Abstract
The combustion front is a crucial parameter in determining the efficiency of in situ combustion techniques during enhanced oil recovery. Nowadays, catalytic systems are widely believed to be an efficient tool to stabilize the combustion front. This study aimed to investigate the synthesis and catalytic activity of manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles in the high-temperature oxidation of heavy oils. The synthesis and catalytic activity of manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles in the high and low-temperature oxidation regions of heavy oil were investigated in this study. The obtained nanoparticles were characterized and studied by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TG), nitrogen adsorption and desorption measurements, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermal analysis combined with the Kissinger isoconversional method. The obtained results showed that the synthesized nanoparticles had an average size of 17 ± 4 nm and a specific surface area of 38.2 ± 0.1 m2 g−1, with a pore size distribution of ~8 nm. The low and high-temperature oxidation processes’ activation energies were found to be 98.9 ± 0.7 kJ/mol and 151.9 ± 0.6 kJ/mol, respectively, in the presence of nanoparticles. However, these parameters were found to be equal to 110.1 ± 1.8 kJ/mol and 142.8 ± 8.3 kJ/mol, respectively, in the absence of nanoparticles. These data were processed further by calculating the corresponding reaction rates. The obtained results indicated that the rate of heavy oil oxidation was higher in the presence of the synthesized nanoparticles, which could play a critical role in stabilizing the combustion front in the in situ combustion process.
1. Introduction
As the need for energy continues to rise, unconventional oil resources like heavy oils and bitumen are becoming more significant [1]. These resources are crucial for supporting economic growth and providing the energy needs of a constantly growing global population. They constitute a sizable supply of power that can supplement or even take the place of conventional oil sources that are running out [2]. In order to ensure energy security and lessen reliance on a few select oil-producing nations, unconventional oil resources must be fully exploited [2]. Heavy oil extraction has a long and evolving history, dating back to the early twentieth century. Heavy oils were initially considered uneconomical to produce and were frequently left in the ground. However, technological advancements and rising energy demand have rekindled interest in these resources [3]. Various thermal recovery methods for extracting heavy oils were developed in the 1950s and 1960s, including steam injection and in situ combustion [4,5,6,7].
As a result of enabling the direct oxidation of some of the oil inside the reservoir and producing heat and pressure, in situ combustion is a crucial thermally enhanced oil recovery technique. Despite its potential, in situ combustion still has various application restrictions and knowledge gaps [8]. For instance, choosing the right combustion front is essential to the process’s effectiveness, yet forecasting the front’s movement is still difficult. Additionally, the extreme conditions inside the reservoir can eventually cause equipment to decay, which can cause problems with operation [9,10,11].
In situ combustion front stabilization by catalytic application has been thoroughly researched in the literature for a variety of reservoir types, including heavy oil and coal-bed methane [12,13,14,15]. The use of various catalysts, including zeolites, metal oxides, and noble metals, has been investigated by researchers as a way to increase combustion efficiency and lower NOx emissions. According to the findings, the catalytic effect is influenced by the catalyst’s size and type, reaction temperature, and fluid composition in the reservoir. Studies have also looked at the workings of catalytic reactions and how they affect combustion. For instance, it has been discovered that the catalytic oxidation of CO and H2 raises the temperature of the combustion front, resulting in a more reliable and effective combustion process.
Several studies have shown that the addition of clays, minerals, and metal-based catalysts can significantly enhance the combustion of oil in porous media [16,17,18,19]. Out of the various catalytic systems, the micro and nanoparticles of transition metals and metal oxides have been found to be the most promising for use in pilot tests [14,20]. For instance, oleylamine-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles that are 80 nm in size have been shown to catalyze fuel deposition and high-temperature oxidation reactions, as well as speed up the propagation of the combustion front [21]. Additionally, research on the impact of copper, chromium, and titanium nanoparticles on the oil oxidation process revealed that these catalysts could reduce the amount of fuel deposited and consumed during combustion and increase oil production by 20% [22]. The combination of low-temperature oxidation inhibition and high-temperature oxidation acceleration was observed in experiments with copper nano and sub-microparticles. The results showed that the presence of nanoparticles leads to a higher combustion front temperature [23]. The use of NiO nanoparticles in combustion tubes was found to increase the combustion front velocity by 9%, improve oil recovery by 4%, and reduce oil viscosity by 61% [24]. The oxidation of heavy oils and their high molecular weight components was tested using Zr, Ce, and Pd compounds in the form of nanoparticles [25,26]. Research shows that catalysts made of noble and rare earth metals exhibit higher catalytic activity, but their cost makes them uneconomical for use in oil production.
Manganese-based catalysts have a crucial role in the in situ combustion process, as they enhance the oxidation of heavy oils and increase the efficiency of the process [27,28,29]. The high catalytic activity of these catalysts leads to a reduction in the activation energy required for the combustion process, making it easier for the heavy oils to ignite and burn. This results in a more efficient and cost-effective in situ combustion process, with higher yields of lighter, more valuable products and lower emissions of harmful pollutants.
Moreover, the use of manganese-based catalysts in the in situ combustion process can also improve the stability of the reaction, reducing the likelihood of unwanted side reactions and ensuring a consistent and controlled process [30,31,32]. The use of these catalysts also enhances the distribution of oxygen throughout the oil reservoir, ensuring uniform combustion and maximizing the utilization of heavy oils. Overall, the use of manganese-based catalysts in the in situ combustion process represents a significant step forward in the development of more sustainable and efficient methods for heavy oil recovery.
It is crucial to acknowledge that the size and shape of nanocatalysts have a significant impact on their catalytic activity [33]. Generally, nanocatalysts with a large specific surface area, resulting from smaller particle sizes, exhibit improved catalytic performance. However, this small particle size also reduces their aggregative stability, negatively affecting their catalytic activity. Moreover, large aggregates can obstruct pore channels, hindering oil flow [34].
This study shed light on the influence of manganese oxide nanoparticles on the process of heavy oil oxidation during the application of in situ combustion technology.
2. Results and Discussion
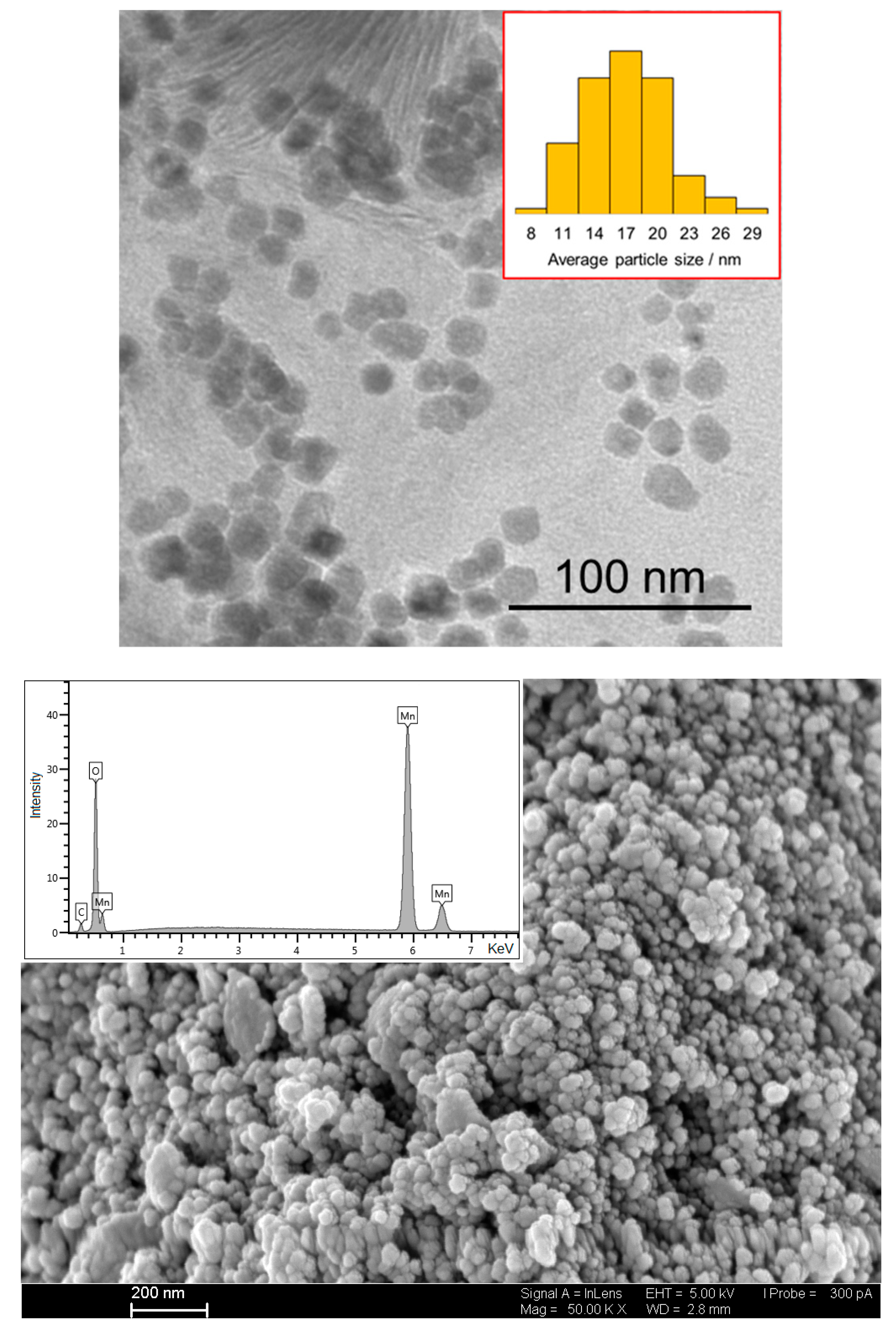
SEM, EDX, and TEM can be used to identify the crystal structure and internal structure of the particles, which can provide insights into the synthesis process and any potential impurities present. Furthermore, these methods of analysis can be used to determine the size distribution of the nanoparticles, which is crucial for characterizing the performance of the material in various applications. Overall, SEM, EDX, and TEM provide a valuable and comprehensive characterization of the nanoparticles and are essential tools for understanding their behavior and properties.
In this study, TEM and SEM were used to determine the average size of the synthesized nanoparticles; meanwhile, EDX was utilized to highlight the elemental content of the obtained particles. The results showed that the particles have an average size of 17 ± 4 nm (Figure 1). TEM provided a high-resolution image of the nanoscale structure, making it possible to observe the fine details and uniformity of the nanoparticles. This information is critical for understanding the properties and performance of the material.
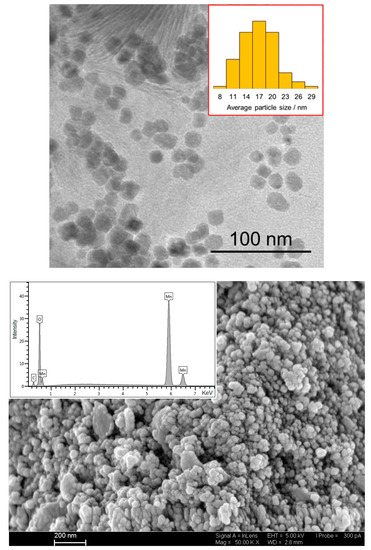
Figure 1.
SEM, EDX, and TEM analysis of the obtained MnO nanoparticles. The particle size distribution is shown in the inset.
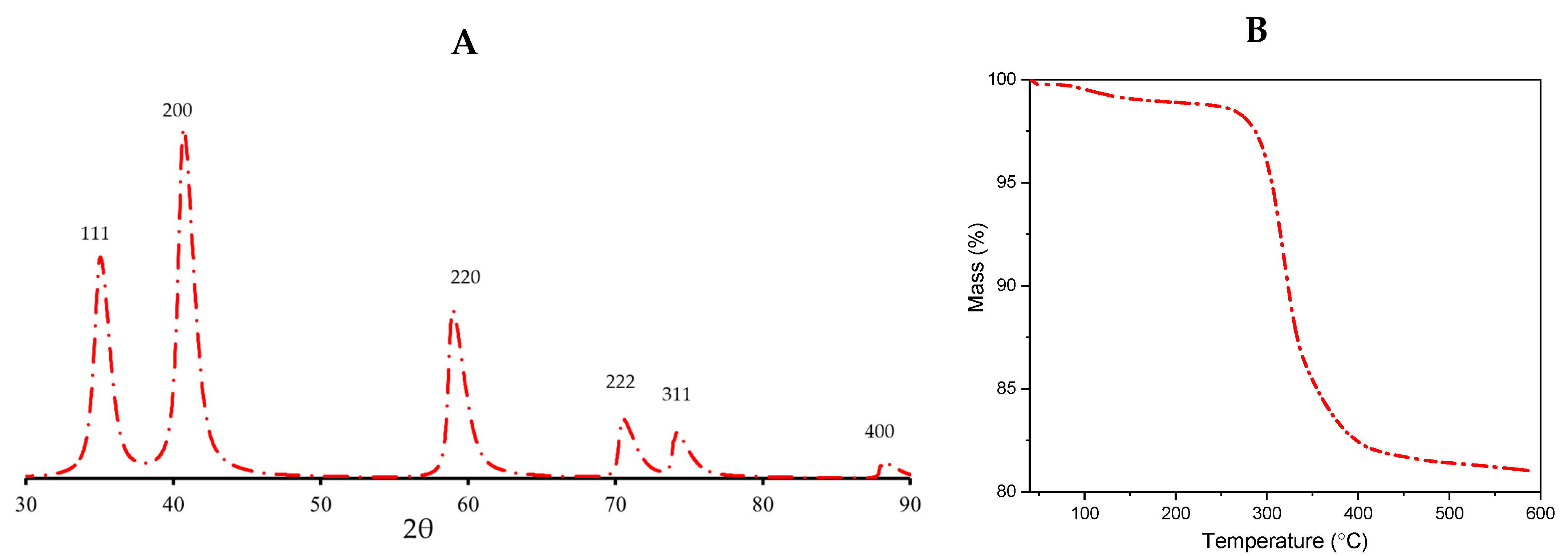
Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRPD) analysis is a powerful tool for characterizing the structural and crystalline properties of materials. In this study, XRPD was used to examine the composition of MnO nanoparticles. The results (Figure 2A) showed the presence of a single phase of MnO with an average particle size of 5 nm, as calculated using the Scherrer equation. It is important to note, however, that the Scherrer equation may not accurately reflect the true particle size in cases where there are other factors contributing to peak broadenings, such as crystal defects and distortions. Additionally, Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG) was performed to determine the presence of oleic acid on the surface of the particles (Figure 2B). The results indicated that there was approximately 18% oleic acid present and that this coating decomposed in the temperature range of 300–400 °C. These findings provide valuable information about the structure and stability of the MnO nanoparticles and offer insights into their potential applications.
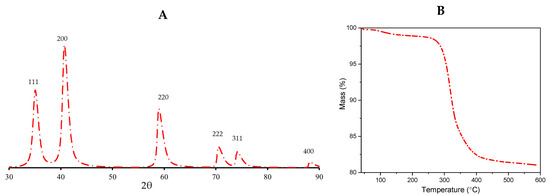
Figure 2.
X-ray phase analysis (A) and TG curve (B) at 10 °C min−1 heating rate of the synthesized nanoparticles.
The specific surface area of the catalysts produced in this study was determined through nitrogen adsorption measurements. The BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) method, which was used in this study, is a commonly used method to calculate the specific surface area from the nitrogen adsorption isotherm. The BET method is based on the adsorption of nitrogen molecules onto the surface of the material, and the subsequent measurement of the amount of nitrogen adsorbed at different relative pressures. This information is then used to calculate the specific surface area and pore volume of the material.
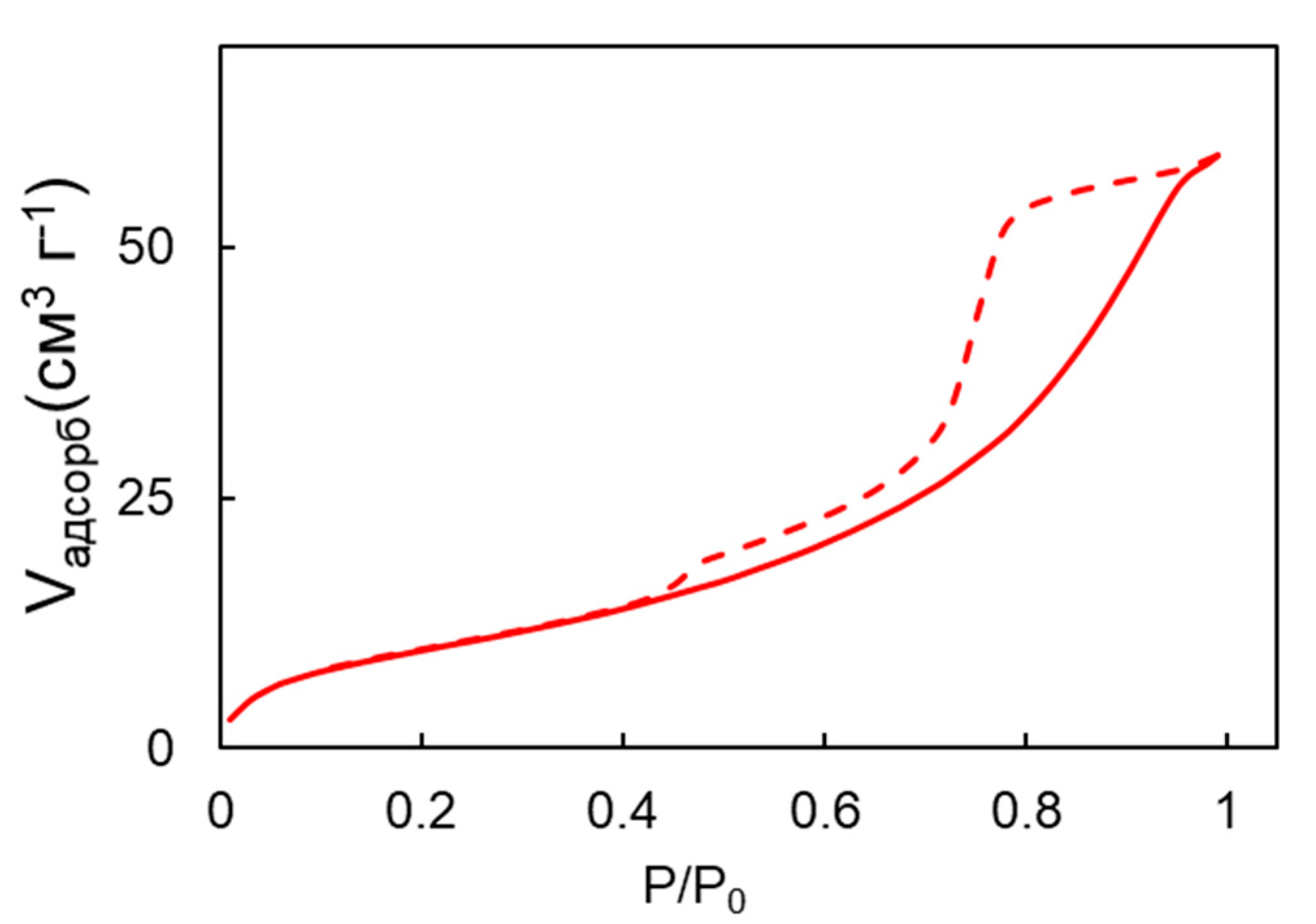
The obtained results showed that the specific surface area was 38.2 ± 0.1 m2 g−1 (Figure 3), demonstrating the presence of a complex network of mesopores in the bulk catalyst sample. The nitrogen adsorption isotherm obtained was a type IV isotherm with an H2-type hysteresis loop between the desorption and adsorption branches. This hysteresis loop indicates the presence of mesopores, which are pores with diameters ranging from 2 to 10 nm (Figure 4). The pore network observed in the catalyst sample is a result of the voids between the particles and not due to the porosity of the nanoparticles themselves. This is a crucial point to consider when evaluating the performance of the catalyst, as the pore network can greatly impact the accessibility of the active sites and, in turn, the efficiency of the catalytic reaction.
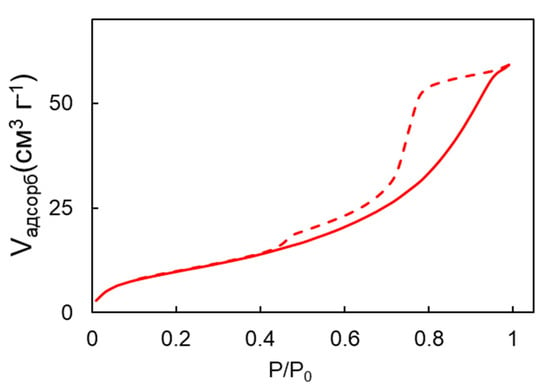
Figure 3.
Isotherms of nitrogen adsorption and desorption of the synthesized nanoparticles.
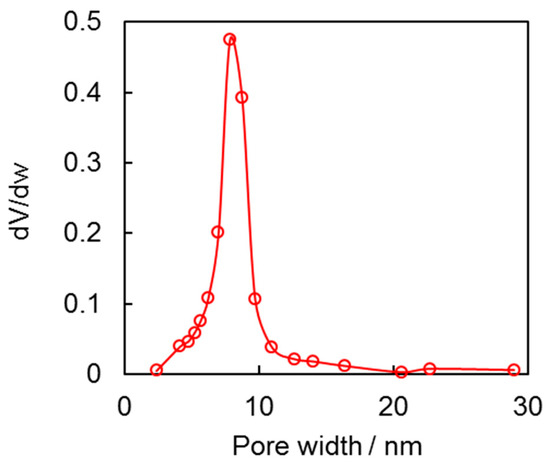
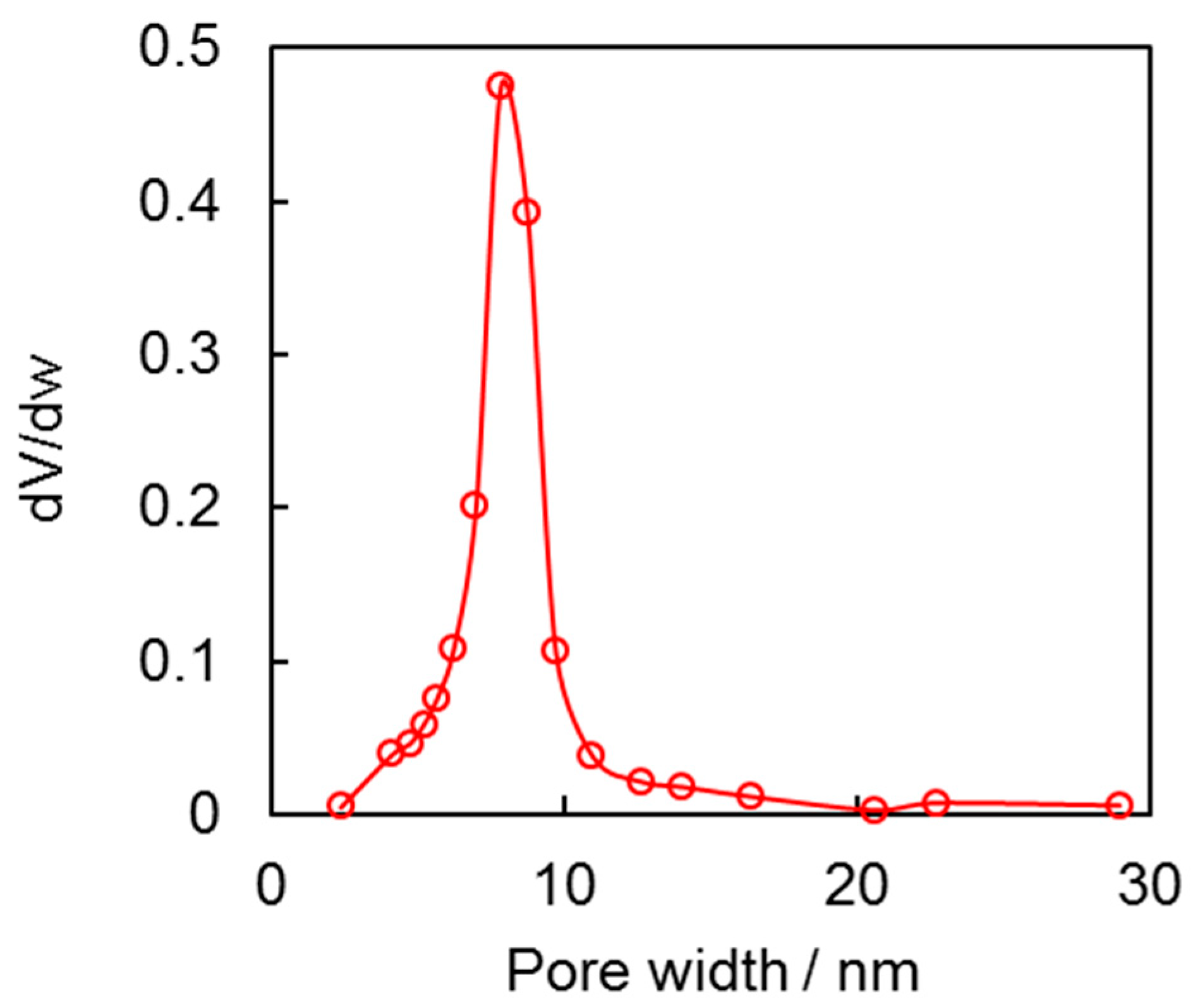
Figure 4.
Pore size distribution of the synthesized nanoparticles.
The size of pore channels in the aggregates of nanoparticles was estimated using a unique approach that compared their structure to that of bulk samples. This method involved assuming that the pore channels in the aggregates were similar in size to those in the bulk samples. The pore size distribution was calculated from the desorption isotherm, which provided a detailed picture of the pore structure of the aggregates. The calculation resulted in peaks at around 8 nm, as shown in Figure 4. The ability to accurately measure the pore size distribution in aggregates of nanoparticles will enable researchers to optimize their performance and properties for specific applications.
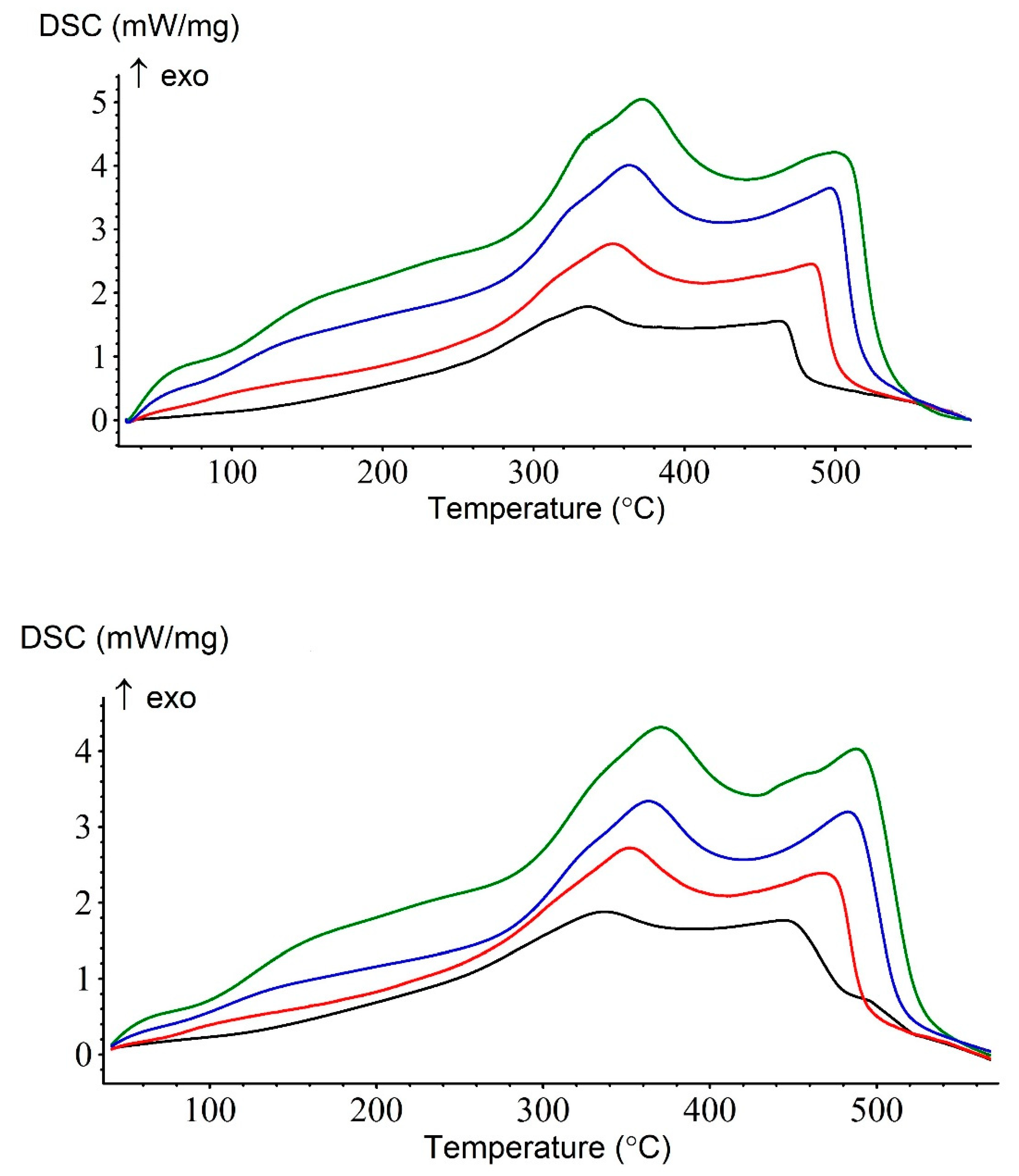
Oil oxidation is a complex process that is widely studied due to its implications in various industries, such as petrochemical and fuel production. This reaction is exothermic, making calorimetry a useful tool for analyzing its kinetics. In this study, the reaction kinetics were examined using nonisothermal differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (Figure 5). The DSC method involves heating a sample at varying rates and measuring the heat evolved as a function of temperature. The results of this study were presented in the form of DSC curves, which displayed two distinguishable exothermic signals. The first signal, referred to as low-temperature oxidation (LTO), was due to the formation of oxygen-containing organic compounds, such as peroxides, alcohols, and carbonyl compounds. The second signal, referred to as high-temperature oxidation (HTO), was due to the oxidation of coke and the production of carbon oxides and water. The results showed that the catalytic reaction occurred at lower temperatures, indicating an acceleration of the oxidation process. This was demonstrated by the shift in the exothermic signal to lower temperatures in the catalytic oxidation curve compared to the noncatalytic oxidation curve. The results of this study provide valuable insights into the kinetics of oil oxidation, which can be applied to the optimization of various industrial processes that involve oil oxidation reactions.
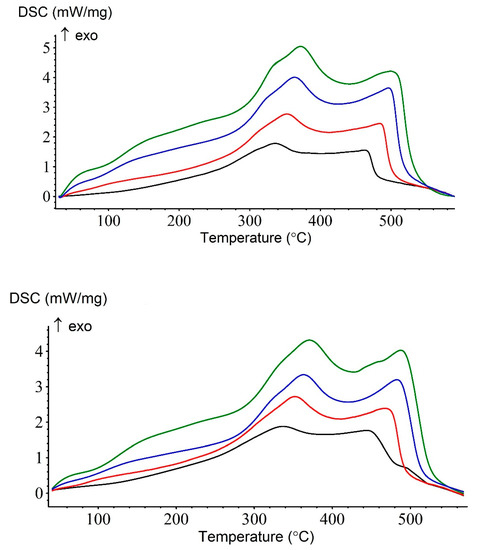
Figure 5.
DSC curves for noncatalytic (top) and catalytic (bottom) heavy oil oxidation at different heating rates (5—black, 10—red, 15—blue, and 20—green) in K/min.
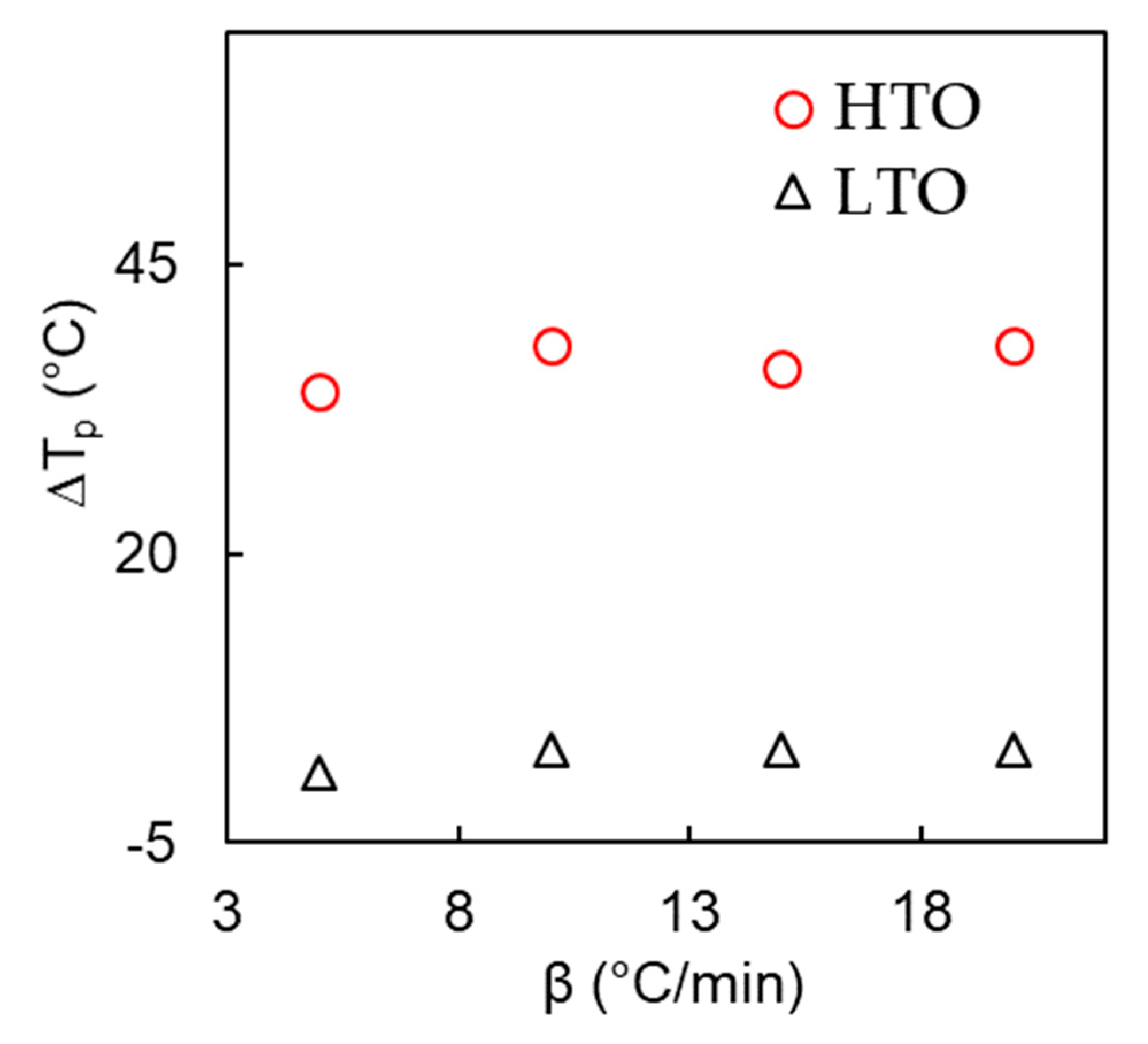
Table 1 and Figure 6 present the results of a study that compares the reaction intervals and peak temperatures of noncatalytic and catalytic cycles of low-temperature and high-temperature oxidation processes. The results show that the catalyst has a significant impact on the high-temperature oxidation (HTO) process, as evidenced by the differences in the corresponding Tp values of the noncatalytic and catalytic processes depicted in Figure 6. However, the effect of the catalyst on the low-temperature oxidation (LTO) process is relatively minor. These findings highlight the importance of using a catalyst in high-temperature oxidation processes to improve reaction efficiency and enhance the final product quality. The data presented in Table 1 and Figure 6 can be used as a reference for the optimization of oxidation processes in enhanced oil recovery fields.

Table 1.
Reaction intervals and peak temperatures for noncatalytic and catalytic oil oxidation.
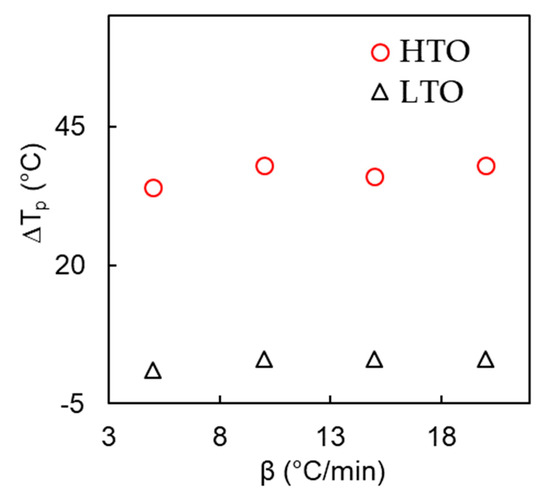
Figure 6.
Differences between peak temperatures (ΔTp) for catalytic and noncatalytic heavy oil oxidation at different heating rates.
In order to estimate the kinetic parameters of heavy oil oxidation, the Kissinger method was employed [25]. This method allows for the calculation of the kinetic parameters of the oil oxidation process by linking the change in peak temperatures (Tp) of DSC curves with different temperature programs (β) to the Arrhenius parameters of the reaction (Equation (1)).
The Kissinger method was selected over other methods used for calculating kinetic parameters [26,27,28,29] due to the complexity of the process, making it challenging to choose a baseline. The Kissinger method was deemed a reasonable alternative as the peak temperatures needed for the calculations are only weakly dependent on the baseline choice.
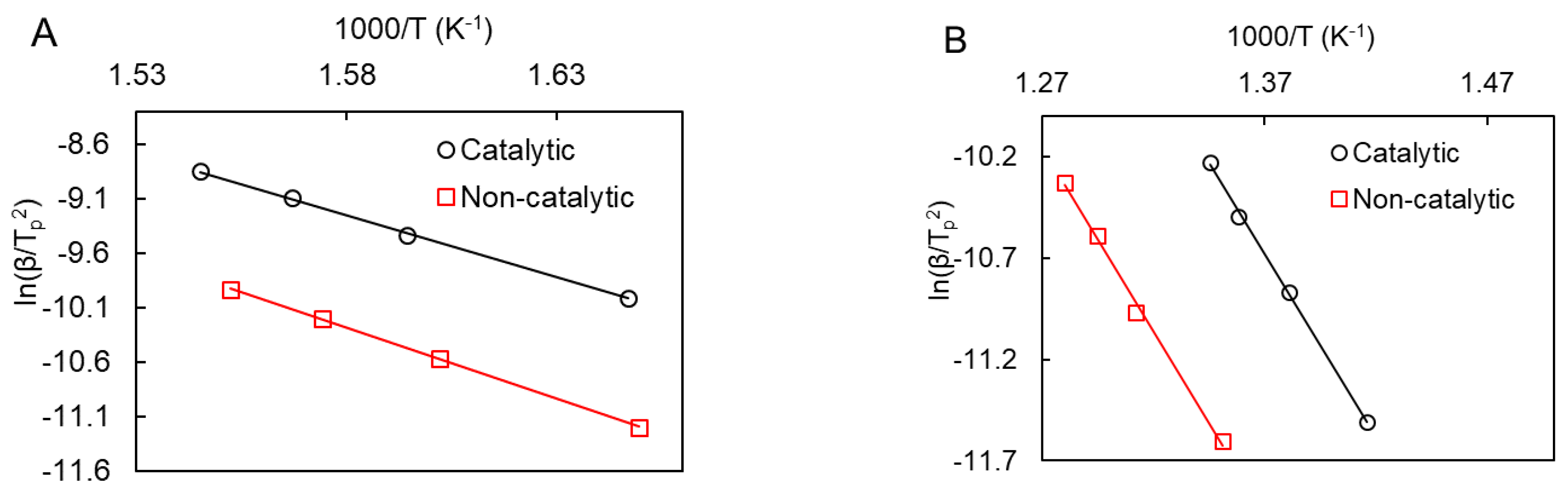
Figure 7 shows Kissinger plots for heavy oil oxidation in the presence and absence of manganese oxide nanoparticles. The obtained kinetic parameters for these processes are presented in Table 2.
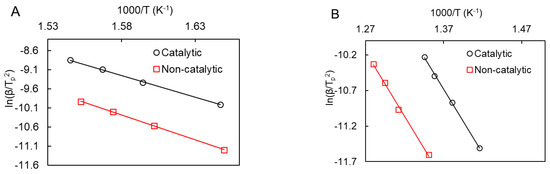
Figure 7.
Kissinger plots for catalytic and noncatalytic oxidation for LTO (A) and HTO (B).

Table 2.
Arrhenius parameters of oxidation processes.
The results from the kinetic parameters calculation demonstrate the significant impact of the synthesized nanoparticles on low-temperature oxidation. Table 2 reveals that both catalytic and noncatalytic processes have similar Arrhenius parameters, indicating comparable reaction rates. On the other hand, the high-temperature oxidation process exhibits a distinct pattern. The activation energy of the noncatalytic reaction is significantly lower, implying a faster reaction rate compared to the catalytic process. Despite this, the noncatalytic HTO has a lower pre-exponential factor A, which suggests a slower reaction rate compared to the catalytic oxidation reaction.
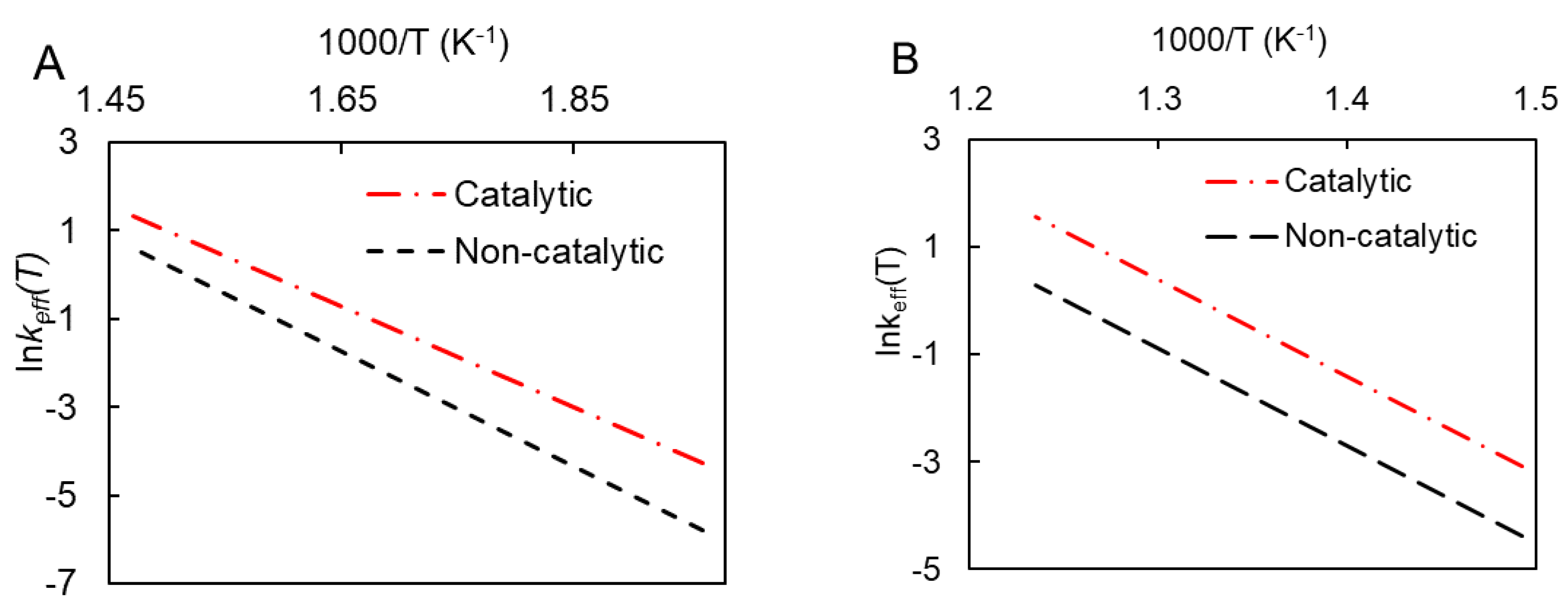
The combined effect of these two parameters on the reaction kinetics was evaluated by calculating the dependence of the effective rate constant (K) on the reciprocal temperature using the following equation:
Figure 8 illustrates that the rate constant difference between noncatalytic and catalytic combustion is smaller for LTO than for HTO. The results suggest that the acceleration of HTO’s catalytic process is primarily driven by a lower value of pre-exponential factor A.
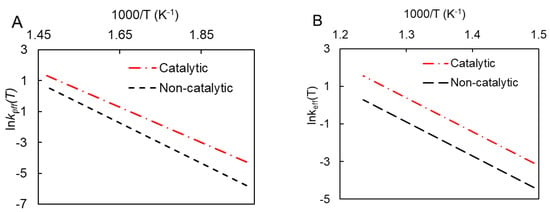
Figure 8.
Change in effective rate constants depending on temperature for catalytic and noncatalytic low-temperature (A) and high-temperature (B) oxidation.
The results show that the noncatalytic and catalytic processes have similar Arrhenius parameters, which means that the reaction rate is comparable for both processes. However, when it comes to the high-temperature oxidation process, there is a noticeable difference between the noncatalytic and catalytic reactions. The activation energy for the noncatalytic reaction is significantly lower, which implies that the reaction rate is faster than that of the catalytic process.
Despite the higher activation energy of the catalytic process, the results show that the catalytic oxidation reaction has a higher pre-exponential factor A. This indicates that the reaction rate of the catalytic process is faster than that of the noncatalytic reaction. This result is significant as it suggests that the synthesized nanoparticles play a significant role in enhancing the reaction rate of the catalytic high-temperature oxidation process.
The findings of this study highlight the impact that synthesized nanoparticles can have on the reaction rate of high-temperature oxidation processes. The results demonstrate that while the noncatalytic process may have a lower activation energy, the catalytic process has a higher pre-exponential factor A, which contributes to the overall faster reaction rate of the catalytic process. These findings have important implications for the design and optimization of catalytic processes for high-temperature oxidation.
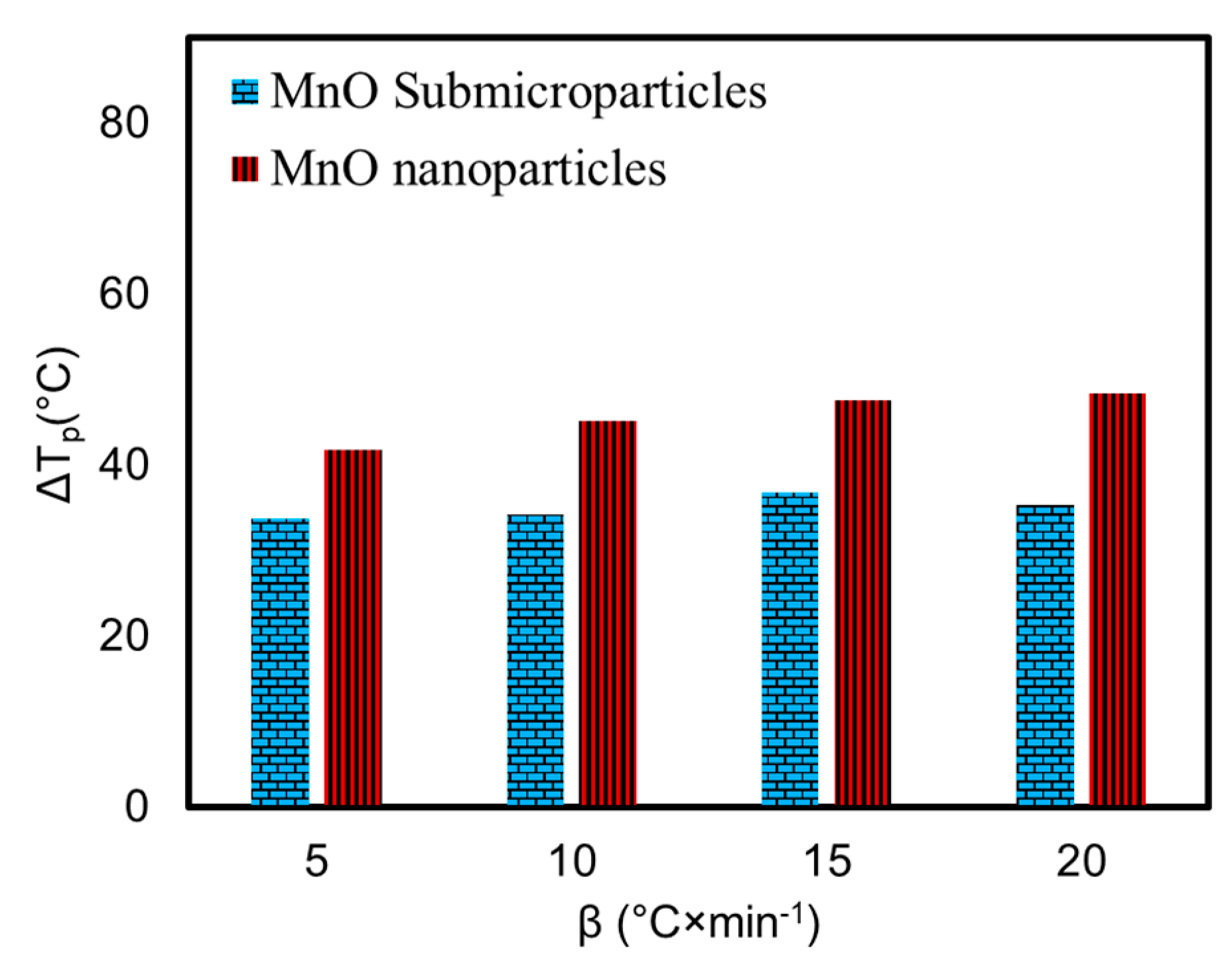
Figure 9 shows a comparative analysis of the effect generated by the application of manganese oxide particles with different sizes and shapes. As can be seen from Figure 9, the impact generated by manganese oxide sub-microparticles, which were obtained in our previous work [27] with an octahedral shape, has been found to be less significant than the impact of the manganese oxide nanoparticles obtained in the current work. It has been shown that manganese oxide sub-microparticles shift the high-temperature oxidation peak at different heating rates by 33.7; 34.2; 36.7, and 35.3 °C for 5, 10, 15, and 20 °C/min. However, this shift in the high-temperature oxidation region peaks in the presence of manganese oxide nanoparticles was found to be equal to 41.7, 45.2, 47.6, and 48.4 °C for 5, 10, 15, and 20 °C/min, respectively.
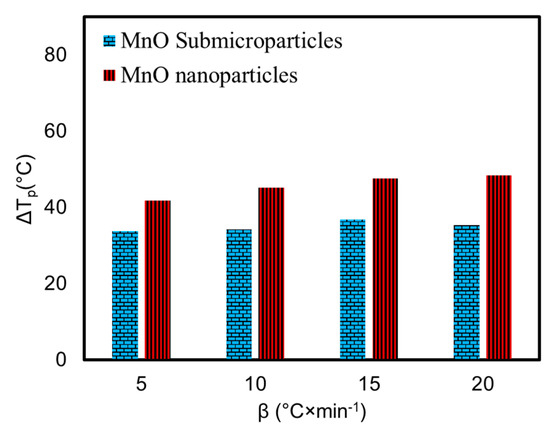
Figure 9.
Differences between peak temperatures (ΔTp) for heavy oil oxidation at different heating rates in the presence of MnO particles with different sizes and shapes.
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Materials
Manganese (III) tris-acetylacetonate (97%, Acros Organics), oleic acid (99%, Sigma Aldrich (Taufkirchen, Germany)), 1-octadecene (90%, Acros Organics), 1-dodecanol (98%, Acros Organics), methanol (99.9%). %, Sigma Aldrich (Taufkirchen, Germany)) were purchased and used without purification. To study the process of catalytic oxidation of heavy oils, we used Ashalcha oil (Tatarstan, Russia). A detailed description of the properties of the used heavy oil is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Viscosity, density, SARA fractions, and elemental analysis of the studied heavy crude oil.
3.2. Synthesis of MnO Nanoparticles
A total of 0.8 g of manganese (III) tris-acetylacetonate was dissolved in a mixture of 1.1 g of oleic acid, 10 mL of 1-octadecene, and 0.56 g of 1-dodecanol. The synthesis was carried out in a Parr Instruments 4560 batch reactor. The reaction mixture was heated to 270 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere and kept at this temperature for 1 h; the stirring speed was 100 rpm. Then the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and 100 mL of methanol was added to precipitate the product. Target nanoparticles were isolated by centrifugation and dried in a desiccator. The UP200Ht ultrasonic homogenizer was used for all ultrasound examinations.
3.3. MnO Nanoparticles Characterization
3.3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) is a powerful analytical technique that allows for the characterization of crystalline materials. The XRPD study performed using the MiniFlex 600 diffractometer offers several advantages over other methods. Firstly, the use of Cu Kα1 radiation provides high-quality data with high resolution and sensitivity. Secondly, the D/teX Ultra detector allows for efficient detection of the X-rays scattered by the sample, providing detailed information on the structure of the material. Thirdly, the study was conducted at a controlled temperature of 25 °C, which eliminates any temperature-related effects on the sample and ensures the reproducibility of the results. Fourthly, the use of a 2θ range of 2° to 100° in 0.02° steps and an exposure time of 0.24 s at each point allows for a comprehensive analysis of the sample. Additionally, the absence of sample rotation ensures that the results accurately represent the sample’s true structure. In conclusion, the XRPD study using the MiniFlex 600 diffractometer equipped with the D/teX Ultra detector offers a highly accurate, sensitive, and efficient method for characterizing crystalline materials.
3.3.2. Electron Microscopy Analysis
Electron microscopy analysis is a powerful tool for imaging and analyzing the structure and properties of materials at the nanoscale. In this study, SEM, EDX, and TEM analyses were acquired using a Hitachi HT7700 Excellence instrument. To prepare the sample, 10 μL of the nanoparticle suspension was placed on a carbon-coated copper grid and dried. This allowed for high-resolution imaging of the individual nanoparticles. The analysis was performed at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV in TEM mode, providing clear and detailed images of the particle structure and morphology. Particle size was estimated by measuring 100 individual particles, providing quantitative information on the size distribution of the nanoparticles. The use of SEM, EDX, and TEM in this study offers several advantages, including the ability to study the internal structure of materials, to analyze small structures in great detail, and to perform microanalysis for chemical composition. These capabilities make SEM, EDX, and TEM valuable tools for a wide range of applications in the research community.
3.3.3. Measurements of Nitrogen Adsorption and Desorption
The measurement of nitrogen adsorption and desorption is a crucial technique to determine the properties of materials and catalysts at a molecular level. In this study, the measurements were conducted at 77 K using the ASAP 2020 MP instrument (Micromeritics). The samples were degassed before the measurements to ensure accurate results. The adsorption and desorption isotherms consisted of about 80 points and provided valuable information about the specific surface area and pore size distribution of the synthesized catalyst. The specific surface area was calculated by the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method, which uses the relative pressure range of 0.05–0.30. The pore size distribution was calculated using the Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) method, which employs a cylindrical pore model. The use of nitrogen adsorption and desorption measurements in combination with these methods provides a comprehensive understanding of the properties of catalysts and materials, including the surface area, pore size, and distribution, making it a valuable tool in characterizing and optimizing these materials.
3.3.4. Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis is a powerful tool for studying the thermal behavior of materials and their physical and chemical changes during heating or cooling. The study of the thermal properties of materials provides valuable information about their behavior during processing and their stability under different conditions. The experiments were carried out using an STA 449 F1 Jupiter thermal analyzer, which is a state-of-the-art instrument with high accuracy and precision. The temperature range used in the experiments was from 30 to 600 °C, which is wide enough to cover the majority of the temperature range required for thermal analysis studies. The experiments were carried out in an air flow atmosphere, which is a commonly used environment for thermal analysis, providing a controlled and stable atmosphere for the experiments. The samples were prepared by mixing heavy oil and pure quartz sand with a fraction of 43–64 μm, and in the case of catalytic experiments, the initial oil sample contained 2.0 wt.% nanoparticles. This preparation method ensures that the sample is homogeneous and representative of the material being studied.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the optimization of in situ combustion with manganese (II) oxide nanoparticle-catalyzed heavy oil oxidation was studied in this paper. The synthesis and characterization of manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles were performed, and their catalytic activity in the high- and low-temperature oxidation of heavy oils was evaluated. The results showed that the synthesized nanoparticles had an average size of 17 ± 4 nm and a specific surface area of 38.2 ± 0.1 m2 g−1. The calculated reaction rates indicated that the rate of heavy oil oxidation was higher in the presence of the synthesized nanoparticles.
These findings demonstrate the potential of manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles as a catalyst for enhancing the in situ combustion process. The stabilized combustion front could improve the efficiency and effectiveness of heavy oil extraction, providing new opportunities for the development of sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies in the oil and gas industry. The results obtained in this study can also be applied to other types of fuels and combustion systems, as well as other fields, such as energy storage and conversion, catalysis, and environmental protection.
It should be noted that further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of the catalytic action of manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles and to optimize the synthesis process to produce nanoparticles with improved properties. The study of the long-term stability and durability of the nanoparticles under various conditions and the examination of their interactions with the environment are also essential for the practical application of these materials.
The obtained results indicated that the synthesized nanoparticles had promising catalytic activity in stabilizing the combustion front in the in situ combustion process. However, further studies are necessary to optimize the use of these nanoparticles in a commercial setting.
In future work, we plan to investigate the effects of varying the concentration and size of the nanoparticles, as well as their performance under different conditions. Additionally, we will conduct cost-benefit analyses and feasibility studies to assess the economic viability of using manganese oxide nanoparticles in in situ combustion technology on a larger scale.
Overall, this research provides a valuable contribution to the optimization of in situ combustion for heavy oil extraction and highlights the potential of using manganese oxide nanoparticles as a catalyst in this process.
This study provides a new insight into the optimization of in situ combustion by utilizing manganese (II) oxide nanoparticles as a catalyst. The results offer a promising approach to enhancing the stability of the combustion front and improving the efficiency of heavy oil extraction. The potential applications of this technology in various fields, such as energy and environmental protection, highlight the importance and relevance of this research.
Author Contributions
M.-A.K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Visualization, Supervision, Formal analysis, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Resources; A.A.E.: investigation and data curation; M.A.V.: Conceptualization, Reviewing and Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 22-73-00329, https://rscf.ru/en/project/22-73-00329/).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Meyer, R.F.; Attanasi, E.D.; Freeman, P.A. Heavy Oil and Natural Bitumen Resources in Geological Basins of the World: Map Showing Klemme Basin Classification of Sedimentary Provinces Reporting Heavy Oil or Natural Bitumen. US Geol. Surv. Open-File Rep. 2007, 2007, 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Kapustin, N.O.; Grushevenko, D.A. Global Prospects of Unconventional Oil in the Turbulent Market: A Long Term Outlook to 2040. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. d’IFP Energ. Nouv. 2018, 73, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumanyan, B.P.; Romanov, G.V.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Kayukova, G.P.; Petrukhina, N.N. Promising Aspects of Heavy Oil and Native Asphalt Conversion under Field Conditions. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2014, 50, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.G.; Laureshen, C.J.; Belgrave, J.D.M.; Ursenbach, M.G.; (Raj) Mehta, S.A. In Situ Combustion in Canadian Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Fuel 1995, 74, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanier, L.M.; Brigham, W.E. Upgrading of Crude Oil via in Situ Combustion. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2003, 39, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.W.; McNeil, J.S. How to Engineer an In-Situ Combustion Project. Oil Gas J. 1961, 58, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, K.; Lu, N.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced Oil Recovery Techniques for Heavy Oil and Oilsands Reservoirs after Steam Injection. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1190–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, G.; Salvador, S.; Debenest, G.; Thovert, J.F. New Granular Model Medium to Investigate Smoldering Fronts Propagation-Experiments. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 6780–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Guan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, C.; Wang, B.; Li, X. Propagation and Control of Fire Front in the Combustion Assisted Gravity Drainage Using Horizontal Wells. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelkhal, M.A.; Eskin, A.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Vakhin, A.V.A. V Thermal Study on Stabilizing the Combustion Front via Bimetallic Mn@Cu Tallates during Heavy Oil Oxidation. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5121–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, A.; Khelkhal, M.A.; Tajik, A.; Lapuk, S.E.; Rezaeisadat, M.; Eskin, A.A.; Rodionov, N.O.; Vakhin, A.V. Effect of Ligand Structure on the Kinetics of Heavy Oil Oxidation: Toward Biobased Oil-Soluble Catalytic Systems for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 14713–14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mishaal, O.F.; Suwaid, M.A.; Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Khelkhal, M.A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Djimasbe, R.; Zairov, R.R.; Saeed, S.A.; Vorotnikova, N.A.; Shestopalov, M.A. Octahedral Cluster Complex of Molybdenum as Oil-Soluble Catalyst for Improving In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Crude Oil: Synthesis and Application. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, S.M.; Scott, C.E.; Chen, Z.; Pereira-Almao, P. In-Situ Upgrading and Enhanced Recovery of Heavy Oil from Carbonate Reservoirs Using Nano-Catalysts: Upgrading Reactions Analysis. Fuel 2019, 252, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, N.; Mortazavi, Y.; Bahramian, A.; Khodatars, L.; Khodadadi, A.A. Enhanced Pyrolysis and Oxidation of Asphaltenes Adsorbed onto Transition Metal Oxides Nanoparticles towards Advanced In-Situ Combustion EOR Processes by Nanotechnology. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 477, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, M.A.; Yuan, C.; Bolotov, A.V.; Minkhanov, I.F.; Mehrabi-Kalajahi, S.; Saifullin, E.R.; Marvanov, M.M.; Baygildin, E.R.; Sabiryanov, R.M.; Rojas, A. Effect of Copper Stearate as Catalysts on the Performance of In-Situ Combustion Process for Heavy Oil Recovery and Upgrading. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelkhal, M.A.; Lapuk, S.E.; Ignashev, N.E.; Eskin, A.A.; Glyavin, M.Y.; Peskov, N.Y.; Krapivnitskaia, T.O.; Vakhin, A.V. A Thermal Study on Peat Oxidation Behavior in the Presence of an Iron-Based Catalyst. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M. Influence of Reservoir Rock Composition on Crude Oil Pyrolysis and Combustion. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1993, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Filgueiras, E.; Morales, A.; Scott, C.E.; Gonzalez-Gimenez, F.; Pierre Embaid, B. Use of a Dispersed Iron Catalyst for Upgrading Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Using Methane as Source of Hydrogen. Fuel 2003, 82, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Chen, Q.; Castanier, L.M.; Kovscek, A.R. Improved In-Situ Combustion Performance with Metallic Salt Additives. In Proceedings of the SPE Western Regional Meeting; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Irvine, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 421–437. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrlu, Y.H.; Maham, Y.; Tan, X.; Babadagli, T.; Gray, M. Enhancement of the Efficiency of in Situ Combustion Technique for Heavy-Oil Recovery by Application of Nickel Ions. Fuel 2013, 105, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilnezhad, E.; Karimian, M.; Choi, H.J. Synthesis and Thermal Analysis of Hydrophobic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Improving In-Situ Combustion Efficiency of Heavy Oils. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanam, U.U.; Koh Yoo, K.H.; Castanier, L.; Kovscek, A.R. Investigation of the Effects of Select Metal Nanoparticles on Heavy Oil Combustion in Porous Media. Energy Fuels 2019, 34, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanam, U.U.; Kovscek, A.R. Analysis of the Effects of Copper Nanoparticles on In-Situ Combustion of Extra Heavy-Crude Oil. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 152, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Z. Enhanced in Situ Combustion of Heavy Crude Oil by Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 3399–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N.; Hassan, A.; Vitale, G. Comparing Kinetics and Mechanism of Adsorption and Thermo-Oxidative Decomposition of Athabasca Asphaltenes onto TiO2, ZrO2, and CeO2 Nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 484, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.; Argel, B.L.; Nassar, N.N.; Franco, C.A.; Cortés, F.B. Kinetics and Mechanisms of the Catalytic Thermal Cracking of Asphaltenes Adsorbed on Supported Nanoparticles. Pet. Sci. 2016, 13, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galukhin, A.V.; Khelkhal, M.A.; Eskin, A.V.; Osin, Y.N. Catalytic Combustion of Heavy Oil in the Presence of Manganese-Based Submicroparticles in a Quartz Porous Medium. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 11253–11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelkhal, M.A.; Eskin, A.A.; Sharifullin, A.V.; Vakhin, A.V. Differential Scanning Calorimetric Study of Heavy Oil Catalytic Oxidation in the Presence of Manganese Tallates. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galukhin, A.; Nosov, R.; Eskin, A.; Khelkhal, M.; Osin, Y. Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles Immobilized on Silica Nanospheres as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Heavy Oil Oxidation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8990–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.J.; Kondrat, S.A.; Taylor, S.H. Total Oxidation of Naphthalene Using Copper Manganese Oxide Catalysts. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandon, M.; Carnö, J.; Järås, S.; Björnbom, E. Total Oxidation Catalysts Based on Manganese or Copper Oxides and Platinum or Palladium II: Activity, Hydrothermal Stability and Sulphur Resistance. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 180, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Luo, J.; Deng, C.C.; Guo, Y.A.; Zhao, S.K.; Zhou, H.; Wei, S. Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene with Molecular Oxygen over Manganese Tetraphenylporphyrin Supported on Chitosan. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 338, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry Thermodynamics, Structure, and Change; WH Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Isakov, D.R.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Shaposhnikov, D.A.; Mingazov, B.M. Physico-Chemical and Technological Aspects of the Use of Catalysts during In-Situ Combustion for the Production of High-Viscosity Crude Oils and Natural Bitumens. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2015, 50, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).