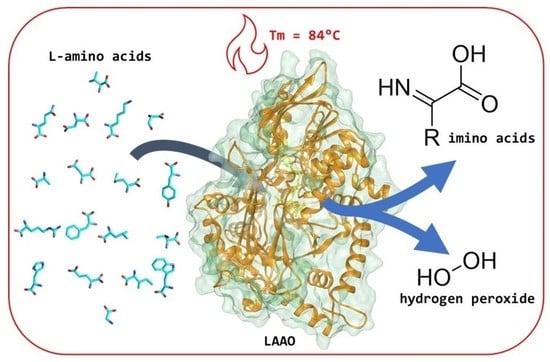
Kinetic and Structural Properties of a Robust Bacterial L-Amino Acid Oxidase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression and Purification
2.2. Thermostability
2.3. Kinetic Properties
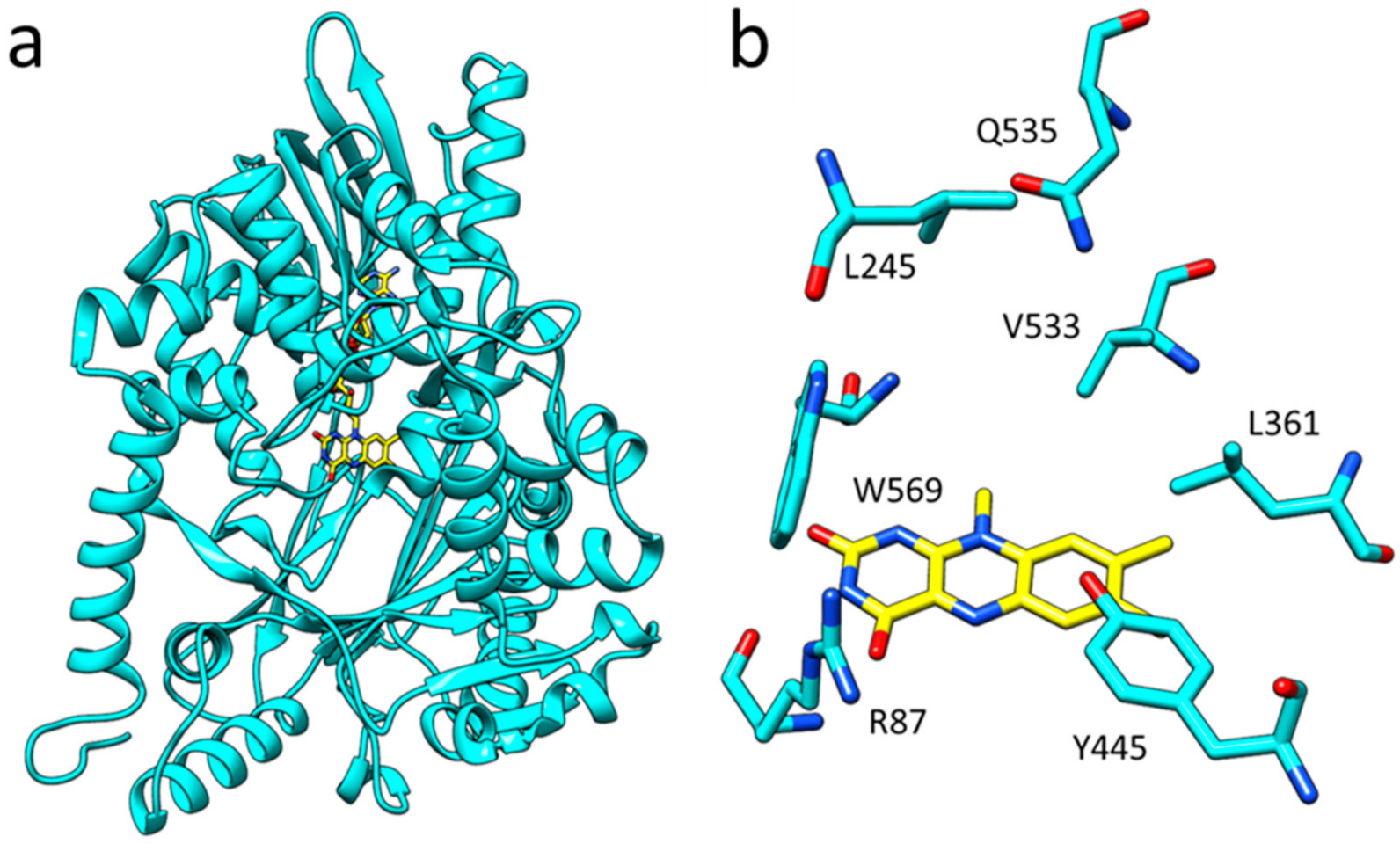
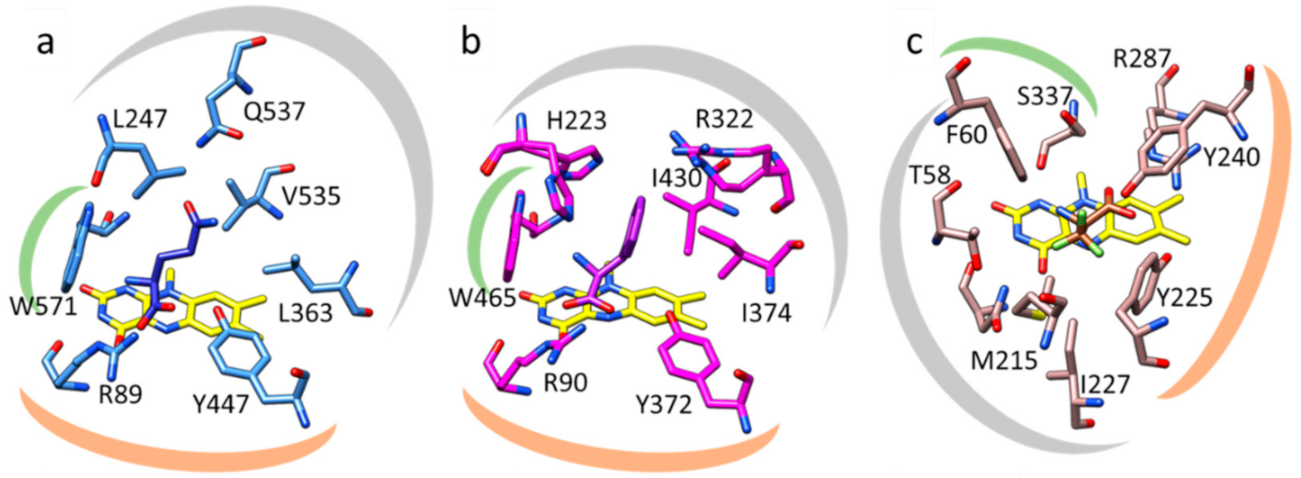
2.4. Structure Elucidation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Protein Expression and Purification
4.3. Determination of the Extinction Coefficient and Stability
4.4. Mutagenesis
4.5. Kinetic Analysis
4.6. Crystallisation and Structure Determination
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasai, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Miura, T. Antibacterial properties of L-amino acid oxidase: Mechanisms of action and perspectives for therapeutic applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7847–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, M.Z. Past decade study of snake venom L-amino acid oxidase. Toxicon 2012, 60, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izidoro, L.F.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.D.M.; Da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; et al. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: Trends in pharmacology and biochemistry. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawelek, P.D.; Cheah, J.; Coulombe, R.; Macheroux, P.; Ghisla, S.; Vrielink, A. The structure of L-amino acid oxidase reveals the substrate trajectory into an enantiomerically conserved active site. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4204–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.M.; Sheu, F.S.; Sheu, S.Y. Novel L-amino acid oxidase with algicidal activity against toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa synthesized by a bacterium Aquimarina sp. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samel, M.; Tõnismägi, K.; Rönnholm, G.; Vija, H.; Siigur, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Siigur, E. L-Amino acid oxidase from Naja naja oxiana venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2008, 149, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Kayano, A.M.; Zaqueo, K.D.; Neto, A.C.; Sampaio, S.V.; Soares, A.M.; Stabeli, R.G. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: Some consideration about their functional characterization. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Yu, T.F.; Lian, E.C. Purification and characterization of L-amino acid oxidase from king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) venom and its effects on human platelet aggregation. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.L.; Tan, N.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Sekaran, S.D. Antibacterial action of a heat-stable form of L-amino acid oxidase isolated from king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 153, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Pundir, C.S. L-amino acid biosensor based on L-amino acid oxidase immobilized onto NiH-CNFe/c-MWCNT/PPy/GC electrode. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 54, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Nakano, M.; Ohishi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Miura, T. Antimicrobial properties of L-amino acid oxidase: Biochemical features and biomedical applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4819–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.W.; Yokoigawa, K.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Total conversion of racemic pipecolic acid into the L-enantiomer by a combination of enantiospecific oxidation with D-amino acid oxidase and reduction with sodium borohydride. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 2081–2082. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, F.; Brummund, J.; Calderini, E.; Schürmann, M.; Kourist, R. Cofactor generation cascade for α-ketoglutarate and Fe(II)-dependent dioxygenases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8604–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-Vidal, A.; Sanchez-Amat, A.; Campillo-Brocal, J.C. The Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea L-amino acid oxidase with antimicrobial activity is a flavoenzyme. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, S.; Kozuka, K.; Minamino, Y.; Karasuda, H.; Hasebe, F.; Ito, S. Ancestral L-amino acid oxidases for deracemization and stereoinversion of amino acids. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Minamino, Y.; Hasebe, F.; Ito, S. Deracemization and stereoinversion to aromatic D-amino acid derivatives with ancestral L-amino acid oxidase. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10152–10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollegioni, L.; Motta, P.; Molla, G. L-amino acid oxidase as biocatalyst: A dream too far? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9323–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnudurai, G.; Chung, M.C.; Tan, N.H. Purification and properties of the L-amino acid oxidase from Malayan pit viper (Calloselasma rhodostoma) venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 313, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Foster, S.; Lyubimov, A.Y.; Vrielink, A. Crystal structure of LAAO from Calloselasma rhodostoma with an L-phenylalanine substrate: Insights into structure and mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 364, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umhau, S.; Pollegioni, L.; Molla, G.; Diederichs, K.; Welte, W.; Pilone, M.S.; Ghilsa, S. The x-ray structure of D-amino acid oxidase at very high resolution identifies the chemical mechanism of flavin-dependent substrate dehydrogenation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12463–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forneris, F.; Orru, R.; Bonivento, D.; Chiarelli, L.R.; Mattevi, A. ThermoFAD, a Thermofluor-adapted flavin ad hoc detection system for protein folding and ligand binding. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66 Pt 2, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.W.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarakatsannis, J.N.; Duan, Y. Statistical characterization of salt bridges in proteins. Proteins 2005, 60, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 2.0; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Chovancová, E.; Pavelka, A.; Benes, P.; Strnad, O.; Brezovsky, J.; Kozlikova, B.; Góra, A.; Sustr, V.; Klvana, M.; Medek, P.; et al. CAVER 3.0: A tool for the analysis of transport pathways in dynamic protein structures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Substrate | kcat (s−1) | Km (mM) | kcat/Km (s−1 mM−1) | Vmax (U/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-leucine | 72 | 0.40 | 180 | 58 |
| L-methionine | 63 | 0.42 | 150 | 51 |
| L-phenylalanine | 52 | 0.34 | 150 | 42 |
| L-glutamine | 136 | 2.4 | 56 | 110 |
| L-tryptophan | 36 | 1.5 | 25 | 29 |
| L-glutamate | >30 | >6.9 | 4.4 | 24 |
| L-isoleucine | 25 | 11 | 2.3 | 20 |
| L-arginine | 43 | 25 | 1.7 | 35 |
| L-valine | 9.4 | 9.5 | 0.99 | 7.5 |
| L-histidine | 5.3 | 11 | 0.48 | 4.3 |
| L-alanine | 14 | 48 | 0.30 | 11.3 |
| L-lysine | 7.2 | 57 | 0.13 | 5.8 |
| L-serine | 0.21 | 14 | 0.015 | 0.17 |
| L-tyrosine | >0.75 | >10 | 0.075 | 0.60 |
| L-asparagine | 0.46 | 8.7 | 0.053 | 0.37 |
| L-aspartate | >0.023 | >3.8 | 0.0061 | 0.018 |
| L-threonine | 0.05 | 14 | 0.0035 | 0.040 |
| L-glycine | 0.01 | 30 | 0.0003 | 0.0081 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savino, S.; Meijer, J.D.-M.; Rozeboom, H.J.; van Beek, H.L.; Fraaije, M.W. Kinetic and Structural Properties of a Robust Bacterial L-Amino Acid Oxidase. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111309
Savino S, Meijer JD-M, Rozeboom HJ, van Beek HL, Fraaije MW. Kinetic and Structural Properties of a Robust Bacterial L-Amino Acid Oxidase. Catalysts. 2021; 11(11):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavino, Simone, J. Daniël-Moráh Meijer, Henriëtte J. Rozeboom, Hugo L. van Beek, and Marco W. Fraaije. 2021. "Kinetic and Structural Properties of a Robust Bacterial L-Amino Acid Oxidase" Catalysts 11, no. 11: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111309
APA StyleSavino, S., Meijer, J. D.-M., Rozeboom, H. J., van Beek, H. L., & Fraaije, M. W. (2021). Kinetic and Structural Properties of a Robust Bacterial L-Amino Acid Oxidase. Catalysts, 11(11), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11111309