Rh-Catalyzed Environmentally Benign Selective Hydrogenation of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups Using Al-Water as a Hydrogen Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
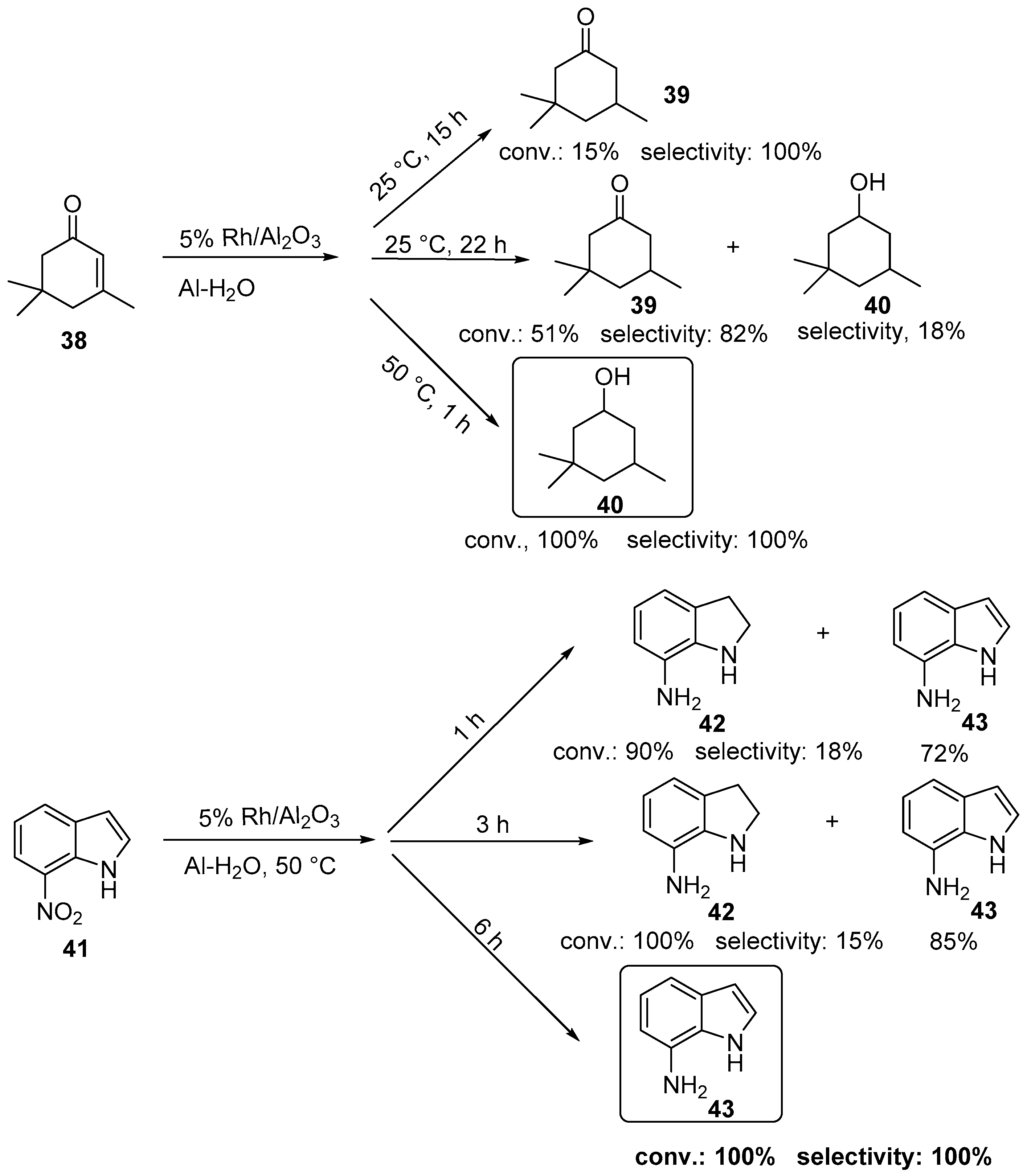
2.1. Rh-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Aliphatic C–C Multiple Bonds
2.2. Rh-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Aromatic Rings in Carbocyclic and Heterocyclic Compounds
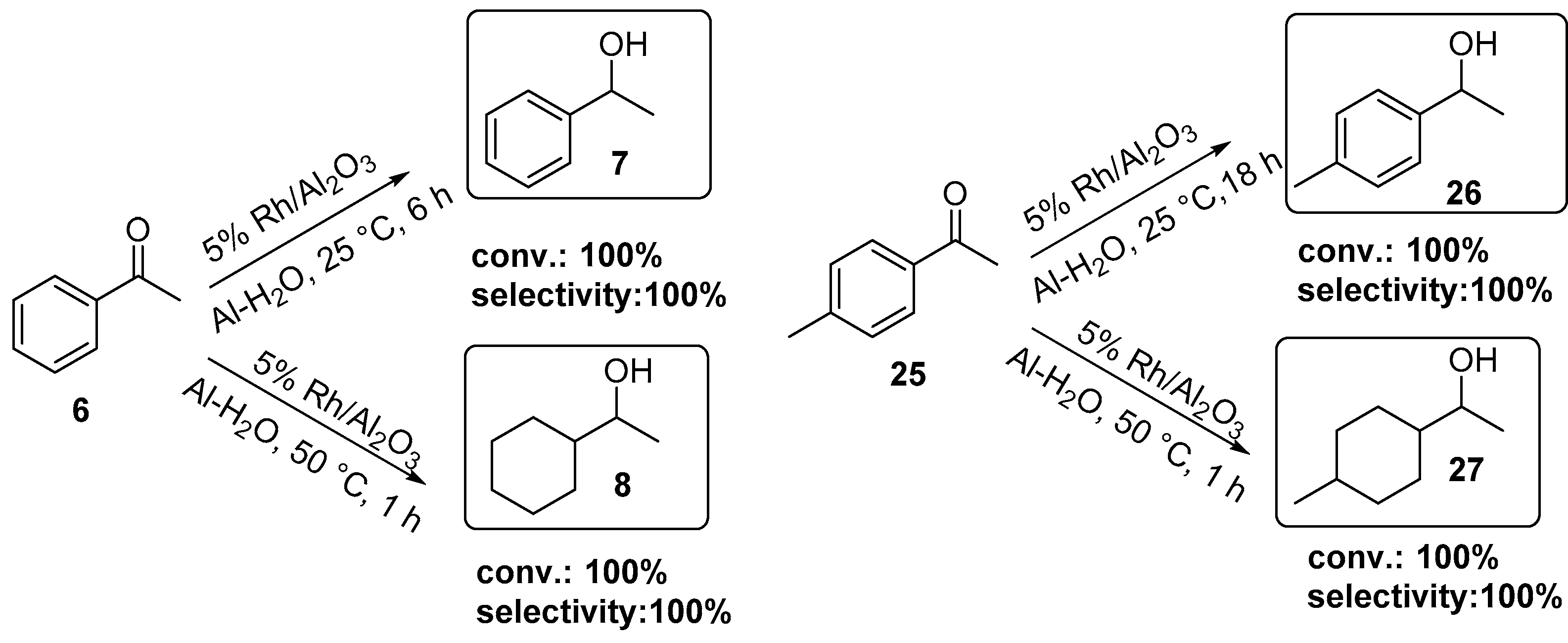
2.3. Rh-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Carbonyl Compounds
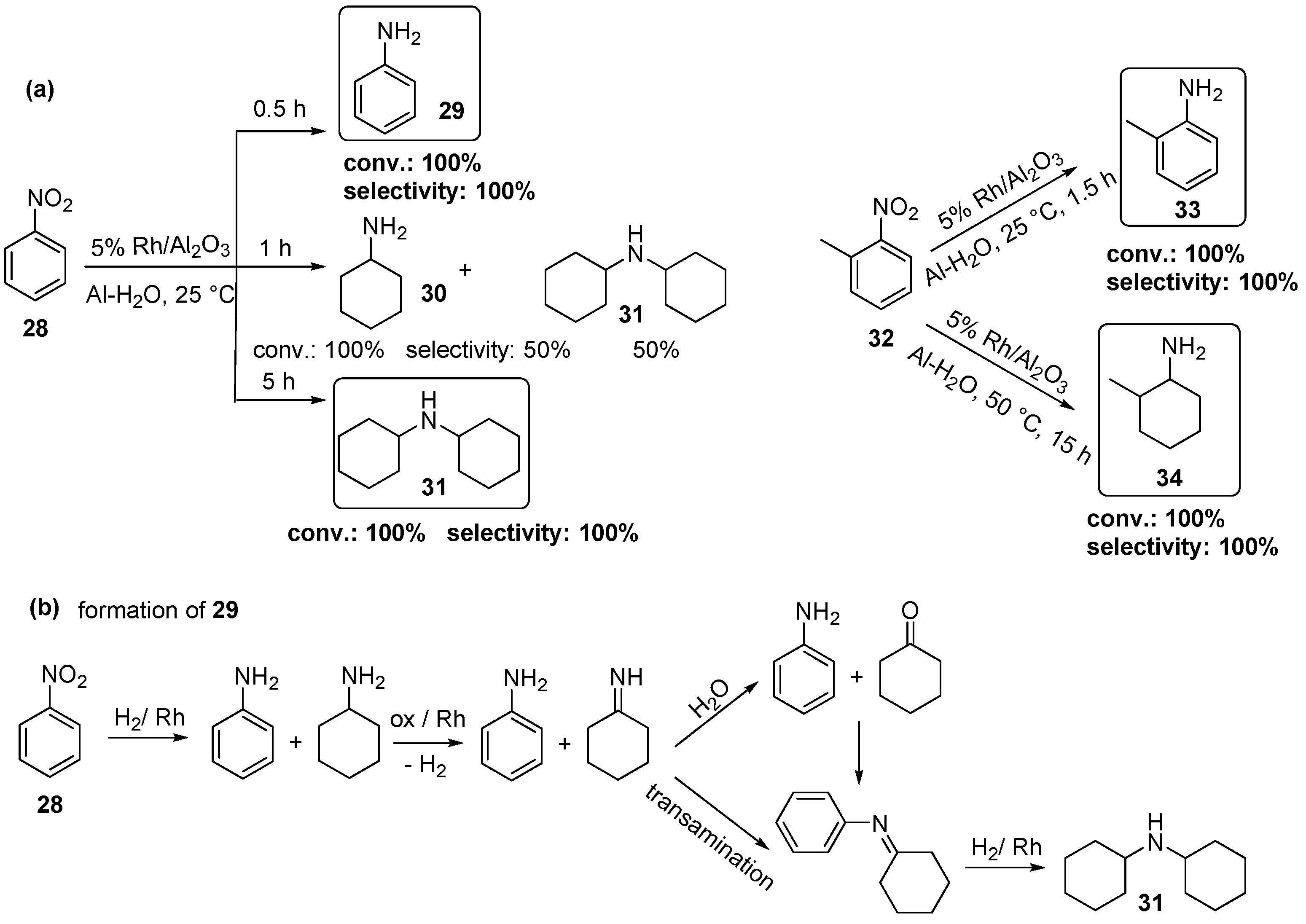
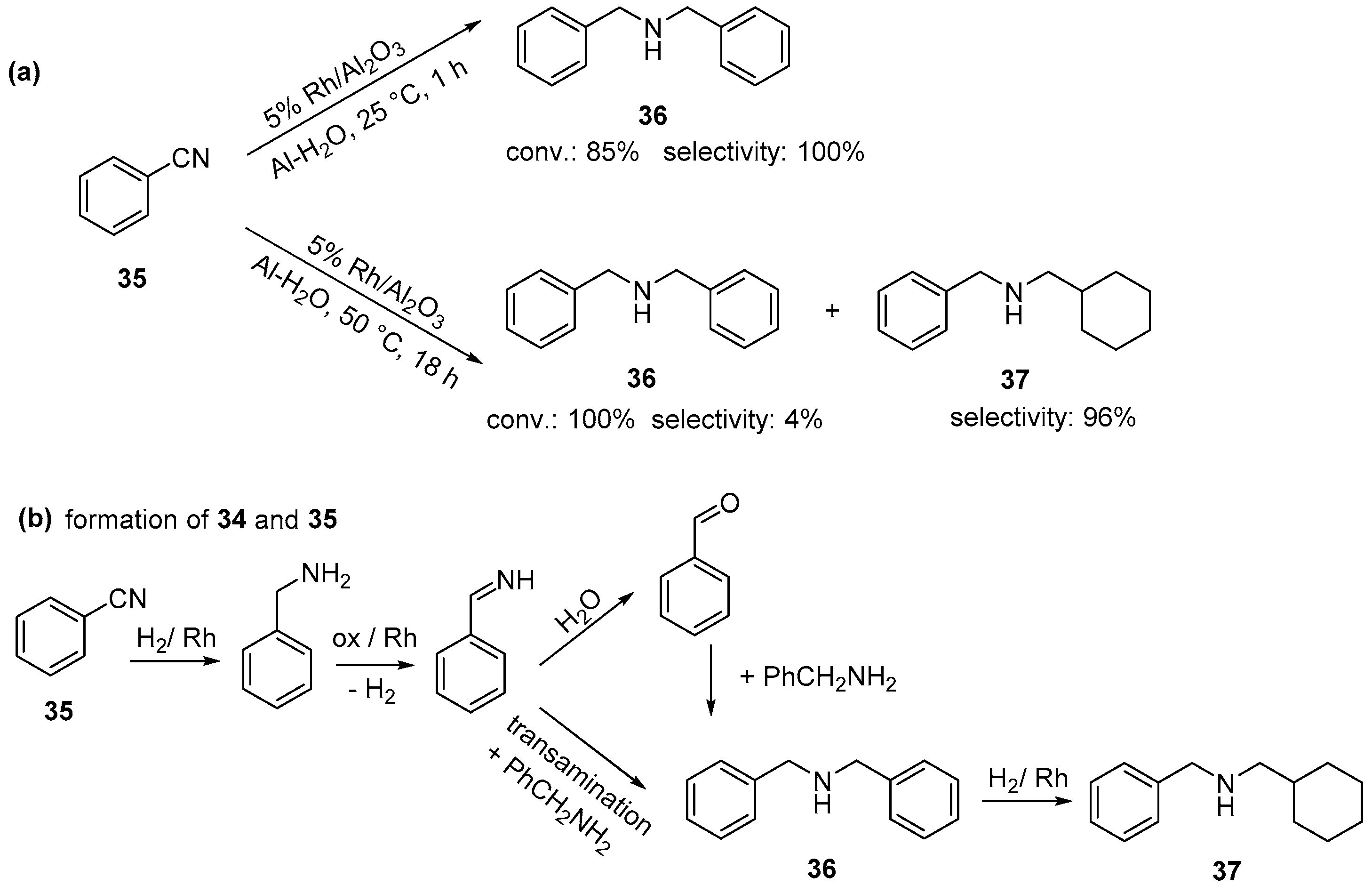
2.4. Rh-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Nitriles and Nitro-Compounds
2.5. Rh-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Compounds with Multiple Functional Groups
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.B.; March, J. March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 6th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Török, B.; Schäfer, C.; Kokel, A. Hydrogenation in Heterogeneous Catalysis in Sustainable Synthesis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Cambridge, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2021; Chapter 3.1; pp. 85–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, S. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Blaser, H.-U.; Malan, C.; Pugin, B.; Spindler, F.; Steiner, H.; Studer, M. Selective hydrogenation for fine chemicals: Recent trends and new developments. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 103–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Török, B. Heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenations as an environmentally benign tool for organic synthesis. Curr. Org. Synth. 2011, 8, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, R.J.; Santhanam, K.S.V.; Miri, M.J.; Bailey, A.V.; Takacs, G.A. Introduction to Hydrogen Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Chapter 4.1; pp. 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Török, B.; Dransfield, T. Green Chemistry: An Inclusive Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Cambridge, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukinoki, T.; Kanda, T.; Liu, G.; Tsuzuki, H.; Tashiro, M. Organic reaction in water. Part 3: A facile method for reduction of aromatic rings using a raney Ni–Al alloy in dilute aqueous alkaline solution under mild conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 5865–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, K.; Mitoma, Y.; Nagashima, A.; Tashiro, H.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Olah, G.A.; Tashiro, M. Reduction of carbonyl groups to the corresponding methylenes with Ni–Al alloy in water. Chem. Commun. 2003, 514–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, J.; He, H.; Yang, H.; Thiemann, T.; Tashiro, H.; Tashiro, M. New method for the reduction of benzophenones with Raney Ni-Al alloy in water. Synth. Commun. 2008, 38, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, C.; Nisanci, B.; Bere, M.P.; Dastan, A.; Török, B. Heterogeneous Catalytic Reductive Amination of Carbonyl Compounds with Ni-Al Alloy in Water as Solvent and Hydrogen Source. Synthesis 2016, 48, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, C.; Ellstrom, C.J.; Cho, H.; Török, B. Pd/C-Al-Water Facilitated Selective Reduction of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhan, U.; Kowser, Z.; Redshaw, C.; Yamato, T. Reduction of diphenylacetylene using Al powder in the presence of noble metal catalysts in water. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 6943–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Schäfer, C.; Török, B. Hydrogenations and Deuterium Labeling with Aluminum-based Metal Alloys under Aqueous Conditions. Curr. Org. Synth. 2016, 13, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhan, U.; Kowser, Z.; Islam, M.N.; Yamato, T. A Review on the Recent Advances in the Reductions of Carbon–Carbon/Oxygen Multiple Bonds Including Aromatic Rings Using Raney Ni–Al Alloy or Al Powder in the Presence of Noble Metal Catalysts in Water. Top. Catal. 2018, 61, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomin, A.; Lazarev, A.; Bere, M.P.; Redjeb, H.; Török, B. Selective reduction of ketones using water as a hydrogen source under high hydrostatic pressure. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 7321–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Török, F.; Török, B. Selective reduction of condensed N-heterocycles using water as a solvent and a hydrogen source. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilamanova, M.; Mastyugin, M.; Schäfer, C.; Kokel, A.; Török, B. Heterogeneous Metal Catalysis for the Environmentally Benign Synthesis of Medicinally Important Scaffolds, Intermediates and Building Blocks. Curr. Org. Chem. 2021, 25, 2304–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, P.N. Catalytic Hydrogenation over Platinum Metals; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.; Török, B. Heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of unprotected indoles in water: A green solution to a long-standing challenge. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5124–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pálinkó, I. Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Fundamental Pillar of Sustainable Synthesis. In Green Chemistry: An inclusive Approach; Török, B., Dransfield, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Chapter 12; pp. 416–447. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, R.; Selent, D.; Börner, A. Applied Hydroformylation. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5675–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balayeva, N.O.; Mamiyev, Z.; Dillert, R.; Zheng, N.; Bahnemann, D.W. Rh/TiO2-Photocatalyzed Acceptorless Dehydrogenation of N-Heterocycles upon Visible-Light Illumination. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5542–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayeva, N.O.; Zheng, N.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.W. Visible-Light-Mediated Photocatalytic Aerobic Dehydrogenation of N-heterocycles by Surface-Grafted TiO2 and 4-amino-TEMPO. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10694–10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokel, A.; Schäfer, C.; Török, B. Application of microwave-assisted heterogeneous catalysis in sustainable synthesis design. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3729–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Török, B. K-10 montmorillonite-catalyzed solid phase diazotizations: Environmentally benign coupling of diazonium salts with aromatic hydrocarbons to biaryls. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5390–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Twardy, D.; Ellstrom, C.; Wheeler, K.A.; Dembinski, R.; Török, B. Catalyst-free ambient temperature synthesis of isoquinoline-fused benzimidazoles from 2-alkynylbenzaldehydes via alkyne hydroamination. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, C.; Cho, H.; Vlocskó, R.B.; Xie, G.; Török, B. Recent Advances in the Green Synthesis of Heterocycles: From Building Blocks to Biologically Active Compounds. Curr. Org. Synth. 2022, 19, 426–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coq, B.; Figueras, F. Structure–activity relationships in catalysis by metals: Some aspects of particle size, bimetallic and supports effects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1998, 178–180, 1753–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A. Preparation and catalytic properties of new mesoporous materials. Top. Catal. 1997, 4, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.J. New perspectives on basic zeolites as catalysts and catalyst supports. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokel, A.; Kadish, D.; Török, B. Preparation of Deuterium Labeled Compounds by Pd/C-Al-D2O Facilitated Selective H-D Exchange Reactions. Molecules 2022, 27, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Török, B.; Balázsik, K.; Felföldi, K.; Bartók, M. Asymmmetric Reactions in Sonochemistry. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 2001, 8, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálinkó, I.; Notheisz, F.; Bartók, M. A Competitive Reaction which is Able to Make Fine Distinctions Between Reacting Surfaces. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1989, 48, 729–737. [Google Scholar]
- Ferranti, A.; Garuti, L.; Giovanninetti, G.; Gaggi, R.; Roncada, P.; Nardi, P. Preparation and analgesic activity of tetrahydroquinolines and tetrahydroisoquinolines. Farmaco Sci. 1987, 42, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi, Y.; Shiokawa, K.; Goto, T.; Kagabu, S.; Kamochi, A.; Moriya, K.; Hayakawa, H. Eur. Patent 173208. Chem. Abstr. 1986, 105, 78937s. [Google Scholar]
- Nizamov, S.; Sednev, M.V.; Bossi, M.L.; Hebisch, E.; Frauendorf, H.; Lehnart, S.E.; Belov, V.N.; Hell, S.W. “Reduced” Coumarin Dyes with an O-Phosphorylated 2,2-Dimethyl-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline Fragment: Synthesis, Spectra, and STED Microscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lévay, K.; Hegedűs, L. Recent Achievements in the Hydrogenation of Nitriles Catalyzed by Transitional Metals. Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 1881–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesh, A.M.; Weiguny, J. A Review of the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds into Aromatic Amines, Isocyanates, Carbamates, and Ureas Using CO. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2035–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Huang, Z.-F.; Pan, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.-J. Review on selective hydrogenation of nitroarene by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 227, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landge, S.M.; Atanassova, V.; Thimmaiah, M.; Török, B. Microwave-assisted oxidative coupling of amines to imines on solid acid catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5161–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, V.; Ganno, K.; Kulkarni, A.; Landge, S.M.; Curtis, S.; Foster, M.; Török, B. Mechanistic study on the oxidative coupling of amines to imines on K-10 montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadgut, S.C.; Török, M.; Esquibel, J.; Török, B. Highly asymmetric heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of isophorone on proline modified base-supported palladium catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 238, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadgut, S.C.; Török, M.; Dasgupta, S.; Török, B. Nature of Proline-induced Enantiodifferentiation in Asymmetric Pd Catalyzed Hydrogenations: Is the Catalyst Really Indifferent? Catal. Lett. 2008, 123, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst/Supplier | Time (h) | T (°C) | Conversion (%) | Yield of 2 (%) | Yield of 3 (%) |
| 1 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (TS) | 24 | 25 | 22 | 22 | 0 |
| 2 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (reduced) (AA) | 24 | 25 | 83 | 80 | 3 |
| 3 | 5% Rh/C (AA) | 24 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 1% Rh/PEI/SiO2 (AA) | 24 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Time (h) | T (°C) | Conversion (%) | Yield of 2 (%) | Yield of 3 (%) |
| 1 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (TS) | 24 | 25 | 7 | 2 | 5 |
| 2 | 5%Rh/Al2O3 (reduced) (AA) | 24 | 25 | 96 | 23 | 73 |
| 3 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (AA) | 24 | 50 | 12 | 4 | 8 |
| 4 | 5% Rh/C (AA) | 24 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 5 | 1% Rh/PEI/SiO2 (AA) | 24 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Time (h) | T (°C) | Conversion (%) | Yield of 2 (%) | Yield of 3 (%) |
| 1 | 5% Rh/Al2O3(TS) | 24 | 25 | 85 | 73 | 12 |
| 2 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (reduced) (AA) | 24 | 25 | 71 | 66 | 5 |
| 3 | 5% Rh/Al2O3 (AA) | 24 | 50 | 87 | 82 | 5 |
| 4 | 5% Rh/C (AA) | 24 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 5 | 1% Rh/PEI/SiO2 (AA) | 24 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Time (h) | T (°C) | Conversion (%) | Yield of 7 (%) | Yield of 8 (%) |
| 1 | 5%Rh/Al2O3(TS) | 6 | 25 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | 5%Rh/Al2O3 (reduced)(AA) | 6 | 25 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 3 | 5% Rh/C (AA) | 6 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 1% Rh/PEI/SiO2 (AA) | 6 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, G.; Török, B. Rh-Catalyzed Environmentally Benign Selective Hydrogenation of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups Using Al-Water as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121578
Xie G, Török B. Rh-Catalyzed Environmentally Benign Selective Hydrogenation of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups Using Al-Water as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts. 2022; 12(12):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121578
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Guoshu, and Béla Török. 2022. "Rh-Catalyzed Environmentally Benign Selective Hydrogenation of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups Using Al-Water as a Hydrogen Source" Catalysts 12, no. 12: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121578
APA StyleXie, G., & Török, B. (2022). Rh-Catalyzed Environmentally Benign Selective Hydrogenation of a Broad Variety of Functional Groups Using Al-Water as a Hydrogen Source. Catalysts, 12(12), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121578






