Accelerated Removal of Acid Orange 7 by Natural Iron Ore Activated Peroxymonosulfate System with Hydroxylamine for Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
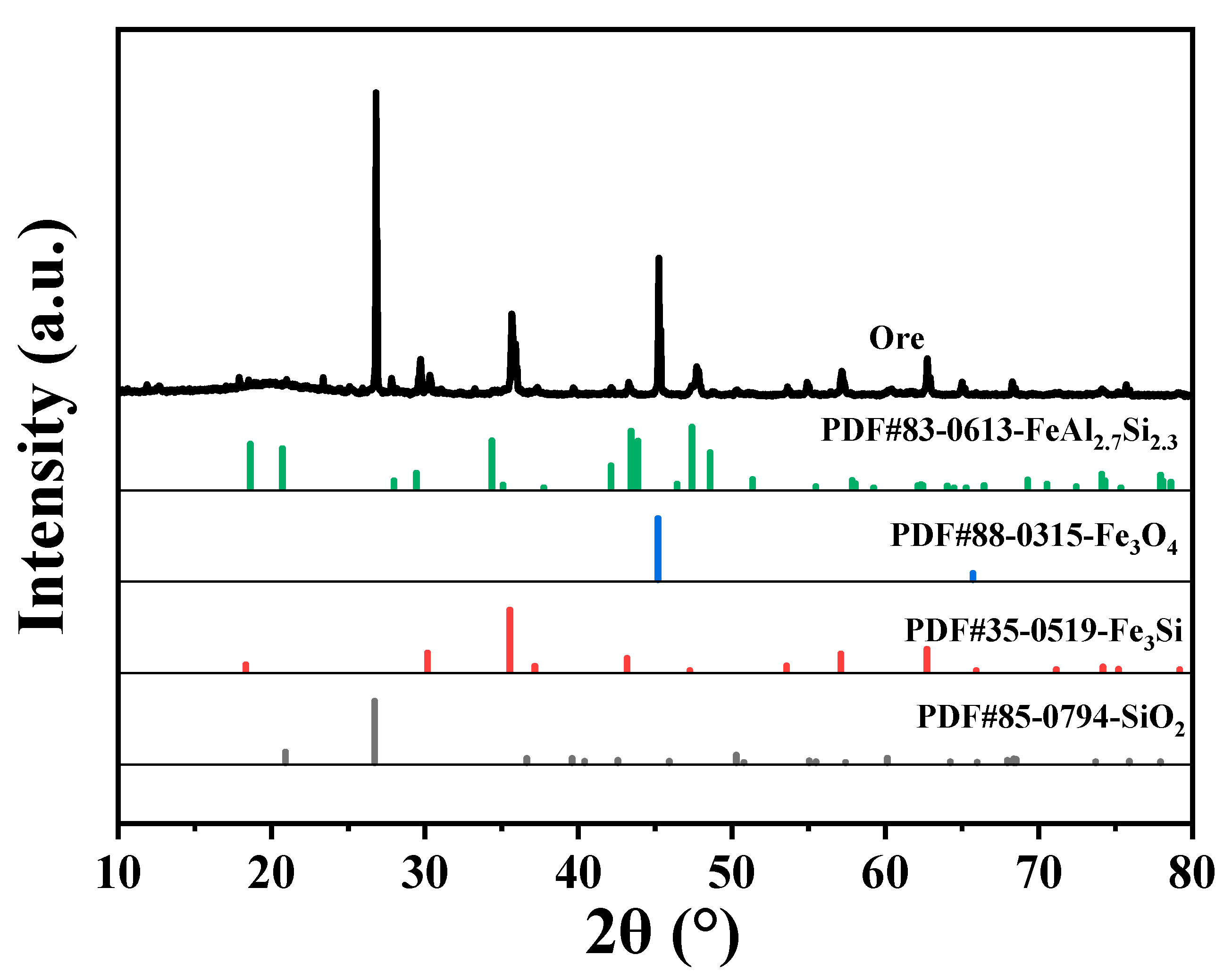
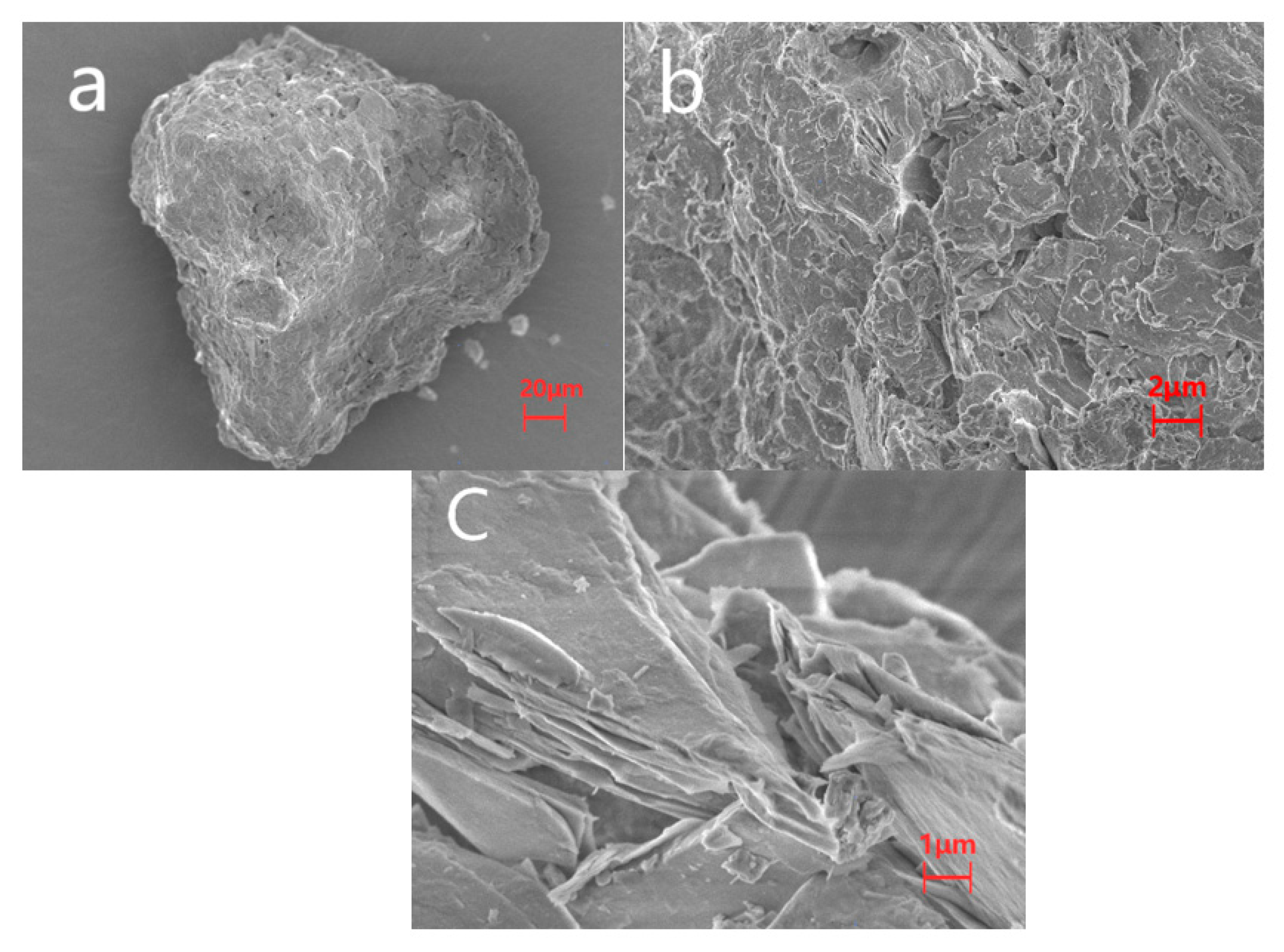
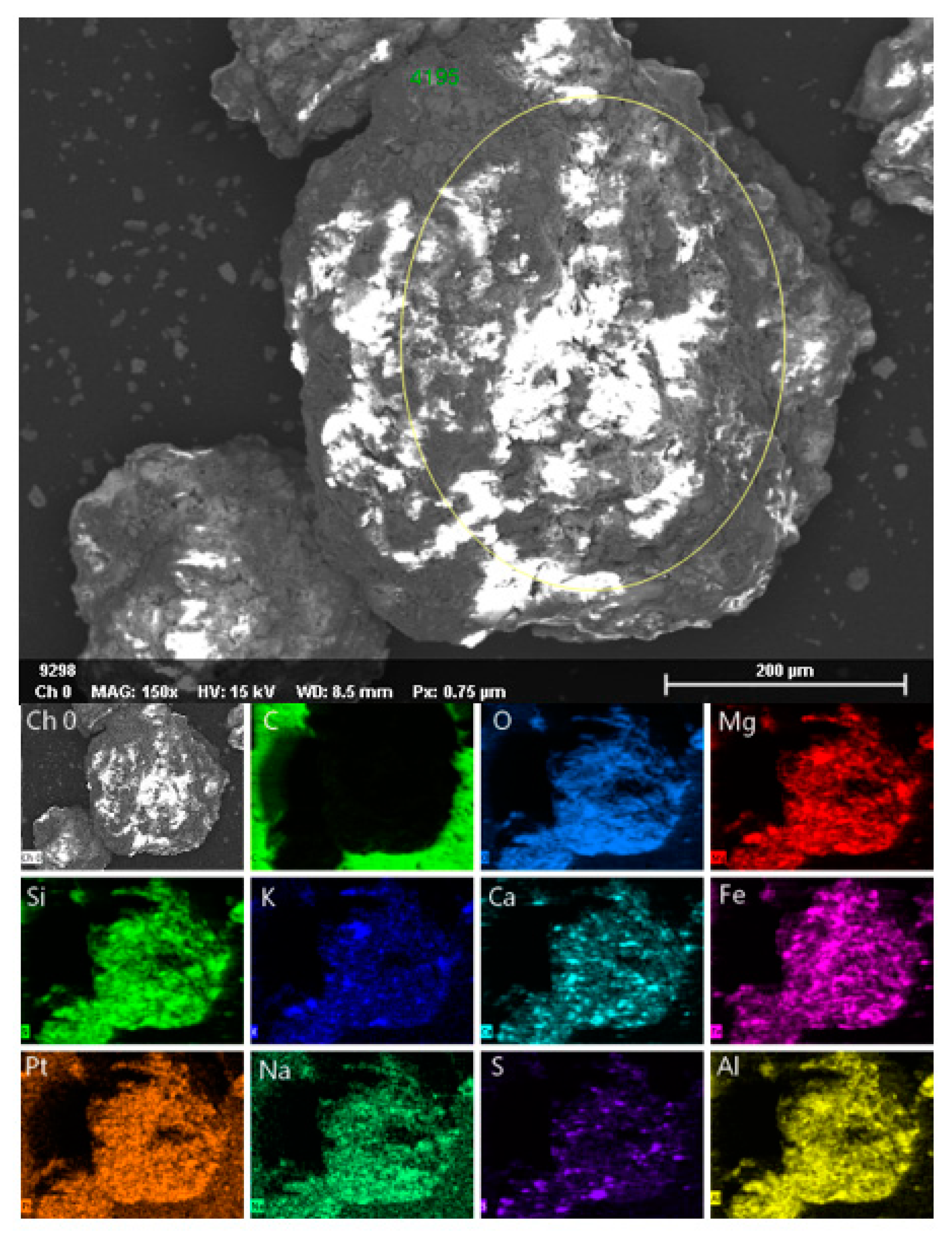
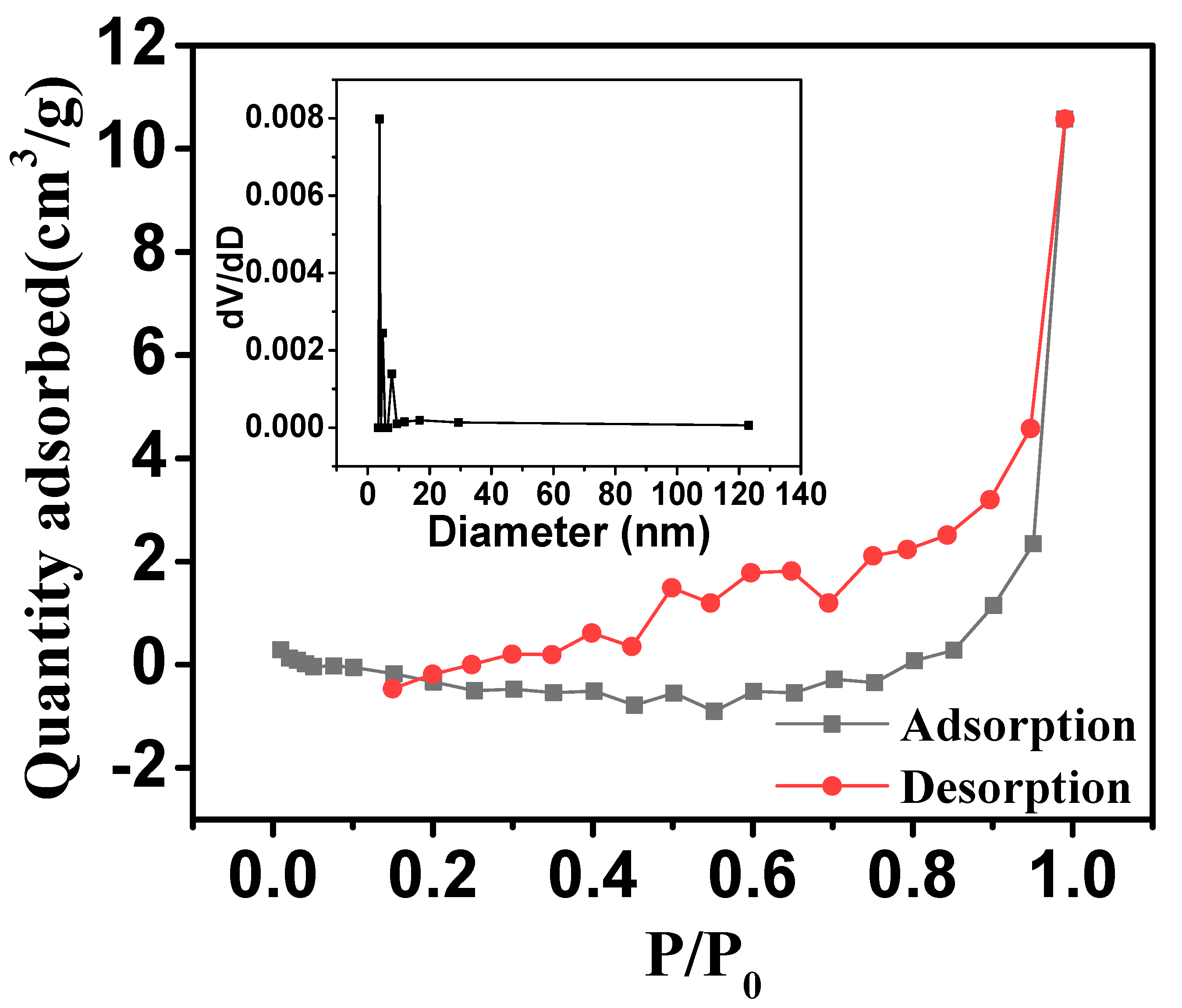
2.1. Characterization of Ore
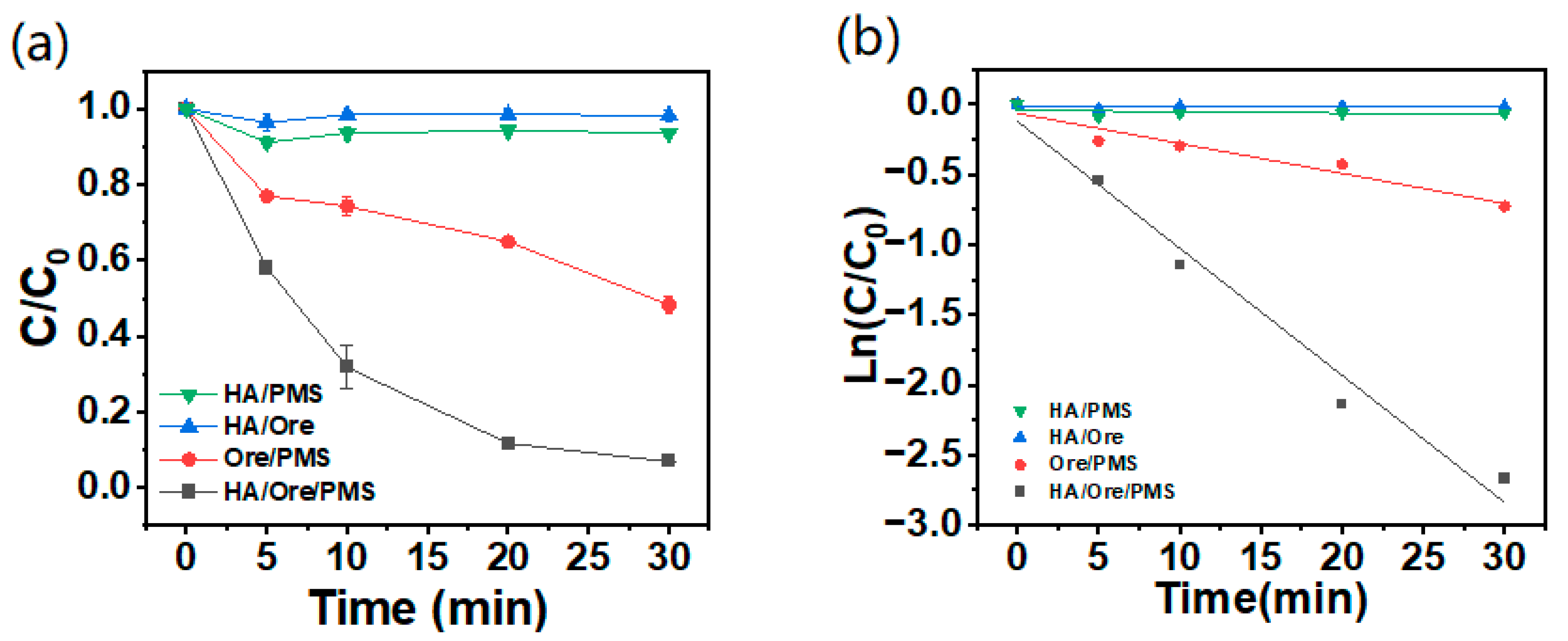
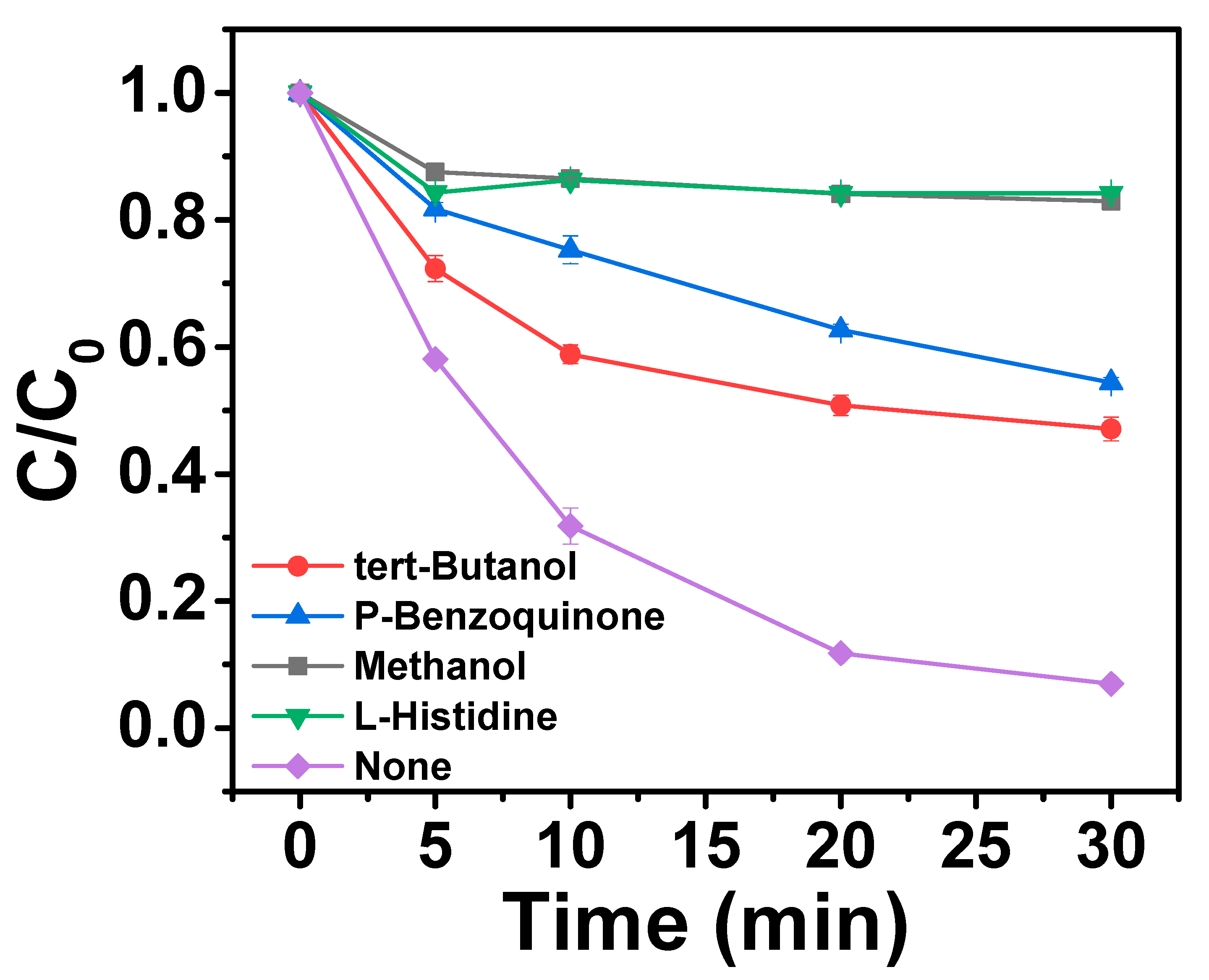
2.2. Effect of Different Reaction Systems on AO7 Degradation
2.3. Influencing Factors of HA/Ore/PMS System
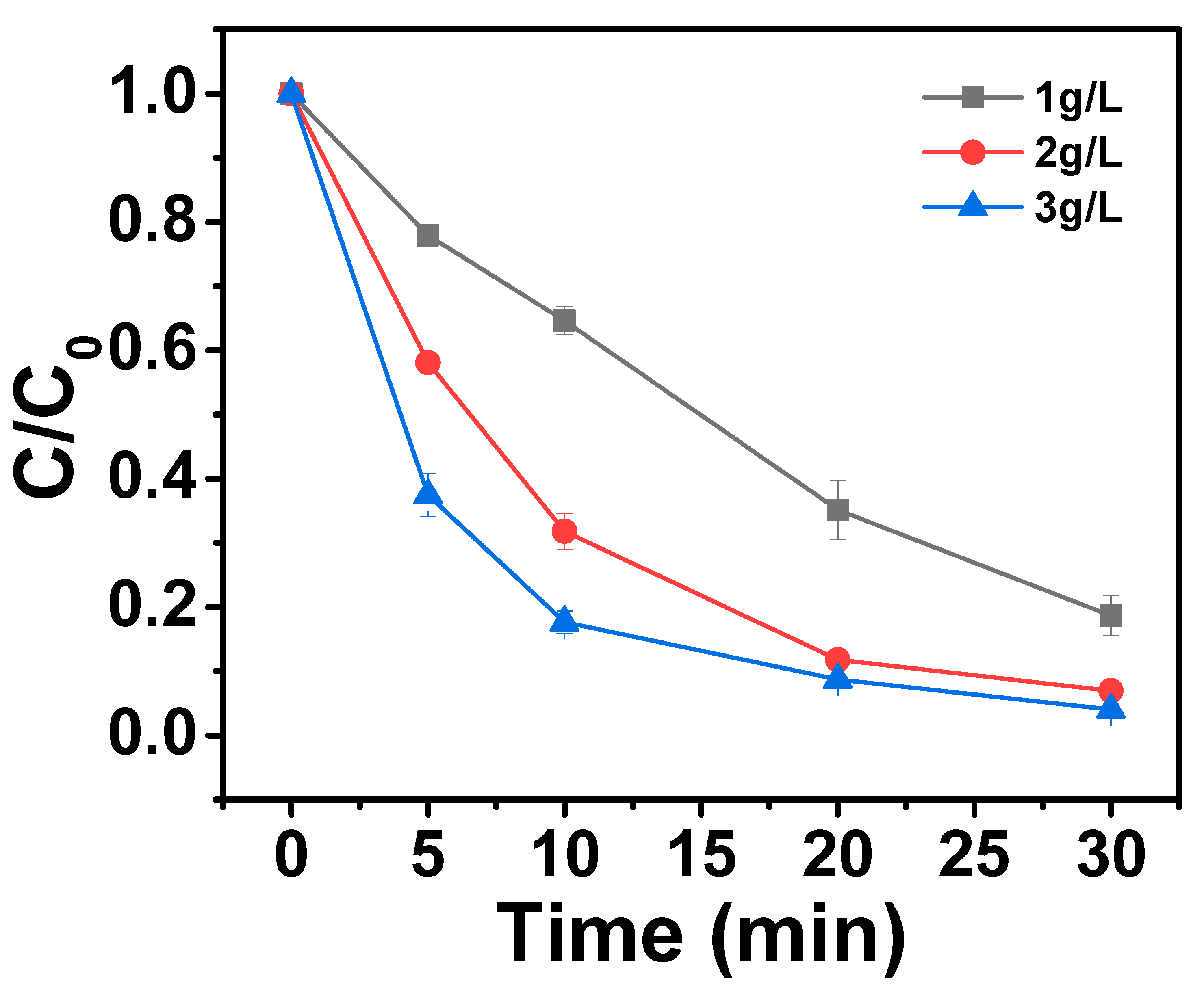
2.3.1. Effect of Catalyst Dosage on AO7 Removal
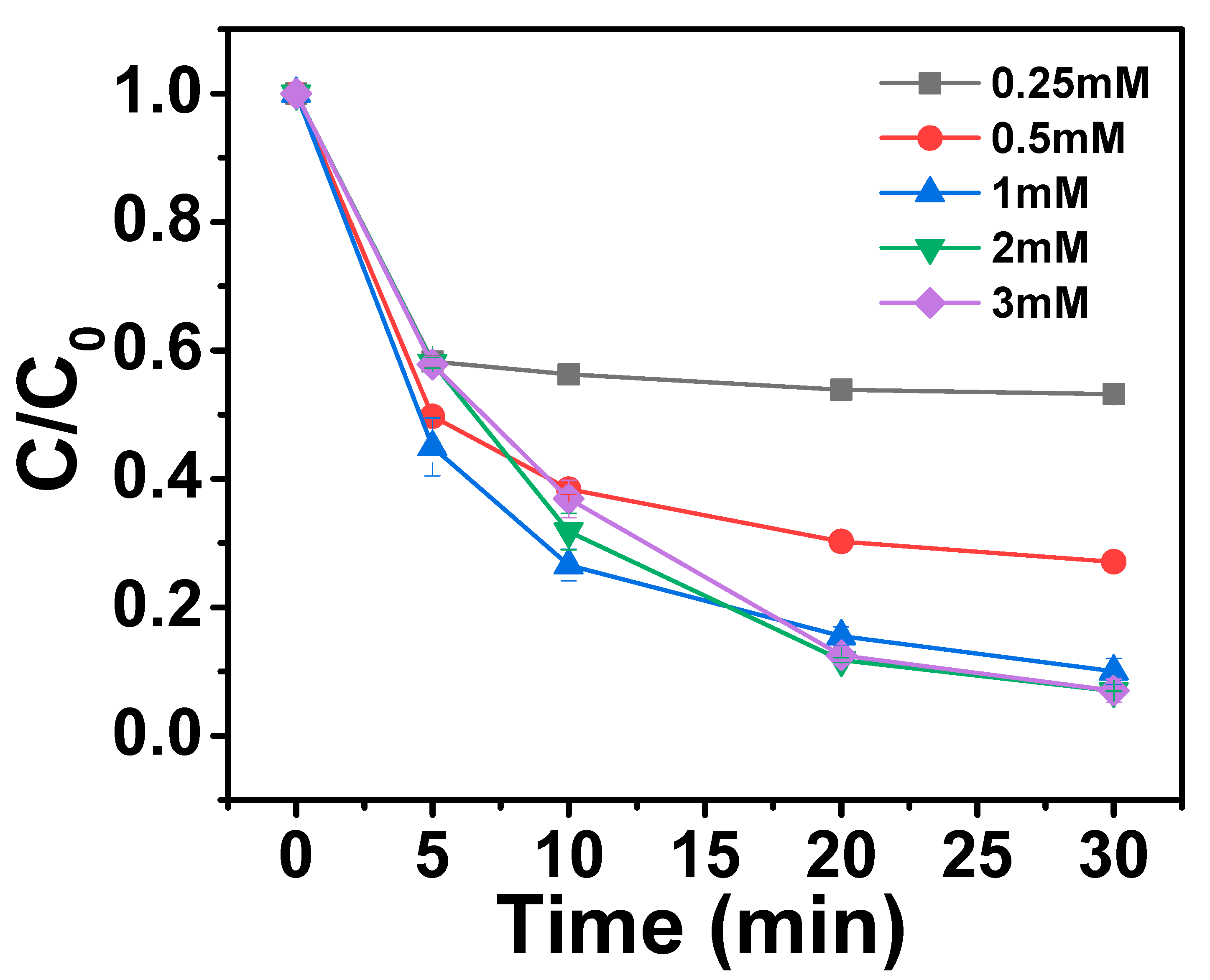
2.3.2. Effects of PMS Dosage on AO7 Removal
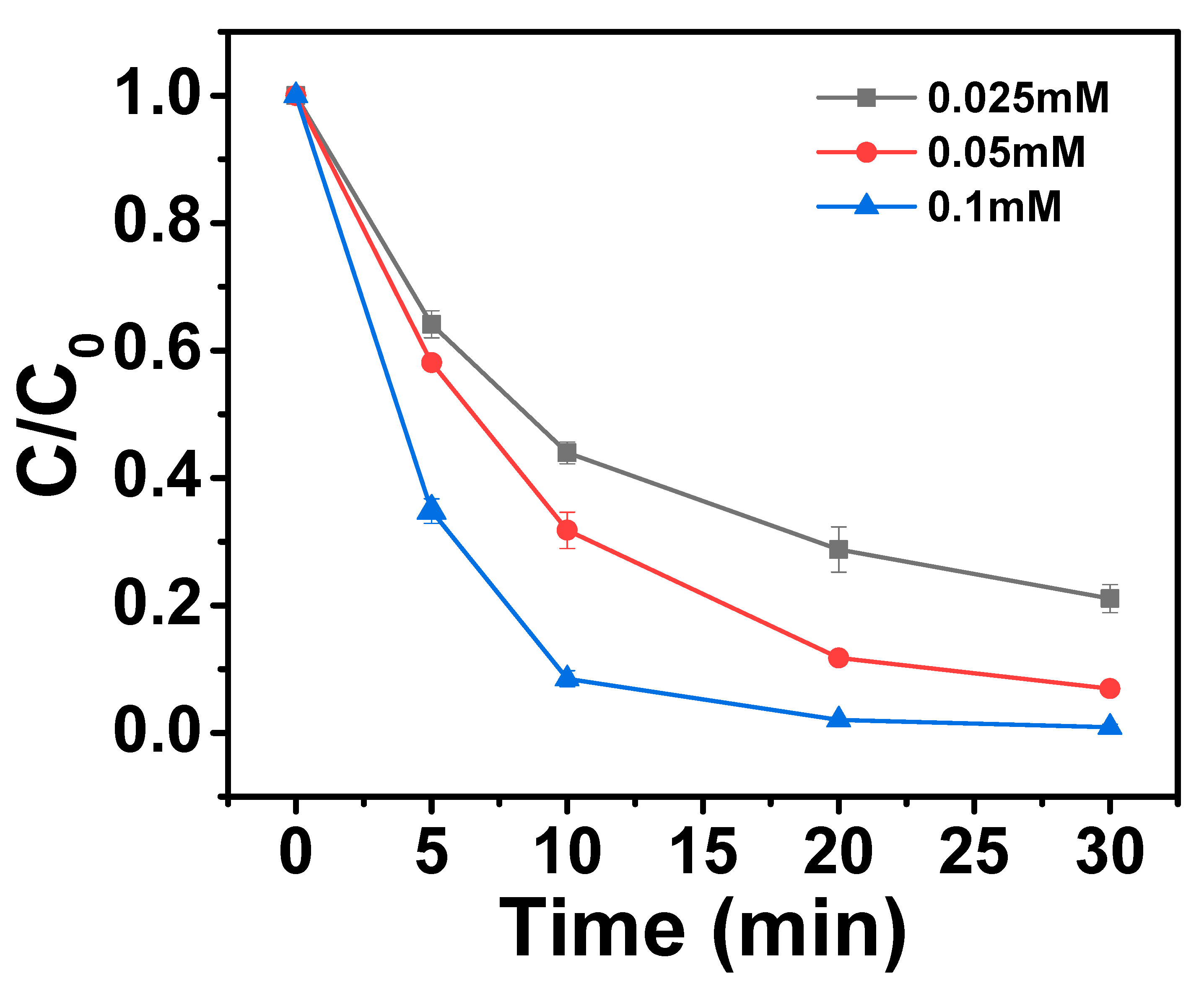
2.3.3. Effects of HA Dosage on AO7 Removal
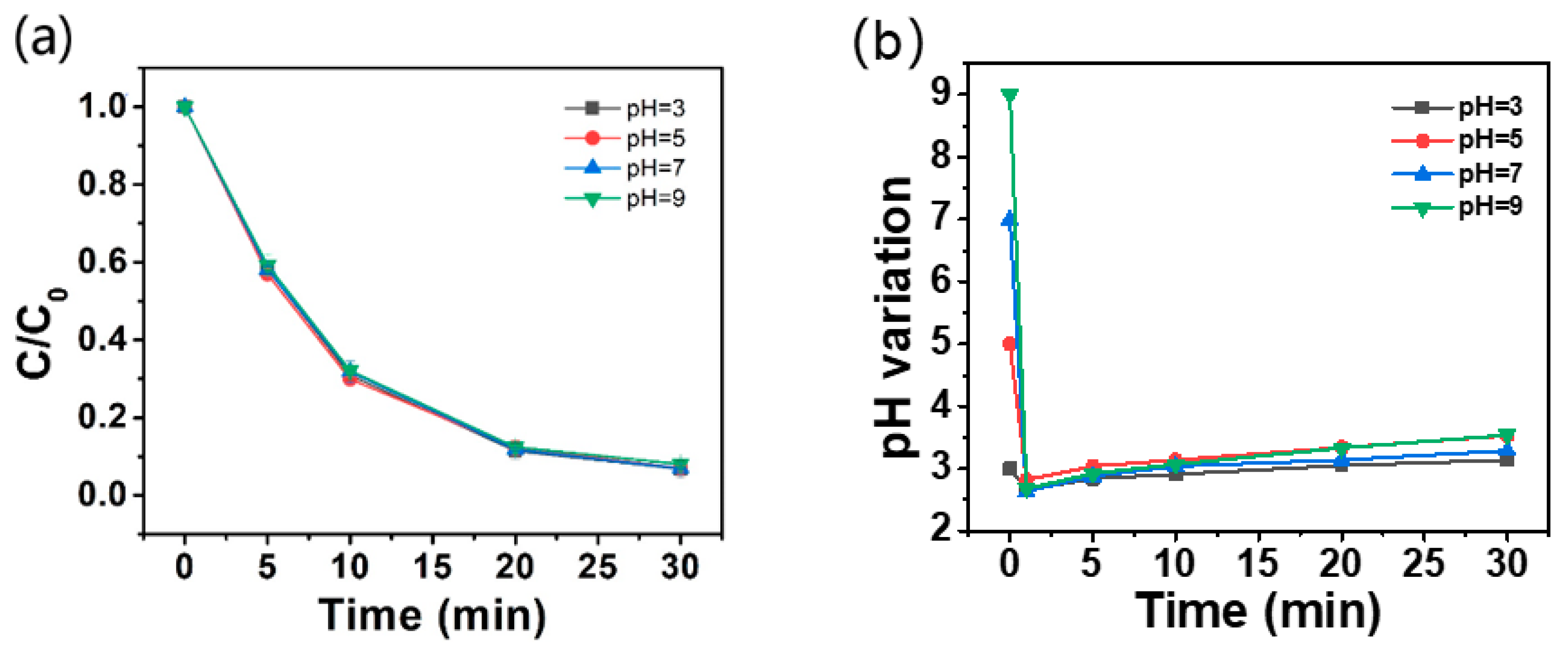
2.3.4. Effect of Initial pH on AO7 Removal
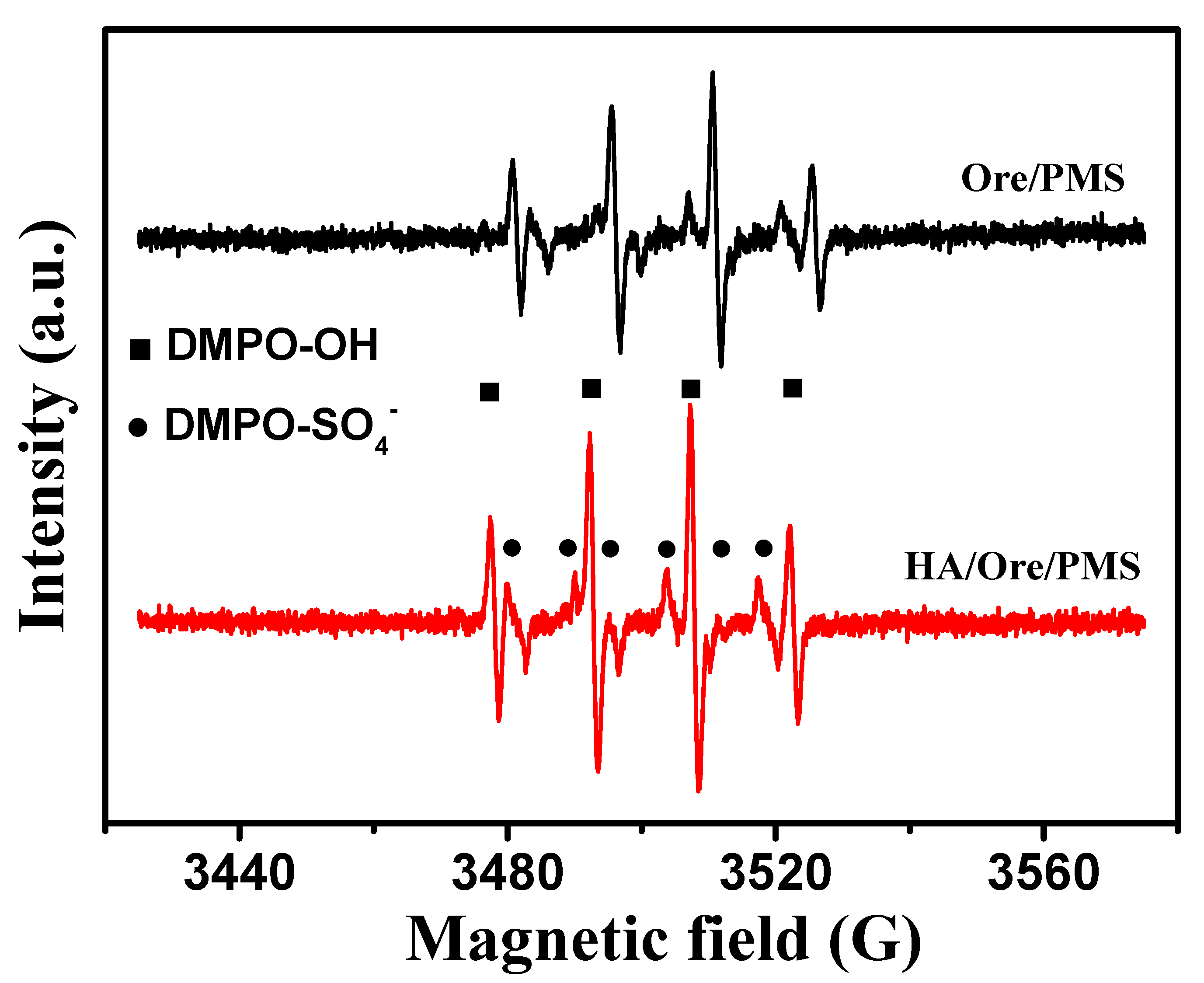
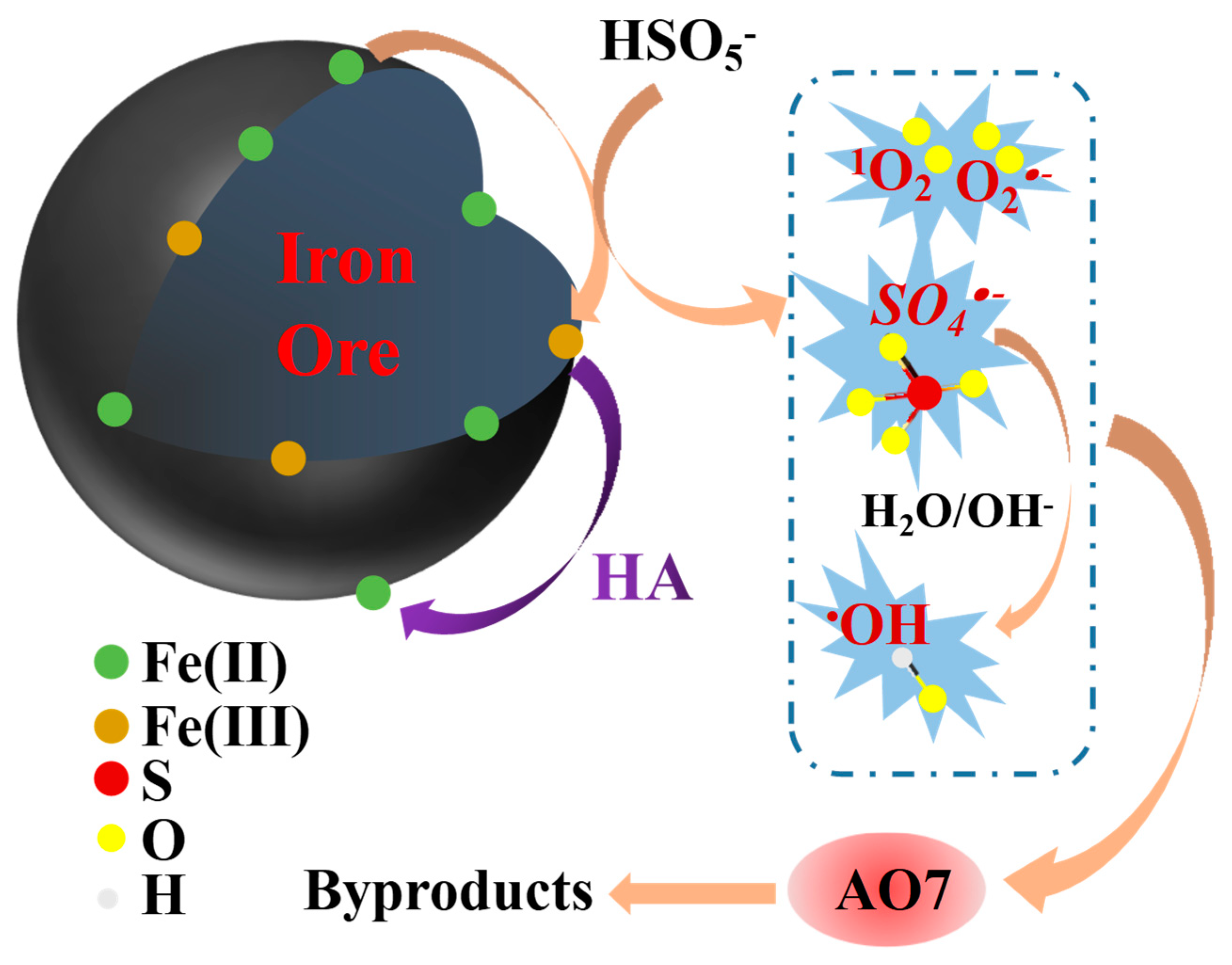
2.4. Reaction Mechanism
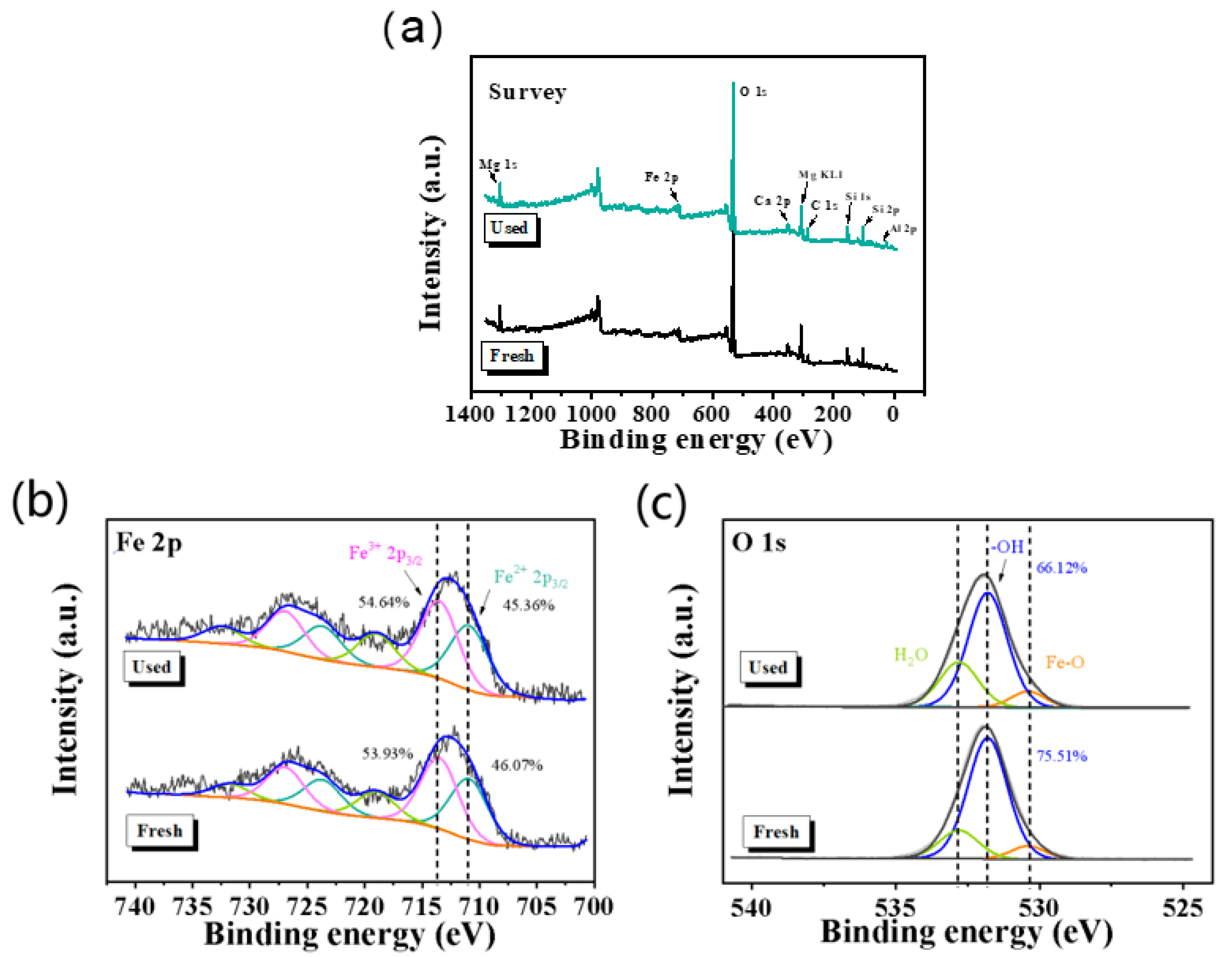
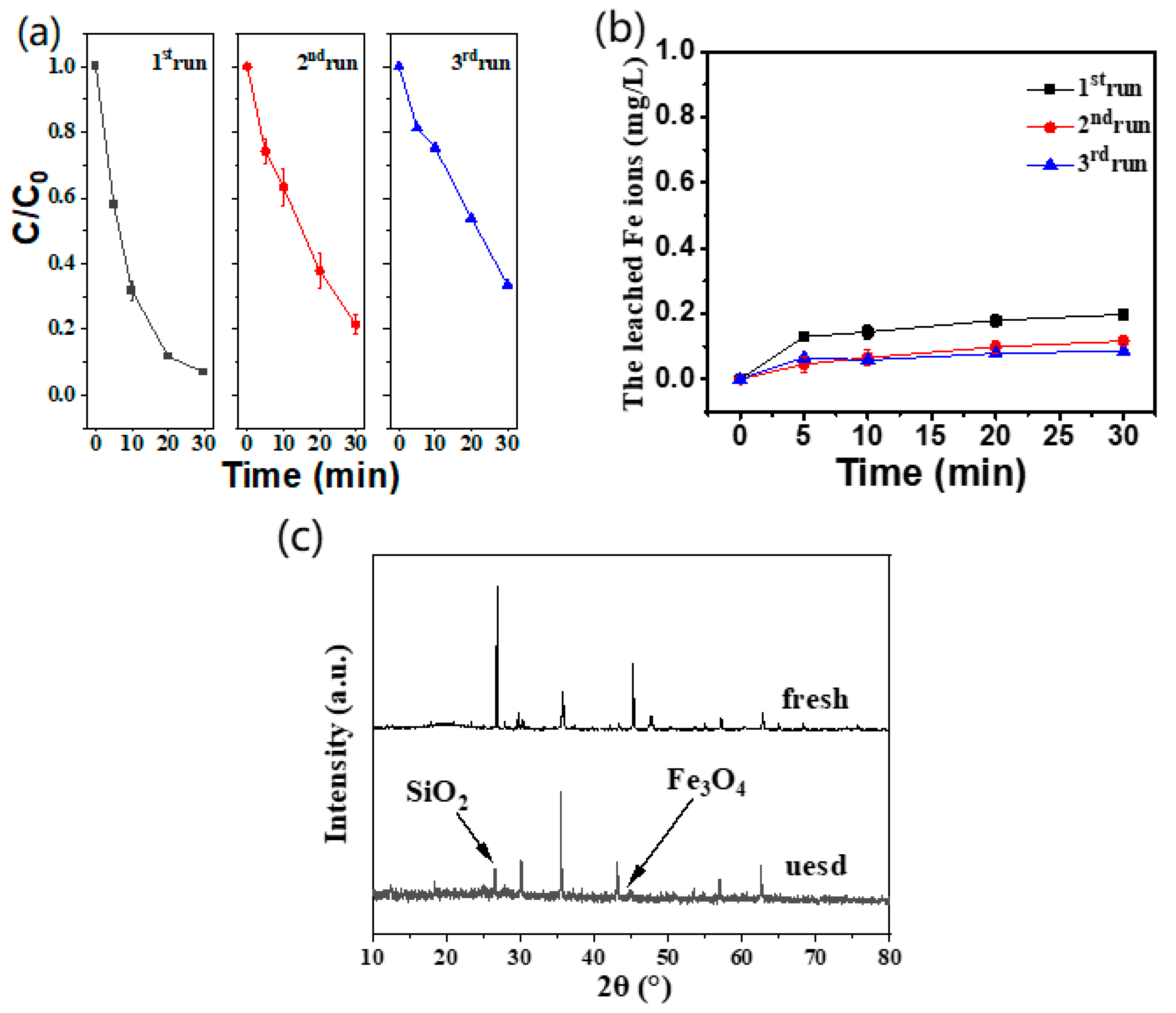
2.5. Recyclability of Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, K.-T. Azo dyes and human health: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2016, 34, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís, M.; Solís, A.; Pérez, H.I.; Manjarrez, N.; Flores, M. Microbial decolouration of azo dyes: A review. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1723–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faryal, R.; Hameed, A. Isolation and Characterization of various fungal strains from textile effluent for their use in bioremediation. Pak. J. Bot. 2005, 37, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Choi, H.; Chen, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D. Heterogeneous Activation of peroxymonosulfate by supported cobalt catalysts for the degradation of 2,4-Dichlorophenol in water: The Effect of support, cobalt precursor, and UV Radiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 77, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi Ahmed, M.; Barbati, S.; Doumenq, P.; Chiron, S. Sulfate radical anion oxidation of diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole for water decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.-C.; Fang, J.-Y.; Chen, L.-W. Influence of PH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the UV/Peroxymonosulfate system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Lin, C.; Ma, J.; He, M.; Ouyang, W. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.-D.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.-W.; Han, X. Efficient oxidation of phenol by persulfate using manganite as a catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2016, 411, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betterton, E.A.; Hoffmann, M.R. Kinetics and mechanism of the oxidation of aqueous hydrogen sulfide by peroxymonosulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fang, G.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Qin, W.; Zhou, D. Efficient transformation of DDTs with persulfate activation by zero-valent iron nanoparticles: A mechanistic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xiong, P.; Zhan, W.; Xiong, L. Degradation of ethylthionocarbamate by pyrite-activated persulfate. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Zero-valent copper-mediated peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient degradation of azo dye orange G. Catalysts 2022, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.S.; El-Bahy, S.M.; Mannaa, M.A. Sulfamic acid supported on mesoporous MCM-41 as a Novel, efficient and reusable heterogenous solid acid catalyst for synthesis of xanthene, dihydropyrimidinone and coumarin derivatives. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altass, H.M.; Morad, M.; Khder, A.E.-R.S.; Mannaa, M.A.; Jassas, R.S.; Alsimaree, A.A.; Ahmed, S.A.; Salama, R.S. Enhanced catalytic activity for CO oxidation by highly active Pd nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide /copper metal organic framework. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 128, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Chu, W. Degradation of a xanthene dye by Fe(II)-mediated activation of oxone process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Fronaeus, S.; Bengtsson-Kloo, L. The kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of hydroxylamine by iron(III). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2002, 12, 2548–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Hu, L.; Xia, D.; Yang, J.; He, C.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, J. Hydroxylamine promoted Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle on ilmenite surface to enhance persulfate catalytic activation and aqueous pharmaceutical ibuprofen degradation. Catal. Today 2020, 358, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Hornstein, B.J. The kinetics and mechanism of the ferrate(VI) oxidation of hydroxylamines. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 6923–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, R.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, W. Trace Cu(II) can enhance the degradation of orange II in Fe(II)/hydroxylamine/persulfate system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Campos, L.C. Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole by the Fe(II)/HSO5- process enhanced by hydroxylamine: Efficiency and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. Surface Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle promoted the degradation of atrazine by peroxymonosulfate activation in the presence of hydroxylamine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 256, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E.; Ross, A.B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 1027–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Phillips Helman, W.; Ross, A.B.; Tsang, W. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (ṠOH/ṠO- in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M. Chapter fourteen—Surface area: Brunauer–emmett–teller (BET). In Progress in Filtration and Separation; Tarleton, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 585–608. ISBN 978-0-12-384746-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, W.; Li, Z.; Huang, M.; Wu, X.; Li, D.; Mei, L.; Cui, J. Enhanced transition metal oxide based peroxymonosulfate activation by hydroxylamine for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Lee, C.-S.; Kang, Y.-G.; Chang, Y.-S. Hydroxylamine-assisted Peroxymonosulfate activation using cobalt ferrite for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 123751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusic, H.; Peternel, I.; Ukic, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Bolanca, T.; Papic, S.; Bozic, A.L. Modeling of Iron activated persulfate oxidation treating reactive azo dye in water matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, S. Modeling of Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation using atrazine as a target contaminant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 169, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.N.; Nicklin, H.G.; Shrimanker, K. Autoxidation of hydroxylamine in alkaline solutions. Part II. kinetics. the acid dissociation constant of hydroxylamine. J. Chem. Soc. Inorg. Phys. Theor. 1971, 3485–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J. Unraveling the interaction of hydroxylamine and Fe(III) in Fe(II)/persulfate system: A kinetic and simulating study. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ai, J.; Zhang, H. The Mechanism of degradation of bisphenol a using the magnetically separable CuFe2O4/peroxymonosulfate heterogeneous oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Cong, S.; Liu, M.; Zou, D. Hydroxylamine facilitated heterogeneous fenton-like reaction by nano micro-electrolysis material for rhodamine B degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Fang, C.; Geng, Z.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y. Significantly enhanced base activation of peroxymonosulfate by polyphosphates: Kinetics and mechanism. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.U.; Kasha, M. Singlet molecular oxygen in the haber-weiss reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12365–12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Iron Ore | Values |
|---|---|
| Specific surface area (BET)/(m2 g−1) | 0.962 |
| Average pore volume/(cm3 m−1) | 0.016 |
| Average pore size/(nm) | 6.805 |
| Target Pollutant | Activation System | Removal Rate (%) | k (min−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrazine | HA/Fe3O4/PMS | 94 | 0.152 | [22] |
| Sulfamethoxazole | HA/Fe2O3/PMS | 90.8 | 0.077 | [26] |
| Sulfamethoxazole | HA/CoFe2O4/PMS | 100 | 0.034 | [27] |
| AO7 | HA/Ore/PMS | 93.1 | 0.091 | This work |
| Phase Name | Fe3O4 | Fe2(CO3)3 | Fe2O3 | FeS | Fe2(SiO3)3 | Full Iron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 24.47 | 0.87 | 3.15 | 1.74 | 0.35 | 30.58 |
| Distribution rate (%) | 80.02 | 2.85 | 10.29 | 5.70 | 1.14 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, L.; He, D.; Cai, J.; He, W.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Accelerated Removal of Acid Orange 7 by Natural Iron Ore Activated Peroxymonosulfate System with Hydroxylamine for Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101148
Li H, Wang L, He D, Cai J, He W, Liu F, Chen H, Zhang H, Xu Y. Accelerated Removal of Acid Orange 7 by Natural Iron Ore Activated Peroxymonosulfate System with Hydroxylamine for Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle. Catalysts. 2022; 12(10):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101148
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haibo, Linfeng Wang, Dingyuan He, Jie Cai, Wenjie He, Fuzhen Liu, Hanxiao Chen, Hui Zhang, and Yin Xu. 2022. "Accelerated Removal of Acid Orange 7 by Natural Iron Ore Activated Peroxymonosulfate System with Hydroxylamine for Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle" Catalysts 12, no. 10: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101148
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, L., He, D., Cai, J., He, W., Liu, F., Chen, H., Zhang, H., & Xu, Y. (2022). Accelerated Removal of Acid Orange 7 by Natural Iron Ore Activated Peroxymonosulfate System with Hydroxylamine for Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle. Catalysts, 12(10), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101148








