Identification of Novel Potential Heparanase Inhibitors Using Virtual Screening
Abstract
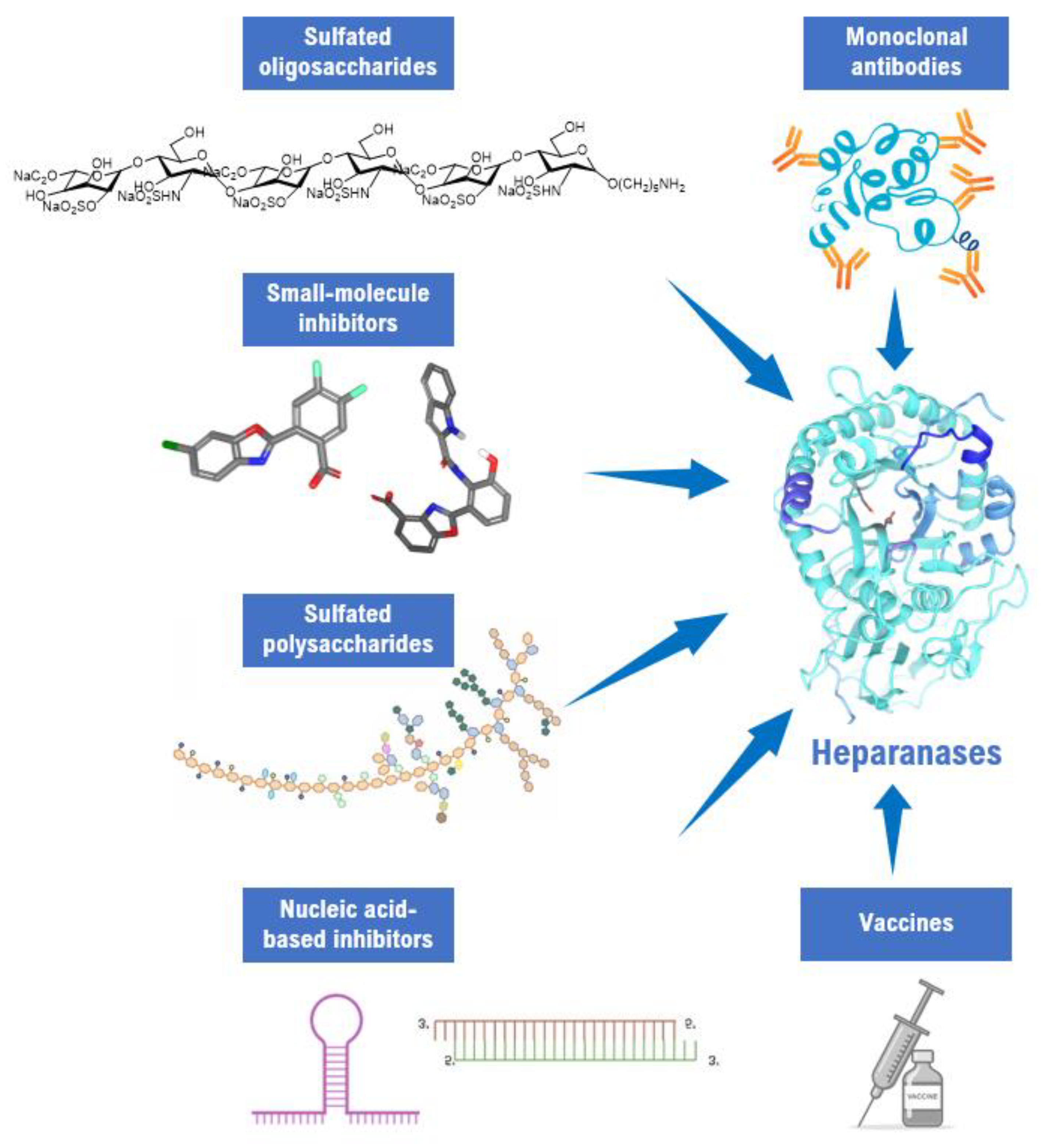
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Evaluation of Reported Inhibitors
2.2. Virtual Screening of Structurally Related Chemical Databases
3. Materials and Methods
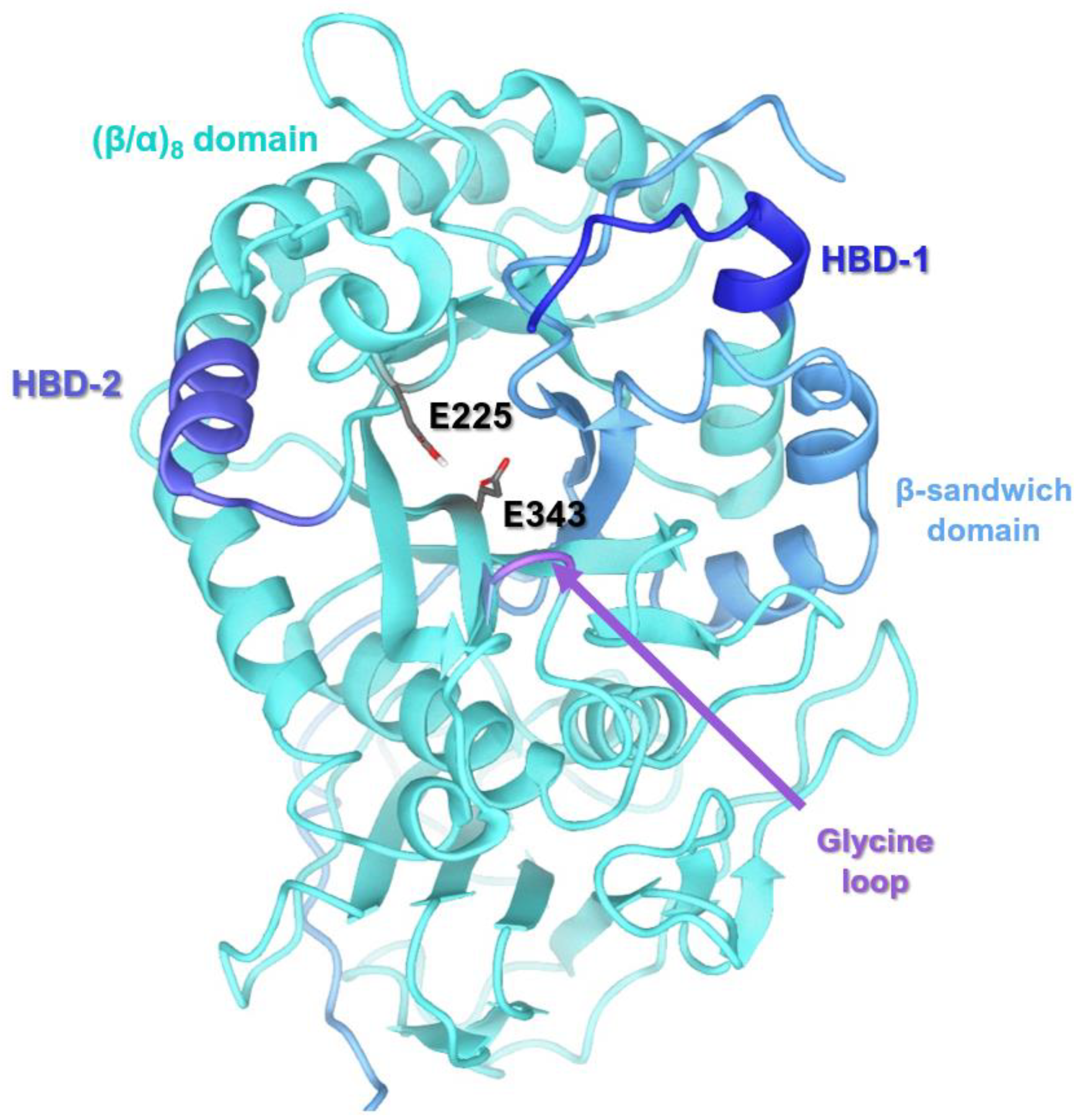
3.1. Receptor Structure
3.2. Chemical Database Curation
3.2.1. Previously Reported inhibitors
3.2.2. Similarity Libraries
3.2.3. Ligand Preparation
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies
3.3.1. Grid GENERATION
3.3.2. HTVS and XP Docking
3.3.3. Additional Selection Criteria
In Silico ADME Parameters
PAINS Identification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannini, G.; Battistuzzi, G.R.S. Heparanase: From Basic Research to Clinical Applications; Vlodavsky, I., Sanderson, R.D., Ilan, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 567–598. ISBN 9783030345204. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, N.J. Heparanase involvement in physiology and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Viola, C.M.; Brzozowski, A.M.; Davies, G.J. Structural characterization of human heparanase reveals insights into substrate recognition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coombe, D.R.; Gandhi, N.S. Heparanase: A Challenging Cancer Drug Target. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterson, S.; Liu, J. Deciphering mode of action of heparanase using structurally defined oligosaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 34836–34843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Williams, A.; Zhang, X.; Fu, L.; Xia, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Koffas, M.; Linhardt, R.J. Specificity and action pattern of heparanase Bp, a β-glucuronidase from Burkholderia pseudomallei. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy-Adam, F.; Abboud-Jarrous, G.; Guerrini, M.; Beccati, D.; Vlodavsky, I.; Ilan, N. Identification and characterization of heparin/heparan sulfate binding domains of the endoglycosidase heparanase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20457–20466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudchadkar, R.; Gonzalez, R.; Lewis, K.D. PI-88: A novel inhibitor of angiogenesis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-J.; Yuan, L.; Hu, J.; Yu, H.-H.; Li, T.; Lin, S.-F.; Tang, S.-B. Phosphomannopentaose sulfate (PI-88) suppresses angiogenesis by downregulating heparanase and vascular endothelial growth factor in an oxygen-induced retinal neovascularization animal model. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Roy, S.; Cochran, E.; Zouaoui, R.; Chu, C.L.; Duffner, J.; Zhao, G.; Smith, S.; Galcheva-Gargova, Z.; Karlgren, J.; et al. M402, a Novel Heparan Sulfate Mimetic, Targets Multiple Pathways Implicated in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macdonald, A.; Priess, M.; Curran, J.; Guess, J.; Farutin, V.; Oosterom, I.; Lin Chu, C.; Cochran, E.; Zhang, L.; Getchell, K.; et al. Small Molecule Therapeutics Necuparanib, a Multitargeting Heparan Sulfate Mimetic, Targets Tumor and Stromal Compartments in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Reilly, E.M.; Roach, J.; Miller, P.; Yu, K.H.; Tjan, C.; Rosano, M.; Krause, S.; Avery, W.; Wolf, J.; Flaherty, K.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Antitumor Activity of Necuparanib Combined with Nab-Paclitaxel and Gemcitabine in Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: Phase I Results. Oncologist 2017, 22, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbieri, P.; Paoletti, D.; Giannini, G.; Sanderson, R.D.; Noseda, A. Roneparstat and Heparanase Inhibition: A New Tool for Cancer Treat-ment. J. Pharmacol. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 5, 1071. [Google Scholar]
- Pala, D.; Rivara, S.; Mor, M.; Milazzo, F.M.; Roscilli, G.; Pavoni, E.; Giannini, G. Kinetic analysis and molecular modeling of the inhibition mechanism of roneparstat (SST0001) on human heparanase. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassinelli, G.; Favini, E.; Bo, L.D.; Tortoreto, M.; De Maglie, M.; Dagrada, G.; Pilotti, S.; Zunino, F.; Zaffaroni, N.; Lanzi, C. Antitumor efficacy of the heparan sulfate mimic roneparstat (SST0001) against sarcoma models involves multi-target inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47848–47863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.P.; Ramani, V.C.; Ren, Y.; Naggi, A.; Torri, G.; Casu, B.; Penco, S.; Pisano, C.; Carminati, P.; Tortoreto, M.; et al. SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossini, A.; Zunino, F.; Ruggiero, G.; De Cesare, M.; Cominetti, D.; Tortoreto, M.; Lanzi, C.; Cassinelli, G.; Zappasodi, R.; Tripodo, C.; et al. Microenvironment modulation and enhancement of antilymphoma therapy by the heparanase inhibitor roneparstat. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Chatterjee, M.; Grasso, M.; Specchia, G.; Magen, H.; Einsele, H.; Celeghini, I.; Barbieri, P.; Paoletti, D.; Pace, S.; et al. Phase I study of the heparanase inhibitor roneparstat: An innovative approach for multiple myeloma therapy. Haematologica 2018, 103, e469–e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dredge, K.; Hammond, E.; Davis, K.; Li, C.P.; Liu, L.; Johnstone, K.; Handley, P.; Wimmer, N.; Gonda, T.J.; Gautam, A.; et al. The PG500 series: Novel heparan sulfate mimetics as potent angiogenesis and heparanase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferro, V.; Liu, L.; Johnstone, K.D.; Wimmer, N.; Karoli, T.; Handley, P.; Rowley, J.; Dredge, K.; Li, C.P.; Hammond, E.; et al. Discovery of PG545: A highly potent and simultaneous inhibitor of angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3804–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, M.; Bhattacharya, U.; Feld, S.; Hammond, E.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I. The heparanase inhibitor PG545 is a potent anti-lymphoma drug: Mode of action. Matrix Biol. 2019, 77, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E.; Handley, P.; Dredge, K.; Bytheway, I. Mechanisms of heparanase inhibition by the heparan sulfate mimetic PG545 and three structural analogues. FEBS Open Bio 2013, 3, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loka, R.S.; Sletten, E.T.; Barash, U.; Vlodavsky, I.; Nguyen, H.M. Specific Inhibition of Heparanase by a Glycopolymer with Well-Defined Sulfation Pattern Prevents Breast Cancer Metastasis in Mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madia, V.N.; Messore, A.; Pescatori, L.; Saccoliti, F.; Tudino, V.; De Leo, A.; Bortolami, M.; Scipione, L.; Costi, R.; Rivara, S.; et al. Novel Benzazole Derivatives Endowed with Potent Antiheparanase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6918–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, H.; Furuya, K.; Takahashi, S.; Takahashi, M.; Tanzawa, K. Trachyspic Acid, a New Metabolite Produced by Talaromyces trachyspermus, that Inhibits Tumor Cell Heparanase: Taxonomy of the Producing Strain, Fermentation, Isolation, Structural Elucidation, and Biological Activity. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, B. Total synthesis of CRM646-A and -B, two fungal glucuronides with potent heparinase inhibition activities. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 8884–8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yan, K.; Kun, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, Q.; Tang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Gu, G.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Z. Berberine inhibits the migration and invasion of T24 bladder cancer cells via reducing the expression of heparanase. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Nan, N.; Cao, K.-X.; Ma, C.; Yang, G.-W.; Yu, M.-W.; Yang, L.; Li, J.-P.; Wang, X.-M.; et al. Elemene inhibits the migration and invasion of 4T1 murine breast cancer cells via heparanase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.K. Biological activities of Carrageenan. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 72, pp. 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Poupard, N.; Groult, H.; Bodin, J.; Bridiau, N.; Bordenave-Juchereau, S.; Sannier, F.; Piot, J.M.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Maugard, T. Production of heparin and λ-carrageenan anti-heparanase derivatives using a combination of physicochemical depolymerization and glycol splitting. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, S.M.; Hay, P.A.; Buck, R.T.; Colville, C.S.; Porter, D.W.; Scopes, D.I.C.; Pollard, F.C.; Page, M.J.; Bennett, J.M.; Hircock, M.L.; et al. 2,3-Dihydro-1,3-dioxo-1H-isoindole-5-carboxylic acid derivatives: A novel class of small molecule heparanase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; DeChavigny, A.; Johnson, C.E.; Hamada, J.I.; Stein, C.A.; Nicolson, G.L. Suramin: A potent inhibitor of melanoma heparanase and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9661–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayal-Hershkovitz, M.; Miron, D.; Levy, O. Benz-1,3-azole Derivatives and Their Uses as Heparanes Inhibitors. WO2002060374, 8 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Courtney, S.M.; Hay, P.A.; Buck, R.T.; Colville, C.S.; Phillips, D.J.; Scopes, D.I.C.; Pollard, F.C.; Page, M.J.; Bennett, J.M.; Hircock, M.L.; et al. Furanyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl and benzoxazol-5-yl acetic acid derivatives: Novel classes of heparanase inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2295–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburajeev, C.P.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Mason, D.J.; Fuchs, J.E.; Bender, A.; Barash, U.; Vlodavsky, I.; Basappa; Rangappa, K.S. Identification of Novel Class of Triazolo-Thiadiazoles as Potent Inhibitors of Human Heparanase and their Anticancer Activity. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozalbes, R.; Mosulén, S.; Ortí, L.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Carbajo, R.J.; Melnyk, P.; Pineda-Lucena, A. Hit identification of novel heparanase inhibitors by structure- and ligand-based approaches. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masola, V.; Bellin, G.; Gambaro, G.; Onisto, M. cells Heparanase: A Multitasking Protein Involved in Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Remodeling and Intracellular Events. Cells 2018, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; De Veij, M.; Félix, E.; Magariños, M.P.; Mosquera, J.F.; Mutowo, P.; Nowotka, M.; et al. ChEMBL: Towards direct deposition of bioassay data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Nowotka, M.; Papadatos, G.; Dedman, N.; Gaulton, A.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.; Overington, J.P. ChEMBL web services: Streamlining access to drug discovery data and utilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W612–W620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Smirkin, A.; Itai, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Tanaka, J. Involvement of heparanase in migration of microglial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messore, A.; Madia, V.N.; Pescatori, L.; Saccoliti, F.; Tudino, V.; De Leo, A.; Bortolami, M.; De Vita, D.; Scipione, L.; Pepi, F.; et al. Novel Symmetrical Benzazolyl Derivatives Endowed with Potent Anti-Heparanase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10834–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 1-(3-O,5-O-Diacetyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-5-methyl-5-fluoro-6-hydroxydihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione|C14H19FN2O9—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/101687126 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 2-[(3-Ethoxycarbonylpiperidine-1-carbonyl)amino]-3-hydroxybutanoic Acid|C13H22N2O6—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/61187649 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- (2R)-4-Hydroxy-2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)piperidine-1-carbonyl]amino]butanoic acid|C11H17F3N2O4—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/107828179 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 4-[Methyl-[(1-methyl-6-oxopiperidin-3-yl)carbamoyl]amino]oxolane-3-carboxylic acid|C13H21N3O5—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/66265156 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Tipparaju, S.K.; Joyasawal, S.; Pieroni, M. In Pursuit of Natural Product Leads: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 2-[3-hydroxy-2-[(3-hydroxypyridine-2-carbonyl)amino]phenyl]benzoxazole-4-carboxylic acid (A-33853) and Its Analogues: Discovery of N-(2-Benzoxazol-2-ylphenyl)benzamides as Novel Antileishmanial Chemotypes. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7344–7347. [Google Scholar]
- 3-Phenanthro[9,10-d][1,3]oxazol-2-ylpropanoic acid|C18H13NO3—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/23794729 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 2-(6-Fluoro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid|C16H12FNO3—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/103430682 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 2-[[3-(1,3-Benzoxazol-2-yl)propanoylamino]methyl]-3-(3-methylphenyl)propanoic acid|C21H22N2O4—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/119243009 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 2-(6-Chloro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-4,5-difluorobenzoic acid|C14H6ClF2NO3—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/81421830 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Stephen, I.; Courtney, M.; Hay, P.A.; Ian, D.; Scopes, C.; Gb, O. Phtalamide Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. US-7138425-B2, 21 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 2’-(Benzo[d]oxazol-2-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate|C20H12NO3—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/155906206 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 5-[2-(1,3-Benzoxazol-2-ylsulfanyl)propanoylamino]-2-chlorobenzoic acid|C17H13ClN2O4S—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/23886486 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- 5-[3-(1,3-Benzoxazol-2-yl)anilino]-5-oxopentanoate|C18H15N2O4—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6968873 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; Von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An open-source program for chemistry aware data visualization and analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.R.; Calkins, D.; Sullivan, A.P.; Shelley, J.C. Towards the comprehensive, rapid, and accurate prediction of the favorable tautomeric states of drug-like molecules in aqueous solution. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving force field accuracy on challenging regimes of chemical space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.L.; Andrews, C.W.; Capelli, A.M.; Clarke, B.; LaLonde, J.; Lambert, M.H.; Lindvall, M.; Nevins, N.; Semus, S.F.; Senger, S.; et al. A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5912–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capuzzi, S.J.; Muratov, E.N.; Tropsha, A. Phantom PAINS: Problems with the Utility of Alerts for Pan-Assay in terference Compounds. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4-Hydroxy-1-(4,4,4-trifluorobutylcarbamoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid|C10H15F3N2O4—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/113327907 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
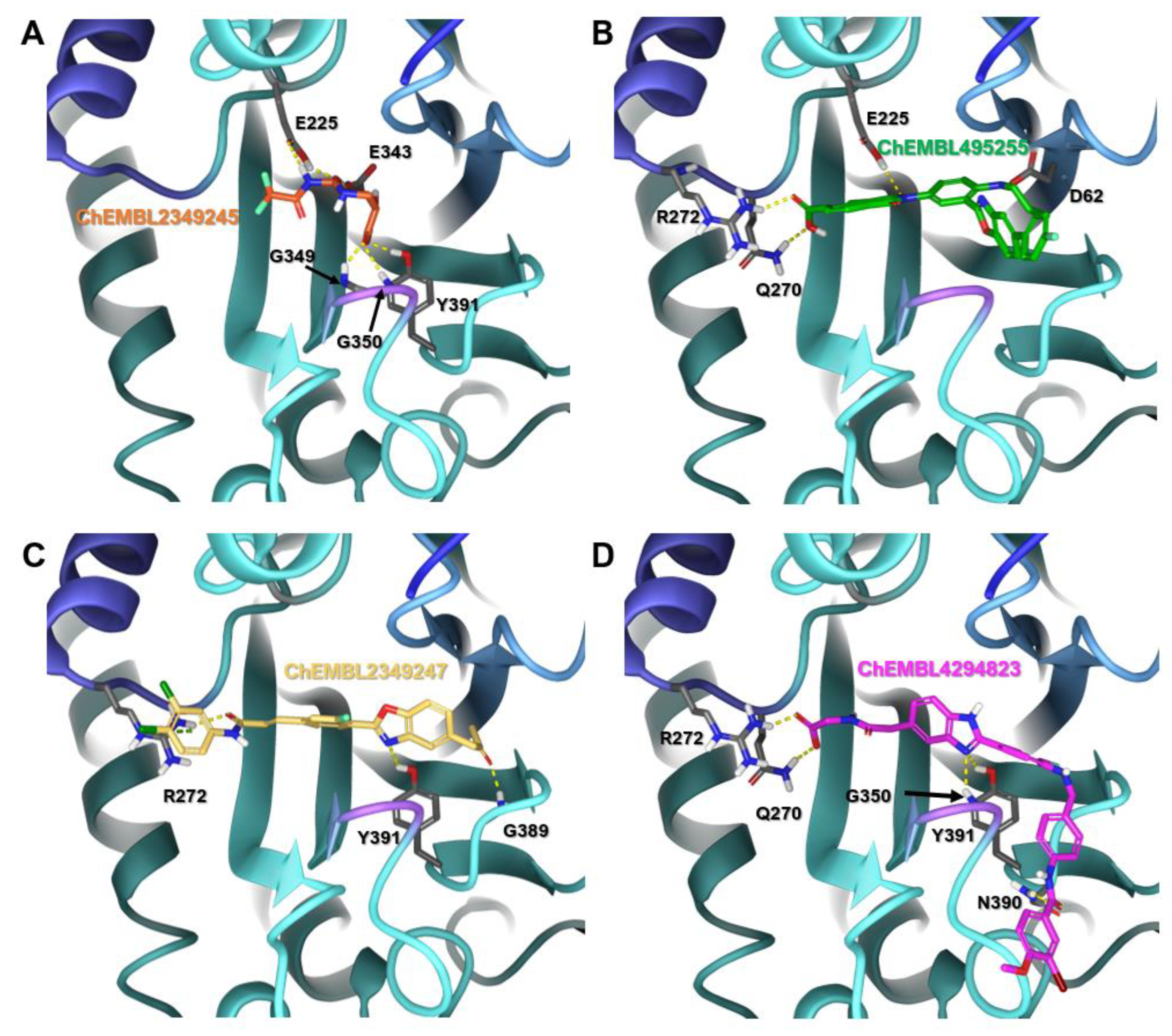
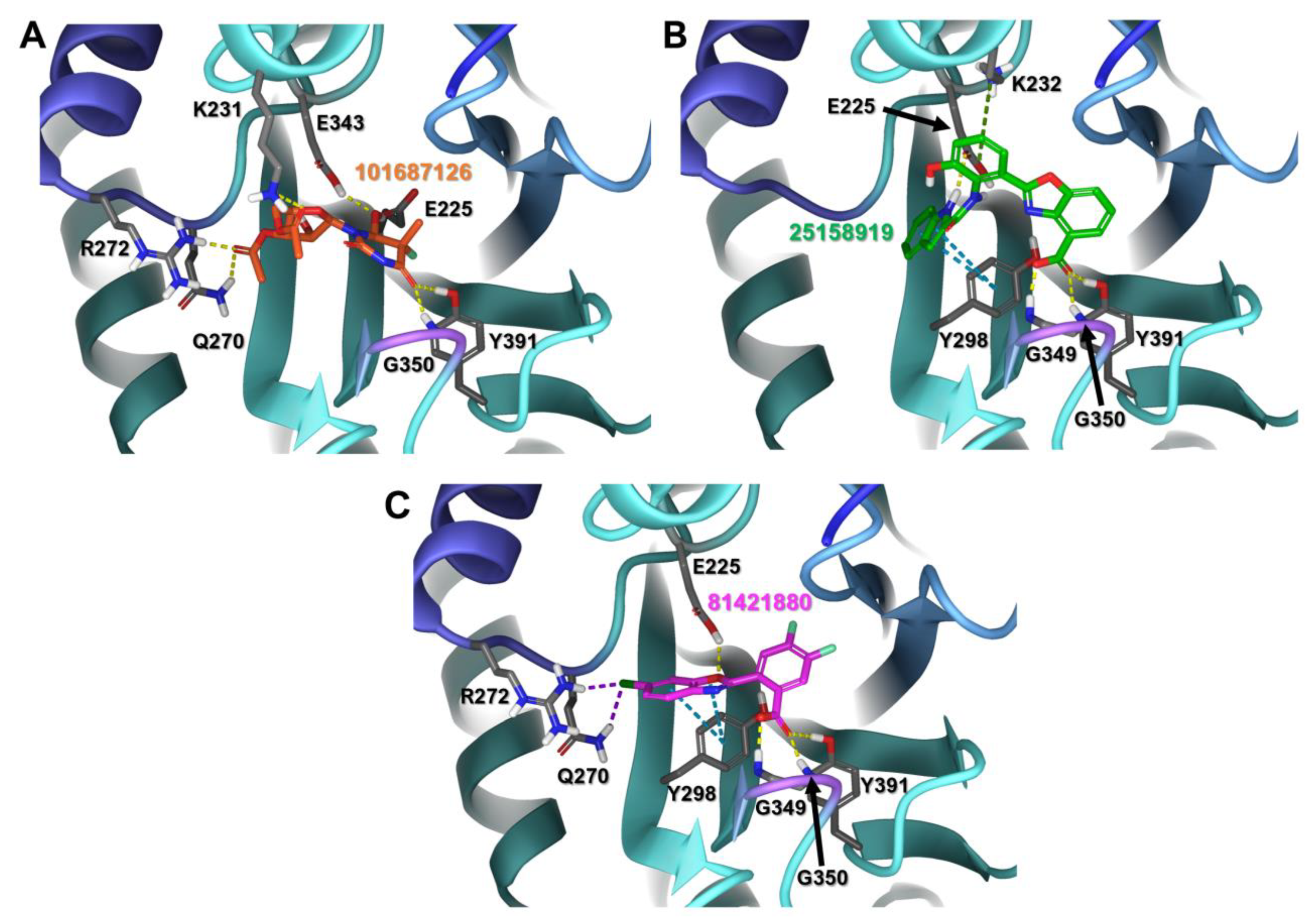
| Compound ID | Structure | Glide Score (kcal/mol) | IC50 (µM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChEMBL2349245 | 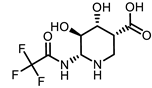 | −7.86 | 1 | [40] |
| ChEMBL495255 | 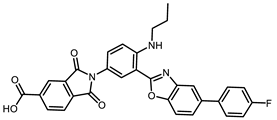 | −5.79 | 0.50 | [36] |
| CHEMBL2349247 | 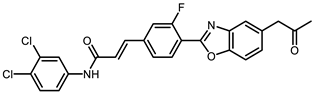 | −5.60 | 0.20 | [36] |
| CHEMBL4294823 |  | −7.91 | 0.64 | [41] |
| Compound ID | Structure | Glide Score (kcal/mol) | HPSE IC50 (µM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChEMBL2349245 | 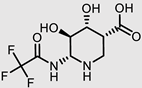 | −7.86 | 1.00 | [40] |
| 101687126 | 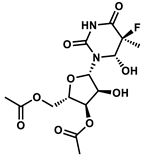 | −10.80 | NR | [44] |
| 61187649 |  | −9.53 | NR | [45] |
| 107828179 | 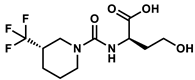 | −9.04 | NR | [46] |
| 66265156 | 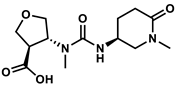 | −8.88 | NR | [47] |
| 113327907 | 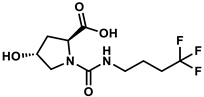 | −8.54 | NR | [47] |
| ChEMBL495255 | 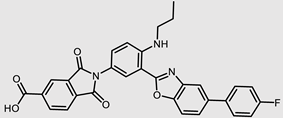 | −5.79 | 0.50 | [36] |
| 25158919 | 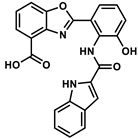 | −9.33 | NR | [48] |
| 23794729 | 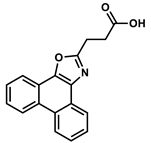 | −8.31 | NR | [49] |
| 103430682 | 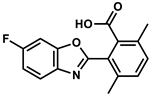 | −8.01 | NR | [50] |
| 119243009 |  | −7.44 | NR | [51] |
| ChEMBL2349247 |  | −5.60 | 0.20 | [36] |
| 81421830 |  | −7.90 | NR | [52] |
| 58743027 |  | −7.46 | NR | [53] |
| 155906206 | 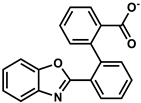 | −7.15 | NR | [54] |
| 23886486 |  | −6.81 | NR | [55] |
| 6968873 | 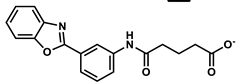 | −6.62 | NR | [56] |
| Compound | QPlogS a | QPlogHERG b | QPPCaco c | QPlogBB d | % Human Oral Absorption e | PAINS # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChEMBL2349245 | −0.72 | −0.97 | 1.90 | −1.00 | 15 | 0 |
| 101687126 | −2.53 | −3.81 | 78.62 | −1.66 | 44 | 0 |
| 61187649 | −2.77 | −0.67 | 57.15 | −1.23 | 69 | 0 |
| 107828179 | −2.83 | −0.64 | 30.74 | −1.11 | 63 | 0 |
| 66265156 | −0.50 | 1.22 | 30.14 | −0.89 | 52 | 0 |
| 113327907 | −2.13 | −0.47 | 36.73 | −0.93 | 62 | 0 |
| ChEMBL495255 | −8.64 | −6.24 | 23.02 | −2.27 | 58 | 0 |
| 25158919 | −4.68 | −4.76 | 66.73 | −1.28 | 78 | 0 |
| 23794729 | −4.34 | −3.94 | 169.97 | −0.78 | 87 | 0 |
| 103430682 | −4.39 | −3.21 | 411.40 | −0.13 | 94 | 0 |
| 119243009 | −4.82 | −3.64 | 80.58 | −1.38 | 84 | 0 |
| ChEMBL2349247 | −8.32 | −7.43 | 818.21 | −0.75 | 100 | 0 |
| 81421830 | −4.63 | −3.34 | 290.83 | 0.02 | 92 | 0 |
| 58743027 | −6.07 | −4.95 | 27.71 | −1.51 | 73 | 0 |
| 155906206 | −4.35 | −4.08 | 387.64 | −0.38 | 100 | 0 |
| 23886486 | −4.35 | −3.09 | 145.77 | −0.66 | 85 | 0 |
| 6968873 | −4.72 | −4.77 | 58.63 | −1.57 | 75 | 0 |
| Chemical Library 1 (ChEMBL2349245) | Chemical Library 2 (ChEMBL495255) | Chemical Library 3 (ChEMBL2349247) | Chemical Library 4 (ChEMBL4294823) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanimoto similarity index | >70% | >80% | >80% | >80% |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 200–600 | 200–600 | 200–600 | 200–600 |
| Rotatable bond count | 2–10 | 2–10 | 2–10 | 2–10 |
| Heavy atom count | 17–33 | 17–35 | 17–35 | 17–35 |
| xLog(P) | −8–3 | 3–9 | 3–9 | 3–9 |
| No. of compounds returned | 4938 | 9923 | 34,721 | 34,721 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rus, A.; Bolanos-Garcia, V.M.; Bastida, A.; Morales, P. Identification of Novel Potential Heparanase Inhibitors Using Virtual Screening. Catalysts 2022, 12, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050503
Rus A, Bolanos-Garcia VM, Bastida A, Morales P. Identification of Novel Potential Heparanase Inhibitors Using Virtual Screening. Catalysts. 2022; 12(5):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050503
Chicago/Turabian StyleRus, Alfredo, Victor M. Bolanos-Garcia, Agatha Bastida, and Paula Morales. 2022. "Identification of Novel Potential Heparanase Inhibitors Using Virtual Screening" Catalysts 12, no. 5: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050503
APA StyleRus, A., Bolanos-Garcia, V. M., Bastida, A., & Morales, P. (2022). Identification of Novel Potential Heparanase Inhibitors Using Virtual Screening. Catalysts, 12(5), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12050503








