Fast and Complete Destruction of the Anti-Cancer Drug Cytarabine from Water by Electrocatalytic Oxidation Using Electro-Fenton Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
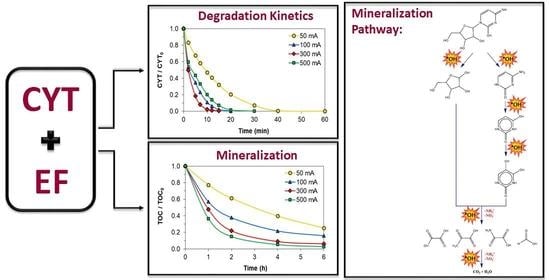
2.1. Oxidative Degradation Kinetics of CYT
2.2. Mineralization of CYT Aqueous Solution
2.3. Formation and Evolution of Carboxylic Acids and Inorganic Ions
2.4. Mineralization Pathway for CYT
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Electrolytic System
3.3. Analytical Procedures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.C.; Giannis, A.; Wang, J.-Y. Removal of cytostatic drugs from aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, J.-P.; Latour, J.-F.; Garric, J. Anticancer drugs in surface waters: What can we say about the occurrence and environmental significance of cytotoxic, cytostatic and endocrine therapy drugs? Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivodia, C.; Sinha, A. Assessment of graphite electrode on the removal of anticancer drug cytarabine via indirect electrochemical oxidation process: Kinetics & pathway study. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, E.; Zamora, P.; Feliu, J.; Barón, M.G. Classification of anticancer drugs—A new system based on therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, N.; Rudd, S.G.; Ljungblad, L.; Sanjiv, K.; Myrberg, I.H.; Paulin, C.B.J.; Heshmati, Y.; Hagenkort, A.; Kutzner, J.; Page, B.D.G. Targeting SAMHD1 with the Vpx protein to improve cytarabine therapy for hematological malignancies. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsakidou, A.; Antonopoulou, M.; Εvgenidou, Ε.; Konstantinou, I.; Lambropoulou, D. A comparative study on the photo-catalytic degradation of Cytarabine anticancer drug under Fe3+/H2O2, Fe3+/S2O82−, and [Fe(C2O4)3]3−/H2O2 processes. Kinetics, identification, and in silico toxicity assessment of generated transformation products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7772–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsakidou, A.; Antonopoulou, M.; Evgenidou, E.; Konstantinou, I.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Cytarabine degradation by simulated solar assisted photocatalysis using TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, V.; Halsall, C.; Llewellyn, N.; Johnson, A.; Williams, R. Prioritising anticancer drugs for environmental monitoring and risk assessment purposes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pieczyńska, A.; Fiszka Borzyszkowska, A.; Ofiarska, A.; Siedlecka, E.M. Removal of cytostatic drugs by AOPs: A review of applied processes in the context of green technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1282–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Viera, S.; Montesdeoca-Esponda, S.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Cytostatic drugs in environmental samples: An update on the extraction and determination procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Ofiarska, A.; Borzyszkowska, A.F.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Pieczyńska, A. Cytostatic drug removal using electrochemical oxidation with BDD electrode: Degradation pathway and toxicity. Water Res. 2018, 144, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oturan, M.A.; Aaron, J.-J. Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: Principles and applications. A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poza-Nogueiras, V.; Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; Sanroman, M.A. Current advances and trends in electro-Fenton process using heterogeneous catalysts—A review. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Sable, S.; El-Din, M.G. Advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of dissolved organics in produced water: A review of process performance, degradation kinetics and pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Zhou, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for the abatement of persistent organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Chen, Z.; Haghighat, F.; Yerushalmi, L. Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by homo/heterogonous Fenton-type processes–A review. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijide, J.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.A. Heterogeneous electro-Fenton as “Green” technology for pharmaceutical removal: A review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sirés, I.; Scialdone, O. Single and coupled electrochemical processes and reactors for the abatement of organic water pollutants: A critical review. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13362–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Mantzavinos, D.; Poulios, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miron, S.M.; Brendlé, J.; Josien, L.; Fourcade, F.; Rojas, F.; Amrane, A.; Limousy, L. Development of a new cathode for the electro-Fenton process combining carbon felt and iron-containing organic–inorganic hybrids. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthi, T.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T.; Nidheesh, P.V. Stabilized landfill leachate treatment using heterogeneous Fenton and electro-Fenton processes. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousset, E.; Wang, Z.; Lefebvre, O. Electro-Fenton for control and removal of micropollutants–process optimization and energy efficiency. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillas, E.; Sirés, I.; Oturan, M.A. Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6570–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moratalla, Á.; Lacasa, E.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Sáez, C. Electro-Fenton-based technologies for selectively degrading antibiotics in aqueous media. Catalysts 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: Today and tomorrow. A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8336–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzenko, O.; Huguenot, D.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Esposito, G.; Oturan, M.A. Electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes for wastewater treatment: A review of the combined approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8493–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Brillas, E.; Vilar, V.J.P. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 217–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Mousset, E.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Trellu, C.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, M.A. Recent advances in electro-Fenton process and its emerging applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Oturan, M.A. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: Advances in formation and detection of reactive species and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirés, I.; Brillas, E. Upgrading and expanding the electro-Fenton and related processes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 27, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaye, M.; Diaw, P.A.; Mbaye, O.M.A.; Oturan, N.; Seye, M.D.G.; Trellu, C.; Coly, A.; Tine, A.; Aaron, J.-J.; Oturan, M.A. Rapid removal of fungicide thiram in aqueous medium by electro-Fenton process with Pt and BDD anodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, O.; Mousset, E.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Lefebvre, O. Electrochemical treatment of highly concentrated wastewater: A review of experimental and modeling approaches from lab-to full-scale. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 240–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag-Siagh, F.; Fourcade, F.; Soutrel, I.; Aït-Amar, H.; Djelal, H.; Amrane, A. Electro-Fenton pretreatment for the improvement of tylosin biodegradability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8534–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, Z.; Pelalak, R.; Alizadeh, R.; Oturan, N.; Shirazian, S.; Oturan, M.A. Application of mineral iron-based natural catalysts in electro-Fenton process: A comparative study. Catalysts 2021, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A. Outstanding performances of the BDD film anode in electro-Fenton process: Applications and comparative performance. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 25, 100925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 11, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florenza, X.; Solano, A.M.S.; Centellas, F.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Brillas, E.; Garcia-Segura, S. Degradation of the azo dye Acid Red 1 by anodic oxidation and indirect electrochemical processes based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Relationship between decolorization, mineralization and products. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 142, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, N.; Bo, J.; Trellu, C.; Oturan, M.A. Comparative performance of ten electrodes in electro-Fenton process for removal of organic pollutants from water. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 3294–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.J.; de Lima, M.D.; da Silva, D.R.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Influence of the water hardness on the performance of electro-Fenton approach: Decolorization and mineralization of Eriochrome Black T. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, C.; Fourcade, F.; Soutrel, I.; Geneste, F.; Floner, D.; Bellakhal, N.; Amrane, A. Degradation of enoxacin antibiotic by the electro-Fenton process: Optimization, biodegradability improvement and degradation mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 165, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, N.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Zhang, H.; Mazeas, L.; Budzinski, H.; Le Menach, K.; Oturan, M.A. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants in landfill leachates treated by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12187–12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousset, E.; Wang, Z.; Hammaker, J.; Lefebvre, O. Physico-chemical properties of pristine graphene and its performance as electrode material for electro-Fenton treatment of wastewater. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 214, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudalle, A.; Djelal, H.; Fourcade, F.; Domergue, L.; Assadi, A.A.; Lendormi, T.; Taha, S.; Amrane, A. Metronidazole removal by means of a combined system coupling an electro-Fenton process and a conventional biological treatment: By-products monitoring and performance enhancement. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimolade, B.O.; Zwane, B.N.; Koiki, B.A.; Rivallin, M.; Bechelany, M.; Mabuba, N.; Lesage, G.; Cretin, M.; Arotiba, O.A. Coupling cathodic electro-Fenton with anodic photo-electrochemical oxidation: A feasibility study on the mineralization of paracetamol. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; de Araújo, M.J.G.; de Araujo Costa, E.C.T.; Santos, J.E.L.; dos Santos, E.V.; Martinez-Huitle, C.A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Design of highly efficient porous carbon foam cathode for electro-Fenton degradation of antimicrobial sulfanilamide. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 283, 119652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Duarte, J.L.; Solano, A.M.S.; Arguelho, M.L.P.M.; Tonholo, J.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; e Silva, C.L.D.P. Evaluation of treatment of effluents contaminated with rifampicin by Fenton, electrochemical and associated processes. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, A.; El Ouadrhiri, F.; Kara, M.; El Manssouri, I.; Assouguem, A.; Almutairi, M.H.; Bayram, R.; Mohamed, H.R.H.; Peluso, I.; Eloutassi, N. Decolorization and degradation of methyl orange azo dye in aqueous solution by the electro Fenton process: Application of optimization. Catalysts 2022, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, M.; Trellu, C.; Darwich, A.; Rivallin, M.; Bechelany, M.; Nagarajan, S.; Lacour, S.; Bellakhal, N.; Lesage, G.; Heran, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using novel electrode materials for mineralization and biodegradability enhancement of nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachates. Water Res. 2019, 162, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, N.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Oturan, N.; Huguenot, D.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A. Kinetics of oxidative degradation/mineralization pathways of the antibiotic tetracycline by the novel heterogeneous electro-Fenton process with solid catalyst chalcopyrite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.M.; Kumaravel, V.; Pillai, S.C. Carbonaceous cathode materials for electro-Fenton technology: Mechanism, kinetics, recent advances, opportunities and challenges. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S.; Oturan, N.; Bellakhal, N.; Dachraoui, M.; Oturan, M.A. Oxidative degradation of direct orange 61 by electro-Fenton process using a carbon felt electrode: Application of the experimental design methodology. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 610, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrinceanu, N.; Hlihor, R.M.; Simion, A.I.; Rusu, L.; Fekete-Kertész, I.; Barka, N.; Favier, L. New evidence of the enhanced elimination of a persistent drug used as a lipid absorption inhibitor by advanced oxidation with UV-A and nanosized catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barhoumi, N.; Oturan, N.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Brillas, E.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Oturan, M.A. Pyrite as a sustainable catalyst in electro-Fenton process for improving oxidation of sulfamethazine. Kinetics, mechanism and toxicity assessment. Water Res. 2016, 94, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopaj, F.; Oturan, N.; Pinson, J.; Podvorica, F.; Oturan, M.A. Effect of the anode materials on the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process for the mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 199, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiadh, L.; Oturan, M.A.; Panizza, M.; Ben Hamadi, N.; Ammar, S. Complete removal of AHPS synthetic dye from water using new electro-Fenton oxidation catalyzed by natural pyrite as heterogeneous catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, N.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M.; Oturan, M.A. Highly efficient and stable FeIIFeIII LDH carbon felt cathode for removal of pharmaceutical ofloxacin at neutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopaj, F.; Oturan, N.; Pinson, J.; Podvorica, F.I.; Oturan, M.A. Effect of cathode material on electro-Fenton process efficiency for electrocatalytic mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Pimentel, M.; Oturan, N.; Sirés, I. Reaction sequence for the mineralization of the short-chain carboxylic acids usually formed upon cleavage of aromatics during electrochemical Fenton treatment. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 54, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of the recalcitrant oxalic and oxamic acids by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using a boron-doped diamond anode. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oturan, N.; Ganiyu, S.O.; Raffy, S.; Oturan, M.A. Sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide as a new anode material for electro-Fenton process: Application to electrocatalytic destruction of antibiotic amoxicillin. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 217, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, N.; Li, Y.; Oturan, M.A. Electrocatalytic destruction of pharmaceutical imatinib by electro-Fenton process with graphene-based cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Skoumal, M.; Arias, C. Electrochemical incineration of diclofenac in neutral aqueous medium by anodic oxidation using Pt and boron-doped diamond anodes. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteil, H.; Oturan, N.; Péchaud, Y.; Oturan, M.A. Electro-Fenton treatment of the analgesic tramadol: Kinetics, mechanism and energetic evaluation. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Oturan, N.; Raffy, S.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, M.A. Electrocatalytic generation of homogeneous and heterogeneous hydroxyl radicals for cold mineralization of anti-cancer drug imatinib. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Leyva-Ramos, R. Degradation of antineoplastic cytarabine in aqueous phase by advanced oxidation processes based on ultraviolet radiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; López-Peñalver, J.J.; Leyva-Ramos, R. Degradation of antineoplastic cytarabine in aqueous solution by gamma radiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Leyva-Ramos, R. Enhancement of the catalytic activity of TiO2 by using activated carbon in the photocatalytic degradation of cytarabine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Mota, A.J.; Sanchez-Polo, M.; Leyva-Ramos, R. Effect of radical peroxide promoters on the photodegradation of cytarabine antineoplastic in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| I (mA) | kapp (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 0.0825 | 0.9893 |
| 100 | 0.2367 | 0.9819 |
| 300 | 0.3616 | 0.9966 |
| 500 | 0.1688 | 0.9880 |
| Compound | Molecular Mass (g mol−1) | Retention Time (min) | Molecular Structure | Analytical Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 150 | 13.46 |  | GC-MS |
| II | 111 | 20.07 |  | GC-MS |
| III | 113 | 23.58 |  | GC-MS |
| IV | 129 | 19.96 |  | GC-MS |
| V | 90 | 6.64 |  | HPLC |
| VI | 46 | 13.55 |  | HPLC |
| VII | 89 | 9.87 |  | HPLC |
| VIII | 88 | 11.28 |  | HPLC |
| Method | Experimental Conditions | Removal (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| UV/H2O2 | [CYT]0 = 10 mg/L [H2O2] = 400 μM pH = 7 | 90% degradation in 120 min | [65] |
| UV/K2S2O8 | [CYT]0 = 10 mg/L [K2S2O8] = 200 μM pH = 7 | 98% degradation in 60 min | [65] |
| Gamma radiation | [CYT]0 = 10 mg/L Dose rate = 1.66 Gy min−1 pH = 7 | 95% degradation in 240 min | [66] |
| UV/TiO2 + activated carbon | [CYT]0 = 50 mg/L Carbon mass = 5 mg TiO2 mass = 5 mg pH = 7 | 90% degradation in 10 min | [67] |
| Photodegradation | [CYT]0 = 10 mg/L [K2S2O8] = 100 μM pH = 7 | 90% degradation in 30 min 45% mineralization in 120 min | [68] |
| Simulated solar photocatalysis | [CYT]0 = 30 mg/L [TiO2] = 300 mg/L [H2O2] = 90 mg/L pH = 6.5 | 100% degradation in 30 min 80% mineralization in 360 min | [7] |
| Photo-Fenton-like treatment | [CYT]0 = 30 mg/L [Fe3+] = 3 mg/L [C2K2O4·H2O] = 90 mg/L pH = 3 | 100% degradation in 30 min 82% mineralization in 360 min | [6] |
| Anodic oxidation | [CYT]0 = 20 mg L−1 Graphite anode Current density = 10 mA cm−2 [NaCl] = 50 mM pH = 3 | 98% degradation in 30 min 60% mineralization in 180 min | [3] |
| Electro-Fenton (present work) | [CYT]0 = 24.32 mgL−1 BDD anode Carbon felt cathode [Na2SO4] = 50 mM pH = 3 | 100% degradation in 15 min 91% mineralization in 240 min at 300 mA (9.375 mA cm−2) 85% mineralization in 120 min at 500 mA (15.625 mA cm−2) 95% mineralization in 240 min at 500 mA (15.625 mA cm−2) | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camcioglu, S.; Özyurt, B.; Oturan, N.; Trellu, C.; Oturan, M.A. Fast and Complete Destruction of the Anti-Cancer Drug Cytarabine from Water by Electrocatalytic Oxidation Using Electro-Fenton Process. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121598
Camcioglu S, Özyurt B, Oturan N, Trellu C, Oturan MA. Fast and Complete Destruction of the Anti-Cancer Drug Cytarabine from Water by Electrocatalytic Oxidation Using Electro-Fenton Process. Catalysts. 2022; 12(12):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121598
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamcioglu, Sule, Baran Özyurt, Nihal Oturan, Clément Trellu, and Mehmet A. Oturan. 2022. "Fast and Complete Destruction of the Anti-Cancer Drug Cytarabine from Water by Electrocatalytic Oxidation Using Electro-Fenton Process" Catalysts 12, no. 12: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121598
APA StyleCamcioglu, S., Özyurt, B., Oturan, N., Trellu, C., & Oturan, M. A. (2022). Fast and Complete Destruction of the Anti-Cancer Drug Cytarabine from Water by Electrocatalytic Oxidation Using Electro-Fenton Process. Catalysts, 12(12), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121598