Evaluation of ·OH Production Potential of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected on TiO2-Supporting Quartz Filters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
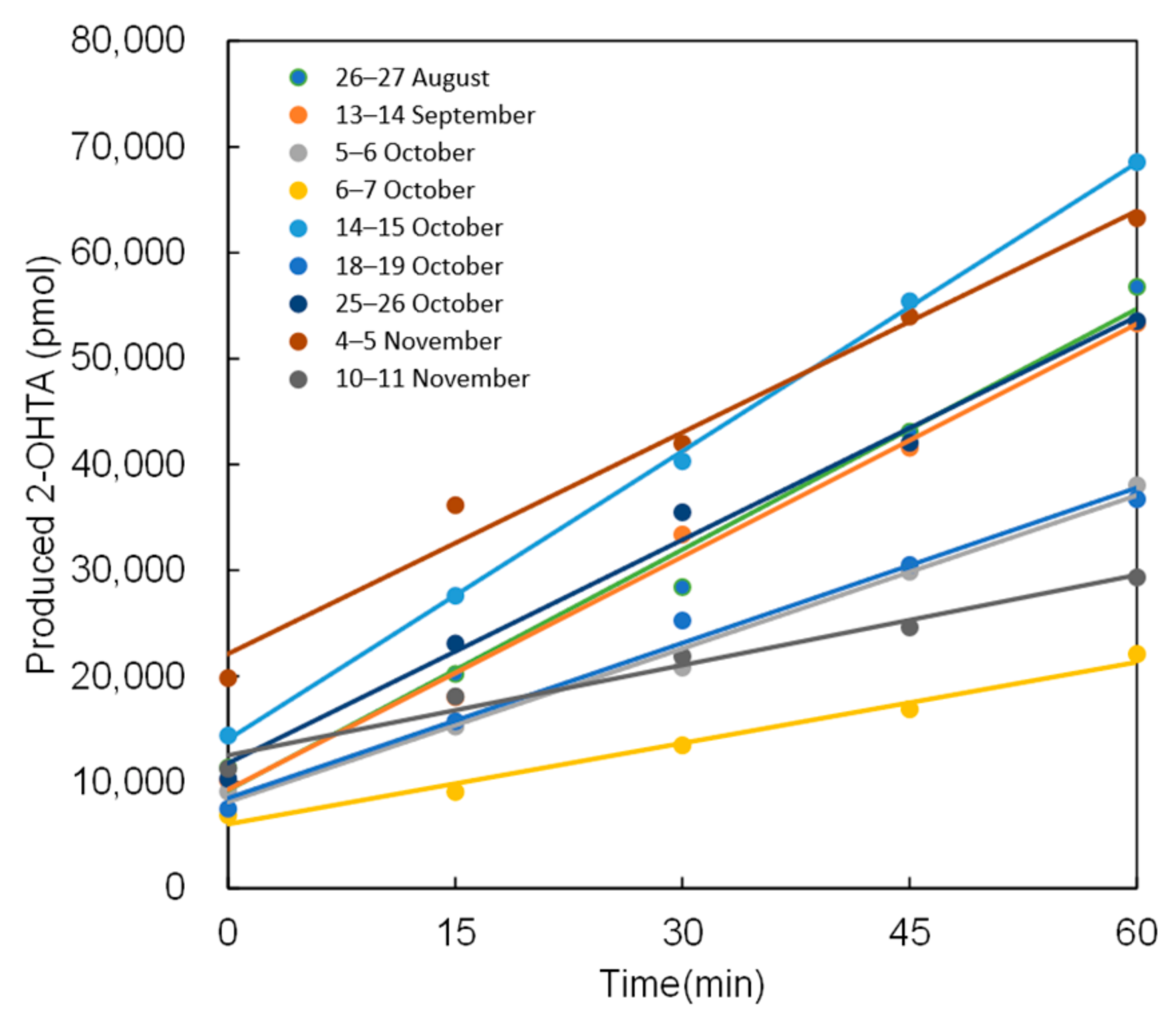
2.1. ·OH Production Potential of PM2.5
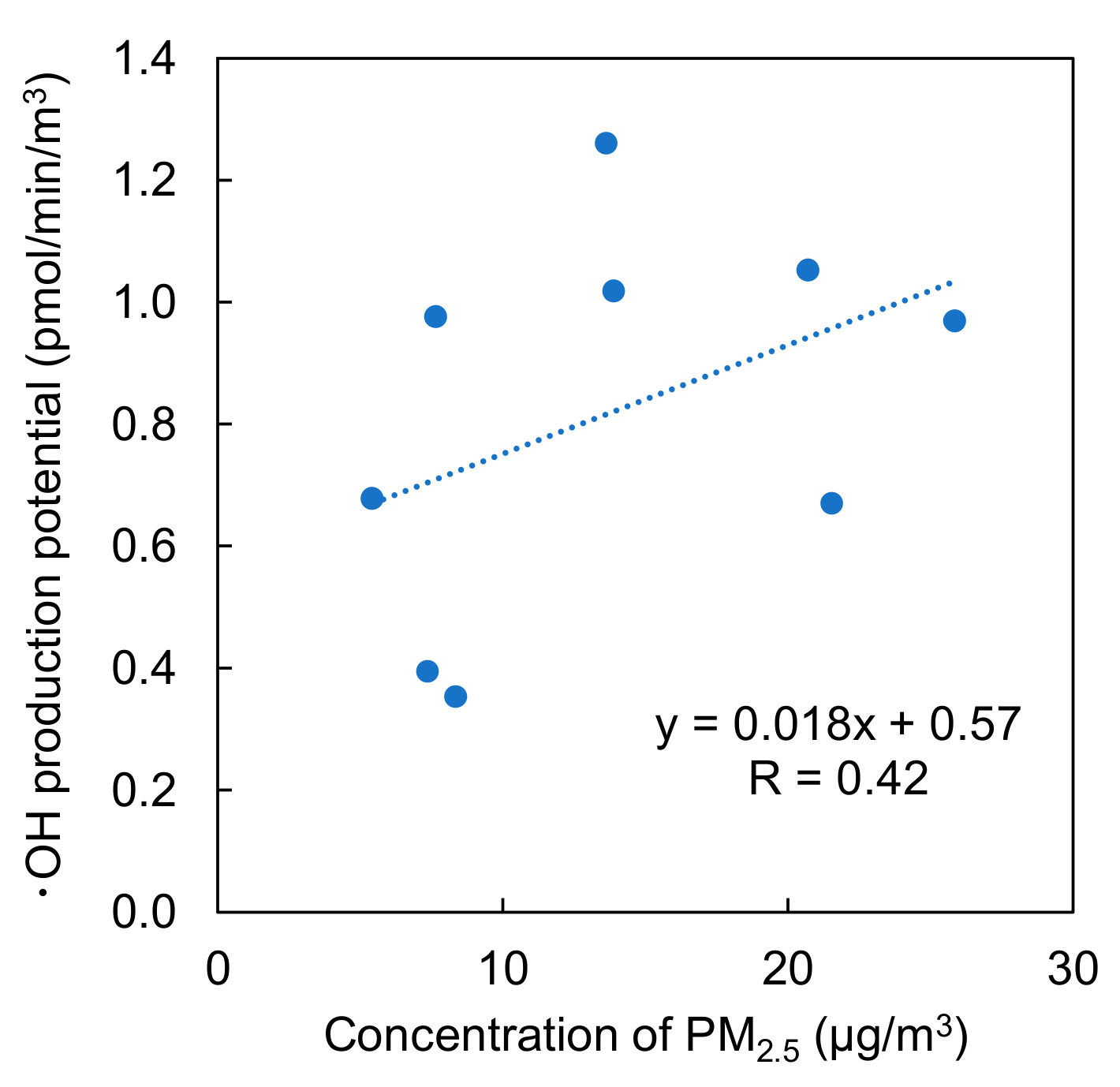
2.2. Attribution of ·OH Production Potential
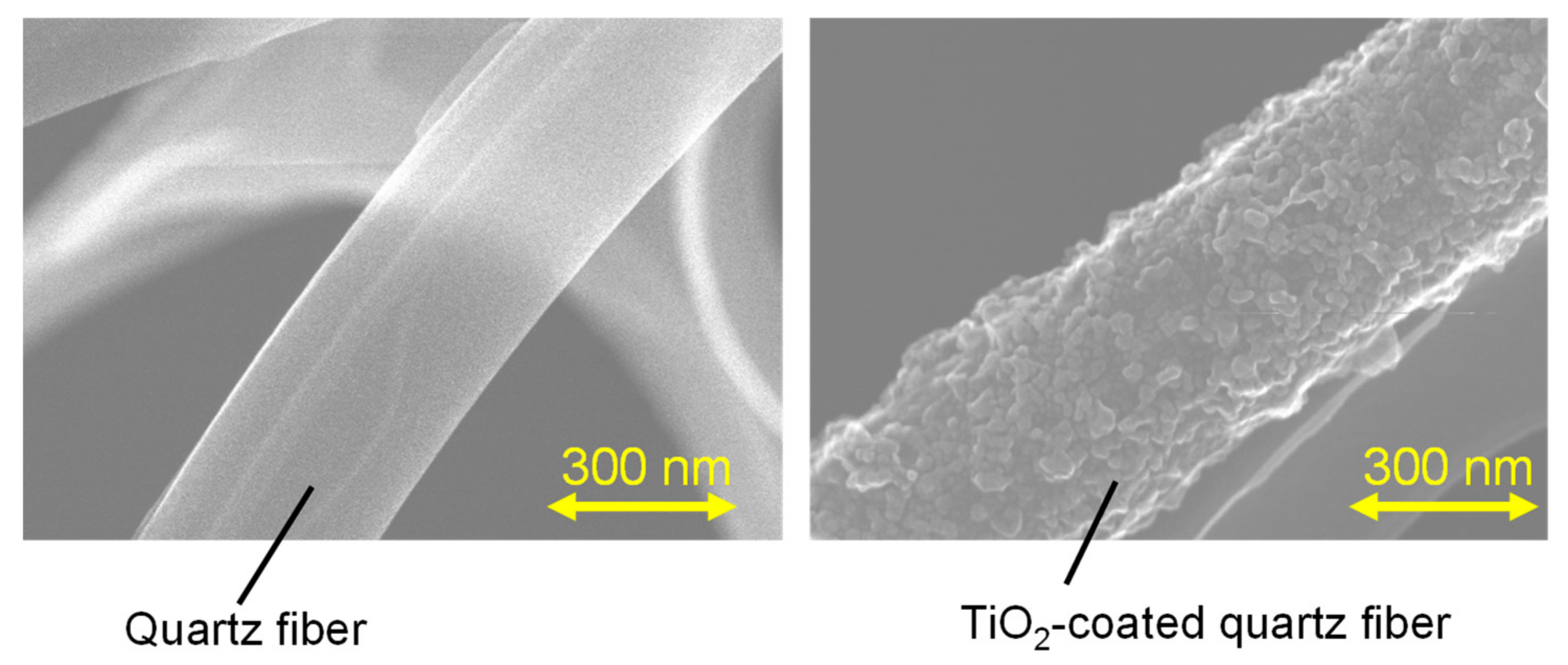
2.3. Reducing the ·OH Production Potential of PM2.5 through UV Irradiation on the TiO2 Filter
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
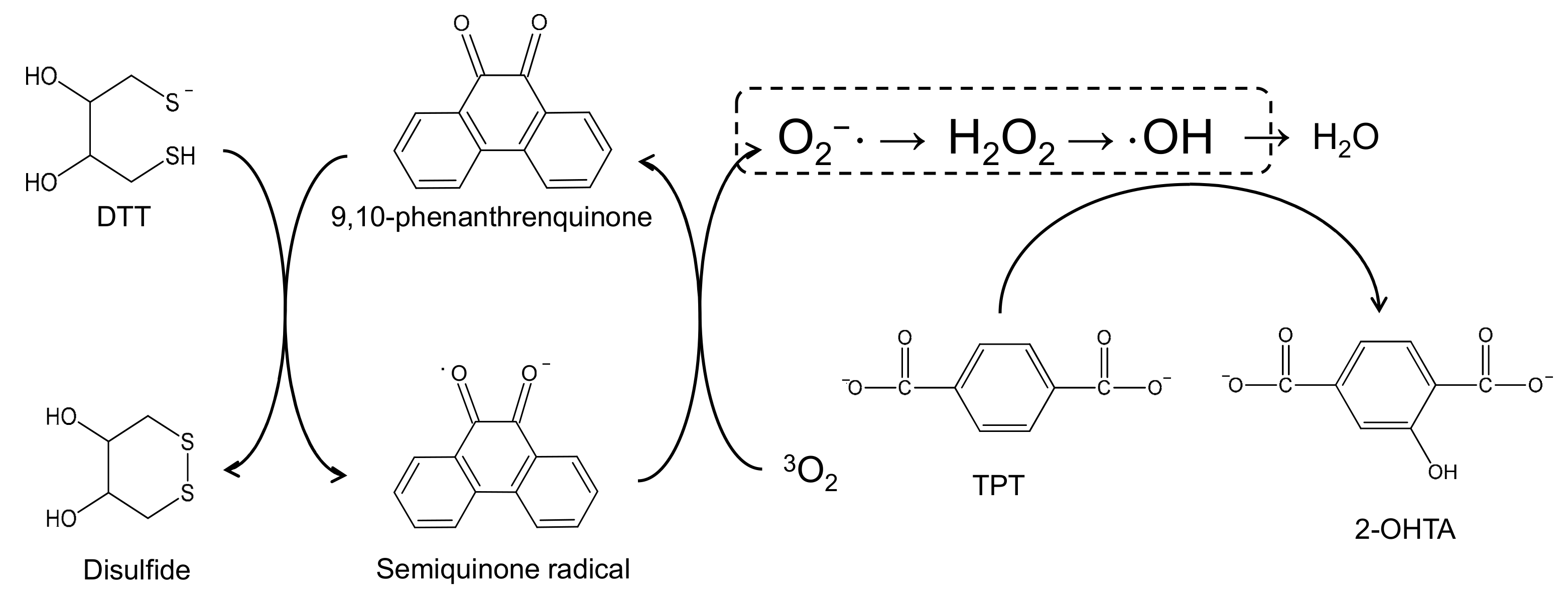
3.2. Measurement of the ·OH Production Potential of PM2.5
3.2.1. Sampling PM2.5 on the Quartz Filter
3.2.2. FIA-TPT Assay
3.3. OC/EC Analysis
3.4. Reducing the ·OH Production Potential of PM2.5
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Haines, A.; Müzel, T. Loss of life expectancy from air pollution compared to other risk factors: A worldwide perspective. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A., III; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G.; Speizer, F.E. An Association between Air Pollution and Mortality in Six US Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Burnett, R.T.; Goldberg, M.S.; Hoover, K.; Siemiatycki, J.; Abrahamowicz, M.; White, W.H. Validation of the Harvard Six Cities Study of particulate air pollution and mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laden, F.; Schwartz, J.; Speizer, F.E.; Dockery, D.W. Reduction in fine particulate air pollution and mortality: Extended follow-up of the Harvard Six Cities study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Thun, M.J.; Namboodiri, M.M.; Dockery, D.W.; Evans, J.S.; Speizer, F.E.; Heath, C.W., Jr. Particulate air pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of U.S. adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thurston, G.D.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Godleski, J.J. Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution—Epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, N.; Ohkubo, N.; Ohyama, K.; Nakashima, K.; Kuroda, N. Chemiluminescence assay for quinones based on generation of reactive oxygen species through the redox cycle of quinone. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 393, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, Y.; Bekki, K.; Chung, S.W.; Tang, N.; Toriba, A.; Taguchi, K.; Hayakawa, K. Oxidative stress more strongly induced by ortho- than para-quinoid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in A549 cells. J. Health Sci. 2009, 55, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, R.; Kumagai, Y.; Nakai, Y.; Ishii, T. 9,10-phenanthrenequinone in diesel exhaust particle downregulates Cu, Zn-SOD and HO-1 in human pulmonary epithelial cells: Intracellular ion scavenger 1,10-phenanthroline affords protection against apoptosis. Free Radical Bio. Med. 2005, 38, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Furuyama, A.; Koike, E.; Kobayashi, T. Oxidative-stress potency of organic extracts of diesel exhaust and urban fine particles in rat heart microvessel endothelial cells. Toxicology 2003, 187, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Envron. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrito, G.L.; Cueto, R.; Dellinger, B.; Pryor, W.A. Quinoid redox cycling as a mechanism for sustained free radical generation by inhaled airborne particulate matter. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Miguel, A.H.; Kumagai, Y.; Schmitz, D.A.; Signgh, M.; Eiguren-Fernadez, A.; Froines, J.R. Redox activity of airborne particulate matter at different sites in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, J.G.; Anastasio, C. On dithiothreitol (DTT) as a measure of oxidative potential for ambient particles: Evidence for the importance of soluble transition metals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11317–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, E.; Reponen, T.; Willeke, K.; Grinshpun, S.A.; Choi, K. Collection of fungal spores on air filters and spore reentrainment from filters into air. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddineni, A.K.; Das, D.; Damodaran, R.M. Inhibition of particle bounce and re-entrainment using oil-treated filter media for automotive engine intake air filtration. Powder Technol. 2017, 322, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, O.; Pironti, C.; Venier, M.; Proto, A. An innovative filtering system for the handling of asbestos-based products: Improvement of safety and quality of work in analysis laboratories. Toxics 2022, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedanekar, R.S.; Shaikh, S.K.; Rajpure, K.Y. Thin film photocatalysis for environmental remediation: A status review. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 931–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscetta, M.; Russo, D. Photocatalytic Applications in Wastewater and Air Treatment: A Patent Review (2010–2020). Catalysts 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xin, X.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y. Aluminium-Based Plastic Photocatalysis. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2017, 34, 1600357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglie, C.D.; Pal, S.; Murgolo, S.; Licciulli, A.; Mascolo, G. Investigation of Photocatalysis by Mesoporous Titanium Dioxide Supported on Glass Fibers as an Integrated Technology for Water Remediation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, A.; Alsheheri, A.Z.; Alsaggaf, W.T.; Al-Hajji, L.A.; Zaki, Z.I. Promoted hexavalent chromium ion photoreduction over visible-light active RuO2/TiO2 heterojunctions prepared by solution process. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2022, 429, 113906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheheri, S.Z.; Shawky, A.; Alsaggaf, W.T.; Zaki, Z.I. Visible-light responsive ZnSe-anchored mesoporous TiO2 heterostructures for boosted photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 305701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinque, B.; Escobedo, S.; de Lasa, H. Hydrogen Production via Pd-TiO2 Photocatalytic Water Splitting under Near-UV and Visible Light: Analysis of the Reaction Mechanism. Catalysts 2021, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, K.; Sekine, Y.; Ksukubo, Y.; Sohara, K. Photocatalytic degradation fine particulate matter (PM2.5) collected on TiO2 supporting quartz fibre filter. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohara, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Sun, X.; Misawa, K.; Sekine, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) collected on TiO2-supporting quartz fibre filters. Catalyst 2021, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, K.; Sohara, K.; Kumai, Y.; Kusukubo, Y.; Sekine, Y. Photocatalytic reduction of oxidative potential of particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5). Indoor Environ. 2019, 22, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, R.; Wei, J.; Verma, V. Rethinking Dithiothreitol-Based Particulate Matter Oxidative Potential: Measuring Dithiothreitol Consumption versus Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6507–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Qiu, X.; Hu, D. Pollutants from primary sources dominate the oxidative potential of water-soluble PM2.5 in Hong Kong in terms of dithiothreitol (DTT) consumption and hydroxyl radical production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, J.; Qin, W.; Ahmad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xin, K.; Ai, J. Oxidative potential associated with water-soluble components of PM2.5 in Beijing: The important role of anthropogenic organic aerosols. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.; Schauer, J.J.; DeMinter, J.T.; Turner, J.J.; Smith, D.; Cary, R.A. Validation of a semi-continuous instrument for elemental carbon and organic carbon using a thermal-optical method. Atmons. Environ. 2004, 38, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y. Human health effect of particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5). Indoor Environ. 2014, 17, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.E.; Arnold, W.A.; McNeill, K. Terephthalate as a probe for photochemically generated hydroxyl radical. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, S. Estimation of disulfide bonds using 2-nitro-5-thiosulfobenzoic acid: Limitations. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 145, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Crow, D.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Merrifield, T. Comparison of IMPROVE and NIOSH Carbon Measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
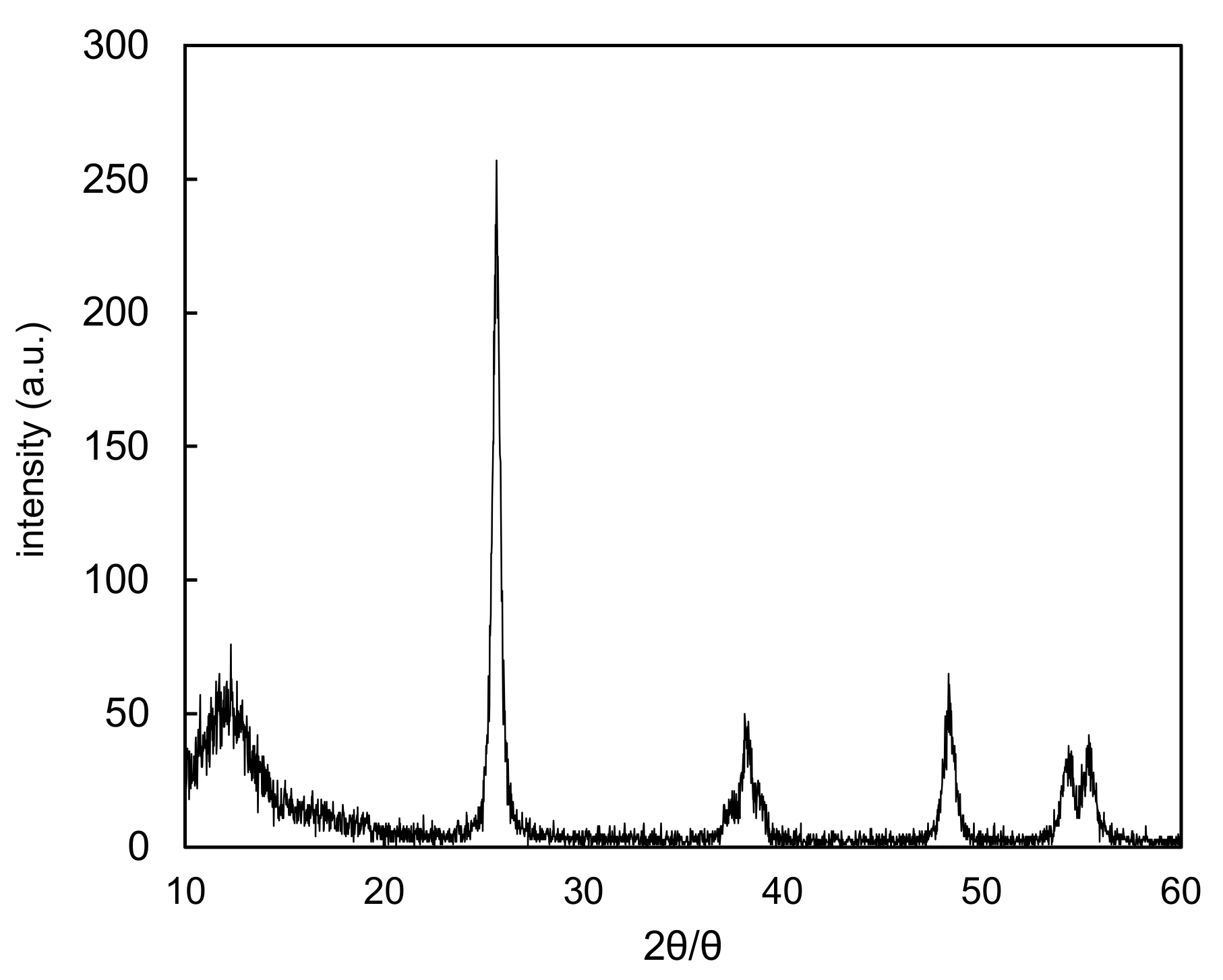


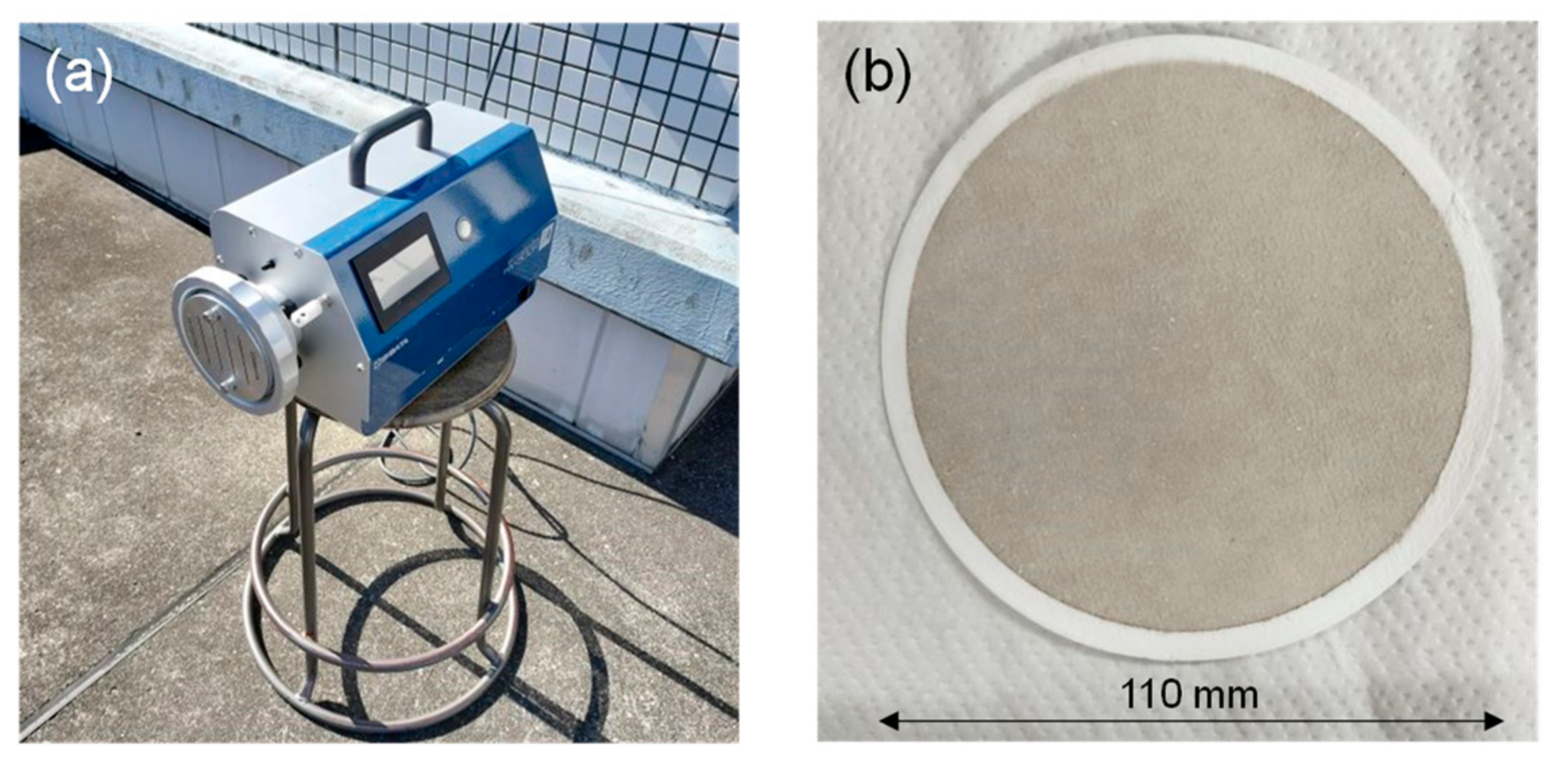
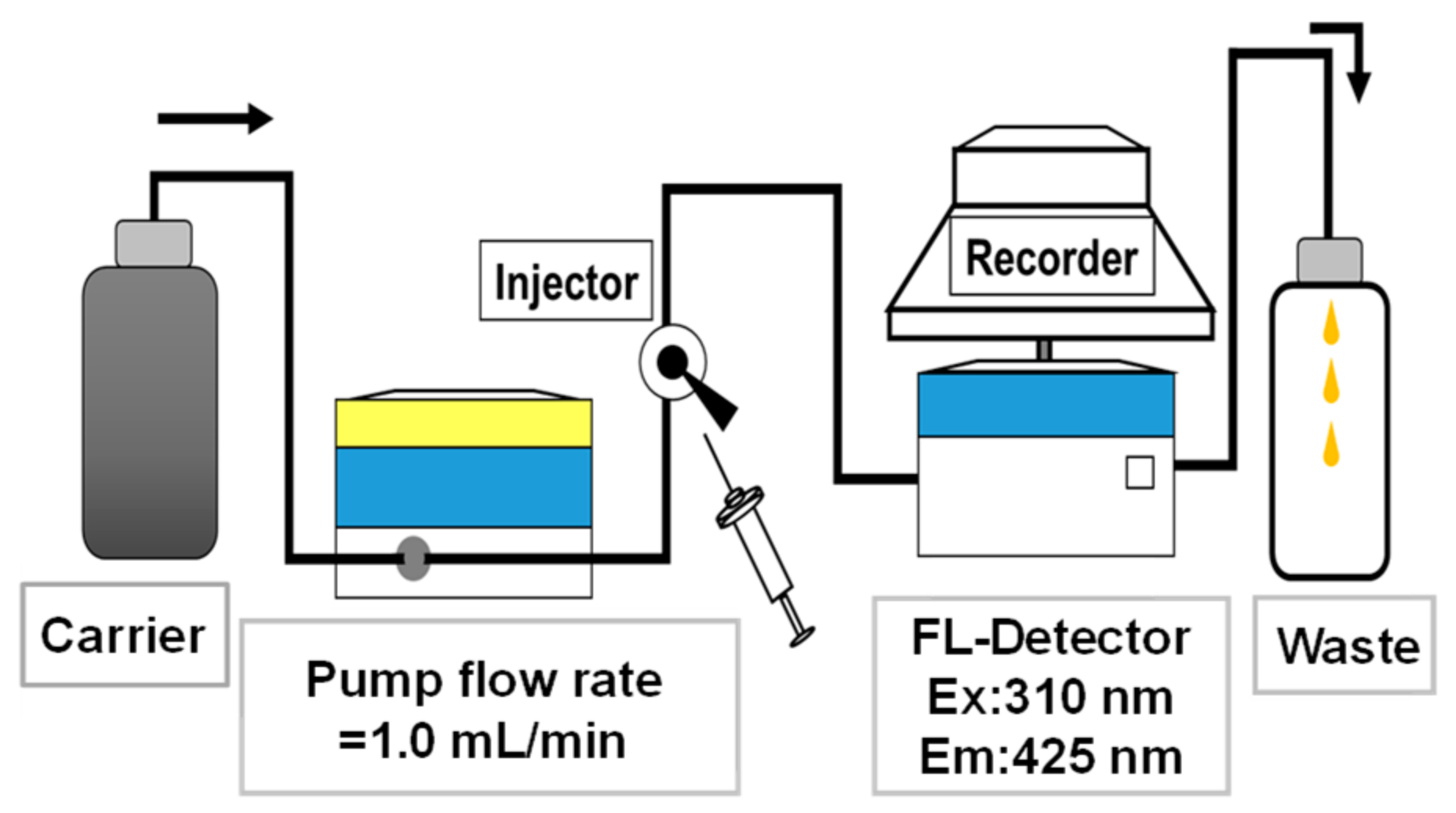
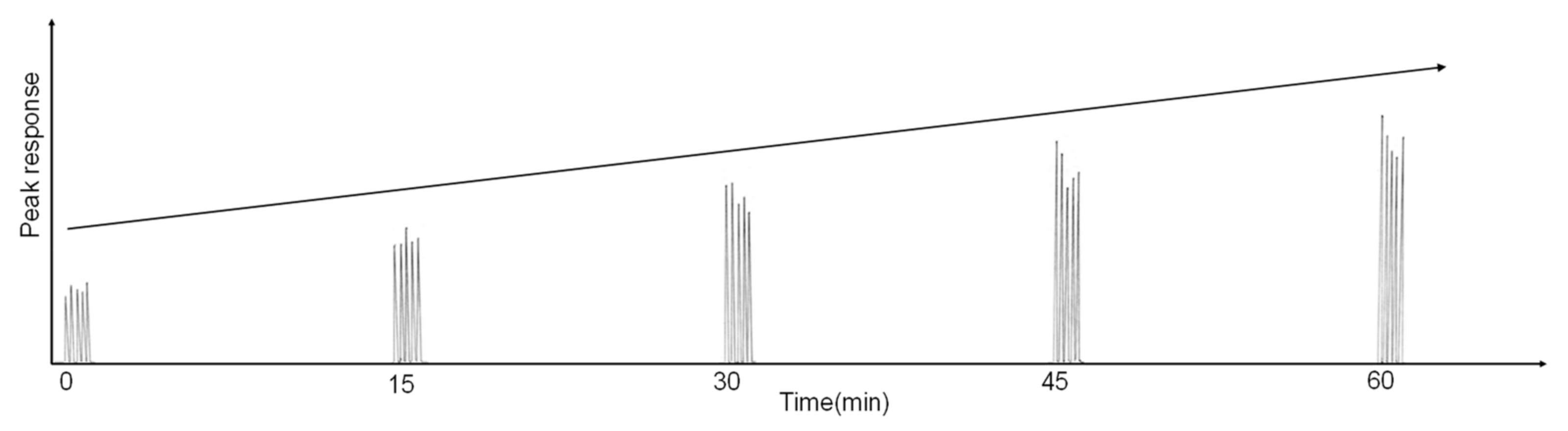
| Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|
| 2-OHTA | 2-hydroxyterephtalic acid |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| EC | Elemental carbon |
| FE-SEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscope |
| FIA | Flow injection analysis |
| IMPROVE | Interagency monitoring of protected visual environments |
| OC | Organic carbon |
| PAH quinones | Quinoid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter 2.5 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TPT | Disodium terephthalate |
| TiO2 filter | TiO2-supporting quartz filter |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| Fraction | Concentration (µg/m3) | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient between Concentration and ·OH Production Potential (r) |
|---|---|---|
| OC1 | 0.063 ± 0.014 | −0.41 |
| OC2 | 0.68 ± 0.26 | 0.60 |
| OC3 | 0.67 ± 0.22 | 0.81 * |
| OC4 | 0.16 ± 0.047 | 0.78 ** |
| EC1 | 1.2 ± 0.50 | 0.72 ** |
| EC2 | 0.17 ± 0.051 | 0.48 |
| EC3 | 0.028 ± 0.0076 | 0.75 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohara, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Sekine, Y. Evaluation of ·OH Production Potential of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected on TiO2-Supporting Quartz Filters. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091016
Sohara K, Yamauchi K, Sekine Y. Evaluation of ·OH Production Potential of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected on TiO2-Supporting Quartz Filters. Catalysts. 2022; 12(9):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohara, Koki, Katsuya Yamauchi, and Yoshika Sekine. 2022. "Evaluation of ·OH Production Potential of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected on TiO2-Supporting Quartz Filters" Catalysts 12, no. 9: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091016
APA StyleSohara, K., Yamauchi, K., & Sekine, Y. (2022). Evaluation of ·OH Production Potential of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Collected on TiO2-Supporting Quartz Filters. Catalysts, 12(9), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091016







