Titanium Dioxide Derived Materials with Superwettability
Abstract
1. Introduction
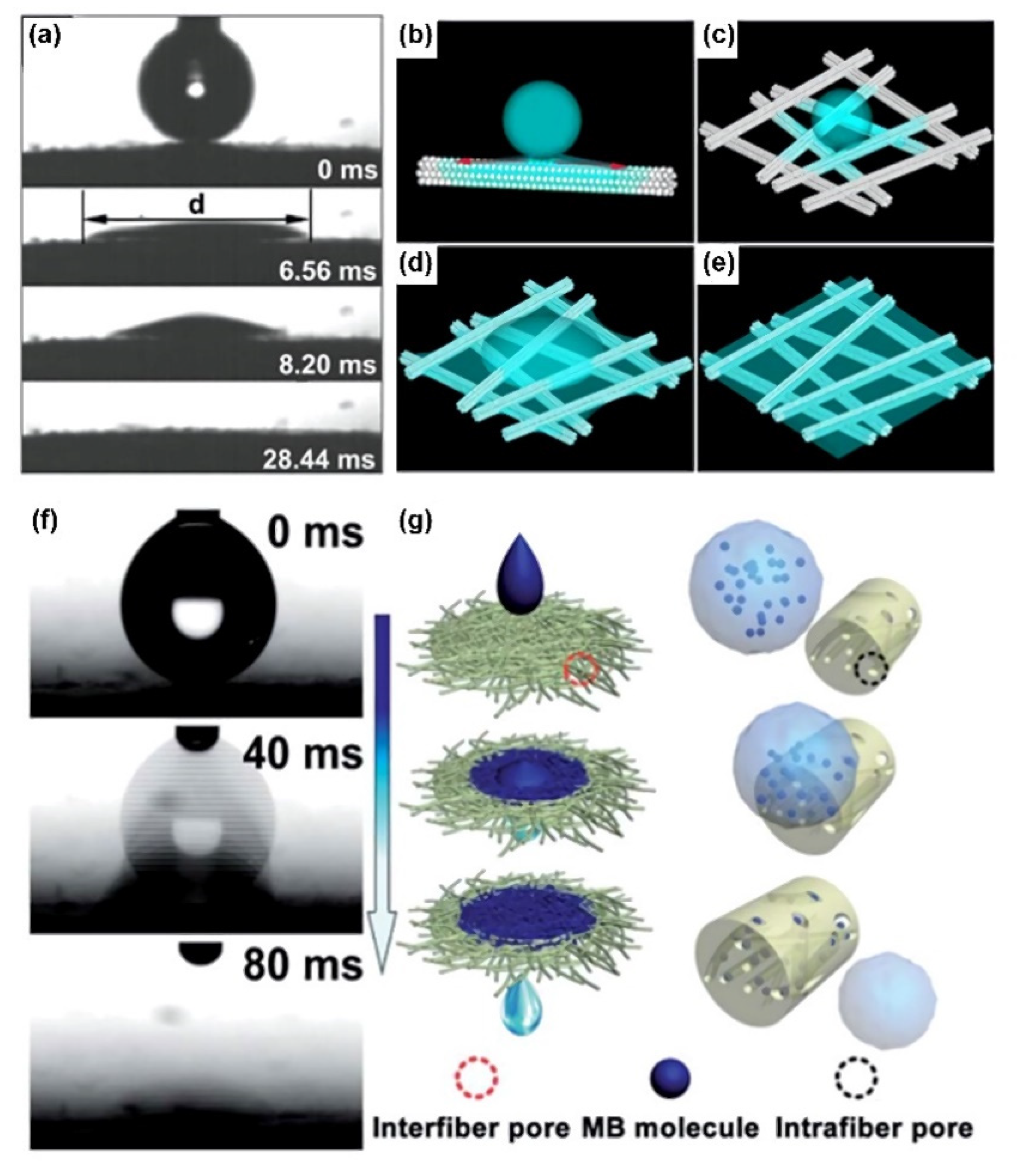
2. Ultra-Fast Spreading with Superwettability
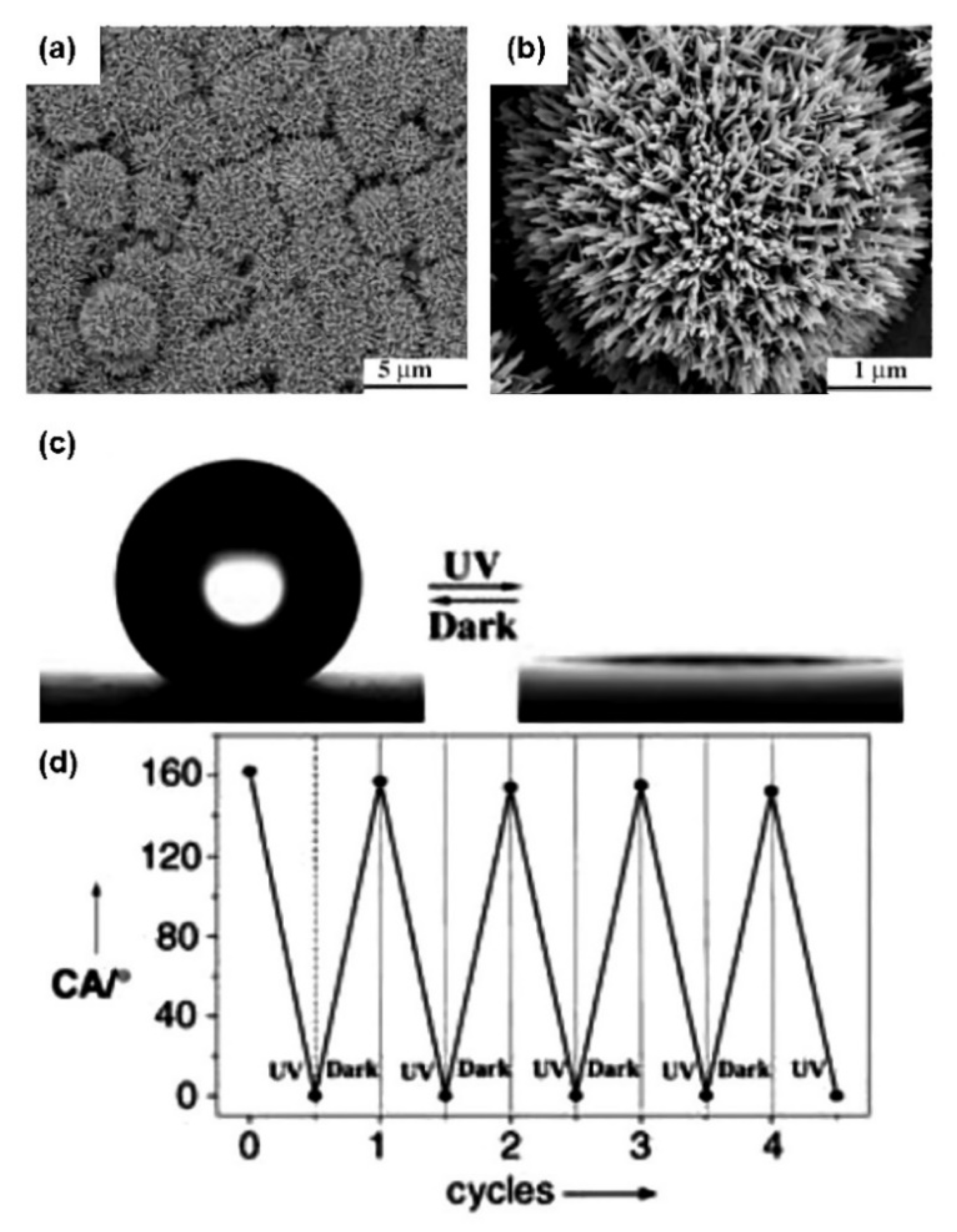
3. Controllable Wettability
4. Interfacial Photocatalysis and Photoelectrochemical Reactions
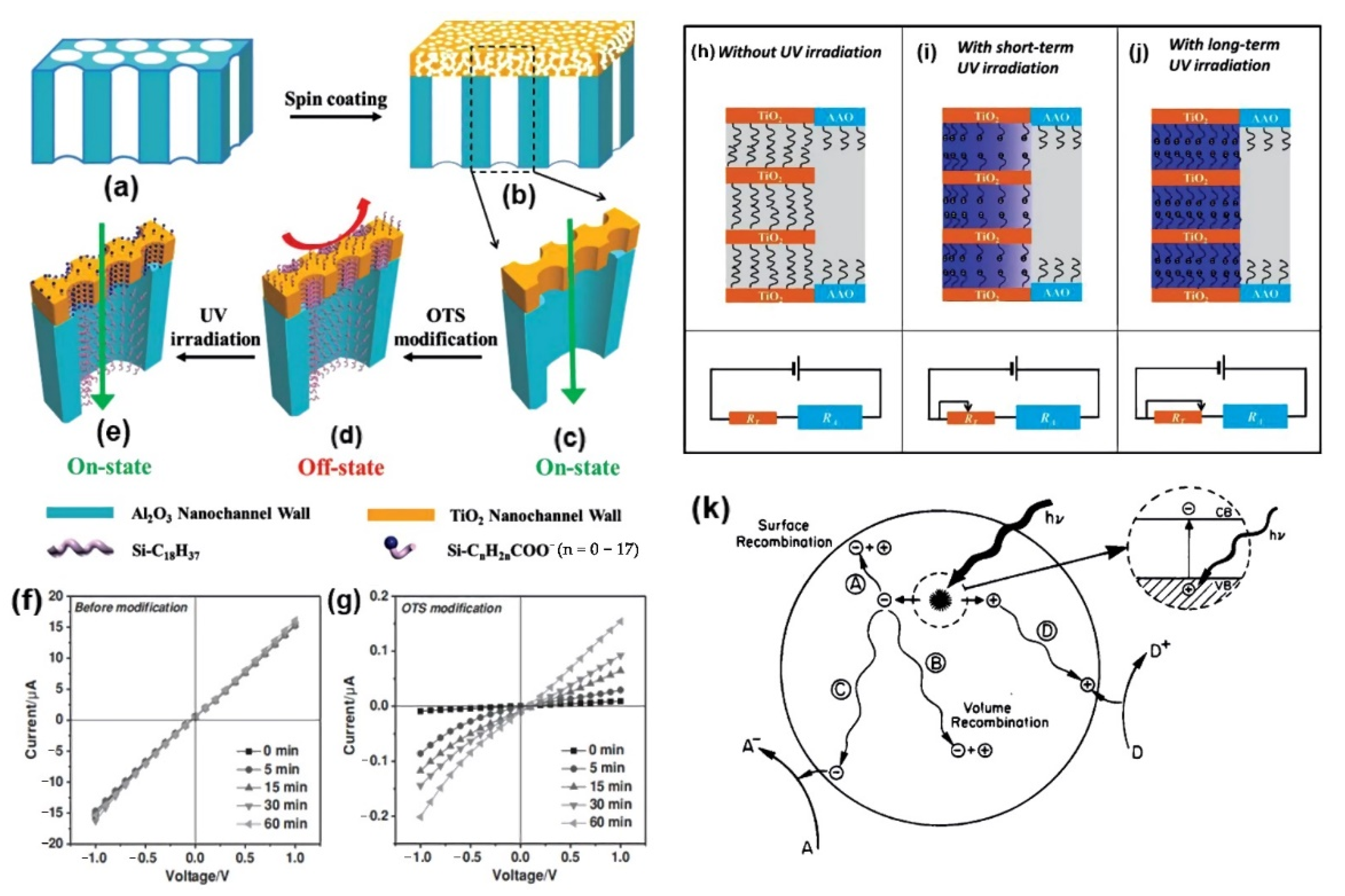
5. Nanochannels for Ion Rectification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittoun, E.; Marmur, A. The Role of Multiscale Roughness in the Lotus Effect: Is It Essential for Super-Hydrophobicity? Langmuir 2012, 28, 13933–13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cao, M.; Fujishima, A.; Jiang, L. Bio-Inspired Titanium Dioxide Materials with Special Wettability and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10044–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesel, L.F.; Greiner, C.; Arzt, E.; Del Campo, A. Gecko-Inspired Surfaces: A Path to Strong and Reversible Dry Adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lin, L.; Zang, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, M. Designing Bioinspired Anti-Biofouling Surfaces based on a Superwettability Strategy. Small 2016, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Fluid drag reduction and efficient self-cleaning with rice leaf and butterfly wing bioinspired surfaces. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7685–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, W.R.; Stier, W.M.; Prezhdo, O.V. AbInitioNonadiabatic Molecular Dynamics of the Ultrafast Electron Injection across the Alizarin−TiO2Interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7941–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowkes, F.M. Attractive Forces at Interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nat. Cell Biol. 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujishima, A.; Chikuni, M.; Kojima, E.; Kitamura, A.; Shimohigoshi, M.; Watanabe, T. Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces. Nat. Cell Biol. 1997, 388, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sakai, N.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, A.T.; Hashimoto, K. Studies of Surface Wettability Conversion on TiO2Single-Crystal Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yun, F.F.; Pan, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X. Crystal face dependent intrinsic wettability of metal oxide surfaces. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Superamphiphilic Silicon Wafer Surfaces and Applications for Uniform Polymer Film Fabrication. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5720–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Green, M.; Just, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, X. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials for photocatalysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 193003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.S.; Engelbrecht, A.D.; Hadley, T.D. Opportunities in the electrowinning of molten titanium from titanium dioxide. JOM 2005, 57, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.D. Application of titanium dioxide nano-particles on textile modification. In Advances in Textile Engineering and Materials Iii, Pts 1 and 2; Zheng, L., Skuroda, S., Liu, H., Du, B., Wei, J., Zhao, Y., Eds.; Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 821–822, pp. 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Y. The application of titanium dioxide of environment-friendly building materials. In Advanced Building Materials and Sustainable Architecture, Pts 1–4; Shao, Y., Hao, S., Luo, Y., Xing, J., Liu, Z., Eds.; Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 174–177, pp. 767–770. [Google Scholar]
- Bayan, E.M.; Lupeiko, T.G.; Pustovaya, L.E. Optimization of Synthesis of Nanosized Titanium Dioxide Powder Materials from Peroxo Titanium Complex. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 13, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K. Relationship between photocatalytic activity, hydrophilicity and self-cleaning effect of TiO2/SiO2 films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.E.O.; Jacoby, W.A. Microfibrous mesh coated with titanium dioxide: A self-sterilizing, self-cleaning filter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.-X.; Lin, N.; Li, X.; Tan, C.-Y. Self-cleaning glass coated with Fe3+-TiO2 thin film. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2004, 11, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohko, Y.; Utsumi, Y.; Niwa, C.; Tatsuma, T.; Kobayakawa, K.; Satoh, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Fujishima, A. Self-sterilizing and self-cleaning of silicone catheters coated with TiO2 photocatalyst thin films: A preclinical work. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, E.J.; Huang, J.; Blake, D.M.; Maness, P.-C.; Huang, Z.; Fiest, J.; Jacoby, W.A. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Bacteria, Bacterial and Fungal Spores, and Model Biofilm Components to Carbon Dioxide on Titanium Dioxide-Coated Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizenberg, J.; Fratzl, P. Biological and Biomimetic Materials. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.; Cardoso, R.; Correia, T.R.; Antunes, B.P.; Correia, I.J.; Ferreira, P. Surface modification of polyurethane films by plasma and ultraviolet light to improve haemocompatibility for artificial heart valves. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anpo, M.; Dohshi, S.; Kitano, M.; Hu, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Matsuoka, M. The preparation and characterization of highly efficient titanium oxide–based photofunctional materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2005, 35, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.; Lee, S.; Mak, C.; Chan, L. Photodegradation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and NO for indoor air purification using TiO2: Promotion versus inhibition effect of NO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, D.; Bouamrirene, F.; Verneuil, É.; Buguin, A.; Silberzan, P.; Moulinet, S. Bouncing or sticky droplets: Impalement transitions on superhydrophobic micropatterned surfaces. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2006, 74, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Di, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J. Flexible inorganic nanofibrous membranes with hierarchical porosity for efficient water purification. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4378–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lai, H.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jiang, L. Under-Oil Switchable Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity Transition on TiO2 Nanotube Arrays. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Chen, Q.; Nie, F.-Q.; Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Patterned Wettability Transition by Photoelectric Cooperative and Anisotropic Wetting for Liquid Reprography. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3744–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Huo, K.; Chu, P.K.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Regulating Water Adhesion on Superhydrophobic TiO2Nanotube Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6381–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Guan, F.; Sun, R.; Jiang, L.; Feng, X. A Reliable Photoelectrochemical Bioassay System Based on Cathodic Reaction at a Solid-Liquid-Air Joint Interface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Light-Gating Titania/Alumina Heterogeneous Nanochannels with Regulatable Ion Rectification Characteristic. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 24, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yun, F.F.; Gong, Z.; Yao, Q.; Dou, S.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X. A novel reusable superhydrophilic NiO/Ni mesh produced by a facile fabrication method for superior oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 10821–10826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Mazare, A.; Gongadze, E.; Perutkova, Š.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Milošev, I.; Schmuki, P.; Iglič, A.; Mozetič, M. Titanium nanostructures for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 062002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, J.; Yen, Y.-M.; Nakamoto, M.; Tanaka, T. Metal–Metal Joining Using Super-Spread Wetting into Interface Fine Mesh Structure. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, J.; Berndt, J.; Feig, S.T.; Holtz, F. The formation of SiO2-rich melts within the deep oceanic crust by hydrous partial melting of gabbros. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2007, 153, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.; Wilson, M.; Parkin, I.P. Antimicrobial surfaces and their potential in reducing the role of the inanimate environment in the incidence of hospital-acquired infections. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3819–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Superwettability: New Insight on Theory, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, W.-G.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of nanostructured metal nitrides with tailored composition and morphology. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3619–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Koshizaki, N. A Hierarchically Ordered TiO2Hemispherical Particle Array with Hexagonal-Non-Close-Packed Tops: Synthesis and Stable Superhydrophilicity Without UV Irradiation. Small 2008, 4, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, V.; Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Superhydrophilic TiO2 surface without photocatalytic activation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 093702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, K.R.; Boxall, C. Photoinduced “Stick−Slip” on Superhydrophilic Semiconductor Surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, V.A.; Nair, A.S.; Raut, H.K.; Walsh, T.M.; Ramakrishna, S. Photocatalytic superhydrophilic TiO2 coating on glass by electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, K.; Nonami, T. Preparation of a Superhydrophilic Thin Film on Glass Substrate Surfaces with Titanium Alkoxide Solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 2782–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Maeda, H.; Konishi, S. Photoresponsive wettability switching of TiO2 -coated micropillar arrays with different geometries of overhang roofs. Micro Nano Lett. 2017, 12, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, Y.S.; Buie, C.R. A Hybrid Method Employing Breakdown Anodization and Electrophoretic Deposition for Superhydrophilic Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 117, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F. Ultra-fast spreading on superhydrophilic fibrous mesh with nanochannels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4944–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. One-Step Multicomponent Encapsulation by Compound-Fluidic Electrospray. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7800–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, N.; Di, J.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-in-Microtube Structured Core/Shell Fibers via Multifluidic Coaxial Electrospinning. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11291–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Di, J.; Wang, N.; Dong, H.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Hierarchically Porous Inorganic Nanofibers by a General Microemulsion Electrospinning Approach. Small 2011, 7, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Sann, E.E.; Mon, K.H.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Bioinspired Slippery Lubricant-Infused Surfaces With External Stimuli Responsive Wettability: A Mini Review. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophilic Coating Induced Temporary Conductivity for Low-Cost Coating and Patterning of Insulating Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 9018–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linlin, H.; He, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Tian, D. External-Field-Induced Gradient Wetting for Controllable Liquid Transport: From Movement on the Surface to Penetration into the Surface. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Guo, Z. Inspired smart materials with external stimuli responsive wettability: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36623–36641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Huang, J.; Cui, Z.; Ge, M.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Chen, Z.; Chi, L. Recent Advances in TiO2-Based Nanostructured Surfaces with Controllable Wettability and Adhesion. Small 2016, 12, 2203–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. TiO2 nanotubular arrays loaded with Ni(OH)2: Naked-eye visible photoswitchable color change induced by oxidative energy storage. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, S.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Switchable Wettability Surface with Chemical Stability and Antifouling Properties for Controllable Oil–Water Separation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, G.R.; Weibel, D.E. UV-induced switchable wettability between superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic polypropylene surfaces with an improvement of adhesion properties. Polym. Bull. 2016, 74, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, G.; Cingolani, R.; Cozzoli, P.D.; Athanassiou, A. Wettability conversion of colloidal TiO2 nanocrystal thin films with UV-switchable hydrophilicity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 3692–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. Towards a tunable and switchable water adhesion on a TiO2 nanotube film with patterned wettability. Chem. Commun. 2009, 10, 7018–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. The Fabrication and Switchable Superhydrophobicity of TiO2 Nanorod Films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5115–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Weng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yu, H. Reversibly switchable wettability between underwater superoleophobicity and oleophobicity of titanium surface via ethanol immersion and dark storage. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.K.; Gao, X.F.; Zhuang, H.F.; Huang, J.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Jiang, L. Designing superhydrophobic porous nanostructures with tunable water adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3799–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, D.; et al. Switchable wettability and adhesion of micro/nanostructured elastomer surface via electric field for dynamic liquid droplet manipulation. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Cai, J.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z. TiO2/RGO composite aerogels with controllable and continuously tunable surface wettability for varied aqueous photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Kong, W.; Bhushan, B.; Zhao, X. Rapid, ultraviolet-induced, reversibly switchable wettability of superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic surfaces. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Jia, X.; Guo, Z. An easy preparation of photo-response TiO2@copper wire mesh with quick on/off switchable superwetting for high efficiency oil–water separation. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17563–17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, J.; Chao, M.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.; Chen, T. CNTs/TiO2 composite membrane with adaptable wettability for on-demand oil/water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tao, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y. A novel TiO2@stearic acid/chitosan coating with reversible wettability for controllable oil/water and emulsions separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cai, J.; Tian, D.; Li, W.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Patterned liquid permeation through the TiO2 nanotube array coated Ti mesh by photoelectric cooperation for liquid printing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zheng, X.; Tian, D.; Song, Y.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Dou, S.; Jiang, L. Photoelectric cooperative patterning of liquid permeation on the micro/nano hierarchically structured mesh film with low adhesion. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12822–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Mammen, L.; Butt, H.-J.; Vollmer, D. Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science 2012, 335, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical glucose sensors and their applications in diabetes management. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Zhang, L.-S.; Chen, C.-Q.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Song, W.-G.; Jiang, L. Hydrophilic TiO2 porous spheres anchored on hydrophobic polypropylene membrane for wettability induced high photodegrading activities. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Sun, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, J.; Shi, S.; He, G.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Enhanced photoelectrochemical properties of nanocrystalline TiO2 electrode by surface sensitization with CuxO quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A graphene-based electrochemical device with thermoresponsive microneedles for diabetes monitoring and therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quéré, D. Superhydrophobic states. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sheng, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Sun, R.; Jiang, L.; Feng, X. High-performance triphase bio-photoelectrochemical assay system based on superhydrophobic substrate-supported TiO2 Nanowire Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lin, P.; Wei, N.; Wang, D. Enhanced photoelectrochemical water-splitting property on TiO2 nanotubes by surface chemical modification and wettability control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20110–20118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieerad, A.; Bushroa, A.; Nasiri-Tabrizi, B.; Vadivelu, J.; Yusof, F.; Baradaran, S. Graphene Oxide Modified Anodic Ternary Nanobioceramics on Ti6Al7Nb alloy for orthopedic and dental applications. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Ion/Molecule transportation in nanopores and nanochannels: From critical principles to diverse functions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8658–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhai, J. Biomimetic stimuli-responsive nanochannels and their applications. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Gao, P.; Ma, Q.; Wang, D.; Xia, F. Biomolecule-functionalized solid-state ion nanochannels/nanopores: Features and techniques. Small 2019, 15, e1804878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Kong, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, G.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Construction and application of photoresponsive smart nanochannels. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2016, 26, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Quantum-confined superfluid: From nature to artificial. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jiang, L. Construction of biomimetic smart nanochannels for confined water. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Huang, J. Control water molecules across carbon-based nanochannels. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yan, J.; Hou, S. Fabrication of nanofluidic biochips with nanochannels for applications in DNA analysis. Small 2012, 8, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Nanochannels regulating ionic transport for boosting electrochemical energy storage and conversion: A review. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15923–15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Fan, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, J. Smart bioinspired nanochannels and their applications in energy-conversion systems. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, L. Wettability and applications of nanochannels. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1804508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Hou, X.; Fan, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Light-regulated ion transport through artificial ion channels based on TiO2 nanotubular arrays. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5901–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-C.; Song, L.-B.; Gao, M.-J.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, C.-Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Chen, W. Ion current rectification in high-salt environment from mesoporous TiO2 microplug in situ grown at the tip of a micropipette induced by space-confined evaporation. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 15377–15381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: Principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Photocatalysis-triggered ion rectification in artificial nanochannels based on chemically modified asymmetric TiO2 nanotubes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4806–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qu, K.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Dai, Z.; Gao, Z.-D.; Song, Y.-Y. Asymmetric coupling of Au nanospheres on TiO2 nanochannel membranes for NIR-gated artificial ionic nanochannels. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14625–14628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Lai, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chou, S.; Jiang, L. Nanoengineering to achieve high sodium storage: A case study of carbon coated hierarchical nanoporous TiO2 microfibers. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, Y.; You, J.; Jiang, L. Titanium Dioxide Derived Materials with Superwettability. Catalysts 2021, 11, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040425
Luo X, Zhu Z, Tian Y, You J, Jiang L. Titanium Dioxide Derived Materials with Superwettability. Catalysts. 2021; 11(4):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040425
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xianfeng, Zhongpeng Zhu, Ye Tian, Jun You, and Lei Jiang. 2021. "Titanium Dioxide Derived Materials with Superwettability" Catalysts 11, no. 4: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040425
APA StyleLuo, X., Zhu, Z., Tian, Y., You, J., & Jiang, L. (2021). Titanium Dioxide Derived Materials with Superwettability. Catalysts, 11(4), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11040425






