Selenium Oxoanions Removal from Wastewater by MoS42− Intercalated FeMgAl LDH: Catalytic Roles of Fe and Mechanism Insights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
2.2. Adsorption of Selenium
2.2.1. Quantitative Study
2.2.2. Sorption Kinetics and Isotherms
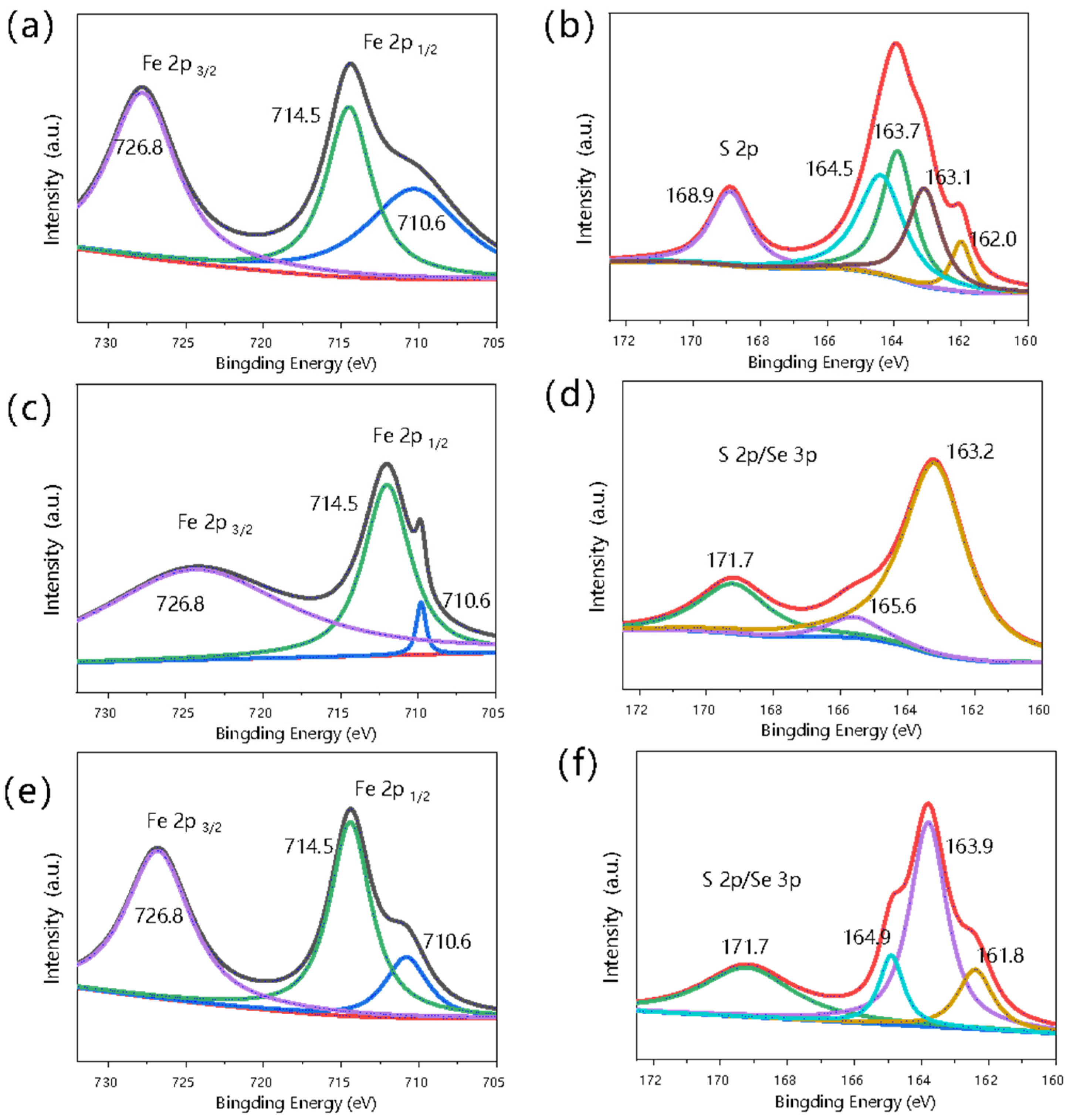
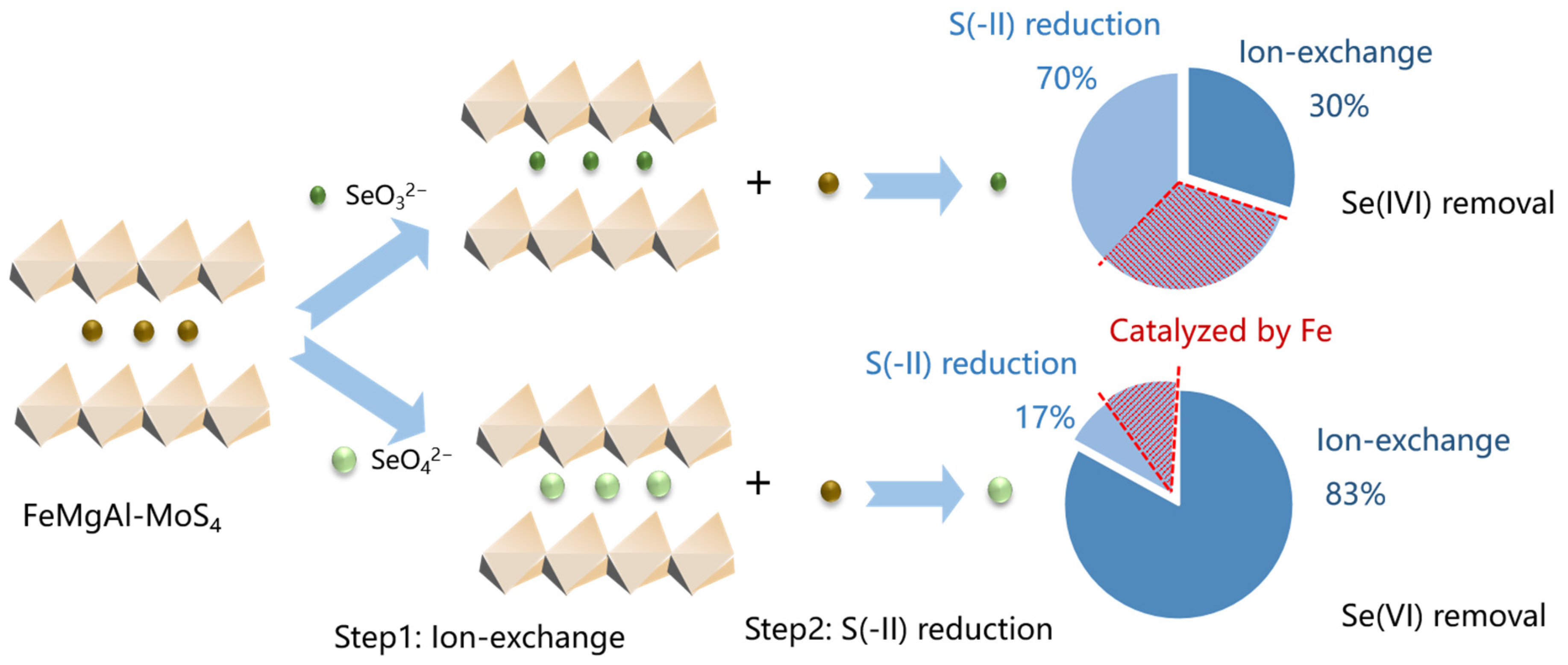
2.3. Adsorption Mechanisms
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Batch Experiments
3.3. Quantitative Study
4. Environmental Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmes, A.B.; Gu, F.X. Emerging nanomaterials for the application of selenium removal for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Grangeon, S.; Tournassat, C.; Findling, N.; Carrero, S.; Tisserand, D.; Bureau, S.; Elkaïm, E.; Marini, C.; et al. Selenite Uptake by Ca–Al LDH: A Description of Intercalated Anion Coordination Geometries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayordomo, N.; Foerstendorf, H.; Lützenkirchen, J.; Heim, K.; Weiss, S.; Alonso, U.; Missana, T.; Schmeide, K.; Jordan, N. Selenium(IV) Sorption Onto γ-Al2O3: A Consistent Description of the Surface Speciation by Spectroscopy and Thermodynamic Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.-B.; Takeichi, Y.; Nitani, H.; Terada, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Tellurium Distribution and Speciation in Contaminated Soils from Abandoned Mine Tailings: Comparison with Selenium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6027–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, S.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Pérez-López, R.; Poulain, A.; Salas-Colera, E.; Nieto, J.M. Arsenate and Selenate Scavenging by Basaluminite: Insights into the Reactivity of Aluminum Phases in Acid Mine Drainage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgen, A.G.; Kruichak, J.N.; Artyushkova, K.; Newville, M.G.; Sun, C. Redox Transformations of As and Se at the Surfaces of Natural and Synthetic Ferric Nontronites: Role of Structural and Adsorbed Fe(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11105–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.-H.; Chen, H.; Hu, S.; Cai, C.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J. Microbial Selenate Reduction Driven by a Denitrifying Anaerobic Methane Oxidation Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4006–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Boyanov, M.I.; Liu, J.; Kemner, K.M.; Fein, J.B. Adsorption of Selenite onto Bacillus subtilis: The Overlooked Role of Cell Envelope Sulfhydryl Sites in the Microbial Conversion of Se(IV). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10400–10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Shan, C.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, B. Effects of brining on the corrosion of ZVI and its subsequent As(III/V) and Se(IV/VI) removal from water. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gang, D.D.; McDonald, L.; Lin, L.-S. Background electrolytes and pH effects on selenate adsorption using iron-impregnated granular activated carbon and surface binding mechanisms. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, P.; Qiao, J.; Guan, X. Unexpected effect of buffer solution on removal of selenite and selenate by zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Katz, M.J.; Wang, T.C.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Chapman, K.W.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. High efficiency adsorption and removal of selenate and selenite from water using metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Chen, G.; Jin, C.; Hu, J.; Huang, C.; Sheng, J.; Sheng, G.; Ma, J.; Huang, Y. Macroscopic and spectroscopic studies of the enhanced scavenging of Cr(VI) and Se(VI) from water by titanate nanotube anchored nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-G.; Kim, S.-B. Removal of arsenic and selenium from aqueous solutions using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle/multi-walled carbon nanotube adsorbents. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28323–28339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Solution and surface chemistry of the Se(IV)-Fe(0) reactions: Effect of initial solution pH. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qiao, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, C. Influence of inherent iron and oxygen concentrations on selenite sorption process using bentonite. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2017, 60, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption study of selenium ions from aqueous solutions using MgO nanosheets synthesized by ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamani, J.S.; Lounsbury, A.W.; Zimmerman, J.B. Adsorption of selenite and selenate by nanocrystalline aluminum oxide, neat and impregnated in chitosan beads. Water Res. 2014, 50, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.; Müller, K.; Franzen, C.; Brendler, V. Temperature impact on the sorption of selenium(VI) onto anatase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 390, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liang, Q.; Qian, T.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of selenite in soil and groundwater using stabilized Fe–Mn binary oxide nanoparticles. Water Res. 2015, 70, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-H.; Lyonga, F.N.; Kang, J.-K.; Seo, E.-J.; Lee, C.-G.; Jeong, S.; Hong, S.-G.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis of Fe-impregnated biochar from food waste for Selenium(Ⅵ) removal from aqueous solution through adsorption: Process optimization and assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyro, S.; Li, H.; Dehkhoda, A.M.; McMillan, R.; Ellis, N.; Baldwin, S.A. Application of Fe-biochar composites for selenium (Se+6) removal from aqueous solution and effect of the presence of competing anions under environmentally relevant conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 277, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifthikar, J.; Jiao, X.; Ngambia, A.; Wang, T.; Khan, A.; Jawad, A.; Xue, Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Sustainable Carboxymethyl Chitosan—Sewage Sludge Biochar for Effective Heavy Metal Chelation and Regeneration. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 262, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Charlet, L. Selenium environmental cycling and bioavailability: A structural chemist point of view. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2009, 8, 81–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Shang, C.; Luo, L.; Gao, J.; Tang, L. Selenium contamination, consequences and remediation techniques in water and soils: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, S.; An, Y.; Yang, S. Transition metal based layered double hydroxides tailored for energy conversion and storage. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Vance, G.F.; Zhao, H. Selenium adsorption on Mg–Al and Zn–Al layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 20, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; He, F.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Foamed urea-formaldehyde microspheres for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2019, 241, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lin, H.; Dai, L.; Qiu, R.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, P.-G.; Ok, Y.S. Waste shrimp shell-derived hydrochar as an emergent material for methyl orange removal in aqueous solutions. Environ. Int. 2019, 134, 105340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Sheng, D.; Yang, S.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; et al. Selenium Sequestration in a Cationic Layered Rare Earth Hydroxide: A Combined Batch Experiments and EXAFS Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Islam, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Highly Selective and Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals by Layered Double Hydroxide Intercalated with the MoS42– Ion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Islam, S.M.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, G.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Selective and Efficient Removal of Toxic Oxoanions of As(III), As(V), and Cr(VI) by Layered Double Hydroxide Intercalated with MoS42–. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3274–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xie, J.; Qu, Z.; Shangguan, W.; Yan, N. [MoS4]2– Cluster Bridges in Co–Fe Layered Double Hydroxides for Mercury Uptake from S–Hg Mixed Flue Gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10109–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, J.; Wang, H.; Ifthikar, J.; Khan, A.; Wang, T.; Zhan, K.; Shahzad, A.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Efficient, stable and selective adsorption of heavy metals by thio-functionalized layered double hydroxide in diverse types of water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Islam, S.M.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Yuan, M.; Sun, G.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Rapid Simultaneous Removal of Toxic Anions [HSeO3]−, [SeO3]2–, and [SeO4]2–, and Metals Hg2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ by MoS42– Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12745–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, K.; Takahashi, Y. Effective Removal of Selenite and Selenate Ions from Aqueous Solution by Barite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9194–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Xiao, L.; Nie, G.; Pan, B.; Wu, J.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, S. Adsorptive selenite removal from water using a nano-hydrated ferric oxides (HFOs)/polymer hybrid adsorbent. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 12, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Kuan, W.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Wang, M.K. Adsorption mechanism of selenate and selenite on the binary oxide systems. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4412–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlachta, M.; Gerda, V.; Chubar, N. Adsorption of arsenite and selenite using an inorganic ion exchanger based on Fe–Mn hydrous oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 365, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrad, M.O.M.; Liu, H.; Fan, M. Evaluation of FeOOH performance on selenium reduction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.; Ritter, A.; Scheinost, A.C.; Weiss, S.; Schild, D.; Hübner, R. Selenium(IV) uptake by maghemite (γ-Fe2O3). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ge, X.; He, J.; Wang, C.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, C. Effects of Mineral Compositions on Matrix Diffusion and Sorption of 75Se(IV) in Granite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.; Finck, N.; Heberling, F.; Pruessmann, T.; Liu, C.; Lützenkirchen, J. Adsorption of Selenium and Strontium on Goethite: EXAFS Study and Surface Complexation Modeling of the Ternary Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, P.C.M.; Sato, T.; Otake, T.; Kasama, T.; Suzuki, S.; Shiwaku, H.; Yaita, T. Mechanisms of Se(IV) Co-precipitation with Ferrihydrite at Acidic and Alkaline Conditions and Its Behavior during Aging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4817–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Shan, C.; Liang, J.; Tong, M. Efficient adsorption of Selenium(IV) from water by hematite modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X. Coupled Effect of Ferrous Ion and Oxygen on the Electron Selectivity of Zerovalent Iron for Selenate Sequestration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5090–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ye, F.; Jin, C.; Ma, X.; Huang, C.; Sheng, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. The enhancement roles of layered double hydroxide on the reductive immobilization of selenate by nanoscale zero valent iron: Macroscopic and microscopic approaches. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zeng, H.; Huang, Y.H. Rapid removal of selenate in a zero-valent iron/Fe3O4/Fe2+ synergetic system. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 184, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Jia, H.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B. Enhanced removal of Se(VI) from water via pre-corrosion of zero-valent iron using H2O2/HCl: Effect of solution chemistry and mechanism investigation. Water Res. 2018, 133, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Kondo, E.; Yoshioka, T. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of Se(vi) removal by Mg–Al layered double hydroxide doped with Fe2+. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61817–61822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Khan, A.; Wang, T.; Ifthikar, J.; Shahzad, A.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Fe-MoS4: An Effective and Stable LDH-Based Adsorbent for Selective Removal of Heavy Metals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28451–28463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Sumona, M.; Gupta, B.S.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Utilization of iron sulfides for wastewater treatment: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Yin, G. Controlled leaching with prolonged activity for Co–LDH supported catalyst during treatment of organic dyes using bicarbonate activation of hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zeng, H.C. Boxlike Assemblages of Few-Layer MoS2 Nanosheets with Edge Blockage for High-Efficiency Hydrogenation of CO2 to Methanol. ACS Catal. 2022, 16, 9872–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Hou, H.; Xin, X.; Hammer, C. M-S (M=Mo, W) cluster compound films on copper surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1995, 89, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, T.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, R.; Zi, W.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hexavalent chromium elimination from wastewater by integrated micro-electrolysis composites synthesized from red mud and rice straw via a facile one-pot method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Duan, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.; Liao, Z. Efficient removal of mercury and chromium from wastewater via biochar fabricated with steel slag: Performance and mechanisms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 961907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tzou, Y.; Kuan, W.; Chang, R.; Wang, M. Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of selenium oxyanions onto Al/Si and Fe/Si coprecipitates. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target | Items | Parameter 1 | Parameter 2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se(IV) | Adsorption Kinetics | |||
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 = 6.9 × 10−3 min−1 | Qe = 320.60 mg g−1 | 0.9111 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K1 = 5.4 × 10−5 mg/g min−1 | Qe = 500.00 mg g−1 | 0.9997 | |
| Adsorption isotherm | ||||
| Langmuir | KL = 1.8 × 10−3 L mg−1 | Qm = 505.05mg g−1 | 0.9998 | |
| Freundlich | n = 0.870 | Kf = 1.38 mg g−1 | 0.9213 | |
| Se(VI) | Adsorption Kinetics | |||
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 = 5.7 × 10−3 min−1 | Qe = 76.08 mg g−1 | 0.9436 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K1 = 2.5 × 10−4 mg/g min−1 | Qe = 169.49 mg g−1 | 0.9999 | |
| Adsorption isotherm | ||||
| Langmuir | KL = 6.1 × 10−3 L mg−1 | Qm = 172.41 mg g−1 | 0.9998 | |
| Freundlich | n = 0.699 | Kf = 2.38mg g−1 | 0.9709 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Z.; He, T.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, R. Selenium Oxoanions Removal from Wastewater by MoS42− Intercalated FeMgAl LDH: Catalytic Roles of Fe and Mechanism Insights. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121592
Liao Z, He T, Shi L, Liu Y, Zhou X, Wang J, Li W, Zhang Y, Wang H, Xu R. Selenium Oxoanions Removal from Wastewater by MoS42− Intercalated FeMgAl LDH: Catalytic Roles of Fe and Mechanism Insights. Catalysts. 2022; 12(12):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121592
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Zhuwei, Tianxu He, Lerong Shi, Yi Liu, Xinquan Zhou, Jia Wang, Wan Li, Yong Zhang, Huabin Wang, and Rui Xu. 2022. "Selenium Oxoanions Removal from Wastewater by MoS42− Intercalated FeMgAl LDH: Catalytic Roles of Fe and Mechanism Insights" Catalysts 12, no. 12: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121592
APA StyleLiao, Z., He, T., Shi, L., Liu, Y., Zhou, X., Wang, J., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., & Xu, R. (2022). Selenium Oxoanions Removal from Wastewater by MoS42− Intercalated FeMgAl LDH: Catalytic Roles of Fe and Mechanism Insights. Catalysts, 12(12), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121592











