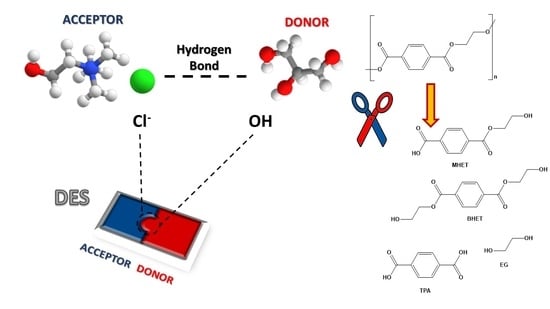
Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs)
3. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Solvents and Catalyst in PET Depolymerization
3.1. PET Degradation with Lewis Acids Containing DESs
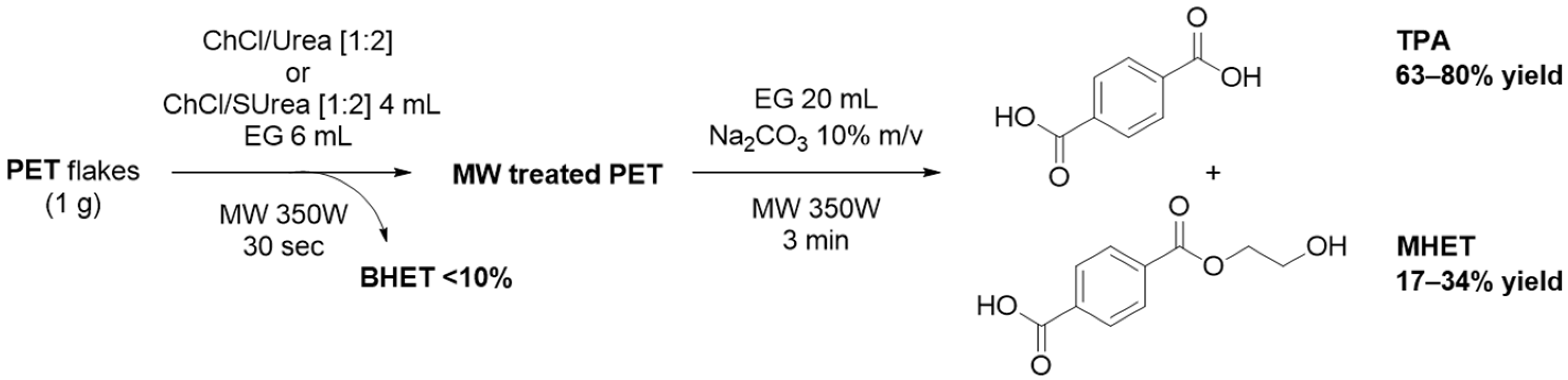
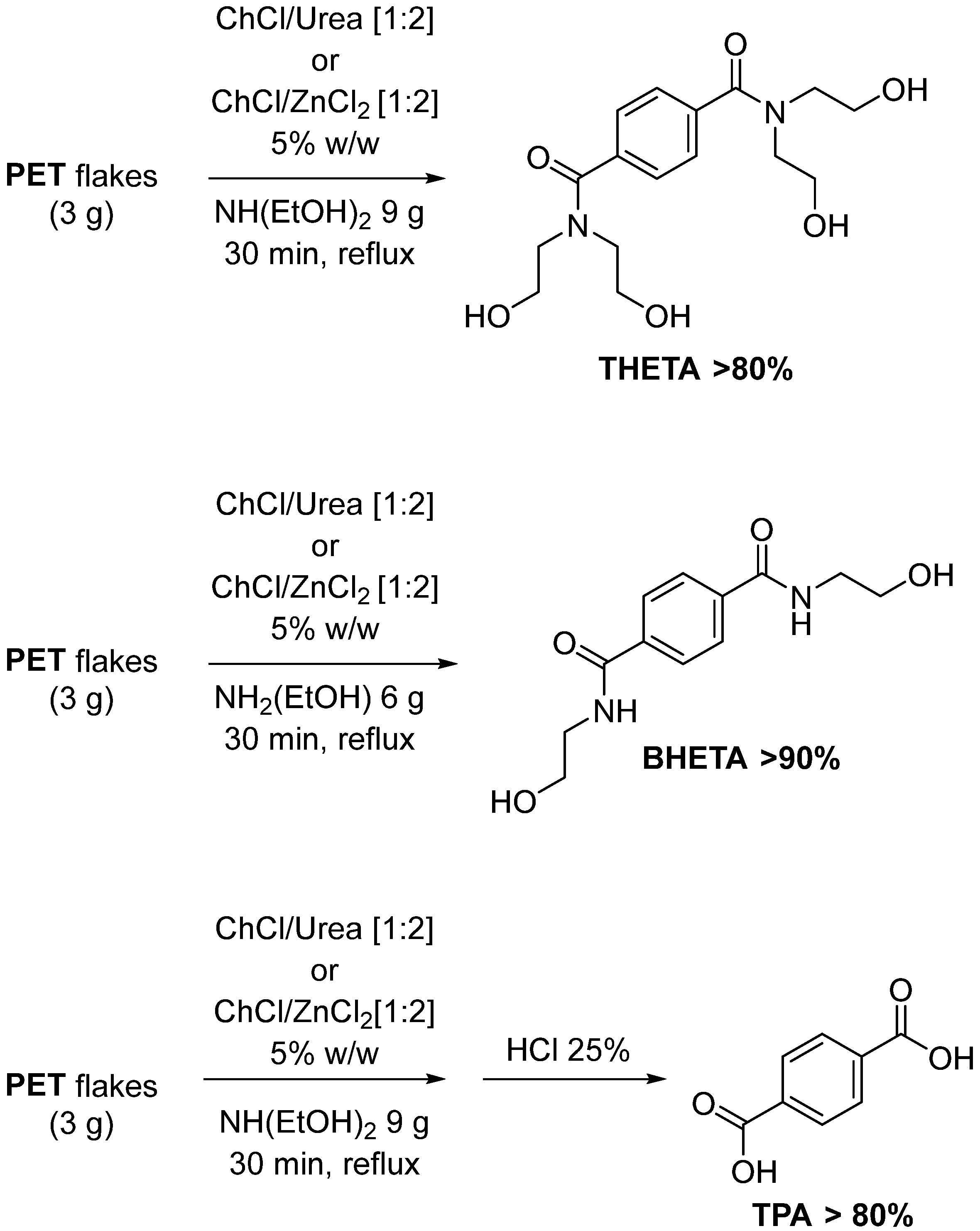
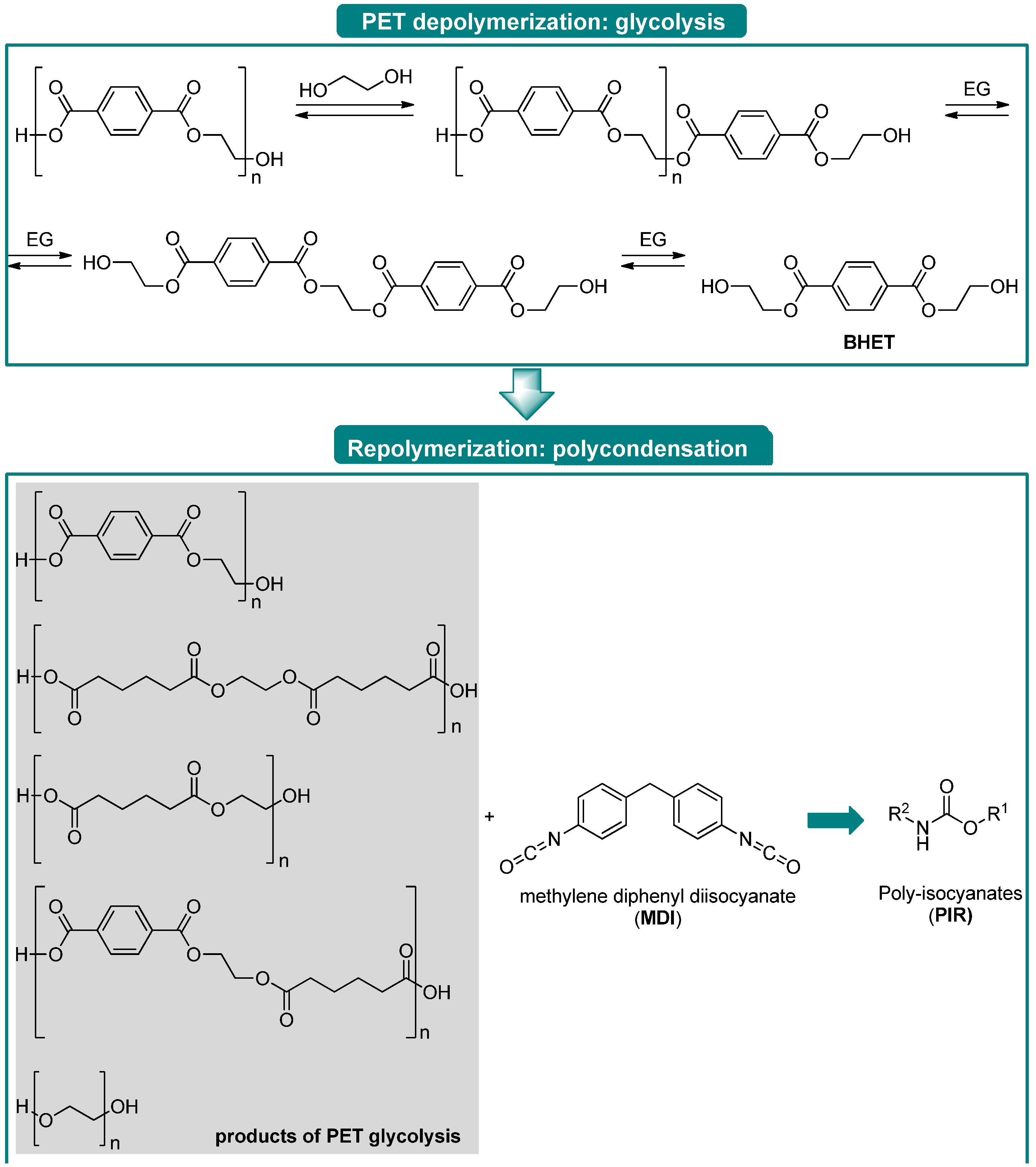
3.2. Lewis Acid-Free PET Solvolysis and Depolymerization by DESs
4. Bio-Based Polymers Degradation with Deep Eutectic Solvents
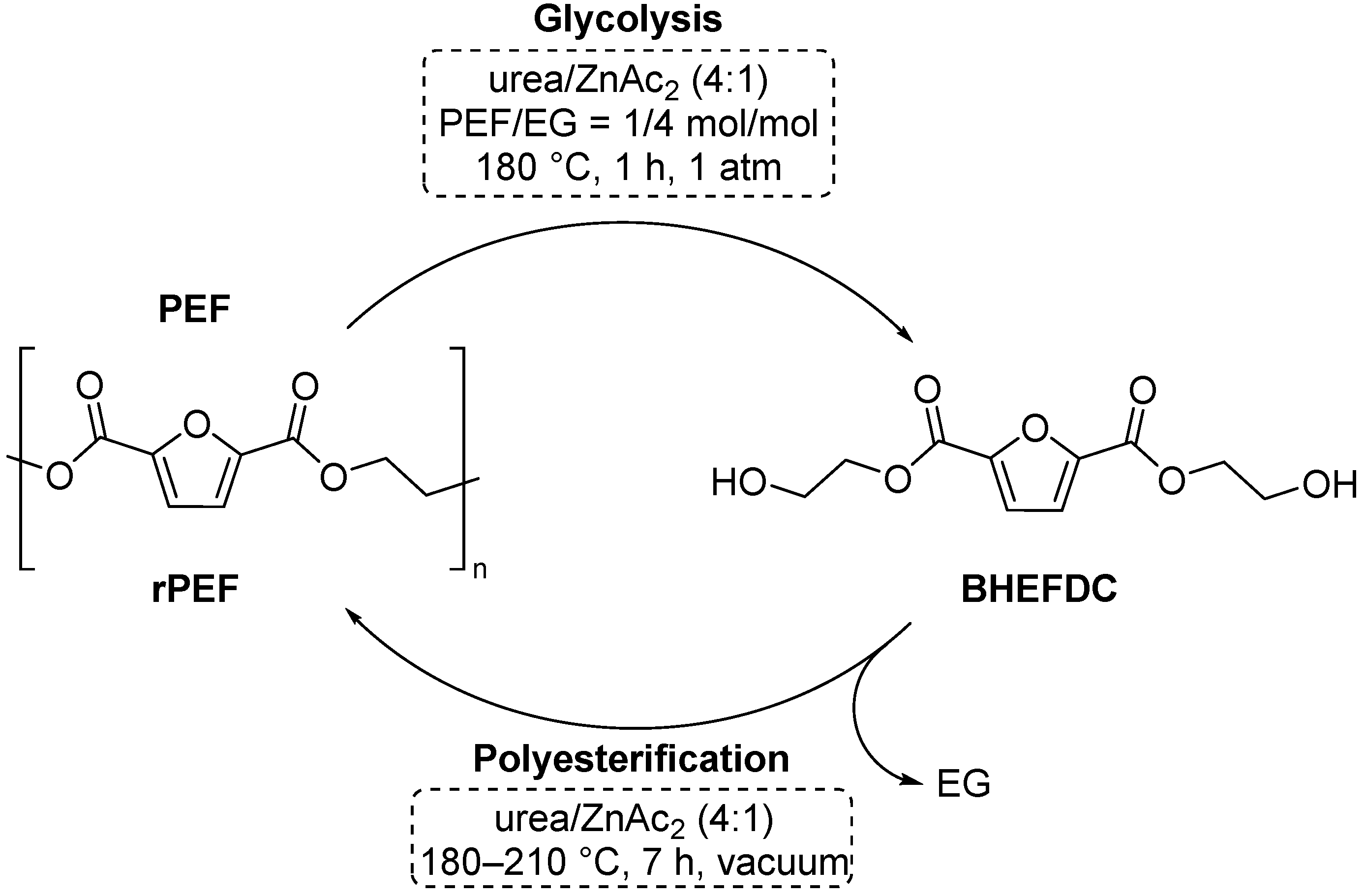
4.1. Depolymerization of Poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid) (PEF)
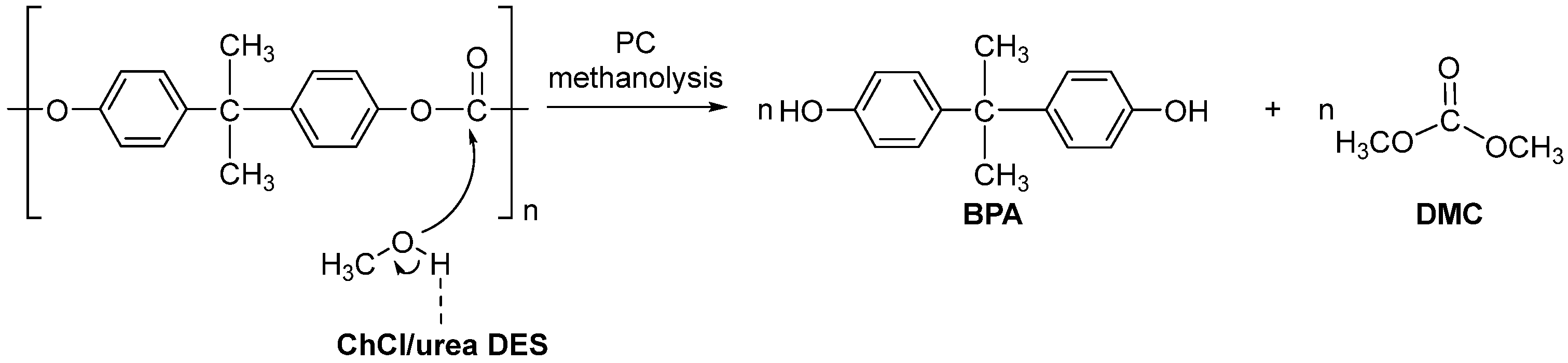
4.2. Depolymerization of Polycarbonate (PC)
4.3. DES-Mediated PolyButylenes and PolyLactic Polymers Degradation
5. Deep Eutectic Solvents Degradation of Other Polymers
5.1. Treatment of Rubber Tires with DES
5.2. Use of DESs in the Treatment of Polyurethane (PU)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Rahimi, A.; García, J.M. Chemical recycling of waste plastics for new materials production. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
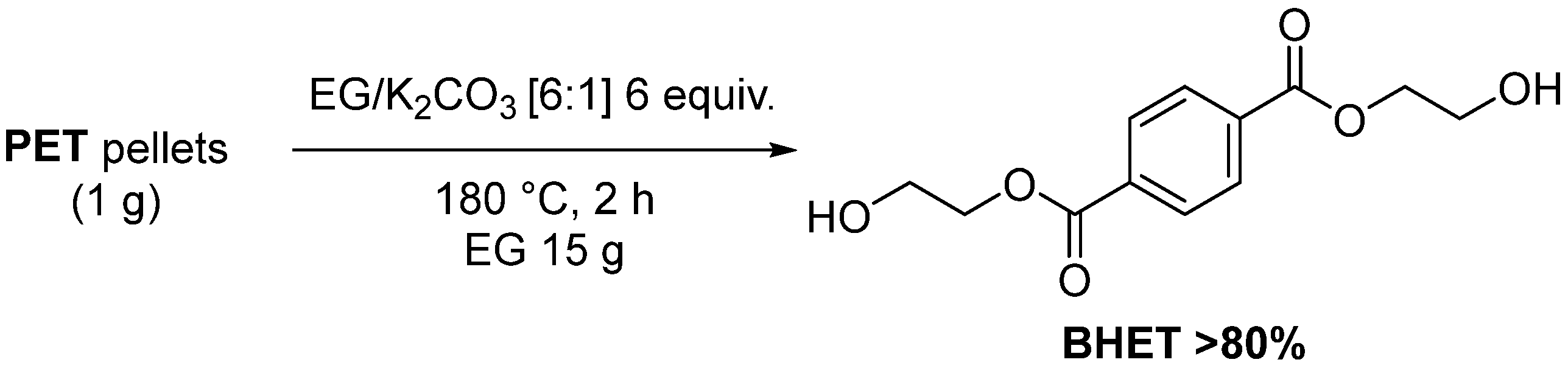
- López-Fonseca, R.; Duque-Ingunza, I.; de Rivas, B.; Flores-Giraldo, L.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Kinetics of catalytic glycolysis of PET wastes with sodium carbonate. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, H. New effective catalysts for glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate waste: Tropine and tropine-zinc acetate complex. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nelson, G.A.; Toland, J.; Holbrey, E.J.D. Glycolysis of PET using 1,3-dimethylimidazolium-2-carboxylate as an organocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13362–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.R.; Harad, A.M. Glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate waste fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Coady, D.J.; Jones, G.O.; Almegren, H.A.; Alabdulrahman, A.M.; Alsewailem, F.D.; Horn, H.W.; Rice, J.E.; Hedrick, J.L. Unexpected efficiency of cyclic amidine catalysts in depolymerizing poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marullo, S.; Rizzo, C.; Dintcheva, N.T.; D’Anna, F. Amino Acid-Based Cholinium Ionic Liquids as Sustainable Catalysts for PET Depolymerization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 15157–15165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.D.; Cho, J. Low-energy catalytic methanolysis of poly(ethyleneterephthalate). Green Chem. 2021, 23, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) catalyzed by ionic liquids. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) using ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Geng, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. First-Row Transition Metal-Containing Ionic Liquids as Highly Active Catalysts for the Glycolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; El Metwally, A.E. Greener routes for recycling of polyethylene terephthalate. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhemileva, L.U.; D’yakonov, V.A.; Seitkalieva, M.M.; Kulikovskaya, N.S.; Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. A large-scale study of ionic liquids employed in chemistry and energy research to reveal cytotoxicity mechanisms and to develop a safe design guide. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6414–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, T. Revisiting greenness of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.; Rasheeda, R.K.; Tambyrajaha, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, Y.; Thickett, S.C. Greener, faster, stronger: The benefits of deep eutectic solvents in polymer and materials science. Polymers 2021, 13, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, K.H. Row. Development of deep eutectic solvents for sustainable chemistry. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musale, R.M.; Shukla, S.R. Deep Eutectic Solvent as Effective Catalyst for Aminolysis of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Waste. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2016, 20, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Choi, H.M.; Oh, K.W. Rapid Hydrophilic Modification of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Surface by Using Deep Eutectic Solvent and Microwave Irradiation. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verbene, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P.; Capriati, V. Organic Synthesis in DESs. In Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Ramón, D.J., Guillena, G., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Chapter 7; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, S.; Messa, F.; Salomone, A. Towards Green Reductions in Bio-Derived Solvents. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, e202201494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Row, K.H. Development of deep eutectic solvents applied in extraction and separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, H. Development and applications of deep eutectic solvent derived functional materials in chromatographic separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1098–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Dixit, G.; Shah, E.; Patel, A.; Boczkai, G.; Kumar, A.K. Techno-economic evaluation of a natural deep eutectic solvent-based biorefinery: Exploring different design scenarios. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2020, 14, 746. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Tu, J.J. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs)-derived advanced functional materials for energy and environmental applications: Challenges, opportunities, and future vision. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8209–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Kumar, K. Deep eutectic solvents in CO2 capture. In CO2-Philic Polymers, Nanocomposites and Chemical Solvents; Nadda, A.K., Sharma, S., Kalia, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
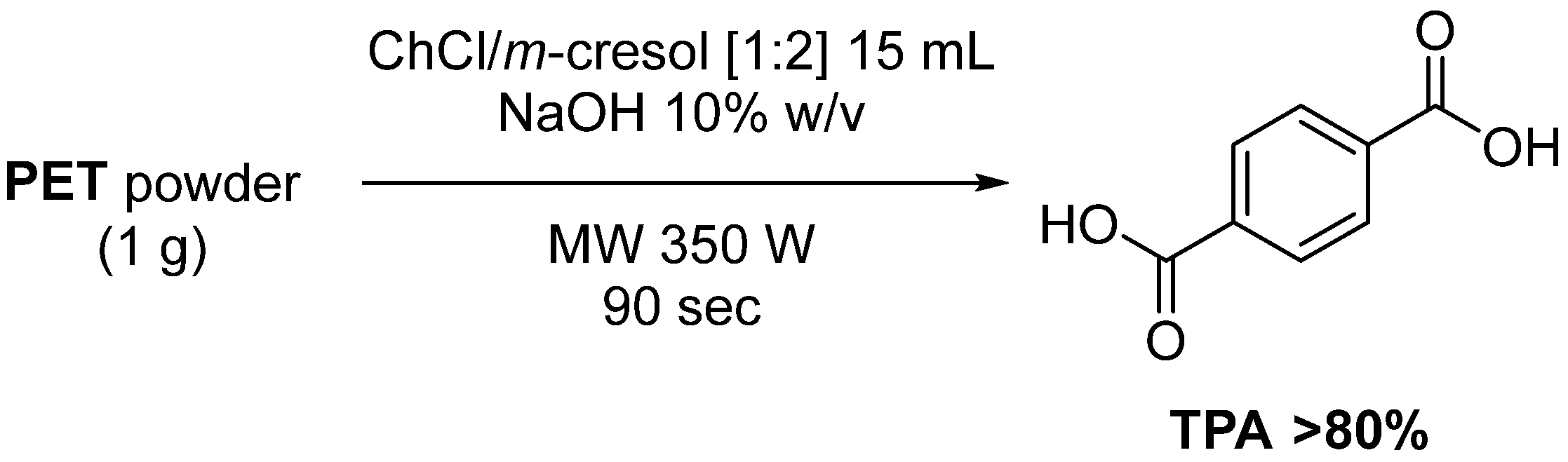
- Joo, S.; Cho, I.J.; Seo, H.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly (ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanno, C.; Flores, I.; Dove, A.P.; Muller, A.J.; Ruiperez, F.; Sardon, H. Organocatalysed depolymerisation of PET in a fully sustainable cycle using thermally stable protic ionic salt. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, R.K.; Gupta, A.A. Preparation and evaluation of waste PET derived polyurethane polymer modified bitumen through in situ polymerization reaction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi-Mani, H.; Terreros, G.; Barroca-Aubry, N.; Aymes-Chodur, C.; Regeard, C.; Roger, P. Poly (ethylene terephthalate) films modified by UV-induced surface graft polymerization of vanillin derived monomer for antibacterial activity. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, N.D.; Palekar, V.S.; Shukla, S.R.J. Glycolysis of postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate waste. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.B.; Wang, C.S.; Wang, H.P.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, S.B. Sodium titanium tris (glycolate) as a catalyst for the chemical recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate) via glycolysis and repolycondensation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 114, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Deep eutectic solvents as highly active catalysts for the fast and mild glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate)(PET). Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fakayode, O.A.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, C. Lignin fractionation from lignocellulosic biomass using deep eutectic solvents and its valorization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 156, 111986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Ju, Z.; Liu, B.; Yao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S. Alcoholysis of polyethylene terephthalate to produce dioctyl terephthalate using choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as efficient catalysts. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
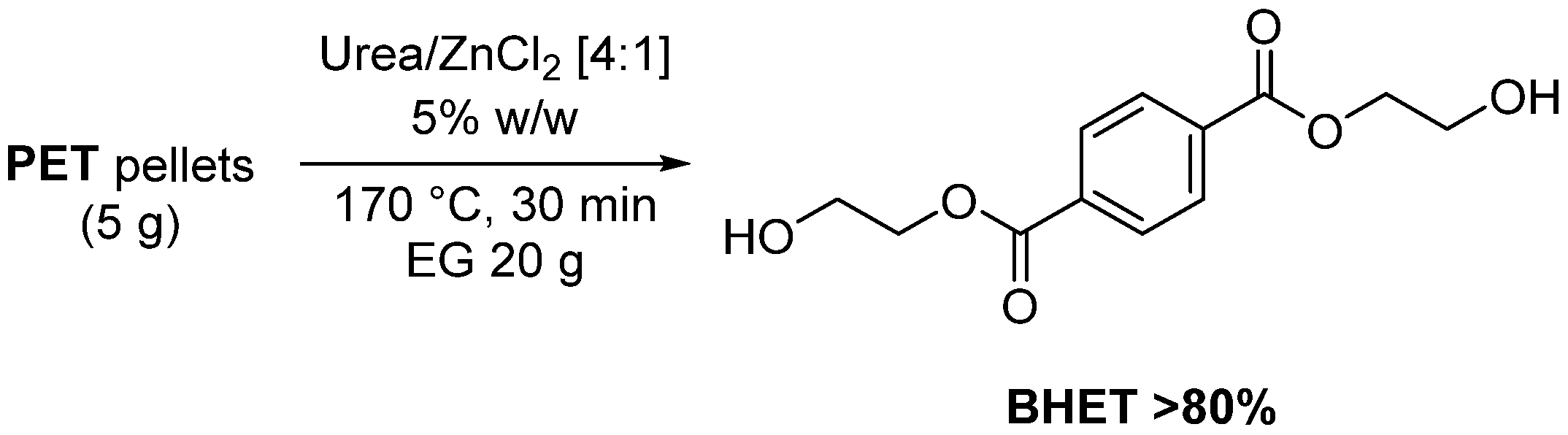
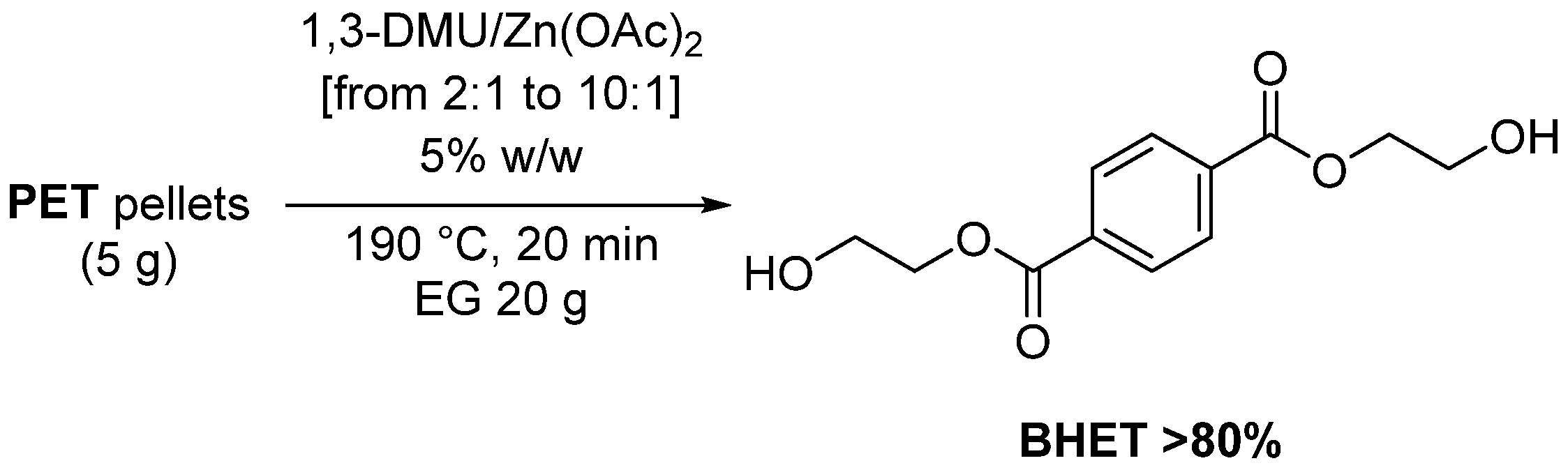
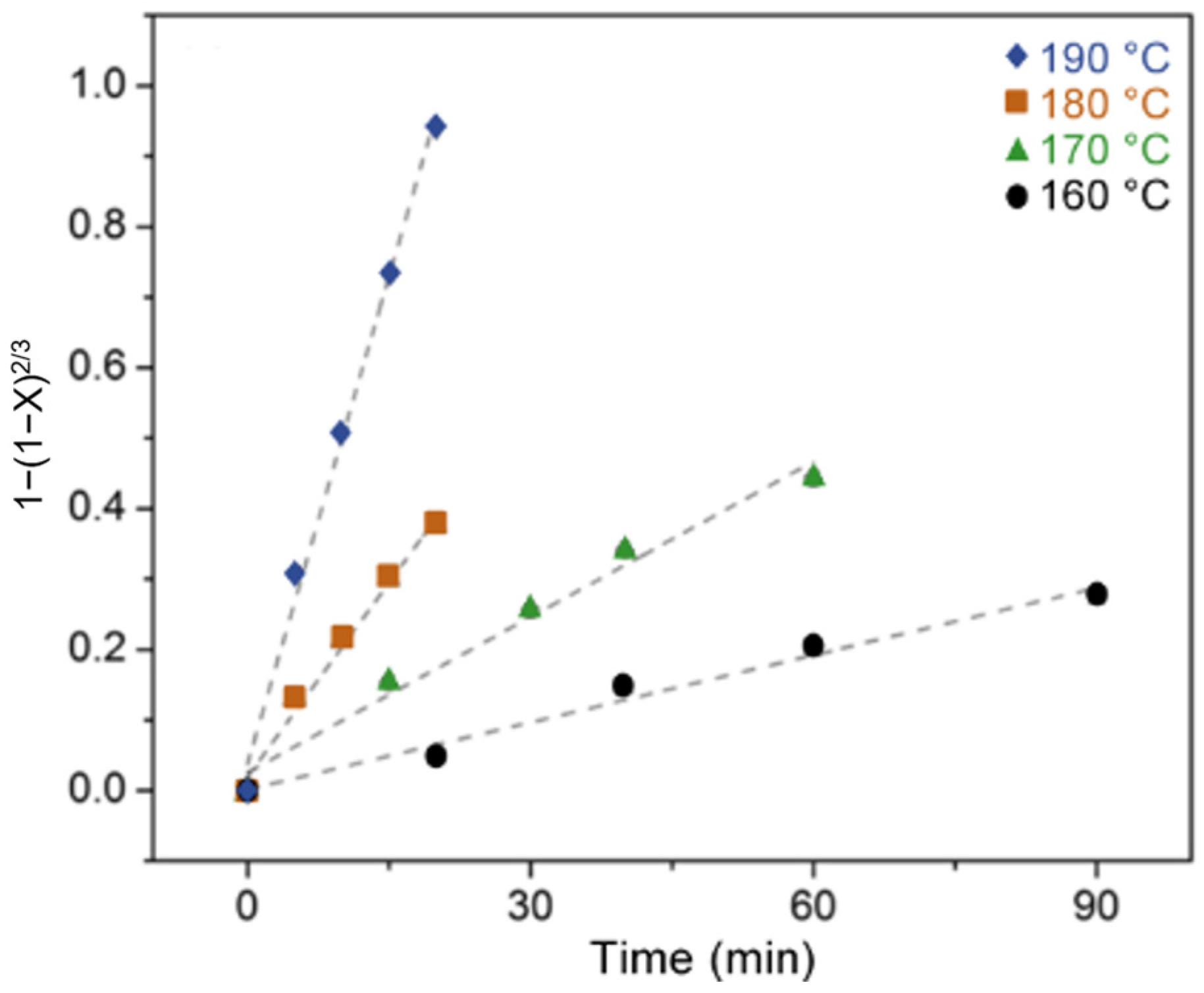
- Liu, B.; Fu, W.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S. Lewis Acid–Base Synergistic Catalysis for Polyethylene Terephthalate Degradation by 1,3-Dimethylurea/Zn(OAc)2 Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
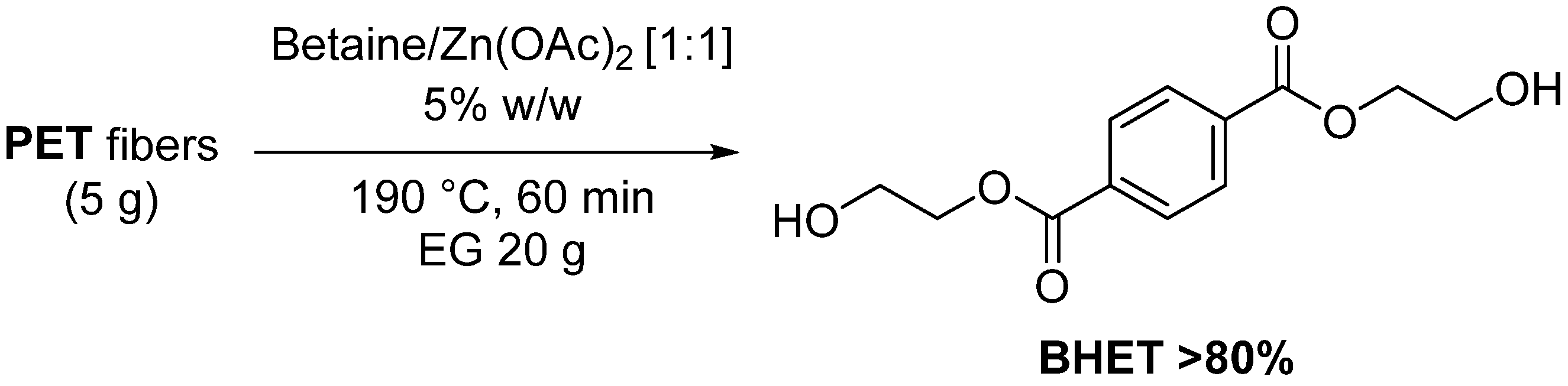
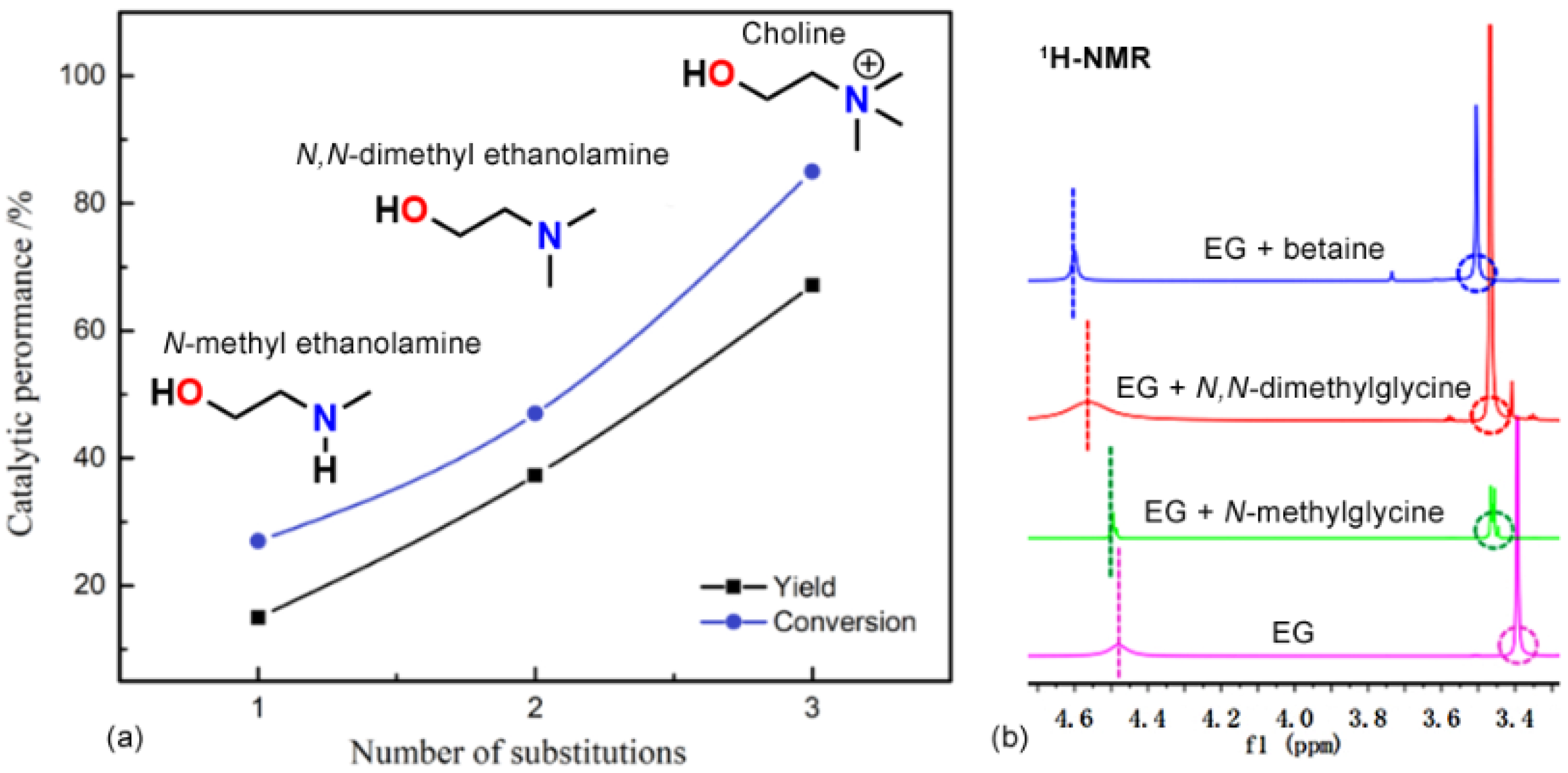
- Liu, L.; Yao, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, X.; Yan, D.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Recycling of full components of polyester/cotton blends catalyzed by betaine-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fan, C.; Hao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, G.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Q. Molecular mechanism of waste polyethylene terephthalate recycling by the 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]decium acetate/zinc acetate deep eutectic solvent: The crucial role of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]decium cation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2022, 641, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Yu, G.; Chen, X. A new class of catalysts for the glycolysis of PET: Deep eutectic solvent@ZIF-8 composite. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 183, 109463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, M.; Raffi, F.; Rossi, E.; Tiecco, M.; Martinelli, E.; Ciancaleoni, G. Depolymerization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) under mild conditions by Lewis/Brønsted acidic deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, E.; Yılmaz, E.; Atalay, F.S. Chemical Recycling of Polyethlylene Terephthalate by Glycolysis. Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.; Janssens, A.; Azeem, M.; Fournet, M.B. Fast, High Monomer Yield from Post-consumer Polyethylene Terephthalate via Combined Microwave and Deep Eutectic Solvent Hydrolytic Depolymerization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 17174–17185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Fournet, M.B.; Attallah, O. Ultrafast 99% Polyethylene terephthalate depolymerization into value added monomers using sequential glycolysis-hydrolysis under microwave irradiation. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Azeem, M.; Nikolaivits, E.; Topakas, E.; Fournet, M.B. Progressing Ultragreen, Energy-Efficient Biobased Depolymerization of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) via Microwave-Assisted Green Deep Eutectic Solvent and Enzymatic Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.S.; Jung, S.M. Single-catalyst reactions from depolymerization to repolymerization: Transformation of polyethylene terephthalate to polyisocyanurate foam with deep eutectic solvents. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangerous diisocyanates (TDI-Toluene Di Isocyanates; MDI-Methylenediphenyl Diisocyanates), phosgene gas and halogenated solvents are frequently used in the synthesis of polyurethanes, contributing to the negative impact of these polymeric materials on the environment. Adequate safety measures are needed in PU production to prevent and mitigate the possible consequences for humans and the environment. Alternative routes for Non-isocyanate based PUR (NIPU) rely on the use of cyclic carbonates and aliphatic and cycloaliphatic amines or silane derivatives. Kathalewar, M.S.; Joshi, P.B.; Sabnis, A.S.; Malshe, V.C. Non-isocyanate polyurethanes: From chemistry to applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4110–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, K.; Zhang, R.; Pereira, I.; Agostinho, B.; Hu, H.; Maniar, D.; Sbirrazzuoli, N.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Guigo, N.; Sousa, A.F. A Perspective on PEF Synthesis, Properties, and End-Life. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, B.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Sousa, A.F. From PEF to RPEF: Disclosing the Potential of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Continuous de-/Re-Polymerization Recycling of Biobased Polyesters. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 3115–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hu, W.; Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, S.; Yu, S.; Liu, F. Methanolysis of Polycarbonate into Valuable Product Bisphenol A Using Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Highly Active Catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatyev, I.A.; Thielemans, W.; Vander Beke, B. Recycling of Polymers: A Review. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Rajeswari, N. ZnO/PBAT Nanocomposite Films: Investigation on the Mechanical and Biological Activity for Food Packaging. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Zhu, G.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Study on the Biodegradation of Polybutylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate/Starch Film Containing Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamarche, E.; Mattlet, A.; Livi, S.; Gérard, J.F.; Bayard, R.; Massardier, V. Tailoring Biodegradability of Poly(Butylene Succinate)/Poly(Lactic Acid) Blends With a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, N.F.; Garcia, R.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Pilakoutas, K.; Guadagnini, M.; Raffoul, S. Composites with Recycled Rubber Aggregates: Properties and Opportunities in Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Mészáros, L.; Bárány, T. Ground Tyre Rubber (GTR) in Thermoplastics, Thermosets, and Rubbers. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, R.; Walvekar, R.; Jayaweera, U.; Khalid, M. Dilution and ZnCl2 Impact on Eutectic Solvents as Devulcanizing Reagent in De-Linking Phenomena of Waste Ground Rubber Tire. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2137, 020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, H.; Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Deng, T. Degradation of polycarbonate-based polyurethane via selective cleavage of carbamate and urea bonds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 181, 109342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicco, L.; Dilauro, G.; Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P.; Capriati, V. Advances in deep eutectic solvents and water: Applications in metal- and biocatalyzed processes, in the synthesis of APIs, and other biologically active compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 2558–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messa, F.; Dilauro, G.; Paparella, A.N.; Silvestri, L.; Furlotti, G.; Iacoangeli, T.; Perrone, S.; Salomone, A. Deep eutectic solvents meet safe, scalable and sustainable hydrogenations enabled by aluminum powder and Pd/C. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4388–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P.; Capriati, V. Deep eutectic solvents and their applications as green solvents. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paparella, A.N.; Perrone, S.; Salomone, A.; Messa, F.; Cicco, L.; Capriati, V.; Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P. Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071035
Paparella AN, Perrone S, Salomone A, Messa F, Cicco L, Capriati V, Perna FM, Vitale P. Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071035
Chicago/Turabian StylePaparella, Andrea Nicola, Serena Perrone, Antonio Salomone, Francesco Messa, Luciana Cicco, Vito Capriati, Filippo Maria Perna, and Paola Vitale. 2023. "Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071035
APA StylePaparella, A. N., Perrone, S., Salomone, A., Messa, F., Cicco, L., Capriati, V., Perna, F. M., & Vitale, P. (2023). Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization. Catalysts, 13(7), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071035