Preferential Oxidation of CO over CoFe2O4 and M/CoFe2O4 (M = Ce, Co, Cu or Zr) Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
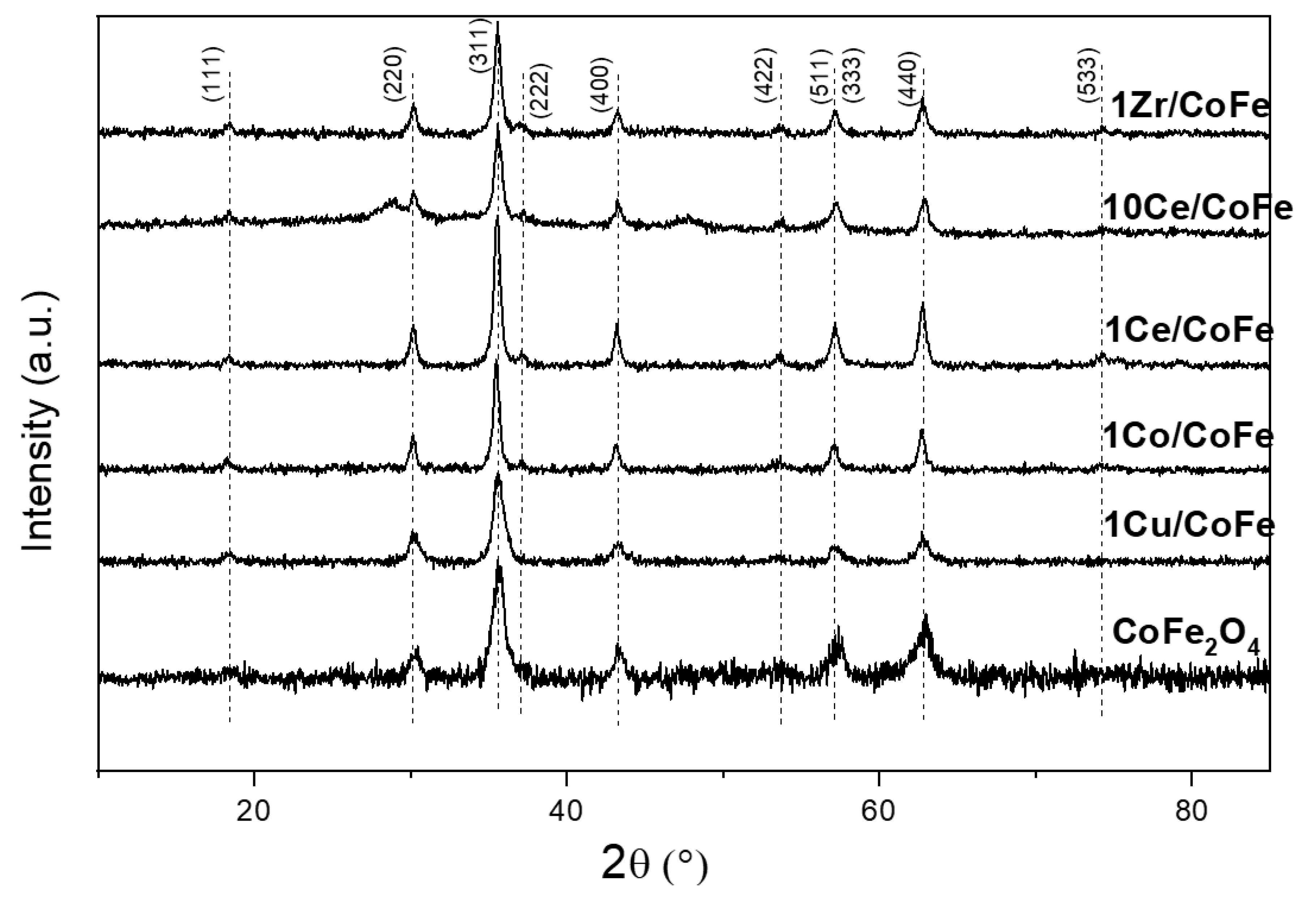
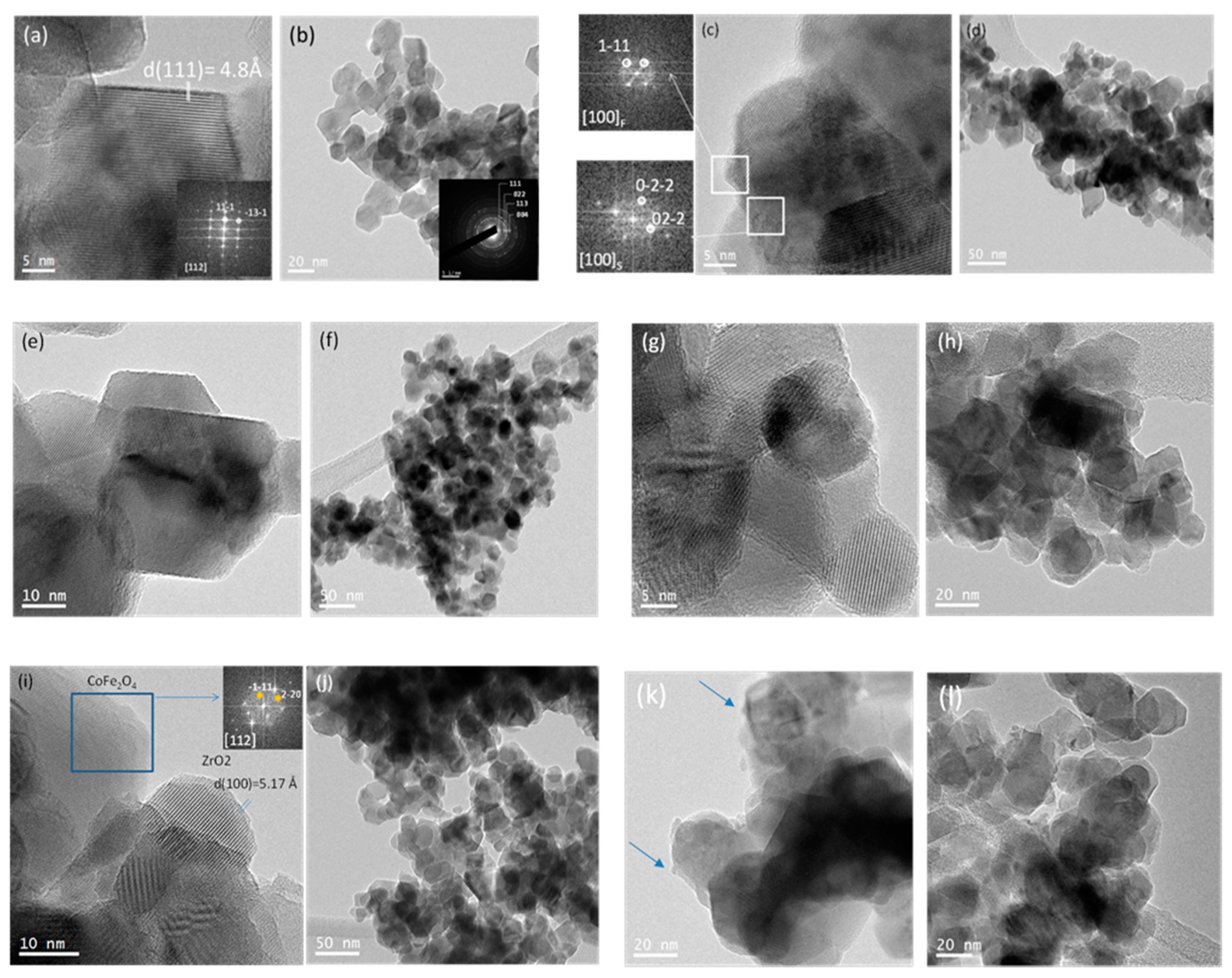
2.1. Characterization
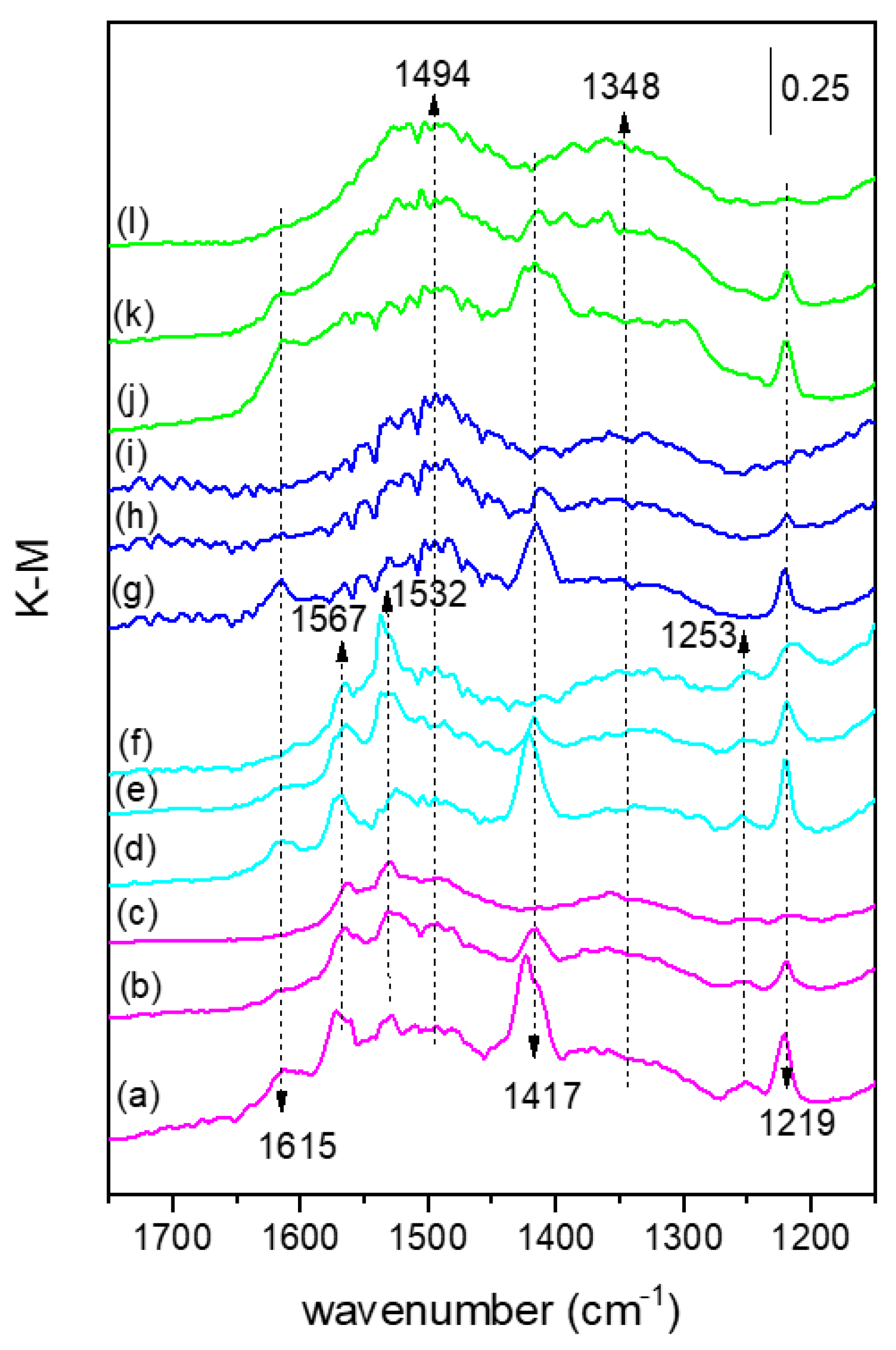
2.2. Catalytic Properties
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinçer, I.; Zamfirescu, C. Sustainable Energy Systems and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 519–632. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, B. Hydrogen and Fuel Cells: Emerging Technologies and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Debe, M.K. Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature 2012, 486, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalamaras, C.M.; Efstathiou, A.M. Hydrogen Production Technologies: Current State and Future Developments. In Conference Papers in Energy; Hindawi Publishing Corporation: London, UK, 2013; Volume 2013, p. 690627. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaidis, P.; Poullikkas, A. A comparative overview of hydrogen production processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M.; Lykaki, M. Recent Advances on the Rational Design of Non-Precious Metal Oxide Catalysts Exemplified by CuOx/CeO2 Binary System: Implications of Size, Shape and Electronic Effects on Intrinsic Reactivity and Metal-Support Interactions. Catalysts 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Gong, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in synergistic effect promoted catalysts for preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bion, N.; Epron, F.; Moreno, M.; Mariño, F.; Duprez, D. Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide in the Presence of Hydrogen (PROX) over Noble Metals and Transition Metal Oxides: Advantages and Drawbacks. Top. Catal. 2008, 51, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Jia, C.-J.; Weidenthaler, C.; Bongard, H.-J.; Spliethoff, B.; Schmidt, W.; Schüth, F. Highly Ordered Mesoporous Cobalt-Containing Oxides: Structure, Catalytic Properties, and Active Sites in Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11407–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, T.; Murayama, T.; Nellaiappan, S.; Katiyar, N.K.; Bera, P.; Safonova, O.; Lin, M.; Priolkar, K.R.; Kundu, S.; Rao, B.S.; et al. Ultra-Low-Temperature CO Oxidation Activity of Octahedral Site Cobalt Species in Co3O4 Based Catalysts: Unravelling the Origin of the Unique Catalytic Property. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 19557–19571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatzky, G.A.; van der Woude, F.; Morrish, A.H. Cation Distributions in Octahedral and Tetrahedral Sites of the Ferrimagnetic Spinel CoFe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 1204–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, D.; Casula, M.F.; Falqui, A.; Loche, D.; Mountjoy, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Corrias, A. A Structural and Magnetic Investigation of the Inversion Degree in Ferrite Nanocrystals MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Co, Ni). J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-L.; Yan, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Bala, H.; Zhang, Z.-Y. CTAB-assisted synthesis of mesoporous CoFe2O4 with high carbon monoxide oxidation activity. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouotou, P.M.; Vieker, H.; Tian, Z.Y.; Ngamou, P.H.T.; el Kasmi, A.; Beyer, A.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K. Structure–activity relation of spinel-type Co–Fe oxides for low-temperature CO oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3359–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Thomas, N.; Girgsdies, F.; Beherns, M.; Huang, X.; Sudheesh, V.D.; Sebastian, V. Synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by constant pH co-precipitation and their high catalytic activity in CO oxidation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7356–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabani-Ravandi, A.; Rezaei, M. Low temperature CO oxidation over Fe–Co mixed oxide nanocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, C.A.; de Souza, E.F.; de Carvalho, M.C.N.A.; Martins, R.L.; Schmal, M. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the preferential oxidation of CO. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 519, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qwabe, L.Q.; Friedrich, H.B.; Singh, S. Preferential oxidation of CO in a hydrogen rich feed stream using Co–Fe mixed metal oxide catalysts prepared from hydrotalcite precursors. J. Mol. Catal. A 2015, 404–405, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, J.; Wermuth, T.B.; Machado, M.C.; Arcaro, S.; Alves, A.K.; Viegas, A.d.; Bergmann, C.P. The influence of solvent composition in the sol-gel synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4): A route to tuning its magnetic and mechanical properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Guo, Z. Synthesis of Efficient Cu/CoFe2O4 Catalysts for Low Temperature CO Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmhamdi, A.; Pascual, L.; Nahdi, K.; Martínez-Arias, A. Structure/redox/activity relationships in CeO2/CuMn2O4 CO-PROX catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 217, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar-Díaz, C.L.; Conesa, J.C.; Corberán, V.C.; Monte, M.; Martínez-Arias, A. Nanostructured Catalysts Based on Combinations of Cobalt and Cerium Oxides for CO Oxidation and Effect of the Presence of Water. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3816–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Cooper, M.E.; Whan, D.A. Temperature programmed reduction of alumina-supported iron, cobalt and nickel bimetallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. 1982, 3, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammiche-Bellal, Y.; Djadoun, A.; Meddour-Boukhobza, L.; Benadda, A.; Auroux, A.; Berger, M.-H.; Mernache, F. Effect of the preparation method on the structural and catalytic properties of spinel cobalt-iron oxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W. Carbon Monoxide Hydrogenation on Cobalt/Zeolite Catalysts. J. Porous Mater. 2005, 12, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantauzzi, M.; Secci, F.; Angotzi, M.S.; Passiu, C.; Cannas, C.; Rossi, A. Nanostructured spinel cobalt ferrites: Fe and Co chemical state, cation distribution and size effects by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19171–19179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghavnian, T.; Moussy, J.-B.; Stanescu, D.; Belkhou, R.; Jedrecy, N.; Magnan, H.; Ohresser, P.; Arrio, M.-A.; Sainctavit, P.; Barbier, A. Determination of the cation site distribution of the spinel in mulltiferroic CoFe2O4/BaTiO3 layers by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2015, 202, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W.; Tang, W.; Shi, J.; Xiong, R. Electronic structure studies of the spinel CoFe2O4 by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6972–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.C.; Harris, S.J.; Jutson, J.A.; Dyke, J.M. A study of a number of mixed transition metal oxide spinels using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1989, 37, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; Biesinger, M.C.; McIntyre, N.S. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 2004, 36, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, J.P.; Alvarez, R.; Munuera, G. Study of CeOx XPS spectra by factor analysis: Reduction of CeO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 161, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparazzo, E. Use and mis-use of x-ray photoemission spectroscopy Ce3d spectra of Ce2O3 and CeO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 343003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-D.; Huebner, W. Size-induced lattice relaxation in CeO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3512–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svintsitskiy, D.A.; Kardash, T.Y.; Stonkus, O.A.; Slavinskaya, E.M.; Stadnichenko, A.I.; Koscheev, S.V.; Chupakhin, A.P.; Boronin, A.I. In Situ XRD, XPS, TEM, and TPR Study of Highly Active in CO Oxidation CuO Nanopowders. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 14588–14599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, M.; Munuera, G.; Costa, D.; Conesa, J.C.; Martínez-Arias, A. Near-ambient XPS characterization of interfacial copper species in ceria-supported copper catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 29995–30004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünert, W.; Hayes, N.W.; Joyner, R.W.; Shpiro, E.S.; Rafiq, M.; Siddiqui, H.; Baeva, G.N. Structure, Chemistry, and Activity of Cu-ZSM-5 Catalysts for the Selective Reduction of NOx in the Presence of Oxygen. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 10832–10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Espinos, J.P.; Caballero, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Mejias, J.A. XPS Study of Interface and Ligand Effects in Supported Cu2O and CuO Nanometric Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7758–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamarra, D.; Cámara, A.L.; Monte, M.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Chinchilla, L.E.; Hungría, A.B.; Munuera, G.; Gyorffy, N.; Schay, Z.; Corberán, V.C.; et al. Preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 over CuO/CeO2 catalysts: Characterization and performance as a function of the exposed face present in the CeO2 support. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 130–131, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, C.; Sanz, J.M.; Galán, L.; Soriano, L.; Rueda, F. An XPS Study of the Interaction of Oxygen with Zirconium. Surf. Sci. 1989, 218, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.D.; Davis, L.E.; Zeller, M.V.; Taylor, J.A.; Raymond, R.H.; Gale, L.H. Empirical Atomic Sensitivity Factors for Quantitative Analysis by Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis. Surf. Interf. Anal. 1981, 3, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.J.; Liu, Z.W.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhong, X.C.; Qiu, W.Q.; Zeng, D.C.; Wen, L.S. Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of partially inverse spinel CoFe2O4: A first-principles study. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 445003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, N.S.; Cook, M.G. X-Ray Photoelectron Studies on Some Oxides and Hydroxides of Cobalt, Nickel, and Copper. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Martens, W.N.; Frost, R.L. Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt Hydroxide, Cobalt Oxyhydroxide, and Cobalt Oxide Nanodiscs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Pan, W.; Wang, F.; Xu, N. Removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) by MFe2O4 nanoparticles from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bärnighausen, H.; Schiller, G. The Crystal Structure of A-Ce2O3. J. Less-Comm. Met. 1985, 110, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, P.; Cámara, A.L.; Hornés, A.; Martínez-Arias, A. Comparative in Situ DRIFTS-MS Study of 12CO- and 13CO-TPR on CuO/CeO2 Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 10689–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arias, A.; Gamarra, D.; Hungría, A.B.; Fernández-García, M.; Munuera, G.; Hornés, A.; Bera, P.; Conesa, J.C.; Cámara, A.L. Characterization of Active Sites/Entities and Redox/Catalytic Correlations in Copper-Ceria-Based Catalysts for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-Rich Streams. Catalysts 2013, 3, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollins, P. The influence of surface defects on the infrared spectra of adsorbed species. Surf. Sci. Rep. 1992, 16, 51–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, P.; Hornés, A.; Cámara, A.L.; Martínez-Arias, A. DRIFTS-MS studies of preferential oxidation of CO in H2 rich stream over (CuO)0.7(CeO2)0.3 and (Cu0.9M0.1O)0.7(CeO2)0.3 (M = Co, Zn and Sn) catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 155, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arias, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Hungría, A.B.; Conesa, J.C.; Munuera, G. Spectroscopic Characterization of Heterogeneity and Redox Effects in Zirconium−Cerium (1:1) Mixed Oxides Prepared by Microemulsion Methods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Catalyst | SBET (m2 g−1) | Pore volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 36.8 | 0.235 | 26.0 |
| 1Cu/CoFe | 27.9 | 0.127 | 17.9 |
| 1Co/CoFe | 27.8 | 0.154 | 20.9 |
| 1Ce/CoFe | 30.1 | 0.156 | 21.2 |
| 10Ce/CoFe | 35.7 | 0.128 | 15.2 |
| 1Zr/CoFe | 36.1 | 0.219 | 23.8 |
| Catalyst | [Co]/([Co] + [Fe] + [O]) | [Fe]/([Co] + [Fe] + [O]) | [M a]/([Co] + [Fe] + [O]) | O/T b (Co 2p) | O/T b (Fe 2p) | sat./main c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 0.104 | 0.268 | - | 0.72/0.28 | 0.72/0.28 | 0.765 |
| 1Ce/CoFe | 0.102 | 0.246 | 0.0189 | 0.75/0.25 | 0.74/0.26 | 0.723 |
| 10Ce/CoFe | 0.0873 | 0.218 | 0.0599 | 0.71/0.29 | 0.72/0.28 | 0.714 |
| 1Co/CoFe | 0.113 | 0.246 | - | 0.72/0.28 | 0.73/0.27 | 0.709 |
| 1Cu/CoFe | 0.104 | 0.236 | 0.0189 | 0.72/0.28 | 0.72/0.28 | 0.711 |
| 1Zr/CoFe | 0.103 | 0.240 | 0.00679 | 0.74/0.26 | 0.73/0.27 | 0.708 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Béjaoui, M.; Elmhamdi, A.; Pascual, L.; Pérez-Bailac, P.; Nahdi, K.; Martínez-Arias, A. Preferential Oxidation of CO over CoFe2O4 and M/CoFe2O4 (M = Ce, Co, Cu or Zr) Catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010015
Béjaoui M, Elmhamdi A, Pascual L, Pérez-Bailac P, Nahdi K, Martínez-Arias A. Preferential Oxidation of CO over CoFe2O4 and M/CoFe2O4 (M = Ce, Co, Cu or Zr) Catalysts. Catalysts. 2021; 11(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBéjaoui, Mehdi, Abdelhakim Elmhamdi, Laura Pascual, Patricia Pérez-Bailac, Kais Nahdi, and Arturo Martínez-Arias. 2021. "Preferential Oxidation of CO over CoFe2O4 and M/CoFe2O4 (M = Ce, Co, Cu or Zr) Catalysts" Catalysts 11, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010015
APA StyleBéjaoui, M., Elmhamdi, A., Pascual, L., Pérez-Bailac, P., Nahdi, K., & Martínez-Arias, A. (2021). Preferential Oxidation of CO over CoFe2O4 and M/CoFe2O4 (M = Ce, Co, Cu or Zr) Catalysts. Catalysts, 11(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010015





