dai, Y.-n.; Shi, J. Electrochemical impedance studies of CO2 reduction in ionic liquid/organic solvent electrolyte on Au electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienen, F.; Kopljar, D.; Löwe, A.; Geiger, S.; Wagner, N.; Klemm, E.; Friedrich, K.A. Revealing mechanistic processes in gas-diffusion electrodes during CO2 reduction via impedance spectroscopy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13759–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.; Orlandi, M.; Berardi, S.; Mazzi, A.; Bazzanella, N.; Caramori, S.; Boaretto, R.; Natali, M.; Fernandes, R.; Patel, N.; et al. Functionalized p-silicon photocathodes for solar fuels applications: Insights from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienen, F.; Kopljar, D.; Geiger, S.; Wagner, N.; Friedrich, K.A. Investigation of CO2 electrolysis on tin foil by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5192–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcandalli, G.; Goyal, A.; Koper, M.T.M. Electrolyte effects on the faradaic efficiency of CO2 reduction to CO on a gold electrode. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4936–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.A.; Ozel, T.; Elias, J.S.; Costentin, C.; Nocera, D.G. Interplay of homogeneous reactions, mass transport, and kinetics in determining selectivity of the reduction of CO2 on gold electrodes. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.F.C.; Harrington, D.A.; Marshall, A.T. Effects of mass transfer on the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction on Cu. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 238, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Koper, M.T.M. The interrelated effect of cations and electrolyte pH on the hydrogen evolution reaction on gold electrodes in alkaline media. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 13452–13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Gattrell, M.; MacDougall, B. Calculation for the cathode surface concentrations in the electrochemical reduction of CO2 in KHCO3 solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 36, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.R.; Clark, E.L.; Bell, A.T. Effects of electrolyte, catalyst, and membrane composition and operating conditions on the performance of solar-driven electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 18924–18936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kas, R.; Kortlever, R.; Yılmaz, H.; Koper, M.T.M.; Mul, G. Manipulating the hydrocarbon selectivity of copper nanoparticles in CO2 electroreduction by process conditions. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, D.; Chaudhry, J.H.; Burdyny, T.; Pidko, E.A.; Smith, W.A. Modeling the electrical double layer to understand the reaction environment in a CO2 electrocatalytic system. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3380–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Murata, A.; Takahashi, R. Formation of hydrocarbons in the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide at a copper electrode in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1989, 85, 2309–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwell, M.; Yang, X.; Setzler, B.P.; Anibal, J.; Yan, Y.; Xu, B. Examination of near-electrode concentration gradients and kinetic impacts on the electrochemical reduction of CO2 using surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3999–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Promotional role of a cation intermediate complex in C2 formation from electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Cu. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12336–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.C.O.; Dattila, F.; Hagedoorn, B.; García-Muelas, R.; López, N.; Koper, M.T.M. Absence of CO2 electroreduction on copper, gold and silver electrodes without metal cations in solution. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, A.H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Woldu, A.R.; He, T. Understanding the Role of Electrolyte Cations on Activity and Product Selectivity of CO2 Reduction over Cu Electrode. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071092
Shah AH, Gong Y, Wang Y, Woldu AR, He T. Understanding the Role of Electrolyte Cations on Activity and Product Selectivity of CO2 Reduction over Cu Electrode. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071092
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Aamir Hassan, Yue Gong, Yanjie Wang, Abebe Reda Woldu, and Tao He. 2023. "Understanding the Role of Electrolyte Cations on Activity and Product Selectivity of CO2 Reduction over Cu Electrode" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071092
APA StyleShah, A. H., Gong, Y., Wang, Y., Woldu, A. R., & He, T. (2023). Understanding the Role of Electrolyte Cations on Activity and Product Selectivity of CO2 Reduction over Cu Electrode. Catalysts, 13(7), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071092