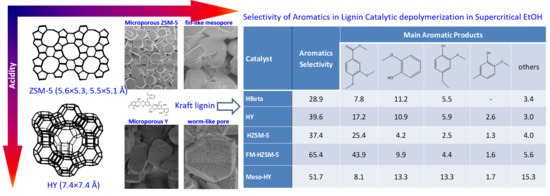
Kraft Lignin Ethanolysis over Zeolites with Different Acidity and Pore Structures for Aromatics Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphology and Textural Properties of Zeolites Used in Lignin Depolymerisation
2.2. Effect of Pore Size and Acidity of Microporous Zeolites in Lignin Depolymerisation
2.3. Zeolites with Different Acidity while Same Micropore Structure in Lignin Depolymerisation
2.4. Importance of Mesopores of Zeolites in Lignin Catalytic Depolymerization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Zeolite Synthesis
4.2.1. ZSM-5 and Fin-like Mesoporous ZSM-5 Synthesis
4.2.2. Y Zeolites Synthesis
4.2.3. Beta Zeolites Synthesis
4.2.4. Ion-Exchange and H-type Zeolites Preparation
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Lignin Depolymerisation Tests
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Jongerius, A.L.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.R. Lignin—from natural adsorbent to activated carbon: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick, W.J.; Hallett, J.P., Jr.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L.; et al. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Beckham, G.T.; Biddy, M.J.; Chandra, R.; Chen, F.; Davis, M.F.; Davison, B.H.; Dixon, R.A.; Gilna, P.; Keller, M.; et al. Lignin valorization: Improving lignin processing in the biorefinery. Science 2014, 344, 1246843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.T.; Armbruster, U.; Martin, A. Heterogeneously catalyzed hydroprocessing of organosolv lignin in sub- and supercritical solvents. Energy Fuel 2011, 25, 4713–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Hao, W.; X. Ma, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Catalytic Ethanolysis of kraft lignin into high-value small-molecular chemicals over a nanostructured α-molybdenum carbide catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7310–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, K.; Taccardi, N.; Boesmann, A.; Wasserscheid, P. Oxidative depolymerization of lignin in ionic liquids. ChemSusChem 2010, 3, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, J.A.; Font, R.; Marcilla, A. A Study of the primary pyrolysis of Kraft lignin at high heating rates: Yields and kinetics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1996, 36, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, D.; Dalai, A.K.; Bej, S.K.; Thring, R.W. Pyrolysis of lignins: Experimental and kinetics studies. Energy Fuel 2002, 16, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rinald, R. Solvent effects on the hydrogenolysis of diphenyl ether with Raney nickel and their implications for the conversion of lignin. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.; Evangelisti, C.; Aronica, L.A. Hydrogenolysis of benzyl protected phenols and aniline promoted by supported palladium nanoparticles. Chem. Sel. 2017, 2, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, F.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Xu, J. Lignin depolymerization (LDP) in alcohol over nickel-based catalysts via a fragmentation–hydrogenolysis process. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 994–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Guvenatam, B.; Geeres, E.H.; Pidko, E.A.; Hensen, E.J. Lewis acid catalyzed depolymerization of soda lignin in supercritical ethanol/water mixtures. Catal. Today 2016, 269, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thring, R.W.; Breau, J. Hydrocracking of solvolysis lignin in a batch reactor. Fuel 1996, 75, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Zhao, C.; Dyson, P.J.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Kou, Y. Selective degradation of wood lignin over noble-metal catalysts in a two-step process. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, V.M.; Stein, V.; Reiner, T.; Lemonidou, A.; Li, X.; Lercher, J.A. Towards quantitative catalytic lignin depolymerization. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 5939–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, D.D.; Tucker, M.P.; Chen, X.; Helms, G.L.; Yang, B. Noble-metal catalyzed hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived lignin to aromatic hydrocarbons. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, A.; Serrano, L.; Labidi, J.; Pineda, A.; Mariana Balu, A.; Luque, R. Heterogeneously catalysed mild hydrogenolytic depolymerisation of lignin under microwave irradiation with hydrogen-donating solvents. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, G.; Hansen, T.S.; Riisager, A.; Beach, E.S.; Barta, K.; Anastas, P.T. Depolymerization of organosolv lignin using doped porous metal oxides in supercritical methanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margellou, A.; Triantafyllidis, K. Catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis reactions for lignin valorization to fuels and chemicals. Catalysts 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Watanabe, T.; Saito, K.; Kuwano, S.; Murakami, Y.; Mimura, N.; Sato, O. Direct conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into aromatic monomers over supported metal catalysts in supercritical water. Mol. Catal. 2019, 477, 110557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, K.; Matson, T.D.; Fettig, M.L.; Scott, S.L.; Iretskii, A.V.; Ford, P.C. Catalytic disassembly of an organosolv lignin via hydrogen transfer from supercritical methanol. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Ma, R.; Ma, X.; Cui, K.; Wu, K.; Chen, M.; Li, Y. Ethanolysis of Kraft lignin to platform chemicals on a MoC 1-x /Cu-MgAlO z catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Yang, S.; Kim, D.H. Depolymerization of Protobind lignin to produce monoaromatic compounds over Cu/ZSM-5 catalyst in supercritical ethanol. Mol. Catal. 2017, 442, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Baxter, N.; Kuo, G.T.; Wang, S. Synthesis of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites by solid-state crystallization and their catalytic properties. J. Catal. 2017, 349, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Bakhshi, N.N. Catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuels 1993, 7, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lercher, J.A. Selective hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenolic monomers and dimmers to cycloalkanes on Pd/C and HZSM-5 catalysts. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, A.K.; Dhepe, P.L. Lignin depolymerisation into aromatic monomers over solid acid catalysts. Acs Catal. 2015, 5, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. One-Step valorization of calcium lignosulfonate to produce phenolics with the addition of solid base oxides in the hydrothermal reaction system. Energy Fuels 2019, 9, b00332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Xue, S.; Yang, Y. Effects of the controllable mesostructure of nano-sized ZSM-5 on the co-cracking of phenolic bio-oil model compounds and ethanol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 3525–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Sharma, B.K.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J. Catalytic valorization of lignin to liquid fuels over solid acid catalyst assisted by microwave heating. Fuel 2019, 239, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Fan, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, X. Catalytic alcoholysis of lignin with HY and ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A. From microporous to mesoporous molecular sieve materials and their use in catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 2373–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yu, J.; Corma, A. Extra-Large-Pore zeolites: Bridging the gap between micro and mesoporous structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3120–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; He, T.; Hu, H.; Wu, J. Hydrodeoxygenation of dibenzofuran over noble metal supported on mesoporous zeolite. Catal. Comm. 2011, 12, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y. From biomass to advanced bio-fuel by catalytic pyrolysis/hydro-processing: Hydrodeoxygenation of bio-oil derived from biomass catalytic pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 108, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Rooke, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Su, B. Hierarchically structured zeolites: Synthesis, mass transport properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17381–17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, Y.; Miao, P.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y. Hydrogenation of naphthalene over noble metal supported on mesoporous zeolite in the absence and presence of sulfur. Fuel 2013, 106, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, S. Hydrodeoxygenation of bio-oil over Pt-based supported catalysts: Importance of mesopores and acidity of the support to compounds with different oxygen contents. Rsc Adv. 2013, 3, 12635–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. New ZnCe catalyst encapsulated in SBA-15 in the production of 1,3-butadiene from ethanol. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ma, R.; Hao, W.; Chen, M.; Yan, F.; Cui, K.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Common pathways in ethanolysis of kraft lignin to platform chemicals over molybdenum-based catalysts. Acs Catal. 2014, 5, 4803–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaino, U.; Maximova, N.; Hortling, B.; Laine, J.; Stenius, P.; Simola, L.; Gravitis, J.; Serimaa, R. Morphology of dry lignins and size and shape of dissolved kraft lignin particles by X-ray scattering. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9736–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Baxter, N.C.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. Guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation over Pd catalyst with mesoporous ZSM-5 support synthesized by solid-state crystallization. Catal. Today 2020, 358, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, P.; Shafaghat, H.; Daud, W. Production of green aromatics and olefins by catalytic cracking of oxygenate compounds derived from biomass pyrolysis: A review. Appl. Catal. A 2014, 469, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyle, M.; Bartholomew, C. Heterogeneous catalyst deactivation and regeneration: A review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 145–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintova, S.; Olson, N.H.; Bein, T. Electron Microscopy Reveals the Nucleation Mechanism of Zeolite Y from Precursor Colloids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3201–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camblor, M.A.; Corma, A.; Mifsud, A.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Valencia, A. Synthesis of nanocrystalline zeolite beta in the absence of alkali metal cations. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1997, 105, 341. [Google Scholar]





| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Smicro a (m2/g) | Sext a (m2/g) | Vtotal b (cm3/g) | VMicro b (cm3/g) | VMeso b (cm3/g) | Pore Size c (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZSM-5 | 354.3 | 222.2 | 132.2 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 2.7 |
| Meso-HZSM-5 | 460.3 | 87.8 | 372.5 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 3.6 |
| HY | 720.6 | 566.1 | 154.5 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 2.6 |
| Meso-HY | 766.3 | 410.5 | 355.8 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 6.9 |
| HBeta | 536.4 | 436.2 | 100.2 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 2.8 |
| Sample | NaY | NaNH4Y | HY | HBeta | HZSM-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak and medium acid sites, μmold/g | 71.6 | 365.8 | 249.0 | 208.8 | 644.7 |
| (percentage in total acidity) | (19.4%) | (51.9%) | (25.4%) | (28.1%) | (55.4%) |
| Strong and ultra-strong acid sites, μmold/g | 298.2 | 338.5 | 730.6 | 535.4 | 518.4 |
| (percentage in total acidity) | (80.6%) | (48.1%) | (74.6%) | (71.9%) | (44.6%) |
| Total acidity, μmold/g | 369.8 | 704.3 | 979.6 | 744.2 | 1163.1 |
| Medium-to-Strong acid ratio | 0.24 | 0.92 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 1.24 |
| Catalyst. | Aromatics Selectivity | Main Aromatic Products | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 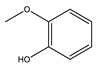 |  | 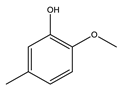 | Others | ||
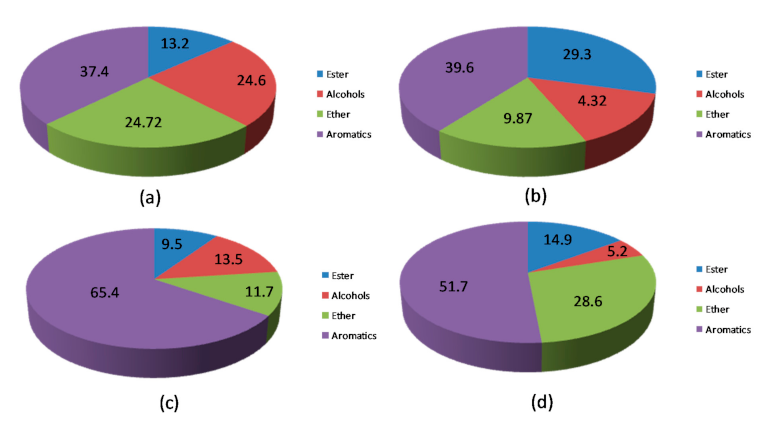
| HBeta | 28.9 | 7.8 | 11.2 | 5.5 | - | 3.4 |
| HY | 39.6 | 17.2 | 10.9 | 5.9 | 2.6 | 3.0 |
| HZSM-5 | 37.4 | 25.4 | 4.2 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 4.0 |
| FM-HZSM-5 | 65.4 | 43.9 | 9.9 | 4.4 | 1.6 | 5.6 |
| Meso-HY | 51.7 | 8.1 | 13.3 | 13.3 | 1.7 | 15.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baxter, N.C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Liao, Y.; Barnett, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. Kraft Lignin Ethanolysis over Zeolites with Different Acidity and Pore Structures for Aromatics Production. Catalysts 2021, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020270
Baxter NC, Wang Y, Huang H, Liao Y, Barnett H, Zhao Y, Wang S. Kraft Lignin Ethanolysis over Zeolites with Different Acidity and Pore Structures for Aromatics Production. Catalysts. 2021; 11(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaxter, Nathan Cody, Yuxin Wang, Huijiang Huang, Yixin Liao, Heath Barnett, Yujun Zhao, and Shengnian Wang. 2021. "Kraft Lignin Ethanolysis over Zeolites with Different Acidity and Pore Structures for Aromatics Production" Catalysts 11, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020270
APA StyleBaxter, N. C., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Liao, Y., Barnett, H., Zhao, Y., & Wang, S. (2021). Kraft Lignin Ethanolysis over Zeolites with Different Acidity and Pore Structures for Aromatics Production. Catalysts, 11(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11020270