Ca-Poisoning Effect on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3-CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts with Different Vanadium Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Activity
2.2. Characterization of Catalysts
2.2.1. XRD
2.2.2. BET and XPS
2.2.3. NH3-TPD
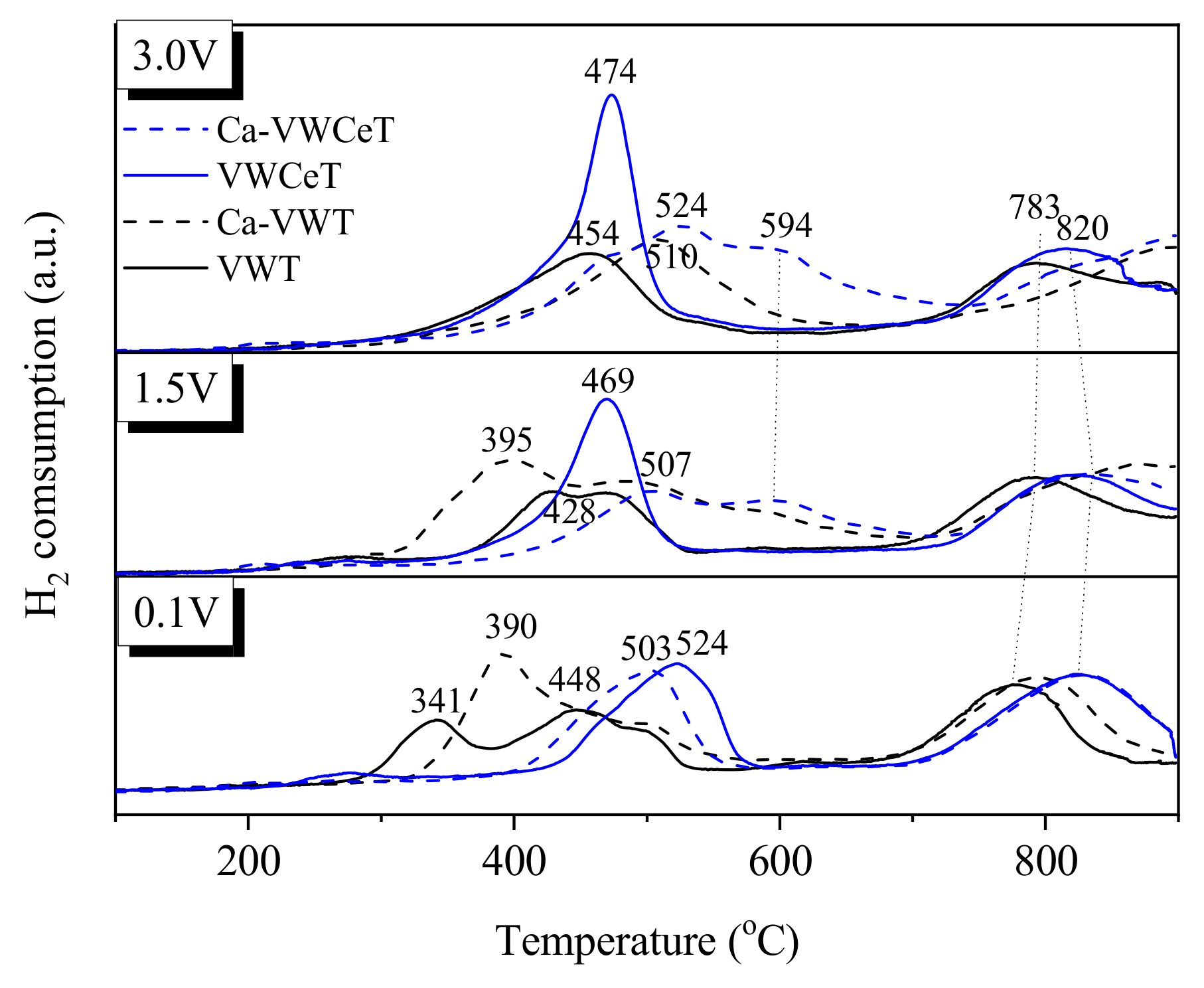
2.2.4. H2-TPR
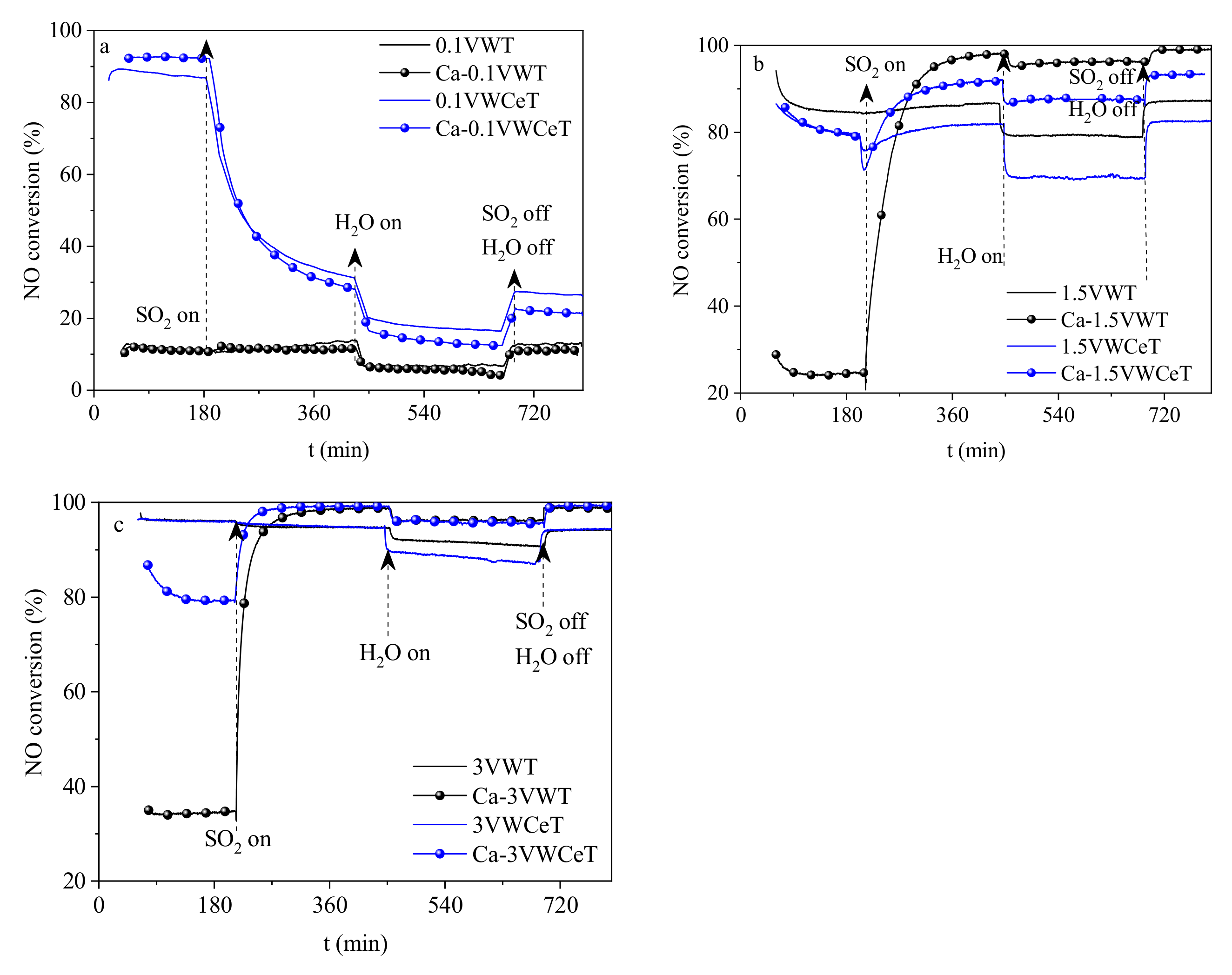
2.3. SO2 and Water Vapor Effect on Catalysts
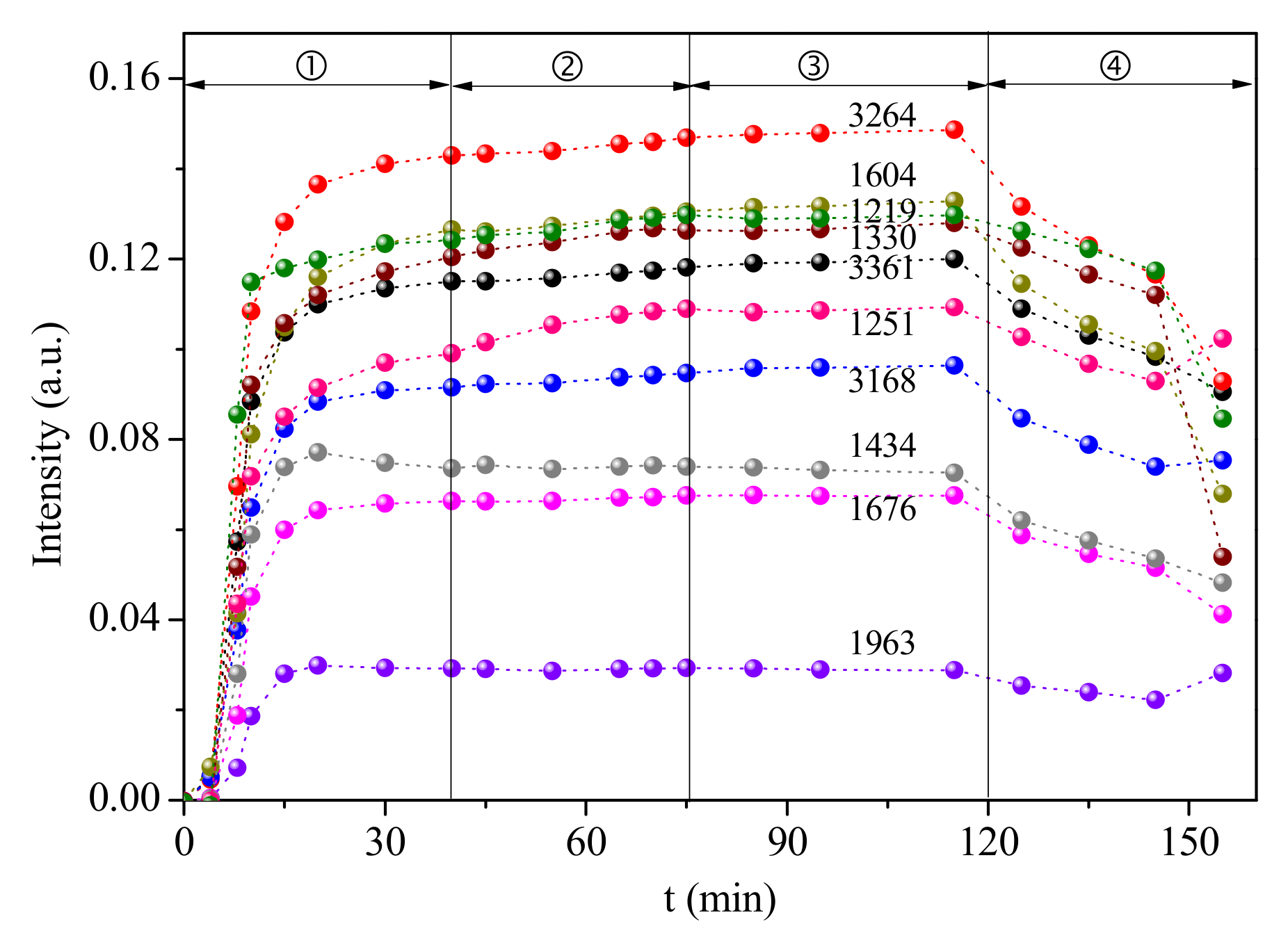
2.4. DRIFT Characterization of Adsorbed NH3
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalysts Pretreatment and Poisoning
3.2. Catalysts Characterization
3.3. Catalysts Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Mu, B.; Liu, P.; Luo, L.; Hao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T. Ammonia emission estimation for the cement industry in northern China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ihl Woo, S. Recent advances in catalytic deNOx science and technology. Catal. Rev. 2006, 48, 43–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröcher, O.; Elsener, M. Chemical deactivation of V2O5/WO3–TiO2 SCR catalysts by additives and impurities from fuels, lubrication oils, and urea solution: I. Catalytic studies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 77, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Chen, X.D.; Gu, J. Research on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) in cement kiln. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 864–867, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Jia, W. Review on the latest developments in modified vanadium-titanium-based SCR catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putluru, S.S.R.; Jensen, A.D.; Riisager, A.; Fehrmann, R. Heteropoly acid promoted V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for NO abatement with ammonia in alkali containing flue gases. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lu, J.; Hums, E.; Huang, Q.; Lu, Z. Study on the Deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Selective Catalytic Reduction Catalysts through Transient Kinetics. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 3890–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.L.; Qiang, S.; Qiang, Y. Mechanism study on the adsorption and reactions of NH3, NO, and O2 on the CaO surface in the SNCR deNOx process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Si, W.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J.; Li, X.; Crittenden, J.; Hao, J. Deactivation and regeneration of a commercial SCR catalyst: Comparison with alkali metals and arsenic. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Xu, B.; Shi, H.; Qiu, J.; Fan, Y. The poisoning effect of Na+ and Ca2+ ions doped on the V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 94, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Hao, J. An efficient novel regeneration method for Ca-poisoning V2O5 -WO3 /TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2016, 87, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, J.H.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.H.; Han, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, W. Alkali metal poisoning of a CeO2-WO3 catalyst used in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: An experimental and theoretical study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Alkali resistance promotion of Ce-doped vanadium-titanic-based NH3-SCR catalysts. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Weng, X. Deactivation mechanism of Ce/TiO2 selective catalytic reduction catalysts by the loading of sodium and calcium salts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Ma, L. Novel V2O5–CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with low vanadium loading for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158–159, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Yang, J.; Tian, Y.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Kong, M. Effect of Ce doping on the resistance of Na over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 104, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Tong, W.; Yang, J.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Tian, Y. K+ deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Effect of vanadium content. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, M. New insights into the role of vanadia species as active sites for selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia over VOX/CeO2 catalysts. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, L.; Mu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T. Ash and alkali-poisoning mechanisms for commercial vanadium-titanic-based catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22418–22426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xin, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L. Ce-Ti amorphous oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Confirmation of Ce-O-Ti active sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9600–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.S.; Li, J.H.; Hao, J.M. High calcium resistance of CeO2-WO3 SCR catalysts: Structure investigation and deactivation analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Ettireddy, P.R.; Somogyvari, A.; Liu, Y.; Vorontsov, A.; McDonald, C.A.; Smirniotis, P.G. Influence of elevated surface texture hydrated titania on Ce-doped Mn/TiO2 catalysts for the low-temperature SCR of NOx under oxygen-rich conditions. J. Catal. 2015, 325, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Liu, Y.; Weng, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. The enhanced performance of ceria with surface sulfation for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal. Commun. 2010, 12, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ding, J. New insight into the promoting role of process on the CeO2–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low-temperature. J. Coll. Interface 2015, 448, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ning, R.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, F. Ce-Doped V2O5-WO3/TiO2 with Low Vanadium Loadings as SCR Catalysts and the Resistance of H2O and SO2. Catal. Lett. 2019, 150, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Si, W.; Luo, J.; Dai, Q.; Luo, X.; Liu, X.; Hao, J. Insight into deactivation of commercial SCR catalyst by arsenic: An experiment and DFT Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13895–13900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Chang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Dispersion of tungsten oxide on SCR performance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2: Acidity, surface species and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Du, X.; Wan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ran, J.; Zhang, L. Alkali-driven active site shift of fast SCR with NH3 on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst via a novel Eley-Rideal mechanism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 6085–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. Improvement in activity and alkali resistance of a novel V-Ce(SO4)2/Ti catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 206, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjkhanlou, Y.; Janssens, T.V.W.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Mino, L.; Paganini, M.C.; Signorile, M.; Bordiga, S.; Berlier, G. Location and activity of VOx species on TiO2 particles for NH3-SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Han, J.W.; Kim, D.H. Chemisorption of NH3 on Monomeric Vanadium Oxide Supported on Anatase TiO2: A Combined DRIFT and DFT Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 16674–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-K.; Wachs, I.E. A Perspective on the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Supported V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6537–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsoe, N.Y.; Topsoe, H.; Dumesic, J.A. Vanadia/Titania catalysts for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitric-oxide by ammonia: I. Combined temperature-programmed in-situ FTIR and on-line mass-spectroscopy studies. J. Catal. 1995, 151, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topsøe, N. Mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia elucidated by in situ on-line fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Science 1994, 265, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Si, W.; He, X.; Hao, J. Regeneration of commercial SCR catalysts: Probing the existing forms of arsenic oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9971–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, W.; Yu, J.; Zeng, J.; Chang, H. Novel Methods for Assessing the SO2 Poisoning Effect and Thermal Regeneration Possibility of MOx-WO3/TiO2 (M = Fe, Mn, Cu, and V) Catalysts for NH3-SCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12612–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Yin, L.; Qiu, T.; He, C. Deactivation mechanism and feasible regeneration approaches for the used commercial NH3-SCR catalysts. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


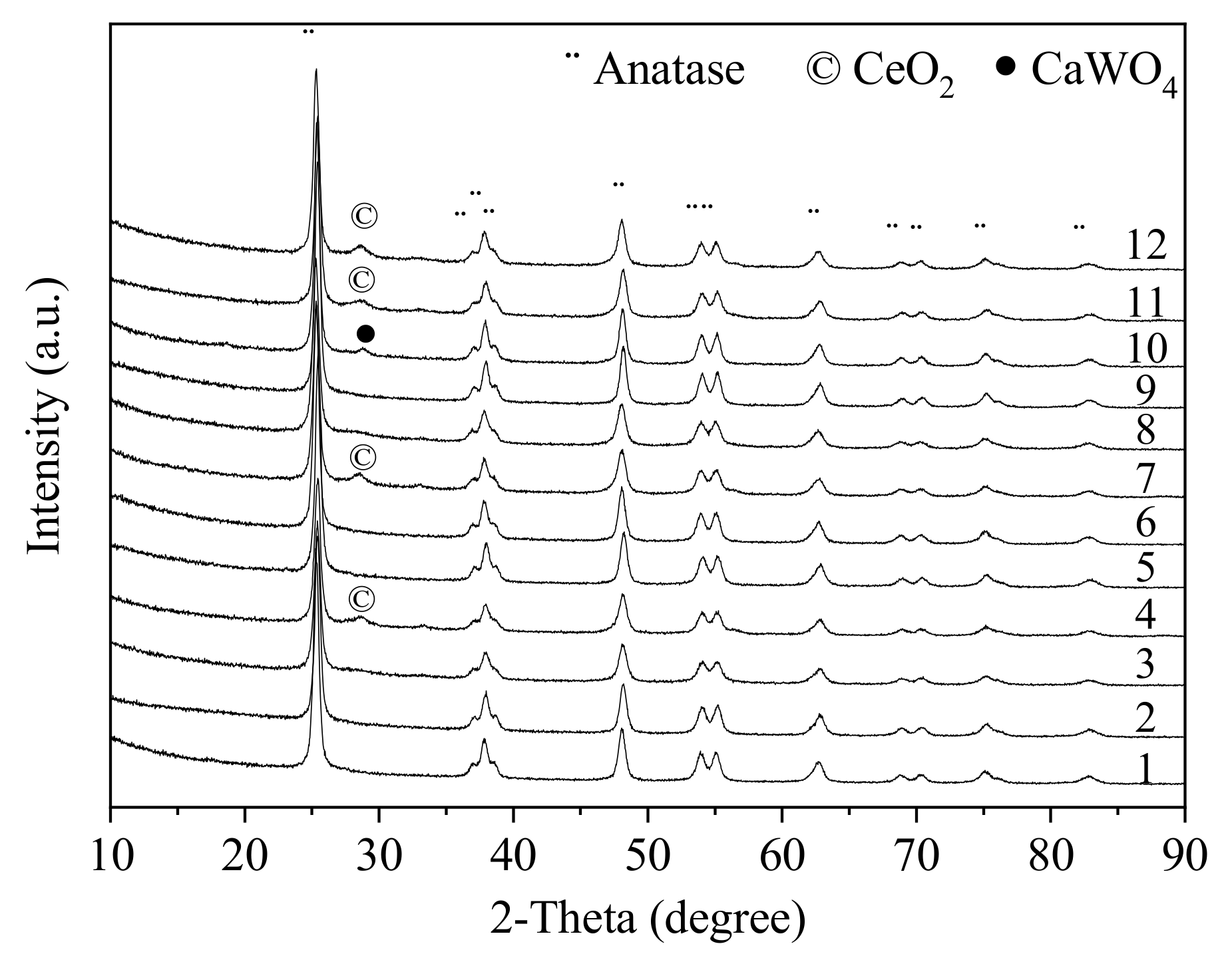
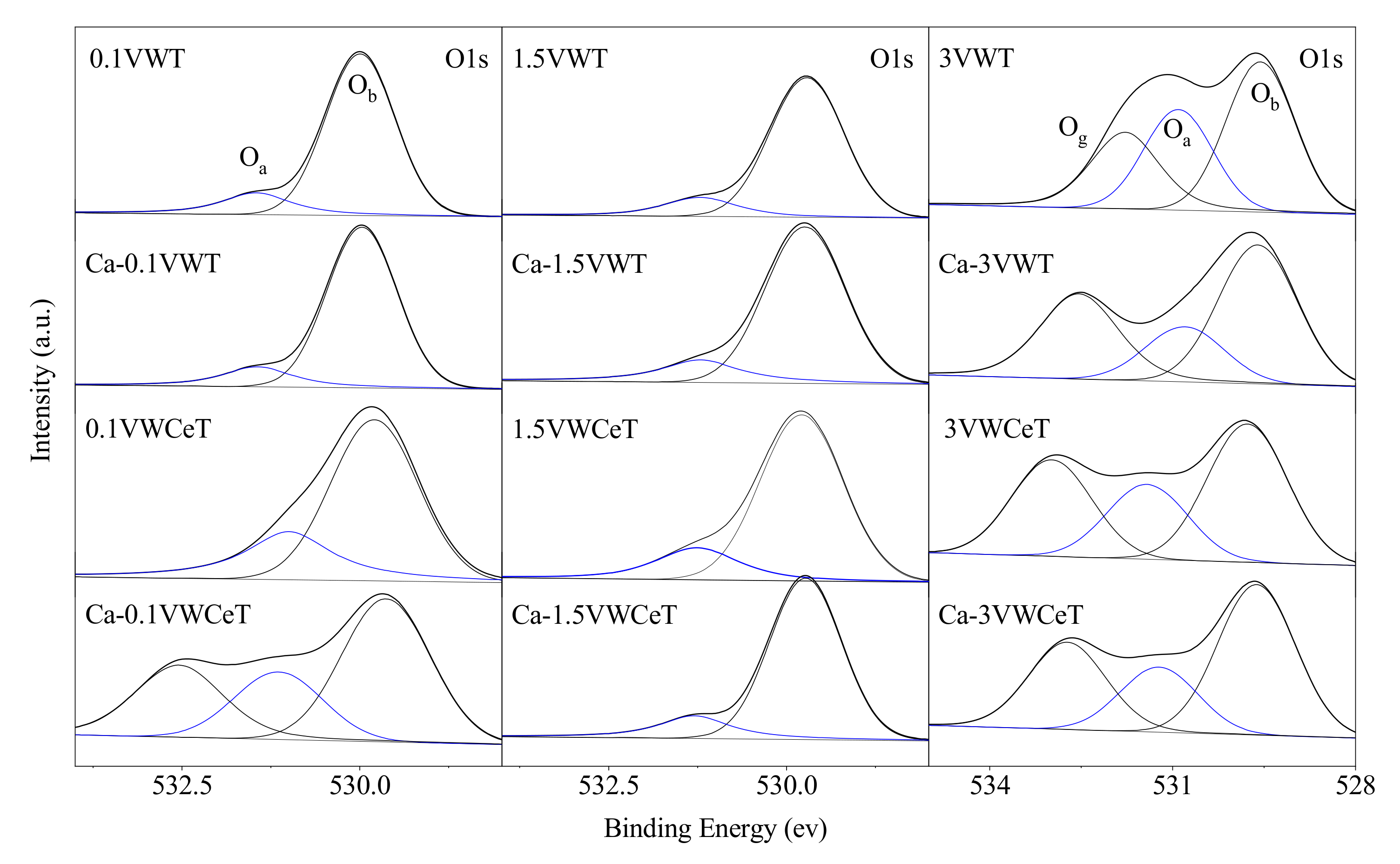
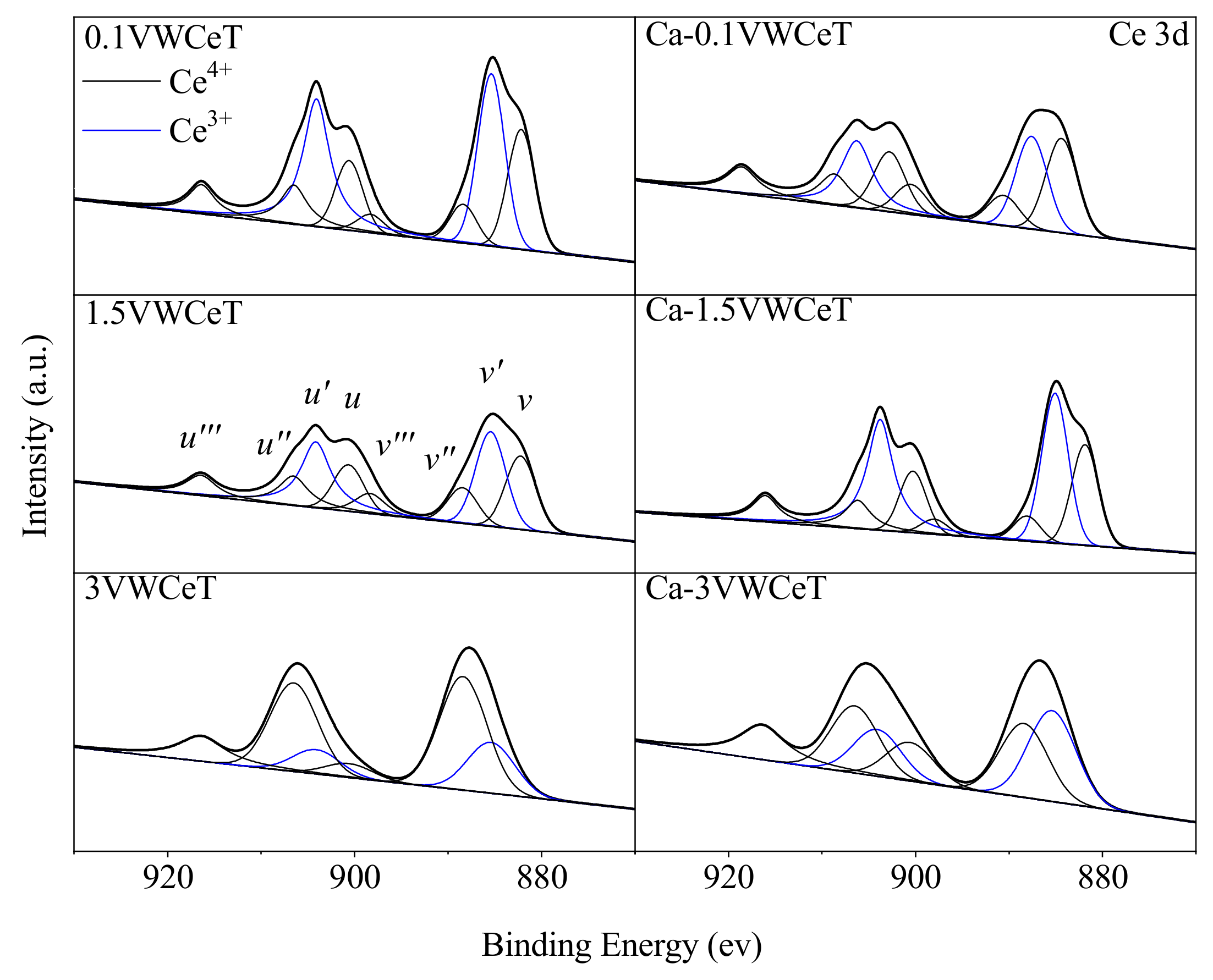

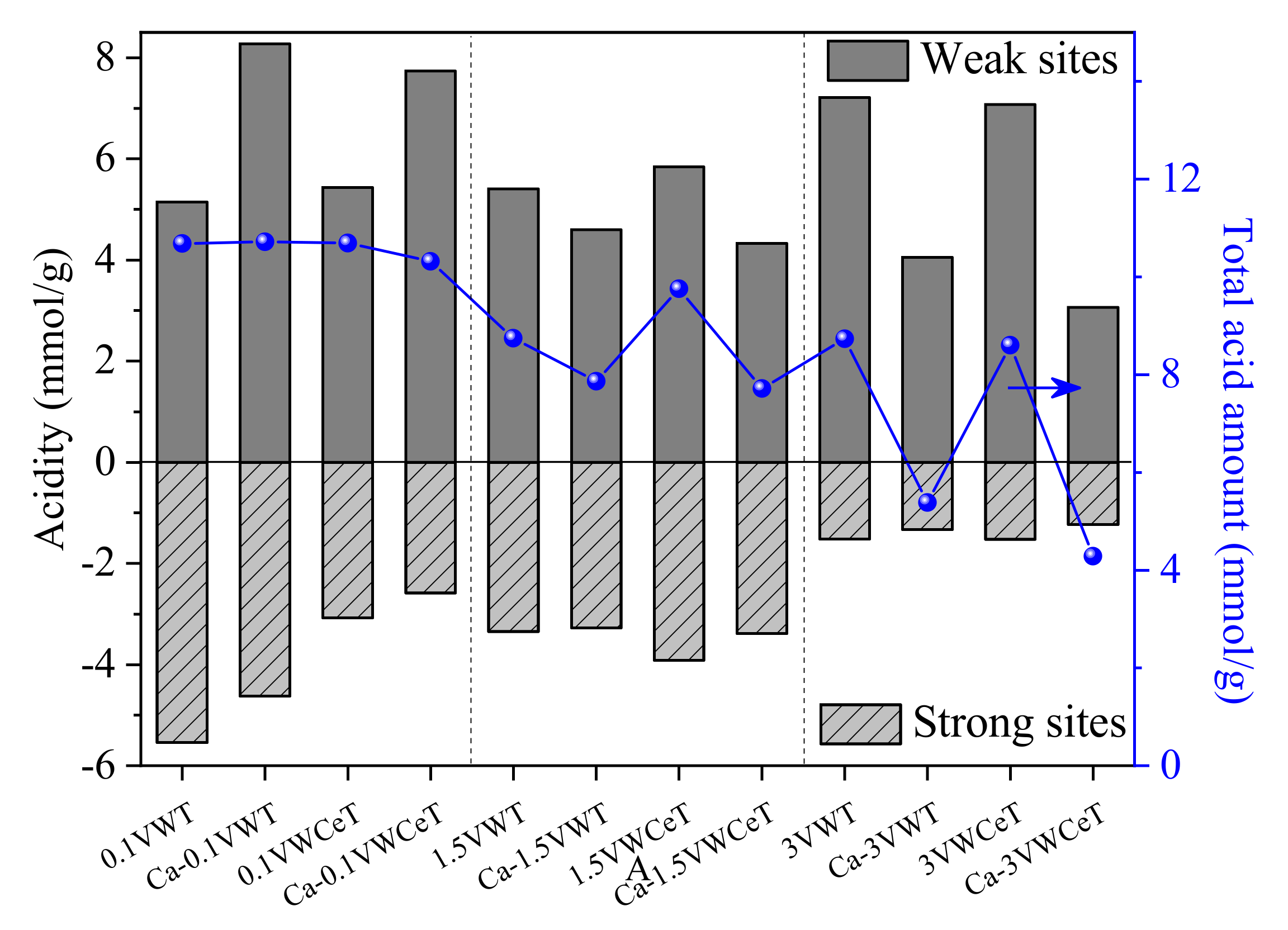


| No. | Sample | XPS | BET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oα/(Oα + Oβ) | Ce3+/(Ce3+ + Ce4+) | SBET | ||
| 1 | 0.1VWT | 0.16 | / | 72.2 |
| 2 | Ca-0.1VWT | 0.15 | / | 68.9 |
| 3 | 0.1VWCeT | 0.27 | 0.51 | 75.4 |
| 4 | Ca-0.1VWCeT | 0.32 | 0.38 | 67.3 |
| 5 | 1.5VWT | 0.15 | / | 83.9 |
| 6 | Ca-1.5VWT | 0.18 | / | 62.6 |
| 7 | 1.5VWCeT | 0.20 | 0.43 | 83.6 |
| 8 | Ca-1.5VWCeT | 0.17 | 0.53 | 81.8 |
| 9 | 3VWT | 0.40 | / | 59.9 |
| 10 | Ca-3VWT | 0.28 | / | 53.8 |
| 11 | 3VWCeT | 0.35 | 0.23 | 62.9 |
| 12 | Ca-3VWCeT | 0.30 | 0.45 | 58.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhu, T. Ca-Poisoning Effect on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3-CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts with Different Vanadium Loading. Catalysts 2021, 11, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040445
Guo Y, Xu X, Gao H, Zheng Y, Luo L, Zhu T. Ca-Poisoning Effect on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3-CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts with Different Vanadium Loading. Catalysts. 2021; 11(4):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040445
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yangyang, Xiaofei Xu, Hong Gao, Yang Zheng, Lei Luo, and Tingyu Zhu. 2021. "Ca-Poisoning Effect on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3-CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts with Different Vanadium Loading" Catalysts 11, no. 4: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040445
APA StyleGuo, Y., Xu, X., Gao, H., Zheng, Y., Luo, L., & Zhu, T. (2021). Ca-Poisoning Effect on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3-CeO2/TiO2 Catalysts with Different Vanadium Loading. Catalysts, 11(4), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040445








