Investigation of Co–Fe–Al Catalysts for High-Calorific Synthetic Natural Gas Production: Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Catalysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of the Co–Fe–Al Catalysts
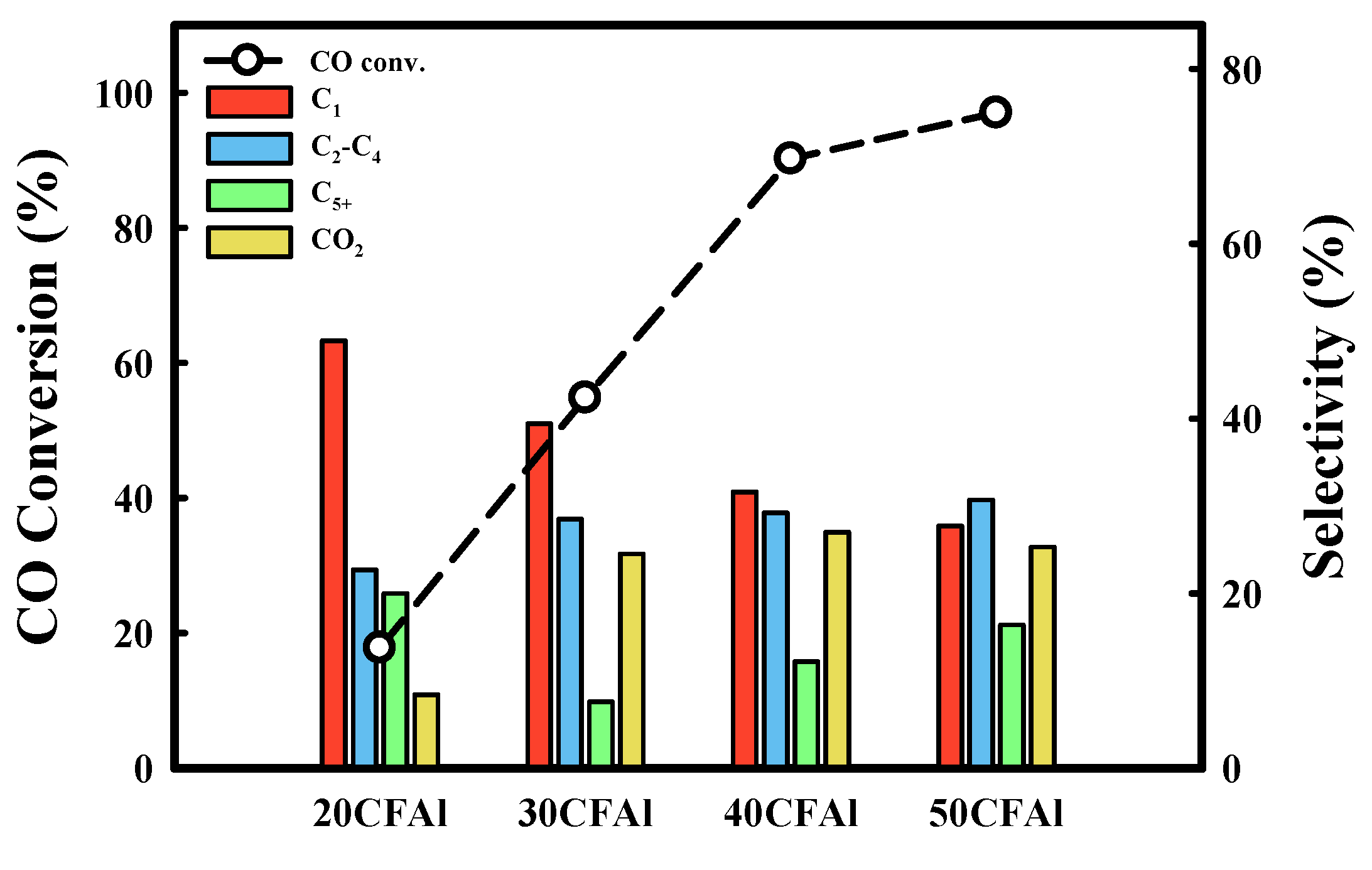
2.2. Catalytic Performance of the Co–Fe–Al Catalysts
2.3. Performance of Pelletized 40CFAl Catalysts
3. Materials and Methods
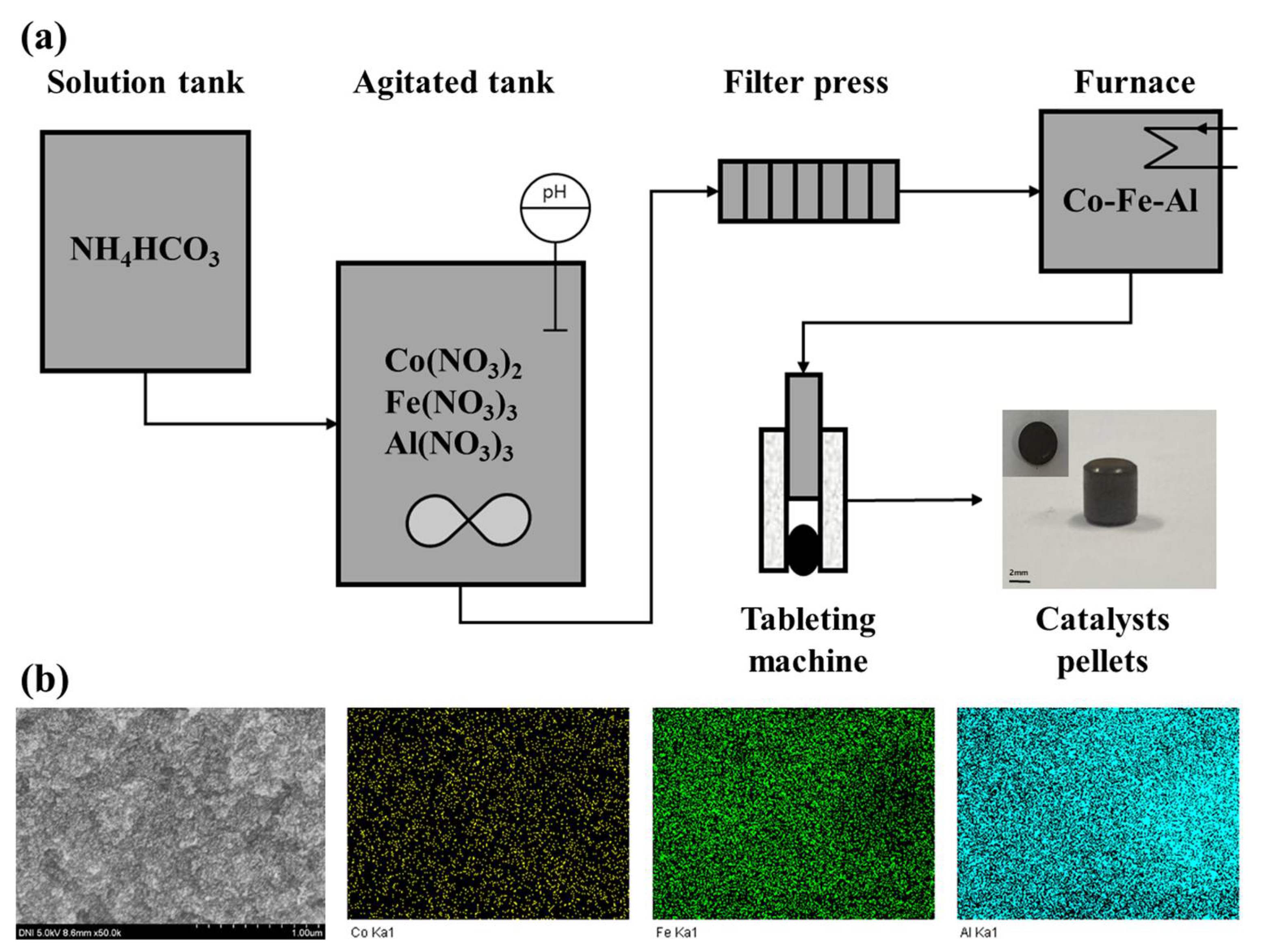
3.1. Catalysts Preparation
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, S.J.; Caldeira, K.; Matthews, H.D. Future CO2 emissions and climate change from existing energy infrastructure. Science 2010, 329, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopyscinski, J.; Schildhauer, T.J.; Biollaz, S.M. Production of synthetic natural gas (SNG) from coal and dry biomass—A technology review from 1950 to 2009. Fuel 2010, 89, 1763–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, J.; Hong, U.G.; Seo, J.G.; Jung, J.C.; Koh, D.J.; Lim, H.; Byun, C.; Song, I.K. Methane production from carbon monoxide and hydrogen over nickel—Alumina xerogel catalyst: Effect of nickel content. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 17, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jia, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Gu, F.; Xu, G.; Zhong, Z.; Su, F. Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for CO methanation: Effect of Al2O3 supports calcined at different temperatures. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X. Syngas methanation over Ni/SiO2 catalyst prepared by ammonia-assisted impregnation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 27073–27083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, Y.; Uba, M.; Nishida, S.; Inui, T. Application of CoMn2O3Ru catalyst to the process for producing high-calorie substitute natural gas from coke oven gas. Appl. Catal. 1989, 47, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, D.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Co-Mn-Ru/Al2O3 catalyst for the production of high-calorific synthetic natural gas. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, D.-W.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, K.-Y. Fe–Zn catalysts for the production of high-calorie synthetic natural gas. Fuel 2015, 159, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, D.-W.; Lee, K.-Y. Production of high-calorie synthetic natural gas using copper-impregnated iron catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 425, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, K.-Y. Effect of surface composition of Fe catalyst on the activity for the production of high-calorie synthetic natural gas (SNG). Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.B.; Chae, H.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Oh, J.U.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, M.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Selective CO hydrogenation over bimetallic Co-Fe catalysts for the production of light paraffin hydrocarbons (C2-C4): Effect of H2/CO ratio and reaction temperature. Catal. Commun. 2018, 117, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.B.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, M.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Hybrid catalysts in a double-layered bed reactor for the production of C2–C4 paraffin hydrocarbons. Catal. Commun. 2019, 127, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.B.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Woo, J.H.; Chae, H.J.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Selective CO hydrogenation over bimetallic Co-Fe catalysts for the production of light paraffin hydrocarbons (C2–C4): Effect of space velocity, reaction pressure and temperature. Catalysts 2019, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Jo, S.B.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Effect of reducibility on the performance of Co-based catalysts for the production of high-calorie synthetic natural gas. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraz, N. The comparative jurisprudence of catalysts preparation methods: I. precipitation and impregnation methods. J. Ind. Environ. Chem. 2018, 2, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Deraz, N.M. The importance of catalyst preparation. J. Ind. Environ. Chem. 2018, 2, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sahli, N.; Petit, C.; Roger, A.-C.; Kiennemann, A.; Libs, S.; Bettahar, M.M. Ni catalysts from NiAl2O4 spinel for CO2 reforming of methane. Catal. Today 2006, 113, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.G.; Youn, M.H.; Nam, I.; Hwang, S.; Chung, J.S.; Song, I.K. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of liquefied natural gas over mesoporous Ni-Al2O3 catalysts prepared by a co-precipitation method: Effect of Ni/Al atomic ratio. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamskar, F.R.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkani, F. The influence of Ni loading on the activity and coke formation of ultrasound-assisted co-precipitated Ni–Al2O3 nanocatalyst in dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lögdberg, S.; Tristantini, D.; Borg, Ø.; Ilver, L.; Gevert, B.; Järås, S.; Blekkan, E.A.; Holmen, A. Hydrocarbon production via Fischer–Tropsch synthesis from H2-poor syngas over different Fe-Co/γ-Al2O3 bimetallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 89, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.; Avdeeva, L.; Khassin, A.; Kustova, G.; Ushakov, V.; Moroz, E.; Shmakov, A.; Kriventsov, V.; Kochubey, D.; Pavlyukhin, Y.T. Coprecipitated iron-containing catalysts (Fe-Al2O3, Fe-Co-Al2O3, Fe-Ni-Al2O3) for methane decomposition at moderate temperatures: I. genesis of calcined and reduced catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 268, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griboval-Constant, A.; Butel, A.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Chernavskii, P.A.; Khodakov, A. Cobalt and iron species in alumina supported bimetallic catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch reaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 481, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.; Wei, S.-H.; Yan, Y.; Al-Jassim, M.; Turner, J.A.; Woodhouse, M.; Parkinson, B. Structural, magnetic, and electronic properties of the Co-Fe-Al oxide spinel system: Density-functional theory calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 165119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Enakonda, L.R.; Saih, Y.; Loptain, S.; Gary, D.; Del-Gallo, P.; Basset, J.-M. Catalytic methane decomposition over Fe-Al2O3. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres Galvis, H.M.; de Jong, K.P. Catalysts for production of lower olefins from synthesis gas: A review. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2130–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio-Fraccari, E.; Bader, G.; Alemany, L.; Mariño, F. Pelletized Cu-Ni/CePr5 catalysts for H2 purification via Water Gas Shift reaction. Fuel 2020, 271, 117653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Chun, D.H.; Lee, H.-T.; Hong, J.-C.; Jung, H.; Yang, J.-I. Mass transfer limitations on fixed-bed reactor for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, A.; Mirzaei, A.A.; Rahimi, R.; Atashi, H. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis on Fe-Co-Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst: A mass transfer, kinetic and mechanistic study. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
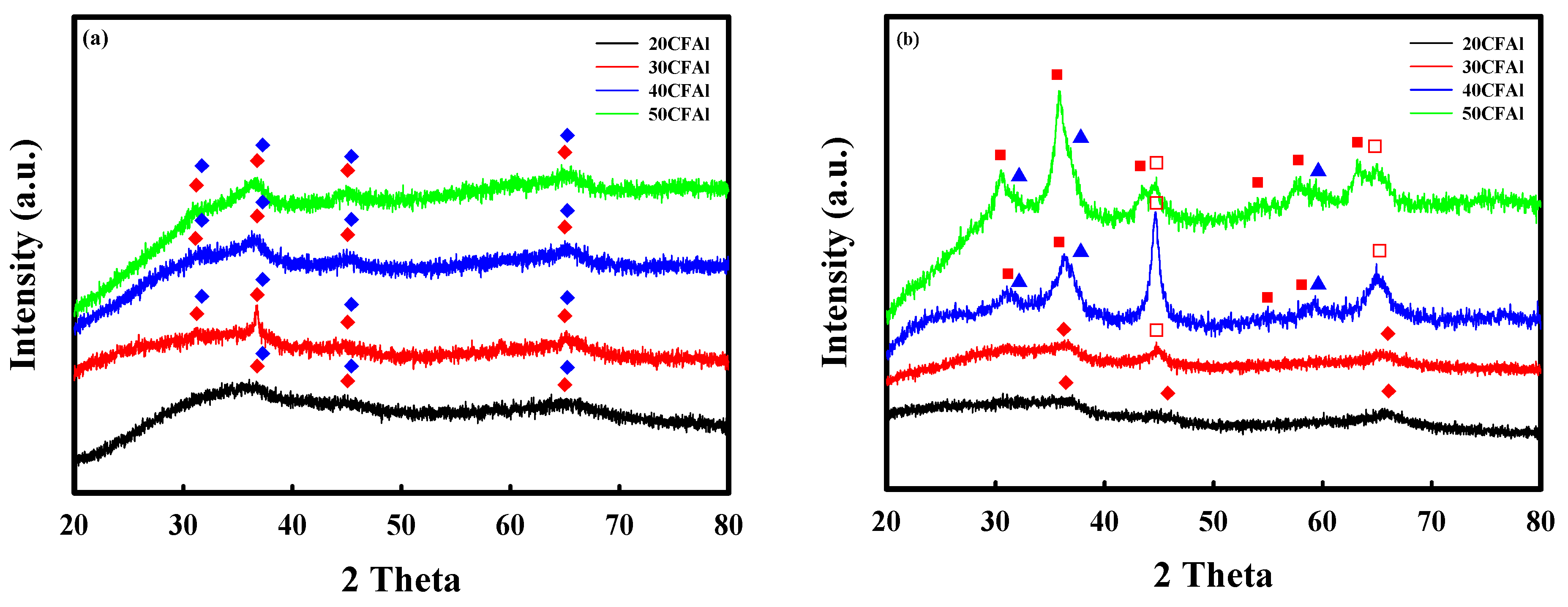
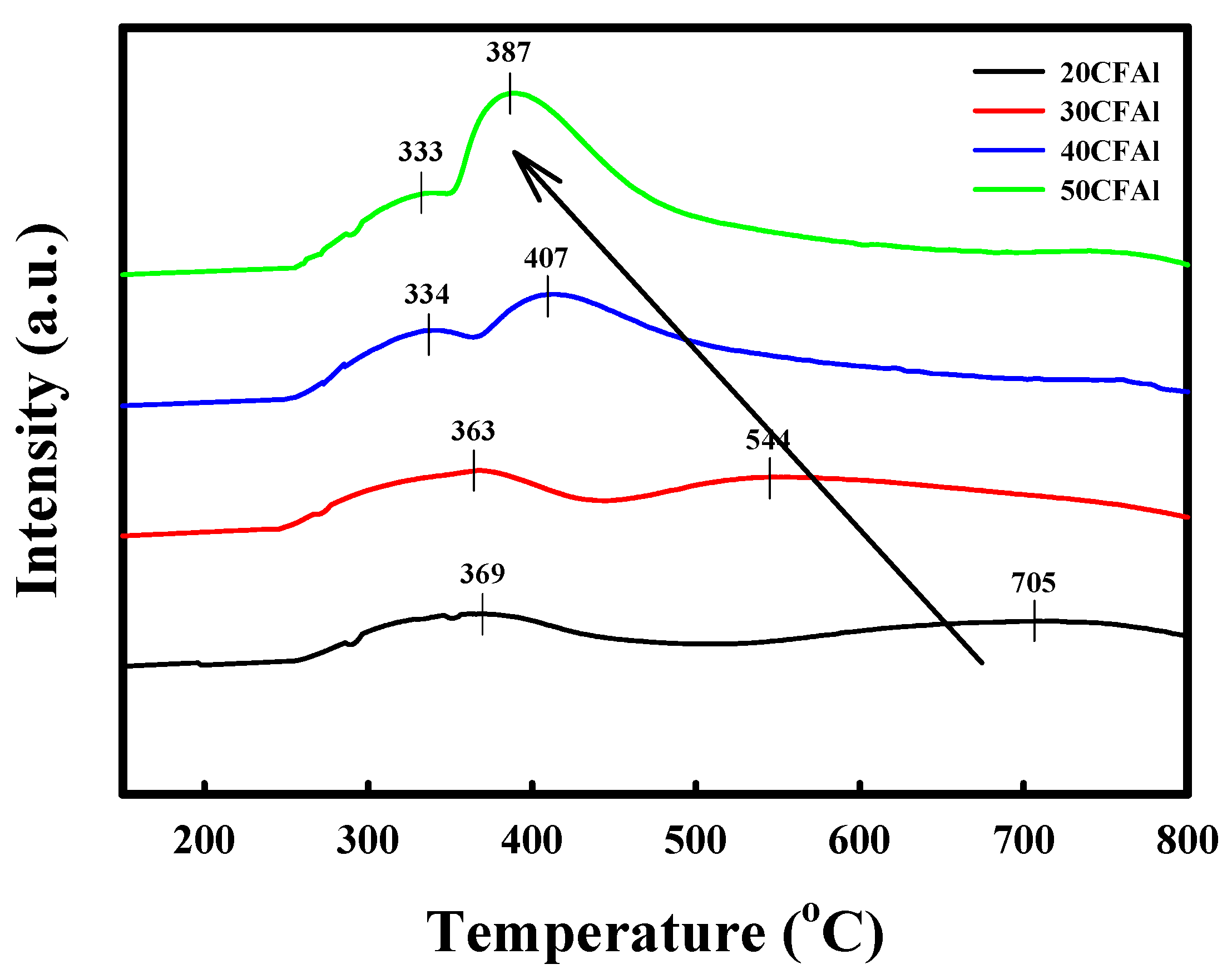
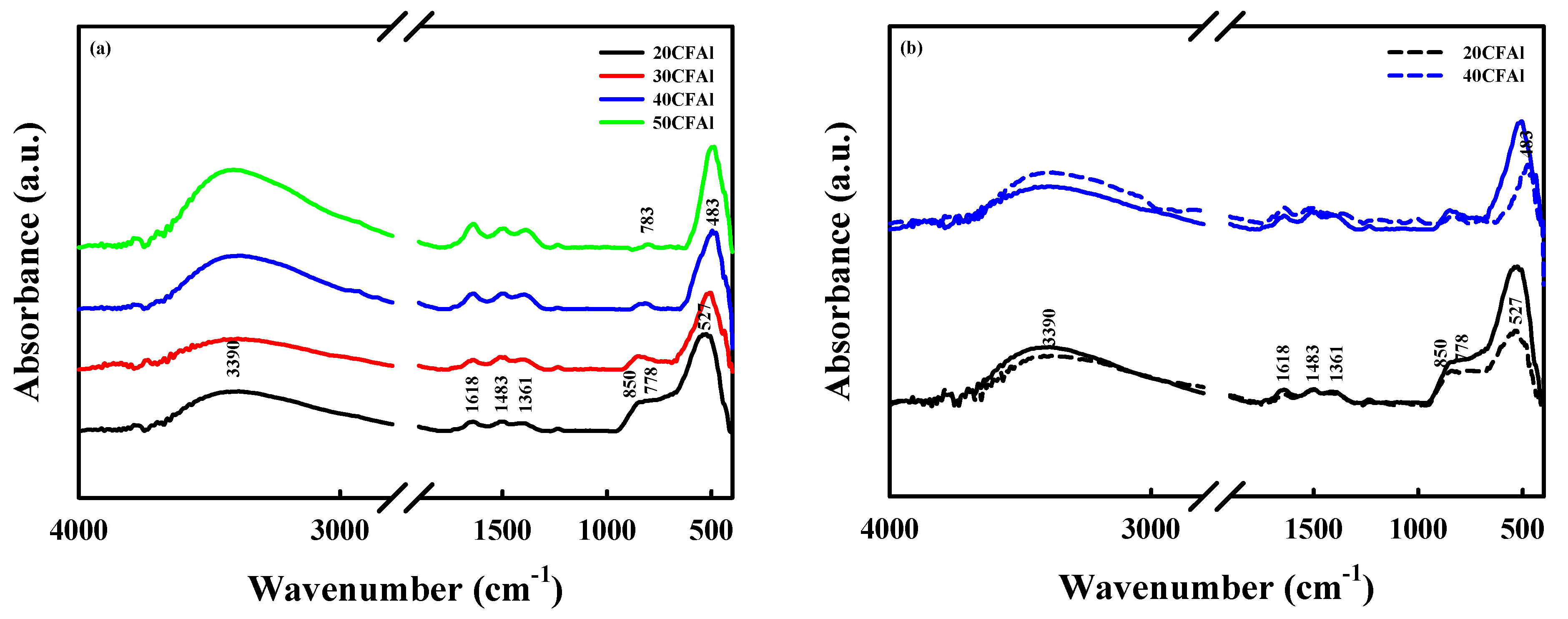


| Notation a | Metal Content (wt.%) b | Relative Atomic Ratio of Metal (%) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Crystalline Size (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Fe | Spinel c | Fe3O4 d | Fe0 d | |||
| 20CFAl | 4.5 | 13.6 | 9.5 | 183.6 | 3.4 | - | - |
| 30CFAl | 6.6 | 22.3 | 16.2 | 201.9 | 3.5 | - | 4.4 |
| 40CFAl | 10.1 | 29.9 | 24.0 | 241.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 10.2 |
| 50CFAl | 12.8 | 37.4 | 32.4 | 214.9 | 4.1 | 12.6 | 7.2 |
| Notation | CO Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | P/(P + O) | C2–C4 Hydrocarbon Time Yield (mmolCO·gmetal−1·h−1) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2–C4 | C5+ | CO2 | ||||
| 20CFAl | 17.8 | 48.9 | 22.7 | 20.0 | 8.4 | 0.60 | 0.84 |
| 30CFAl | 54.4 | 39.4 | 28.5 | 7.6 | 22.1 | 0.85 | 2.04 |
| 40CFAl | 90.2 | 31.6 | 29.2 | 12.2 | 27.0 | 0.94 | 2.49 |
| 50CFAl | 97.0 | 27.7 | 30.7 | 16.4 | 26.7 | 0.94 | 2.24 |
| Notation | Reaction Condition | CO Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | C2–C4 Hydrocarbon Time Yield (mmolCO·gmetal−1·h−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C2–C4 | C5+ | CO2 | ||||
| 40CFAl_P | 6000 mL/g/h, 300 °C, 10 bar | 65.1 | 32.4 | 23.3 | 23.4 | 20.9 | 1.43 |
| 4000 mL/g/h, 350 °C, 20 bar | 87.6 | 59.3 | 18.8 | 4.1 | 17.8 | 1.56 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.Y.; Jo, S.B.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Dhanusuraman, R.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Investigation of Co–Fe–Al Catalysts for High-Calorific Synthetic Natural Gas Production: Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010105
Kim TY, Jo SB, Woo JH, Lee JH, Dhanusuraman R, Lee SC, Kim JC. Investigation of Co–Fe–Al Catalysts for High-Calorific Synthetic Natural Gas Production: Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Catalysts. Catalysts. 2021; 11(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Young, Seong Bin Jo, Jin Hyeok Woo, Jong Heon Lee, Ragupathy Dhanusuraman, Soo Chool Lee, and Jae Chang Kim. 2021. "Investigation of Co–Fe–Al Catalysts for High-Calorific Synthetic Natural Gas Production: Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Catalysts" Catalysts 11, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010105
APA StyleKim, T. Y., Jo, S. B., Woo, J. H., Lee, J. H., Dhanusuraman, R., Lee, S. C., & Kim, J. C. (2021). Investigation of Co–Fe–Al Catalysts for High-Calorific Synthetic Natural Gas Production: Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Catalysts. Catalysts, 11(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010105





