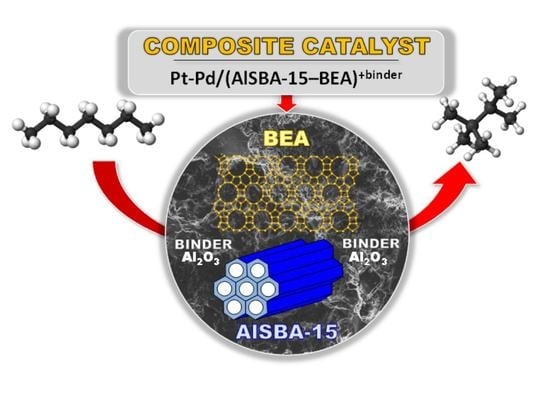
Promotional Effect of Pd Addition on the Catalytic Activity of Composite Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–β Catalyst for Enhanced n-Heptane Hydroisomerization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
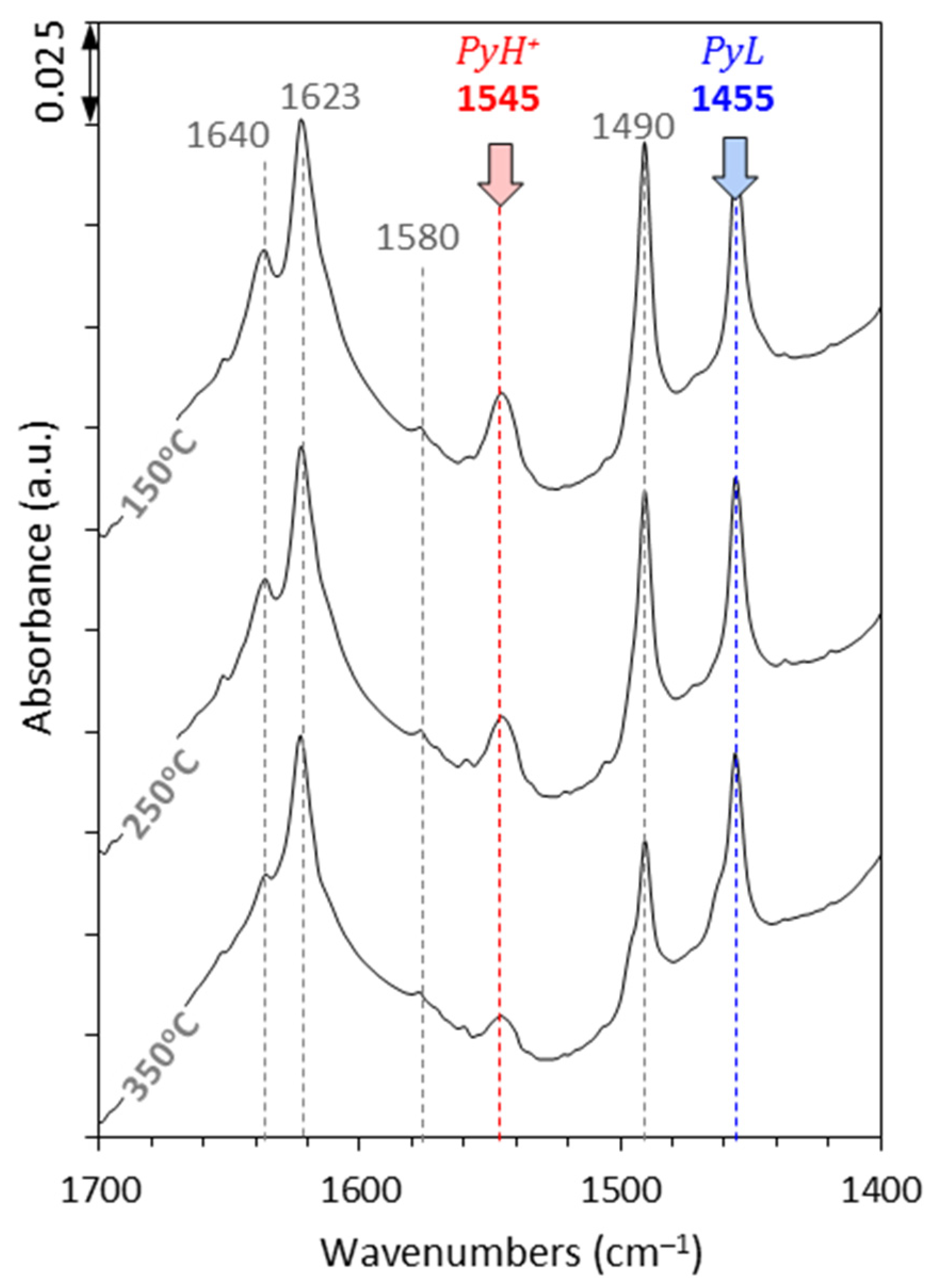
2.1. Catalysts Characterisation
2.2. Effect of the Type of Zeolite Incorporated to Pt/AlSBA-15—Zeolite
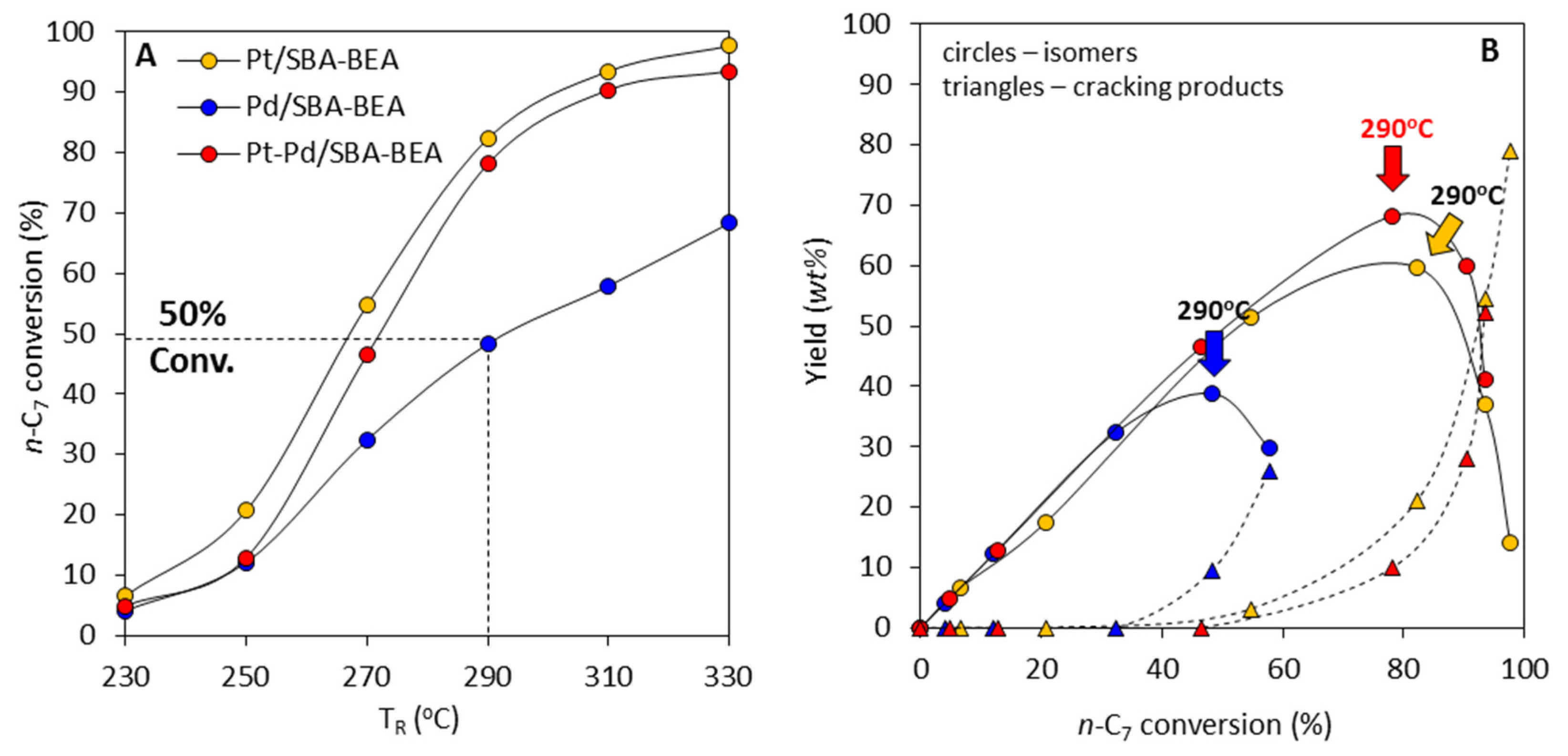
2.3. Effect of Active Phase Composition in Pt, Pd, and Pt-Pd Catalysts Supported on AlSBA-15–BEA
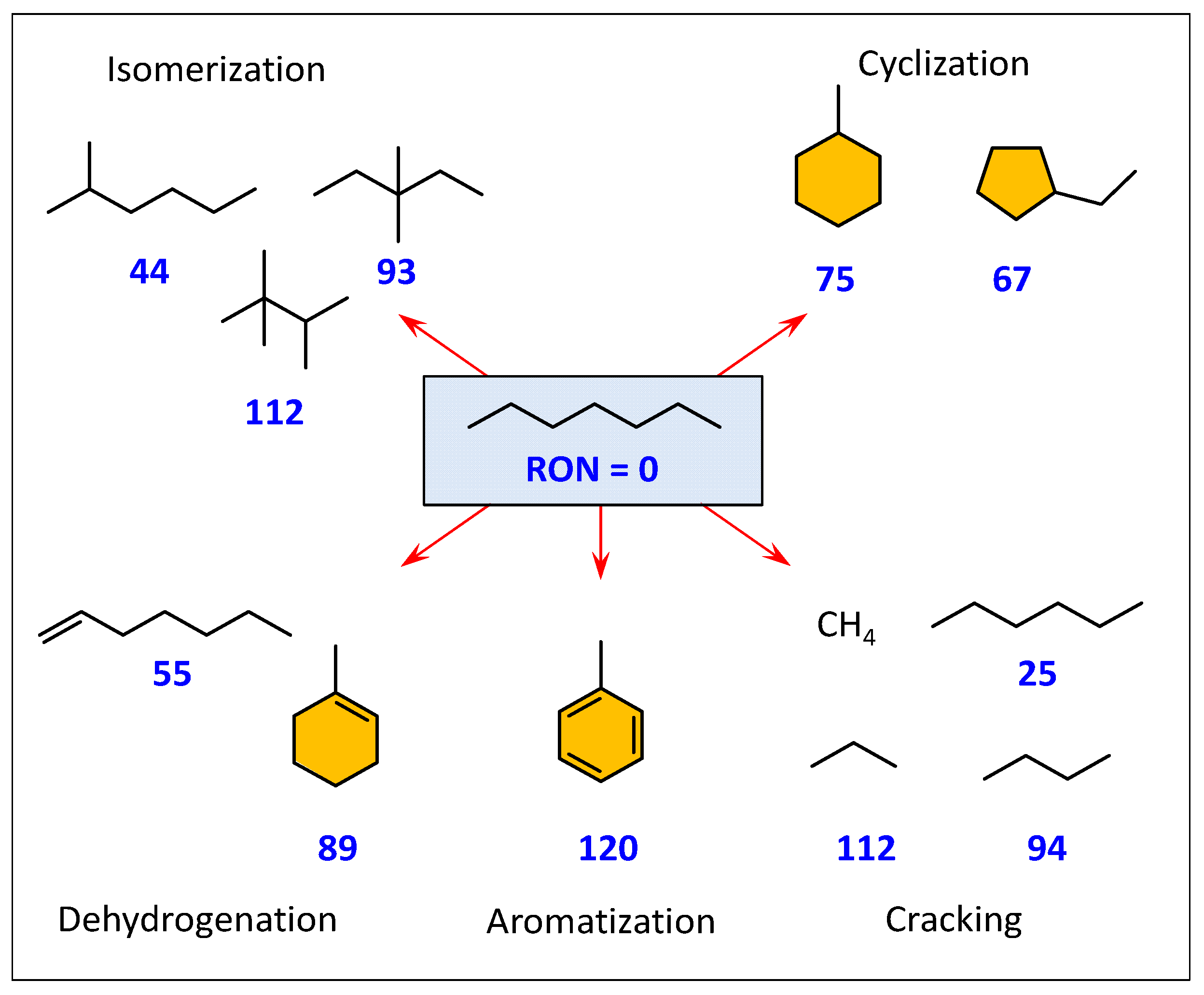
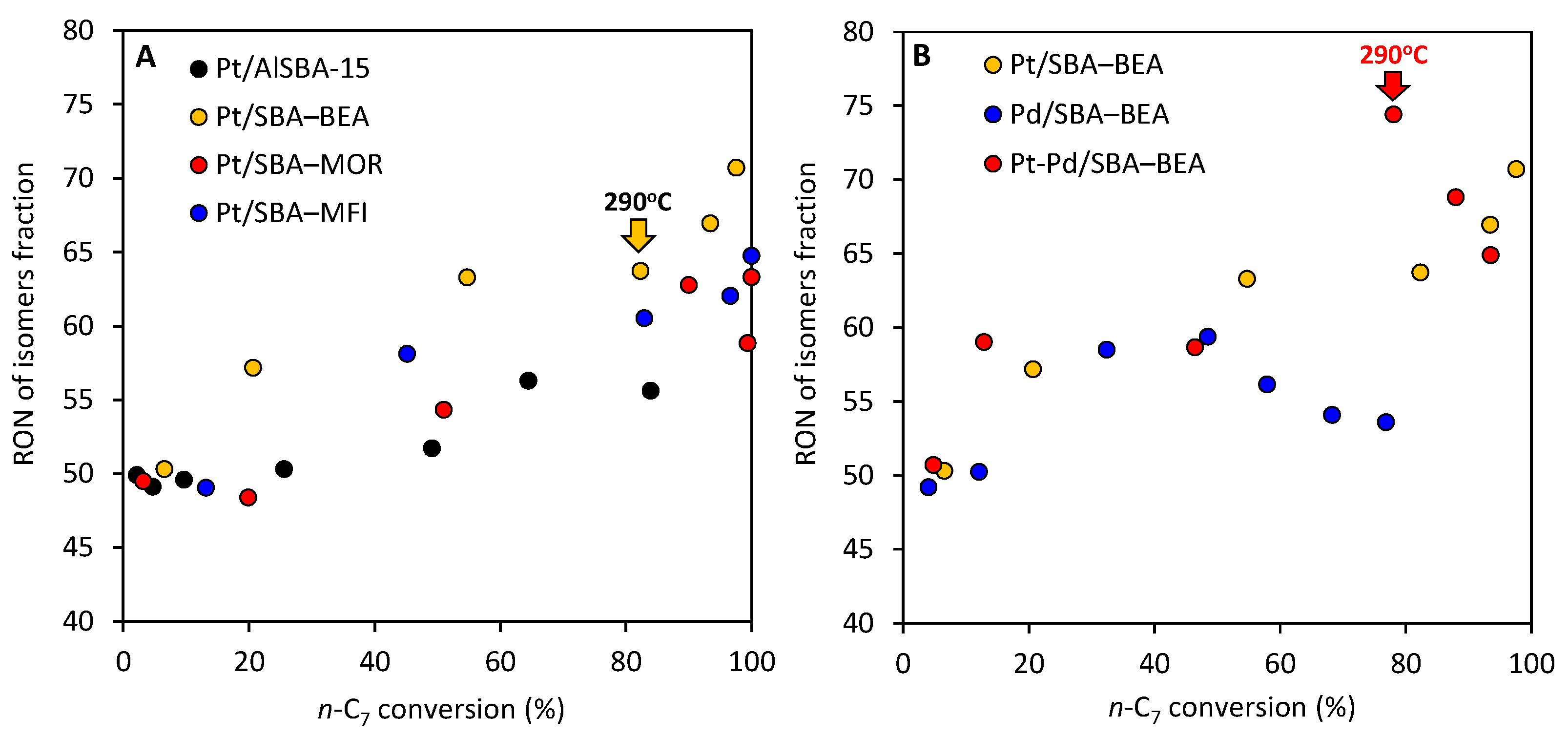
2.4. Research Octane Number
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
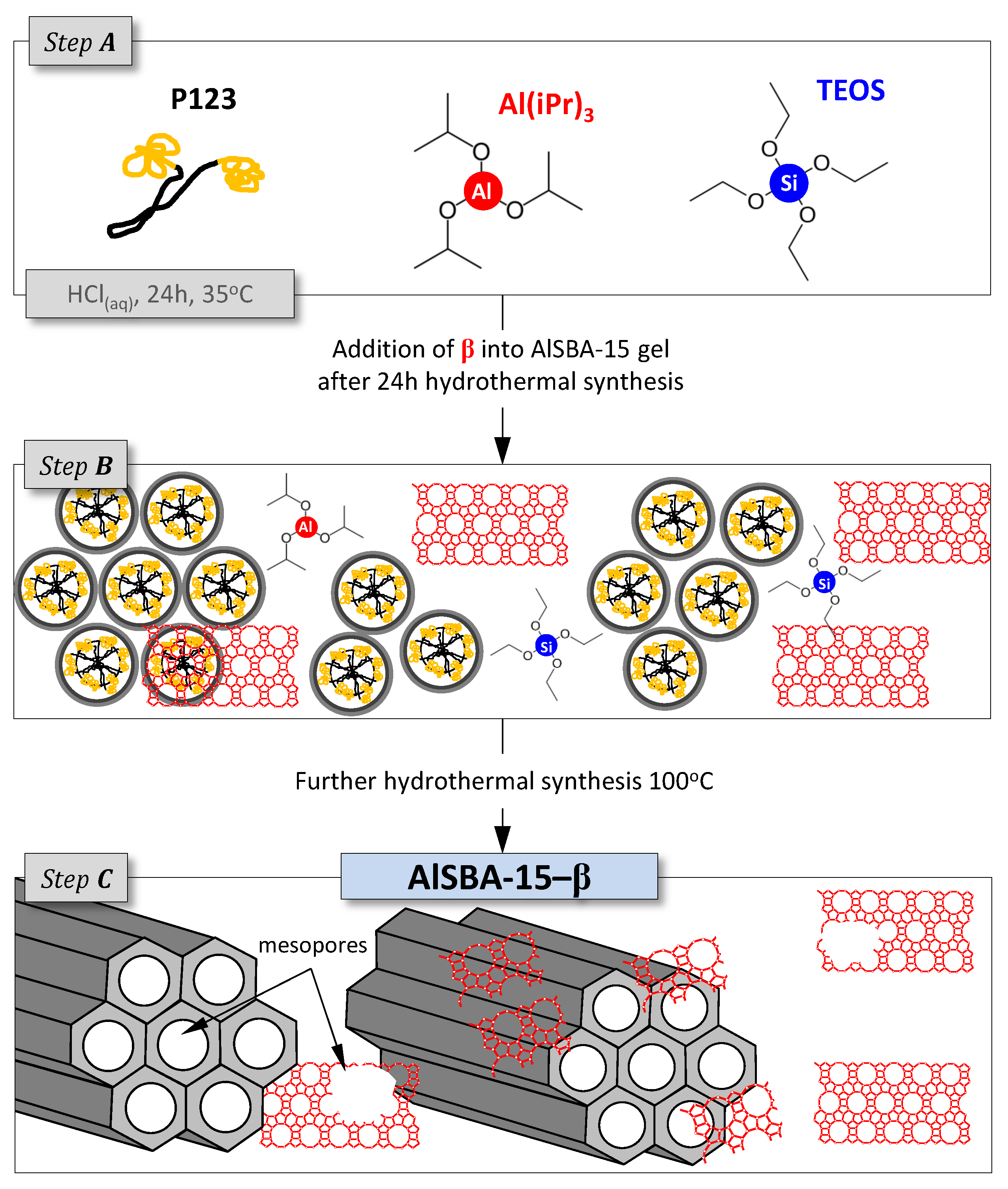
3.2. Supports and Catalysts Preparation
3.3. Catalyst Characterisation
3.4. Catalytic Activity Measurements
- (1)
- iso-C7 (total hydroisomerization products), including MoBC7 (monobranched isomers) and MuBC7 (multibranched isomers),
- (2)
- C3 + C4 (hydrocracking products),
- (3)
- Aro & Cyc, i.e., aromatics (mostly toluene) and cycloalkanes (mostly methylcyclohexane).
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The results clearly show that type of the zeolite (BEA, MOR and MFI) that was introduced into AlSBA-15–zeolite hierarchical supports significantly affects the activity of Pt catalysts in n-C7 hydroisomerization. The Pt/AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst displays the most promising catalytic properties for the isomerization of n-C7, relative to Pt/AlSBA-15 and Pt/zeolite and to the two other catalysts (Pt/AlSBA-15–MOR and Pt/AlSBA-15–MFI). The maximal yield of heptane isomers over Pt/AlSBA-15–BEA amounting to ca. 60% is reached at 82% of the total n-C7 conversion (at 290 °C). This catalyst allows to improve research octane number from 0 to 64. The enhanced performance over Pt/AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst is attributed to not only the well Pt dispersion and moderate acidity but also to the improved textural properties. The method of preparation of biporous supports developed by us provides the formation of some kind micropore—mesopore continuity in AlSBA-15–zeolite which facilitates the suitable transport properties (i.e., fast adsorption and desorption). The presence of mesopores decreases or eliminates diffusion restrictions. It shortens the residence time of the intermediates in catalyst pores and results in diminution of consecutive reactions, such as cracking, and consequently in enhancing isomerization efficiency.
- (2)
- The research onto the modification of the hydrogenating function (Pt, Pd, Pt-Pd) has shown that the most remarkable case is that of the Pt-Pd synergy. Combining Pt and Pd led to a notable synergetic effect, which exceed those of the additive contribution of Pt and Pd in the metallic phase. The hydroisomerization of n-C7 over Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst provides the yield of isomers amounting to 68 wt% without extensive cracking at conversion of up to 78% (at 290 °C). The Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst allows to improve research octane number from 0 to 74. The high isomerization activity of Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst can be considered to come from the micro-mesoporous AlSBA-15–BEA support which supplies a required acidity characterisation and the appropriate transport properties. But first of all the observed synergy in Pt-Pd/ AlSBA-15–BEA catalyst could most likely be attributed to the interaction between Pt and Pd particles.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mascal, M.; Dutta, S. Synthesis of highly-branched alkanes for renewable gasoline. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 197, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatkittipong, W.; Wongsakulphasatch, S.; Tintan, N.; Laosiripojana, N.; Praserthdam, P.; Assabumrungrat, S. Gasoline upgrading by self-etherification with ethanol on modified beta-zeolite. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1999–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.M.; Ahmed, T.S.; Moustafa, T.M. Predictive Modeling and Optimization for an Industrial Penex Isomerization Unit: A Case Study. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7726–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellussi, G.; Pollesel, P. Industrial applications of zeolite catalysis: Production and uses of light olefins. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 158, pp. 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchar, P.; Bricker, J.; Reno, M.; Haizmann, R. Paraffin isomerization innovations. Fuel Process. Technol. 1993, 35, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T. Development of Pt/SO42−/ZrO2 catalyst for isomerization of light naphtha. Catal. Today 2003, 81, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K. Industrial application of solid acid–base catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 181, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Corredores, M.M.; Reomero, T.; González, M. Dehydroisomerization of N-butane on Pt=Zn/H-Mordenite. Pharmacogenetics 2000, 130 C, 2507–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Zbuzek, M.; Černý, R.; Jíša, P.; Herrador, J.M.H. Current uses and trends in catalytic isomerization, alkylation and etherification processes to improve gasoline quality. Open Chem. 2014, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, M.; Vera, C.; Grau, J. Optimal process conditions for the isomerization–cracking of long-chain n-paraffins to high octane isomerizate gasoline over Pt/SO42––ZrO2 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, T.D.; Kriz, J.F.; Stanciulescu, M.; Monnier, J. A study of catalyst formulations for isomerization of C7 hydrocarbons. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 233, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Hager, V.; Schwieger, W.; Wasserscheid, P. Enhanced activity and selectivity in n-octane isomerization using a bifunctional SCILL catalyst. J. Catal. 2012, 292, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses-Ruiz, E.; Laredo, G.C.; Castillo, J.; Marroquin, J.O. Comparison of different molecular sieves for the liquid phase separation of linear and branched alkanes. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 124, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silke, E.J.; Curran, H.J.; Simmie, J.M. The influence of fuel structure on combustion as demonstrated by the isomers of heptane: A rapid compression machine study. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.-J.; Wu, W. Bifunctional catalysts for the hydroisomerization of n-alkanes: The effects of metal–acid balance and textural structure. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 4162–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Arroyo-Ramírez, L.; Wei, J.; Yun, H.; Murray, C.B.; Gorte, R.J. Comparison of HMF hydrodeoxygenation over different metal catalysts in a continuous flow reactor. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 508, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.Q.; Upadhye, A.A.; Olcay, H.; Tompsett, G.A.; Jae, J.; Xing, R.; Alonso, D.M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, T.; Kumar, R.; et al. Production of renewable jet fuel range alkanes and commodity chemicals from integrated catalytic processing of biomass. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1500–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisnet, M. “Ideal” bifunctional catalysis over Pt-acid zeolites. Catal. Today 2013, 218, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Liu, P.; Xi, H.; Ren, J.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Hou, B.; Li, D. Design and synthesis of Pt/ZSM-22 catalysts for selective formation of iso-Dodecane with branched chain at more central positions from n-Dodecane hydroisomerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 562, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, C. Hydroisomerization of n-octane over bimetallic Ni-Cu/SAPO-11 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 543, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.S.; Kumar, A. Hydroisomerization of saturated hydrocarbons with novel MCM-41 immobilized Re(V) complex catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 429–430, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cai, T.; Jing, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Xia, D. Surface chemistry and catalytic performance of amorphous NiB/Hβ catalyst for n-hexane isomerization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, K. Interface mediated crystallization of plate-like SAPO-41 crystals to promote catalytic hydroisomerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 602, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, L.; Zhanga, M.; Wangab, L.; Zhangab, X.; Liab, G. Construction of ordered mesopores outside MTT zeolite for efficient hydroisomerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 602, 117664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastvova, J.; Pilar, R.; Moravkova, J.; Kaucký, D.; Rathousky, J.; Sklenak, S.; Sazama, P. Tailoring the structure and acid site accessibility of mordenite zeolite for hydroisomerisation of n-hexane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 562, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.; Fuentes, G.A.; Navarrete, J.T.L.; Vazquez, A.L.; Zeifert, B.; Salmones, J.; Nuño, L. Structural and catalytic characterization of mechanical mixtures of Pt/WOx–ZrO2 and Al2O3. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 495, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, P.; Dorado, F.; Ramos, M.J.; Romero, R.; Jiménez, V.; Valverde, J.L.; Marcos, M.J.R. Hydroisomerization of C6–C8 n-alkanes, cyclohexane and benzene over palladium and platinum beta catalysts agglomerated with bentonite. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 314, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Z.; Etim, U.J.; Wu, P.; Xing, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, P.; Yan, Z. Superior catalytic performance of micro-mesoporous Beta-SBA-15 composite with a high indexed isomerization factor in hydroisomerization of n-heptane. Fuel 2019, 252, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Z.; Etim, U.J.; Wu, P.; Han, D.; Xing, W.; Mintova, S.; Bai, P.; Yan, Z. Beta-MCM-41 micro-mesoporous catalysts in the hydroisomerization of n-heptane: Definition of an indexed isomerization factor as a performance descriptor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakiss, L.; Gilson, J.-P.; Valtchev, V.; Mintova, S.; Vicente, A.; Vimont, A.; Bedard, R.; Abdo, S.; Bricker, J. Zeolites in a good shape: Catalyst forming by extrusion modifies their performances. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 299, 110114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izan, S.; Triwahyono, S.; Jalil, A.; Majid, Z.; Fatah, N.; Hamid, M.; Ibrahim, M. Additional Lewis acid sites of protonated fibrous silica@BEA zeolite (HSi@BEA) improving the generation of protonic acid sites in the isomerization of C6 alkane and cycloalkanes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 570, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palčić, A.; Valtchev, V. Analysis and control of acid sites in zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 606, 117795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Zhou, X.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; et al. Insight into the Effect of Lewis Acid of W/Al-MCM-41 Catalyst on Metathesis of 1-Butene and Ethylene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 604, 117772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhtiyarova, M.; Toktarev, A.; Kazakov, M.; Kodenev, E.; Pereyma, V.Y.; Gabrienko, A.; Echevsky, G. Effect of sulfosalicylic acid treatment on the properties of Beta zeolite and performance of NiW/Beta-based catalysts in hexadecane hydrocracking. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 598, 117573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, U.; Bai, P.; Wang, Y.; Subhan, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z. Mechanistic insights into structural and surface variations in Y-type zeolites upon interaction with binders. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 571, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. Citric acid-modified beta zeolite for polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers synthesis: The textural and acidic properties regulation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 266, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velisoju, V.K.; Gutta, N.; Tardio, J.; Bhargava, S.K.; Vankudoth, K.; Chatla, A.; Medak, S.; Akula, V. Hydrodeoxygenation activity of W modified Ni/H-ZSM-5 catalyst for single step conversion of levulinic acid to pentanoic acid: An insight on the reaction mechanism and structure activity relationship. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 550, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. Catalytic materials based on silica and alumina: Structural features and generation of surface acidity. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, E.F.; Heracleous, E.; Delimitis, A.; Lappas, A.A. Producing high quality biofuels: Pt-based hydroisomerization catalysts evaluated using BtL-naphtha surrogates. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 145, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, J.; Kubička, D.; Karhu, H.; Österholm, H.; Kumar, N.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. On the mutual interactions between noble metal crystallites and zeolitic supports and their impacts on catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 264, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckel, D. Noble Metal Wax Hydrocracking Catalysts Supported on High-Siliceous Alumina. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3505–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubička, D.; Kumar, N.; Venäläinen, T.; Karhu, H.; Kubičková, I.; Österholm, H.; Murzin, D.Y. Metal−Support Interactions in Zeolite-Supported Noble Metals: Influence of Metal Crystallites on the Support Acidity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4937–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koningsberger, D.; De Graaf, J.; Mojet, B.; Ramaker, D.; Miller, J. The metal–support interaction in Pt/Y zeolite: Evidence for a shift in energy of metal d-valence orbitals by Pt–H shape resonance and atomic XAFS spectroscopy. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 191, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Haller, G.L.; Colby, R.; Kabius, B.; Van Veen, J.R.; Jentys, A.; Lercher, J.A. Tailoring silica–alumina-supported Pt–Pd as poison-tolerant catalyst for aromatics hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2013, 304, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Effect of zeolite protons on Pd particle size and H2 chemisorption. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yao, Y. Investigation of zeolite supported platinum electrocatalyst for electrochemical oxidation of small organic species. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 14747–14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Gheit, N.A.K. Effect of Hydrohalogenation of Metal/Zeolite Catalysts for Cyclohexene Hydroconversion -Part 3- Pd/H-ZSM-5 Catalysts. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ji, S.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Tian, S.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Well-Defined Materials for Heterogeneous Catalysis: From Nanoparticles to Isolated Single-Atom Sites. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 623–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treesukol, P.; Srisuk, K.; Limtrakul, J.; Truong, T.N. Nature of the Metal−Support Interaction in Bifunctional Catalytic Pt/H-ZSM-5 Zeolite. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 11940–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lónyi, F.; Kovács, A.; Szegedi, Á.; Valyon, J. Activation of Hydrogen and Hexane over Pt,H-Mordenite Hydroisomerization Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 10527–10540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.-C.; Wei, X.-Y.; Zong, Z.-M.; Wang, Y.-K. Application of supported metallic catalysts in catalytic hydrogenation of arenes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14219–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, G.D.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Alkane isomerization over solid acid catalysts Effects of one-dimensional micropores. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 137, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewska, K.; Masalska, A.; Grzechowiak, J.; Grams, J. Hydroconversion of 1-methylnaphthalene over Pt/AlSBA-15–Al2O3 composite catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 505, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, I. The role of niobium in MCM-41 supported with Pt and Au—A comparative study of physicochemical and catalytic properties. Catal. Today 2009, 142, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, J.E.; Blanchard, J.; Sayag, C.; Louis, C.; Regalbuto, J.R. The controlled synthesis of metal-acid bifunctional catalysts: Selective Pt deposition and nanoparticle synthesis on amorphous aluminosilicates. J. Catal. 2016, 342, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, J.E.; Blanchard, J.; Sayag, C.; Louis, C.; Regalbuto, J.R. The controlled synthesis of metal-acid bifunctional catalysts: The effect of metal:acid ratio and metal-acid proximity in Pt silica-alumina catalysts for n-heptane isomerization. J. Catal. 2016, 342, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Fotouh, S.M.; Aboul-Gheit, A. Effect of Hydrohalogenation of PtRe/H-ZSM-5 for Cyclohexene Conversion. Chin. J. Catal. 2012, 33, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, H.; Kalantar, A.; Väyrynen, I.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. XPS analysis of chlorine residues in supported Pt and Pd catalysts with low metal loading. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 247, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongpatiwut, S.; Rattanapuchapong, N.; Rirksomboon, T.; Osuwan, S.; Resasco, D.E. Enhanced Sulfur Tolerance of Bimetallic PtPd/Al2O3 Catalysts for Hydrogenation of Tetralin by Addition of Fluorine. Catal. Lett. 2008, 122, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, S.A.; Especel, C.; Vivier, L.; Epron, F.; Pieck, C.L. Influence of the Brønsted acidity, SiO2/Al2O3 ratio and Rh–Pd content on the ring opening: Part I. Selective ring opening of decalin. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 469, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlik, M.; Matus, K.; Karpiński, Z. n-Hexane Hydrogenolysis Behavior of Alumina-Supported Palladium—Platinum Alloys. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Rhee, H.-K. Sulfur tolerance of zeolite beta-supported Pd−Pt catalysts for the isomerization of n-hexane. J. Catal. 1998, 177, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Moussa, O.; Tinat, L.; Jin, X.; Baaziz, W.; Durupthy, O.; Sayag, C.; Blanchard, J. Heteroaggregation and Selective Deposition for the Fine Design of Nanoarchitectured Bifunctional Catalysts: Application to Hydroisomerization. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6071–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, Z.; Bachir, C.; Ziri, S.; Bellahouel, S.; Bengueddach, A.; Villièras, F.; Pelletier, M.; Weidler, P.G.; Hamacha, R. Al-Rich Ordered Mesoporous Silica SBA-15 Materials: Synthesis, Surface Characterization and Acid Properties. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 2116–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. IEP as a parameter characterizing the pH-dependent surface charging of materials other than metal oxides. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, J.; Van Der Wal, L.I.; Zečević, J.; De Jongh, P.E.; De Jong, K.P. Influence of intimacy for metal-mesoporous solid acids catalysts for n-alkanes hydro-conversion. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Smirniotis, P.G. Pt/H-ZSM-12 as a catalyst for the hydroisomerization of C5–C7 n-alkanes and simultaneous saturation of benzene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 247, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaeidesfahani, A.; De Lange, M.F.; Khodadadian, F.; Dubbeldam, D.; Rigutto, M.; Nair, N.; Vlugt, T.J. Product shape selectivity of MFI-type, MEL-type, and BEA-type zeolites in the catalytic hydroconversion of heptane. J. Catal. 2017, 353, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Wu, H.-C.; Tseng, C.-W.; Chen, S.-H. n-Heptane hydroconversion on platinum-loaded mordenite and beta zeolites: The effect of reaction pressure. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2000, 203, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. Effect of pore confinement on the adsorption of mono-branched alkanes of naphtha in ZSM-5 and Y zeolites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnudde, P.; De Wispelaere, K.; Vanduyfhuys, L.; Demuynck, R.; Van Der Mynsbrugge, J.; Waroquier, M.; Van Speybroeck, V. How Chain Length and Branching Influence the Alkene Cracking Reactivity on H-ZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9579–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Etim, U.J.; Shi, Z.; Xing, W.; Wu, P.; Han, D.; Bai, P.; Yan, Z. Predicting Catalytic Performance of Micro-Mesoporous Pt/Beta-KIT-6 Catalyst in n-Heptane Hydroisomerization Using Indexed Isomerization Factor and Experimental Verification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5146–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, J.; Jacobs, P. Chapter 14 Introduction to acid catalysis with zeolites in hydrocarbon reactions. Pharmacogenetics 2001, 137, 633–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinger, G.; Majda, D.; Vinek, H. n-Heptane hydroisomerization over Pt-containing mixtures of zeolites with inert materials. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 225, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewska, K.; Fedyna, M.; Trawczyński, J. Hydroisomerization of long-chain n-alkanes over Pt/AlSBA-15+zeolite bimodal catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 117756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, M.J.; Kooyman, P.J.; Van Der Waal, J.C.; Rigutto, M.S.; Peters, J.A.; Van Bekkum, H. Partial Transformation of MCM-41 Material into Zeolites: Formation of Nanosized MFI Type Crystallites. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Jalil, A.; Khusnun, N.; Fatah, N.; Hamid, M.; Gambo, Y.; Abdulrasheed, A.; Hassan, N. Enhanced n-hexane hydroisomerization over bicontinuous lamellar silica mordenite supported platinum (Pt/HM@KCC-1) catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 18587–18599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammoury, H.; Toufaily, J.; Cherry, K.; Hamieh, T.; Pouilloux, Y.; Pinard, L. Impact of desilication of *BEA zeolites on the catalytic performance in hydroisomerization of n-C 10. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 551, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, R.; Romero, F.J.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Marinas, J.M.; Gómez, J.P. Influence of acidity and pore geometry on the product distribution in the hydroisomerization of light paraffins on zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 288, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Ficht, K.; Bertmer, M.; Einicke, W.-D.; Kuchling, T.; Gläser, R. Hydroisomerization of long-chain paraffins over nano-sized bimetallic Pt–Pd/H-beta catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 4045–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niquille-Röthlisberger, A.; Prins, R. Hydrodesulfurization of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene over Pt, Pd, and Pt–Pd catalysts supported on amorphous silica–alumina. Catal. Today 2007, 123, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fonfé, B.; Jentys, A.; Haller, G.L.; Van Veen, J.R.; Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Lercher, J.A.; Tinoco, O.G. Bimetallic Pt–Pd/silica–alumina hydrotreating catalysts. Part II: Structure–activity correlations in the hydrogenation of tetralin in the presence of dibenzothiophene and quinoline. J. Catal. 2012, 292, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-D.; Vannice, M. Supported platinum, Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Catalusis, Budapest, Hungary, 19–24 July 2021; Volume 75, pp. 861–874. [Google Scholar]
- Chupin, J.; Gnep, N.; Lacombe, S.; Guisnet, M. Influence of the metal and of the support on the activity and stability of bifunctional catalysts for toluene hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 206, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomsma, E.; Martens, J.; Jacobs, P. Isomerization and Hydrocracking of Heptane over Bimetallic Bifunctional PtPd/H-Beta and PtPd/USY Zeolite Catalysts. J. Catal. 1997, 165, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Pawelec, B.; Trejo, J.; Mariscal, R.; Fierro, J. Hydrogenation of Aromatics on Sulfur-Resistant PtPd Bimetallic Catalysts. J. Catal. 2000, 189, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan, R.; Beale, A.; Sanchezsanchez, M.; Romerosalguero, F.; Jimenezsanchidrian, C.; Gomez, J.; Sankar, G. Effect of the impregnation order on the nature of metal particles of bi-functional Pt/Pd-supported zeolite Beta materials and on their catalytic activity for the hydroisomerization of alkanes. J. Catal. 2008, 254, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, N.; Papadopoulos, C.; Gaglias, I.; Pitarakis, K. A new non-linear calculation method of isomerisation gasoline research octane number based on gas chromatographic data. Fuel 2004, 83, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Mohamed, A.; Al-Kandari, H. Semi-industrial studies of Tungsten-based catalyst for hydroisomerization/hydrocracking of n-hexane and n-heptane. Mol. Catal. 2018, 452, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Murugesan, V.; Böhlmann, A.W.; Hartmann†, M. An Optimized Procedure for the Synthesis of AlSBA-15 with Large Pore Diameter and High Aluminum Content. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11496–11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, G.; Canton, P.; Riello, P.; Pernicone, N.; Pinna, F.; Battagliarin, M. Nanostructural Features of Pd/C Catalysts Investigated by Physical Methods: A Reference for Chemisorption Analysis. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4539–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalyst | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Weak | Medium | Strong | A350/A150 d | Total | Weak | Medium | Strong | A350/A150 d | ||
| Pt/AlSBA-15 | 3.43 | 0.42 | 1.32 | 1.68 | 0.12 | 5.36 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 4.03 | 0.75 | 8.79 |
| Pt/BEA | 15.1 | - | 3.43 | 11.6 | 0.77 | 8.13 | - | - | 8.13 | 1.00 | 23.2 |
| Pt/SBA—BEA | 5.18 | 1.32 | 1.75 | 2.1 | 0.16 | 3.55 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 3.01 | 0.81 | 8.73 |
| Pt/SBA—MOR | 3.85 | - | 0.84 | 3.01 | 0.45 | 4.03 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 3.43 | 0.79 | 7.89 |
| Pt/SBA—MFI | 6.02 | 0.84 | 1.69 | 3.49 | 0.36 | 5.06 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 4.03 | 0.75 | 11.1 |
| Pd/SBA—BEA | 3.85 | 0.42 | 1.26 | 2.16 | 0.23 | 2.65 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 2.17 | 0.82 | 6.50 |
| Pt-Pd/SBA—BEA | 8.61 | 0.90 | 3.85 | 3.86 | 0.20 | 6.62 | 0.42 | 1.57 | 4.63 | 0.59 | 15.2 |
| Catalyst | a | b | c | d | e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/AlSBA-15 | 57 | 142 | 2.0 | 1.54 | 0.88 |
| Pt/BEA | 75 | 205 | 1.4 | 1.54 | 1.16 |
| Pt/SBA—BEA | 58 | 144 | 2.0 | 1.54 | 0.90 |
| Pt/SBA—MOR | 48 | 120 | 2.3 | 1.54 | 0.74 |
| Pt/SBA—MFI | 34 | 93 | 3.0 | 1.54 | 0.53 |
| Pd/SBA—BEA | 25 | 63 | 3.7 | 1.54 | 0.39 |
| Pt-Pd/SBA—BEA | 36 | 95 | 2.7 | 1.54 | 0.56 |
| Catalyst | TR (°C) | Conv. (%) | Hydroisomerization (wt%) | Hydrocracking (wt%) | Dehydrocyclization (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total iso-C7 | MoBC7 a | MuBC7 b | 2-MeC6/3-MeC6 | C3 + C4 | Aro & Cyc | |||
| Pt/AlSBA-15 | 350 | 64.5 | 50.2 | 44.0 | 6.1 | 0.92 | 6.7 | 7.7 |
| Pt/BEA | 270 c | 72.0 | 63.9 | 49.2 | 14.7 | 0.86 | 8.1 | - |
| Pt/MOR | 250 | 90.6 | 56.4 | 30.1 | 26.4 | 0.83 | 34.2 | - |
| Pt/MFI | 250 | 99.5 | 52.1 | 27.6 | 24.5 | 0.94 | 47.4 | - |
| Pt/SBA–BEA c | 290 | 82.3 | 59.7 | 42.7 | 16.9 | 0.83 | 21.1 | 1.5 |
| Pt/SBA–MOR | 290 | 90.1 | 48.2 | 30.1 | 18.1 | 0.76 | 41.9 | - |
| Pt/SBA–MFI | 290 | 96.7 | 25.0 | 15.5 | 9.5 | 0.83 | 67.5 | 1.5 |
| Pd/SBA–BEA | 290 | 48.3 | 38.8 | 30.6 | 8.2 | 0.82 | 9.5 | 0.2 |
| PtPd/SBA–BEA | 290 | 78.1 | 68.2 | 47.5 | 20.7 | 0.80 | 9.9 | 1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaroszewska, K.; Fedyna, M.; Masalska, A.; Łużny, R.; Trawczyński, J. Promotional Effect of Pd Addition on the Catalytic Activity of Composite Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–β Catalyst for Enhanced n-Heptane Hydroisomerization. Catalysts 2021, 11, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030377
Jaroszewska K, Fedyna M, Masalska A, Łużny R, Trawczyński J. Promotional Effect of Pd Addition on the Catalytic Activity of Composite Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–β Catalyst for Enhanced n-Heptane Hydroisomerization. Catalysts. 2021; 11(3):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030377
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaroszewska, Karolina, Monika Fedyna, Aleksandra Masalska, Rafał Łużny, and Janusz Trawczyński. 2021. "Promotional Effect of Pd Addition on the Catalytic Activity of Composite Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–β Catalyst for Enhanced n-Heptane Hydroisomerization" Catalysts 11, no. 3: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030377
APA StyleJaroszewska, K., Fedyna, M., Masalska, A., Łużny, R., & Trawczyński, J. (2021). Promotional Effect of Pd Addition on the Catalytic Activity of Composite Pt-Pd/AlSBA-15–β Catalyst for Enhanced n-Heptane Hydroisomerization. Catalysts, 11(3), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030377