Abstract
In recent years, biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) have been gaining importance due to their unique properties and tremendous applications. This study aimed to fabricate ZnO NPs by using extracts from various parts of the traditional medicinal plant Heliotropium indicum (H. indicum) and evaluate their photocatalytic activity. Further, their potential in photoluminescence and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) was assessed. The Ultraviolet-Visible spectrum exhibited a hypsochromic shifted absorption band between 350–380 nm. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis revealed spherical NPs, while X-ray diffraction (XRD) data revealed wurtzite, hexagonal and crystalline nature. The TEM and XRD consistently determined an average particle size range from 19 to 53 nm. The photocatalytic degradation reaches a maximum of 95% for biogenic ZnO NPs by monitoring spectrophotometrically the degradation of methylene blue dye (λmax = 662.8 nm) under solar irradiation. Photoluminescence analysis revealed differentiated spectra with high-intensity emission peaks for biogenic ZnO NPs compared with chemically synthesized ZnO NPs. Eventually, the highest efficiency of FRET (80%) was found in ZnO NPs synthesized from the leaves. This remains the first report highlighting the multifunctional ZnO NPs capabilities mediated by using H. indicum, which could lead to important potential environmental and biomedical applications.
1. Introduction
The synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) has been considered as the preferred field in nanotechnology due to their high surface-area-to-volume ratio, size, morphology, catalytic activity, thermal and electrical conductivity, biological properties, and optical characteristics compared to bulk materials [1,2,3,4,5]. Metal and metal oxide NPs (MONPs) (e.g., gold, silver, nickel, copper, magnesium oxide, titanium dioxide (TiO2), copper oxide, and zinc oxide (ZnO)) play a crucial role in many areas of chemistry, biomedical, and material science due to their unique physical properties, chemical reactivity, and potential applications [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Among MONPs, ZnO NPs are prominent in almost all their applicable fields, being commonly used in ceramics, electronics, cosmetics, piezoelectric transducers, chemical sensors, anti-UV additives, and photocatalysts due to their unique optical and chemical behaviors which can be simply tuned by changing their morphology [3,12,13,14,15,16]. Moreover, ZnO NPs have tremendous potential in biological applications including biological sensing, biological labeling, gene delivery, drug delivery, environmental safety, and nanomedicines [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
ZnO NPs are becoming increasingly important as optoelectronic material, and the defects and impurities of these NPs are playing an important role in the semiconductor industry to develop optoelectronic devices [2,16,18,24,27]. Luminescence is one of the fastest-growing, and most sensitive, nondestructive techniques that help to understand point defects including extrinsic and intrinsic defects of semiconductor materials like ZnO, and TiO2 [13,16,27,28]. ZnO with a wurtzite structure is one of the most promising n-type semiconductors for short-wavelength optoelectronic applications, displaying excellent chemical and thermal properties with a wide bandgap of 3.37 eV and high excitation binding energy of 60 meV at room temperature (RT) [12,14,15,16]. It has attractive and novel optoelectronic properties such as high physical and chemical stability, luminescence, and superior UV emission characteristics at RT than TiO2 [9,15,29,30].
Hence, nanosized semiconductors can act as effective photocatalysts for the degradation of various environmental pollutants (e.g., pesticides, detergents, dyes, and volatile organic compounds) in the presence of UV light and Sunlight irradiation [2,14,23,31]. To date, several methods, such as bio-treatment, incineration, ozonation, and adsorption processes based on solid adsorbents, have been utilized to treat wastewater containing pigments or dyes [15,24,32]. However, these methods are quite expensive and produce toxic non-biodegradable side products. To overcome these drawbacks, ZnO photocatalyst is used because it is non-toxic, contains a large number of active sites, and also can be used as a valuable alternative to TiO2 [16,29,32].
Moreover, ZnO NPs are being applied as bright fluorescent markers with enhanced photostability in fluorescence microscopy, sensor technology, and microarrays due to the interaction of fluorophores with MONPs, displaying various spectral changes such as enhancement in luminescence intensity, photostability, and quantum yield [33,34,35]. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), a non-radiative quantum mechanical process that relies on the distance and energy transfer from an excited state donor to a ground state acceptor through dipole–dipole interactions [33,35,36,37], is being widely used in polymer science, biochemistry, and structural biology [15,35]. The energy transfer between quantum dots has been investigated broadly to design FRET sensors [38,39,40].
To the best of our experience, the present study remains the first endeavor that used biogenic ZnO NPs synthesized from Heliotropium indicum (H. indicum) to investigate the efficacy of FRET. In FRET, when NPs are in close proximity to fluorophores, quenching of the luminescence occurs because the non-radiative decay of the excited molecules will increase due to energy transfer from the dyes to the NPs; conversely, when NPs are located at a greater distance, enhancement of the luminescence is observed due to a decrease in non-radiative decay [15,33,35,36,37]. These effects have been explained by interactions with surface plasmon resonance in the NPs and fluorophore [15,41].
There are different physical and chemical approaches to synthesize ZnO NPs, which include hydrothermal, sonochemical, sol–gel, solvothermal, microemulsion methods, direct precipitation, laser ablation, homogeneous precipitation, reverse micelles, thermal decomposition, and microwave irradiation [1,3,12,13,31,42,43]. Although these physical/chemical methods enable the synthesis of large quantities of NPs with different sizes and morphologies, they require a long reflux time of reaction, as well as eco-toxic and expensive chemicals (e.g., capping agents, hazardous organic solvents, and byproducts) [12,19,20,25,42]. Therefore, green synthesis of NPs has gained great demand in recent years due to the synthesis of NPs with superior morphological, photochemical, photocatalytical and electrochemical properties compared to physio-chemical methods and has become one of the most preferred methods for synthesizing ZnO NPs [14,26,31,44,45].
Nowadays, various biological resources (e.g., plants, bacteria, algae, fungi) provide an ideal platform for the eco-friendly biosynthesis of MONPs [12,46,47]. Among the various approaches to synthesis NPs, plants seem to be the best candidates due to their easy availability, low cost, low toxicity, and capacity for large-scale synthesis of stable, controlled sized and shaped NPs. Moreover, plant extracts naturally act as a reducing, stabilizing, and capping agent for the synthesis of NPs [7,21,32,48].
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the green synthesis and structural characterizations of ZnO NPs using aqueous extracts of the stems, leaves, and inflorescences of H. indicum. H. indicum is a common indigenous medicinal plant native to Sri Lanka. It is widely distributed in tropical and temperate regions, is adding a high value in folklore medicine due to its significant number of activities, including wound healing, antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, thrombolytic, antitumor, antifertility, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, and diuretic [49,50,51]. The main constituents of H. indicum were found to be pyrrolizidine alkaloids (i.e., echinatine, heleurine, lasiocarpine, indicine, indicine N-oxide, retronicine, cynoglossine, and supinine), and phenolic compounds (i.e., terpenoids, tannins, saponins, heliotrine, and quinones) [52,53,54].
Although H. indicum elicits superior medicinal properties, its pharmacological and environmental actions are not fully explored. Hence, this study is an attempt for promoting the use of this plant for biomedical and environmental applications. For this purpose, the photocatalytic, photoluminescence (PL), and FRET activities of synthesized ZnO NPs were assessed for sustainable bioremediation.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis, Optimization of Synthesis Parameters, and Characterization of ZnO NPs
With the aid of two major zinc precursor salts; zinc acetate [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O and zinc nitrate, ZnO NPs can be obtained using physical, chemical, or biological methods [1,12,14,31,43,55]. Among them, physical synthesis techniques such as vapor deposition, ultrasonic, and plasma irradiation are not cost-effective due to the usage of high-energy and robust equipment [12,13,42,56]. Therefore, chemical methods such as sol–gel synthesis and co-precipitation have gained popularity with the use of a metal substrate, a solvent medium (ethanol, toluene, methanol (MeOH), etc.), a chemical reagent to regulate the pH of the solution (sodium hydroxide (NaOH)/potassium hydroxide), chemical stabilizers (citrates, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene glycols, etc.), and high calcinated temperatures up to 1000 °C, used to avoid agglomeration and to control the size of the ZnO NPs [1,14,20,31,42]. Lately, in agreement with the twelve principles of the green chemistry, biological synthesis of NPs introduced to overcome the disadvantages associated with conventional methods [3,12,19,43]. However, the actual mechanism associated with the formation of ZnO NPs in the presence of plant phytochemicals is yet to be discovered, and it is considered that these secondary metabolites behave as the capping material as well as surface stabilizing agents [3,15,21,25,57]. It has been found that varying different volume ratios (plant extract to [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O with or without NaOH were used to optimize the synthesis qualities of NPs [14,58,59]. According to literature, biosynthesis of ZnO NPs with adjusted pH medium gives superior qualities compared to NPs synthesized through conventional chemical synthesis and without NaOH [14,58,59]. This is because the synthesis medium and its pH play an important role in morphology, size (decrease NPs agglomeration), and they increase surface area and affect zero-point charge value [2,14,31,45]. Therefore, this study aimed to produce ZnO NPs with enhanced properties using a low-cost greener method using the H. indicum plant.
Despite the advantages of the green synthesis approach for ZnO NPs, the polydispersity of these NPs remains a challenge [4]. The nature of the plant extract, its concentration, the concentration of the metal salt, pH, temperature, and reaction time (incubation period) have been identified as crucial factors for the biosynthesis of stable monodispersed NPs [3,12,15,17]. Optimization of these critical parameters could affect the rate of production and morphological characteristics of the NPs [14,17,22]. In previous studies, it was stated that pH 12, temperature of 60 °C, reaction time of 2 h, with altered metal concentration ([Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O), and amount of plant extract, were used for biosynthesis of ZnO NPs [3,15,32,46,60]. Thus, the present study aimed to consider a full-scale approach for examining the individual influence of these factors in H. indicum extracts-mediated ZnO NPs synthesis.
UV-Vis (UV-Vis) absorbance spectroscopy was used as the preliminary identification method to monitor the formation of ZnO NPs in an aqueous solution. To characterize the optical absorption properties of NPs dispersed in deionized water (DI H2O), pale white nanopowder obtained from each part of the plant (i.e., stems (HIS), leaves (HIL), and inflorescences (HIF)) was suspended in an equal amount of DI H2O, and spectrum scans were performed.
Various concentrations of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O (from 0.01 M to 0.05 M) were used to optimize the green synthesis of NPs (Figure S1). The dispersion of ZnO NPs was affected by the concentration of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O, which operated as a controller of nucleation [43]. It was observed that concentrations below 0.01 M [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O led to insufficient yield, and the production of NPs increased with increased metal ion concentration [4,17]. As per the results obtained, it was noted that when increasing metal ion concentration from 0.01 M to 0.05 M, the intensity of the peak characteristic of synthesized NPs, which appeared in the range of 350–400 nm, decreased gradually resulting in a substantial broadening of peaks. The spectral pattern obtained with ZnO NPs/HIS (Figure S1a), ZnO NPs/HIL (Figure S1b), and ZnO NPs/HIF (Figure S1c) revealed that the optimum concentration of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O are 0.01 M, 0.02 M, and 0.01 M respectively.
On the same grounds, various concentrations of HIS, HIL, and HIF extracts were explored for optimum metal ion concentrations (Figure S2). A steady improvement in the absorption and peak prominence was observed when increasing the extract volume from 0.50 mL to 3.00 mL, and maximum absorption was observed with 1.00 mL of plant extract. Hence, 1.00 mL was identified as the optimal volume for the synthesis of ZnO NPs from HIS (Figure S2a), HIL (Figure S2b), and HIF (Figure S2c) extracts.
Other major governing factors in the green synthesis of NPs are the pH, temperature, and stirring time/incubation period of the reaction mixture. The optimization of these parameters was determined for HIS-derived NPs synthesis, maintaining 0.01 M [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O and 1 mL plant extract as constant parameters. The experiment was repeated with HIL and HIF to synthesize NPs by applying pre-determined optimum metal ion concentration.
Interestingly, it was noted that an increase in pH from 9 to 12 led to an increase in the absorbance for NPs (Figure S3a). The best spectral absorbance and sharpness were recorded at pH 12 which was identified as optimum pH for NPs synthesis, confirming literature data [3,15,32,46,60]. Additionally, it was noted that particle size (PS) increased with increasing temperature from 50 to 100 °C (Figure S3b). PS and wavelength of NPs showed a direct relationship, and PS increased with increasing temperatures [1,43]. It was stated that as temperature increases, the peak absorbance wavelength becomes a bathochromic shift due to decreasing quantum confinement with increasing particle size [61]. Therefore, a moderate temperature of 60 °C was selected as the drying temperature for all green synthesized NPs.
Eventually, the optimum reaction time for NPs was analyzed by varying the stirring time (Figure S3c). The increase in absorption did not occur in a time-dependent manner and the best sharpening of the peak corresponding to the optimal synthesis of ZnO NPs was observed at 2 h. Additionally, a further 1 hr increase resulted in a substantial broadening of the peak with scattering, which could be explained by the growth of NPs with different PS in the reaction mixture [43]. The overall results are in perfect agreement with previous studies [3,32] related to pH, temperature, and stirring time used for the optimal fabrication of ZnO NPs.
Once all the crucial parameters for optimal green synthesis of ZnO NPs were determined (e.g., 0.01 M [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O, pH 12, 60 °C, 2 h stirring), the experiments were carried out with 1 mL of each plant part extracts. As shown in Figure 1, the optimum λmax values corresponding to the absorption peaks of synthetized ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF were observed at 364 nm, 368 nm, and 370 nm, respectively. Thereby, the peak observed at the given wavelength, according to the plant part extract, is characteristic of the ZnO formation while the confinement in the nanoscale is proved by hypsochromic shift [3,44,62]. This is in accordance with previous studies reporting that ZnO NPs show a maximum absorbance wavelength within the range of 300–400 nm [3,15,24,32,63].
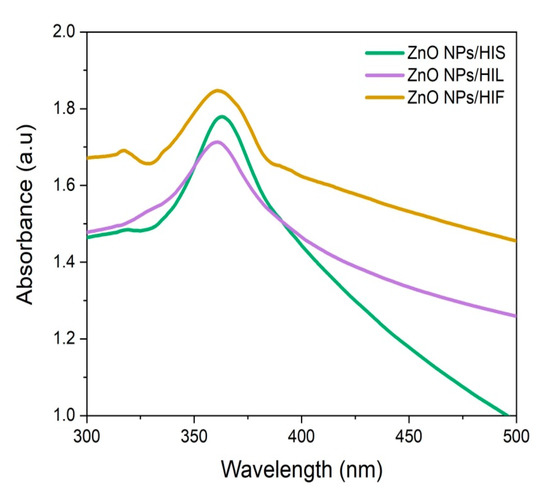
Figure 1.
UV-Vis spectra analysis at optimized conditions.
2.2. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Green Synthesized ZnO NPs
To identify functional groups involved in the stabilization of ZnO NPs, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF and their respective plant part extracts. The resulting spectra are depicted in Figure S4. The phytochemicals present in these extracts are considered to provide the action of capping, and stabilizing agents that aid the formation of ZnO NPs [7,21,32,48]. Substance-specific vibrations of the molecules lead to the specific signals obtained by IR spectroscopy in the range of 400–4000 cm−1.
Consistently, prominent peaks in all spectra were observed in the wavelength ranges of 3200–3350 cm−1, 1670–1820 cm−1, 1500–1680 cm−1, and 500–600 cm−1 which are attributed to –OH, C=O, C=C, and C–Br stretching respectively.
The peak at 2100–2260 cm−1 occurred in HIS, and HIL plant extracts are assigned to the stretching of CC. A low-intensity peak correlated with the –OH stretching was observed in ZnO NPs. In addition to these prominent absorption peaks, characteristic new peaks in all NPs appeared within the ranges of 2850–3000 cm−1, 2300–2380 cm−1, 1350–1400 cm−1, and 800–1000 cm−1, demonstrating the presence of C–H alkene stretch, C–N stretch, C–H bending, =C–H bending respectively. The peak in the region between 500–600 cm−1 is allotted to Zn–O stretching vibration of hexagonal ZnO NPs [15,44,64]. ZnO NPs/HIL and ZnO NPs/HIF show miniature peaks in the ranges of 3300–3750 cm−1 and 1500–1650 cm−1 corresponding to the N–H stretch of the amine group and symmetric stretching of the carbonyl side groups in the amino acid residues of the protein molecules, respectively [21,23]. The discrete peak obtained in the range of 547–555 cm−1 strongly depicted the presence of the C–N stretch amine group and C-Br stretch alkyl halide, respectively [65].
Additional characteristic peaks found in ZnO NPs/HIF could reveal information about the surface adherence of molecules. The peaks at around 1396 cm−1, 1095 cm−1, and 1041 cm−1 resulted from aromatic amines, and C–N stretch of aliphatic amines respectively. The peak at 725 cm−1 corresponds to alkanes and supposedly, C-H bend in alkynes [63].
2.3. Surface Morphology, Particle Size, and Nature of Biosynthesized NPs
To ensure the reliability of the data, scanning electron microscope (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to characterize one or more of key features (e.g., NPs surface morphology, nature, PS). The surface morphology of the ZnO NPs is commonly studied using SEM, and the topographical analysis is performed based upon the surface study [15,21,32,56,66]. Synthesized NPs were imaged at different magnitudes of 25,000× and 50,000×. The SEM micrographs of HI-mediated ZnO NPs are displayed in Figure 2.
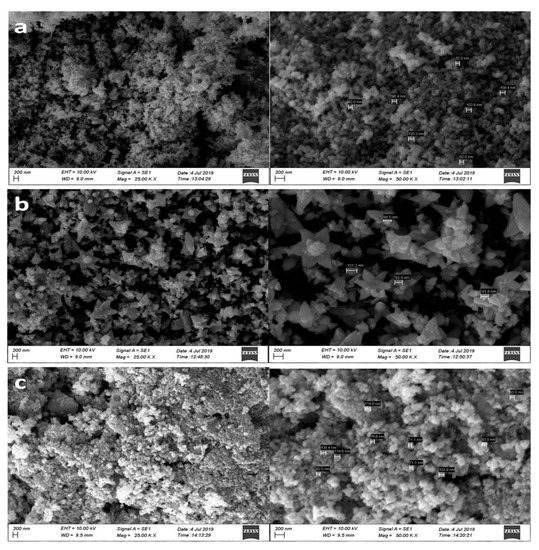
Figure 2.
SEM images of the zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) at different magnitudes. (a) ZnO NPs/HIS; (b) ZnO NPs/HIL; (c) ZnO NPs/HIF.
Closer looks at the images showed some individual crystals and, at the same time, some of the NPs with agglomeration. Synthesized NPs mostly appeared as quasi-spherical shaped (Figure 2a,c), and in one case, flower-shaped NPs were also observed (Figure 2b). Flower-like NP clusters were more likely formed by linking the bases of the crystals with a roughly spherical shape. The flower shape was highly visible in ZnO NPs/HIL, whereas spherical NPs were prominent in ZnO NPs/HIS and ZnO NPs/HIF. The cross-sectional diameter of biogenic NPs was 89.04 ± 7.54 nm, 93.00 ± 39.47 nm, and 84.05 ± 9.60 nm in ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF respectively.
Previous studies showed that hexagonal, rod, spherical, spongy, triangle, radial, and rectangle-shaped ZnO NPs have been commonly obtained through [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O in green synthesis [3,4,15,17,20,67]. However, few reports have indicated the formation of flower-shaped ZnO NPs [15,32]. Further, some reports suggest that annealing temperature could affect the morphology of the NPs [1,32].
The XRD analysis was used to examine the crystal phases and the crystallinity of the synthesized ZnO NPs. XRD spectra of the biosynthesized ZnO NPs from each part of plant extracts are shown in Figure 3. ZnO NPs exist in two crystallographic forms called zinc blend and wurtzite. However, at ambient conditions, wurtzite crystal structure is common [56].
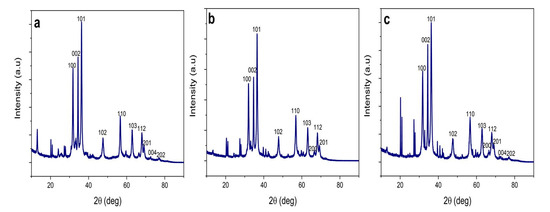
Figure 3.
X-ray diffractograms of biosynthesized ZnO NPs. (a) ZnO NPs/HIS; (b) ZnO NPs/HIL; (c) ZnO NPs/HIF.
According to ICDD data [15,26,68], the main peaks found correspond to Bragg reflections with 2θ values of 31.75, 34.39, 36.19, 47.57, 56.58, 62.83, 66.28, 67.88, 69.01, 72.47, and 76.81. These Bragg reflections were indexed to (100), (002), (101), (102), (110), (103), (200), (112), (201), (004), and (202) crystal planes of ZnO hexagonal wurtzite phase structures, respectively. The location of the peaks was compared to literature values and the presence of ZnO NPs was confirmed [15,46,62,63]. In the present study, ZnO NPs obtained at 60 °C depict wurtzite structures prominently, but interestingly, peaks responsible for zinc blend structure are also shown in all the biosynthesized NPs [56].
The ZnO diffraction peaks were well-defined with high intensity and narrow width which indicates that the resulting biosynthesized ZnO NPs are highly crystalline. The average crystallite size (D) of ZnO NPs was found to be 31.29 nm, 52.55 nm, and 20.26 nm in ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF respectively, after being calculated using Debye–Scherrer’s equation [3,46,67]:
where D represents the crystal size; λ denotes the wavelength of the X-ray radiation, for CuKα; K is the Scherrer constant, θ defines the Bragg diffraction angle, and β stands for the Full-Width Half Maximum (FWHM).
As a complementary technique, the morphology, nature, and size of the biosynthesized ZnO NPs were further assessed by TEM. Analyses of TEM micrographs (Figure 4) revealed well-distributed spherical-shaped NPs of crystalline nature, and this characteristic can be explained by the presence of strong surface protecting ligands [14,21]. ZnO NPs exhibited a size range of 19–53 nm. The average PS was found to be 28.23 ± 14.02 nm, 53.12 ± 16.82 nm and 19.00 ± 5.36 nm in ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF, respectively.
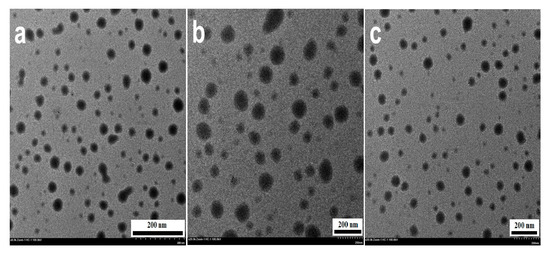
Figure 4.
TEM micrographs of biosynthesized ZnO NPs. (a) ZnO NPs/HIS; (b) ZnO NPs/HIL; (c) ZnO NPs/HIF.
The crystallinity and the PS determined by TEM are in good agreement with XRD data. In TEM analysis, NPs were distributed without aggregation which explained the smaller and more accurate average PS compared to that of SEM (besides TEM measure the NPs core radius in diameter).
The specific surface areas (SSA) of NPs were calculated by the Sauter formula [69]:
where SSA is the specific surface area, is the density of the synthesised ZnO NPs, and D is the PS. Thus, SSA of 0.42 , 0.05 , and 0.62 were obtained for ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF respectively. SSA is prime material property of NPs and the surfaces of the synthesized NPs are found to be large and hence can facilitate reactions on surfaces effectively.
2.4. Photocatalytic Activity of the Biosynthesized ZnO NPs
The quick pace of industrial development (e.g., paper, textile, tannery, pharmaceutical, plastic, and dye), leading to high production of organic pollutants, negatively contributes to the contamination of groundwater and/or surfaces [2,15,70,71,72,73]. Therefore, considerable attention has been focused on the photocatalytic purification of wastewater using semiconductor nanomaterials and the latest advancements of biogenic MONPs are listed in Table 1. Biogenic MONPs are considered as good photocatalysts due to their high photocatalytic efficiency, high physical and chemical stabilities, economic viability, nontoxicity, and cost-effectiveness [14,15,23,24,74,75].

Table 1.
Photocatalytic activity of biosynthesized metal oxide nanoparticles (MONPs).
During the photocatalytic degradation process, when a photocatalyst is exposed to light which contains stronger energy than its bandgap energy, the electron-hole pair generated on the surface of the semiconductor diffuses out to the surface and partakes in the chemical reaction with the electron acceptor, and donor. These free holes and electrons convert O2 and H2O, adsorbed on the surface of the ZnO nanostructures, into hydroxyl radicals (•OH), and superoxide radicals (O2•−). These radicals subsequently act as strong oxidizing agents for the degradation of dyes [2,15,22,32,71,73,74]. The schematic representation of methylene blue (MB)photocatalytic degradation in the presence of biosynthesized ZnO NPs is shown in Figure 5.
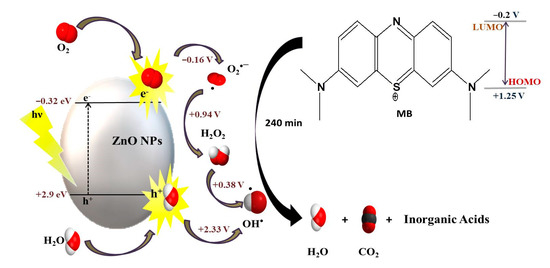
Figure 5.
Photocatalytic mechanism of biosynthesized ZnO NPs.
In this study, ZnO NP-mediated MB photodegradation was investigated in an aqueous solution under Sunlight irradiation. The UV-Vis absorbance plots were gathered to monitor the degradation of the MB dye over time (4 h) at RT by NPs in different physico-chemical conditions (i.e., by varying catalytic load, MB concentration, and pH) (Figure 6). Further, it was observed that the MB dye undergoes self-degradation (without the presence of a catalyst) in a course-time mode under sunlight (Figure 6 and Figure 7a).
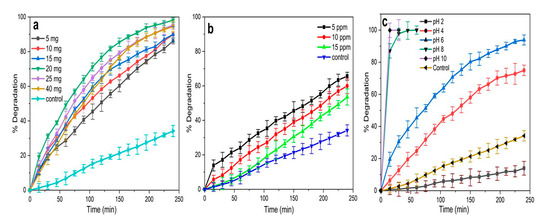
Figure 6.
Physico-chemical optimization parameters for photocatalytic degradation in the presence of ZnO NPs/HIS. (a) catalytic load (ZnO NPs/HIS); (b) MB concentration at a fixed catalytic load of 20 mg; (c) pH at a fixed catalytic load of 20 mg and fixed dye concentration (5 ppm).

Figure 7.
Time dependent absorption spectra of photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) dye under solar irradiation. (a) Control; (b) ZnO NPs/HIS; (c) ZnO NPs/HIL; (d) ZnO NPs/HIF.
Thereby, the effect of the catalyst load on the photodegradation efficiency of MB was studied by considering different amounts (i.e., 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 40 mg) of ZnO NPs into 50.00 mL of 5 ppm dye solution at pH 6 and RT (Figure 6a). These results demonstrated that the photodegradation efficiency of ZnO NPs/ HIS increases with an increased amount of NPs up to 20 mg (0.4 mg/mL). The enhancement of catalytic load led to an increased number of active sites available on the catalyst surface [15,22,24,71,74]. However, the photodegradation efficiency decreased when the catalyst load was above 20 mg, due to the accumulation and sedimentation of the NPs. Indeed, at the higher catalytic load of NPs, the NP sedimentation-induced turbidity and opacity of the suspension caused a decrease in light scattering through the reaction mixture resulting in poor degradation [15,24,74]. Interestingly, any amount of ZnO NPs/HIS was able to increase the degradation of MB dye compared with the test control (which was kept under Sunlight at pH 6 without the involvement of ZnO NPs) (Figure 6a).
Moreover, the effect of a fixed amount (20 mg) of ZnO NPs on photocatalytic degradation of MB was assessed against increased concentrations of the dye (i.e., 5, 10, 15 ppm) at pH 6, at RT, and under direct sunlight (Figure 6b). Interestingly, HIS-mediated NPs exhibited higher efficiency of photodegradation at the lowest concentration of the dye (i.e., 5 ppm). Increasing the initial dye concentration from 5 to 15 ppm caused a decrease in the efficiency of NP-mediated photocatalytic degradation, demonstrating that such an effect was dependent on the MB dye concentration. Still, at 15 ppm MB, it is worth mentioning that the catalyst is more efficient than the control (reaction mixture without ZnO NPs) due to the production of •OH and O2•− which accelerate MB photodegradation [2,15,22,24,32].
Since there is a paucity of reports related to the evaluation of the acidity/alkalinity effect in the reaction mixture, the effect of pH on ZnO NP-mediated photocatalytic degradation of MB was studied at fixed levels of dye (5 ppm) and catalyst (20 mg) by varying the pH from 2 to 10 at RT (Figure 6c). ZnO NPs tend to dissolve at acidic conditions (pH 2 and 4) leading to a poor photocatalytic degradation of MB, whereas the highest rate of MB degradation was obtained in alkaline conditions (pH 8 and 10). According to the literature, this can be explained based on zero potential charge [14,24,31,74]. Due to the difficulty in monitoring the reaction at pH 8 and 10, pH 6 was then selected as the medium of pH to conduct the degradation assay of MB dye.
At the optimized conditions (20 mg catalyst except for control, 5 ppm MB, pH 6, at RT), the catalytic effect was eventually monitored up to 240 min (Figure 7a–d). As evoked earlier, compared to the control (Figure 7a), all the biogenic ZnO NPs were able to increase the photodegradation of the MB dye in a time-dependent manner (Figure 7b–d).
Studies suggest that semiconductor NPs with a radius below 50 nm are most effective, and this is a critical parameter that affects the lifetime and regeneration of a nanocatalyst [32]. The different phytochemicals present in HIS, HIL, and HIF produce semiconducting NPs with different morphologies and sizes, which contributed, to some extent, in the varying effect of the photodegradation.
The degradation efficiency (%) was calculated using the below-mentioned equation [14,15,24,32,74]:
where C0 is the initial concentration of MB dye solution (mg.L−1) and C, the concentration of the MB dye solution (mg.L−1) after a certain time of irradiation.
The half-life of the MB dye degradation by biosynthesized NPs was calculated according to the previously published literature [15,32]. The plots were generated for the change of C/C0 and during the time course (from 0 to 240 min) and the half-life of the ZnO NP-mediated MB degradation was taken at the crossover point of each plot (Figure 8).
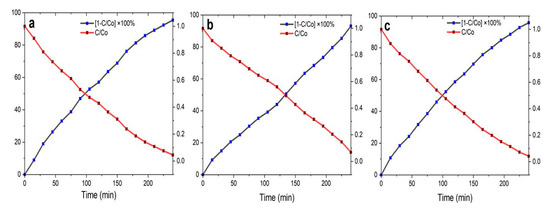
Figure 8.
Half-life photocatalytic degradation plots obtained for MB dye. (a) ZnO NPs/HIS; (b) ZnO NPs/HIL; (c) ZnO NPs/HIF.
Importantly, when the MB dye solution was exposed to the sunlight for 240 min in the presence of the biosynthesized ZnO NPs, the degradation efficiency of MB dye reached more than 93%. Indeed, the highest degradation (95.1%) was obtained for ZnO NPs/HIF with a half-lifetime of 100 min, negligibly followed by ZnO NPs/HIS (95.0%) with a half-lifetime of 97.30 min, and ZnO NPs/HIL (93.1%) with a longer half-lifetime (135 min).
Further, obtained degradation efficiencies show a direct relationship with shape, PS, SSA, and photoluminescence data of ZnO NPs. SSA has particular importance in adsorption, nano-catalysis and reactions on NPs surfaces [69]. From the obtained results, HIF-mediated ZnO NPs that show lower PS and higher SSA (0.62) and surface defects (reduce the recombination of electron–hole) indicate that the highest catalytic degradation facilitates radicals to interact with MB efficiently. Moreover, spherical-shape NPs (ZnO NPs/HIS and ZnO NPs/HIF) show higher catalytic efficiency than flower-shape ZnO NPs/HIL. Altogether, these data clearly suggest a strong photostability of ZnO NPs synthesized from different part extracts of the same plant (Table 2).

Table 2.
Green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) on methylene blue (MB) photocatalytic efficiency and half-lifetime.
2.5. PL Activity of Synthesized ZnO NPs
The understanding of the incorporation and behavior of naturally occurring intrinsic defects in ZnO NPs is essential to develop optoelectronic devices [28]. PL spectroscopy is a sensitive and non-destructive technique, useful to evaluate the quality and physical parameters of semiconductor materials (i.e., identification of extrinsic and intrinsic point defects) [13]. The PL study is therefore identified as a useful method for determining the efficiency of charge carrier separation in semiconductors [15,16,28].
Thereby, PL emission spectra were determined for the biosynthesized ZnO NPs, using HIL, HIS, and HIF, as capping material and compared to chemically synthesized ZnO NPs, used as control (Figure 9). Interestingly, the data revealed higher PL intensity for all biogenic ZnO NPs compared to that of the chemically synthesized ZnO NP-induced PL (Figure 9). However, the PL emission intensity observed for H. indicum-mediated ZnO NPs was found to be significantly lower compared with ZnO NPs synthesized from T. purpurea [15].
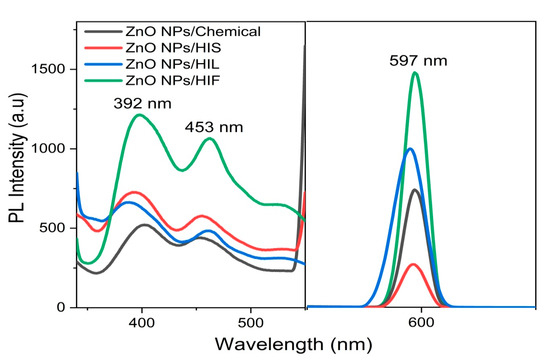
Figure 9.
Photoluminescence (PL) emission spectrums of ZnO NPs at a fixed excitation wavelength of 295 nm.
All ZnO NP-induced PL showed three emission peaks centered at 392, 453, and 597 nm when the material was excited at 295 nm (Figure 9). The emission peak at 392 nm is believed to originate from the electron transition from the localized level slightly below the conduction band to the valence band [1,15]. Additionally, some authors have reported an emission around 392 nm as near band edge emission [1,55]. Moreover, the emission peak at 453 nm was attributed to deep level defect states originating from the zinc interstitials and/or oxygen vacancies [15,23,55]. Indeed, previous studies have reported that the green emission corresponding to 495–530 nm was due to oxygen deficiencies, zinc interstices, and structural defects [1,31]. The oxygen required to compensate the singly ionized oxygen vacancies, responsible for the green emission, could be supplied by the phytochemical constituents adsorbed by ZnO NPs. Therefore, it cannot be observed in the PL spectra related to the biogenic NPs. Eventually, the green fluorescence at 597 nm may have resulted from the quantum confinement effect [15,16].
2.6. FRET Ability of Biosynthesized ZnO NPs
Interaction of NPs with dyes has gained much attention since the optical properties of a fluorescent molecule can both affect the local electric field surrounding them and manipulate the radiative and non-radiative decay of fluorescent dyes [35,36,41].
In FRET, two different dyes are used; one (the “donor”) must be fluorescent while the other (the “acceptor”) could be fluorescent/non-fluorescent. By choosing dyes with the appropriate spectral characteristics, the donor excited by light can transfer energy to the acceptor. The efficiency of energy transfer strongly depends on the distance between two dyes which is approximately 10–75 Å for reasonable energy transfer [33,34,37]. This mechanism is operated through non-radioactive induced dipole-induced dipole interactions [33,34]. If the amount of energy transfer is known, it is then possible to determine the distance between donor and acceptor. FRET has wide applications in biochemistry, polymer science, and structural biology [15,33,35,37]. Among the numerous classes of highly fluorescent dyes, Fluorescein (Flu) and Rhodamine B (RhB) are attractive due to their excellent photophysical properties such as high absorption coefficient, high quantum yield, high photostability, and relatively long emission wavelength [35]. Flu and RhB show maximum absorbance at around 475 nm and 525 nm with the prominent monomer fluorescence band around 510 nm and 552 nm, respectively [15,33,41].
Therefore, the FRET process was conducted using a mixture of two dyes, Flu (donor) and RhB (acceptor), which both were prepared in MeOH solution in the presence and absence of the green synthesized ZnO NPs. Then, the fluorescence emission was recorded and compared with the non-treated dye mixture used as control. The analysis was carried out at a fixed excitation wavelength of 430 nm which was chosen to excite Flu and avoid the direct excitation of RhB and ZnO NPs. Therefore, the fluorescence from ZnO NPs could not affect the FRET process significantly.
As shown in Figure 10, Flu-RhB showed prominent fluorescence enhancement with an increase in the concentration of ZnO NPs. The FRET efficiency was calculated by using the following formula (at 1000 µg/mL of NPs) [15,37]:
where FAD is the relative fluorescence intensity of the donor in the presence of the acceptor and FD is the fluorescence intensity of the donor in the absence of the acceptor. ZnO NPs/HIL showed the best energy transfer efficiency (80%), followed by ZnO NPs/HIF (70%) and ZnO NPs/HIS (37%) (Figure 10). Compared to that of T. purpurea-mediated ZnO NPs, the FRET efficiency observed for 1000 mg of ZnO NPs biosynthesized from H. indicum extracts is significantly low [15].
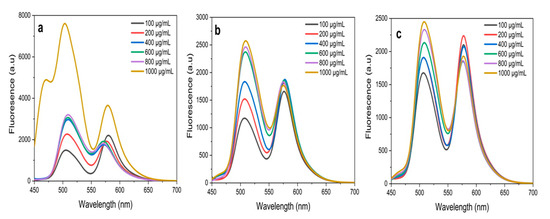
Figure 10.
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) spectrums obtained for Fluorescein (Flu)/ Rhodamine B (RhB) dye mixture in the presence of ZnO NPs at an excitation wavelength of 430 nm.(a) ZnO NPs/HIS; (b) ZnO NPs/HIL; (c) ZnO NPs/HIF.
To have a solid understanding of FRET, sufficient spectral overlap of the fluorescence of Flu and/or RhB with/without HIL-incorporated NPs at the highest concentration (1000 µg/mL) is depicted in Figure 11. Interestingly, it was noted that the fluorescence intensities of Flu and RhB increase in the presence of ZnO NPs compared to pure counterparts. Further, it can be concluded that RhB fluorescence enhancement was insignificant compared to donor fluorescence in the presence of ZnO NPs. These data demonstrated that the fluorescence spectrum of Flu-RhB mixed solution, the fluorescence intensity of Flu decreases, and RhB fluorescence increases due to the light absorption by Flu molecule which did transfer the energy to RhB via FRET. Importantly, the biogenic ZnO NPs were found to display fluorescence enhanced capability and strongly contributed to the energy transfer process between Flu and RhB most likely by reducing the distance between the two dyes.
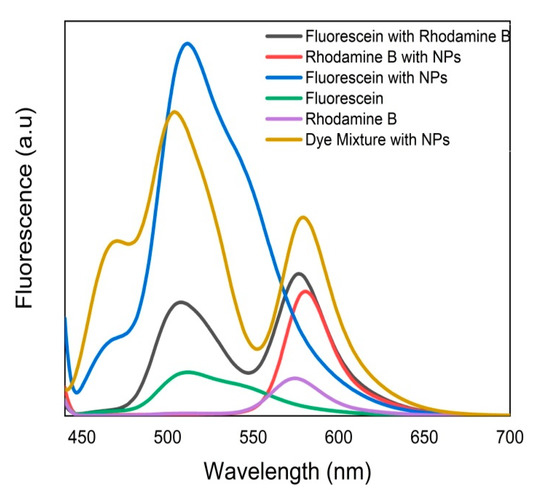
Figure 11.
Variation of fluorescence emission intensity of Flu and/or RhB in the presence of ZnO NPs/HIL (1000 µg/mL) at an excitation wavelength of 430 nm.
3. Materials and Methodology
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Zinc acetate dihydrate (Anala R grade), and fluorescein were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Mumbai, India. Sodium hydroxide pellet (Anala R grade), hydrochloric acid (Anala R grade), and methylene blue were purchased from Sisco research laboratories (Pvt) Ltd., New Mumbai, India. Nylosan rhodamin E-BP300 was purchased from Prym Intimates Lanka (Pvt) Ltd., Biyagama, Sri Lanka. Methanol (Anala R grade) was obtained from BDH Industries Ltd., Mumbai, India.
3.2. Instruments
UV-Vis spectrophotometer (U-2910, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), FTIR spectrometer (Horizon ABB-MB 3000 ATR FT-IR, Ottawa, ON, Canada), Advance vortex mixture (VELP Scientifica ZX3, Usmate Velate, Italy), Spectrofluorometer (F-2700 FL Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), SEM (Carl Zeiss, Evo, CA, USA), TEM (Hitachi H-600, Tokyo, Japan), XRD (Bruker D8 Advance, Tokyo, Japan), Centrifuge (GEMMYCO, PLC-036H, Shandong, China), Analytical balance (RADWAG Wagi Electroniczne, AS-220. R2, Radom, Poland), Oven (universal oven-UN 55, Zwickau, Germany), and pH meter (Jenway, 3510, Mainz, Germany).
3.3. Collection of H. indicum and Preparation of Extracts
The whole plant of H. indicum was collected from different areas of Anuradhapura district, Kurundankulama, Sri Lanka. A sample of plant material was taxonomically identified by National Herbarium, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
The collected plant materials were cleaned by washing several times with running water and subsequently with DI H2O. After dividing the plant into parts of interest, i.e., HIS, HIL, and HIF, they were dried at RT in shade for 14 days until all moisture was lost. Then, the parts of the plant were pulverized by a mechanical grinder. The powder was then stored in an airtight container at RT. For use, 5 g of the finely grounded stems and inflorescences of H. indicum and 2.5 g of H. indicum leaves were separately added to 100 mL of DI H2O. The solution was then heated to 40 °C with constant stirring for 30 min. The resulting extracts were cooled to RT, filtered using Whatman® Grade 1 filter (Ansell Lanka (Pvt) Ltd, Biyagama, Sri Lanka) paper to separate the plant material from the aqueous extract.
3.4. Optimization of Parameters for ZnO NPs Synthesis
The synthesis conditions were optimized for HIS, HIL, and HIF extracts of the plant by varying parameters involved in the synthesis (i.e., concentration of metal, volume of plant extract). Other critical factors (i.e., pH, temperature, and reaction time) were optimized only for HIS and were considered for other plant part extracts because further spectrophotometrically obtained data indicated similar detection of pure synthesized NPs. Thereby, a range of concentrations of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O, varying from 0.01 M to 0.05 M, was used as substrate. Different volumes of plant extract, varying from 0.50 mL to 3.00 mL, were added to 50.00 mL of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O solution. The mixture was stirred continuously using a magnetic stirrer, and optimum stirring time was identified by varying the time from 0.5 to 3 h. The pH of the mixture was optimized by increasing pH values gradually from 9 to 13 using a 2 M NaOH solution. The temperatures were set up either at 50, 60, 80, or 100 °C.
3.5. Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs
For the green synthesis of ZnO NPs, [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O (0.01 M) was first prepared in 50.00 mL of DI H2O under constant stirring for 10 min, followed by the addition of 1.00 mL of plant extract. The pH was then adjusted to 12 using 2 M NaOH, which resulted in a pale white solution. The solution was kept under vigorous stirring for 2 h, after which the synthesized NPs were collected by centrifugation at 4500× g rpm for 15 min. The supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was washed with DI H2O followed by MeOH to remove the impurities. The pale white powder was dried at 60 °C in an oven overnight, and preserved in airtight vials for further studies. ZnO NPs synthesized via H. indicum stems, leaves and inflorescences were denoted as ZnO NPs/HIS, ZnO NPs/HIL, and ZnO NPs/HIF respectively.
3.6. Physical Characterization of ZnO NPs
UV-Vis spectroscopy was used to observe the optical properties of ZnO NPs at RT in the range of 200–800 nm. FTIR was used to analyze the functional groups present both in the plant extracts and the synthesized ZnO NPs using the technique of Attenuated Total Reflectance in the range of 400–4000 cm−1. The size, shape, and morphology of synthesized NPs were analyzed using SEM, and TEM. The crystalline structure and phase purity were analyzed by XRD.
3.7. Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO NPs
Photocatalytic degradation of MB was carried out under direct Sunlight between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. when there were minimum fluctuations in solar intensity (outside temperature was 29–33 °C and average solar radiation was 2.11).To a 50.00 mL of dye solution (5 mg L−1), 20 mg of ZnO NPs were added, and the pH was adjusted to 6. Prior to exposure to Sunlight, the suspension was magnetically stirred in the dark for 30 min. The concentration of residual MB in the solution after irradiation was determined by monitoring the absorbance intensity of solution samples by withdrawing 5.00 mL aliquots from the reaction mixture at every 15 min interval. It was then centrifuged to remove all nanocatalysts from the solution, and the absorbance was recorded at 662.8 nm by using UV–Vis spectrophotometer to assess the rate of percentage degradation.
The same experimental procedure was repeated with varying different experimental parameters such as the catalytic load (2, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 40 mg), the dye concentration (5, 10, and 15 ppm), and pH (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10).
3.8. PL of the Synthesized ZnO NPs
PL measurements of the synthesized ZnO NPs were carried out at RT using a solid sample by spectrofluorometer. The light intensity over the cell surface was changed by varying the slit length. The PL of the biogenic ZnO NPs was compared to the sample of chemically synthesized ZnO NPs following the procedure of previously published works [16,28], and from which we used appropriate modifications to chemically synthesized ZnO NPs [14,45].
3.9. FRET Activity of the Synthesized ZnO NPs
The FRET ability, exerted by ZnO NPs in the presence of Flu and RhB dyes, was evaluated by fluorescence spectrometry. MeOH was used as solvent throughout the whole experiment including for washing and sampling. The concentration series of ZnO NPs, synthesized from HIS, HIL, and HIF were prepared in MeOH from 50 μg mL−1 to 1000 μg mL−1. A solution containing 5 × 10−4 mol dm−3 Flu and 5 × 10−5 mol dm−3 RhB was prepared in MeOH, and 1.00 mL of NPs dispersion from each concentration was mixed with 400 µL of each dye solution making the final volume up to 1800 µL. The treated solutions were mixed thoroughly, and the fluorescence spectra were recorded while the emission wavelength was scanned from 450 nm to 700 nm at fixed excitation of 430 nm.
4. Conclusions
For the first time, pure, and multifunctional ZnO NPs with well faceted, hexagonal, and spherical shapes were produced successfully in an eco-friendly and cost-effective manner using various parts of H. indicum, a traditional medicinal plant native to Sri Lanka. The hypsochromic shifted UV-Vis absorption peak was observed at the range of 350 nm to 380 nm confirming the intrinsic bandgap of ZnO NPs. SEM and TEM images depicted identical morphology of ZnO NPs with spherical shapes. The crystallite size calculated from Scherrer’s formula was in good agreement with that of the average PS estimated from TEM analysis. However, there was a small variation between PS evaluated from XRD and TEM analysis and those obtained from SEM which can be attributed to agglomeration in NPs. XRD patterns revealed a single-phase, hexagonal wurtzite structure and the crystalline nature of NPs. FTIR analysis elucidated the involvement of alcohol, amide, amine, alkane, and carboxylic acid moieties in the stability of NPs production. Moreover, the green synthesized ZnO NPs elicited a fascinating photocatalytic degradation of MB, and the highest photocatalytic performance (about 95%) was observed with ZnO NPs synthesized from H. indicum stems and inflorescences extracts. The PL properties of the ZnO NPs were a strong function of the excitation intensity. The behavior of ZnO NP-mediated PL intensities was higher and asymmetric compared with the chemically synthesized ZnO NPs. To the best of our knowledge, ZnO NP-mediated FRET between Flu and RhB was evaluated for the first time using H. indicum, and confirmed the role of the biogenic ZnO NPs as potent intermediate energy molecules capable of successfully transferring energy from Flu to RhB. Moreover, enhanced photocatalytic and electro-chemical activities of the phytosynthesized NPs are noteworthy and the diversity of NPs morphology caused different effectiveness towards same application by various parts of the plant.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal11070831/s1, Figure S1: Effect of [Zn(CH3COO)2].2H2O concentrations for the biosynthesis of ZnO NPs, Figure S2: Effect of volume-dependent concentrations of plant extracts on ZnO NPs synthesis, Figure S3: Effect of critical physical parameters for ZnO NPs/HIS synthesis, Figure S4: FTIR spectrograms of plant part, and derived extract mediated ZnO NPs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization; G.T.; Data Curation; G.T., U.W., F.M.; Formal analysis G.T., U.W., F.M., A.R.; Funding acquisition G.T.; Investigation G.T., U.W.; Methodology G.T., U.W., H.I., F.M.; Project administration G.T.; Resources G.T.; Software G.T., U.W., H.I.; Supervision G.T.; Validation G.T., F.M.; Visualization G.T.; Roles/Writing—original draft G.T., U.W.; Writing—review & editing G.T., U.W., F.M.; APC Support: G.T., F.M., H.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by College of Chemical Sciences, Institute of Chemistry Ceylon, Sri Lanka.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
College of Chemical Sciences, Institute of Chemistry Ceylon, Sri Lanka, is acknowledged for their continued support.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| DI H2O | Deionized water |
| Flu | Fluorescein |
| FRET | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| H. indicum | Heliotropium indicum |
| MB | Methylene blue |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MONPs | Metal oxide nanoparticles |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| O2•− | Superoxide radicals |
| •OH | Hydroxyl radicals |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| PS | Particle size |
| PSD | Particle size distribution |
| RhB | Rhodamine B |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SSA | Specific surface area |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-Visible |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
References
- Parra, M.R.; Haque, F.Z. Aqueous chemical route synthesis and the effect of calcination temperature on the structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-F.M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Sone, M.; Hsu, Y.-J. Mechanistic Insights into Photodegradation of Organic Dyes Using Heterostructure Photocatalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2018, 30, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, H.; Kumar, S.V.; RajeshKumar, S. A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles—An eco-friendly approach. Resour. Technol. 2017, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, K.; Sundarraj, S.; Paulpandi, M.; Vengatesan, S.; Kannan, S. Green synthesized doxorubicin loaded zinc oxide nanoparticles regulates the Bax and Bcl-2 expression in breast and colon carcinoma. Process. Biochem. 2014, 49, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Ndiaye, S.; Mothudi, B.M.; Ishaq, A.; Rajendran, V.; Maaza, M. Structural, optical and photocatalytic applications of biosynthesized NiO nanocrystals. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perera, K.M.K.G.; Kuruppu, K.A.S.S.; Chamara, A.M.R.; Thiripuranathar, G. Characterization of spherical Ag nanoparticles synthesized from the agricultural wastes of Garcinia mangostana and Nephelium lappaceum and their applications as a photo catalyzer and fluorescence quencher. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminuzzaman, M.; Kei, L.M.; Liang, W.H. Green synthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their photocatalytic activities. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyothi, P.; Cha, S.J.; Yang, I.J.; Sreekanth, T.; Kim, K.J.; Shin, H.M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Polygala tenuifolia root extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 146, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, L.S.R.; Lingaraju, K.; Prasad, B.D.; Kavitha, C.; Banuprakash, G.; Nagaraju, G. Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles: Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, T.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Degradation of organic pollutants by bio-inspired rectangular and hexagonal titanium dioxide nanostructures. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 169, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.; Crespo, J.D.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of the synthesis methodology and mechanism of formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavalingiah, K.R.; Harishkumar, S.; Nagaraju, G.; Rangappa, D. Highly porous, honeycomb like Ag–ZnO nanomaterials for enhanced photocatalytic and photoluminescence studies: Green synthesis using Azadirachta indica gum. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.A.; Ravikumar, C.; Nagaswarupa, H.; Purshotam, B.; Gonfa, B.; Murthy, H.A.; Sabir, F.K.; Tadesse, S. Evaluation of bi-functional applications of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by green and chemical methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Iqbal, H.; Menaa, F. Biomimetic Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer, Photoluminescence, and Photocatalytic Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, D.; Shobharani, R.; Nethravathi, P.; Kumar, M.P.; Bhushana, N.; Sharma, S. Artocarpus gomezianus aided green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Luminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant properties. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 141, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications–An updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, D.; Verduin, J.; Shah, M.; Sharma, S.B.; Poinern, G.E.J. A Review of Current Research into the Biogenic Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via Marine Algae and Seagrasses. J. Nanosci. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, N.; Prasad, T.N.V.K.V.; Krishna, T.G.; David, E. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark-extract-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nithya, K.; Kalyanasundharam, S. Effect of chemically synthesis compared to biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of C. halicacabum and their antibacterial activity. OpenNano 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.F.; Rehman, M.; Hussain, S.Z.; Huma, Z.-E.; Shahnaz, G.; Qureshi, O.S.; Khalid, Q.; Mirza, S.; Hussain, I.; Webster, T.J. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Neem extract as multi-facet therapeutic agents. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, D.; Nethravathi, P.; Rajanaika, H.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S. Green synthesis of multifunctional zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Cassia fistula plant extract and their photodegradative, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Bharath, G.; Banat, F.; Show, P.L. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Phoenix dactylifera waste as bioreductant for effective dye degradation and antibacterial performance in wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nethravathi, P.; Shruthi, G.; Suresh, D.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S. Garcinia xanthochymus mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Photoluminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant activity studies. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8680–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarirad, S.; Mehrabi, M.; Divband, B.; Kosari-Nasab, M. Biofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using fruit extract of Rosa canina and their toxic potential against bacteria: A mechanistic approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, K.S.; Reddy, A.R.; Sujatha, C.; Reddy, K.V. Optimization of UV emission intensity of ZnO nanoparticles by changing the excitation wavelength. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talakonda, P.R. Excitation-Intensity (EI) Effect on Photoluminescence of ZnO Materials with Various Morphologies. In Luminescence—An Outlook on the Phenomena and Their Applications; Thirumalai, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amini, M.; Ashrafi, M. Photocatalytic degradation of some organic dyes under solar light irradiation using TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Nano. Chem. Res. 2016, 1, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Thandapani, K.; Kathiravan, M.; Namasivayam, E.; Padiksan, I.A.; Natesan, G.; Tiwari, M.; Giovanni, B.; Perumal, V. Enhanced larvicidal, antibacterial, and photocatalytic efficacy of TiO2 nanohybrids green synthesized using the aqueous leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 10328–10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.E.; Pozina, G.; Willander, M.; Nur, O. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by co-precipitation method for solar driven photodegradation of Congo red dye at different pH. Photon. Nanostructures Fundam. Appl. 2018, 32, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppu, K.A.S.S.; Perera, K.M.K.G.; Chamara, A.M.R.; Thiripuranathar, G. Flower shaped ZnO—NPs; phytofabrication, photocatalytic, fluorescence quenching, and photoluminescence activities. Nano Express 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Roy, A.D.; Dey, D.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Paul, P.K.; Das, R.; Hussain, S.A. Effect of Zinc oxide nanoparticle on Fluorescence Resonance Energy transfer between Fluorescein and Rhodamine 6G. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 175, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Roy, A.D.; Dey, D.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Hussain, S.A. Role of quantum dot in designing FRET based sensors. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, M.E.M.; Kana, M.T.H.A.; Fattah, G.A. Fluorescence enhancement monitoring of pyrromethene laser dyes by metallic Ag nanoparticles. Luminescence 2014, 29, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovmachenko, O.G.; Graf, C.; Heuvel, D.J.V.D.; Van Blaaderen, A.; Gerritsen, H.C. Fluorescence Enhancement by Metal-Core/Silica-Shell Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Hussain, S.A. Development of hard water sensor using fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xiong, H.-M. Photoluminescent ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Biological Applications. Materials 2015, 8, 3101–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lai, E.P. Fluorescence Detection of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Water Contamination Analysis based on Surface Reactivity with Porphyrin. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2018, 5, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Cheng, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Fluorescence Property of ZnO Nanoparticles and the Interaction with Bromothymol Blue. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 21, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalele, S.; Deshpande, A.C.; Singh, S.B.; Kulkarni, S.K. Tuning luminescence intensity of RHO6G dye using silver nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Arshad, M.; Chaudhari, S.K. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Revolutionizing Agriculture: Synthesis and Applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide—From Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnanasangeetha, D.; Thambavani, D. Biogenic Production of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Acalypha Indica. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. 2014, 4, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, D.; Mustafa, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using Zinc Acetate Dihydrate and Sodium Hydroxide. J. Nanosci. Nanoeng. 2015, 1, 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mishra, K.; Khanuja, M.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safawo, T.; Sandeep, B.; Pola, S.; Tadesse, A. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using tuber extract of anchote (Coccinia abyssinica (Lam.) Cong.) for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity assessment. OpenNano 2018, 3, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažeka, D.; Car, J.; Klobučar, N.; Jurov, A.; Zavašnik, J.; Jagodar, A.; Kovačević, E.; Krstulović, N. Photodegradation of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B Using Laser-Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles. Materials 2020, 13, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, G.K.; Murthy, P.N. Studies on Wound Healing Activity of Heliotropium indicum Linn. Leaves on Rats. ISRN Pharmacol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adjagba, M.; Awede, B.; Osseni, R.; Dougnon, G.; Dosseh, W.; Lagnika, L.; Darboux, R.; Laleye, A. Effects of crude aqueous extracts of Heliotropium indicum Linn (Boraginaceae) on blood pressure in Wistar rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 7, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourin, N.A.; Sharmin, T.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Islam, F.; Rahman, M.S.; Rashid, M.A. Evaluation of bioactivities of Heliotropium indicum, a medicinal plant of Bangladesh. Pharma. Innov. 2013, 2, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachitra, J.; Bharathim, M. In vitro studies on phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of Heliotropium indicum linn. Int. J. Res. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2016, 5, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, N.; Sharma, S. Bioactive phytoconstituents and plant extracts from genus Heliotropium. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Chowdhury, G. Pharmacological Activities of Indian Heliotrope (Heliotropium Indicum L.): A Review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015, 4, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Liu, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, P.; Yao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Jing, X. Photoluminescence studies from ZnO nanorod arrays synthesized by hydrothermal method with polyvinyl alcohol as surfactant. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2637–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseem, M.; Umar, A.; Hahn, Y. ZnO Nanoparticles: Growth, Properties, and Applications. In Metal Oxide Nanostructures and Their Applications; American Scientific Publishers: Stevenson Ranch, CA, USA, 2010; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Manokari, M.; Shekhawat, M.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using whole plant extracts of Cassia tora L. and their characterization. J. Sci. Achiev. 2017, 2, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alamdari, S.; Ghamsari, M.S.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Aslam, U.; Khalid, B.; Chen, B. Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasangeetha, D.; Saralathambavani, D. One Pot Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Chemical and Green Method. Res. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Koshy, J.; Samuel, M.S.; Chandran, A.; George, K.C. Optical Properties of CuO Nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1391, 576–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.K.; Boruah, F.; Parween, N. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles using Leaf Extract of Camellia sinesis and Evaluation of their Antimicrobial Efficacy. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R.; Długaszewska, J. Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suresh, J.; Pradheesh, G.; Alexramani, V.; Sundrarajan, M.; Hong, S.I. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticle using insulin plant (Costus pictus D. Don) and investigation of its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activities. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhoshkumar, J.; Kumar, S.V.; RajeshKumar, S. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resour. Technol. 2017, 3, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.T.; Ovais, M.; Ullah, I.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Khamlich, S.; Maaza, M. Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its biological applications. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1767–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, S.; Jamzad, M.; Fard, H.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comparison. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2019, 12, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingaraju, K.; Naika, H.R.; Manjunath, K.; Basavaraj, R.B.; Nagabhushana, H.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D. Biogenic synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruta graveolens (L.) and their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, B.; Barbhuiya, T.F. Studies on the density and surface area of nanoparticles from Camellia sinensis, A natural source. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2014, 6, 608–610. [Google Scholar]
- Fowsiya, J.; Madhumitha, G.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Photocatalytic degradation of Congo red using Carissa edulis extract capped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Azab, W.I.M.E.; Ali, H.R.; Mansour, M.S.M. Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of anthracene. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripireddy, B.; Mandal, B.K. Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathi, S.; Tatsugi, J.; Shin, P.-K.; Santhakumar, K. Facile biosynthesis, characterization, and solar assisted photocatalytic effect of ZnO nanoparticles mediated by leaves of L. speciosa. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 167, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Tahir, R.; Gillani, S.S.A.; Tahir, M.B.; Shakil, M.; Iqbal, T.; Abdellahi, M.O. Plant-mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Syzygium Cumini for seed germination and wastewater purification. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Ullah, Z.; Fazal, A.; Irfan, M. Use of Vegetable Waste Extracts for Controlling Microstructure of CuO Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Applications. J. Chem. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Sinha, T. A novel approach for the synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles and its application as a catalyst in the reduction and photodegradation of organic compounds. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishnoi, S.; Kumar, A.; Selvaraj, R. Facile synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using inedible Cynometra ramiflora fruit extract waste and their photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingaraju, K.; Naika, H.R.; Manjunath, K.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D.; Bhushana, N. Rauvolfia serpentina-Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles and Its Multidisciplinary Studies. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2015, 28, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).