Promotion Effect of Palladium on BiVO4 Sensing Material for Epinephrine Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
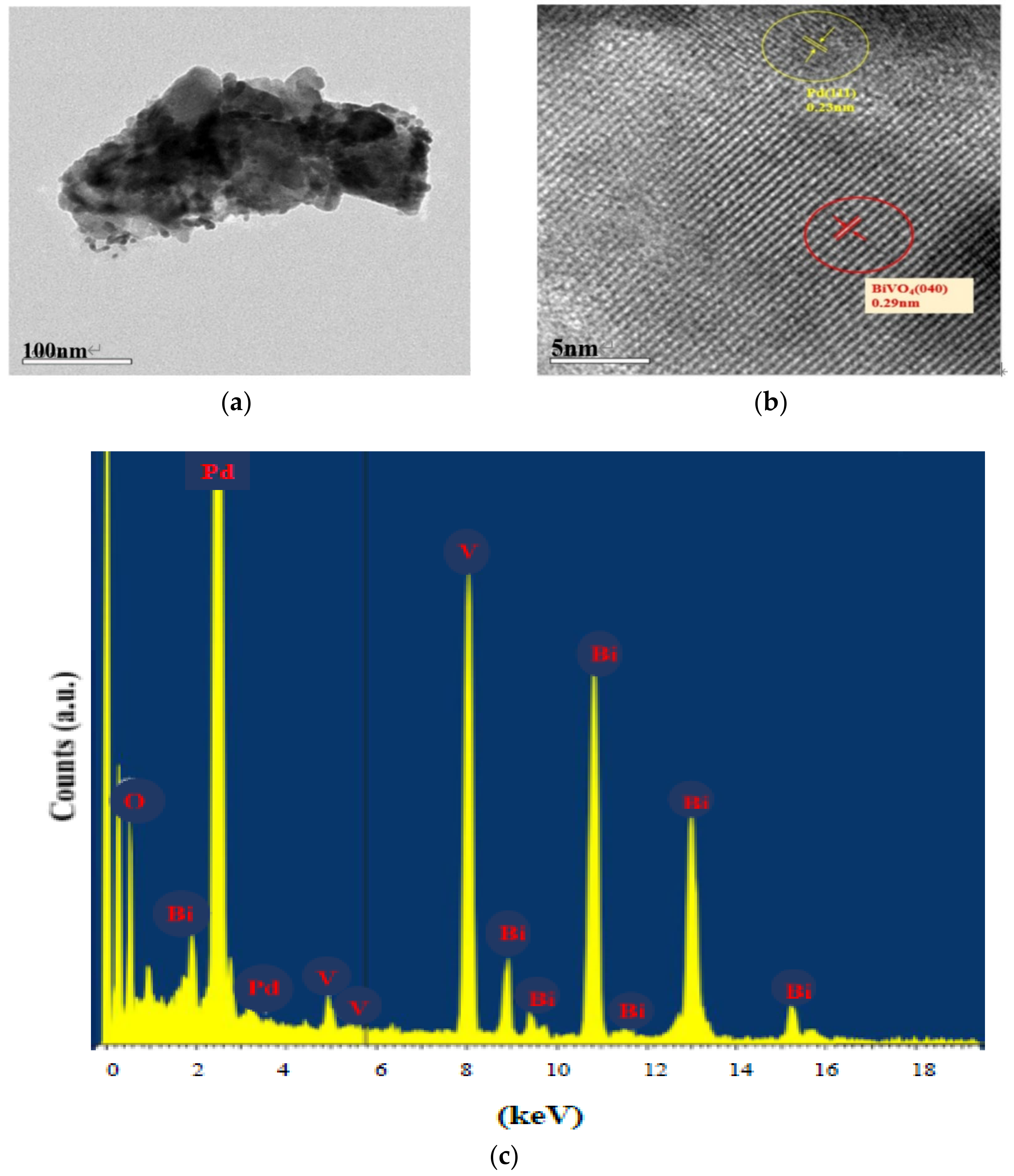
2.1. Characterization of the Sensing Materials
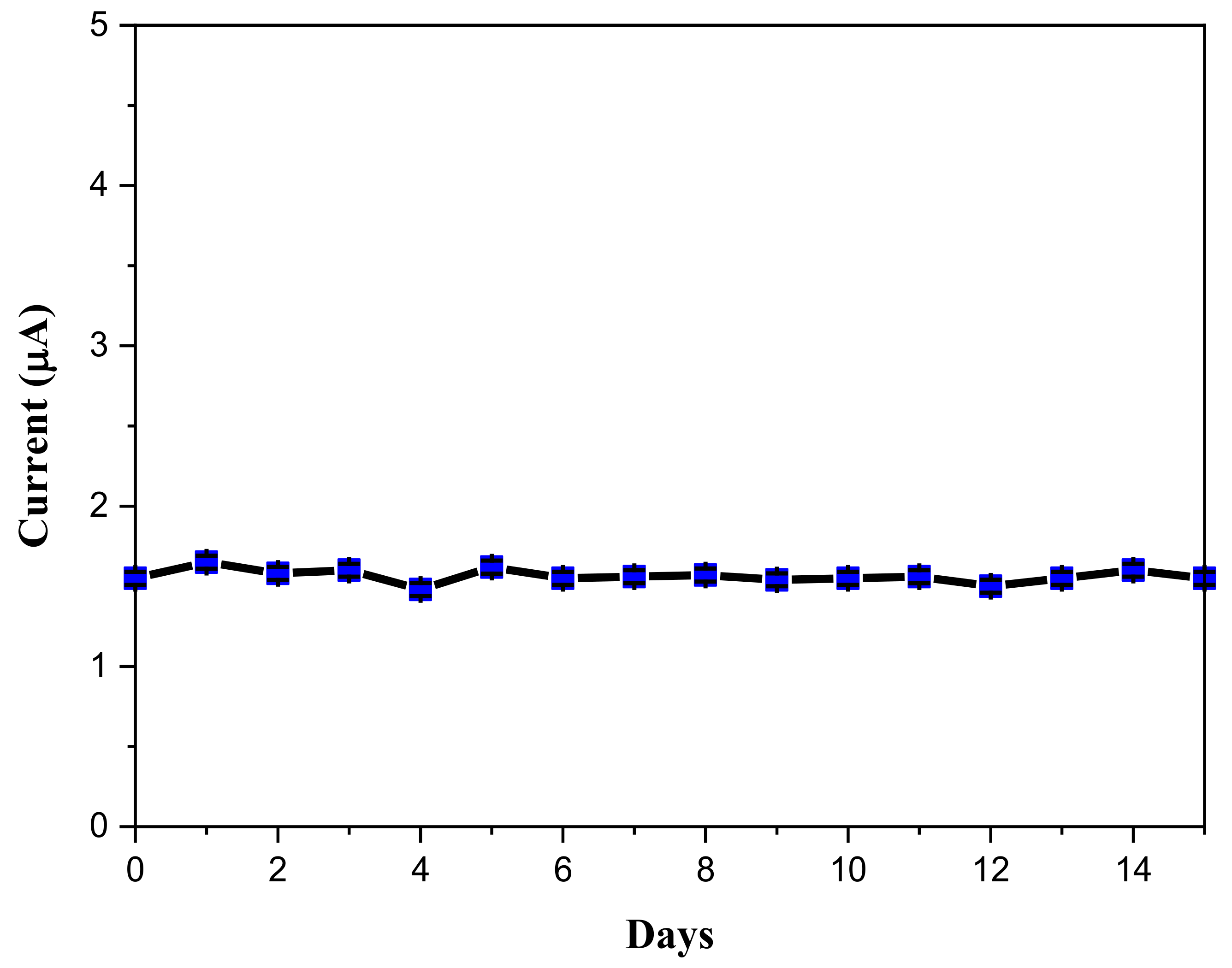
2.2. Electrochemical Sensor Behavior
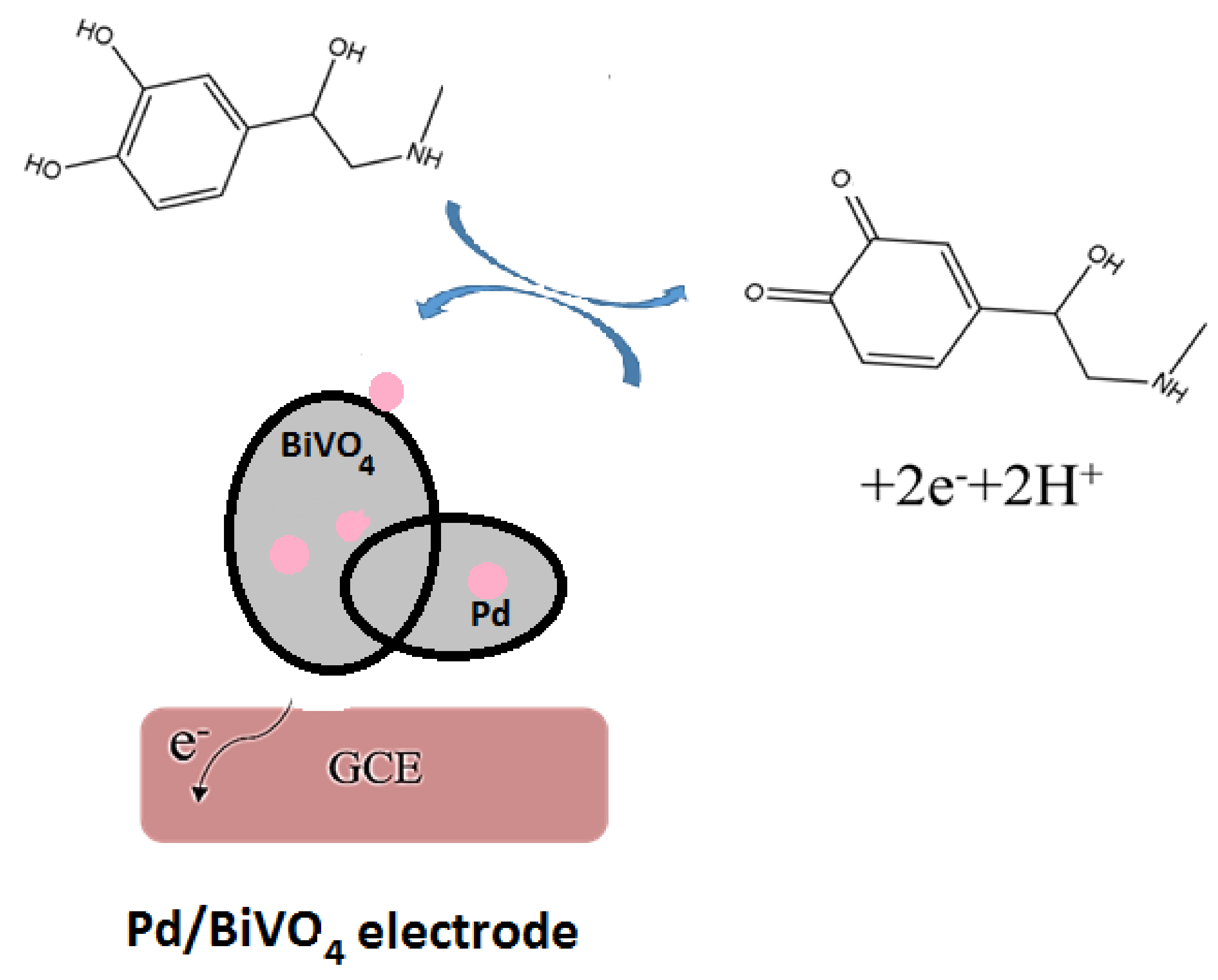
2.3. Sensing Mechanism
3. Experiment
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Sensing Materials
3.3. Preparation of Pd-BiVO4/GCE
3.4. XRD, SEM and TEM/EDX
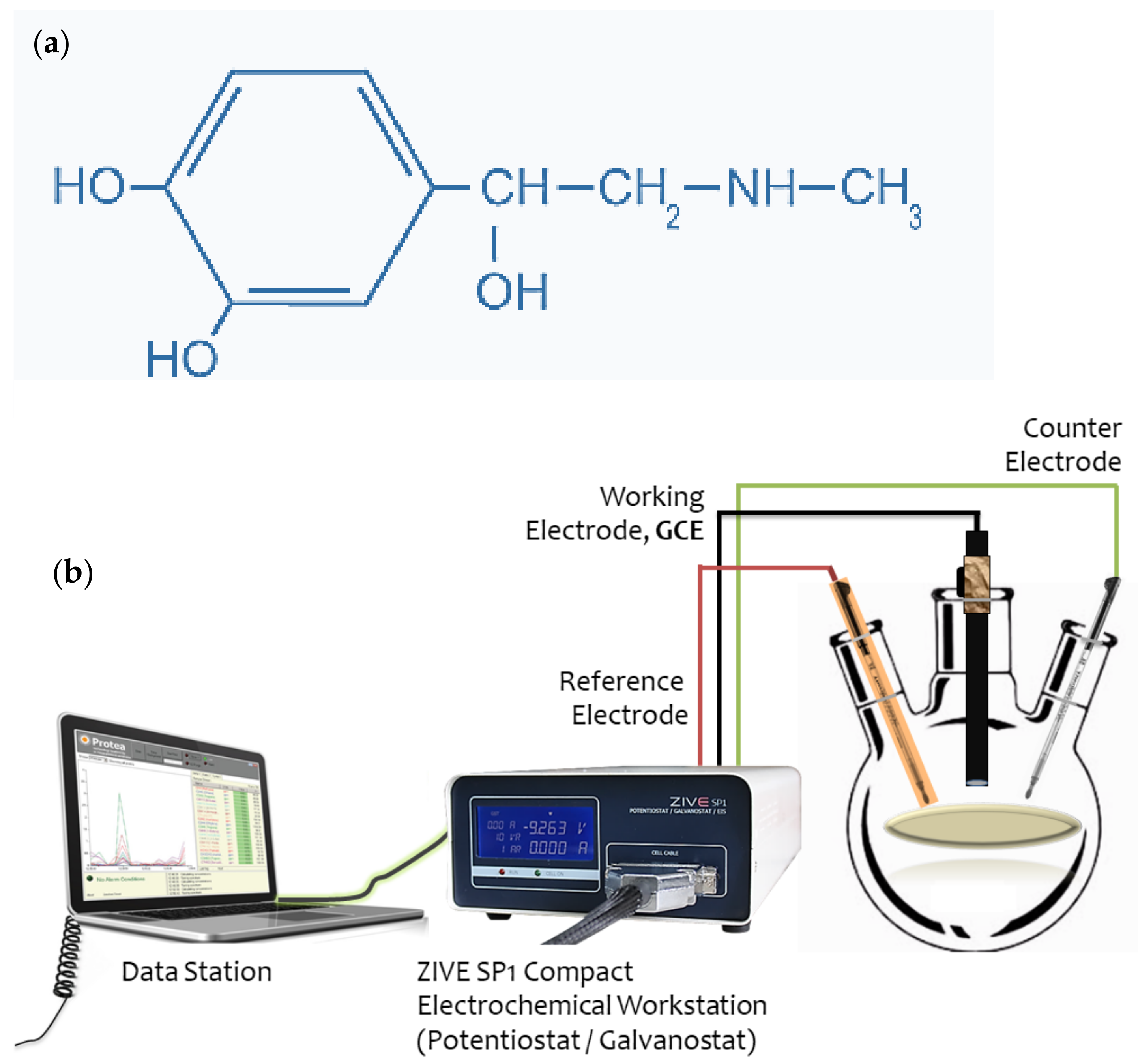
3.5. Electrochemical Detection System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emran, M.Y.; Khalifa, H.; Gomaa, H.; Shenashen, M.; Akhtar, N.; Mekawy, M.; Faheem, A.; El-Safty, S.A. Hierarchical C-N doped NiO with dual-head echinop flowers for ultrasensitive monitoring of epinephrine in human blood serum. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.; Grau, J.B.; Fortier, J.; Salvati, E.; Levy, R.J.; Ferrari, G. Serotonin and catecholamines in the development and progression of heart valve diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, C.; McDonald, T.; Walton, J.; Groeber, E.A.; Steenwyk, R.C.; Lin, Z. Ultra sensitive measurement of endogenous epinephrine and norepinephrine in human plasma by semi-automated SPE-LC–MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 895–896, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davletbaeva, P.; Falkova, M.; Safonova, E.; Moskvin, L.; Bulatov, A. Flow method based on cloud point extraction for fluorometric determination of epinephrine in human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 911, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Fu, Z. Highly sensitive trivalent copper chelate-luminol chemiluminescence system for capillary electrophoresis detection of epinephrine in the urine of smoker. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 911, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Sulka, G.D. Nanoporous spongelike Au–Ag films for electrochemical epinephrine sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 762, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Szultka-Młyńska, M.; Buszewski, B.; Sulka, G.D. Epinephrine sensing at nanostructured Au electrode and determination its oxidative metabolism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Sulka, G.D. Fabrication of highly ordered nanoporous thin Au films and their application for electrochemical determination of epinephrine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ren, Y.; Bai, Z.; Jiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, Q. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral Au-Pd core–shell nanocrystals and reduction of graphene oxide for the electrochemical detection of epinephrine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashkhourian, J.; Nami-Ana, S.F.; Shamsipur, M. Designing a modified electrode based on graphene quantum dot-chitosan application to electrochemical detection of epinephrine. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, S.; Ye, B. Gold nanoparticles/polyaniline Langmuir–Blodgett Film modified glassy carbon electrode as voltammetric sensor for detection of epinephrine and uric acid. Talanta 2013, 117, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavandpour, R.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Asif, M.; Gupta, V.K.; Atar, N.; Abbasghorbani, M. Liquid phase determination of adrenaline uses a voltammetric sensor employing CuFe2O4 nanoparticles and room temperature ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Geng, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Shao, Z. Novel monoclinic ABO4 oxide with single-crystal structure as next generation electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Elaiyappillai, E.; Anandaraj, S.; Duvaragan, B.K.; Johnson, P.M. Study on the electrochemical behavior of BiVO4/PANI composite as a high performance supercapacitor material with excellent cyclic stability. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 861, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangkun, N.; Ponchio, C. Photoelectrodeposition of BiVO4 layer on FTO/WO3 photoanodes for highly efficient photoelectrocatalytic chemical oxygen demand sensor applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 526, 146686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Miao, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Di, J. An enzyme-free photoelectrochemical glucose sensor based on coupling BiVO4 with gold nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 125, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bian, Z. Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol on Pd-BiVO4 under visible light irradiation. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikshavali, P.; Reddy, T.M.; Gopal, T.V.; Venkataprasad, G.; Kotakadi, V.S.; Palakollu, V.; Karpoormath, R. A simple sonochemical assisted synthesis of nanocomposite (ZnO/MWCNTs) for electrochemical sensing of Epinephrine in human serum and pharmaceutical formulation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 584, 124038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.-N.; Dai, T.-H.; Wu, R.-J.; Chavali, M. Sensing properties of Pt@SnO2 core-shell nanocomposite detecting Epinephrine. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Banerjee, M.B.; Biswas, S.; Hamizi, N.A.; Das, D.K.; Bhar, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Pramanik, P. An Efficient Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Nanomolar Epinephrine and Uric Acid using Low Temperature Synthesized Nano-sized Copper Telluride. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Author/Year/Reference | Sensing Material | Range of Detection (µM) | Detection Limit (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. Wierzbicka /2016/[8] | Nano Au/high ordered anodic Al2O3 | 10–150 | 3 |
| W. Dong/2018/[9] | Au-Pd@reduced graphene oxide | 0.001–1000 | 0.0012 |
| J. Tashkhourian /2018/[10] | Graphene | 0.36–380 | 0.16 |
| L. Zou/2018/[11] | Au-polyaniline | 0.4–10 | 0.08 |
| This work | 1% Pd/BiVO4 | 0.9–27.5 | CV: 0.262 (R2 = 0.9998) DPV: 0.154 (R2 = 0.9998) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luk, H.-N.; Chou, T.-Y.; Huang, B.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Li, H.; Wu, R.-J. Promotion Effect of Palladium on BiVO4 Sensing Material for Epinephrine Detection. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091083
Luk H-N, Chou T-Y, Huang B-H, Lin Y-S, Li H, Wu R-J. Promotion Effect of Palladium on BiVO4 Sensing Material for Epinephrine Detection. Catalysts. 2021; 11(9):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091083
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuk, Hsiang-Ning, Tsong-Yung Chou, Bai-Hao Huang, Yu-Syuan Lin, Hui Li, and Ren-Jang Wu. 2021. "Promotion Effect of Palladium on BiVO4 Sensing Material for Epinephrine Detection" Catalysts 11, no. 9: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091083
APA StyleLuk, H.-N., Chou, T.-Y., Huang, B.-H., Lin, Y.-S., Li, H., & Wu, R.-J. (2021). Promotion Effect of Palladium on BiVO4 Sensing Material for Epinephrine Detection. Catalysts, 11(9), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11091083







