Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Muconic Acid to Bio-Adipic Acid
Abstract
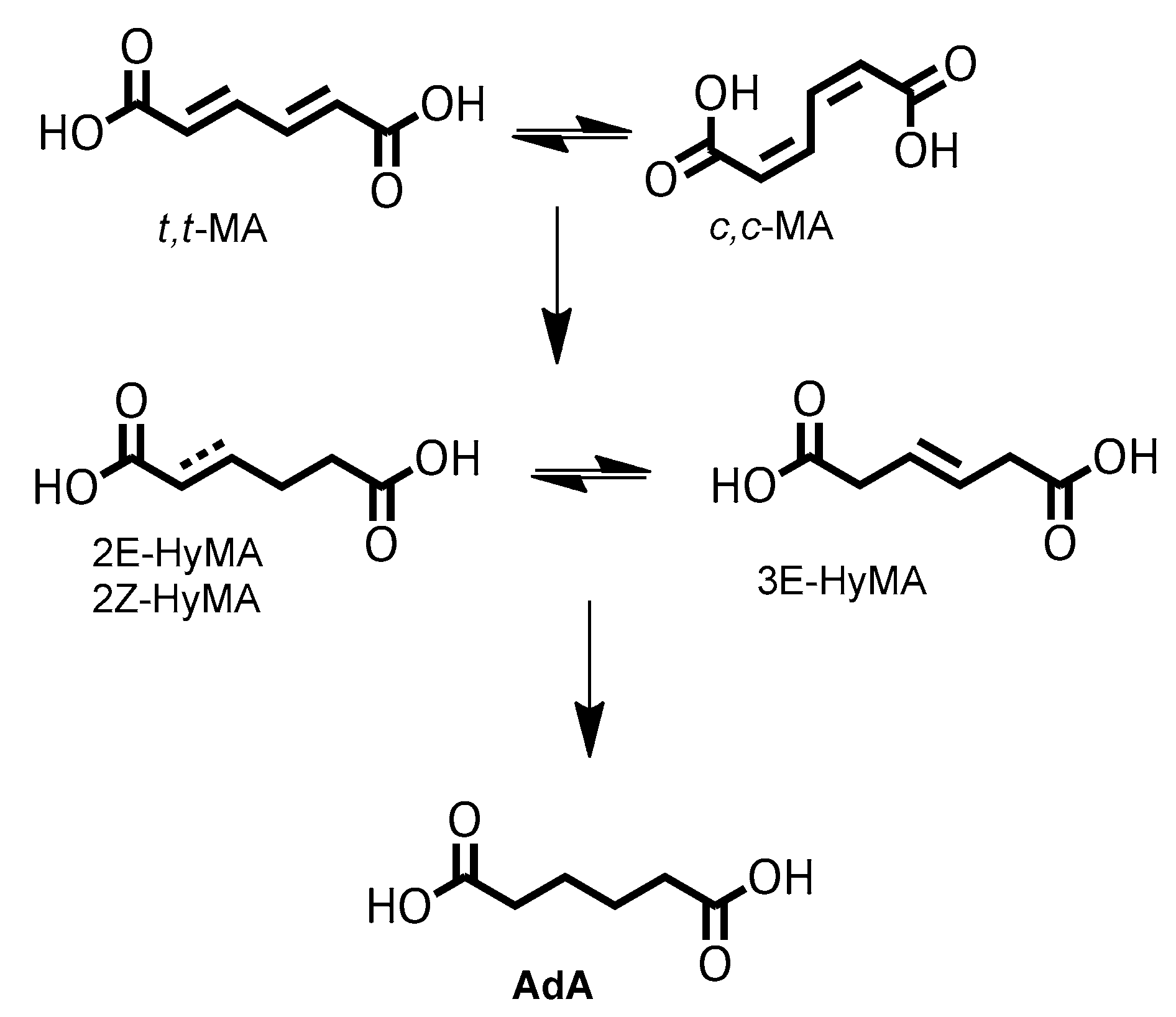
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
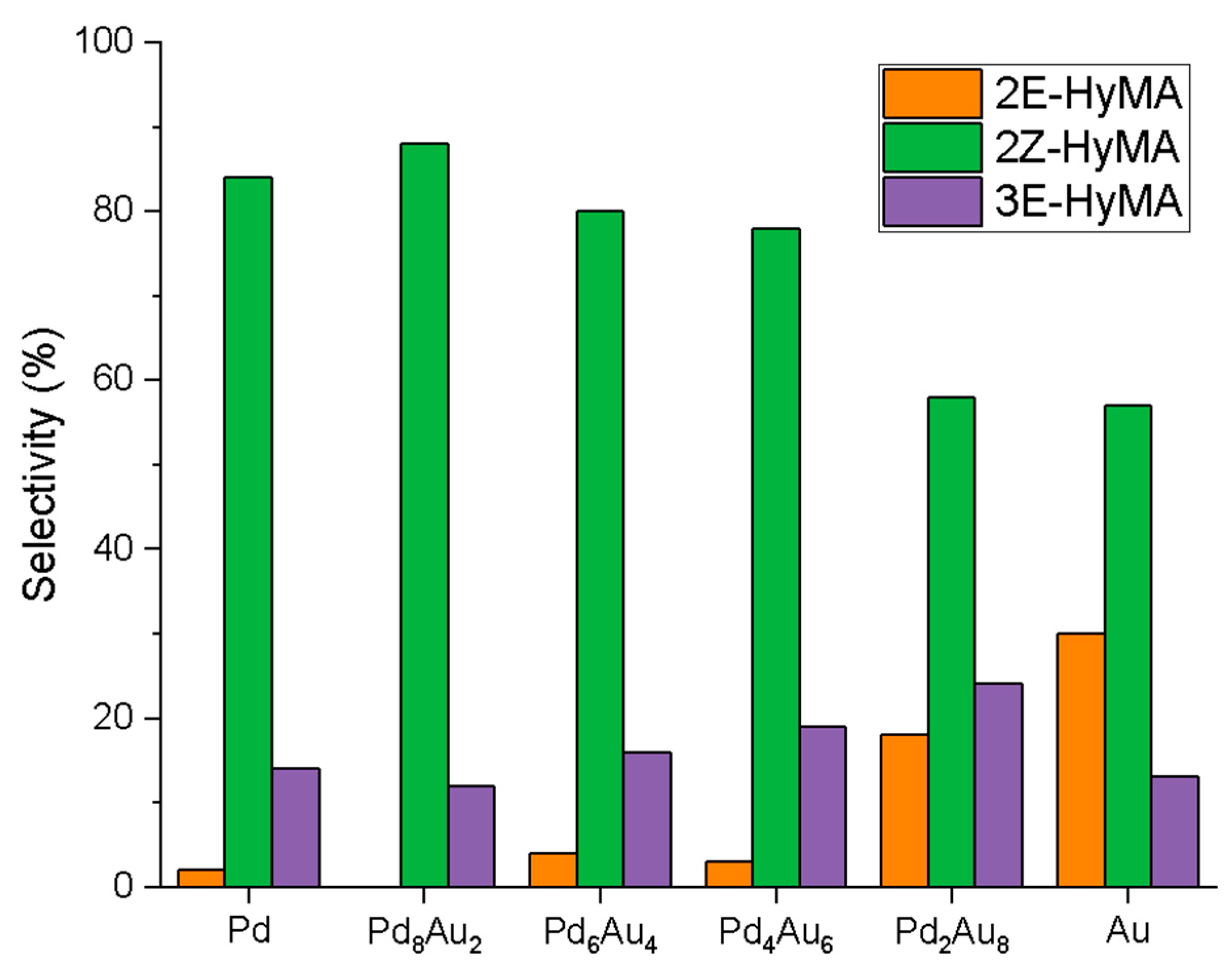
2.2. Hydrogenation Reaction
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalyst Synthesis
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Hydrogenation Reaction
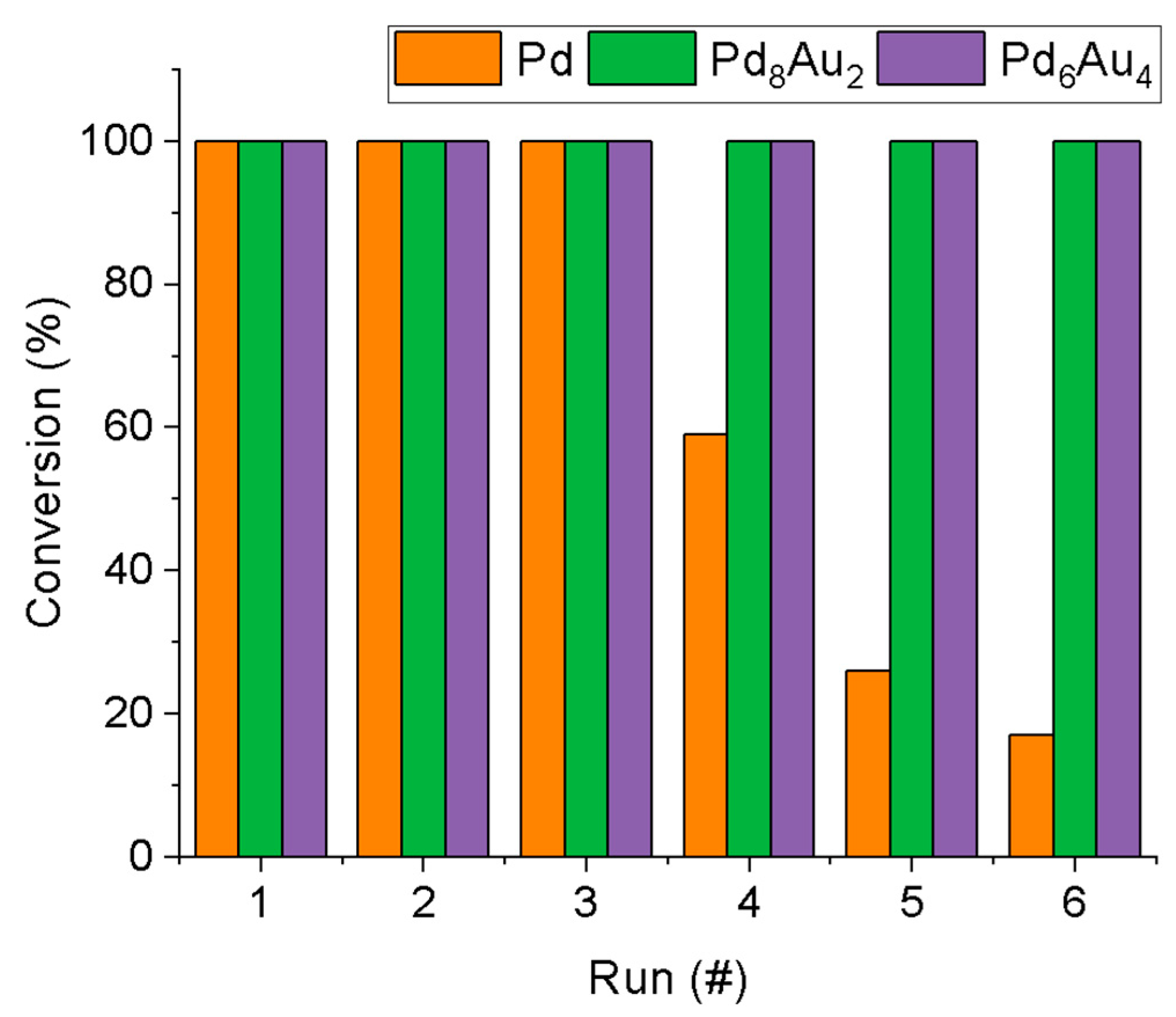
3.4. Recycle Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, B. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts: A Review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 145, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Tian, K.; He, Y.-R.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.-Q. High-Yield Harvest of Nanofibers/Mesoporous Carbon Composite by Pyrolysis of Waste Biomass and Its Application for High Durability Electrochemical Energy Storage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13951–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, A.; Ishii, Y.; Kirimura, K. High-Yield Production of cis,cis-Muconic Acid from Catechol in Aqueous Solution by Biocatalyst. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Mizuno, S.; Ohta, K.; Suzuki, M. Microbial Production of Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid. J. Biotechnol. 1990, 14, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocum, R.R.; Gong, W.; Dole, S.; Sillers, R.; Gandhi, M.; Pero, J.G. Production of Muconic Acid from Genetically Engineered Microorganisms. WO Patent 2013116244 A1, 8 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, S.; Yoshikaw, N.; Seki, M.; Mikawa, T.; Imada, Y.; Yoshikawa, N.; Seki, M.; Mikawa, T.; Imada, Y. Microbial Production of Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid from Benzoic Acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotecnol. 1988, 28, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, Y.; Yoshikawa, N.; Mizuno, S.; Takashi, M. Process for Preparing Muconic Acid. U.S. Patent No. US4871667A, 26 November 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Vardon, D.R.; Rorrer, N.A.; Salvachúa, D.; Settle, A.E.; Johnson, C.W.; Menart, M.J.; Cleveland, N.S.; Ciesielski, P.N.; Steirer, K.X.; Dorgan, J.R.; et al. Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid: Separation and Catalysis to Bio-Adipic Acid for Nylon-6,6 Polymerization. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3397–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraher, J.M.; Pfennig, T.; Rao, R.G.; Shanks, B.H.; Tessonnier, J.-P. Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid Isomerization and Catalytic Conversion to Biobased Cyclic-C6-1,4-Diacid Monomers. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scelfo, S.; Pirone, R.; Russo, N. Highly Efficient Catalysts for the Synthesis of Adipic Acid from Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid. Catal. Commun. 2016, 84, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, S.; Motta, D.; Evangelisti, C.; Dimitratos, N.; Prati, L.; Pirola, C.; Villa, A. Bio Adipic Acid Production from Sodium Muconate and Muconic Acid: A Comparison of Two Systems. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, S.; Motta, D.; Evangelisti, C.; Dimitratos, N.; Prati, L.; Pirola, C.; Villa, A. Effect of Carbon Support, Capping Agent Amount, and Pd NPs Size for Bio-Adipic Acid Production from Muconic Acid and Sodium Muconate. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardon, D.R.; Franden, M.A.; Johnson, C.W.; Karp, E.M.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Linger, J.G.; Salm, M.J.; Strathmann, T.J.; Beckham, G.T. Adipic Acid Production from Lignin. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Debnath, B.; Sahoo, R.; Chandrakumar, K.R.S.; Ray, C.; Jana, J.; Pal, T. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Ag/Rh Bimetallic Nanomaterial: Evidence of an Ensemble Effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5457–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Guo, S.; Fang, T. Enhancing the Catalytic Activity and Selectivity of PdAu/SiO2 Bimetallic Catalysts for Dodecahydro-N-Ethylcarbazole Dehydrogenation by Controlling the Particle Size and Dispersion. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 7233–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Naushad, M.; Prakash Dwivedi, R.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Mola, G.T. Novel Development of Nanoparticles to Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Composites: A Review. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2019, 31, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Segre, C.U.; Ramaker, D.; Caldwell, K.; Trahan, M.; Mukerjee, S. Structure–Property–Activity Correlations of Pt-Bimetallic Nanoparticles: A Theoretical Study. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellamorte, J.C.; Lauterbach, J.; Barteau, M.A. Palladium–Silver Bimetallic Catalysts with Improved Activity and Selectivity for Ethylene Epoxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlocco, I.; Capelli, S.; Zanella, E.; Chen, X.; Delgado, J.J.; Roldan, A.; Dimitratos, N.; Villa, A. Synthesis of Palladium-Rhodium Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Formic Acid Dehydrogenation. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 52, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.C.; Sharma, A.G.; Yadav, G.D. Biobased Process Intensification in Selective Synthesis of γ-Butyrolactone from Succinic Acid via Synergistic Palladium–Copper Bimetallic Catalyst Supported on Alumina Xerogel. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhao, M.; Vora, M.; Shen, J.; Zeng, C.; Yan, W.; Thapa, P.S.; Subramaniam, B.; Chaudhari, R.V. Synergistic Effects of Bimetallic PtPd/TiO2 Nanocatalysts in Oxidation of Glucose to Glucaric Acid: Structure Dependent Activity and Selectivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 2932–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, G.; Guillemot, D.; Polisset-Thfoin, M.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Fraissard, J. Preparation, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of Gold-Based Nanoparticles on HY Zeolites. Catal. Today 2002, 72, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.W.J.; Wilson, O.M.; Oh, S.-K.; Kenik, E.A.; Crooks, R.M. Bimetallic Palladium−Gold Dendrimer-Encapsulated Catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15583–15591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, T.J.; Lyman, S.D.; Motagamwala, A.H.; Mellmer, M.A.; Dumesic, J.A. Selective Hydrogenation of Unsaturated Carbon–Carbon Bonds in Aromatic-Containing Platform Molecules. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Du, Y.; Feng, J.; Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Li, D. Fabrication of Supported PdAu Nanoflower Catalyst for Partial Hydrogenation of Acetylene. J. Catal. 2014, 317, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Liao, S.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Su, Y. High-Performance Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalyst with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Support and Its Catalysis of Cinnamaldehyde Hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2012, 291, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Duan, Z.; Li, H.; Kim, J.; Henkelman, G.; Crooks, R.M. Tunability of the Adsorbate Binding on Bimetallic Alloy Nanoparticles for the Optimization of Catalytic Hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5538–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Quesada, M.; Dykeman, R.R.; Laurenczy, G.; Dyson, P.J.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Supported Nitrogen-Modified Pd Nanoparticles for the Selective Hydrogenation of 1-Hexyne. J. Catal. 2011, 279, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turáková, M.; Králik, M.; Lehocký, P.; Pikna, Ľ.; Smrčová, M.; Remeteiová, D.; Hudák, A. Influence of Preparation Method and Palladium Content on Pd/C Catalysts Activity in the Liquid Phase Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to Aniline. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 476, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlocco, I.; Capelli, S.; Lu, X.; Bellomi, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Prati, L.; Dimitratos, N.; Roldan, A.; Villa, A. Disclosing the Role of Gold on Palladium—Gold Alloyed Supported Catalysts in Formic Acid Decomposition. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 4210–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Yang, W. Optimizing the Activity of Pd Based Catalysts towards Room-Temperature Formic Acid Decomposition by Au Alloying. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Tsumori, N.; Kitta, M.; Xu, Q. Phosphate-Mediated Immobilization of High-Performance AuPd Nanoparticles for Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid at Room Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
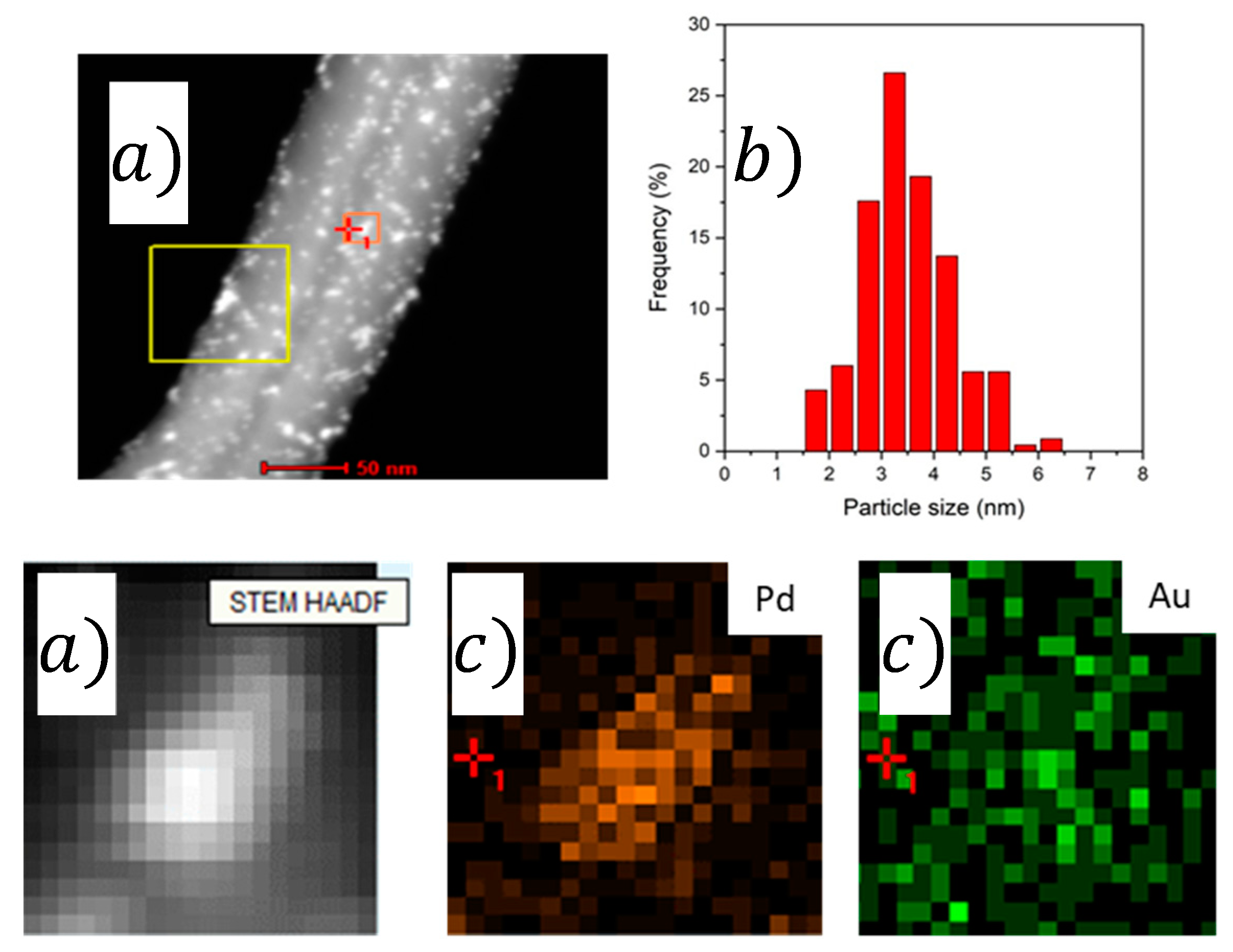
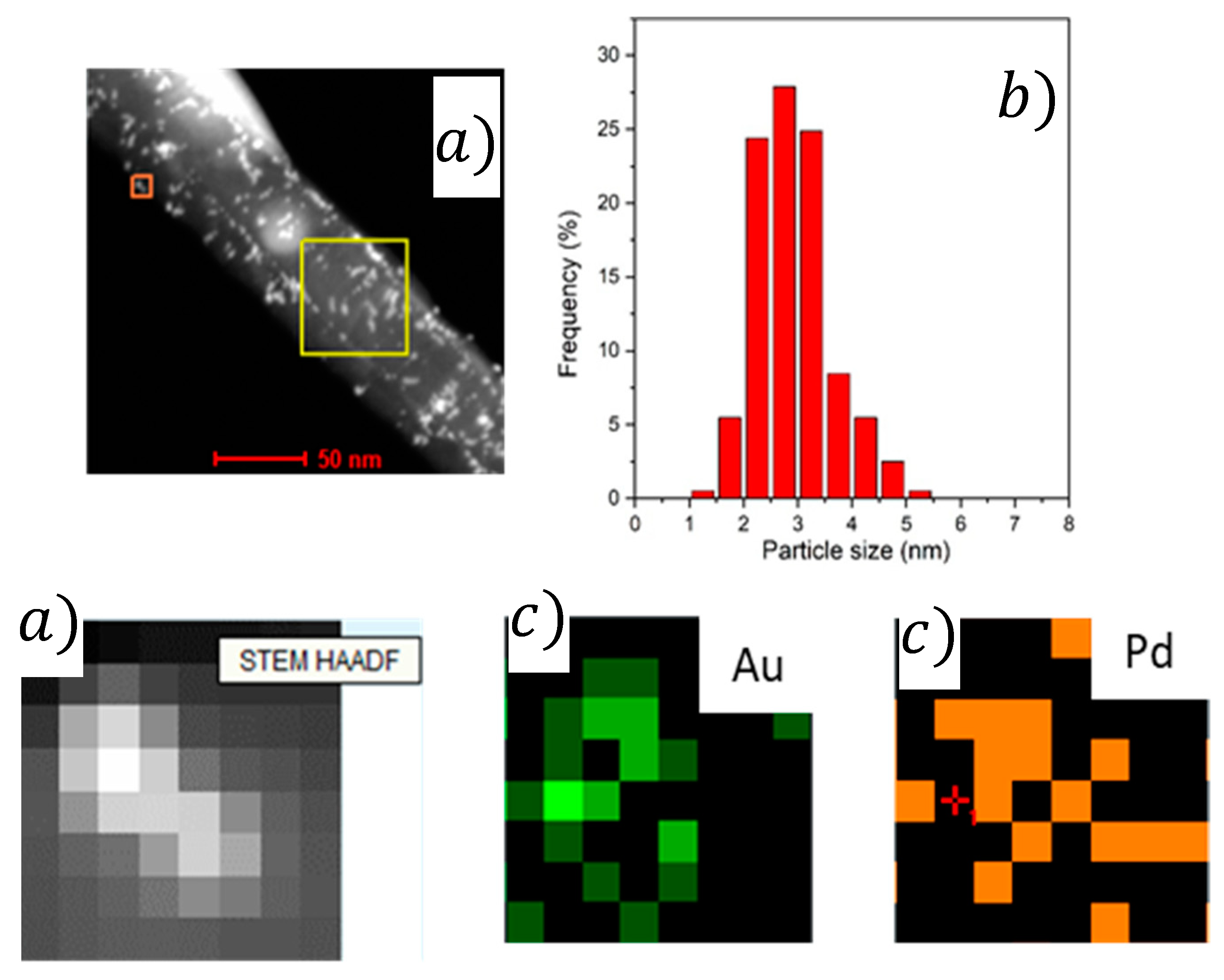
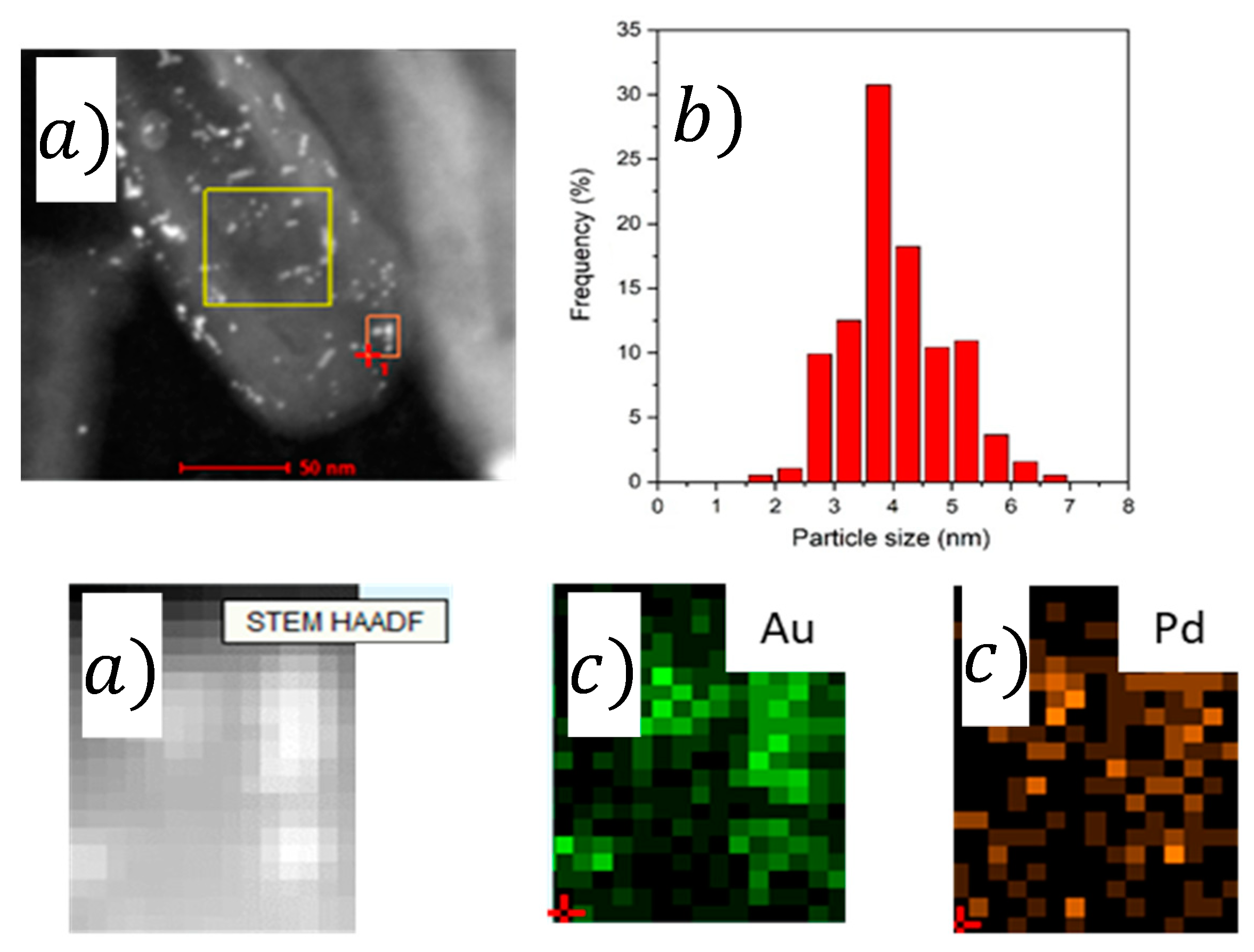
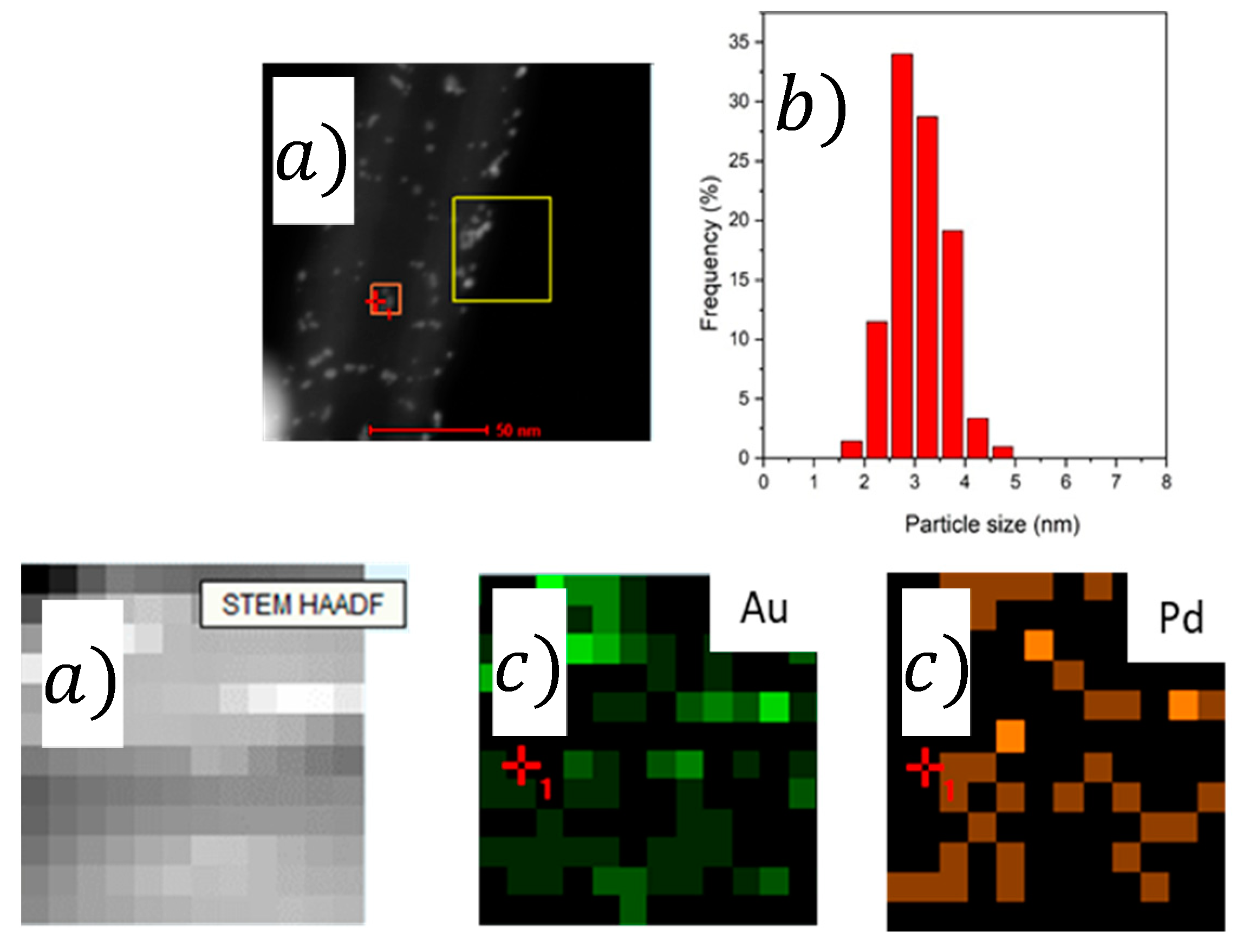

| Catalyst | Pd/Aunominal (Molar Ratio) | Pd/AuEDX (Molar Ratio) | Pd/Aunominal (Molar Ratio) | Pd/AuEDX (Molar Ratio) | Average Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/HHT | - | - | - | - | 3.9 ± 1.2 |
| Pd8Au2/HHT | 8.0–2.0 | 8.3–1.7 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 3.5 ± 0.9 |
| Pd6Au4/HHT | 6.0–4.0 | 5.9–4.1 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 2.9 ± 0.7 |
| Pd4Au6/HHT | 4.0–6.0 | 4.5–5.5 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 4.0 ± 0.8 |
| Pd2Au8/HHT | 2.0–8.0 | 1.3–8.7 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 3.1 ± 0.6 |
| Au/HHT | - | - | - | - | 3.4 ± 1.2 |
| Catalyst | C 1s | O 1s | Au 4f | Pd 3d | Pd/Aunominal | Pd/Ausurface | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.6 | 532.6 | - | 337.6 | - | - |
| %At. | 92.1 | 7.3 | - | 0.6 | |||
| Pd8Au2/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.2 | 532.2 | 83.4 | 335.4 | 4.0 | 6.5 |
| %At. | 91.2 | 7.3 | 0.2 | 1.3 | |||
| Pd6Au4/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.4 | 532.4 | 83.4 | 335.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| %At. | 95.5 | 3.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 | |||
| Pd4Au6/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.3 | 532.3 | 84.3 | 335.6 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| %At. | 96.2 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |||
| Pd2Au8/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.5 | 532.5 | 83.5 | 335.5 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| %At. | 92.3 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||
| Au/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 284.3 | 532.3 | 83.3 | - | - | |
| %At. | 97.8 | 2.1 | 0.1 |
| Au0 | Auδ+ | Au0/Auδ+ | Pd0 | PdII | Pdsat | Pd0/PdII | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/HHT | B.E. (eV) | - | - | - | 336.7 | 337.8 | 342.1 | 10.2 |
| %at. | - | - | 80.7 | 7.9 | 11.4 | |||
| Pd8Au2/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 84.1 | 85.3 | 1.0 | 335.6 | 337.1 | 347.1 | 3.1 |
| %at. | 50.8 | 49.2 | 68.5 | 21.8 | 9.7 | |||
| Pd6Au4/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 84.3 | 85.6 | 2.1 | 335.6 | 337.0 | 342.5 | 3.6 |
| %at. | 67.8 | 32.2 | 67.1 | 18.8 | 14.1 | |||
| Pd4Au6/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 84.1 | 85.6 | 2.1 | 335.5 | 337.2 | 342.3 | 4.8 |
| %at. | 67.7 | 32.3 | 79.9 | 16.8 | 31.3 | |||
| Pd2Au8/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 84.2 | 85.4 | 3.2 | 335.5 | 337.2 | 342.3 | 2.1 |
| %at. | 76.0 | 24.0 | 61.9 | 29.4 | 8.7 | |||
| Au/HHT | B.E. (eV) | 84.2 | 85.6 | 9.1 | - | - | - | - |
| %at. | 90.1 | 9.9 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capelli, S.; Barlocco, I.; Scesa, F.M.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Tessore, F.; Villa, A.; Di Michele, A.; Pirola, C. Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Muconic Acid to Bio-Adipic Acid. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111313
Capelli S, Barlocco I, Scesa FM, Huang X, Wang D, Tessore F, Villa A, Di Michele A, Pirola C. Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Muconic Acid to Bio-Adipic Acid. Catalysts. 2021; 11(11):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111313
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapelli, Sofia, Ilaria Barlocco, Federico Maria Scesa, Xiaohui Huang, Di Wang, Francesca Tessore, Alberto Villa, Alessandro Di Michele, and Carlo Pirola. 2021. "Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Muconic Acid to Bio-Adipic Acid" Catalysts 11, no. 11: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111313
APA StyleCapelli, S., Barlocco, I., Scesa, F. M., Huang, X., Wang, D., Tessore, F., Villa, A., Di Michele, A., & Pirola, C. (2021). Pd–Au Bimetallic Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Muconic Acid to Bio-Adipic Acid. Catalysts, 11(11), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111313











