Sulfate Decelerated Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Azo Dye Reactive Brilliant Red: Influence Factors, Mechanisms, and Control Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
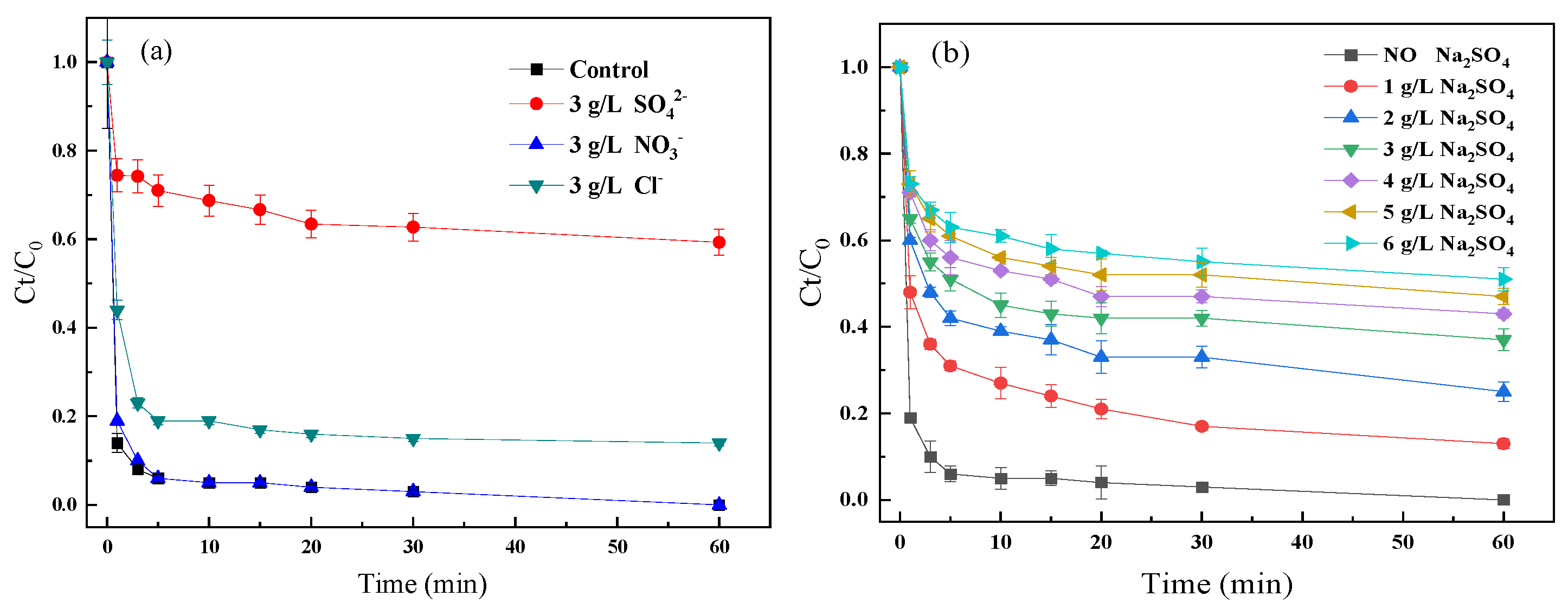
2.1. Effect of Different Anions
2.2. Comprehensive Influences of SO42− with Other Operation Factors
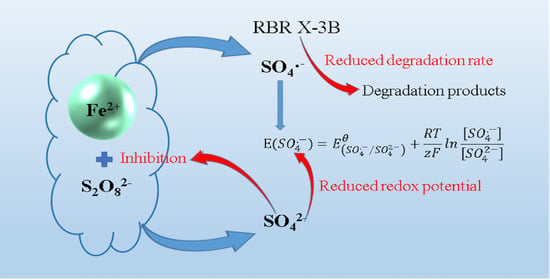
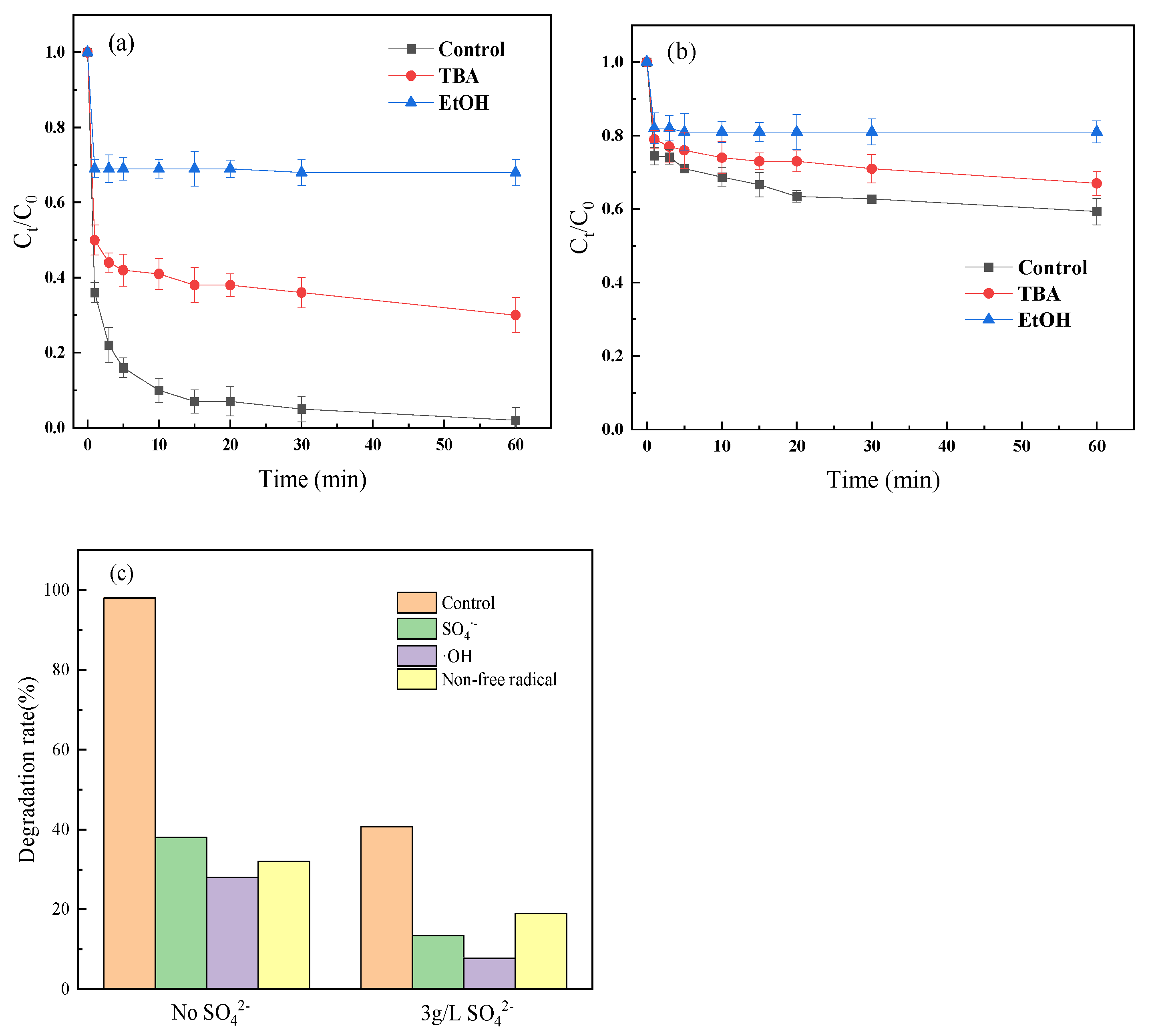
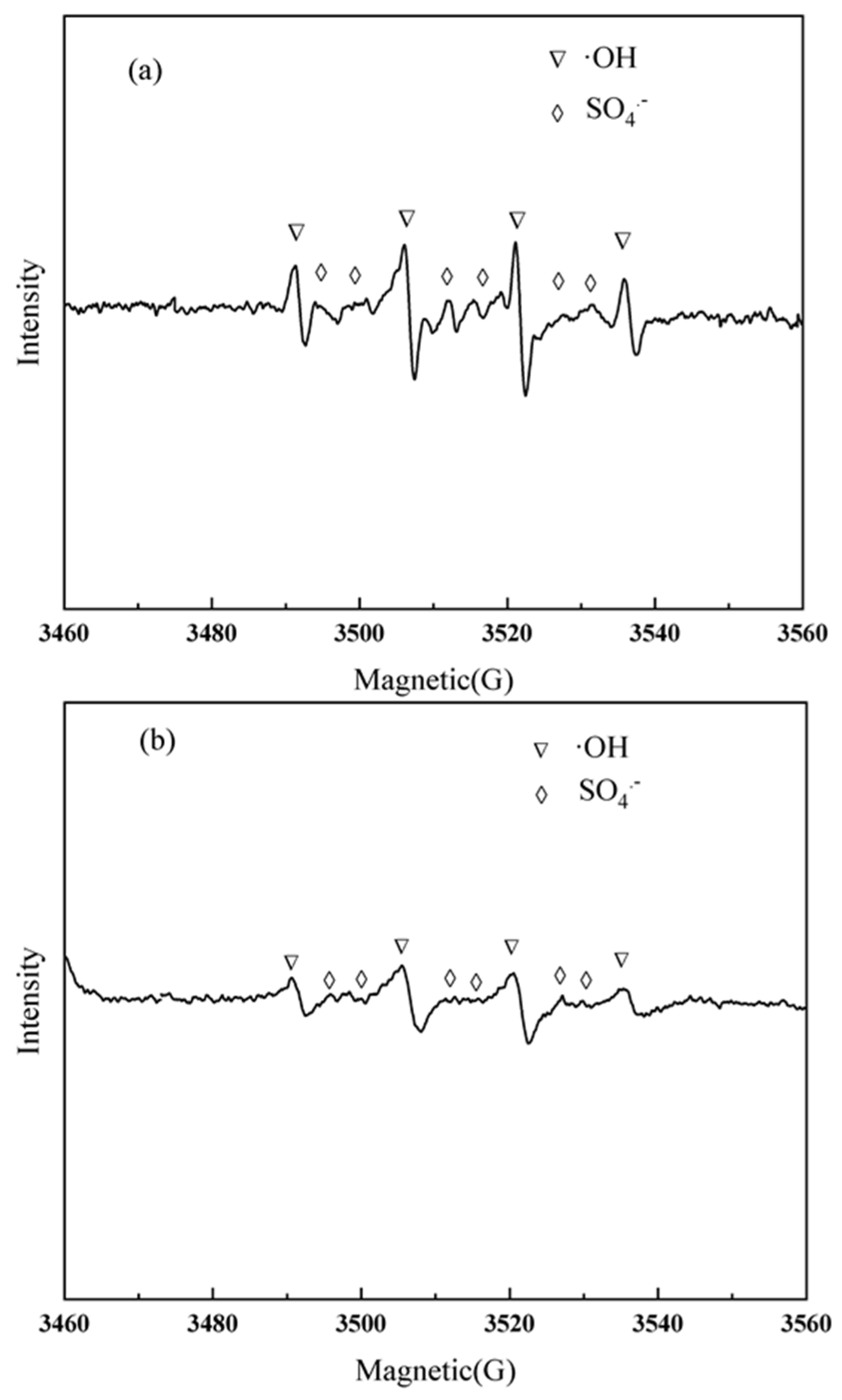
2.3. Influence Mechanism of SO42−
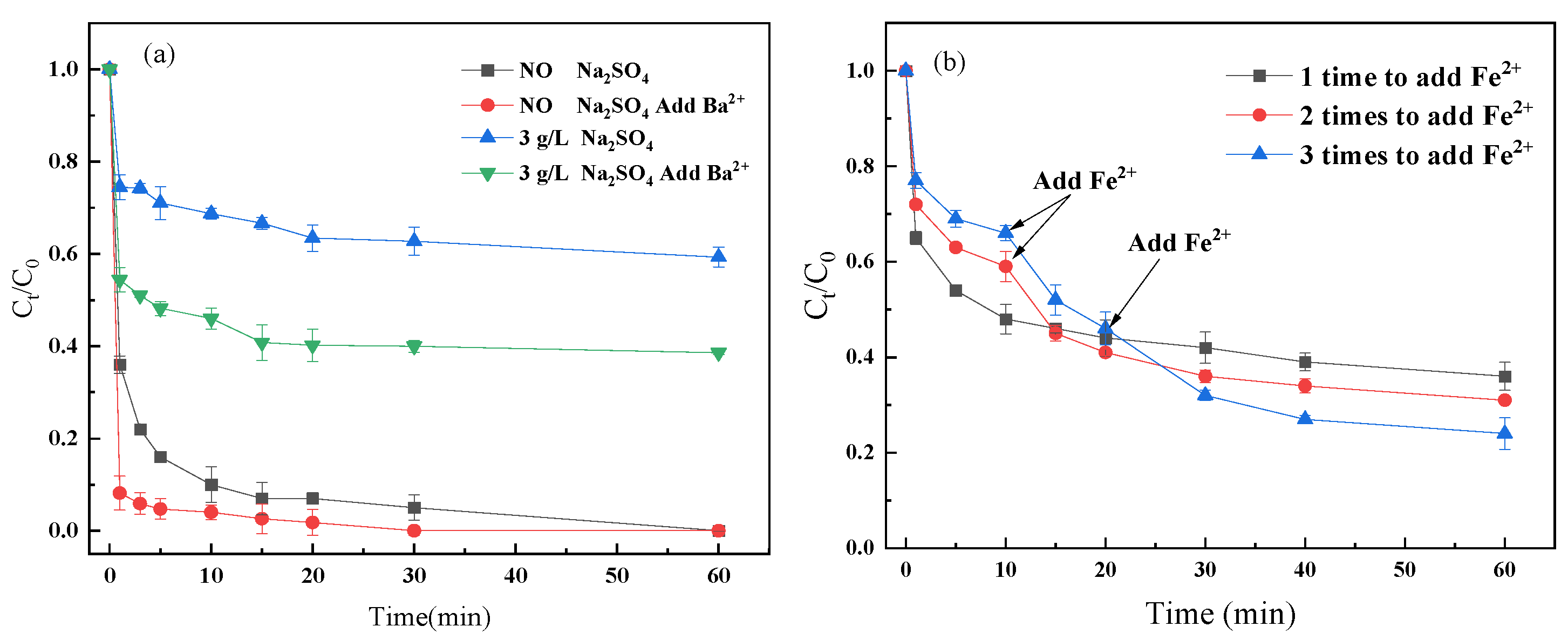
2.4. Methods to Counteract the Influence of SO42−
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Degradation Experiment
3.3. EPR Experiment
3.4. Controlling Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Ma, Y.; Wan, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Efficient degradation of Orange G with persulfate activated by recyclable FeMoO4. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Shao, X.T.; Niu, R. Degradation efficiencies of azo dye Acid Orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.H.; Cao, H.; Qi, C.D.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wen, Y.N.; Xu, C.M.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhou, S.H.; Yang, B.; et al. L-cysteine boosted Fe(III)-activated peracetic acid system for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of L-cysteine and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.S.; Yi, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, X.G.; Huo, X.Q.; An, Z.W.; Li, L.; Fu, Y.K.; Li, B.S.; Zhang, M.M.; et al. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhu, W.H.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.L.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, J.F.; Huang, T.L. Characteristics and mechanism of electrochemical peroxymonosulfate activation by a Co-N@CF anode for pollutant removal. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. 2022, 8, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, J.H.; Ding, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.W.; Xu, X.; Fang, Z.D. Ultrasound irritation enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4 for degradation of azo dye. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.; Vasquez, L.; Costa, D.; Romero, A.; Santos, A. Oxidation of Orange G by persulfate activated by Fe(II), Fe(III) and zero valent iron (ZVI). Chemosphere 2014, 101, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fu, L.Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.J.; Zhou, Y.X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.Y. Potential for colloid removal from petrochemical secondary effluent by coagulation-flocculation coupled with persulfate process. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. 2022, 8, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.D.; Wen, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.J.; Dai, Y.H.; Li, Y.P.; Xu, C.M.; Yang, S.G.; He, H. Enhanced degradation of organic contaminants by Fe(III)/peroxymonosulfate process with l-cysteine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.B.; Wang, Q.F.; Mu, K.; Rao, P.H.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.D.; Gao, N.Y.; Wang, J.C. Degradation of sulfachloropyridazine by UV-C/persulfate: Kinetics, key factors, degradation pathway. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. 2020, 6, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhuan, R. Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, S.Z. Effect of inorganic anions on the performance of advanced oxidation processes for degradation of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.J.; Pi, Z.J.; Yao, F.B.; Wu, B.; He, L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.B.; Dong, H.R.; Yang, Q. A critical review on the mechanisms of persulfate activation by iron-based materials: Clarifying some ambiguity and controversies. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by Sulfate Radical-based Advanced Oxidation Processes (SR-AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, Q.H. Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, S.Z. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.D.; Long, M.C. Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: A review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 181, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.B.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.F. Different activation methods in sulfate radical-based oxidation for organic pollutants degradation: Catalytic mechanism and toxicity assessment of degradation intermediates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, M.P.; Aravindakumar, C.T.; Shah, N.S.; Boczkaj, G. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) based wastewater treatment—Unexpected nitration side reactions-a serious environmental issue: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Wang, J.L. Radiation-induced degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the presence of various inorganic anions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.C.H.; Xie, Z.T.; Li, X.X.; Chen, C.Z.; Chen, H.K. Impacts of inorganic anions and natural organic matter on thermally activated persulfate oxidation of BTEX in water. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Thao, T.T.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, I. Effects of the formation of reactive chlorine species on oxidation process using persulfate and nano zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, D.; Kamath, D.; Maetzold, S. Mechanistic Insight into the Reactivity of Chlorine-Derived Radicals in the Aqueous-Phase UV Chlorine Advanced Oxidation Process: Quantum Mechanical Calculations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.B.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, B.J.; Gong, Z.M.; Wang, M.J.; Dong, H.; Shi, J.L.; et al. Enhanced removal of methylparaben mediated by cobalt/carbon nanotubes (Co/CNTs) activated peroxymonosulfate in chloride-containing water: Reaction kinetics, mechanisms and pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.H.; Yan, C.X.; Li, M.; Wang, X.N.; Bi, W.L.; Dong, W.B. Degradation of chloramphenicol by persulfate activated by Fe2+ and zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of Halide Impacts on the Efficiency of Contaminant Degradation by Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.J.; Liu, X.N.; Liu, B.H.; Akram, M.; Li, Y.W.; Pan, J.W.; Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Xu, X. Effect of phosphate on peroxymonosulfate activation: Accelerating generation of sulfate radical and underlying mechanism. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2021, 298, 120532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.Y.; Wu, L.X.; Guo, Y.G.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Xiao, D.X.; Fang, C.L.; Liu, J.S.; Zhao, J.C.; Lu, S.Y. Peroxymonosulfate activation by phosphate anion for organics degradation in water. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Yang, C.P.; Zeng, G.M.; Li, H.R.; Chen, Y.J. Treatment of Organic Wastewater Containing High Concentration of Sulfate by Crystallization-Fenton-SBR. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, M.P.; Lee, C.S.; Aravind, U.K.; Aravindakumar, C.T.; Chang, Y.S. Oxidative degradation of benzoic acid using Fe0- and sulfidized Fe0- activated persulfate: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Gu, X.G.; Lu, S.G.; Qiu, Z.F.; Sui, Q.; Zang, X.K.; Miao, Z.W.; Xu, M.H. Strong enhancement of trichloroethylene degradation in ferrous ion activated persulfate system by promoting ferric and ferrous ion cycles with hydroxylamine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Wan, Y.J.; Peng, J.L.; Yao, G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lai, B. Efficient degradation of atrazine by LaCoO3/Al2O3 catalyzed peroxymonosulfate: Performance, degradation intermediates and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Song, H.L.; Wei, S.Z.; Liu, Q.J.; Li, X.N.; Qian, X.W. Effect of direct electrical stimulation on decolorization and degradation of azo dye reactive brilliant red X-3B in biofilm-electrode reactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 93, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.S.; Hou, H.B.; Song, B.Y. Adsorption of Reactive Brilliant Red X-3B in Aqueous Solutions on Clay-Biochar Composites from Bagasse and Natural Attapulgite. Water 2018, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rodriguez, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Singh, D.N.; Rodriguez-Chueca, J. Assessment of Sulfate Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Water 2018, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, E.T.; Yoo, H.Y.; Bae, H.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, J. Exploring the Role of Persulfate in the Activation Process: Radical Precursor Versus Electron Acceptor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10090–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.J.; Chen, H.; Lian, C.; Wei, F.Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Wu, G.D.; Chen, B.J.; Wang, S.B. Fe, Co, Ni nanocrystals encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as Fenton-like catalysts for organic pollutant removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 314, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.C.; Kong, W.J.; Gao, Y.; Kong, Y.; Dai, Z.G.; Dan, H.B.; Shang, Y.A.; Wang, S.Q.; Yin, F.J.; Yue, Q.Y.; et al. Removal of chloramphenicol by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron activated persulfate: Performance, salt resistance, and reaction mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Wieckowska, A.; Stepnowski, P. Influence of inorganic ions on MTBE degradation by Fenton’s reagent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Ai-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous-peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2009, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.F.; Qu, L.; Yang, H.S.; Chu, W. Degradation of carbamazepine by Fe(II)-activated persulfate process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Zhang, G.K.; Guo, S. Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by manganese oxide for the degradation of azo dye at ambient condition. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.P.; Zhang, Y.T.; Cheng, L.B.; Wu, Q.; Xue, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Meng, X. Removal of reactive brilliant red X-3B by a weak magnetic field enhanced Fenton-like system with zero-valent iron. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 32671–32677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Long, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhu, X. Sulfate Decelerated Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Azo Dye Reactive Brilliant Red: Influence Factors, Mechanisms, and Control Methods. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101207
Tang C, Long Z, Wang Y, Ma D, Zhu X. Sulfate Decelerated Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Azo Dye Reactive Brilliant Red: Influence Factors, Mechanisms, and Control Methods. Catalysts. 2022; 12(10):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chenliu, Zhicheng Long, Yidan Wang, Dongze Ma, and Xiaobiao Zhu. 2022. "Sulfate Decelerated Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Azo Dye Reactive Brilliant Red: Influence Factors, Mechanisms, and Control Methods" Catalysts 12, no. 10: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101207
APA StyleTang, C., Long, Z., Wang, Y., Ma, D., & Zhu, X. (2022). Sulfate Decelerated Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Azo Dye Reactive Brilliant Red: Influence Factors, Mechanisms, and Control Methods. Catalysts, 12(10), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101207