Interfering with mRNA Methylation by the 2′O-Methyltransferase (NSP16) from SARS-CoV-2 to Tackle the COVID-19 Disease
Abstract
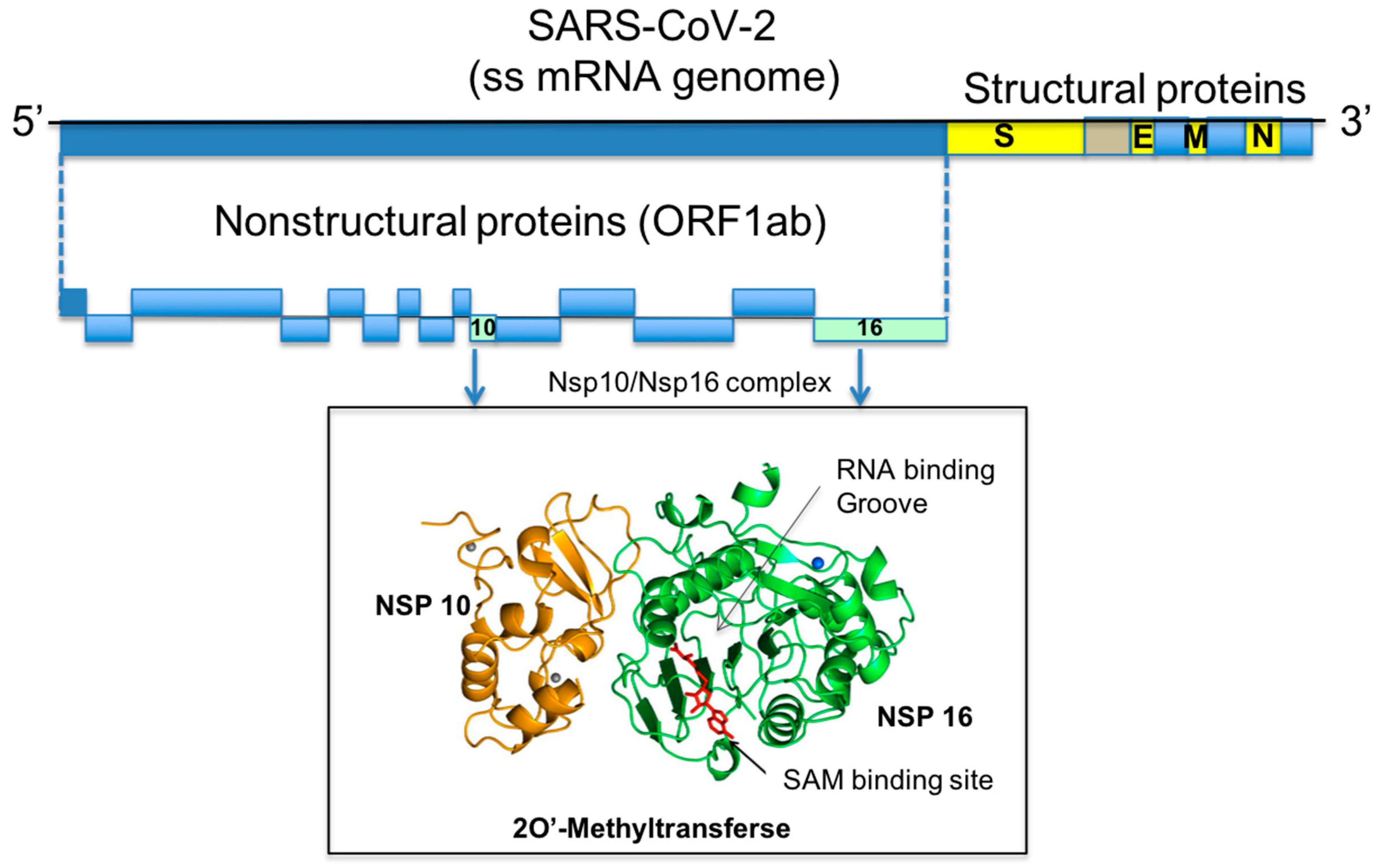
1. Introduction
2. Results
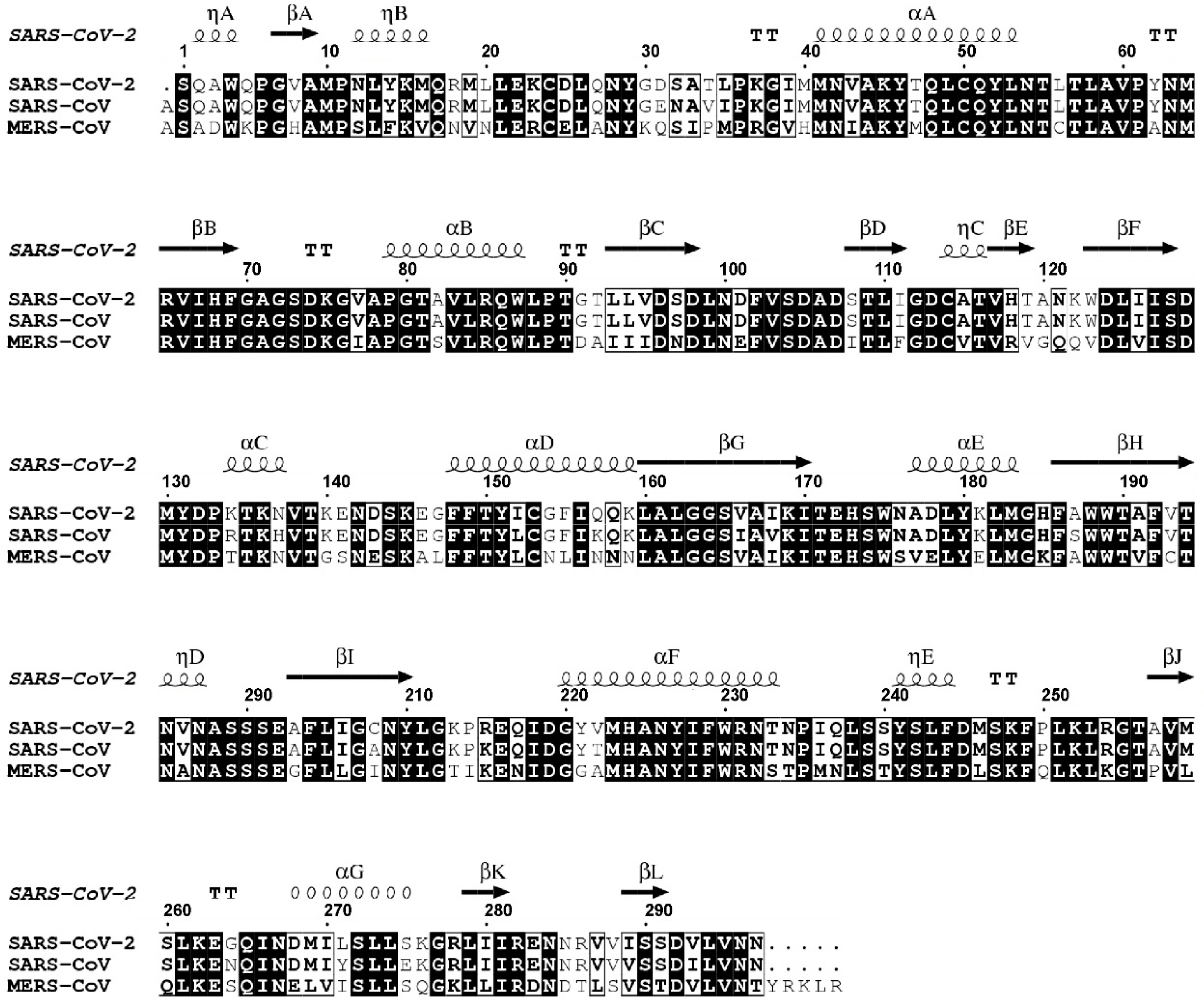
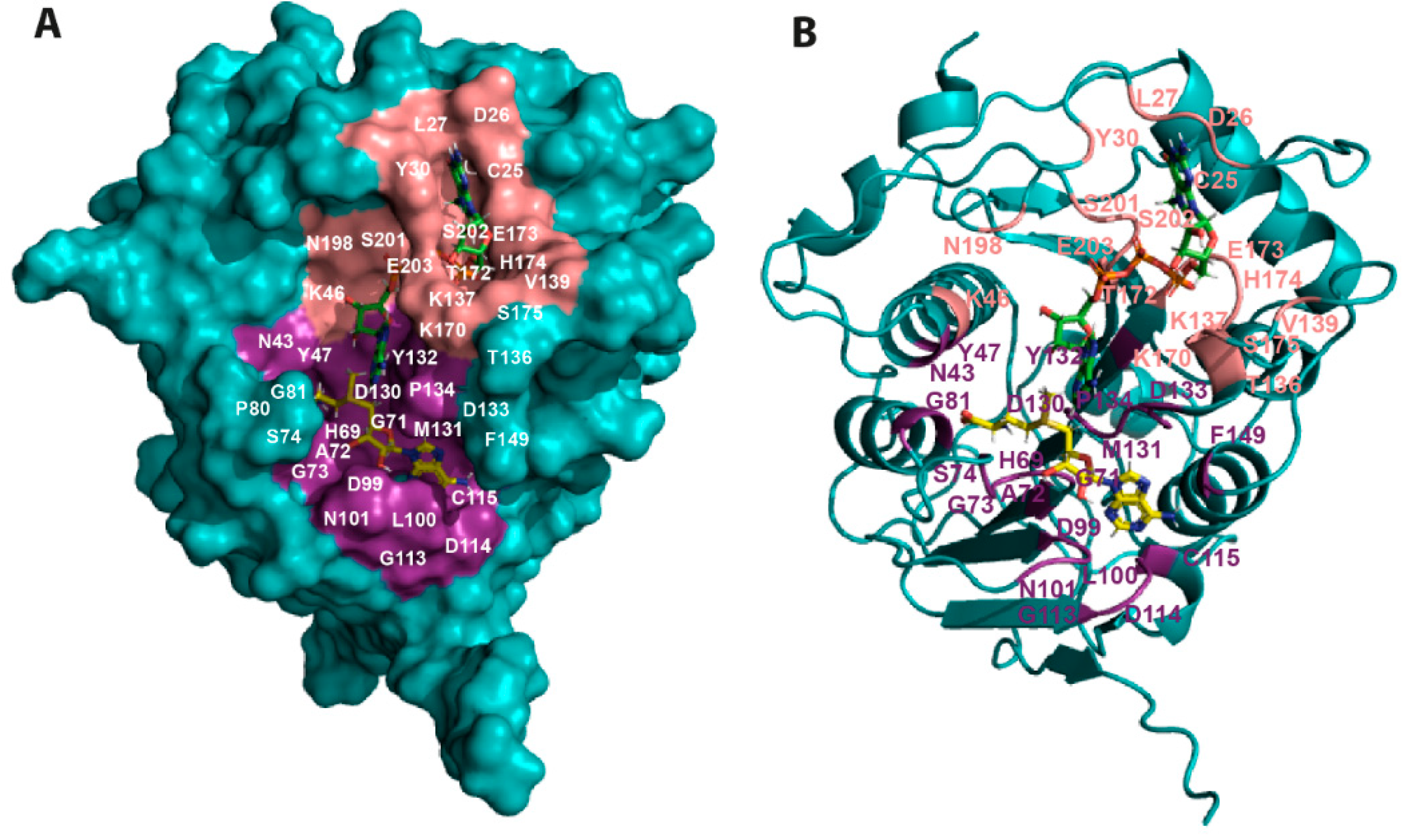
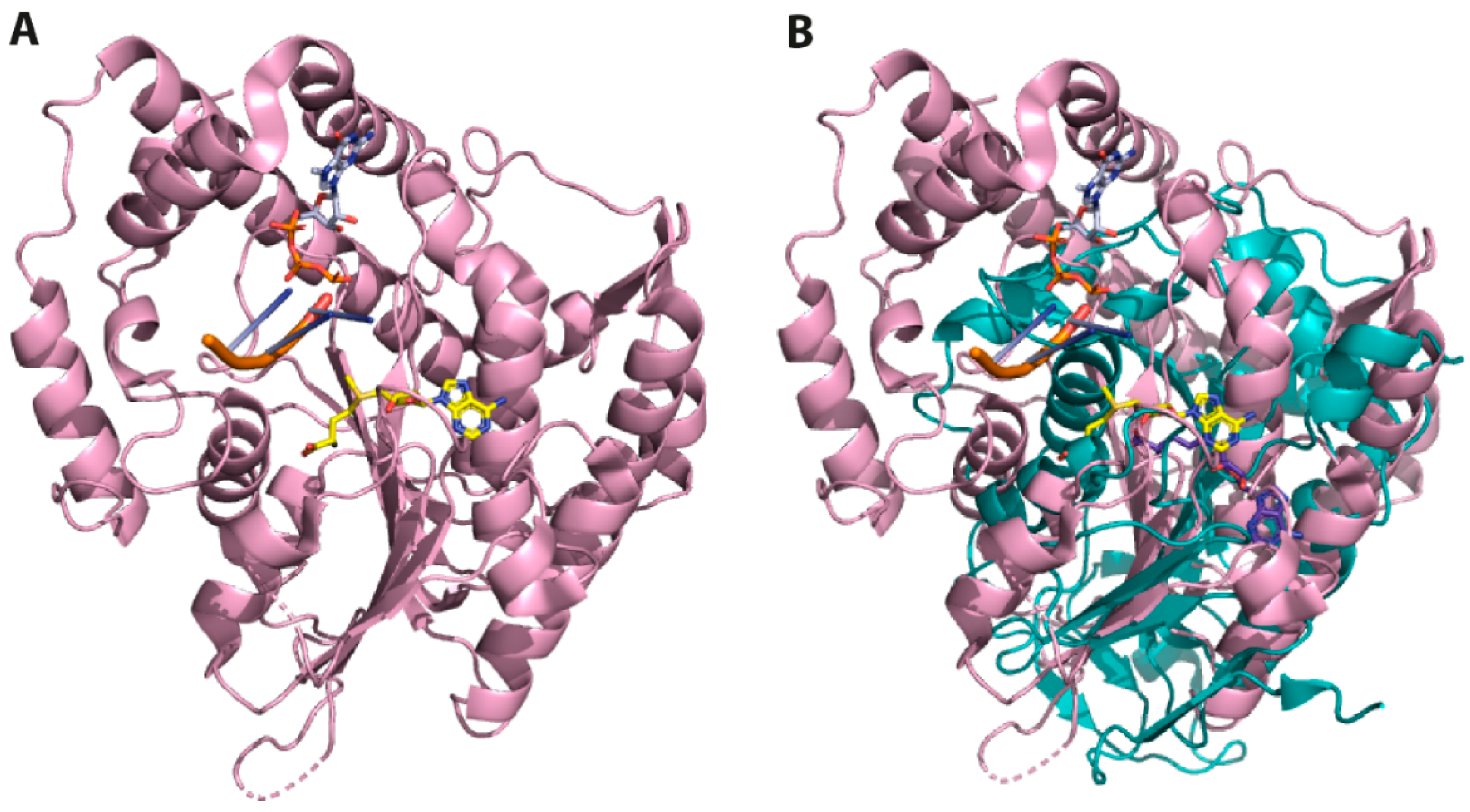
2.1. Comparative Analysis and Structural Characterisation of 2′O-MTase from Coronavirus
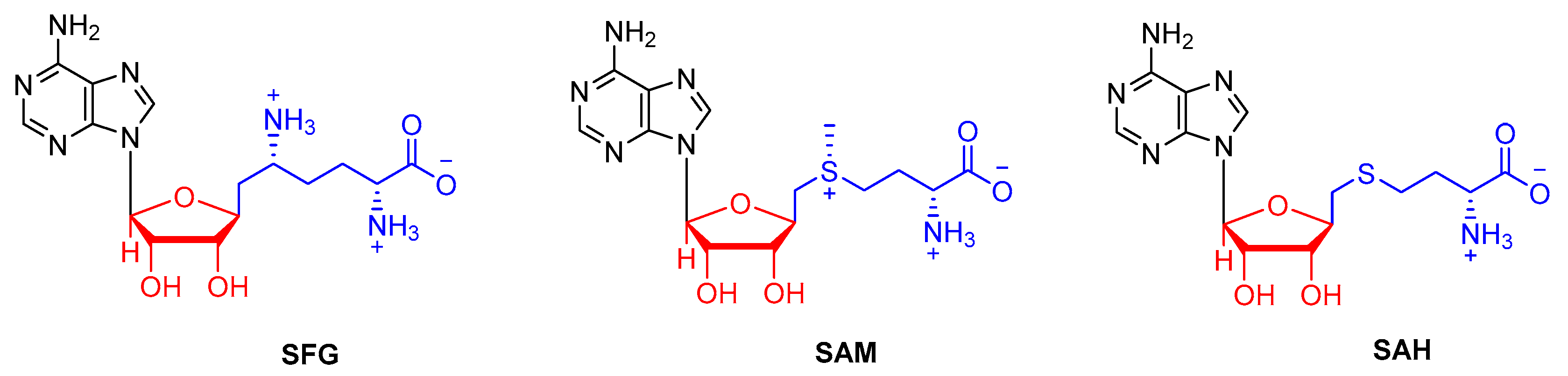
2.1.1. NSP16 is a Suitable Drug Target
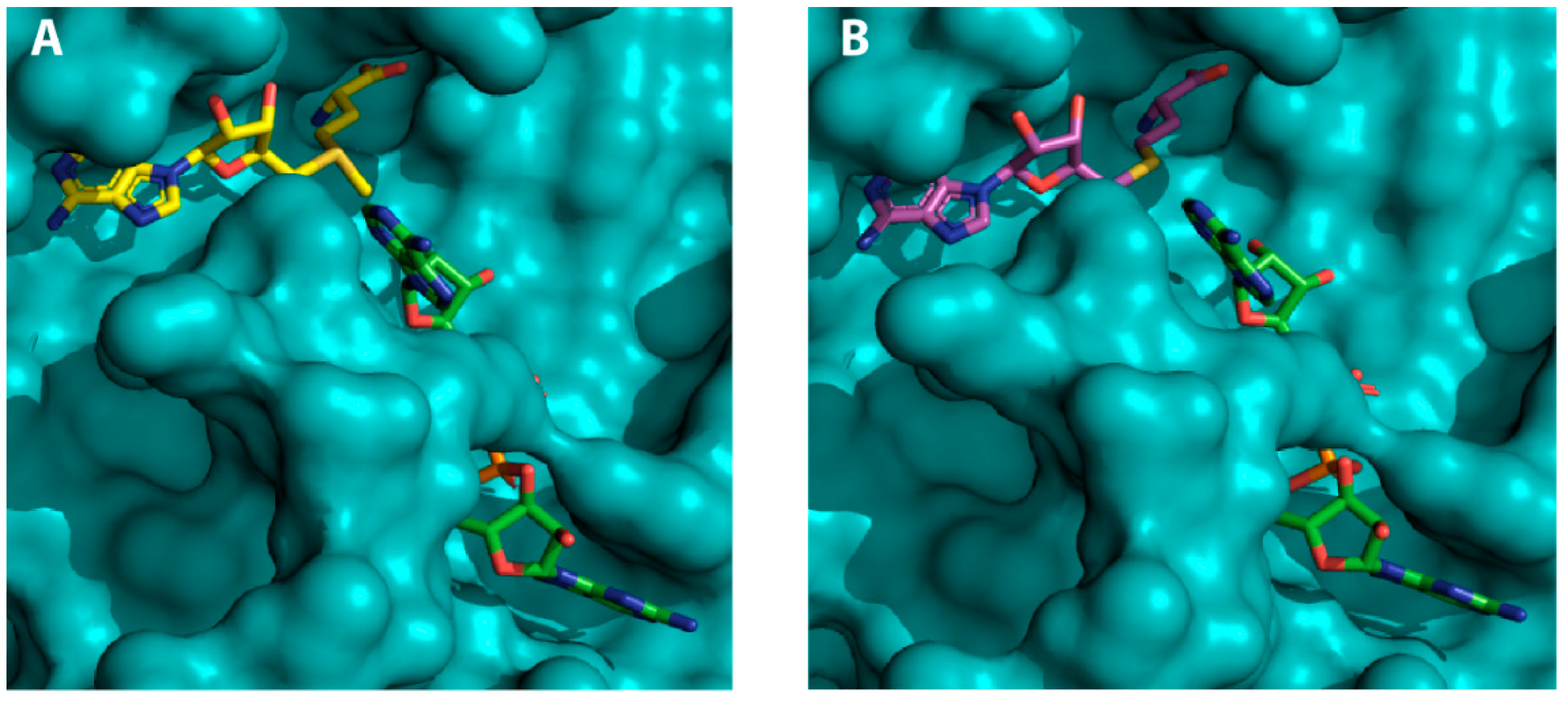
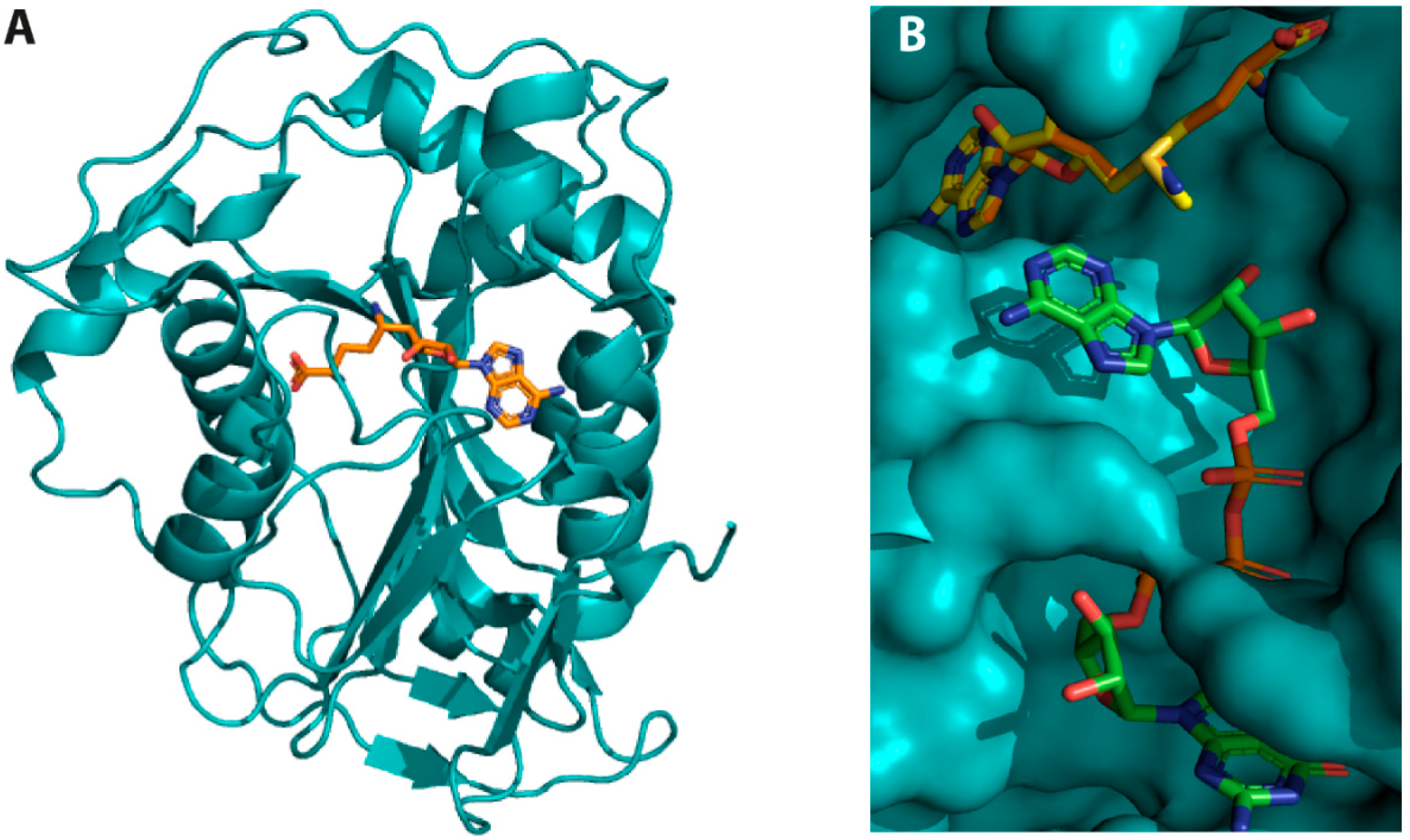
2.1.2. NSP16 Exhibits a Druggable Pocket
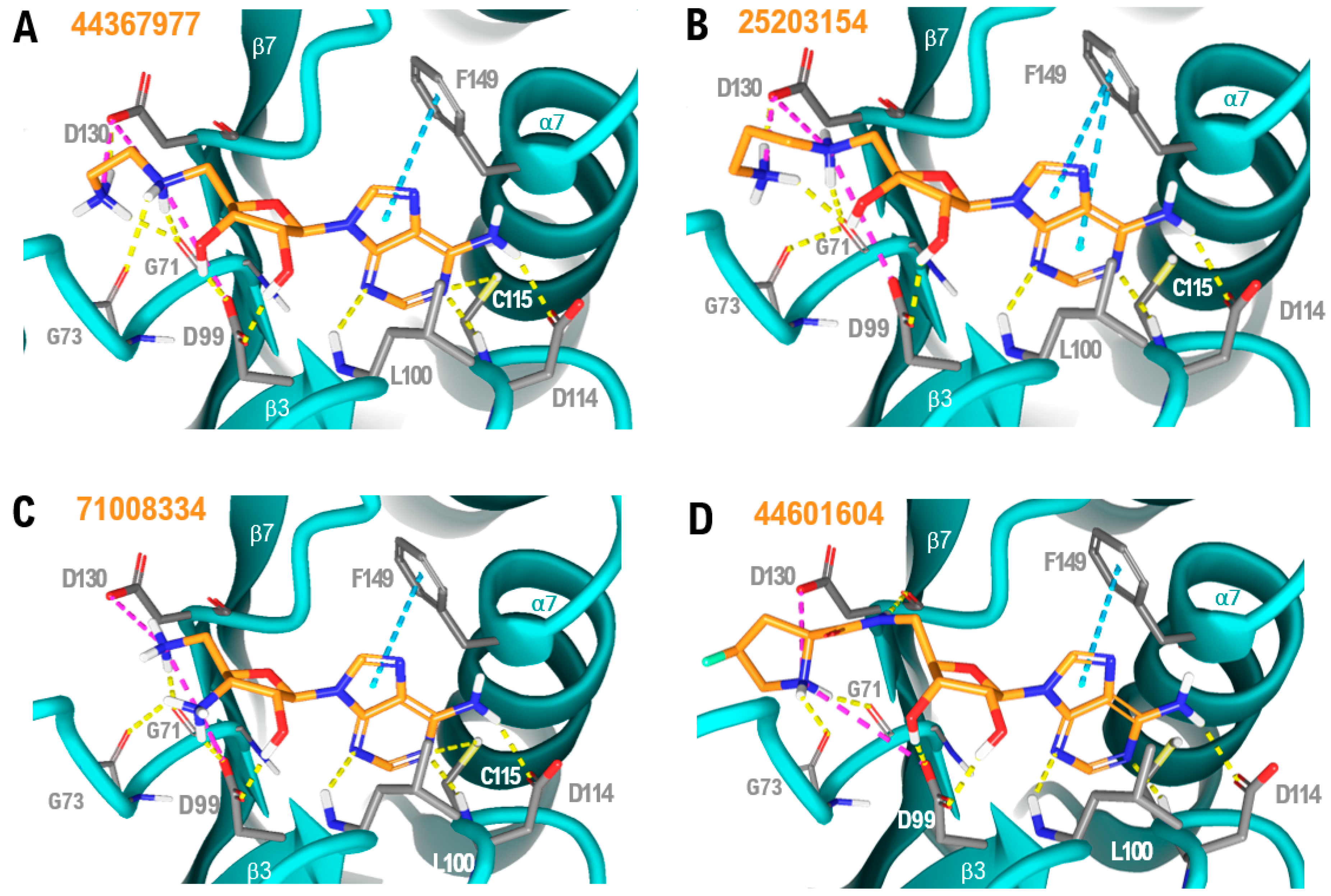
2.2. Virtual Screening
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virtual Screening
4.1.1. Ligand Preparation
4.1.2. High-Throughput Virtual Screening (HTVS)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Medicines Agency. First COVID-19 treatment recommended for EU authorisation. In European Medicines Agency EMA/264817; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, E.J.; Decroly, E.; Ziebuhr, J. The Nonstructural Proteins Directing Coronavirus RNA Synthesis and Processing. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 59–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Su, C.; Ke, M.; Jin, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tien, P.; et al. Biochemical and structural insights into the mechanisms of sars coronavirus RNA ribose 2′-O-methylation by nsp16/nsp10 protein complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroly, E.; Debarnot, C.; Ferron, F.; Bouvet, M.; Coutard, B.; Imbert, I.; Gluais, L.; Papageorgiou, N.; Sharff, A.; Bricogne, G.; et al. Crystal structure and functional analysis of the SARS-coronavirus RNA cap 2′-o-methyltransferase nsp10/nsp16 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Lemus, M.; Minasov, G.; Shuvalova, L.; Inniss, N.; Brunzelle, J.; Satchell, K.J.F. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 2′-O-methyltransferase heterodimer with RNA Cap analog and sulfates bound reveals new strategies for structure-based inhibitor design. Bio Rxiv 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, J.L.; Diamond, M.S. Innate immune restriction and antagonism of viral RNA lacking 2′-O methylation. Virology 2015, 479–480, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Robb, G.B.; Chan, S.H. mRNA capping: Biological functions and applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7511–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Chuaqui, C.; Singh, J. Structural Interaction Fingerprint (SIFt): A Novel Method for Analyzing Three-Dimensional Protein-Ligand Binding Interactions. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.L.; Andrews, C.W.; Capelli, A.M.; Clarke, B.; LaLonde, J.; Lambert, M.H.; Lindvall, M.; Nevins, N.; Semus, S.F.; Senger, S.; et al. A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5912–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuzzi, S.J.; Muratov, E.N.; Tropsha, A. Phantom PAINS: Problems with the Utility of Alerts for Pan-Assay Interference Compounds. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.O.M.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2001, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Duffy, E.M. Prediction of drug solubility from structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafcikova, P.; Silhan, J.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. Structural analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex involved in coronaviral RNA cap creation. Bio Rxiv 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.R.; Calkins, D.; Sullivan, A.P.; Shelley, J.C. Towards the comprehensive, rapid, and accurate prediction of the favorable tautomeric states of drug-like molecules in aqueous solution. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
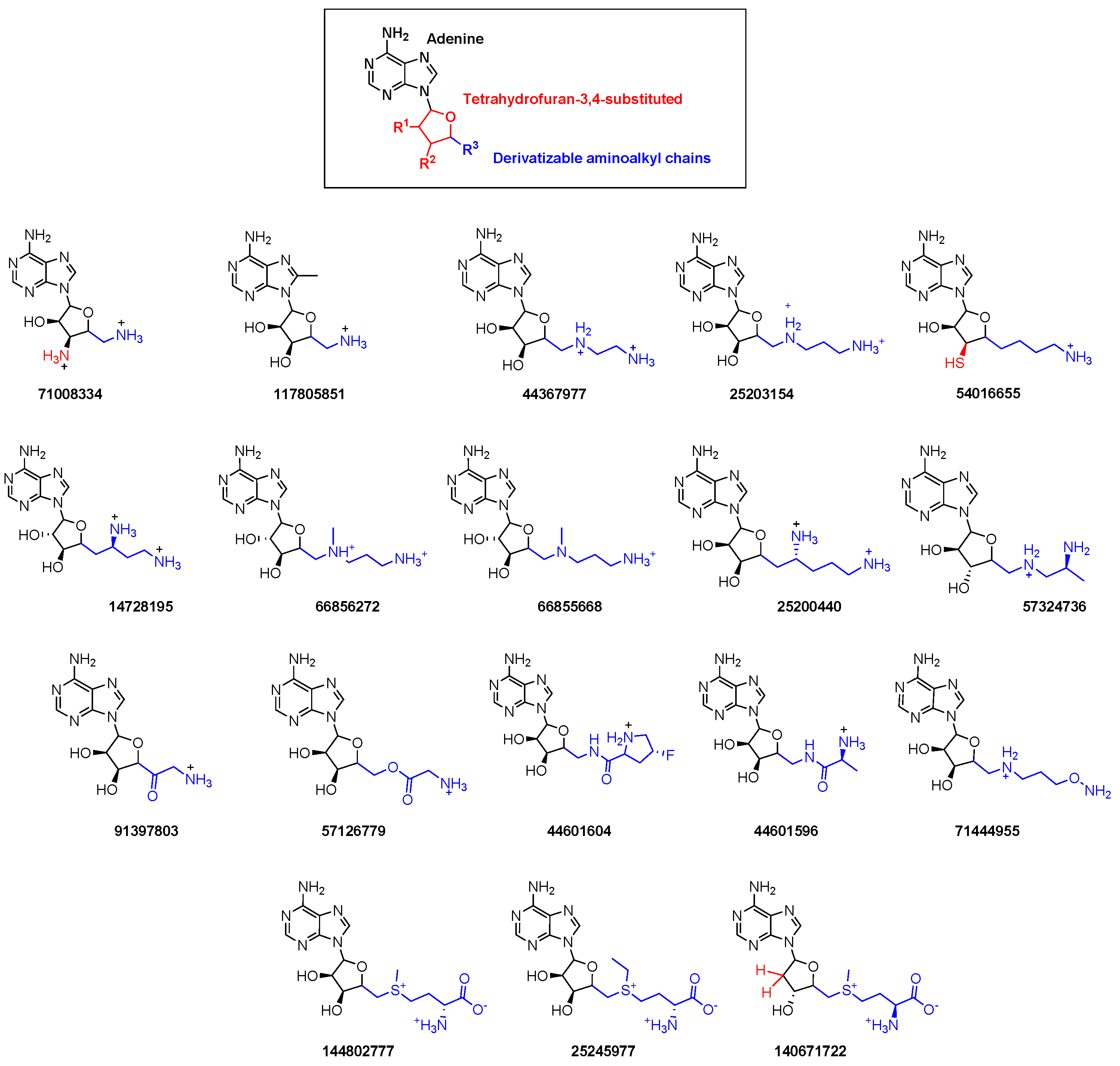
| Compound (PubChem ID) | QPlogS a | QlogBB b | QPlogKp c | QPlogKhsa d | Docking Score e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44367977 | 0.20 | −1.82 | −9.60 | −0.99 | −12.05 |
| 25203154 | 0.33 | −1.56 | −9.04 | −0.94 | −11.83 |
| 71008334 | 0.45 | −1.41 | −9.96 | −0.81 | −11.81 |
| 14728195 | 0.45 | −1.86 | −9.77 | −0.92 | −11.66 |
| 25200440 | 0.34 | −1.96 | −9.67 | −0.90 | −11.63 |
| 66856272 | 0.17 | −1.68 | −9.27 | −0.91 | −11.57 |
| 44601596 | −0.48 | −2.52 | −8.14 | −1.29 | −11.50 |
| 44601604 | −1.32 | −2.00 | −7.62 | −1.16 | −11.42 |
| 66855668 | 0.36 | −1.54 | −9.39 | −0.91 | −11.04 |
| 57126779 | −0.96 | −2.71 | −8.96 | −0.94 | −11.00 |
| 54016655 | −1.51 | −1.53 | −6.63 | −0.67 | −10.83 |
| 57324736 | −0.02 | −1.92 | −9.82 | −0.89 | −10.11 |
| 117805851 | −0.87 | −1.70 | −7.80 | −0.78 | −10.06 |
| 91397803 | −0.76 | −2.26 | −8.43 | −0.92 | −9.95 |
| 71444955 | −0.99 | −2.60 | −7.69 | −1.08 | −9.94 |
| SFG | −0.39 | −3.17 | −11.50 | −1.29 | −8.09 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales, P.; Curtis, N.L.; Zárate, S.G.; Bastida, A.; Bolanos-Garcia, V.M. Interfering with mRNA Methylation by the 2′O-Methyltransferase (NSP16) from SARS-CoV-2 to Tackle the COVID-19 Disease. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091023
Morales P, Curtis NL, Zárate SG, Bastida A, Bolanos-Garcia VM. Interfering with mRNA Methylation by the 2′O-Methyltransferase (NSP16) from SARS-CoV-2 to Tackle the COVID-19 Disease. Catalysts. 2020; 10(9):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091023
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales, Paula, Natalie L. Curtis, Sandra G. Zárate, Agatha Bastida, and Victor M. Bolanos-Garcia. 2020. "Interfering with mRNA Methylation by the 2′O-Methyltransferase (NSP16) from SARS-CoV-2 to Tackle the COVID-19 Disease" Catalysts 10, no. 9: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091023
APA StyleMorales, P., Curtis, N. L., Zárate, S. G., Bastida, A., & Bolanos-Garcia, V. M. (2020). Interfering with mRNA Methylation by the 2′O-Methyltransferase (NSP16) from SARS-CoV-2 to Tackle the COVID-19 Disease. Catalysts, 10(9), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10091023







