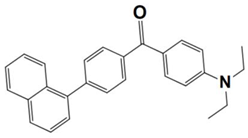
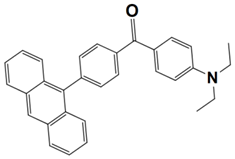
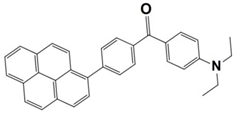
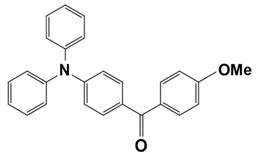
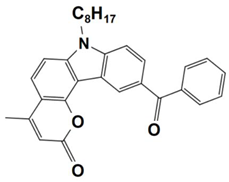
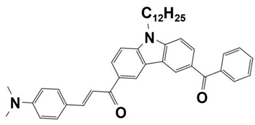
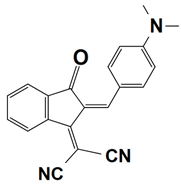
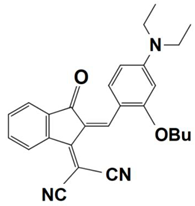
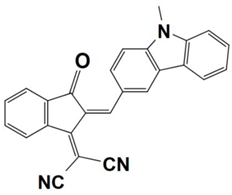
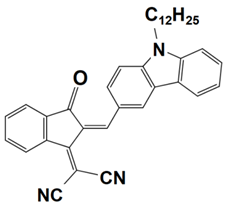
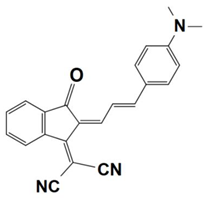
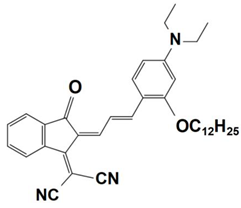
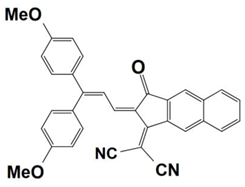
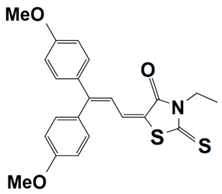
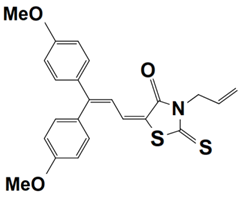
Abstract
Even though numerous organic dyes which are used as photoinitiators/photocatalysts during photopolymerization have been systematically investigated and collected in previous reviews, further designs of these chromophores and the developments in high-performance photoinitiating systems have emerged in recent years, which play the crucial role in 3D printing/Vat polymerization. Here, in this mini-review, various families of organic dyes that are used as newly synthesized photoinitiators/photocatalysts which were reported in literature during 2021–2022 are specified by their photoinitiation mechanisms, which dominate their performance during photopolymerization, especially in 3D printing. Markedly, visible light-induced polymerization could be employed in circumstances not only upon the irradiation of artificial light sources, e.g., in LEDs, but also in sunlight irradiation. Furthermore, a short overview of the achievements of newly developed mechanisms, e.g., RAFT, photoinitiator-RAFT, and aqueous RAFT using organic chromophores as light-harvesting compounds to induce photopolymerization upon visible light irradiation are also thoroughly discussed. Finally, the reports on the semiconducting nanomaterials that have been used as photoinitiators/photocatalysts during photopolymerization are also introduced as perspectives that are able to expand the scope of 3D printing and materials science due to their various advantages such as high extinction coefficients, broad absorption spectra, and having multiple molecular binding points.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, 3D printing/vat photopolymerization, namely additive manufacturing, has been widely known as a powerful tool in rapid prototype design and in the production of three-dimensional objects [1,2,3]. Indeed, a number of 3D objects have been successively prototyped in academic laboratories around the world, remarkably, the photopolymerization process has already found an uncontested place in the stereolithography technique or in 3D printing [4,5,6]. This approach provides an efficient way to solidify liquid resins into designed objects under light irradiation, among various 3D printing technologies [7,8,9]. Moreover, photopolymerization is also regarded as an emerging technique for many other fields, e.g., (i) regenerative medicine and photocurable dental composites [10,11], (ii) drug delivery [12], and (iii) 4D printing [13,14]. In particular, Light Emitted Diodes (LEDs) with a safe amount of violet light were widely used as a reliable artificial light sources to activate the polymerization process by a number of research groups due to them having numerous advantages such as a low-cost, spatial control, a highly efficient process in mild conditions, and being safe [4,15]. Obviously, the wavelength and intensity of the light source affect the performance of the polymerization process [16,17]. On the other hand, sunlight is a natural light source that tends to be more widely used for photopolymerization in the laboratory due to its advantages, e.g., it has a broad emission spectrum and it is free and unlimited, which are parallel to the artificial light sources [18,19,20].
Besides the appropriate light sources, other factors such as the viscosity of the monomer(s), whether there are added organic fillers in the resin, etc. [21], can also affect the efficiency of the photopolymerization processes. Currently, one of the main obstacles to achieving a high-performance photopolymerization reaction is the selection of the appropriate photomediators, which can fully adapt to the specific irradiation wavelength, e.g., 405 nm [22,23,24,25,26]. Commonly, charge transfer reactions between the photomediators and the co-initiator(s)/additives in the photoinitiating systems (PISs) occur upon the absorption of light, and the charges can also transfer back to the electron donor from the electron acceptor [27]. In this article, the photomediators are separated into two categories: the photoinitiators (PIs) and the photocatalysts (PCs), depending on the completeness of the catalytic cycles that are involved. Based on their different mechanisms of interacting with the co-initiator (or additives) to generate active free radicals or cations, PIs/PCs can also be divided into Type I and Type II in photoinduced polymerization [28,29].
To evaluate the efficiency of the polymerization reaction, Real-Time Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (RT-FTIR) has been used as the most popular technique to monitor the conversion of the monomer over time [30,31]. Precisely, the conversion of the monomer can be evaluated by the characteristic band (C=C bond or ether bond) decreases in the vibration peak area (A) at ~6130 cm−1 or 1630 cm−1 in the FTIR spectra following the monomers’ conversion into a polymer. Hence, the conversions of the monomers can be quantified from the peak area and the irradiation time by the following equation [32]:
conversion (%) = (A0 − At)/A0 × 100
Recently, many developments of efficient PIs/PCs that are based on organic dyes and metal complexes have been developed in order to use them as photoinitiators for 3D printing under visible light irradiation [33,34,35]. Here, in this review, a short overview of the newly developed organic dyes exhibiting remarkable visible light absorption properties and excellent photoactivation capabilities which were published during the 2021–2022 period were discussed. The context was classified into two main parts: Type I and II photoinitiators. Furthermore, the recent works which can significantly contribute to exploring the new reaction mechanisms of photopolymerization were also presented. We believe these intense research efforts from chemists and material scientists on the design of dye-based photoinitiating systems were likely to promote the rapid expansion of visible light-induced photopolymerization and their applications in 3D printing [36]. A review of these works can undoubtedly speed up the development of dye-initiated photopolymerization, and it can have a long-term impact on the 3D printing technique.
2. State-of-the-Art Techniques
In the past few years, many newly synthesized organic dyes were extensively introduced into the field of photopolymerization as PIs/PCs. Among them, many chromophores with appealing features such as high molar extinction coefficients, high thermal stability, and good light absorption properties over the visible range (mostly in the 400–700 nm range) were successfully characterized in the previous literature [32,33,34]. As is it known, the photochemical/chemical reactivity of these dyes, e.g., their molar extinction coefficients, and their redox properties, govern the performance of the PIs/PCs during photopolymerization [36]. Herein, some works that have been published for the dye-based PISs which act as Type Ⅰ and Type Ⅱ PIs are mainly summarized in this review:
- (1)
- There are Type I photoinitiators, which induce the photopolymerization by the following mechanisms [36]:PI → PI* (hν)→R● + R●′
Several series of organic dyes which are used as Type I photoinitiators were depicted as examples, e.g., N-naphthalimide ester, a nitrocarbazole-based oxime esters derivative.
- (2)
- There are Type II photoinitiators, which induce the photopolymerization by the following mechanisms [36]:PI → PI* (hν) + DH→RH● + D●
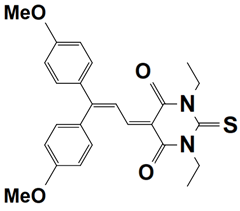
Similarly, several families of organic dyes which are used as Type II photoinitiators are discussed as examples in this part, e.g., benzophenone, 4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-allylidene, indane- 1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3 (2H)-dione derivatives. Commonly, Type II photoinitiators usually are combined with Iodonium salt and ethyl-4-dimethylaminobenzoate (EDB) to induce free-radical polymerization by constituting a three-component PIS as follows [37]:
PI + photon → PI*
PI* + Ar2I+ → PI●+ + Ar● + Ar2I●
PI●+ + EDB → PI + EDB●+
Recently, iodonium salts have been widely used as a co-initiator in PISs for photopolymerization due to their relatively good electron-accepting capability and solubility in numerous photocurable resins [38,39]. Oppositely, amines exhibit excellent electron-donating abilities on the nitrogen atom, which can remarkably improve the photoinitiation efficiency of the PISs during photopolymerization [40,41].
In order to present the developments of photopolymerization comprehensively and systematically, the dyes are used as either Type I or Type II photoinitiators that exhibit high molar extinction coefficients and excellent photoinitiation abilities; some newly reported PIs/PCs which can conduct the proper mechanisms during photopolymerization, such as Photo-Reversible Deactivation Radical Polymerization (photo-RDRP) and Photoinitiator-RAFT, are discussed in the following context.
2.1. Type I Photoinitiators
As it is aforementioned in the text, Type Ⅰ photoinitiators are single molecules that are capable of generating active radicals by the homolytic cleavage of the chemical bonds under light irradiation [42]. Even if numerous organic chromophores with different structures were reported for photopolymerization and 3D printing, only a few commercial Type Ⅰ PIs can follow the Type I mechanisms effectively during photopolymerization [43]. Recently, some highly reactive Type I photoinitiators with interesting structures or photoinitation mechanisms were designed, and their promising performances upon their exposure to LEDs during photopolymerization were reported [44]. Here, in this part, several series of newly synthesized chromophores that have been used as Type Ⅰ PIs, e.g., N-hydroxynaphthalimide esters, bis-chalcones-based oxime ester, nitrocarbazole based oxime esters and some newly developed dyes following the Type I mechanisms, e.g., light-driven reversible deactivation radical polymerization (photo-RDRP) and light-driven reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (photo-RAFT) were collected and discussed.
2.1.1. N-hydroxynaphthalimide Esters
Previously, naphtalimide-based derivatives have been chemically modified to fulfill the requirements of PIs [45,46,47]. Indeed, these naphtalimide derivatives which are regulated by various substituents were not only designed for two/three-component photoinitiating systems (PISs), but they were also used for one-component photoinitiating systems. The absorption properties of naphtalimide derivatives can be tuned by various substituents. Recently, Liu et al. evaluated the photoinitiation abilities of nine N-hydroxynaphthalimide esters (which are noted as NPIE1-NPIE9, Table 1) with different structures which were used as Type I PIs during photopolymerization upon their exposure to 405 nm and 455 nm LEDs. In the results, these dyes exhibit high molar extinction coefficients in the visible range and excellent performances in the free-radical polymerization of acrylate monomers (TMPTA). Remarkably, NPIE1 exhibited a better photoinitiation ability than the benchmark PI diphenyl (2,4,6-trimethyl- benzoyl)phosphine oxide (TPO) did in both of the cases of 405 and 455 nm irradiation (final conversion of TPO: 66% @405nm LED, no polymerization @455 nm LED). In addition, a decarboxylation reaction was also detected, thus the mechanisms of Type Ⅰ PI that occurred during the polymerization process can be imagined. Finally, a high thermal stability of the investigated NPIEs in the acrylate monomers was found, and their good photoinitiation abilities were also verified by the success of the 3D printing experiments [48].
2.1.2. Bis-chalcones Based Oxime Ester Derivatives
In photochemistry, an oxime ester is also commonly regarded as Type Ⅰ photoinitiator. Numerous families of oxime esters which are derived from coumarin-carbazole, nitro-carbazole, and phenylthioether thiophene dyes were designed for LED photopolymerization [49,50,51]. In 2022, Wu, X. et al. firstly synthesized three bis-chalcones-based oxime ester dyes (marked as TA1–3), and they used them as Type I PIs to conduct the photopolymerization of an acrylate monomer (1, 6-hexanediol diacrylate, HDDA) under its exposure to a 455 nm LED for 30 min. In this polymerization process, the monomer that was initiated by the TA2 with benzylidene cyclopentanone oxime ester exhibited the highest final conversion (see Table 1) and photoinitiation efficiency owing to its best electron delocalization among the three chromophores. Remarkably, a photobleaching phenomenon was also observed on these dyes with the same concentration (1 × 10−6 mol∙g−1) in the HDDA system via the photocuring depth experiment upon its exposure to a 455 nm LED (see Figure 1). The colors of all of the dyes seem to be completely disappeared. Surprisingly, the largest photobleaching height of the columns was achieved by the photopolymerization that was initiated by TA2, reaching the depth of 32mm in thickness (see Figure 1b). Indeed, their photobleaching properties are likely to expand the knowledge of the structural design of the dyes and reveal the potential in deep photocuring and the applications for visible light photoinitiators, e.g., 3D printing and dental materials [52].
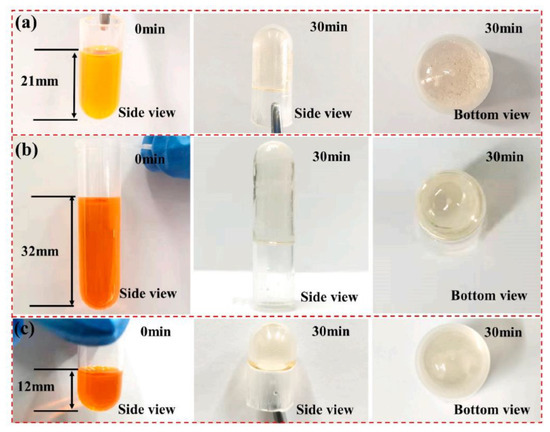
Figure 1.
Photobleaching of (a) TA1, (b) TA2, and (c) TA3 in the HDDA system under argon upon the LED@455 nm for 30 min ([PI] = 1 × 10−6 mol g−1, I = 80 mW cm−2). Adapted from [52] with permission from Elsevier.

Table 1.
Newly developed N-hydroxynaphthalimide esters applicable in PISs as Type I photoinitiators [48,52].
Table 1.
Newly developed N-hydroxynaphthalimide esters applicable in PISs as Type I photoinitiators [48,52].
| No. | OXEs | Absorption Properties | Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 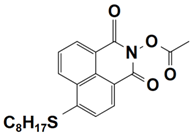 NPIE-1 | λmax~397 nm εmax~16,000 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~15,000 M−1 cm−1 | ~69% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 2 | 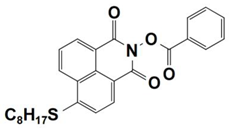 NPIE-2 | λmax~398 nm εmax~15,200 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~14,400 M−1 cm−1 | ~57% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 3 | 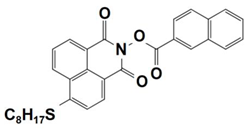 NPIE-3 | λmax~398 nm εmax~15,600 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~14,900 M−1 cm−1 | ~61% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 4 | 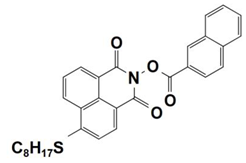 NPIE-4 | λmax~397 nm εmax~14,100 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~13,100 M−1 cm−1 | ~15% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 5 | 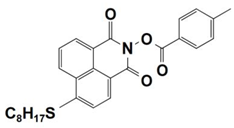 NPIE-5 | λmax ~ 397 nm εmax ~ 15,300 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~ 14,500 M−1 cm−1 | ~64% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 6 | 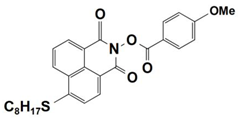 NPIE-6 | λmax~397 nm εmax~14,700 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~13,800 M−1 cm−1 | ~54% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 7 | 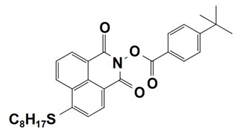 NPIE-7 | λmax~397 nm εmax~13,500 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~12,800 M−1 cm−1 | ~67% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 8 | 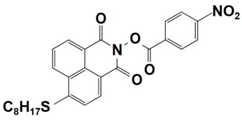 NPIE-8 | λmax~397 nm εmax~12,900 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~12,000 M−1 cm−1 | ~58% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 9 | 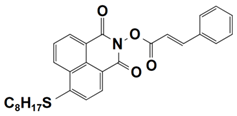 NPIE-9 | λmax~397 nm εmax~14,900 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~14,000 M−1 cm−1 | ~68% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 10 | 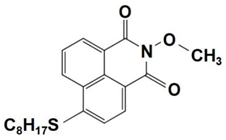 NPIEMO | λmax~394 nm εmax~11,600 M−1 cm−1 ε405nm~10,200 M−1 cm−1 | ~62% in TMPTA @405 nm |
| 11 | 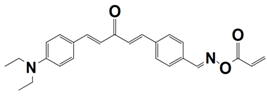 TA1 | λmax~437 nm εmax~33,750 M−1 cm−1 ε455nm~30,450 M−1 cm−1 | ~78% in HDDA @455 nm |
| 12 | 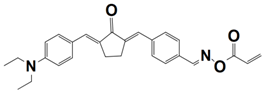 TA2 | λmax~465 nm εmax~39,530 M−1 cm−1 ε455nm~37,830 M−1 cm−1 | ~66% in HDDA @405 nm ~75% in HDDA @455 nm ~79% in HDDA @470 nm ~72% in HDDA @490 nm |
| 13 | 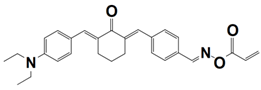 TA3 | λmax~436 nm εmax~29,380 M−1 cm−1 ε455nm~25,830 M−1 cm−1 | ~56% in HDDA @455 nm |
2.1.3. Nitrocarbazole-Based Oxime Esters
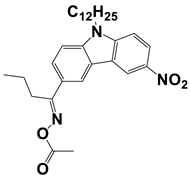
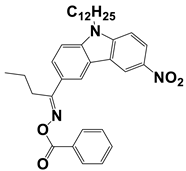
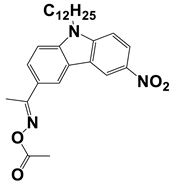
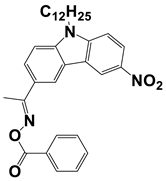
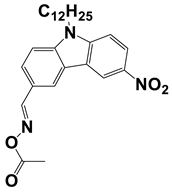
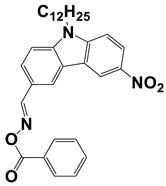
In 2021, Liu, S. et al. examined three nitrocarbazole oxime esters which were used as Type I photoinitiators (PIs) for visible light photopolymerization. The chemical structures of four investigated dyes (OXE-M, OXE-V, OXE-P, and OXE-H) and their absorption properties are listed in Table 2. Among them, three PIs with acetyl (OXE-M), acryloyl (OXE-V), and benzoyl (OXE-P) terminal groups within the oxime ester group were firstly synthesized. Remarkably, the three PIs exhibited excellent photoinitiation abilities during the photopolymerization of the acrylate monomers (TMPTA) under 405 nm LED irradiation. Specifically, the OXE-M/TMPTA system achieved higher final conversion (~69% for TMPTA) than that of the commercial Type I photoinitiator system ((diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide TPO/TMPTA, ~65%) [53].

Table 2.
Newly developed oxime esters (OXEs) that are applicable as Type I photoinitiators [53,54].
In addition, the chemical mechanisms of the OXEs during the polymerization process are proposed and depicted in Figure 2a. Upon their irradiation under a 405 nm LED, the iminyl and acyloxy radicals were generated from the cleavage of the N–O bond, which occurred upon the excitation of the OXE. Subsequently, a highly active free radical (R●) can be released from the acyloxy radical by a decarboxylation process to promote the polymerization of the acrylate monomers. Finally, the direct laser writing experiments and 3D printing were applied on an OXE-M/TMPTA system to confirm the high reactivity of the proposed PIs in the TMPTA. The letter pattern “OXE” with smooth surfaces and a good spatial resolution was observed as is shown in Figure 2c. Moreover, a square frame was also printed (see Figure 2d) by using a low light intensity 3D printer at 405 nm laser diode (110 mW cm−2) under air. Owing to the excellent performances of the nitrocarbazole oxime esters during photopolymerization, they could be ideal Type I photoinitiators for highly efficient 3D printing. Furthermore, the success in preparing the carbon fiber composites with the OXE-M-based system also revealed the dual photo/thermal initiation behaviors of OXE-M since minor light transmission was observed during the preparation process.
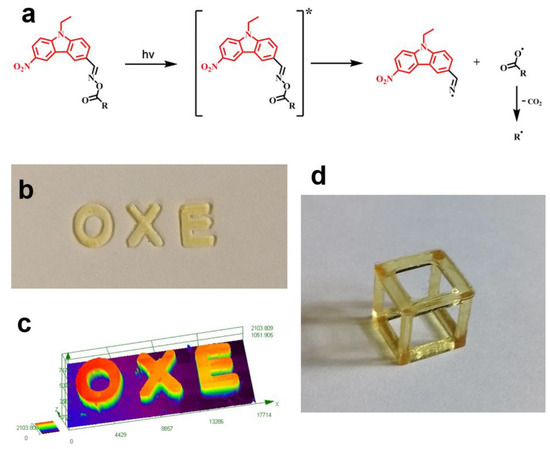
Figure 2.
(a) Proposed photochemical mechanisms for OXEs, []*: excited state of OXEs. (b) The letter pattern “OXE” obtained by direct laser write technique. (c) characterization of the letter pattern “OXE”. (d) 3D-printed object of square frame (7 × 7 × 7 mm3). Adapted from [53] with permission from Wiley.
In a continuation of the previous research, Liu, S. et al. introduced 50 newly synthesized nitrocarbazole oxime esters with different structures in five series [54]. Ten of these chromophores were systematically investigated, and their light absorption properties and the final conversions (FCs) of the TMPTA in the presence of the OXEs upon their exposure to an LED@405 nm are depicted (which are marked as the numbers 5–14) in Table 2. In this work, the chromophores with the methyl substituent on the oxime ester group (B1, C1, D1, E1, and F1) exhibited the best performances and photoinitiation ability during the polymerization process owing to their specific structures which allow for the generation of highly reactive radicals. Interestingly, the decarboxylation reactions that occurred more easily in D1 than they did in D2 were observed by establishing a profile of the absorption intensity curves (absorbance vs. irradiation time) to monitor the generation of CO2 (see Figure 3b). As a result, the decarboxylation reactions that appeared within the first 16s of the photopolymerization process are proven, which promotes the polymerization process. This phenomenon could also be regarded as an important reason why D1 shows better a photoinitiation ability than D2 does upon its exposure to both an LED@405 nm and an LED@365 nm. To certify the excellent photoinitiation capability of the nitrocarbazole oxime ester, the D1/TMPTA system was selected and studied in direct laser writing (DLW) experiments due to its high photoinitiation efficiency at 405 nm. As expected, a letter pattern “ET” (thickness ∼1600 μm, see Figure 3c) and two 3D objects (thickness ∼2 mm) with high spatial resolutions were successfully obtained within a short time (∼2 min) by using a stereolithography 3D printer.
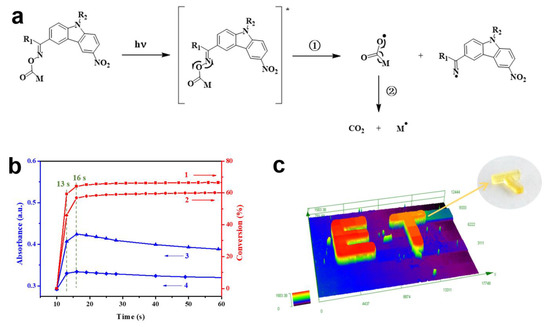
Figure 3.
(a) Proposed photoinitiation mechanism of OXEs ([]*: excited state of OXEs). (b) Line 1: photopolymerization profiles (acrylate function conversion vs. irradiation time) of the D1/TMPTA system. Line 2: photopolymerization profiles (acrylate function conversion vs. irradiation time) of the D2/TMPTA system. Line 3: the curve of absorption intensity (absorbance vs. irradiation time) of CO2 that was obtained from the D1/TMPTA system. Line 4: the curve of absorption intensity (absorbance vs. irradiation time) of CO2 that was obtained from the D2/TMPTA system. (c) Letter pattern that was observed using a digital microscope. Adapted from [54] with permission from the American Chemistry Society.
2.2. Type II Photoinitiators
As it is aforementioned in the text, a wide range of chromophores with different structures have been investigated as reliable Type II photoinitiators to activate free-radical photopolymerization. Remarkably, intense efforts were not only devoted to the development of photopolymerization upon the irradiation of a 405 nm light-emitting diode (LED), but they were also devoted noticeably to sunlight-induced photopolymerization [18,19,20], which is introduced in the following context. Similar to the mechanisms that are shown in Equations (2)–(4), the reactions that occurred in the dye-based three-component systems (dye/co-PI/additive) during the free-radical polymerization processes can be supported by two existing interactions between the dye/co-PI and the dye/additive (Equations (7)–(11), photoinitiation mechanisms of dyes/Iodonium/amine redox combination [33,37]). Indeed, the reaction mechanisms of the Type II photoinitiatiator/photocatalyst have been introduced in the previous literature, precisely and systematically [33,37].
Dye → *Dye (hν)
*Dye + Ar2I+ → Dye●+ + Ar2I● → Dye●+ + Ar● + ArI
*Dye + EDB →Dye●− + EDB●+ → Dye-H● + EDB●(-H)
Dye●+ + EDB → Dye + EDB●+
Dye-H● + Ar2I+ → Dye + Ar● + ArI + H+
2.2.1. Benzophenone Derivatives
Benzophenone derivatives are commonly used as Type II photoinitiators after the chemical modifications of them have been performed by moieties such as triphenylamine [55], carbazole [56], stilbene [57], and naphthalimide [58]. As possible hydrogen acceptors, benzophenone derivatives are often paired with other co-initiators acting as hydrogen donors to proceed with the electron/proton transfer. However, they have also been used in a one-component photoinitiating system (PIS) to initiate photopolymerization efficiently [26,59].
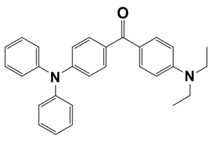
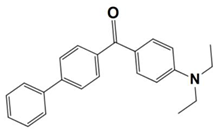
Recently, Huang, T. synthesized five benzophenone derivatives (BPN-D, BPN-P, BPN-N, BPN-An, and BPN-Py) by chemically modifying benzophenone with a tertiary amine, and they used them as one-component PISs during the photopolymerization of trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate (TMPTMA) under the irradiation both of a UV lamp and a 405 nm LED. Here, the light absorption properties of benzophenone derivatives (which are noted as dyes 1–5) and the conversions of the acrylates are summarized in Table 3. From the results, the highest acrylate conversion that occurred under the UV lamp irradiation could be observed when BPN-Ph acted as a photoinitiator (FC~30%), while the highest conversion under the 405 nm LED irradiation was achieved by using BPN-An as photoinitiator (FC~22%). After comparing them with the commercial analogs, 4-(diethylamino) benzophenone (BPN), and 4,4′-bis(diethylamino) benzophenone (EMK), the newly synthesized derivatives were regarded as efficient Type I photoinitiators with enhanced photosensitivity, organic solubility, and optical and thermal properties during the photopolymerization process [60].

Table 3.
Newly developed benzophenone derivatives that are applicable as Type II photoinitiators [60,61].
On the other hand, the dye-based PISs with benzophenone derivatives can not only be used to initiate free-radical photopolymerization (FRP), but they can also be used to initiate cationic photopolymerization (CP). In 2021, Liu et al. synthesized seven new chromophoroes with benzophenone moieties as Type II photoinitiators for photopolymerization upon their irradiation under a 405 nm LED. Precisely, the investigated dyes could be divided into two series by their functional groups, (1) the dyes with benzophenone-triphenylamine hybrid structures (which are noted as BT1–BT4) and (2) the dyes with benzophenone-carbazole hybrid structures (which are noted as BC1–BC3). Markedly, their specific chemical structures contribute to the red-shift of the absorption maxima and the enhancement of their molar extinction coefficients (see Table 3, dyes 6–12). In this work, all of the one-component PISs (the dyes alone), two-component PISs (dye/Iod or dye/EDB), and three-component PISs (dye/Iod/EDB) were investigated for photopolymerization upon their irradiation with a 405 nm LED. The polymerization profiles are presented in Figure 4, and the final function conversions (FCs) were collected, and they are presented in Table 3. In terms of the results, all of the benzophenone derivatives could initiate the photopolymerization of the TMPTA, either in one- (dye alone), two- (dye/Iod or dye/EDB), or three-component (dye/Iod/EDB) PISs. (see Figure 4a,b (or c),d, respectively). Remarkably, better hydrogen abstraction abilities were found for the benzophenone-triphenylamine derivatives, BT2, BT3, and BT4, rather than the commercial photoinitiator, 2-isopropylthioxanthone. Among them, BT3, with a high molecular weight, trifunctional character, and excellent migration stability, was applied in 3D printing and good 3D patterns were attained [61].
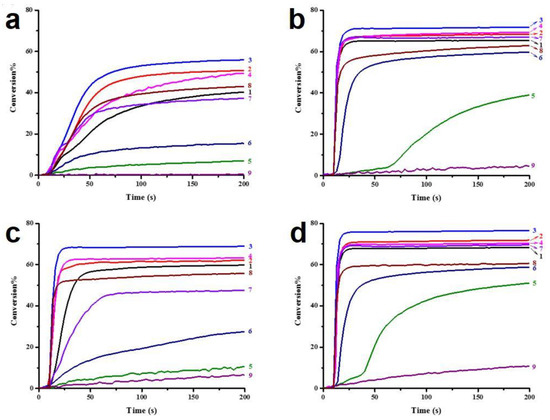
Figure 4.
Photopolymerization profiles of TMPTA (acrylate function conversion vs. irradiation time) in laminate (~25 μm) under LED@405 nm irradiation in the presence of (a) PI alone (0.3%, mol), (b) PI/Iod (0.3%/1%, mol/mol), (c) PI/EDB (0.3%/1%, mol/mol), and (d) PI/Iod/EDB (0.3%/1%/1%, mol/mol/mol): curve 1: PI = BT1; curve 2: PI = BT2; curve 3: PI = BT3; curve 4: PI = BT4; curve 5: PI = BC1; curve 6: PI = BC2; curve 7: PI = BC3; curve 8: PI = ITX; curve 9: PI = BP. The photopolymerization starts at t = 10 s. Adapted from [61] with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry and the Chinese Chemical Society.
2.2.2. Newly Developed Push–Pull Dyes
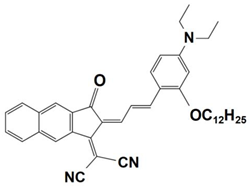
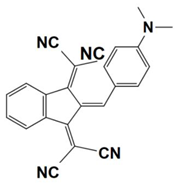
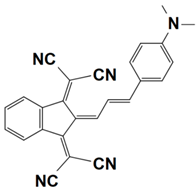
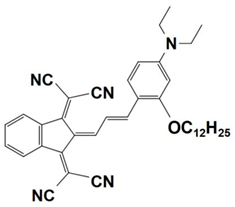
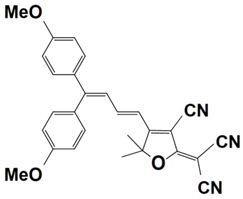
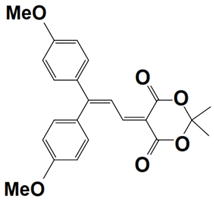
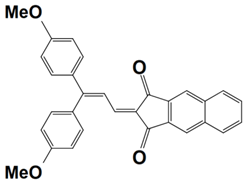
Previously, a wide range of push–pull dyes have been investigated as reliable photoinitiators (PIs) to activate free-radical photopolymerization [18,19,20,34]. In the previous research, the photoinitiation capabilities of two series of push–pull dye-based three-component systems comprising iodonium salt and EDB during free-radical polymerization were examined under the irradiation by a 405 nm LED or sunlight in the same conditions (e.g., at room temperature, etc.). In the following context, the Indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3 (2H)-dione derivatives are marked as dyes 1–13; the 4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-allylidene derivatives are marked as dyes 14–25. The weight ratios of the three components in the monomer (TMPTA) were all set as 0.1%: 2%: 2% (dye: Iod: EDB) [62].
Indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)-dione Derivatives
In 2022, a series of indane-1,3-dione and 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)-dione derivatives (which are noted as dyes 1–13) were initially synthesized by Sun, K. et al., and then, the photopolymerization of the benchmark acrylate monomer (TMPTA) which was initiated by the dyes 1–13-based three-component PISs was also examined by RT-FTIR experiments upon their irradiation with a 405 nm LED at room temperature. The photopolymerization profiles and conversions of the TMPTA are presented in Figure 5a and Table 4, respectively. Among them, the final acrylate conversions of the TMPTA that were obtained in the presence of the dyes 7, 9, and 11-based PISs (≈97–99%) were markedly higher than those of the reference system (Iod/EDB combination without dye, noted dye 0, FC~60%). Moreover, the efficient dyes 7, 9, and 11-based systems were selected to activate the sunlight-induced photopolymerizations of the TMPTA. As expected, the three selected dyes produced high FCs in 30 min of sunlight irradiation, (FC~99% for dye 7, FC~95% for dye 9, and FC~92% for dye 11, see Table 4 and Figure 5b), which again certified the outstanding photoinitiation abilities of the indane-1,3-dione and 1H-cyclopenta[b] naphthalene-1,3(2H)-dione derivatives and their potential use as efficient light-harvesting compounds, both under artificial and natural light sources [62].
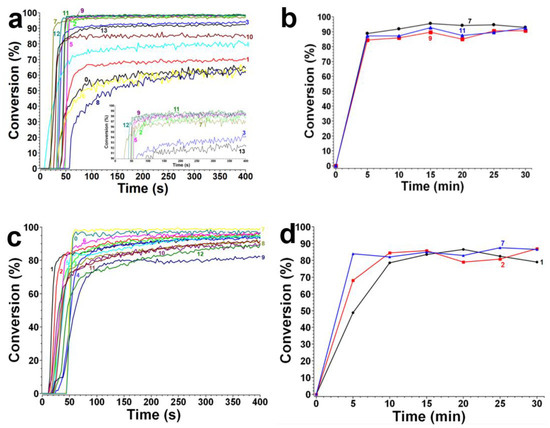
Figure 5.
(a) Photopolymerization profiles of TMPTA (conversion of C=C bonds vs. irradiation time) initiated by an iodonium salt and EDB upon exposure to LED@405 nm in laminate in the presence of dyes 1–13 at the same weight ratio: dye:Iod:EDB = 0.1%:2%:2% in TMPTA. Curve 0: Iodonium salt: EDB = 2%:2% in TMPTA without dye. (b) Photopolymerization profiles of TMPTA (conversion of C=C bonds vs. irradiation time) initiated by the iodonium salt and EDB upon exposure to sunlight in laminate in the presence of dyes at the weight ratio: dye:Iod:EDB = 0.1%:2%:2% in TMPTA; (black) dye 7; (red) dye 9; (blue) dye 11. (c) Photopolymerization profiles of TA (conversion of C=C bonds vs. irradiation time) initiated by an iodonium salt and EDB upon exposure to LED@405nm in laminate in the presence of dyes 14–25 at the same weight ratio: dye:Iod:EDB = 0.1%:2%:2% in TA. Curve 0′: Iodonium salt: EDB = 2%:2% in TA without dye. (d) Photopolymerization profiles of TA (conversion of C=C bonds vs. irradiation time) initiated by the iodonium salt and EDB upon exposure to sunlight in laminate in the presence of dyes at the weight ratio: dye:Iod:EDB = 0.1%:2%:2% in TA; (black) dye 14; (red) dye 15; (blue) dye 20. Adapted from [62] with permission from Wiley.

Table 4.
Newly developed indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)- dione derivatives that are based on push–pull dyes which are applicable in PISs. Adapted from [62] with permission from Wiley.
4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-allylidene Derivatives
As an additional piece of research on the N-ethylcarbazole-1-allylidene derivatives, 12 derivatives with substitutions of the 4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-allylidene groups were examined for their use as three-component PISs. Similarly, they exhibited outstanding photochemical properties and chemical reactivity in promoting the FRP processes. Here, Table 5 summarizes their photochemical properties, chemical structures, absorption properties, and the final conversions of the monomer that was under initiation is listed as follows after referring to the published review and literature [37,62].

Table 5.
Newly developed 4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-allylidene derivatives that are based on push–pull dyes which are applicable in PISs. Adapted from [37] with permission from Wiley.
As shown in Figure 5c, dye 20 produced the highest FC (≈99%) among dyes 14–25 in monomer TA, which reveal its excellent photinitiation ability. However, other dyes showed lower FCs than that of the reference system (≈97%, cited as dye 0′ in Figure 5c, Iod/EDB system without dye), even lower than the results of N-ethylcarbazole-1-allylidene derivatives in a tetrafunctional polyether acrylate monomer (2-((2-((acryloyloxy)methyl)-2-(((1-hydroxyallyl)oxy)methyl)butoxy)methyl)-2-ethylpropane-1,3-diyl diacrylate, noted as TA). Nevertheless, high photoinitiation performances under sunlight irradiation were observed and depicted in Figure 5d for dyes 14 (FC ≈ 87%), 15 (FC ≈ 79%) and 20 (FC ≈ 87%) during the photopolymerization.
Combining with the results achieved from the family of N-ethylcarbazole-1-allylidene derivatives mentioned above, sunlight is proved repeatedly to be a reliable natural light source for free-radical polymerization, and the group of push–pull dyes with high photoinitiation abilities upon sunlight irradiation is expanded as well.
In Sun’s work, the Direct Laser Writing/3D printing experiments were also applied to the three-component PISs using the indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)- dione derivatives. After the printing process, the 3D patterns were successfully fabricated using the all of the chosen dye-based three-component PISs with/without silica powders as fillers in an acrylate monomer (TMPTA). As shown in Figure 6, the 3D profiles with smooth surfaces and excellent spatial resolutions were profilometrically observed by numerical optical microscopy (“LZ” for dye 7, “CD” for dye 9, “YR” for dye 11, “RUY” for dye 7/silica, “SAQ” for dye 9/silica, and “HUI” for dye 11/silica), thereby giving powerful support to the truth that the dyes with indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)-dione can be regarded as reliable Type II photinitiators with a high light absorption capacity and excellent photoinitiation abilities in FRP. As a conclusion, the photocomposites that were attained in the presence of silica fillers are able to be utilized as useful photochemical materials in the fields of additive manufacturing/vat photopolymerization, etc.

Figure 6.
Free-radical photopolymerization experiments initiated by indane-1,3-dione, 1H-cyclopenta[b]naphthalene-1,3(2H)-dione derivative-based PISs in DLW experiments in acrylate monomer. Characterization of 3D overall appearance of 3D color patterns by numerical optical microscopy in the presence of: (a) dye 7/Iod/EDB (0.1%/2%/2% w/w/w in TMPTA); (b) dye 9/Iod/EDB (0.1%/2%/2% in TMPTA, w/w/w); (c) dye 11/Iod/EDB (0.1%/2%/2% in TMPTA, w/w/w); (d) dye 7/Iod/EDB/silica (0.1%/2%/2%/20% in TA, w/w/w/w); (e) dye 9/Iod/EDB/silica (0.1%/2%/2%/20% in TMPTA, w/w/w/w); (f) dye 11/Iod/EDB/silica (0.1%/2%/2%/20% in TMPTA, w/w/w/w). Adapted from [62] with permission from Wiley.
2.3. Mechanisms of Newly Developed Photo-Reversible Deactivation Radical Polymerization (Photo-RDRP Polymerization) and Their Applications in 3D Printing
Although the basic mechanisms of the free-radical polymerization that is mentioned above have been systematically discussed and applied in the synthesis of polymer networks and 3D printing, another radical polymerization mechanism that is called reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) is also well adopted. It can be further categorized into four classes: 1.nitroxide-mediated polymerization (NMP), 2. photoiniferter polymerization (mechanisms shown as Figure 7a), 3. atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP, mechanisms shown as Figure 7b), and 4. reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT, mechanisms shown as Figure 7c). Interestingly, they offer stronger capabilities to control the polymer architectures and propagate dormant reactivatable species than the conventional polymerization process does [63]. Inspired by the traditional RDRP systems that use thermal initiators to generate active radicals, the photo-RDRPs have been designed to form active radicals and promote chain extension due to the light stimulus. In particular, photoinduced reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (photo-RAFT) has been widely used in numerous fields as an efficient switchable polymerization technique owing to its easy operational process and high tolerance to solvents and monomer functional groups. Specifically, a photoinduced electron/energy transfer (PET) mechanism is commonly adopted to regulate the polymerization process [27,64,65,66,67]. The generation of active radicals can be repeated by the electron or the energy transfer between the excited catalyst and a RAFT agent under the light irradiation condition. Markedly, if we introduce the advantages of RAFT polymerization into photocured 3D printing, e.g., stereolithography (SLA) and digital light projection (DLA), an efficient RAFT polymerization system that is activated by light will be a crucial factor to allow accurate printing and fast building speeds to be achieved. Four-dimensional printing with the RAFT polymerization technique is also possible with a further modification of the basis of 3D printing [68].
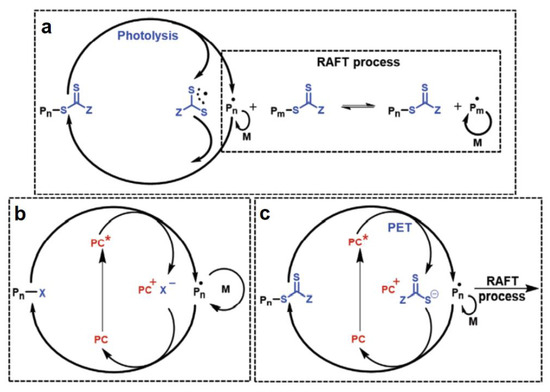
Figure 7.
Representative example mechanisms for photoRDRP. (a) Photoiniferter polymerization. (b) Photoactivated atom transfer radical polymerization (photoATRP). (c) Photoinduced electron/energy-transfer reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (PET-RAFT) polymerization. PC: photocatalyst (PC•+ was denoted as PC+ in the figures); Pn•: propagating radical species; M: monomer; PC*: excited state of photocatalyst. Adapted from [63] with permission from Wiley.
2.3.1. Photoinitiator-Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization (Photoinitiator-RAFT Polmyerization)
Even if some attempts using the organic dye/initiator-mediated systems have been performed in RAFT polymerization to print well-defined objects, these photo-RAFT polymerization systems are considered to be used in the cases when very high concentrations of divinyl monomers exist ([crosslinker]:[monomer] > 70:30). In 2021, Lee, K. et al. reported using a photoinitiator-RAFT system containing diphenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide (TPO) and 2-(n-butylthiocarbonothioylthio) propanoic acid (BTPA) as a Norrish Type I photoinitiator and RAFT agent, respectively, to conduct a RAFT polymerization on two acrylate monomers (N,N-dimethylacrylamide, DMAm, and a poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, PEGDA, which was used as crosslinker). Surprisingly, a complicated 3D Eiffel Tower arch was obtained with good resolution and fine details at a rapid printing speed (2.1 cm h−1) under 405 nm of violet light irradiation by using a low concentration of crosslinker, where the ratio was set as [PEGDA]:[DMAm] = 40:160 in the presence of BTPA and TPO, respectively (see Figure 8). Specifically, with the use of the photoinitiator-RAFT system, no significant difference in the layer shrinkage was found when the authors 3D printed two resins with 200 μm thickness containing different amounts of crosslinker: monomer molar ratios ([PEGDA]:[DMAm] = 40:160 and 140:60, respectively). However, the real build speeds were significantly different, with there being 9.1 cm h−1 for [PEGDA]:[DMAm] = 140:60 and there being 2.1 cm h−1 for [PEGDA]:[DMAm] = 40: 160, respectively. Nevertheless, the build speeds undoubtedly outcompeted the build speeds that were achieved when other authors used commercial resins (2 cm h−1) or PET-RAFT polymerization (1.2 cm h−1) [69].
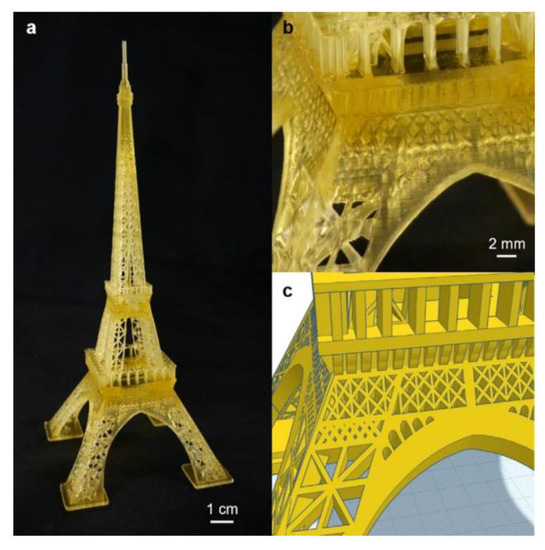

Figure 8.
Eiffel Tower figurine that was 3D-printed using novel resins containing BTPA as RAFT agent. (a) Full-sized 3D-printed object; (b) close-up of 3D-printed figurine showing intricate, high-resolution details, and (c) the corresponding close-up of the original 3D model design. Object was printed using a ratio of [BTPA]:[PEGDA]:[DMAm]:[TPO] = 1:40:160:2 under violet light (λmax = 405 nm, I0 = 0.81 mW cm−2) irradiation. Adapted from [69] with permission from Wiley.
2.3.2. Oxygen-Tolerant Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization (Oxygen Tolerant RAFT Polymerization)
In the light-induced RDRP, deoxygenation is essential to avoid the occurrence of uncontrolled polymerization since the existing oxygen may interact with the initiation of the radicals during the polymerization process. Thus, an oxygen-tolerant RAFT polymerization was carried out in the early works to prevent the oxygen inhibition during polymerization that happened in a complex system. In the previous research, some methods such as freeze–pump–thaw cycles, inert gas bubbling, and the use of reducing agents in the activators were commonly utilized to remove the oxygen, and some industrial applications of oxygen-tolerant RAFT polymerization were achieved successfully [70,71,72,73]. Alternatively, the possibility of efficiently preventing oxygen inhibition in open air by using photoredox catalysts or other additives has been proved. For instance, a previous enzyme strategy by Enciso, A. E. et al. which used glucose oxidase (GOx) was reported to deoxygenate and initiate the polymerization process [74].
Recently, Huang Y. et al. developed a simple and green method for oxygen-tolerant RAFT polymerization to occur under aqueous conditions in the open air. In this work, only 4-cyanopentanoic acid dithiobenzoate (CPADB) was used as an intrinsic photoredox catalyst to generate the dithioester anions without the use of another photocatalyst/photoinitiator. In detail, the generated dithioester anions could be stabilized by the amine radical cations that were released from a self-catalyzing monomer, 2-(dimethylamino) ethylmethacrylate (DMAEMA), as an electron donor. Specifically, the mechanisms of the deoxygenation process that occur during photopolymerization are shown in Figure 9. In terms of the results, the photoinduced RAFT polymerization of the mixture in the ratio of [DMAEMA]0:[CPADB]0 = 400:1 during a flame-sealing process without prior deoxygenation successfully proceeded in a controlled fashion, and it produced a high conversion rate of 75% after 24 h. Remarkably, the monomer conversions also increased with the molecular weight and viscosity, proving the fact that dithioester can be used as an iniferter agent to conduct RAFT polymerization under light irradiation. Interestingly, the polymerization in this work was carried out under a simple light source from a household lamp (14 W, 2.4 mW/cm2) [75].

Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of oxygen-tolerant RAFT polymerization using dithioester as a photoredox catalyst and amine monomer as an electron donor. []*: excited state of photoredox catalyst. Adapted from Reference [75] with permission from the European Chemical Societies.
2.3.3. Light-Induced Aqueous Reversible Addition–Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization (Aqueous Photo-RAFT Polymerization)
As a non-toxic, cheap, and environmentally friendly solvent, water also can be utilized for photopolymerizations to replace the organic solvents that are used in the traditional method. Combined with the advantages of RAFT polymerization, aqueous RAFT can be potentially applied for many applications due to its benefits, such as the spatiotemporal control of the polymerization process by turning the light source on/off [76]. Commonly, aqueous RAFT photopolymerization is separated into three main categories: one that is catalyzed by the external photoinitiators, e.g., sodium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl phosphinate (SPTP) and (2,4,6-Trimethylbenzoyl)diphenylphosphine oxide (TPO) [77], one that is catalyst free (photoiniferter) [78], and the aqueous PET-RAFT one [79]. Moreover, aqueous RAFT polymerization can be integrated with other fields to produce functional materials. For instance, McClelland et al. introduced the nanoparticles, e.g., CdSe quantum dots which are used as photocatalysts that can be easily separated and recycled from the polymer product for the aqueous photo-RAFT polymerization [80]. Nowadays, many organic/inorganic chemicals were designed to catalyze the RAFT photopolymerization in the water as a reliable polymerization solvent, and these significantly expanded the applications of aqueous RAFT polymerization in the controlled synthesis of ultra-high molecular weight polymers, polymerization-induced self-assembly, and biocompatible polymerizations [81].
3. Perspective: Semiconducting Nanomaterials Used as Photoinitiators/Photocatalysts during Photopolymerization
In recent years, semiconducting nanomaterials (SNMs) have been proven to be a potential substitution for metal complexes and organic PCs as photoinitiators/photocatalysts during photopolymerization due to their high extinction coefficients (>105 M−1 cm−1), broad absorption spectra, and multiple molecular binding points [82,83]. However, little attention has been paid to SNM-induced photopolymerization due to the broad gap between nanotechnology and polymerization science. In the previous literature, the SNMs have been proven to initiate polymerization by the generation of radical species from the co-initiators upon the application of light irradiation, and the proposed photoinitiation mechanisms of this are fully discussed by Zhu et al. [84]. In their review, the SNM-induced photopolymerization could be mainly divided into three possible categories: (A) A newly established photoinduced polymerization wherein the SNM serves as the photocatalysts to conduct a catalytic cycle as shown in Figure 10a. In this cycle, the active radicals can be generated via the direct reduction of the initiators (or polymer chain ends) by SNM during the polymerization process. Then, the radicals can propagate by transferring the electrons back to SNMs at the end of the photoinduced electron transfer process. (B) Photoinduced polymerization wherein the SNM serves as the photoactivators, donating excited electrons or holes to the co-initiators, e.g., tertiary amines, iodonium salts, and RAFT agents, etc., in the polymerization system, and provides the radical sources to initiate the monomers (See Figure 10b for the mechanism of this). (C) A photoinduced polymerization that is initiated by a radical species that is generated from the co-initiators; here, the SNMs act as photoinitiators to activate the co-initiators. According to different the photoinitiation mechanisms of SNMs which act as PIs, this kind of photopolymerization could be mainly divided into three possible pathways: (1) the direct photoreduction of the monomer via electron transfer from the SNMs’ conduction band to the monomers with a proper band gap energy (see Figure 10c); (2) the direct oxidation of the monomer via hole transfer from the SNMs’ valence band to the monomers with a proper band gap energy (see Figure 10d); (3) the initiation of polymerization via a charge transfer from the anion-localized surface of the SNMs to the monomers (see Figure 10e). Moreover, the use of SNMs as photoinitiators/photocatalysts without the use of a co-initiator during the polymerization process has become increasingly popular recently. Due to the aforementioned advantages of SNM, such as a high absorption coefficient and a tunable solubility, SNM-photoinduced polymerization gives new opportunities to expand the fields of photo-3D printing. As a perspective, the use of SNMs for photopolymerization in 3D printing could be achieved with a lower initiator/catalyst loading time, a higher conversion rate, the versatile functionalization of it, and it could even be performed in the aqueous phase.
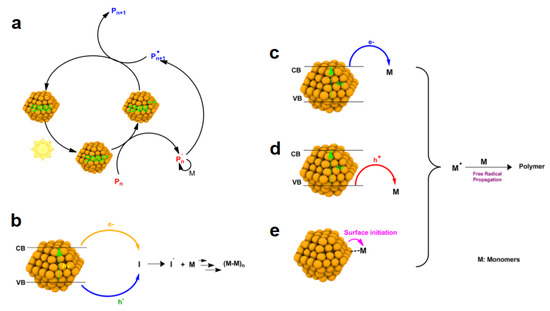
Figure 10.
(a) SNMs serve as photocatalysts during photopolymerization processes. (b) SNMs serve as photoactivators in the presence of co-initiators for conventional free-radical photopolymerization and SNMs serve as photoinitiators during photopolymerizations: (c) the reduction of monomer via electron transfer from conduction band, (d) oxidation of monomer via hole transfer from valence band, and (e) radical generation on the SNMs’ surface (CB is the conduction band and VB is the valence band). Adapted from [83] with permission from the American Chemical Societies.
4. Conclusions
According to the previous literature, numerous newly developed dye-based PISs following the Type II mechanisms exhibited efficient performances during light-induced polymerization, and as well as this, the attempts to explore the new mechanisms for photopolymerization following the Type I mechanism which were performed on RAFT, Photo-RAFT polymerized materials, Photoinitiator-RAFT polymerized materials, even performed in the aqueous phase, were successfully developed. Among these research studies, most of organic dye-based PISs and photochemical mechanisms are applicable in many applications, e.g., 3D printing and photocomposites, etc. To gain another perspective, the chemical modification of the existing organic dyes with a versatile functionalization to achieve a higher conversion rate for the acrylate monomer with a lower initiator/catalyst should be continued in the future. Furthermore, the SNMs with a high absorption coefficient and tunable solubility acting as photoinitiators/photocatalysts during the polymerization process provides new opportunities to expand the applications for photopolymerization, e.g., photo-3D printing. In conclusion, the photopolymerization has been proven to take an important place in 3D printing, and the molecular design of new photoinitiators/photocatalysts that are based on organic dyes can be regarded as an efficient bridge between the photopolymer materials and 3D printing orother technologies such as photolithography.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S., T.G. and P.X.; methodology, K.S., T.G. and P.X.; software, K.S.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, K.S., T.G. and P.X.; investigation, K.S.; resources, T.G. and P.X.; data curation, all authors; writing—original draft preparation, K.S.; writing—review and editing, X.P., Z.G. and X.L.; supervision, T.G. and P.X.; project administration, W.C.; funding acquisition, T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (grant number 2022A1515011724). And The APC was funded by Institute of Ultrasonic Technology, Institute of Intelligent Manufacturing Technology, Shenzhen Polytechnic (504-602231Y003P).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
K.S. acknowledges the supporting from Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. T.G. wish to thank the Featured Innovation Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education 2021KTSCX275, the Post-doctoral Later-stage Foundation Project of Shenzhen Polytechnic 6021271014K, the Shenzhen Polytechnic Scientific Research Start-up Project 6022312028K.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Shin, K.; Hong, J.; Jang, J. Micropatterning of graphene sheets by inkjet printing and its wideband dipole-antenna application. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkus, K.; Scott, A. Zeolite coatings on three-dimensional objects via laser ablation. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumbleston, J.; Shirvanyants, D.; Ermoshkin, N.; Janusziewicz, R.; Johnson, A.R.; Kelly, D.; Chen, K.; Pinschmidt, R.; Rolland, J.; Ermoshkin, A.; et al. Continuous liquid interface production of 3D objects. Science 2015, 347, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Jambou, C.; Sun, K.; Lalevée, J.; Simon-Masseron, A.; Xiao, P. Effect of zeolite fillers on the photopolymerization kinetics for photocomposites and lithography. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mousawi, A.; Kermagoret, A.; Versace, D.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, T.; Graff, B.; Dumur, F.; Gigmes, D.; Fouassier, J.; Lalevée, J. Copper photoredox catalysts for polymerization upon near UV or visible light: Structure/reactivity/efficiency relationships and use in LED projector 3D printing resins. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mousawi, A.; Garra, P.; Dumur, F.; Bui, T.; Goubard, F.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, T.; Graff, B.; Gigmes, D.; Fouassier, J.; et al. Novel carbazole skeleton-based photoinitiators for led polymerization and LED projector 3D printing. Molecules 2017, 22, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zips, S.; Wenzel, O.J.; Rinklin, P.; Grob, L.; Terkan, K.; Adly, N.Y.; Weiß, L.; Wolfrum, B. Direct stereolithographic 3D printing of microfluidic structures on polymer substrates for printed electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarek, M.; Layani, M.; Cooperstein, I.; Sachyani, E.; Cohn, D.; Magdassi, S. 3D printing of shape memory polymers for flexible electronic devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4449–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espera, A.H.; Dizon, J.R.C.; Chen, Q.; Advincula, R.C. 3D-printing and advanced manufacturing for electronics. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 4, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.B.; Rizkalla, A.S.; Hall, G.C. Effect of stepped light exposure on the volumetric polymerization shrinkage and bulk modulus of dental composites and an unfilled resin. Am. J. Dent. 2000, 13, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Topa, M.; Ortyl, J. Moving Towards a Finer Way of Light-Cured Resin-Based Restorative Dental Materials: Recent Advances in Photoinitiating Systems Based on Iodonium Salts. Materials 2020, 13, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroli, B. Photopolymerization of biomaterials: Issues and potentialities in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and cell encapsulation applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2006, 81, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.C.; Maleksaeedi, S.; Eng, H.; Wei, J.; Su, P.C. 4D printing of high performance shape memory polymer using stereolithography. Mater. Des. 2017, 126, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, R.; Li, X.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W. 4D printing of shape memory polyurethane via stereolithography. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Dumur, F.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Chen, H.; Dietlin, C.; Graff, B.; Lalevée, J.; Xiao, P. In silico rational design by molecular modeling of new ketones as photoinitiators in three-component photoinitiating systems: Application in 3D printing. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2230–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouassier, J.P.; Lalevée, J. Photoinitiators for Polymer Synthesis–Scope, Reactivity, and Efficiency; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fouassier, J.P.; Allonas, X.; Burget, D. Photopolymerization reactions under visible lights: Principle, mechanisms and examples of applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2003, 47, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, S.; Pigot, C.; Brunel, D.; Graff, B.; Nechab, M.; Gigmes, D.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, P.; et al. Novel Push–Pull Dyes Derived from 1H-cyclopenta [b] naphthalene-1, 3 (2H)-dione as Versatile Photoinitiators for Photopolymerization and Their Related Applications: 3D Printing and Fabrication of Photocomposites. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Pigot, C.; Nechab, M.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. N-ethyl Carbazole-1-Allylidene-Based Push-Pull Dyes as Efficient Light Harvesting Photoinitiators for Sunlight Induced Polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. High-performance Sunlight Induced Polymerization Using Novel Push-Pull Dyes with High Light Absorption Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 151, 110410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K. Photoinitiating Systems for Visible Light: Towards Sunlight Induced Polymerization. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Haute Alsace-Mulhouse, Mulhouse, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Balta, D.; Arsu, N. Thioxanthone-ethyl anthracene. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 257, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corakci, B.; Hacioglu, S.; Toppare, L.; Bulut, U. Long wavelength photosensitizers in photoinitiated cationic polymerization: The effect of quinoxaline derivatives on photopolymerization. Polymer 2013, 54, 3182–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğruyol, S.; Doğruyol, Z.; Arsu, N. Thioxanthone based 9-[2-(methyl-phenyl-amino)-acetyl]-thia-naphthacene-12-one as a visible photoinitiator. J. Lumin. 2013, 138, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadły, R.; Strzelczyk, R. N-substituted quinoxalinobenzothiazine/ iodonium salt systems as visible photoinitiators for hybrid polymerization. Dye. Pigment. 2013, 97, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, R.; Shi, S.; Nie, J. Synthesis and characterization of polymerizable one-component photoinitiator based on sesamol. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhong, M.; Johnson, J.A. Light-Controlled Radical Polymerization: Mechanisms, Methods, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10167–10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Cao, D.; Hu, T.; Ye, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T. Novel Norrish Type I flavonoid photoinitiator for safe LED light with high activity and low toxicity by inhibiting the ESIPT process. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 184, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Hammoud, F.; Hijazi, A.; Graff, B.; Lalevee, J.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and free radical photopolymerization of triphenylamine-based oxime ester photoinitiators. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Fouassier, J.P. Photoinitiator, Photopolymerization and Photocuring: Fundamentals and Applications; HanserPublishers: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, P.; Lalevée, J.; Allonas, X.; Fouassier, J.P.; Ley, C.; El Roz, M.; Shi, S.Q.; Nie, J. Photoinitiation mechanism of free radical photopolymerizationin the presence of cyclic acetals and related compounds. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 5758–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Ding, Z.F.; Liu, F.Y.; Sun, K.; Dietlin, C.; Lalevee, J.; Xiao, P. 3D Printing of polydiacetylene photocomposite materials: Two wavelengths for two orthogonal chemistries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Pigot, C.; Chen, H.; Nechab, M.; Gigmes, D.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Liu, S.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; et al. Free radical photopolymerization and 3D printing using newly developed dyes: Indane-1, 3-dione and 1H-cyclopentanaphthalene-1, 3-dione derivatives as photoinitiators in three-component systems. Catalysts 2020, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Noirbent, G.; Zhang, Y.; Brunel, D.; Gigmes, D.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Novel D–π-A and A–π-D–π-A three-component photoinitiating systems based on carbazole/triphenylamino based chalcones and application in 3D and 4D printing. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 6512–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjigin, T.; Noirbent, G.; Gigmes, D.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. The new LED-Sensitive photoinitiators of Polymerization: Copper complexes in free radical and cationic photoinitiating systems and application in 3D printing. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 162, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Zhang, J.; Dumur, F.; Tehfe, M.A.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Gigmes, D.; Fouassier, J.P.; Lalevee, J. Visible light sensitive photoinitiating systems: Recent progress in cationic and radical photopolymerization reactions under soft conditions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 41, 32–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Organic dye-based photoinitiating systems for visible-light-induced photopolymerization. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1338–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabatc, J.; Ortyl, J.; Kostrzewska, K. New kinetic and mechanistic aspects of photosensitization of iodonium salts in photopolymerization of acrylates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41619–41629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brömme, T.; Oprych, D.; Horst, J.; Pinto, P.S.; Strehmel, B. New iodonium salts in NIR sensitized radical photopolymerization of multifunctional monomers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69915–69924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Luo, X.; Yin, J. Polymeric photoinitiators containing in-chain benzophenone and coinitiators amine: Effect of the structure of coinitiator amine on photopolymerization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2015, 174, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Jiang, X.; Yin, J. Highly efficient sulfur-containing polymeric photoinitiators bearing side-chain benzophenone and coinitiator amine for photopolymerization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 186, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Jin, J. Photopolymerization in 3D Printing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdelen, M.A.; Lalevée, J.; Yagci, Y. Photoinduced free radical promoted cationic polymerization 40 years after its discovery. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitterbauer, M.; Knaack, P.; Naumov, S.; Markovic, M.; Ovsianikov, A.; Moszner, N.; Liska, R. Acylstannanes: Cleavable and Highly Reactive Photoinitiators for Radical Photopolymerization at Wavelengths above 500 nm with Excellent Photobleaching Behavior. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12146–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noirbent, G.; Dumur, F. Recent advances on naphthalic anhydrides and 1,8-naphthalimide-based photoinitiators of polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 132, 109702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, C.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, H. A Green and Highly Efficient Naphthalimide Visible Photoinitiator with an Ability Initiating Free Radical Polymerization under Air. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1800256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Frigoli, M.; Tehfe, M.-A.; Graff, B.; Fouassier, J.P.; Gigmes, D.; Lalevée, J. Naphthalimide based methacrylated photoinitiators in radical and cationic photopolymerization under visible light. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 5440–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Giacoletto, N.; Graff, B.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Nechab, M.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. N-naphthalimide ester derivatives as Type I photoinitiators for LED photopolymerization. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, F.; Giacoletto, N.; Noirbent, G.; Graff, B.; Hijazi, A.; Nechab, M.; Gigmes, D.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Substituent effects on the photoinitiation ability of coumarin-based oxime-ester photoinitiators for free radical photopolymerization. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 8361–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Sun, X.; Mhanna, R.; Malval, J.-P.; Jin, M.; Pan, H.; Wan, D.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Chaumeil, H.; Joyeux, C. Wavelength-Dependent, Large-Amplitude Photoinitiating Reactivity within a Carbazole-Coumarin Fused Oxime Esters Series. ACS Appl. Polym. 2020, 2, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jin, M.; Malval, J.-P.; Fu, J.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Pan, H.; Wan, D. Substituted stilbene-based oxime esters used as highly reactive wavelength-dependent photoinitiators for LED photopolymerization. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6609–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gong, S.; Chen, Z.; Hou, J.; Liao, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, H. Photobleachable bis-chalcones-based oxime ester dyes for radical visible photopolymerization. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 205, 110556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Graff, B.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Nitro-Carbazole Based Oxime Esters as Dual Photo/Thermal Initiators for 3D Printing and Composite Preparation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Giacoletto, N.; Schmitt, M.; Nechab, M.; Graff, B.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Effect of Decarboxylation on the Photoinitiation Behavior of Nitrocarbazole-Based Oxime Esters. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Brunel, D.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Novel photoinitiators based on benzophenone-triphenylamine hybrid structure for LED photopolymerization. Macromolar Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Noirbent, G.; Pigot, C.; Brunel, D.; et al. Monocomponent photoinitiators based on benzophenone-carbazole structure for LED photoinitiating systems and application on 3D printing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Ding, G.; Gong, Y.; Jing, C.; Peng, G.; Liu, S.; Niu, L.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Stilbene-benzophenone dyads for free radical initiating polymerization of methyl methacrylate under visible light irradiation. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 132, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zivic, N.; Dumur, F.; Xiao, P.; Graff, B.; Gigmes, D.; Fouassier, J.; Lalevee, J. A benzophenone-naphthalimide derivative as versatile photoinitiator of polymerization under near UV and visible lights. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2015, 53, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbaraci, V.; Aydogan, B.; Talinli, N.; Yagci, Y. Naphthodioxinone-1,3- benzodioxole as photochemically masked one-component Type II photoinitiator for free radical polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2612–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and free radical photopolymerization of one-component Type II photoinitiator based on benzophenone segment. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 429, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Brunel, D.; Noirbent, G.; Mau, A.; Chen, H.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Gigmes, D.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; et al. New multifunctional benzophenone-based photoinitiators with high migration stability and their applications in 3D printing. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 1982–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Pigot, C.; Zhang, Y.; Borjigin, T.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Graff, B.; Nechab, M.; Xiao, P.; Dumur, F.; Lalevée, J. Sunlight Induced Polymerization Photoinitiated by Novel Push–Pull Dyes: Indane-1, 3-Dione, 1H-Cyclopenta [b] Naphthalene-1, 3 (2H)-Dione and 4-Dimethoxyphenyl-1-Allylidene Derivatives. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2100439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Fellows, C.; Boyer, C. Reversible deactivation radical polymerization: From polymer network synthesis to 3D printing. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phommalysack-Lovan, J.; Chu, Y.; Boyer, C.; Xu, J. PET-RAFT polymerisation: Towards green and precision polymer manufacturing. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6591–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, N.; Shanmugam, S.; Xu, J.; Boyer, C. Photocatalysis in organic and polymer synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6165–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashi-Silab, S.; Doran, S.; Yagci, Y. Photoinduced electron transfer reactions for macromolecular syntheses. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10212–10275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Tasdelen, M.A.; Laun, J.; Junkers, T.; Yagci, Y.; Matyjaszewski, K. Photomediated controlled radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 73–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shanmugam, S.; Fu, C.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F.; Boyer, C. Selective photoactivation: From a single unit monomer insertion reaction to controlled polymer architectures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3094–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Corrigan, N.; Boyer, C. Rapid High-Resolution 3D Printing and Surface Functionalization via Type I Photoinitiated RAFT Polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Jakubowski, W.; Matyjaszewski, K. AGET ATRP in the presence of air in miniemulsion and in bulk. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Matyjaszewski, K. ARGET ATRP of 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate as an intrinsic reducing agent. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6868–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Peng, L.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luan, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, H. Synthesis of star-glycopolymers by Cu (0)-mediated radical polymerisation in the absence and presence of oxygen. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Leng, X.; Sun, H.; Percec, V. Single-electron transfer-living radical polymerization of oligo (ethylene oxide) methyl ether methacrylate in the absence and presence of air. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 3110–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso, A.; Fu, L.; Russell, A.; Matyjaszewski, K. A breathing atom-transfer radical polymerization: Fully oxygen-tolerant polymerization inspired by aerobic respiration of cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, W. A Simple and Green Oxygen-Tolerant RAFT Polymerization without Additional Catalyst and Initiator. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, G.; Gao, H.; Lu, L.; Cai, Y. Effect of mild visible light on rapid aqueous RAFT polymerization of water-soluble acrylic monomers at ambient temperature: Initiation and activation. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3917–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L. Low-Temperature Synthesis of Thermoresponsive Diblock Copolymer Nano-Objects via Aqueous Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly (Photo-PISA) using Thermoresponsive Macro-RAFT Agents. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, T. Iniferter concept and living radical polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 2121–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jung, K.; Atme, A.; Shanmugam, S.; Boyer, C. A Robust and Versatile Photoinduced Living Polymerization of Conjugated and Unconjugated Monomers and Its Oxygen Tolerance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5508–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, K.; Clemons, T.; Stupp, S.; Weiss, E. Semiconductor quantum dots are efficient and recyclable photocatalysts for aqueous PET-RAFT polymerization. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 9, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortenberry, A.; Jankoski, P.; Stacy, E.; McCormick, C.; Smith, A.; Clemons, T. A Perspective on the History and Current Opportunities of Aqueous RAFT Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 2200414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Nie, S. Semiconductor Nanocrystals: Structure, Properties, and Band Gap Engineering. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miller, K.A.; Zhu, H.; Egap, E. Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals as Photocatalysts for PET-RAFT Polymerization under Visible and Near-Infrared Irradiation. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Egap, E. Light-Mediated Polymerization Induced by Semiconducting Nanomaterials: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. ACS Polym. Au 2021, 1, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).