Abstract
The pervasive use of toxic nitroaromatics in industrial processes and their prevalence in industrial effluent has motivated the development of remediation strategies, among which is their catalytic reduction to the less toxic and synthetically useful aniline derivatives. While this area of research has a rich history with innumerable examples of active catalysts, the majority of systems rely on expensive precious metals and are submicron- or even a few-nanometer-sized colloidal particles. Such systems provide invaluable academic insight but are unsuitable for practical application. Herein, we report the fabrication of catalysts based on ultralow loading of the semiprecious metal ruthenium on 2–4 mm diameter spherical alumina monoliths. Ruthenium loading is achieved by atomic layer deposition (ALD) and catalytic activity is benchmarked using the ubiquitous para-nitrophenol, NaBH4 aqueous reduction protocol. Recyclability testing points to a very robust catalyst system with intrinsic ease of handling.
1. Introduction
Nitroaromatics represent a family of broadly used compounds in industrial processes; for example, in pesticide, fungicide, textile and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Consequently, they are a common pollutant in aqueous industrial effluent, notably displaying acute toxicity and potential carcinogenicity. This has motivated the study of remediation strategies, namely the mild-conditions -NO2 group reduction to yield their less toxic and synthetically useful aniline (-NH2) derivatives. Among this general reaction family, the catalytic reduction of para- or 4-nitrophenol (4NP) specifically has emerged as the benchmark test for catalysts—not only for relevant environmental remediation, but also as a universal rapid screening test for heterogeneous catalyst reduction activity [1,2,3]. Most typically, catalytic reduction of 4NP is conducted in deionized water (DIW) with a large excess of a hydrogen source, such as sodium borohydride (NaBH4), which provides surface -H species; H2 generated by competing NaBH4 hydrolysis may also play a role under certain conditions. The reaction is readily monitored through Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometry by tracking the decrease in absorbance at λmax = 400 nm, associated with 4-nitrophenolate (4NP*), the anionic derivative of 4NP which forms in the presence of NaBH4. Reaction kinetics (kapp = apparent rate) are derived from the slope of ln(A/A0) which correlate to 4NP* concentrations (C/C0) (Equation (1)). The reaction is typically described in terms of the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and the large excess of NaBH4 not only provides an ample H-source, but also creates a pseudo-first-order process, allowing facile interpretation of kinetics [4,5,6].
Historically, catalytic reduction of 4NP has been promoted primarily with catalytic noble metal nanoparticles [7,8,9,10,11,12], to a lesser extent with non-noble metal nanoparticles [13,14,15,16,17], and more recently nonmetal species [18,19,20,21]. A significant majority of these catalyst systems are submicron- or even a few-nanometer-sized colloidal particles. Although very catalytically efficient for lab-scale testing and generation of fundamental knowledge, the use of nanocatalysts in the environment can be challenging to manage, and their fate and transport are complex and may pose hazards [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. We endeavored to develop a robust and more applicable nitroaromatic reduction catalyst, which circumvents the need for submicron or even ultrasmall colloidal nanoparticles. Herein, we report the fabrication of catalysts based on ultralow loading of semiprecious metal ruthenium on 2–4 mm diameter spherical alumina monoliths. Controllable, ultralow ruthenium loading is achieved by atomic layer deposition (ALD). ALD is a self-limiting technique which provides a highly precise and reproducible coating thickness. Because of the high level of control afforded, it is not surprising that ALD is emerging as a powerful tool for catalyst synthesis. ALD-synthesized catalysts have been previously studied for hydrolysis reactions [29,30,31]; notably, Jiang et al. reported the use of an ALD-Ni coated catalyst for nitrophenol reduction [32]. Ruthenium was chosen due to its well-established catalytic activity in reduction reactions [33,34,35,36,37,38], lower cost compared to Pd and Au catalysts which dominate nitroaromatic reductions, and the availability of a well-defined ALD process for Ru films, as developed by one of our groups [39]. The ALD-Ru on alumina monolith catalysts is highly active, exhibiting reaction rates competitive with precious metal catalysts, and is recyclable for up to five trials as tested with no significant loss in activity from trials 2 to 5. Notably, the millimeter-sized materials are robust, and facile to handle and separate from reaction solutions.
2. Results and Discussion
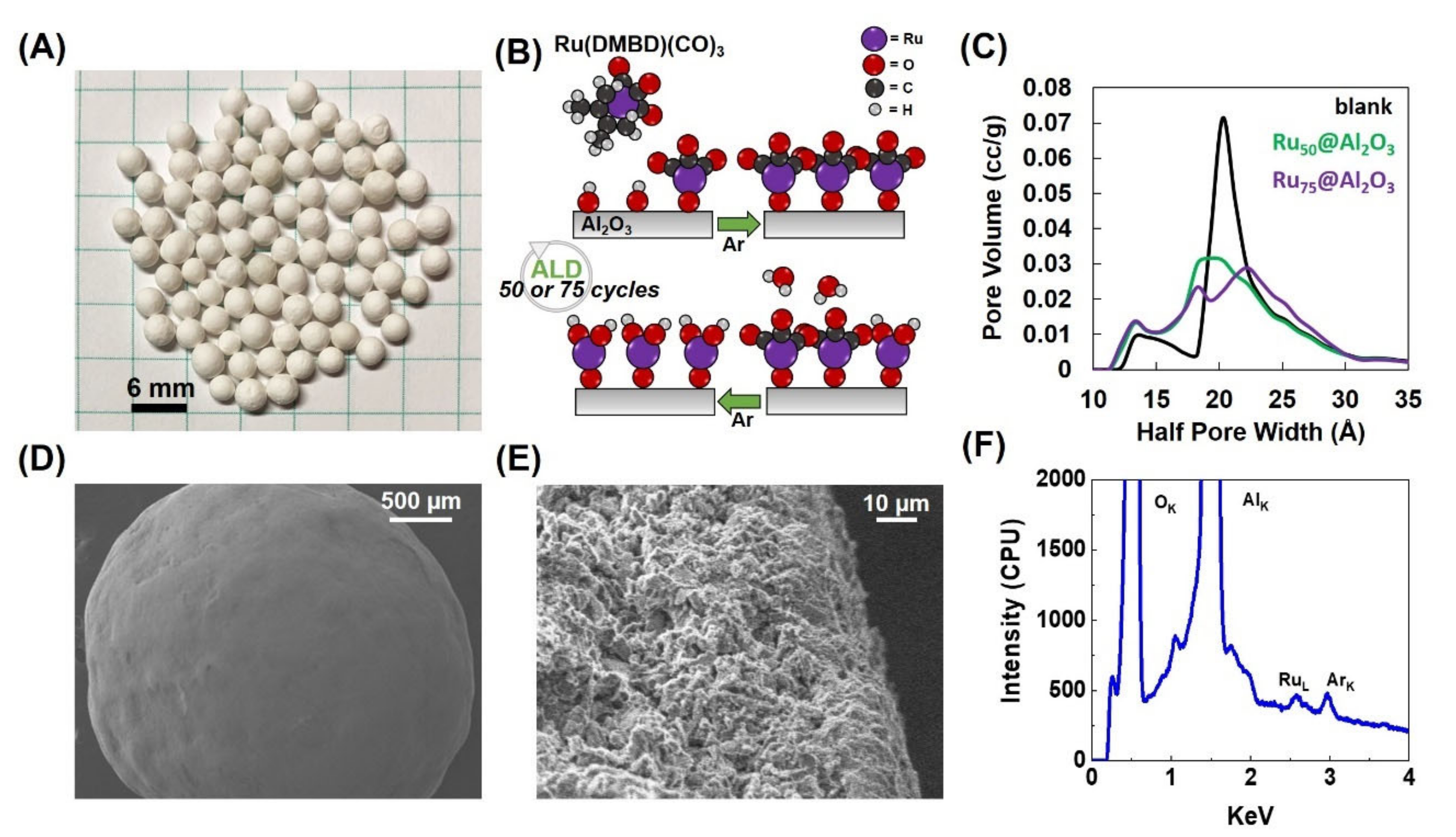
Synthesis and Characterization: Prospective catalysts were prepared by coating 2–4 mm diameter spherical Al2O3 monoliths (Figure 1A) with an ultrathin layer of Ru by ALD. Growth was achieved utilizing an A-B cycle of alternating η4-2,3-dimethylbutadiene ruthenium tricarbonyl (Ru(DMBD)(CO)3) as a zero-valent ruthenium precursor and water as a co-reactant (Figure 1B). Previous work from one of our groups has shown this specific process to produce metallic Ru [39]. Using A-B cycle sets of 50 and 75, two different materials were prepared: denoted as Ru50@Al2O3 and Ru75@Al2O3, respectively. In this instance, the as-deposited Ru materials are a combination of metallic Ru0 and Ru4+ oxides. Further details are provided in the Materials and Methods.
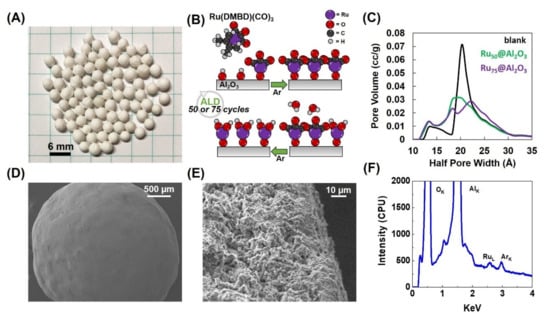
Figure 1.
Blank Al2O3 spheres (A); schematic representation for atomic layer deposition (ALD) growth of Ru film (B); pore volume (C); Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) micrographs (D,E); Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) of Ru75@Al2O3 (F).
To delineate the effect of Ru deposition on pore size, N2 physisorption was performed on an uncoated “blank” Al2O3 sphere, Ru50@Al2O3 and Ru75@Al2O3 (Figure 1C). The blank displayed a bimodal pore size distribution with the bulk of pore radii between 13.25 and 20.25 Å with pore volumes of 0.009–0.071 cc/g, respectively. After 50 (Ru50@Al2O3) and 75 cycles (Ru75@Al2O3), the pore volume centered around pore radii of 20.25 Å decreased to 0.031 and 0.029 cc/g, respectively, and pore volumes centered around pore radii of 13.25 Å increased to 0.013 and 0.014 cc/g, respectively. This result is attributed to the Ru deposition and conformal coverage of the porous network ultimately reducing the total volume and increasing the number of smaller pores. The increase in pore radius after 75 cycles compared to the blank may be due to changes in the internal structure during ALD. Overall, the total pore volume decreased as the Ru deposition constricted the pores after ALD; this is consistent with prior literature [39,40].
The surface morphology of Ru75@Al2O3 was imaged by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) (Figure 1D,E). The material exhibits a complex microstructure with numerous fissures and pores commensurate with the findings of the N2 sorption analysis. Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) of the surface was used qualitatively. Nonetheless, EDX confirmed the deposition of Ru (Figure 1F) as well as oxygen, aluminum, and argon (Ar). The presence of Ar can be attributed to the Ar gas used in the purge steps of the ALD super cycles. Mass percent of Ru for both materials was determined via inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS)—1.70 × 10−3 ± 3.63 × 10−4% by mass for Ru50@Al2O3 and 1.98 × 10−3 ± 1.04 × 10−4% by mass for Ru75@Al2O3. The increase in Ru loading is commensurate with the 50% increase in number of ALD cycles. Our initial attempt to characterize the nature of Ru by XPS on Ru50@Al2O3 did not result in a significant Ru signal. We can attribute this to the highly porous structure of the Al2O3 sphere and the presence of high C on this surface. It is to be noted that the Ru-3d signal (280.1 with a spin-orbit splitting of 4.17 eV) strongly overlapped with carbon-1s (284.5 eV), making the analysis necessarily difficult in the first place. These results suggest that a simpler analogue to monitor the chemical state of Ru on Al2O3 needs to be formulated. Therefore, we have taken a planar substrate consisting of a Si wafer with 10 nm of Al2O3 deposited using ALD followed by 5 nm of ALD Ru. This system reasonably represents the chemical nature of the Ru that is present on the Al2O3 spheres without the surface topological complexity and porosity that the Al2O3 spheres present. Therein, the Ru is a mixture of metal (Ru0) and Ru4+ at 43.22 and 56.78 atomic %, respectively (Figure S1, Table S1).
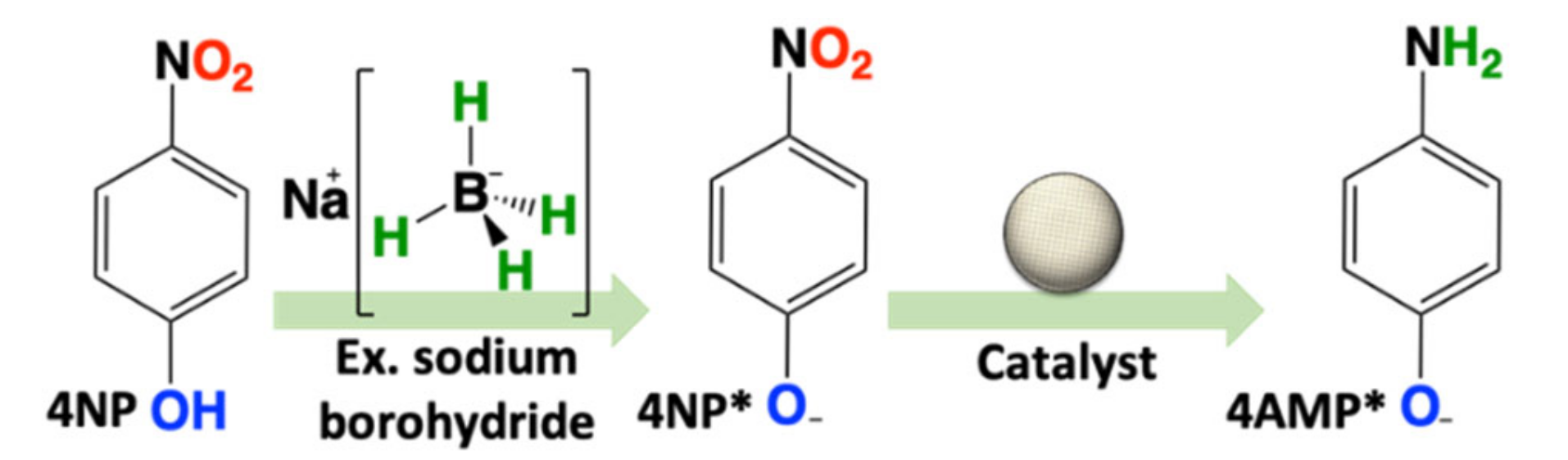
Catalytic Testing: The catalytic activity towards the reduction of 4NP of both materials was tested in the presence of excess NaBH4. To validate both the ease of handling and recyclability of the catalysts, five consecutive recycle trials were performed. This was repeated a second time and the results were averaged. Reactions were conducted in a 1 cm quartz cell and monitored directly by UV–Vis spectroscopy for the decrease in absorbance for 4NP* at λmax = 400; 4NP is deprotonated to form 4-nitrophenolate (4NP*) in the presence of excess NaBH4. This decrease in absorbance was accompanied by an increase at λmax = 300 nm, pertaining to the formation of 4-aminophenolate (4AMP*) (Scheme 1). As noted in the introduction (vide supra), the reaction is typically interpreted according to the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and due to the large excess of H-source (NaBH4), the kinetics are treated as a pseudo-first-order process. Thus it was surprising that the initial catalytic trial for both Ru50@Al2O3 and Ru75@Al2O3 could be fitted with superior confidence to a zero-order process (Figure 2A,B). However, subsequent recycle trials (2–5) for both materials yielded kinetics which fit a first-order process. We attributed this to leaching of very reactive Ru-based species upon introduction to a high pH (~10.4) NaBH4-rich environment. This likely creates an environment with multiple active catalysts, prohibiting the clear determination of a reaction order. Subsequent trials show remarkably steady performances, commensurate with a robust, highly recyclable catalyst.
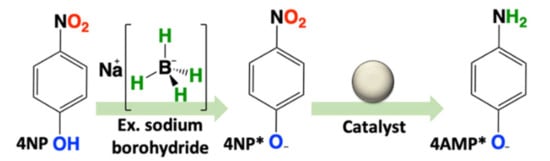
Scheme 1.
Reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4NP) in water with large excess NaBH4.
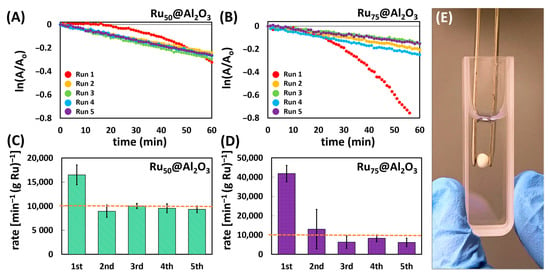
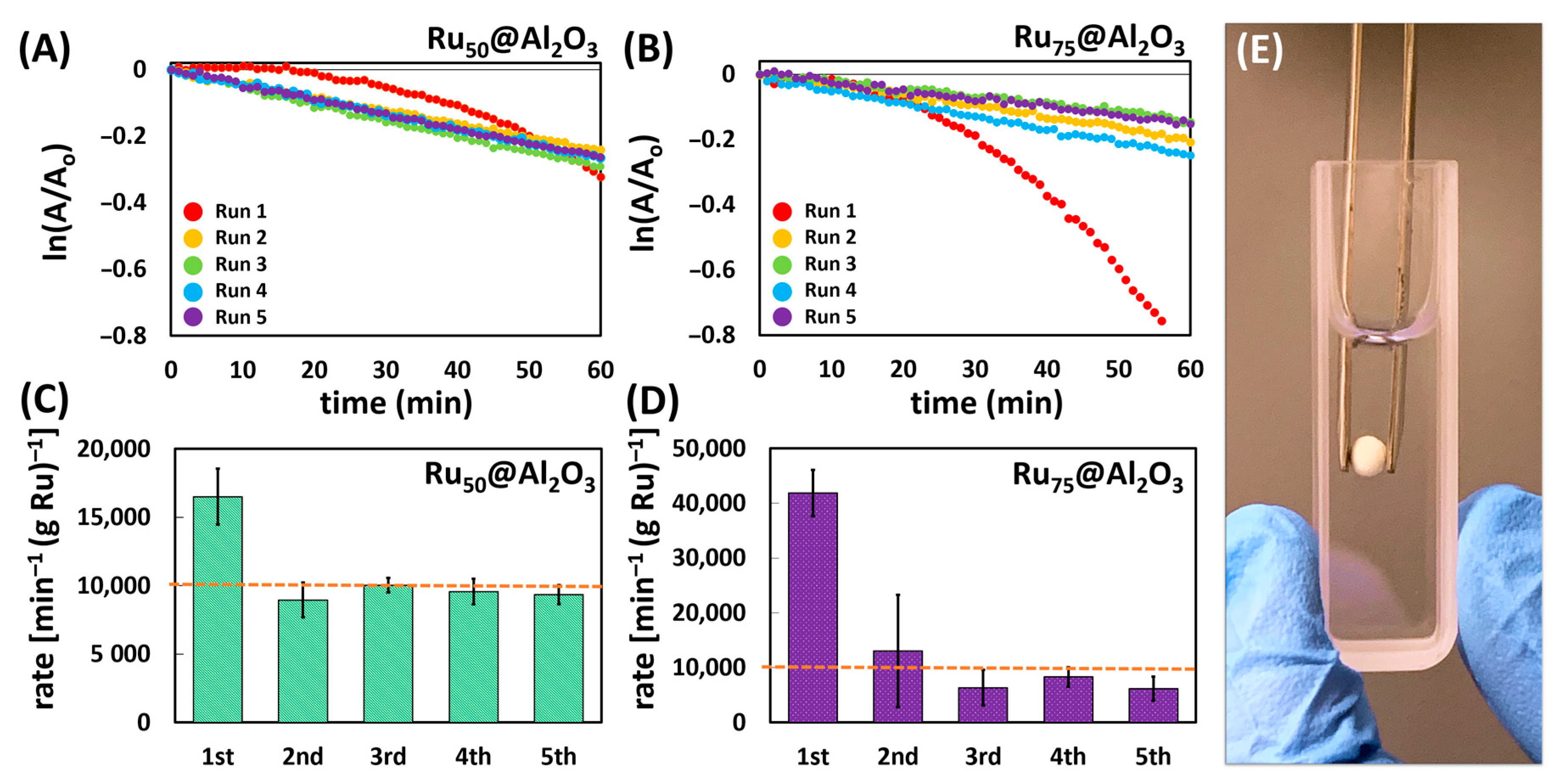
Figure 2.
One 5-trial sequence of pseudo-first-order kinetics plotted for the reduction of 4NP using Ru50@Al2O3 (A) and Ru75@Al2O3 (B). Kinetic rates normalized to the mass of Ru over five trials for the Ru50@Al2O3 (C) and Ru75@Al2O3 (D); dashed line shown to facilitate rate comparison. (E) Photograph highlighting ease of handling.
Interestingly, while the mass-normalized (to Ru) observed rates (K) for Ru50@Al2O3 and Ru75@Al2O3 differed dramatically in the initial run (Ru50@Al2O3 K = 16,500 ± 2042 min−1gRu−1; Ru75@Al2O3 K = 41,857 ± 4235 min−1gRu−1), they rapidly normalize to ca. K = 10,000 min−1gRu−1 for both catalysts in recycle trials 2–5 (Figure 2A–D). We postulate this similarity in trials 2–5 regardless of initial Ru loading is likely due to the presence of loosely bound surface species which arise after an initial coating threshold is reached after X number of ALD cycles (X < 50). Thus, Ru deposited beyond this threshold is amenable to leaching, likely as highly reactive nanoparticles. Accordingly, the higher loading Ru75@Al2O3 yielded a higher observed rate in the first run due to more catalytically active material being released into the solution.
To corroborate the proposed leaching, the reaction solution post reduction of 4NP using Ru50@Al2O3 (trial 1) was measured by ICP-MS. The initial solution leached 1.83 × 10−3 ± 2.27 × 10−4 µg Ru/mg catalyst. Repeating the ICP-MS measurement under similar conditions upon completion of trial 2 indicated that 3.80 × 10−4 ± 1.77 × 10−5 µg Ru/mg leached—a nearly five-fold decrease. The mass percent of Ru on Ru50@Al2O3 after all five consecutive trials was determined to be 1.63 × 10−3 ± 1.32 × 10−4% Ru by mass compared to 1.70 × 10−3 ± 3.63 × 10−4% for Ru50@Al2O3 prior to catalysis. Thus, for Ru50@Al2O3, the Ru coating is remarkably stable and overall the catalyst is robust, particularly from trials 2–5. However, the small amount of Ru that does leach during the initial trial clearly forms highly reactive nanoparticles which accounts for the intractable observed kinetics; once these particles are removed from the system, the catalyst behavior is remarkably consistent.
Notably, the mass-normalized observed rate of ca. K = 10,000 min−1gRu−1 attained in trials 2–5 for both catalysts is very competitive. To allow comparison to other, highly reactive systems from the literature, we further normalized to reaction volume, yielding an “activity parameter” κ (s−1g−1L) [41,42,43]. Therein, our catalysts had a κ value of ca. 0.5 s−1g−1L. This is competitive with a number of recent literature reports for highly active precious metal nanoparticles: Au@Fe3O4 (0.061 s−1g−1L) [44]; Pd@Fe3O4/dextran (3.65 s−1g−1L) [42]; Pd@Fe3O4/SiO2 (0.402 s−1g−1L) [45]; Pd@Camorphous (1.67 s−1g−1L) [43]. To confirm that no reactivity could be attributed to the Al2O3 support, a blank trial was conducted with an uncoated sphere and no conversion was observed (Figure S4). To further validate the broader substrate scope and potential for our catalyst system, as a proof of concept, we tested the single run activity of Ru75@Al2O3 towards the reduction of several amino-nitrophenols and azo dyes (methyl red and methyl orange). The catalyst performed well, and similar trends with respect to superior fitting to zero-order vs. first-order kinetics were observed. Further details are provided in the Supporting Information (Figures S5–S8).
For the initial run with both catalysts, there was a noteworthy induction period (10–25 min) before the reaction proceeds. This induction period is common among previously reported 4NP catalytic reductions and has been attributed to a number of effects including catalyst surface restructuring [11,46,47,48,49,50], or more recently due to the effects of dissolved oxygen [51,52,53] and the influence of surface ligands [52]. In our case, dissolved O2 was clearly present both in the solution and likely within the monolith pore structure and was likely a significant contributor to the initial induction period, thus negating significant contribution from surface ligands (note, no efforts were made to exclude dissolved O2). The decomposition/leaching of the ALD-adlayer, which includes both ligands and loosely bound Ru species, also cannot be ignored as a contributor to the induction period as ICP-MS points to an initial Ru mass loss after trial 1 which quickly stabilizes over subsequent trials. This initial leaching is also commensurate with the very high initial kapp observed due to what we postulate to be release of very small and highly active Ru-based nanoparticles. This loss of material invariably causes some surface restructuring. Furthermore, the subsequent stability and lack of induction period in trials 2–5 are attributed to both the removal of this adlayer and weakly bound surface Ru, as well as the effect of a BH4− “treatment” in trial 1, which served to remove adsorbed O2 from the monolith; dissolved O2 in subsequent trials was not excluded from the reaction solution so its effects were not excluded, but are comparatively minimal with respect to the induction period. Overall, beyond trial 1, the catalysts remain very reactive and consistent. When compounded with the ease of handling/manipulation as pictured in Figure 2E, the ALD-Ru@Al2O3 monolith platform is a facile, robust, and effective catalyst system.
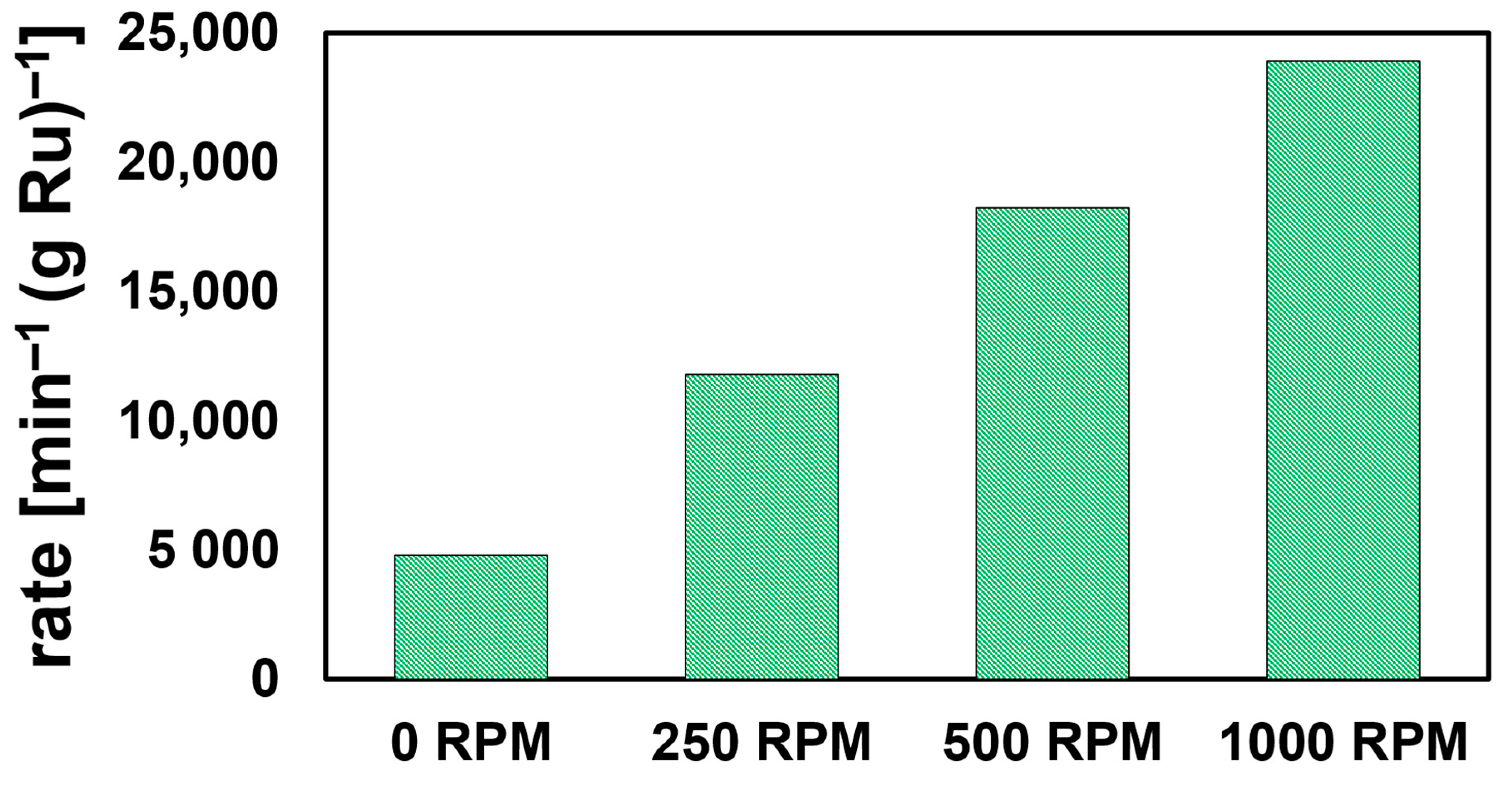
As reactions were conducted in a UV–Vis cuvette with no external agitation, the obtained rates were mass-transport limited; concomitant evolution of H2 from NaBH4 hydrolysis does, however, facilitate enhanced mixing compared to a completely non-agitated solution. To validate mass-transport effects, we conducted a separate set of 4NP reduction experiments with a UV–Vis dip-probe in a stirred solution. While reaction volume and reagent concentrations were scaled six-fold, a single sphere of Ru50@Al2O3 was used to minimize H2 evolution which causes gas bubble build-up on the probe, thus hampering accurate measurement. To negate the effects of Ru-leaching (vide supra), the sphere was pretreated with NaBH4. Subsequent measurements fit well to pseudo-first-order kinetics (Figure S9). Reactions conducted at 0, 250, 500, and 1000 rpm showed a clear increase in observed rate as a function of stirring rate (Figure 3). At 1000 rpm, Ru50@Al2O3 exhibited a κ value of ca. 7.2 s−1g−1L. Further details are provided in the Supporting Information.
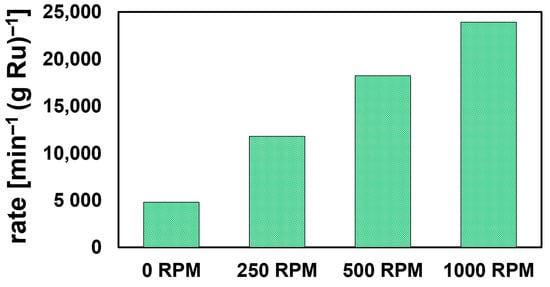
Figure 3.
Ru mass-normalized pseudo-first-order kinetics plotted for the reduction of 4NP using NaBH4-pretreated Ru50@Al2O3 at different stir rates (rpm = revolutions per minute).
3. Materials and Methods
ALD: Atomic layer deposition of ruthenium was performed using a home-built system coupled with a downstream quadrupole mass spectrometer (QMS), as described in our previous work [39,54,55,56]. Briefly, we used a load-locked, hot-wall, viscous flow reactor, 24 in. long with a 2.5 in. internal diameter, with an internal base pressure of 6.1 × 10−3 Torr as monitored by a Piezo/Pirani Dual Transducer (Model No TRN-910) from A&N Corporation. Purge gas control was obtained using a mass flow controller (Parker, 601 Series) and all the valves were pneumatically controlled ALD Valves (Swagelok). Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 (EMD Performance Materials) and DIW were used for the metal film deposition onto alumina supports (from Sorbtech). The Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 and DIW reactants were kept at 25 ± 1 °C. The ALD furnace temperature was held at 185 °C and the inlet gas lines were held at 80 °C. Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 was stored in a stainless steel bubbler and was carried into the reaction chamber by 99.999% pure Ar gas at rate of 25 standard cubic centimeters per minute (sccm) for 5 s. Each Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 pulse was followed by a purge step of 75 sccm Ar for 25 s. A subsequent vacuum step returned the chamber pressure to baseline before the following reactant DIW was directly introduced from a single outlet ampoule for 2s. The purge step followed with 75 sccm Ar for 25 s then a vacuum step to finish the super cycle. The reaction mechanism is described by Gao et al. [39], where a growth rate on planar silicon susbtrate of 1 Å/cycle is reported.
For deposition on Al2O3 spheres, a batch of 20× spheres were loaded inside a “steel barrel” mini-reactor. The mini-reactor had an inlet and exhaust port to allow the flow of gases inside the holder, exposing the Al2O3 spheres to the ALD chemistry. Details of this procedure will be provided in a subsequent publication. The mini-reactor was then inserted inside the ALD furnace. The reactor was rotated on its cylindrical axis by magnetically coupling it to an external servo motor (from Transfer Engineering and Manufacturing Inc.®, Fremont, CA, USA). The rotations per minute (rpm) were fixed at 8 rpm. Each cycle was repeated 50 and 75 times to create varying thicknesses of Ru deposition on Al2O3 spheres targeting thicknesses of 50 and 75 Å, respectively.
Characterization: A JEOL JSM-6480 SEM was used to record images at 5.0 kV of a blank sphere. Additionally, EDX analysis was completed on Ru75@Al2O3 with a beam energy of 15.00 kV at a 15 mm working distance to verify Ru deposition. Nitrogen sorption isotherms were measured at 77 K with a Quantachrome Autosorb iQ. Before measurements, the samples were degassed in a vacuum at 400 °C for 1 h. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method was utilized to calculate the specific surface areas using adsorption data in a relative pressure range from 0.05 to 0.35. The pore volumes and pore size distributions were calculated using the density functional theory model. Ru mass percent was determined through ICP-MS using an iCAP RQ Thermoscientific mass spectrometer. Ru-101 was used as the isotope of analysis, and kinetic energy discrimination (KED mode) was utilized to minimize interferences. To prepare the analysis solution, each sphere was crushed and dissolved in nearly boiling 10 M plasma grade sodium hydroxide (Thermo) and diluted to ~2% plasma grade nitric acid (Thermo). The content was compared to a calibration curve using standard Ru (American Standards, plasma grade, 1000 mg L−1). Three analysis solutions for each catalyst were prepared and three readings of each solution were performed and averaged. To test for Ru-metal leaching, a similar protocol was performed on the solution remaining post 4NP reduction and physical removal of Ru50@Al2O3.
Catalytic Investigations: UV–Vis measurements were carried out using an Agilent Cary 60 spectrophotometer under ambient conditions. Solutions were prepared in 1 cm quartz cuvettes and the reaction solution was scanned at timed intervals of 1 min. The 4NP solutions were prepared by dissolving 0.39 µmol of 4NP and 0.2 mmol of NaBH4 in 3 mL of DIW. Five consecutive runs were completed with a DIW rinse between each run. Reaction rates were monitored by the decreasing absorbance at λmax = 400 nm (4NP*). Dip-probe reactions to delineate effects of stirring rate were carried out using an Agilent Cary 60 spectrophotometer with optical dip-probe under ambient conditions and monitored similarly as mentioned above. The 4NP solutions were prepared by dissolving 2.34 µmol of 4NP and 1.2 mmol of NaBH4 in 18 mL of DIW.
4. Conclusions
The use of ALD facilitates the controllable ultralow loading of the semiprecious metal Ru on commercially available Al2O3 monoliths with no additional pre- or post-treatments. The resulting catalysts, Ru50@Al2O3 and Ru75@Al2O3, provide a stable and highly recyclable platform for the reduction of environmentally relevant, and the reduction catalysis benchmark, substrate 4NP. The normalized observed rates are competitive with typical precious metal-based nanoparticle species (e.g., Pd and Au). Critically, the millimeter-sized Al2O3 platform allows for truly facile handling and recyclability, which when coupled with the robust nature of the material is promising for future applications in both pollutant remediation and organic transformations.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/11/2/165/s1, Figure S1: XPS analysis of model ALD Ru on Al2O3 film, Table S1: atomic % Ru by XPS, Figure S2: UV–Vis spectra and kinetics for the Ru50@Al2O3 reduction of 4NP, Table S2: 1st and 0th order kinetics for the Ru50@Al2O3 reduction of 4NP, Figure S3: UV–Vis spectra and kinetics for the Ru75@Al2O3 reduction of 4NP, Table S3: 1st and 0th order kinetics for the Ru75@Al2O3 reduction of 4NP, Figure S4: UV–Vis spectra for the blank Al2O3 sphere test for reduction of 4NP, Figures S5–S8: reduction of other nitro and azo-based molecules, and Figures S9 and S10: reduction of 4NP with stirring.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.J., P.B., C.F. and L.R.S.; methodology, T.J., P.B., L.R.S. and C.F.; synthesis, C.F. and Z.G.; catalysis, L.R.S.; ICP-MS, J.S., and V.A.A.; SEM and EDS, C.F.; BET, S.X. and F.L.; writing—original draft preparation and review and editing, L.R.S., T.J., C.F., P.B., F.L. and V.A.A.; supervision, T.J., P.B., F.L. and V.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained in the article and supplementary material. Any additional data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the NSF MRI: ECCS: 1726636 and MCF-AMPAC facility, MSE and CECS. Z.G. acknowledges support from the Preeminent Postdoctoral Program (P3) fellowship at the University of Central Florida. P.B. and C.F. acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation (NSF) under Award No. 1808625. Support from EMD Performance Materials(c) for supplying the Ru precursor molecule Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 is acknowledged
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aditya, T.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Nitroarene reduction: A trusted model reaction to test nanoparticle catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9410–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Rehan, R.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Butt, Z.; Ashraf, S. Physical chemistry of catalytic reduction of nitroarenes using various nanocatalytic systems: Past, present, and future. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Huang, Z.-F.; Pan, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.-J. Review on selective hydrogenation of nitroarene by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 227, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herves, P.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Dzubiella, J.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M. Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Model reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5577–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, H.K.; Tilve, S.G. Advancement in methodologies for reduction of nitroarenes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83391–83407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, X.; Huang, D.; Yang, G.; Astruc, D. Basic concepts and recent advances in nitrophenol reduction by gold-and other transition metal nanoparticles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingwa, N.; Meijboom, R. Kinetic evaluation of dendrimer-encapsulated palladium nanoparticles in the 4-nitrophenol reduction reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19849–19858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatkhah, A.; Jani, P.; Wilson, L.D. Redox-responsive polymer template as an advanced multifunctional catalyst support for silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10560–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.; Loganathan, B.; Dinesh, S.; Raghu, K. Strategic green synthesis, characterization and catalytic application to 4-nitrophenol reduction of palladium nanoparticles. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Saenz-Arana, R.; Wang, H.; Bernal, R.; Noveron, J.C. Green synthesis of gold, silver, platinum, and palladium nanoparticles reduced and stabilized by sodium rhodizonate and their catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and methyl orange. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6472–6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Sharma, G.; Lu, Y.; Ballauff, M.; Drechsler, M.; Irrgang, T.; Kempe, R. High catalytic activity of platinum nanoparticles immobilized on spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12229–12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, S.B. Catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol by using platinum nanoparticles stabilised by guar gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Xie, S.; Lin, H.; Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Han, Z.; Dai, H. Fe2O3/3DOM BiVO4: High-performance photocatalysts for the visible light-driven degradation of 4-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.R.; McCullough, B.; Newsome, W.J.; Ali, H.; Shaw, T.E.; Davis, K.O.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Baudelet, M.; Jurca, T. A Combined Mechanochemical and Calcination Route to Mixed Cobalt Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitrophenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogudi, B.M.; Ncube, P.; Bingwa, N.; Mawila, N.; Mathebula, S.; Meijboom, R. Promotion effects of alkali-and alkaline earth metals on catalytic activity of mesoporous Co3O4 for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Eshkalak, S.K.; Baskar, C.; Khatibzadeh, M.; Kowsari, E.; Ramakrishna, S. Flower-like 3-dimensional hierarchical Co3O4/NiO microspheres for 4-nitrophenol reduction reaction. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, T.; Jana, J.; Singh, N.K.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Remarkable Facet Selective Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol by Morphologically Tailored (111) Faceted Cu2O Nanocatalyst. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 1968–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, R.; Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Pu, Y.; Chen, J.-F. Sulfurized graphene as efficient metal-free catalysts for reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13610–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Nezafat, Z.; Gorab, M.G.; Sajjadi, M. Recent progresses in graphene-based (photo)catalysts for reduction of nitro compounds. Mol. Catal. 2020, 484, 110758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.-K.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.-W. Metal-free catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol by N-doped graphene. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3260–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, R.; Sui, X.; Li, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q. Conversion of chicken feather waste to N-doped carbon nanotubes for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10191–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, B.; Fang, T. Chemical transformation of silver nanoparticles in aquatic environments: Mechanism, morphology and toxicity. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smita, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Bartonova, A.; Dusinska, M.; Gutleb, A.C.; Rahman, Q. Nanoparticles in the environment: Assessment using the causal diagram approach. Environ. Health 2012, 11, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, A.; Das, M.; Dwivedi, P.D. Interactive threats of nanoparticles to the biological system. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 158, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, A.L. What can be inferred from bacterium–nanoparticle interactions about the potential consequences of environmental exposure to nanoparticles? Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-T. Nanoparticles and their biological and environmental applications. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Ghosh, I.; Godderis, L.; Hoet, P.; Mukherjee, A. Genotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles in higher plants. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Envirol. Mutagen. 2019, 842, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Wu, C.-Y. Nanoparticles and the Environment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 708–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Yan, W.; Duan, F.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Y. Ni nanoparticles supported on CNTs with excellent activity produced by atomic layer deposition for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2112–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, S.; Hu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y. Highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes produced by atomic layer deposition for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D.K.; Manna, J.; Dhara, A.; Sharma, P.; Sarkar, S.K. Atomic layer deposited cobalt oxide: An efficient catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2016, 34, 01A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Shang, Z.; Liang, X. Chemoselective Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes Catalyzed by Highly Dispersed, Supported Nickel Nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4814–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvo, Y.; Czarkie, D. Catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics with carbon monoxide and water using tricarbonyltetraphenylcyclopentadienone ruthenium(0). J. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 368, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Feng, C.; Deng, G. Ruthenium-Catalyzed One-Pot Aromatic Secondary Amine Formation from Nitroarenes and Alcohols. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambabu, D.; Pradeep, C.P.; Dhir, A. New self-assembled material based on Ru nanoparticles and 4-sulfocalix[4]arene as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for reduction of brilliant yellow azo dye in water: A new model catalytic reaction. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Chung, Y.K.; Park, K.H. Ruthenium Nanoparticle-Catalyzed, Controlled and Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes using Ethanol as a Hydrogen Source. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemraj-Benny, T.; Tobar, N.; Carrero, N.; Sumner, R.; Pimentel, L.; Emeran, G. Microwave-assisted synthesis of single-walled carbon nanotube-supported ruthenium nanoparticles for the catalytic degradation of Congo red dye. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, A.I.; Stamplecoskie, K.G.; Marin, M.L.; Scaiano, J.C. ‘From the mole to the molecule’: Ruthenium catalyzed nitroarene reduction studied with ‘bench’, high-throughput and single molecule fluorescence techniques. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Le, D.; Khaniya, A.; Dezelah, C.L.; Woodruff, J.; Kanjolia, R.K.; Kaden, W.E.; Rahman, T.S.; Banerjee, P. Self-Catalyzed, Low-Temperature Atomic Layer Deposition of Ruthenium Metal Using Zero-Valent Ru(DMBD)(CO)3 and Water. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detavernier, C.; Dendooven, J.; Sree, S.P.; Ludwig, K.F.; Martens, J.A. Tailoring nanoporous materials by atomic layer deposition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5242–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, C.; Thünemann, A.F. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol Using Silver Nanoparticles with Adjustable Activity. Langmuir 2016, 32, 7383–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, L.R.S.; Zottis, A.D.; Elias, W.C.; Faggion, D.; Maduro de Campos, C.E.; Acuña, J.J.S.; Domingos, J.B. The catalytic evaluation of in situ grown Pd nanoparticles on the surface of Fe3O4@dextran particles in the p-nitrophenol reduction reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8289–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, L.R.; Hu, L.; Preradovic, K.; Beazley, M.J.; Feng, X.; Jurca, T. Cover Feature: A Broader-scope Analysis of the Catalytic Reduction of Nitrophenols and Azo Dyes with Noble Metal Nanoparticles. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-H.; Doong, R.-A. Bifunctional Au−Fe3O4 Heterostructures for Magnetically Recyclable Catalysis of Nitrophenol Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6591–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Cui, J.; Wang, L. Magnetic Recyclable Nanocomposite Catalysts with Good Dispersibility and High Catalytic Activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3062–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, G.; Panda, D.; Chen, P. Size-Dependent Catalytic Activity and Dynamics of Gold Nanoparticles at the Single-Molecule Level. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Kong, J.S.; Yeh, Y.-T.E.; Chen, P. Single-molecule nanocatalysis reveals heterogeneous reaction pathways and catalytic dynamics. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder, S.; Lu, Y.; Albrecht, M.; Ballauff, M. Catalytic activity of faceted gold nanoparticles studied by a model reaction: Evidence for substrate-induced surface restructuring. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalekar, A.M.; Sharma, K.K.K.; Lehoux, A.; Audonnet, F.; Remita, H.; Saha, A.; Sharma, G.K. Investigation into the Catalytic Activity of Porous Platinum Nanostructures. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11431–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.M.; Kitchens, C.L. Impact of Gold Nanoparticle Stabilizing Ligands on the Colloidal Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5553–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menumerov, E.; Hughes, R.A.; Neretina, S. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol: A Quantitative Assessment of the Role of Dissolved Oxygen in Determining the Induction Time. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7791–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, R.D.; Hughes, R.A.; Sapkota, P.; Ptasinska, S.; Neretina, S. Effect of Nanoparticle Ligands on 4-Nitrophenol Reduction: Reaction Rate, Induction Time, and Ligand Desorption. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10040–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 196, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Myung, Y.; Banerjee, P. Configurational Entropy of Adlayers in Atomic Layer Deposition. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5458–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wu, F.; Myung, Y.; Fei, R.; Kanjolia, R.; Yang, L.; Banerjee, P. Standing and sitting adlayers in atomic layer deposition of ZnO. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film 2016, 34, 01A143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Myung, Y.; Huang, X.; Kanjolia, R.; Park, J.; Mishra, R.; Banerjee, P. Doping mechanism in transparent, conducting tantalum doped ZnO films deposited using atomic layer deposition. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).