Abstract
Metal organic framework (MOF) is a type of porous organic material. In this work, three catalysts loaded with noble metal Pt were prepared by NaBH4 reduction method with three different morphologies of Ce–MOF as carriers. Their physicochemical properties were characterized by XRD, Raman, FTIR, N2 adsorption, SEM, XPS, and TGA. The catalytic performances of different catalysts were evaluated via toluene oxidation and CO2 selectivity. Rod–shaped Pt/MOF–BTC exhibited best catalytic performance compared to Pt/MOF–808 and Pt/UiO–66, its T50 and T90 were 140 °C and 149 °C, respectively. After deducting the effect of specific surface, Pt/MOF–BTC still had the lowest apparent activation energy (62.8 kJ·mol−1), which is due to the abundant atomic Pt and oxygen vacancy content on its surface. After the reaction, the structure of Pt/MOF–BTC may become amorphous according to XRD results. Furthermore, the presence of amorphous structure had no effect on the catalytic activity of the catalyst. In the stability test of Pt/MOF–BTC to toluene oxidation, both toluene conversion and CO2 selectivity remained at 100%, and remained stable for 11 h. Moreover, Pt/MOF–BTC also had better resistance to high weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) or water resistance. The catalyst maintained high catalytic activity for 3 times reusability. This study provides valuable experience for the future work of MOF in the field of VOC catalytic oxidation.
1. Introduction
Most volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are toxic and harmful to human beings. The emission of VOCs is increasing year by year. The sources of VOCs are numerous, such as automobile industries, fuel, chemical industries, combustion, printing presses, insulating materials, office supplies, and printers [1,2,3,4]. Most of them are toxic and harmful to human beings. Moreover, VOCs can react with other gases or particles in the air to form secondary aerosol which is one of the major air pollutants and can cause ozone layer destruction, photochemical smog, and greenhouse effect. Therefore, the elimination of VOCs is of great urgency. Many technologies have been developed in recent years to remove VOCs, including adsorption [5,6,7], photocatalysis [8,9], catalytic oxidation, plasma, biological, and combustion [10,11,12,13,14]. Among them, catalytic oxidation has attracted great interest due to its properties by which it can convert VOCs into carbon dioxide and water in an environmentally friendly way under moderate conditions without producing other secondary pollutants.
In various catalysts used for the catalytic oxidation of VOCs, noble metal catalysts have been considered to be very promising due to their excellent catalytic activity and unique physicochemical properties. The traditional supports of noble metal catalysts are usually metal oxides and molecular sieves [15]. By adding Pt on nanorod CeO2 for the catalytic oxidation of toluene, the catalyst exhibited excellent catalytic activity. This may be due to its higher oxygen vacancy concentration, which may be related to the exposed crystal plane [16]. In other research, it was found that the precursor of Pt nanoparticles and the morphologies of TiO2 support had an effect on the electronegativity of Pt on the catalyst surface and thus affecting the catalytic activity of the catalyst [17,18].
In recent years, as an emerging porous material, metal organic frameworks (MOFs) have been studied in multiple fields, such as adsorption [19], photocatalysis [20], proton–conducting membranes [21], drug delivery [22], chemical sensors [23], and electrocatalysis [24]. They exhibit excellent physical and chemical characteristics. MOFs have been considered as an excellent catalyst support due to its huge specific surface area, regular channel, and adjustable aperture. Among many MOFs materials, Ce–MOFs have been widely studied due to cerium 4f orbitals being beneficial for the formation of oxygen vacancy [25]. For instance, Zhang et al. [26] synthesized CeO2 derived from Ce–BTC (benzene tricarboxylate) used for the oxidation of CO which showed great catalytic activity on account of the higher oxygen vacancy content.
In this study, three different Ce–MOFs (MOF–808, UiO–66, and MOF–BTC) were synthesized via hydrothermal and solvothermal method. With the loading of Pt to different Ce–MOF, this research investigated the effect of carriers on the content of Ce3+, oxygen vacancies, and Pt species. The vibration of surface chemical state and structure properties over different catalysts were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and Raman spectra were performed to test the difference of functional groups between different catalysts. Thermogravimetric analysis was carried out to investigate the thermal stability of samples, and the catalytic oxidation of toluene was tested to evaluate the catalytic activity of the obtained Pt/Ce–MOF. Furthermore, the recycle stability, long–time operation and water resistance were measured to evaluate the catalytic activity to toluene combustion.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalysts Characterization
2.1.1. Phase and Stability Analysis
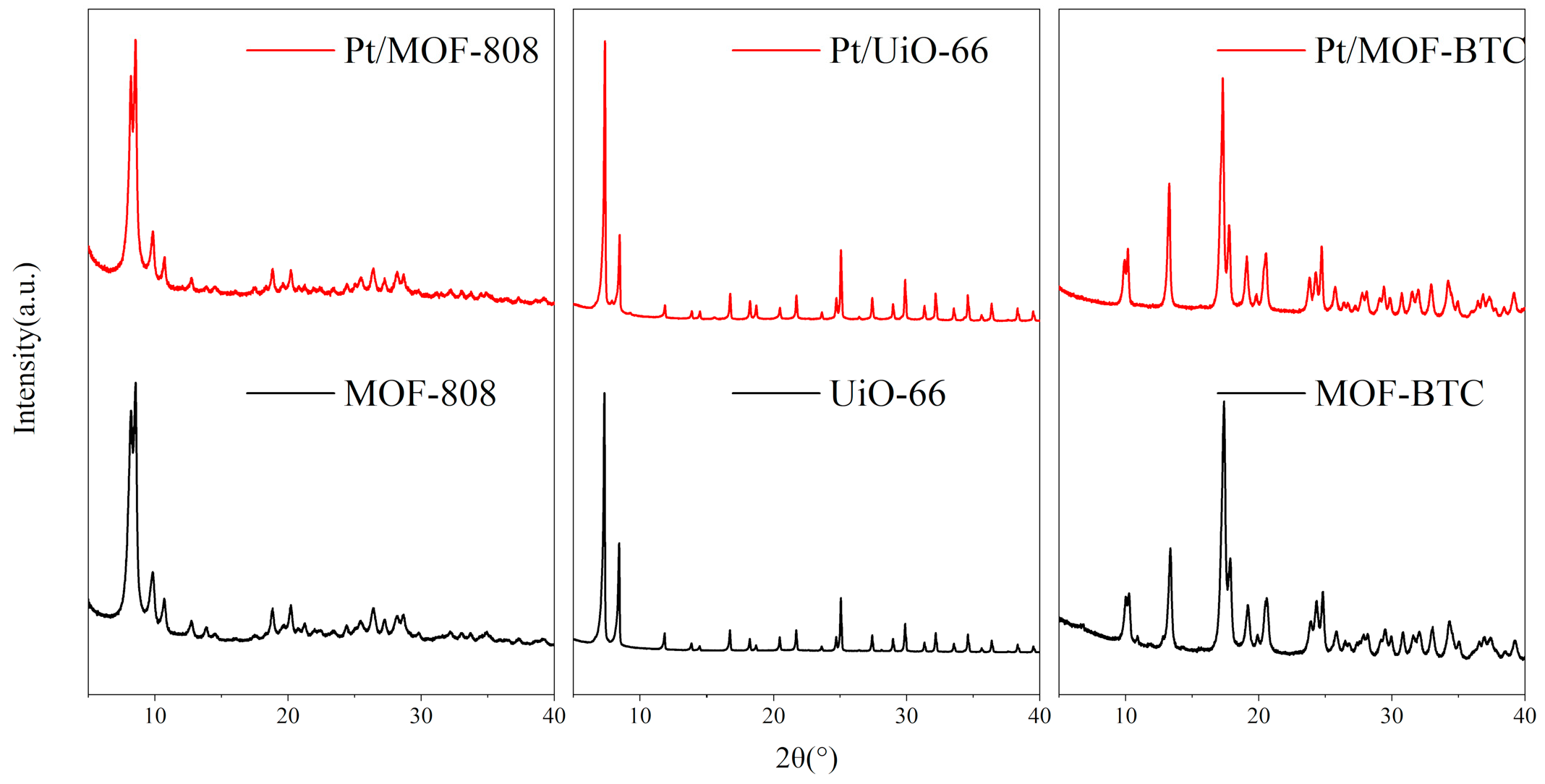
To study the difference of phase composition, the XRD patterns of these catalysts were presented in Figure 1. These were consistent with previous literature [27]. The diffraction peaks of all samples remained unchanged irrespective of Pt was added, indicating that all three MOFs were stable. Additionally, there was no peak assigned to Pt or PtOX, suggesting the high dispersion of Pt species [16,28].
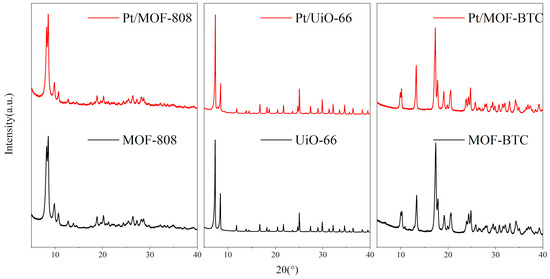
Figure 1.
The XRD patterns of different catalysts.
The thermal stability of three Ce–MOFs was evaluated with thermogravimetric analysis under air atmosphere (supplementary Figure S1). The initial weight loss stage below 150 °C was assigned to the evaporation of physically adsorbed water on the catalyst surface [29,30,31]. The subsequent weight loss was related to the volatilization of residual DMF and part of coordinated water. With the further increase of temperature, the framework decomposition of three Ce–MOFs was observed at 300 °C, 330 °C, and 388 °C. Moreover, the complete decomposition temperature of MOF–BTC was found at 428 °C, which was 58 °C and 63 °C higher than that of MOF–808 and UiO–66, indicating the better thermal stability of rod–shaped MOF–BTC [32].
2.1.2. Morphology and Pore Structure Analysis
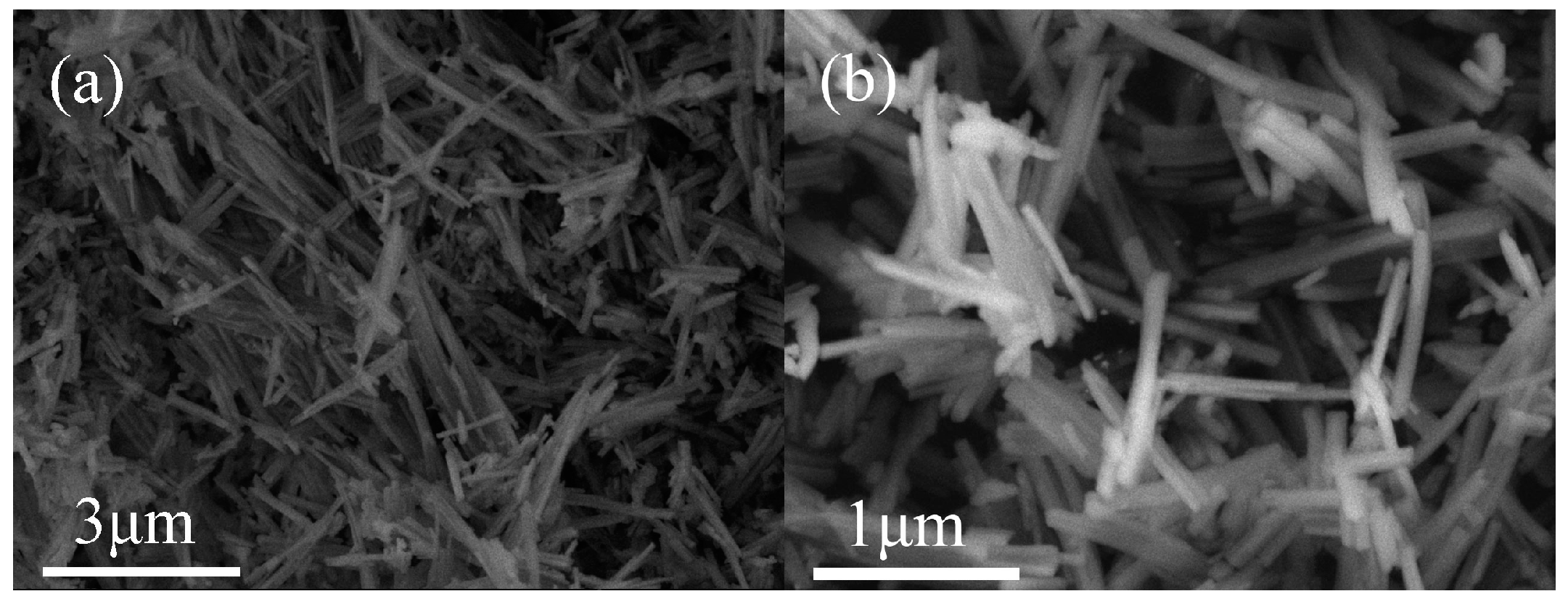
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of catalysts before and after the loading of Pt are demonstrated in Figure 2 and Figure S2. As shown in Figure 2, MOF–BTC displayed stick morphology, while MOF–808 and UiO–66 catalysts exhibited granular morphology (Figure S2). MOF–BTC had a more regular shape compared to MOF–808 and UiO–66. The particle size of UiO–66 is larger, which could be related to the ligands used in the synthesis of MOFs. The different morphology of the support indicates that the crystal growth mode is different, which further leads to the difference of Ce coordination environment.
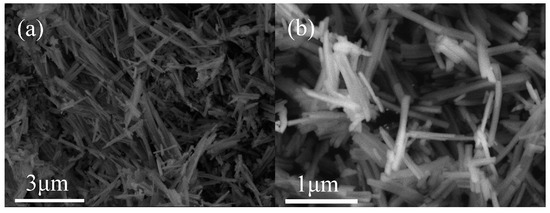
Figure 2.
The SEM images of catalysts: (a) MOF–BTC and (b) Pt/MOF–BTC.
With the presence of Pt, the size for MOF–808 or UiO–66 was smaller and the surfaces of catalysts became rougher (shown in Figure S2b,d). This result indicated the etching effect of reducing agent. However, for Pt/MOF–BTC, the etching effect was not obvious according to SEM images (Figure 2b). The morphology of Pt/MOF–BTC was kept with the loading of Pt. This could be due to other characteristics, such as pore volume, which will be discussed later.
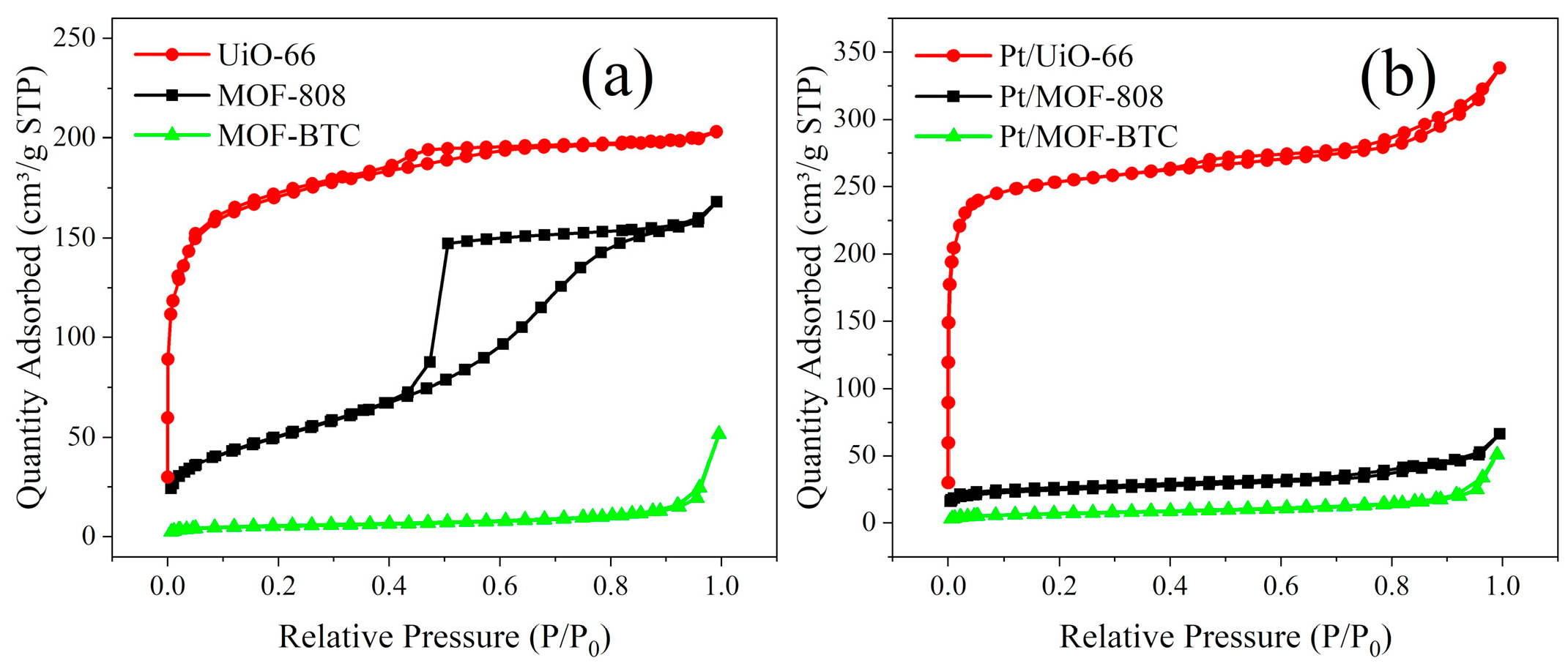
In order to further investigate the MOF physical characteristics, the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms study was carried out. The results are presented in Figure 3 and Table 1. All the samples had typical type IV isotherms indicating the formation of uniform mesoporous structure [33,34]. After loading with Pt, the isotherms of MOF–808 translated to H3 type hysteresis loops from H1 hysteresis. This result suggests that the particle packing type changed [35]. From SEM photos (Figure S2a,b), the morphology of Pt/MOF–808 was irregular compared to MOF–808. The pore volume of Pt/MOF–808 was smaller than that of MOF–808, which might be related to the blockage of smaller pores. By contrast, the BET specific surface area and pore volume of UiO–66 and MOF–BTC were both increased after Pt were added. For UiO–66, the etching effect was more obvious. The pore volume of MOF–BTC is the lowest, this led it to keep its morphology after the etching effect of the reducing agent. Additionally, amorphous structure was observed for fresh Pt/MOF–BTC (not shown in the text), which is consistent with previous literature [36,37]. The amorphous part may contribute to low BET surface area of fresh Pt/MOF–BTC.
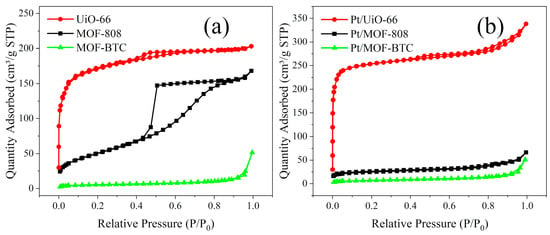
Figure 3.
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of (a) Ce–MOF and (b) Pt/Ce–MOF.

Table 1.
BET surface areas, pore volume, percentages of Ce3+, Pt0, and Oad of all samples.
2.1.3. Analysis of Surface Chemical Properties
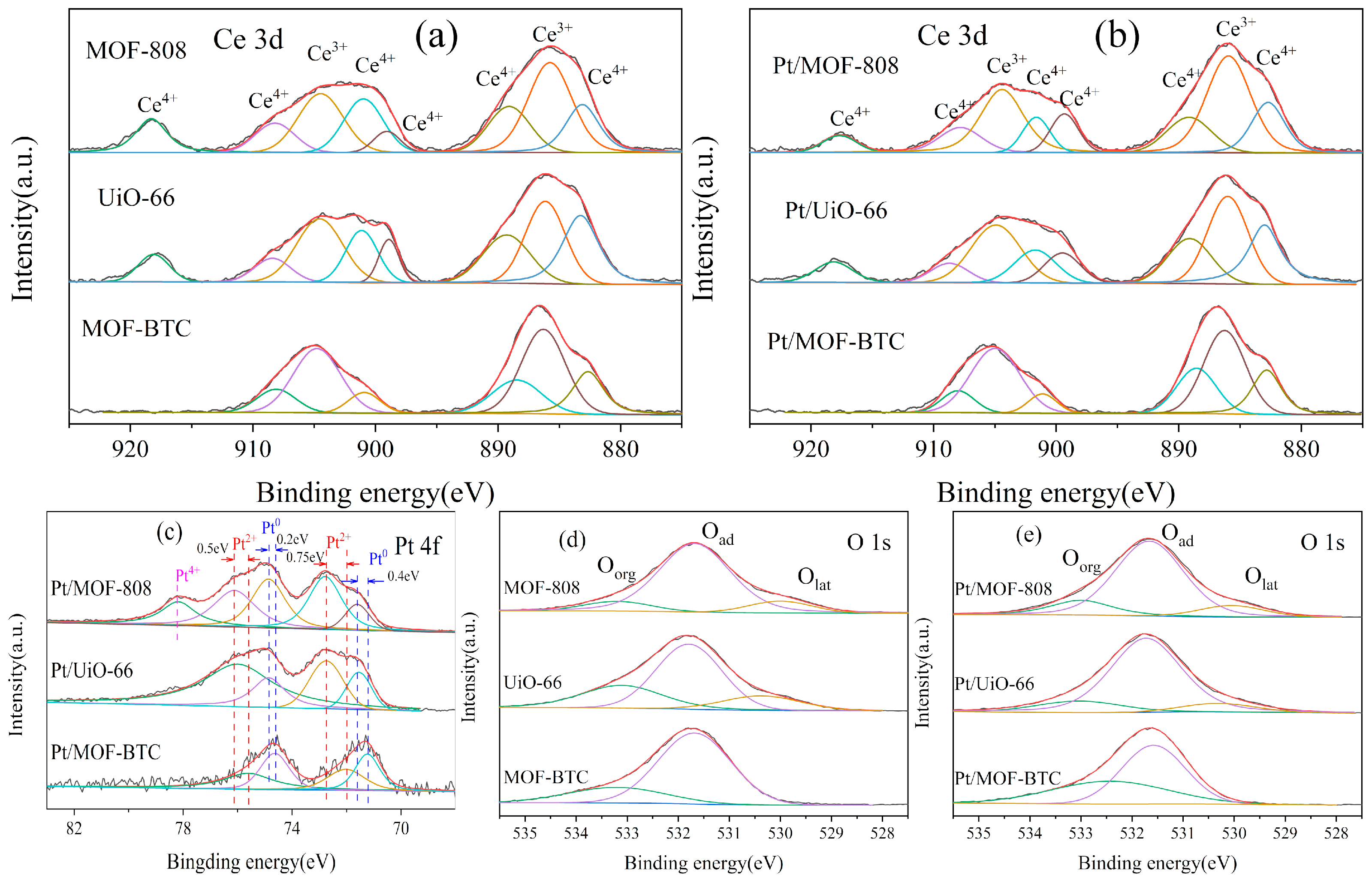
To better understand the coordination environment of cerium and the surface composition on the catalysts surface, XPS measurements were performed and the results are displayed in Figure 4. The Ce 3D of MOF–808 and UiO–66 could be divided into eight peaks at 918.1, 908.2, 904.5, 901.1, 899.8, 888.8, 885.7, and 883.2 eV. The peaks at 918.1, 908.2, 901.1 899.8, 888.8, and 883.2 eV were assigned to Ce4+ and the other two peaks at 904.5 and 885.7 eV belonged to Ce3+ (Figure 4a) [38,39,40]. However, the Ce 3D spectra of MOF–BTC was different from the other two catalysts. The peaks of Ce 3D in MOF–BTC could be deconvoluted into six peaks at 908.1, 901.1, 888.8, and 883.2 eV corresponding to Ce4+ and 904.5 and 885.7 eV correlated to Ce3+. Two peaks belonging to Ce4+ at 918.1 and 899.8 eV disappeared. This difference indicated that the coordination environment of Ce over rod–shaped MOF–BTC was different from the other two particle–shaped catalysts. According to previous literature [16,36,41], the coexistence of Ce3+ and Ce4+ species indicates the existence of oxygen vacancies. The position and FWHM of Ce over different samples were listed in Table S1. The ratios of Ce3+/(Ce3+ + Ce4+) for all samples were listed in Table 1 and ranked as follows: MOF–BTC > MOF–808 > UiO–66. The XPS result of Ce for three Ce–MOF catalysts indicate that the coordination environment of cerium in MOF–BTC was more conducive to the formation of Ce3+.
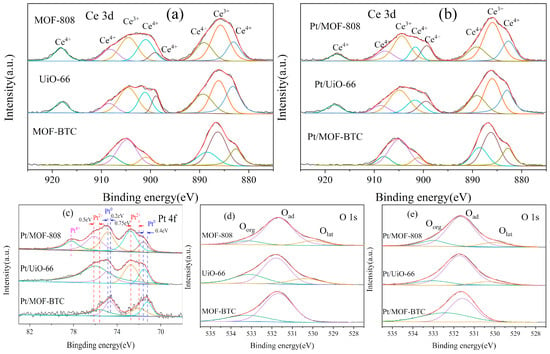
Figure 4.
The XPS spectra of different samples (a) Ce 3d for Ce–MOF, (b) Ce 3d for Pt/Ce–MOF, (c) Pt 4f for Pt/Ce–MOF, (d) O 1s for Ce–MOF and (e) O 1s for Pt/Ce–MOF.
Furthermore, by fitting the Pt 4f spectra, Pt4+, Pt2+, and Pt0 species were observed in three Pt/Ce–MOF catalysts (Figure 4c) with the position and FWHM of Pt over different samples were listed in Table S4 An extra peak at 78.2 eV for Pt/MOF–808 was found, which was assigned to Pt4+ [42]. The peaks at 76.1 and 72.7 eV over Pt/MOF–808 and Pt/UiO–66 were associated with Pt2+ species, while the peaks at 74.7 and 71.6 eV were attributed to Pt0 species [41]. The binding energy of peaks of Pt/MOF–BTC were obviously shifts to low binding energy, indicating a weaker interaction between Pt and O atoms [43]. According to other literature, the increased electron density caused by oxygen vacancies can reduce the binding energy of lattice oxygen [32], which results in weakening Pt–O bond strength. Therefore, the weakened Pt–O bond may facilitate the formation of atomic Pt in the reduction of Pt species and the formation of oxygen vacancies. Pt0 was the main active site compared to Ptσ+ in the oxidation of CO. The electron–rich Pt0 is more conducive to the transfer of electrons from Pt species to the reaction substrate [32]. Additionally, some studies suggested that the atomic Pd0 species, rather than ionic Pdσ+, was the active site. Therefore, Pt/MOF–BTC with the highest ratio of Pt0/Pttotal was more conductive to the oxidation of toluene theoretically. This theory was verified in Section 3.2.
On the other hand, oxygen species are also an important factor affecting the catalytic performance of catalysts and the position and FWHM of O over different sample were shown in Table S2 As shown in Figure 4d,e, the O 1s spectra of samples was fitted to three peaks at 529.6, 531.5, and 533.0 eV, corresponding to lattice oxygen (Olat), surface adsorbed oxygen (Oads), and carboxyl group organic oxygen (Ocar), respectively. It should be noted that there is no consensus on whether Oads or Olat plays a key role in toluene oxidation. There are reports proving that abundant Oads could significantly improve the catalytic performance of catalysts in the toluene oxidation process [44,45]. Some other studies preferred Olat as conductive to the oxidation of toluene [46,47]. In this work, the Oads of Pt/MOF–BTC was almost as same as that of Pt/UiO–66. Therefore, in this study, the excellent catalytic performance of Pt/MOF–BTC was attributed to its abundant Ce3+ and high Pt0/Pttotal ratio.
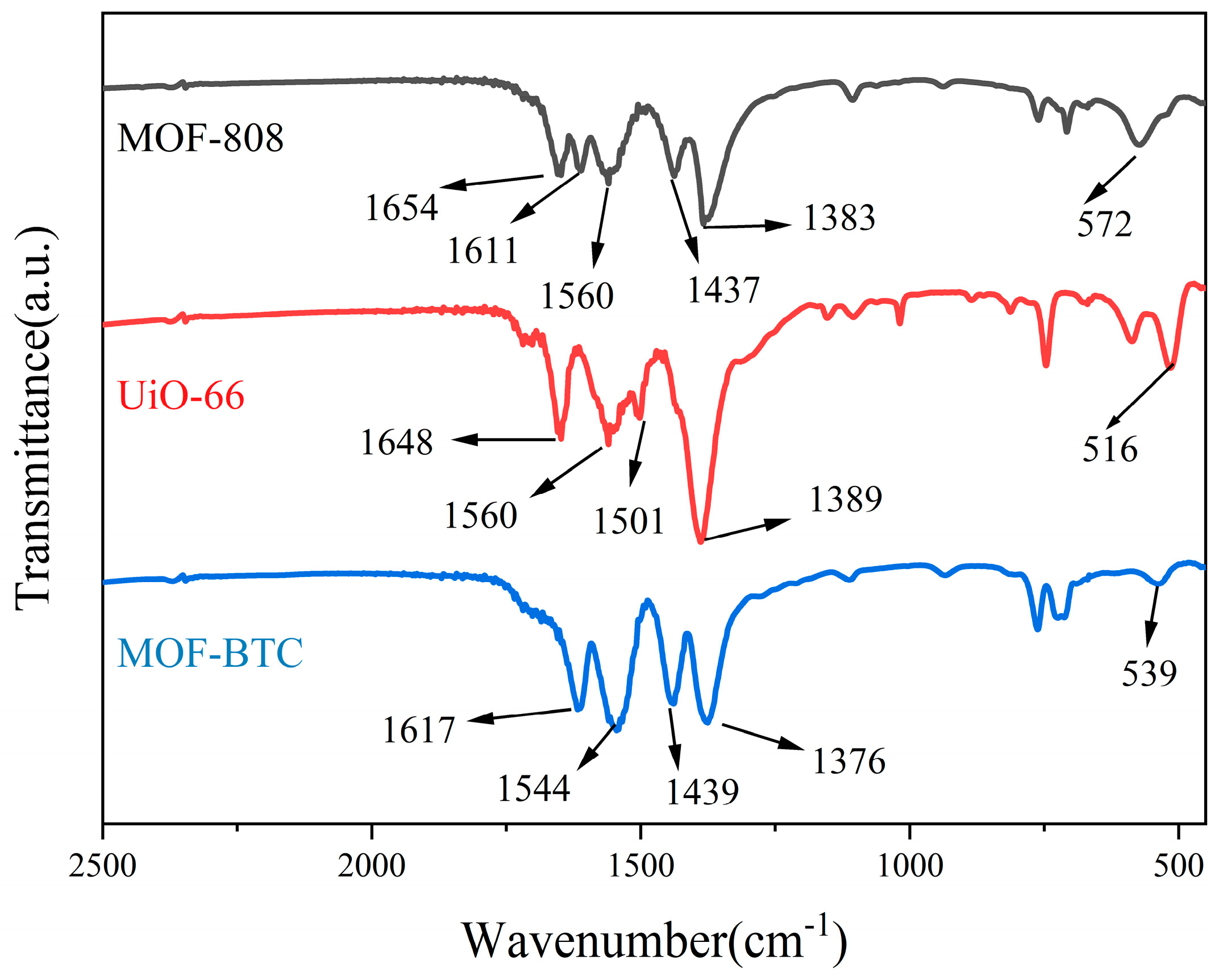
The FTIR and Raman spectra were studied to analyze the topology and structure of the three Ce–MOF catalysts. As shown in Figure 5, the FTIR spectra of three Ce–MOF catalysts were similar with the band from 1376 to 1654 cm−1 corresponding to carboxylate groups and aromatic rings of trimesic acid or adsorbed water [34,48]. In MOF–BTC and UiO–66, the Ce–O vibration appeared at 539 and 516 cm−1, respectively, while that of MOF–808 was observed at 572 cm−1 [32,49]. The difference indicated the different Ce–O distance [50], which indicated the coordination environment of Ce was different over three samples. The Raman spectrum of MOF–808 was mainly correlated to trimesic acid ligands (shown in Figure S3). The peaks at 1000, 1356, and 1558 cm−1 were attributed to the C=C vibration of aromatic ring, while the peak at 1444 cm−1 was from the COO groups [47]. In addition, the out-of-plane vibration of C–H groups was observed at 793 cm−1. The spectrum of UiO–66 was identical to previous study [51] and the peaks at 1607, 1417, 1136, and 852 cm−1 correspond to the C=C, COO, C–C, and C–H vibration, respectively. Compared to MOF–808, there was a weak peak at 415 cm−1 corresponding to the vibration band of Ce–O.
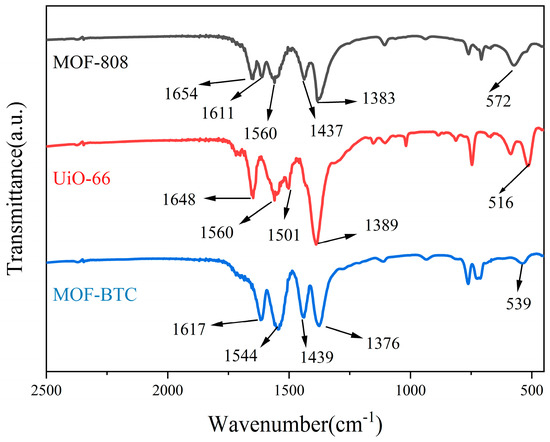
Figure 5.
FTIR spectra of MOF–808, UiO–66, and MOF–BTC samples.
The spectrum of MOF–BTC was different from the two other catalysts, except for the peaks at 1565, 1450, 998, and 801 cm−1 corresponding to the vibration of asymmetric and symmetric COO, C=C, and C–H, respectively. The other two peaks at 392 and 243 cm−1 were assigned to the stretching vibration of Ce–O and Ce–Ce, respectively. The appearance of Ce–Ce stretching vibration peak at 243 cm−1 further shows the coordination environment of Ce in MOF–BTC.
2.2. Catalyst Performance
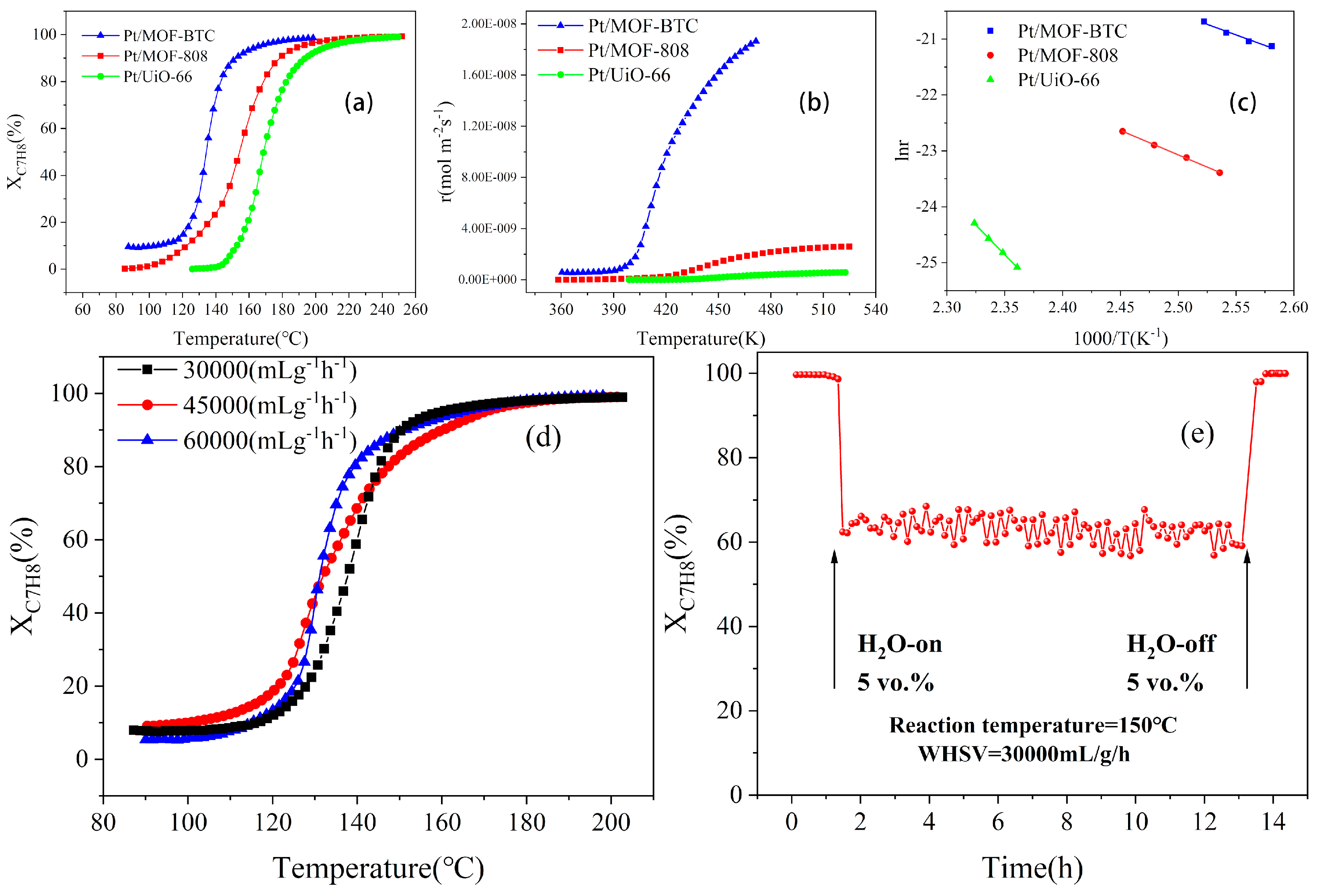
The catalyst performance of toluene conversion is presented in Figure 6. The catalytic activity sequence ranked as follows: Pt/MOF–BTC > Pt/MOF–808 > Pt/UiO–66. With the temperature at 80 °C, the Pt/MOF–BTC catalyst showed catalytic activity with the toluene conversion efficiency around 10%. By contrast, the Pt/UiO–66 was observed with little catalytic activity when the temperature was higher than 150 °C. The T50 and T90 (the temperature corresponding to toluene conversion of 50% and 90%, respectively) of the supported catalysts were summarized in Table 2. Pt/MOF–BTC exhibited excellent catalytic performance when the T50 and T90 were 140 °C and 149 °C, which were 28 °C and 30 °C lower than that of Pt/MOF–808 and 42 °C and 45 °C lower than that of Pt/UiO–66, respectively. From XPS results, the higher catalytic performance could be attributed to its higher Ce3+ content and high Pt0 content, which favors the activation of oxygen adjacent to Pt species via the spillover effect [16,52].
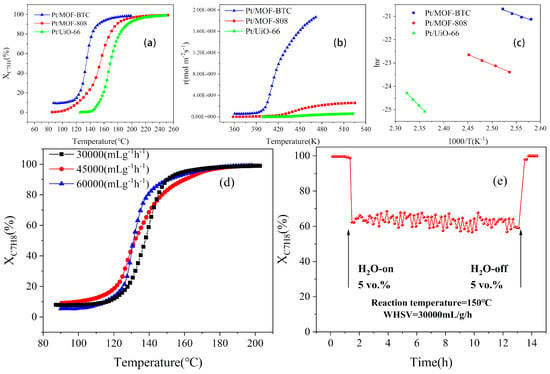
Figure 6.
(a) The toluene conversion, (b) the reaction rate, and (c) the Arrhenius plots for toluene oxidation over three samples; (d) the effect of different WHSV and (e) water on catalytic activity of Pt/MOF–BTC.

Table 2.
Catalytic activities of the different Pt–based catalysts.
Considering the large difference of the specific surface area of the three catalysts, the normalized reaction rate of the specific surface area of different catalysts calculated according to Equation (3) is shown in Figure 6b. The reaction rate of Pt/MOF–BTC increased almost linearly higher than 120 °C, while the reaction rate of Pt/MOF–88 and Pt/UiO–66 remained at a low level until the temperature was higher than 250 °C. By deducting the effect of the BET area, the Pt/MOF–BTC showed the best catalytic effect to toluene. This indicates that the surface area is not the key factor to determine the activity of Ce–MOF–based catalysts [16].
Figure 6c demonstrates the Arrhenius plots for the catalytic combustion of toluene at a conversion efficiency less than 20% over the three catalysts. The linearity of these plots indicates that the reaction only remains in the kinetically controlled region at low temperatures where the conversion is less than 20%, which was documented in a previous study [53]. The apparent activation energies (Ea) were summarized in Table 2. The Ea values decreased in the following order: Pt/UiO–66 (176.7 kJ·mol−1) > Pt/MOF–808 (72.7 kJ·mol−1) > Pt/MOF–BTC (62.8 kJ·mol−1). The Pt/MOF–BTC with the lowest Ea exhibited the best catalytic activity for toluene oxidation.
Figure S4 exhibits the CO2 selectivity curves calculated based on Equation (2). It is worth pointing out that the toluene conversion to CO2 over three Pt/Ce–MOF exceeded 100% with the increase of temperature due to the accumulation of intermediates formed at a low temperature region [54]. Moreover, it was clear that the conversion to CO2 over Pt/MOF–808 and Pt/UiO–66 was higher than 150% in the highest temperature region, indicating their poor selectivity to CO2 and poor oxidation ability to intermediate products. In contrast, Pt/MOF–BTC exhibited better selectivity to CO2 and oxidation ability to intermediate products. Moreover, Pt/MOF–BTC sample was tested by XRD (Figure S5) after reaction. The used Pt/MOF–BTC catalyst may be transformed into amorphous structure, which was consistent with previous study [55]. However, the presence of amorphous structure does not affect the performance of the catalyst (Figure 7a). The relationship between amorphous structure and catalyst performance deserves further study.
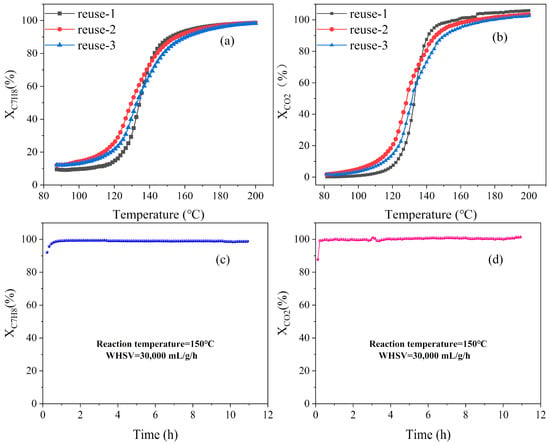
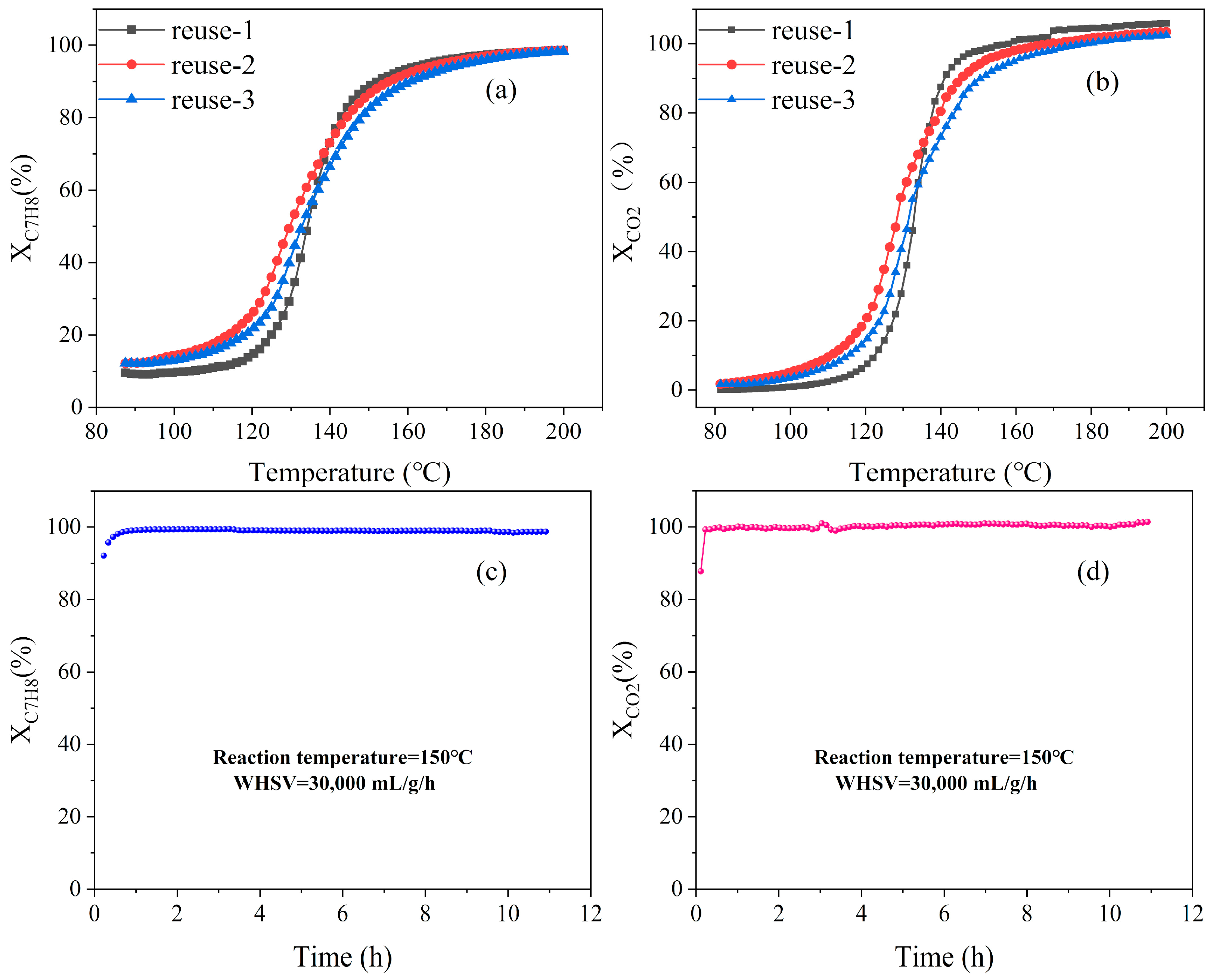
Figure 7.
The toluene conversion (a) and CO2 selectivity (b) of Pt/MOF–BTC in the reusability test; the toluene conversion (c) and CO2 selectivity (d) of Pt/MOF–BTC in the stability test.In order to eliminate the influence of toluene adsorption at low temperature on the calculation of toluene conversion over three Ce–MOF catalysts, only the CO2 selectivity curve was shown in Figure S4b. All three Ce–MOF catalysts showed poor catalytic performance in the whole temperature region, with their CO2 selectivity no more than 8% even at the highest temperature region. Therefore, based on the above results, the introduction of Pt could exactly improve the catalytic activity to toluene oxidation.
To further investigate the catalytic performance of Pt/MOF–BTC, the effect of WHSV and water was measured, with the results displayed in Figure 6d,e. The catalytic activity to toluene combustion presented Figure 6d did not change significantly with the increase of WHSV from 30,000 mL/g/h to 60,000 mL/g/h, which indicated a great resistance to WHSV of Pt/MOF–BTC.
Considering the real reaction conditions, 5 vol.% water was added to the reaction system. As depicted in Figure 6e, with the introduction of water, the toluene conversion decreased from 100% to around 65%. When the water was off, the toluene conversion reached 100% again, suggesting that Pt/MOF–BTC had a good water–resistance. Therefore, the decrease of toluene conversion might be due to the competition between water and toluene for active sites.
2.3. Reusability and Stability
The recyclability of Pt/MOF–BTC to the toluene oxidation test was repeated three times with the same catalyst (Figure 7a,b). Notably, during the second and third cycle, the low temperature oxidation performance of the catalyst was slightly improved, which indicates that the surface environment might be restructured in the oxidation of toluene [56]. The CO2 selectivity remained stable during the repeat tests.
To examine the catalytic stability of Pt/MOF–BTC, the on–stream reaction was conducted at 150 °C for more than 10 h. As shown in Figure 7c, toluene was quickly converted in a very short time and showed no significant decrease in the 10 h, indicating the good stability of Pt/MOF–BTC in toluene oxidation. Additionally, the CO2 selectivity also reached 100% in a very short time and remained stable (Figure 7d), which indicated that Pt/MOF–BTC had a wonderful selectivity to CO2 and excellent oxidation ability to intermediates. Table S3 demonstrated the catalytic activity for toluene combustion of several Pt catalysts compared with other Pt catalysts, such as Pt/ZrO2 [57], Pt/Al2O3 [58], and Pt/Mn3O4 [59]. The activation or reaction temperature of Pt/MOF–BTC was lower for toluene oxidation.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Cerium (IV) ammonium nitrate (Ce (NH4)2(NO3)6, AR) and ethanol (99.0%) were purchased from Sino reagent (Shanghai, China). Cerium nitrate hexahydrate (Ce (NO3)3·6H2O, 99%), 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid (H3–BTC, C6H3(CO2H)3, 98%), N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF, C3H7NO, 99.5%), and platinum nitrate solution (Pt, 18.02 wt.%) were bought from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). Formic acid (CH2O2, 98%), 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (H2–BDC, C8H6O4, 99%), and sodium tetra hydroborate (NaBH4, 98%) were obtained from Macklin (Shanghai, China). Toluene which was balanced with nitrogen was supplied from Yancheng Guanghua Gas Co., Ltd (Yancheng, China). All chemical reagents were used directly.
3.2. Catalysts Preparation
All catalysts used in this work were prepared via hydrothermal and solvothermal method combined with NaBH4–reduction method based on the literature with few modifications [25,26,27].
3.2.1. Synthesis of MOF–808
The synthesis process of MOF–808 was as follows: 7.306 g Ce (NH4)2(NO3)6 was dissolved in 25.0 mL deionizer water (Solution A). Then, 0.224 g H3–BTC and 2.57 mL HCOOH were added into 12.0 mL DMF at the same time (Solution B). Then, Solution A and Solution B were mixed to obtain Solution C. Solution C was sealed and heated at 100 °C. After stirring for 30 min, the suspension was centrifuged and washed with DMF and ethanol three times. Finally, the obtained slurry was dried at 70 °C in an oven for 12 h and collected as MOF–808 powder.
3.2.2. Synthesis of MOF–BTC
To obtain MOF–BTC catalyst, 2.100 g H3–BTC was dissolved into 10.0 mL ethanol and 10.0 mL deionized water (Solution A). Then, 4.340 g Ce (NO3)3·6H2O was dissolved in 45 mL deionized water (Solution B). Then, Solution A and Solution B were mixed to obtained suspension which was heated at 60 °C for 1 h with continuous stirring. The suspension solution was centrifuged and washed with deionized water and ethanol three times. Finally, the obtained slurry was dried at 70 °C in an oven for 12 h and collected as MOF–BTC powder.
3.2.3. Synthesis of UiO–66
The synthesis method of UiO–66 was modified based on that of MOF–808. H2–BDC (0.531 g) was dispersed in 12.0 mL DMF followed by adding 6 mL aqueous solution of Ce (NH4)2(NO3)6 prepared in Section 3.2.1. The subsequent steps were the as same as Section 3.2.1.
3.2.4. Synthesis of Pt/M (M = MOF–808, MOF–BTC, UiO–66)
Pt/M catalysts were synthesized via NaBH4–reduction. The M (0.600 g) catalyst were dispersed in 40.0 mL DMF. The suspension was activated at 140 °C in a vacuum oven for 6 h. Then, 3.33 mL platinum nitrate solution was added to the suspension solution. The mixture was stirred under room temperature for 24 h. Afterwards, a certain amount of NaBH4 (NaBH4/Pt = 10, molar ratio) was added dropwise into the mixture with stirring, with stirring continued for 2 h. In the dropping process, the color of catalysts gradually changed from light yellow or white to gray, indicating the reduction of Pt species. Finally, the gray precipitations were centrifuged and washed with ethanol three times, and then dried at 70 °C overnight.
3.3. Catalysts Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker D8 Advance, Karlsruhe, DE) equipped with a Cu Kα (40 Kev, 40 mA) radiation monochromatic detector was used to analyze the crystallinity of all samples with a scan rate of 10°/min. The scanning range was 5–90°. The specific surface areas, pore size distribution, and pore volume were characterized by N2 adsorption–desorption at 77 K on a Quanta chrome autosorb–iQ–2MP (ASAP 2460, Atlanta, GA, USA) apparatus after a pretreatment under vacuum at 140 °C for 4 h to remove impurities. Morphology images of samples were observed by a scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL JSM–7900F, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a Philips FEIXL–30. Three catalysts were characterized via a Fourier transform infrared (FTIR, Thermo Fisher Scientific Nicolet iS50 spectrometer, Waltham, MA, USA) spectroscopy and Raman spectra (Thermo Scientific DXR SmartRaman, Renishaw, London, UK) at an excitation wavelength of 532 nm. The chemical states and surface composition of all catalysts were characterized by the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS, THERMO ESCALAB 250Xi, Waltham, MA, USA) with Al Kα as radiation. The thermal stability analysis over different catalysts were carried out on a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, Shimadzu SDT650, New Castle, DE USA) apparatus.
3.4. Catalyst Characterization
First, 100 mg of as–prepared catalyst (40–60 mesh) was packed into a quartz tube (outside diameter 6 mm) for the toluene oxidation test. Toluene (500 ppm, balanced with N2) and 20% O2 in N2 were mixed and stabilized for 30 min. The mixture of gases was controlled by a mass flow controller. The temperature of the reactor was increased from room temperature to target temperature with a heating rate of 1 °C/min. The outlet toluene concentration was detected via MKS instruments (651 Lowell St., Methuen, MA, USA) digital flow meters. T50 and T90 were recorded to evaluate the catalytic activity of the catalysts. In order to investigate the water resistance during toluene combustion, 5 vol.% water was injected to the system with bubbling method.
Toluene conversion and carbon dioxide selectivity were calculated according to Equations (1) and (2) as follows:
where XC7H8 is the toluene conversion, XCO2 represents the CO2 selectivity, [Toluene]in, [Toluene]out and [CO2]out refer to the inlet and outlet concentration of toluene and outlet CO2 concentration, respectively.
XC7H8 (%) = ([Toluene]in − [Toluene]out)/[Toluene]in × 100%
XCO2 (%) = [CO2]out/7[Toluene]in × 100%
The normalized initial reaction rate (r, mol·m−2 s−1) was calculated as Equation (3):
where F is flow rate, m and SBET refer catalyst amount and its BET surface area, respectively. P represents standard atmospheric pressure and R is molar gas constant.
r = −F/(m·SBET) × P/RT × Ln (1 − XC7H8) × [Toluene]in
The apparent activation energy Ea of the catalyst was obtained by fitting the Arrhenius curve (toluene conversion is less than 20%), which was calculated as Equation (4):
lnr = −Ea/RT + lnA
4. Conclusions
In this work, three different morphologies of Ce–MOF, i.e., MOF–BTC, UiO–66, and MOF–808, were synthesized with loading Pt for the oxidation of toluene. MOF–BTC had the best thermal stability, and its rod morphology was kept after the noble metals were loaded. During the toluene combustion test, Pt/MOF–BTC showed the best catalytic activity, its T50 and T90 were 140 °C and 149 °C, respectively, which were 42 °C and 45 °C lower than that of Pt/UiO–66 with the lowest activity. Its apparent activation energy is 62.8 kJ·mol−1, which was also lowest among three catalysts. Compared with the traditional Pt–based catalysts, such as Pt/ZrO2, Pt/Al2O3, and Pt/Mn3O4, Pt/MOF–BTC still exhibited lower reaction temperature. The performance of Pt/MOF–BTC benefits from the abundant atomic Pt and oxygen vacancy content on its surface. In addition, Pt/MOF–BTC also exhibited tolerance capability to water or WHSV. For water, 5 vol. % water induced 35% efficiency drop. However, when the water was cut off, the catalytic capability recovered to 100%. For WHSV, ranging from 30,000 to 60,000 mL/g/h, the oxidation of toluene over Pt/MOF–BTC had no obvious effect. Moreover, in the three cycle tests, the catalytic activity of Pt/MOF–BTC remained basically stable. In the stability test of Pt/MOF–BTC, the toluene conversion and CO2 selectivity increased to 100% and remained stable for 11 h. It should be pointed out that part of Pt/MOF–BTC was amorphous structure, its catalytic performance was not affected according to the cyclic test. The effects of the amorphous part on the catalytic characteristics need further study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://zenodo.org/deposit/6574053, Figure S1: The TGA plots of MOF–808, UiO–66, and MOF–BTC; Figure S2: The SEM images (a) of MOF–808, (b) Pt/MOF–808, (c) UiO–66, and (d) of Pt/UiO–66; Figure S3: Raman spectra of MOF–808, UiO–66, and MOF–BTC (the laser wavelength = 514 nm); Figure S4: The CO2 selectivity of different catalysts in the oxidation of toluene (the total flow rate was 50 mL/min with the weight hourly space velocity WHSV = 30,000 mL/g/h and the toluene concentration was 500 ppm); Figure S5: The XRD pattern of Pt/MOF–BTC after toluene oxidation; Table S1: The position and FWHM of Ce over different samples; Table S2: The position and FWHM of O over different samples; Table S3: Comparison of the activities of different Pt–based catalysts for toluene combustion; Table S4: The position and FWHM of Pt over different samples. References [57,58,59] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
H.N.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision. Y.L.: validation, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. G.C.: visualization. J.C.: supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41807304).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available form authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, B.; Lei, C.; Wei, C.; Zeng, G. Chlorinated volatile organic compounds (Cl–VOCs) in environment—Sources, potential human health impacts, and current remediation technologies. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Y.; Ran, J. Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption process: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Shao, Q.; Long, C. Porous polymeric resin for adsorbing low concentration of VOCs: Unveiling adsorption mechanism and effect of VOCs’ molecular properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nie, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Hao, Z. Characterization and assessment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions from typical industries. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, G. The preparation of defective UiO–66 metal–organic framework using MOF–5 as structural modifier with high sorption capacity for gaseous toluene. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chen, D.; Cui, L. Adsorption/desorption kinetics and breakthrough of gaseous toluene for modified microporous–mesoporous UiO–66 metal organic framework. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Enhanced adsorption performance of gaseous toluene on defective UiO–66 metal organic framework: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zhen, W.; Ma, J.; Lu, G. High efficient solar hydrogen generation by modulation of Co–Ni sulfide (220) surface structure and adjusting adsorption hydrogen energy. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 206, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Liao, G.; Pan, Z. Self–template synthesis of double–shell TiO2@ZIF–8 hollow nanospheres via sonocrystallization with enhanced photocatalytic activities in hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 241, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ran, J. A review of microscopic seepage mechanism for shale gas extracted by supercritical CO2 flooding. Fuel 2019, 238, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Detection of hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by metal oxide nanostructures–based gas sensors: A review. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15119–15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Liland, S.E.; Yang, J.; Rout, K.R.; Ran, J.; Chen, D. Effect of oxide additives on the hydrotalcite derived Ni catalysts for CO2 reforming of methane. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 377, 119763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Kuru, C.; Aykac, H.; Kaya, S. VOC separation using immobilized liquid membranes impregnated with oils. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 153, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Feng, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Pan, W.; Li, L.; Yang, Z. Thermal management and catalytic combustion stability characteristics of premixed methane/air in heat recirculation meso-combustors. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, U.; Kraus, M.; Holzer, F.; Trommler, U.; Kopinke, F.-D. Selective dielectric heating for efficient adsorptive–catalytic cleaning of contaminated gas streams. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 474, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Ye, D. Shape effect of Pt/CeO2 catalysts on the catalytic oxidation of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1234–12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.P.; Park, H.J.; Prasad, T.K.; Lim, D.-W. Hydrogen Storage in Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 782–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Liu, N.; Wu, M.; Tang, L. g–C3N4/UiO–66 nanohybrids with enhanced photocatalytic activities for the oxidation of dye under visible light irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 99, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Suh, K.; Natarajan, S.; Kim, K. Proton Conduction in Metal–Organic Frameworks and Related Modularly Built Porous Solids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Pashow, K.M.L.; Della Rocca, J.; Xie, Z.; Tran, S.; Lin, W. Postsynthetic Modifications of Iron–Carboxylate Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for Imaging and Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14261–14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreno, L.E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O.K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Hupp, J.T. Metal–Organic Framework Materials as Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.-Y.; Hwang, Y.K.; Serre, C.; Ferey, G.; Chang, J.-S. Porous Chromium Terephthalate MIL–101 with Coordinatively Unsaturated Sites: Surface Functionalization; Encapsulation, Sorption and Catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Michaelides, A.; Jenkins, S.J. Theory of gold on ceria. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y. A facile synthesis for cauliflower like CeO2 catalysts from Ce–BTC precursor and their catalytic performance for CO oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, M.; Glissmann, C.; Reinsch, H.; Stock, N. Synthesis and Characterization of New Ce(IV)–MOFs Exhibiting Various Framework Topologies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; You, H.; Jia, G.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Hierarchically Nanostructured Coordination Polymer: Facile and Rapid Fabrication and Tunable Morphologies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Shen, W. Insights into the Pyrolysis Processes of Ce–MOFs for Preparing Highly Active Catalysts of Toluene Combustion. Catalysts 2019, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Ye, D. Enhanced oxygen vacancies to improve ethyl acetate oxidation over MnOx–CeO2 catalyst derived from MOF template. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, M.; Zelenak, V.; Opanasenko, M.; Cisarova, I. Ce(III) and Lu(III) metal–organic frameworks with Lewis acid metal sites: Preparation, sorption properties and catalytic activity in Knoevenagel condensation. Catal. Today 2015, 243, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaeva, V.I.; Belyaeva, E.V.; Fitch, A.N.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Klyamkin, S.N.; Kustov, L.M. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of a Series of Novel Zn(II)–based MOFs with Pyridine–2,5–dicarboxylate Linkers. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 5305–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guo, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. The controlled regulation of morphology and size of HKUST–1 by “coordination modulation method”. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 173, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, K.; Liang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.-F.; Zhan, G. Structural Isomerism of Two Ce–BTC for Fabricating Pt/CeO(2)Nanorods toward Low–Temperature CO Oxidation. Small 2020, 16, 2003597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Qu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Fu, Q.; Sun, H.; Duan, X. Revealing the Highly Catalytic Performance of Spinel CoMn2O4 for Toluene Oxidation: Involvement and Replenishment of Oxygen Species Using In Situ Designed–TP Techniques. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6698–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, M.; Wharmby, M.T.; Smolders, S.; Bueken, B.; Lieb, A.; Lomachenko, K.A.; De Vos, D.; Stock, N. Cerium–based metal organic frameworks with UiO–66 architecture: Synthesis, properties and redox catalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12578–12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Fu, M.; Mo, D.; et al. Highly efficient mesoporous MnO2 catalysts for the total toluene oxidation: Oxygen–Vacancy defect engineering and involved intermediates using in situ DRIFTS. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 264, 118464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jing, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Structural Reconstruction of Ce–MOF with Active Sites for Efficient Electrocatalytic N–2 Reduction. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 12128–12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.; Gong, T.; Jiao, L.; Jiang, H.-L. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) beyond crystallinity: Amorphous MOFs, MOF liquids and MOF glasses. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10562–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Ce(III) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce–MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Buzo, S.; Concepcion, P.; Luis Olloqui-Sariego, J.; Moliner, M.; Corma, A. Metalloenzyme–Inspired Ce–MOF Catalyst for Oxidative Halogenation Reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31021–31030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, J.-J. Electrochemical sensor based on Ce–MOF/carbon nanotube composite for the simultaneous discrimination of hydroquinone and catechol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mo, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Ye, D. In situ DRIFT spectroscopy insights into the reaction mechanism of CO and toluene co–oxidation over Pt–based catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 4538–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Serrano-Lotina, A.; Han, W.; Portela, R.; Wang, R.; Banares, M.A.; Yeung, K.L. Operando Investigation of Toluene Oxidation over 1D Pt@CeO2 Derived from Pt Cluster–Containing MOF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Deng, J.; Impeng, S.; Li, S.; Yan, T.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Boosting Toluene Combustion by Engineering Co–O Strength in Cobalt Oxide Catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10342–10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, X.; Bi, F.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y. Highly efficient Mn2O3 catalysts derived from Mn–MOFs for toluene oxidation: The influence of MOFs precursors. Mol. Catal. 2020, 482, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Zeng, K.; Wang, Z.; Jia, H.-p.; Li, X. Insights into the size and structural effects of zeolitic supports on gaseous toluene oxidation over MnOx/HZSM–5 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.W.; Liu, F.-C.; Hung, L.-F.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lien, S.-B.; Lin, L.-C.; Lai, J.-H.; Ho, L.-J. Chondroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Dextromethorphan: Repurposing Antitussive Medication for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, Z.; Song, W.; Xiao, W.; Guo, Y.; Ding, J.; Suib, S.L.; Gao, P.-X. Low temperature propane oxidation over Co3O4 based nano–array catalysts: Ni dopant effect, reaction mechanism and structural stability. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.; Lan, Q.; Xie, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Label–Free Electrochemical Immunosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Carbohydrate Antigen 125 Based on Antibody–Immobilized Biocompatible MOF–808/CNT. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3295–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjun, N.; Jacob, M.; Varalakshmi, P.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A. UiO–66(Ce) metal–organic framework as a highly active and selective catalyst for the aerobic oxidation of benzyl amines. Mol. Catal. 2021, 499, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Arab, P.; El-Kaderi, H.M.; El-Shall, M.S. Palladium Nanoparticles Supported on Ce–Metal–Organic Framework for Efficient CO Oxidation and Low–Temperature CO2 Capture. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17961–17968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarjun, N.; Concepcion, P.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A. Influence of oxophilic behavior of UiO–66(Ce) metal–organic framework with superior catalytic performance in Friedel–Crafts alkylation reaction. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Sun, H.; Zhang, N.; Che, L.; Shan, S.; Luo, J.; Zheng, J.; Yang, L.; Peng, D.-L.; Zhong, C.-J.; et al. Surface Partial–Charge–Tuned Enhancement of Catalytic Activity of Platinum Nanocatalysts for Toluene Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7431–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Jiang, S.; Li, J. Pd–Co based spinel oxides derived from pd nanoparticles immobilized on layered double hydroxides for toluene combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lassen, K.; Descorme, C.; Valverde, J.L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Effect of the precipitation pH on the characteristics and performance of Co3O4 catalysts in the total oxidation of toluene and propane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 282, 119566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Meng, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Dai, B. Heterogeneous Amorphous Cu–MOF–74 Catalyst for C–N Coupling Reaction. Chemistryselect 2018, 3, 10694–10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Excellent catalytic activity and water resistance of UiO–66–supported highly dispersed Pd nanoparticles for toluene catalytic oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 269, 118767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, S.; Chen, C.; He, H.; Jin, Z.; Luo, M.; Chen, J. Understanding the crucial roles of catalyst properties in ethyl acetate and toluene oxidation over Pt catalysts. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 11352–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.F.; Ousmane, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Pantaleo, G.; Deganello, G.; Boreave, A.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic Removal of Toluene over Co3O4–CeO2 Mixed Oxide Catalysts: Comparison with Pt/Al2O3. Catal. Lett. 2009, 127, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, J.; Cheng, H.; Mo, S.; Ke, Y.; Ren, Q.; Fu, M.; Chen, P.; Wu, J.; Ye, D. Investigation into the roles of different oxygen species in toluene oxidation over manganese–supported platinum catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2021, 507, 111569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).