Abstract
Porous organic polymers (POPs) are widely used in various areas such as adsorption, separation and catalysis. In the present work, ionic liquid-modified porous organic polymers (IL-POPs) synthesized by dispersion polymerization were applied to immobilize metallocene catalysts for olefin polymerization. The prepared IL-POPs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), nitrogen sorption porosimetry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis. The IL-POPs obtained pores with surface specific area (SSA) ranging from 16.9 m2/g to 561.8 m2/g, and total pore volume (TPV) ranging from 0.08 cm3/g to 0.71 cm3/g. The supported catalysts Zr/MAO@IL-POPs exhibit great activity (3700 kg PE/mol·Zr·bar·h) in ethylene polymerization, and the GPC-IR results show that the polyethylene has narrow molecular weight distribution (2.2 to 2.8). The DSC results show that the melting point of prepared polyethylene was as high as 138 °C, and the TREF analysis results indicate that they have similar chemical composition distribution with elution temperature at 100.5–100.7 °C.
1. Introduction
Since Kaminsky and Sinn discovered polymerization activity could be greatly improved by methylaluminoxane (MAO), the manufacture of metallocene polyolefins with controlled chain structure and narrow molecular weight distribution developed rapidly, and the metallocene and post-metallocene catalysts attract great attention of chemists [1,2,3,4,5]. Nevertheless, metallocene catalysts cause reactor fouling, and most industrial olefin polymerization is conducted in gas or slurry process with heterogeneous catalysts. Therefore, the metallocene/MAO catalysts should be immobilized on support to avoid reactor fouling, to help control the morphology of polymer particles and to reduce the cost of cocatalyst [6,7].
A great number of publications reported inorganic and organic porous materials as metallocene supports. Inorganic supports, represented by SiO2, Al2O3 and zeolite with hard surface and massive acidic groups, may cause a problem of deactivation and high cocatalyst costs [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. In comparison, kinds of soft organic supports such as polystyrene, polysiloxane and POPs [17,18,19,20,21,22,23] provide an analogous environment to homogeneous polymerization and could be used without complex pre-treatment [24]. A series of functionalized POPs with tunable pore structures were synthesized by our team, they showed better catalytic activity than silica supports, and can be optimized by changing the functional comonomer for better immobilization, introducing metal oxide templates and altering the solvent to acquire well-shaped particles.
More recently, the molten salts named ionic liquids (ILs) aroused attention in the field of materials science, which has witnessed widely development in heterogeneous catalysts. The combination of the anion and the cation gives ILs special physical and chemical properties of low volatility, high thermal stability and ion conductivity, etc.; moreover, the typical composition also provides ILs a multiple synthetic choice and diverse applications as a platform compound [25,26,27,28]. In a recent work, Wioletta et al. used ionic liquid-modified silica (SIL)-supported metallocene to catalyze ethylene polymerization and obtained linear polyethylene with a high melting temperature and crystallinity, thus proving that the ionic liquid could be used as an olefin polymerization catalyst component [29]. Compared to the POPs supports through one-pot synthesis, the SIL supports were prepared under strict conditions by a complex synthetic route.
Considering that the typical ionic composition of ILs may have a positive effect on MAO/metallocene immobilization, we introduce 1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium-chloride ([BVIM] [Cl]) as a functional comonomer for the synthesis of mono-functional-group and dual-functional-group IL-POPs. The prepared IL-POPs obtained good porosity, and the pore structure can be modulated by adjusting the comonomer contents and solvent system. IL-POPs supports exhibited great ethylene polymerization activity, which would be potential supports for the future heterogeneous olefin polymerization industry.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Divinylbenzene (DVB, mixtures of isomers, 80%), 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate (HEMA, ≥98%), 2,2′-azo-bis-isobutyronitrile (AIBN) were all provided by Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). DVB was extracted by NaOH solution (5 wt%) to remove the stabilizer and HEMA was passed through neutral aluminum oxide column before use. Ethanol (≥99.5%, CP) was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-vinylimidazolium-chloride ([BVIM] [Cl]) was purchased from Zhengzhou Alfachem Co., Ltd. (Zhengzhou, China). Methylaluminoxane (MAO, 10% in toluene) was purchased from Albemarle Co., Ltd. (Charlotte, NC, USA), the toluene was distilled under reduced pressure to obtain white solid MAO before use. Poloxamer 407 (F127, BASF), zirconocene ((n-BuCp)2ZrCl2), DALCHEM, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia) and other reagents were used directly as received.
2.2. Preparation of Ionic Liquid-Modified Porous Organic Polymer Supports
Porous poly (DVB-co-[BVIM] [Cl]) supports were synthesized via a dispersion polymerization strategy. An amount of 140 mL of ethanol was charged into a 250 mL multi-necked flask, which was equipped with a mechanical agitator. Typically, 4.84 g (37.1 mmol) of DVB, 6.94 g (37.2 mmol) of [BVIM] [Cl] and 0.59 g (5 wt% of monomers) of F127 were added into the system and stirred at 50 °C. After 30 min, 0.35 g (3 wt% of monomers) of AIBN was charged into the solution and stirred at 70 °C for 3 h, then the reaction was carried out at 80 °C for 5 h. Finally, the particles were filtered off and washed with ethanol and dried under vacuum for further use. While in the ternary system, HEMA was used as a second functional comonomer, and the poly (DVB-co-HEMA-co-[BVIM] [Cl]) support was synthesized in the same way.
2.3. Preparation of Ionic Liquid-Modified POPs Supported Catalysts
The immobilization of metallocene on IL-POPs supports was carried out under N2 atmosphere. Typically, 1.67 g of MAO was transferred to a multi-necked flask containing 3 g of poly (DVB-co-[BVIM] [Cl]) supports. Then, 50 mL of dehydrated toluene was charged into the flask and stirred at room temperature for 1 h. Subsequently, 0.04 g of (n-BuCp)2ZrCl2 was added and stirred for another 3 h. The solid was isolated by filtration and washed with toluene and hexane, and the residual solvents were completely removed under vacuum to obtain Zr/MAO@IL-POPs catalysts.
2.4. Ethylene Polymerization in Slurry Process
Ethylene polymerization was conducted in an 800 mL stainless steel reactor equipped with a mechanical agitator and an external oil bath. An amount of 300 mL of hexane and 3 mL of TEAL (Aluminum triethyl, 10% in hexane) were added into the reactor and stirred for 5 min at room temperature; about 120–160 mg of supported catalysts was charged sequentially. Ethylene was continuously fed under the pressure of 0.40–0.45 MPa during polymerization at 80 °C, thirty minutes later, the reactor was cooled to room temperature and the remaining gas was vented off, the generated polymer was collected by filtration and drying.
2.5. Characterization
N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of IL-POPs were analyzed by a Quantachrome Nova 2000e N2 sorption at 77.3 K, the particles were degassed at 120 °C overnight before analysis. The FT-IR of IL- POPs and supported catalysts were analyzed on the NEXUS 670 FTIR and the thermal stability of the supports was tested by a DSC Q2000 thermal gravimetric analysis. SEM analysis of IL-POPs and the polyethylene samples was carried out on a HITACHI S4800. The molecular weight and its distribution of polymers were analyzed by GPC-IR from Polymer Char, using 1,2,4-trichlorobenzenen as solvent. Differential scanning calorimeter 214 was used to analyze the melting temperature of the polyethylene particles. The loading of zirconium and aluminum were determined by VISTA-MPX (Agilent). The chemical composition distribution (CCD) of polyethylene from Zr/MAO@IL-POPs was analyzed on temperature rising elution fractionation (TREF) 300 from Polymer Char.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Ionic Liquid-Modified Porous Organic Polymer
In the present work, [BVIM] [Cl] was used as a functional comonomer (FC) for ionic liquid-modified mono-functional and dual-functional porous organic polymers synthesis. As shown in Figure 1, IL-POPs were synthesized by free radical polymerization, firstly, monomers were dispersed in the solvent and the polymerization was initiated by AIBN. In the ternary system, HEMA was used as the second functional comonomer, and the influence of HEMA on the IL-POPs’ pore structure, MAO/metallocene immobilization and ethylene polymerization were also investigated.
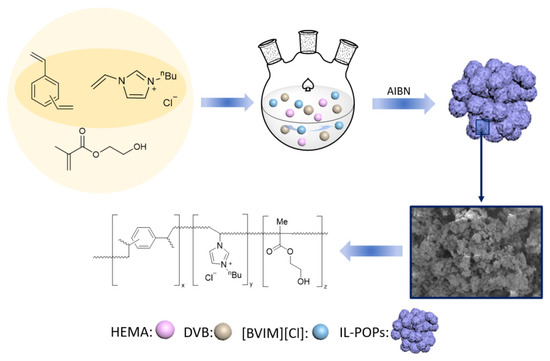
Figure 1.
Preparation of ionic liquid-modified POPs.
The porosity of IL-POPs was evaluated by nitrogen sorption analysis, the measured BET specific surface area (SSA) and the non-local density functional theory (NLDFT) simulated total pore volume (TPV) and average pore diameter (PD) results were listed in Table 1. Pore parameters of ionic liquid-modified POPs.

Table 1.
Pore parameters of ionic liquid-modified POPs.
3.2. Pore Structure of Ionic Liquid-Modified Porous Organic Polymer
According to Table 1, the prepared IL-POPs exhibit good porosity and are quite different with different comonomer contents. The value of SSA ranges from 16.9 m2/g to 561.8 m2/g, and the TPV ranges from 0.08 cm3/g to 0.71 cm3/g, and the PD ranges from 3.08 nm to 18.90 nm.
The influence of [BVIM] [Cl] contents on the formation of pore structure of the IL-POPs with mono-function-group was investigated. As shown in Table 1, while the [BVIM] [Cl] adding amount was only 5%, POP-5 was poorly porous with 47.8 m2/g of SSA, the NLDFT simulated PD was 6.80 nm that the obtained pores exhibited low surface area and pore volume, and the TPV was only 0.08 cm3/g. When increasing the [BVIM] [Cl] adding amount to 33%, POP-2 obtained a higher porosity than POP-3 (FC content = 25%) and POP-6 (FC content = 20%) with the SSA value of 550.1 m2/g, 496.0 m2/g and 331.5 m2/g, respectively. According to Figure 2b, POP-2 contained more larger pores (PD > 4 nm) than POP-3 and POP-6, and the cumulative pore volume of POP-2 was higher than the others. It can be seen from Figure 2c that, in the pore size range of 1 nm to 4 nm, pores with high surface area of POP-6 were less than POP-2 and POP-3, then POP-6 obtained lower cumulative surface area. The polarity of prepared IL-POPs was changed by adjusting the FC content, thus the thermodynamic compatibility between solvent system and polymers was changed. Furthermore, we can infer that the pores with larger PD (>4 nm) contribute more to the TPV, while pores with smaller PD (1 nm < PD < 4 nm) contribute more to the SSA. POP-4, with the [BVIM] [Cl] adding amount at 40%, was also highly porous with relatively higher SSA, TPV and PD value than POP-2. As shown in Figure 2b, in the range of PD above 4 nm, POP-4 obtained larger pore volume than POP-2, then the TPV value was higher than POP-2 as a result. However, when the [BVIM] [Cl] adding amount was increased to 50%, an almost nonporous structure was acquired that the SSA of POP-1 decreased sharply to 16.9 m2/g, which could be explained by the poor thermal compatibility.
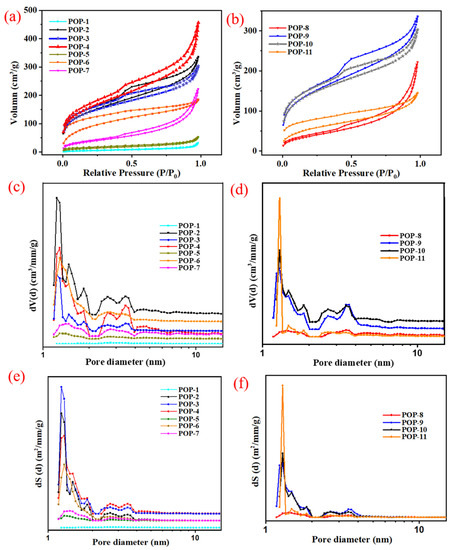
Figure 2.
(a,d) N2 sorption isotherms of IL-POPs prepared with different functional comonomer contents; (b,e) NLDFT simulated pore-size distribution curves of dV (d) vs. d; (c,f) NLDFT simulated pore-size distribution curves of dS (d) vs. d.
Compared to POP-6, POP-7 was synthesized in the solvent system of EtOH/H2O (V:V = 9:1) and the prepared particles were less porous than POP-6. Therefore, the deionized water has a negative effect on the formation of pores with high surface area and pore volume, which can be ascribed to the thermodynamic compatibility change.
As for the ternary system with [BVIM] [Cl] and HEMA as dual functional comonomers, the prepared IL-POPs also obtained tunable pore structure and POP-9 exhibited best both in SSA and TPV. When the total FC content decreased from 43% to 25%, the SSA of POP-9 increased to 506 m2/g from 139 m2/g of POP-8. From Figure 2f, it is obvious that in the pore size range of 1 nm to 10 nm, POP-8 was almost non-porous. When increasing the DVB to [BVIM] [Cl] ratio from 4:1 to 6:1 that the cross-linking degree of prepared IL-POPs was changed, compared to POP-10, the SSA and TPV of POP-9 was increased a little. POP-11 obtained lower SSA than POP-9, and it had the highest peak at pore diameter of 1.3 nm both in the differential SSA vs. pore diameter and TPV vs. pore diameter curves, but the deionized water had a negative effect on the formation of pores thus POP-11 was poorly porous
3.3. IR, TGA and SEM Analysis of IL-POPs
The grafting of [BVIM] [Cl], HEMA and DVB was confirmed by the typical functional group signals from FT-IR spectrums. As shown in Figure 3a, the bands at 1170 cm−1 and 1652 cm−1 were attributed to C–N and C=N stretching vibration of imidazole group, respectively. Additionally, the peak at 1724 cm−1 assigned to the stretching vibrations of the carbonyl groups in the HEMA functional comonomer, verifying the ternary polymerization of HEMA, [BVIM] [Cl] and DVB [30,31].
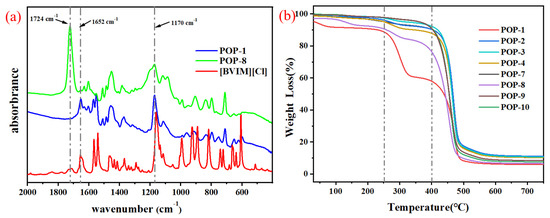
Figure 3.
(a) FT-IR spectra of [BVIM] [Cl], POP-1 and POP-8; (b) Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of ionic liquid-modified POPs.
Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to measure the decomposition temperature of the IL-POPs. As shown in Figure 3, the prepared supports exhibit great thermal stability, the major weight loss occurs above 250 °C for POP-8 and POP-1. Surprisingly, the other supports dramatically losing weight until 400 °C. As shown in Table 1, these particles still maintain porosity after high-temperature processing, which provides further evidence for good thermal stability of the IL-POPs.
According to the SEM images (Figure 4) of IL-POPs, the prepared supports are deposited by submicron spheres and thus are highly porosity enough to immobilize metallocene. To some extent, the ionic liquid-modified POPs are verified to be a potential candidate for metallocene immobilization.
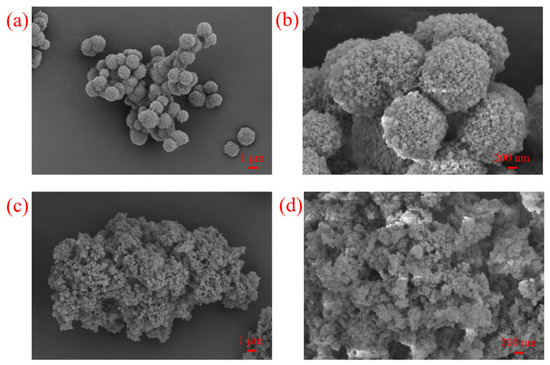
Figure 4.
SEM images of the IL-POPs (a,b) POP-3; (c,d) POP-8.
3.4. IL-POPs Supported Zr/MAO Catalysts
As illustrated in Figure 5, IL-POPs were pretreated with MAO and reacted with (BuCp)2ZrCl2 subsequently to obtain IL-POPs supported metallocene catalysts, and the prepared IL-POPs were treated under vacuum at 80 °C to remove impurities before use.
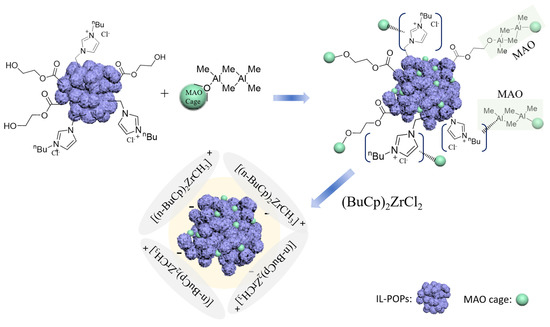
Figure 5.
The schematic preparation of Zr/MAO@IL-POPs.
It can be seen from the IR spectrum (Figure 6) that the hydroxyl bands (from HEAM groups and adsorbed water) of supported catalysts disappeared after MAO pretreating, and the broad and strong bands of Zr/MAO@IL-POPs system at 683 cm−1 assigned to Al-O stretching vibration, confirming that MAO cages were successfully immobilized on IL-POPs [32]. Moreover, the C–H stretching vibration of imidazolium cation at 3100 cm−1 disappeared, so we infer that part of MAO cages were anchored on the imidazolium cations.
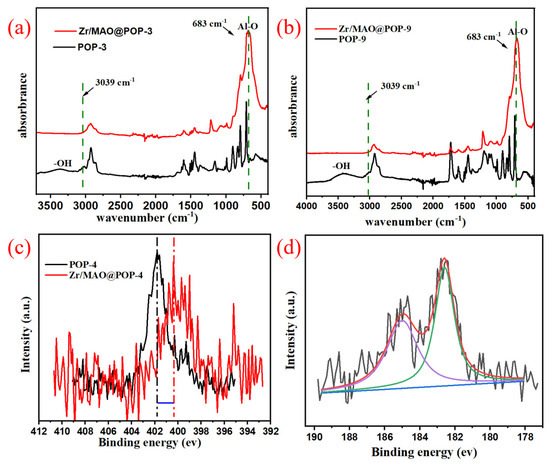
Figure 6.
(a,b) FT-IR spectra of IL-POP supports and Zr/MAO@IL-POPs; (c) N 1s XPS spectra of POP-3 and Zr/MAO@POP-3; (d) Zr 3d XPS spectra of BCZ-1@POP-3.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis displays a good advantage in studying the chemical composition and state information on samples’ surface [33]. In this work, comparing the chemical state of nitrogen shown in the N 1s XPS spectra of POP-3 and Zr/MAO@POP-3 [Figure 5a], an obvious shift of the peak to lower binding energy (BE) was observed, implying that nitrogen becomes electron-rich after being treated by MAO. Besides, when analyzing Zr XPS spectra in Figure 5b, due to the spin-orbit coupling of the 3d electrons, the Zr 3d spectrum can be separated to two peaks at BE of 182.6 ev (3d5/2) and 185.0 ev (3d3/2), respectively. The reported BE of (n-BuCp)2ZrCl2 in free form is 181.6 ev with Zr 3d5/2, the shift to higher BE could be ascribed to the methylation of zirconium by MAO [34,35,36]. It can be deduced that an ion pair with [(n-BuCp)2ZrCH3]+ as cation and [(MAO@IL-POPs)-Cl]− as the anion has formed after the immobilization of Zr/MAO in IL-POPs, and the formed ion pair has a great influence on the activity of ethylene polymerization initiated by Zr/MAO@IL-POPs [37,38].
The contents of zirconium and aluminum loaded in IL-POPs were determined by ICP analysis after calcination and acidolysis. It can be seen from Table 2 that different quantities of zirconium and aluminum were loaded on different supports, for the reason that supports obtained different pore structure, and it is also affected by the functional groups on IL-POPs. As high as 43.8 μmol of zirconium (Al/Zr ratio at 94.7) was immobilized on 1 g of POP-3 (SSA = 496.0 m2/g), and the ethylene polymerization activity of POP-3 supported catalyst was 3606 kg PE/mol·Zr·bar·h. POP-5 with low IL adding amount and SSA value, 5% and 47.8 m2/g, respectively, immobilized less zirconium and MAO, and exhibited low polymerization activity as a result. POP-9 and POP-10 also exhibit a high porosity, and the supported catalysts perform greatly in polymerization, with activity of 3700 kg PE/mol·Zr·bar·h and 3219 kg PE/mol·Zr·bar·h, respectively. This is higher than the Zr/MAO@Silica-2408 system (2595 kg PE/mol·Zr·bar·h from the reference [16]).

Table 2.
Zirconium and aluminum loading contents of Zr/MAO@IL-POPs and ethylene polymerization results.
3.5. Characterization of Prepared Polyethylene
As can be seen from Table 3, IL-POPs-supported catalysts exhibited a high activity in ethylene polymerization, and the obtained PEs reveal a narrow distribution (2.2–2.8) with the weight average molecular ranging from 18.3 × 104 to 28.7 × 104 g/mol. The metallocene compound anchored on the IL-POPs forms an identical active site [(n-BuCp)2ZrCH3]+, and the polymer chains grow on the same active site, then polymers with narrow PDI were obtained as a result [5].

Table 3.
DSC and GPC results of PEs from IL-POPs supported Zr/MAO catalysts.
While polyethylene chains crystallize, the CH2-CH2 bond rotates rapidly, and the polyethylene chains fold several times to form lamellae in which the distance between two adjacent chains is about 4.4 to 4.6 Å. The melting temperature (Tm) and crystallinity () of polyethylene can be analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), as shown in Figure 7a, the melting curves of samples were recorded after crystallizing and annealing. It is surprising that the prepared PEs melt at a high temperature of 138 °C, about 4 °C higher than the ones that prepared by p(DVB-co-HEMA)-supported Zr/MAO catalysts with Tm at 132–134 °C [17]. Crystallinity can be calculated by the formula , where is the crystallinity, is the melting endothermic enthalpy that can be integrated and calculated according to the area under the melting curve, and which is equal to 293.0 J/g, is the melting endothermic enthalpy of polymer with 100% crystallinity. The calculated values of PE-1, PE-3 and PE-4 are above 60%, whereas the of PE-2 is only 54.0%. Rungswang W et al. [39] proposed that the formation of lamellar crystal is also restricted by the mobility of high weight chains; therefore, we infer that PE-2 with high molecular weight (Mw = 28.7 × 104 g/mol) possesses a relatively low crystallinity.
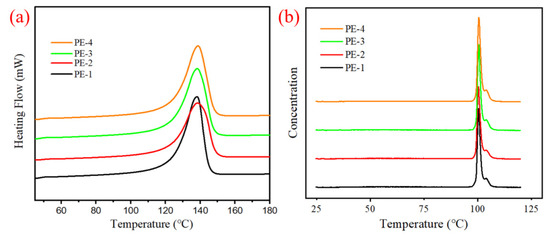
Figure 7.
(a) DSC curves of prepared PEs; (b) TREF curves of prepared PEs.
Chemical composition distributions (CCDs) were investigated by temperature rising elution fractionation (TREF), and the result was shown in Table 4. It can be seen from Figure 4b that the four PEs are similar in TREF curves that the soluble fraction is less than 1.2% and the elution temperature peaks within the scope of 100.5–100.7 °C, indicating that PEs have similar CCDs. We infer that the CCDs of different PEs are mainly affected by the active sites loaded on the supports, the pore structure of supports has less effectiveness on the chemical composition distributions.

Table 4.
Temperature rising elution fractionation results of PEs.
From the SEM images in Figure 8, PE particles were aggregated from microsphere which was held up by nano filament-like lamella crystals, and amorphous holes among the filaments can also be observed.
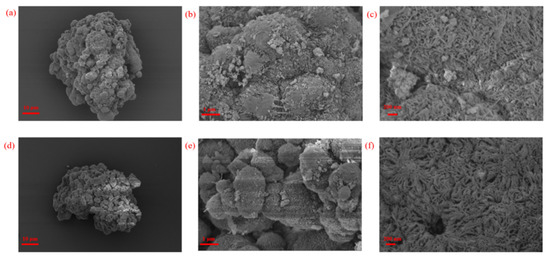
Figure 8.
(a–c) SEM images of PE-1 at different magnifications; (d–f) SEM images of PE-3 at different magnifications.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, ionic liquid-modified porous organic polymers were synthesized by free radical polymerization. The prepared IL-POPs with tunable pore structure show different abilities in loading MAO and metallocene chemicals, the loading amounts of aluminum and zirconium depend on the pore structure and the porous polymer itself. According to the results of ethylene polymerization initiated by the Zr/MAO@IL-POP catalyst, the IL-POPs exhibited a relatively higher activity than inorganic support. Polyethylene obtained from Zr/MAO@IL-POP catalysts show different molecular weight but all possess a narrow molecular weight distribution and high melting temperature than non-IL-modified POPs. The current work clearly demonstrated the potential applications of heterogeneous catalysis of ionic liquid-based POPs in the polyolefin industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W.; Formal analysis, W.K. and S.C.; Investigation, S.C., X.H. and M.D.; Methodology, X.W.; Project administration, G.L.; Writing—original draft, W.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by PetroChina Company Limited (2020B-2621).
Acknowledgments
The financial support of this work by PetroChina Company Limited is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaminsky, W. The discovery of metallocene catalysts and their present state of the art. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 3911–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, W. Polymerisation Catalysis. Springer Ser. Chem. Phys. 2004, 75, 403–440. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky, W. The discovery and evolution of metallocene-based olefin polymerization catalysts. Rend. Lincei 2017, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, W. Production of polyolefins by metallocene catalysts and their recycling by pyrolysis. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 360, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.M.; Sun, M.J.; Baek, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, Y.; Chung, S.; Lee, B.Y. Dinuclear Metallocene Complexes for High-Performance Supported Catalysts. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 144, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi-Dehaghani, Z.A.; Arabi, H.; Thalheim, D.; Vidakovic, D.; Haghighi, M.N.; Veith, L.; Klapper, M. Organic Versus Inorganic Supports for Metallocenes: The Influence of Rigidity on the Homogeneity of the Polyolefin Microstructure and Properties. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 2667–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naundorf, C.; Ferrari, D.; Rojas, G.; Fink, G.; Klapper, M.; Müllen, K. Hard versus Soft Materials as Supports for Metallocene and Post-Metallocene Catalysts. Macromol. React. Eng. 2009, 3, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, A.; Marques, M.F.V. Magnesium chloride supported metallocene catalysts in olefin polymerizations. Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fátima, V.; Marques, M.; Alcantara, M. Alumina as support for metallocene catalyst in ethylene polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias, C.; Quijada, R.; Rojas, R. Ethylene polymerization using dealuminated ZSM-2 zeolite nanocrystals as an active metallocene catalyst support. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 347, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Stork, M.; Klapper, M.; Müllen, K.; Gregorius, H. Immobilization of metallocenes through noncovalent bonding via MAO to a reversibly cross-linked polystyrene. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 7713–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yi, J. Preparation, characterization, and activity of α-Ti(HPO4)2 supported metallocene catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, V.M.; Silva, O.F.C.; Coutinho, A.C.; de Araujo, A.S. Ethylene polymerization catalyzed by metallocene supported on mesoporous materials. Polym. Bull. 2008, 61, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, M.A.; Vancompernolle, T.; Gauvin, R.M.; Delevoye, L.; Merle, N.; Monteil, V.; Taoufik, M.; McKenna, T.F.L.; Boisson, C. Silica/MAO/(n-BuCp)2ZrCl2 catalyst: Effect of support dehydroxylation temperature on the grafting of MAO and ethylene polymerization. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtefeu, B.; Bouilhac, C.; Cloutet, E.; Taton, D.; Deffieux, A.; Cramail, H. Polymer support of “single-site” catalysts for heterogeneous olefin polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 89–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britcher, L.; Rahiala, H.; Hakala, K.; Mikkola, A.P.; Rosenholm, J.B. Preparation, characterization, and activity of silica supported metallocene catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5713–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Han, X. Metal oxide as a template in the preparation of porous poly (2-hydroxyethylmethylacrylate-co-divinylbenzene) particles as a metallocene catalyst support. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 52464–52474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Synthesis and characterization of functional porous organic polymers as efficient metallocene catalyst supports. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8324–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Han, Z.; Bai, Y. Highly tunable porous organic polymer (POP) supports for metallocene-based ethylene polymerization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, P. Feasibility study on the design and synthesis of functional porous organic polymers with tunable pore structure as metallocene catalyst supports. Polymers 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Ren, F.; Xu, R.; Bai, Y. Porous organic polymers-supported metallocene catalysts for ethylene/1-hexene copolymerization. Catalysts 2018, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.; Gao, L.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y. Highly Flowable Nano TiO2/Porous Organic Polymer (POP) Supports for Efficient Metallocene Catalysts. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Jia, H.; Gao, D. Porous organic polymer/MMT hybrid supports for efficient metallocene catalysts. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 19253–19266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, G. High Melting Point of Linear, Spiral Polyethylene Nanofibers and Polyethylene Microspheres Obtained Through Confined Polymerization by a PPM-Supported Ziegler-Natta Catalyst. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babucci, M.; Fang, C.Y.; Hoffman, A.S.; Bare, S.R.; Gates, B.C.; Uzun, A. Tuning the selectivity of single-site supported metal catalysts with ionic liquids. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6969–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Tavakolian, M. Halloysite-Poly (ionic liquid) Nanocomposite as an Efficient Catalyst Support: Study of the Effects of Ionic Liquid Nature and Content on the Catalytic Activity. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 3369–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids in catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2459–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, H.; Shiri, P.; Aberi, M. An overview on recent advances in the synthesis of sulfonated organic materials, sulfonated silica materials, and sulfonated carbon materials and their catalytic applications in chemical processes. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2745–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochędzan-Siodłak, W.; Dziubek, K. Metallocenes and post-metallocenes immobilized on ionic liquid-modified silica as catalysts for polymerization of ethylene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 484, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckowski, Ł.; Zalesińska, E.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Rafiński, Z.; Studzińska, S. Poly (ionic liquid) s as new adsorbents in dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of unmodified and modified oligonucleotides. Talanta 2021, 221, 121662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chen, B.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G.; He, M. Cross-linked poly (ionic liquid) as precursors for nitrogen-doped porous carbons. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8137–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eilertsen, J.L.; Rytter, E.; Ystenes, M. In situ FTIR spectroscopy during addition of trimethylaluminium (TMA) to methylaluminoxane (MAO) shows no formation of MAO–TMA compounds. Vib. Spectrosc. 2000, 24, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, M.H.; Droubay, T.C.; Du, Y. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Applications; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA; Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL): Richland, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vayá, V.I.C.; Belelli, P.G.; Santos, J.H.Z.D.; Ferreira, M.L.; Damiani, D.E. Influence of acidic support in metallocene catalysts for ethylene polymerization. J. Catal. 2001, 204, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capeletti, L.B.; Alves, M.C.M.; Cardoso, M.B.; Dos Santos, J.H.Z. Hybrid silica based catalysts prepared by the encapsulation of zirconocene compound via non-hydrolytic sol-gel method for ethylene polymerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 560, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, G.B.; Seferin, M.; Guimarães, R.; Rohrmann, J.A.; Stedile, F.C.; dos Santos, J.H. Evaluation of silica-supported zirconocenes in ethylene/1-hexene copolymerization. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 189, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, W.; Sinn, H. Methylaluminoxane: Key Component for New Polymerization Catalysts. In Polyolefins: 50 Years after Ziegler and Natta II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Talsi, E.P.; Bryliakov, K.P.; Semikolenova, N.V.; Zakharov, V.A.; Ystenes, M.; Rytterc, E. 1H NMR characterization of intermediates formed by the activation of zirconocenes with methylaluminoxane at high Al/Zr ratios. Mendeleev Commun. 2003, 13, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungswang, W.; Jarumaneeroj, C.; Parawan, T.; Jirasukho, P.; Juabrum, S.; Soontaranon, S.; Rugmai, S. Influences of molecular weight and thermal history on partial melting of polyethylene: Existence of non-lamellar crystallite. Polymer 2020, 211, 123096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).